The Response of HeLa Cells to Fluorescent NanoDiamond Uptake
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culturing
2.2. Diamond Uptake
2.3. Microscopic Analysis
2.4. Cellular Viability
2.5. Total ROS Activity
2.6. RNA Isolation and Real-Time PCR
2.7. Western Blot
3. Results
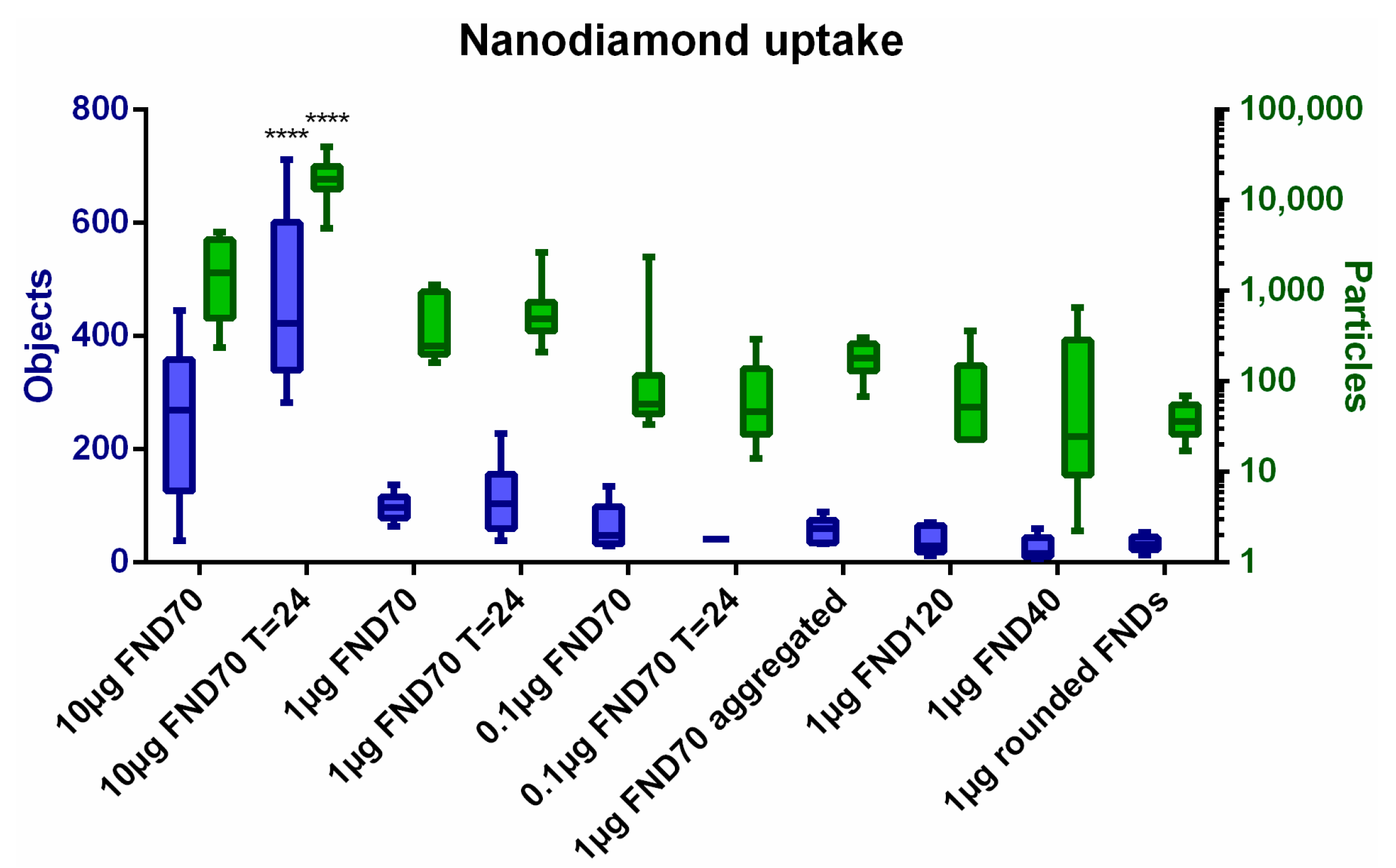
3.1. Uptake of FNDs in HeLa Cells
3.2. Biocompatibility of Nanodiamonds
3.3. Total ROS Activity
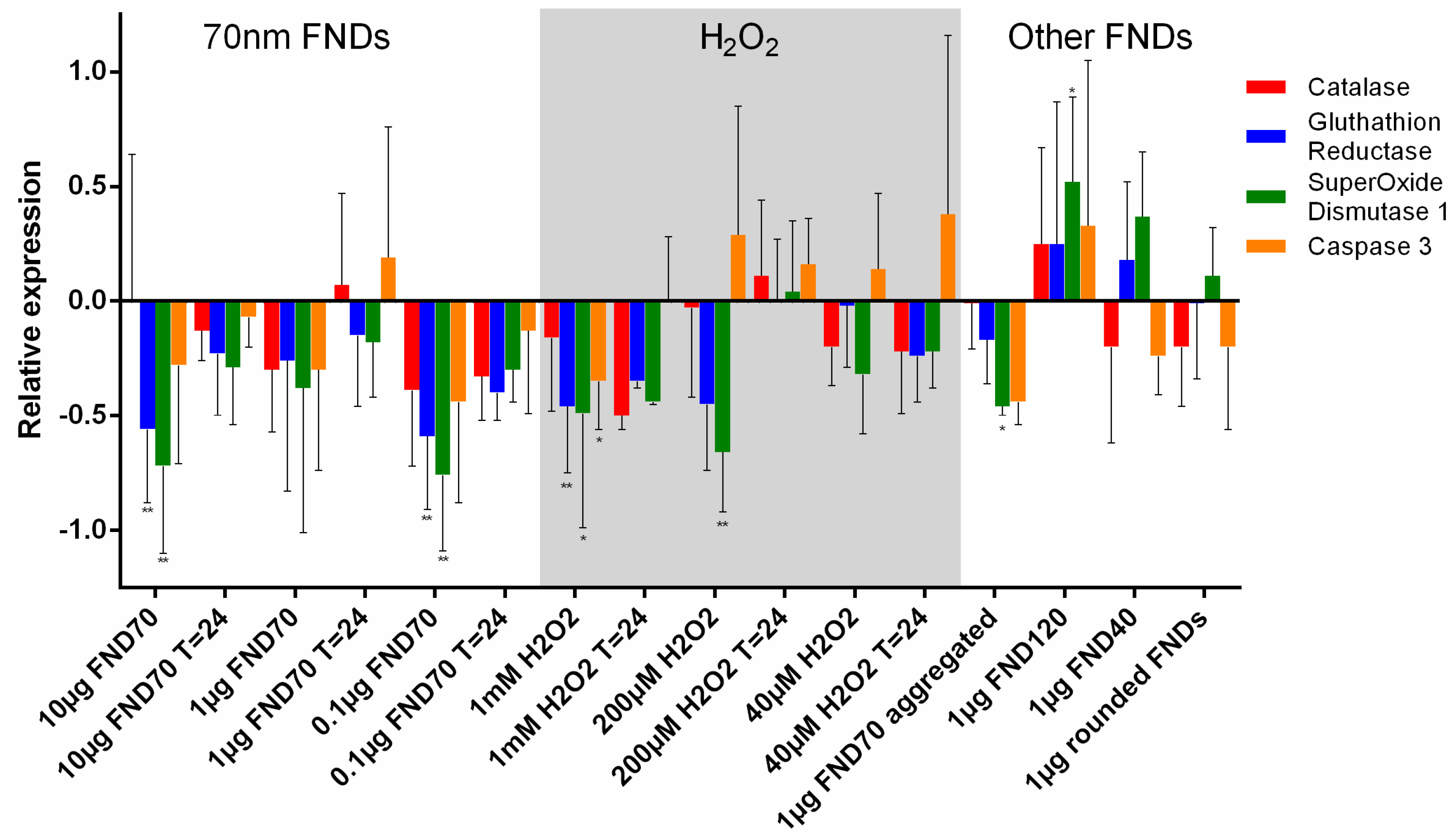
3.4. Real-Time PCR
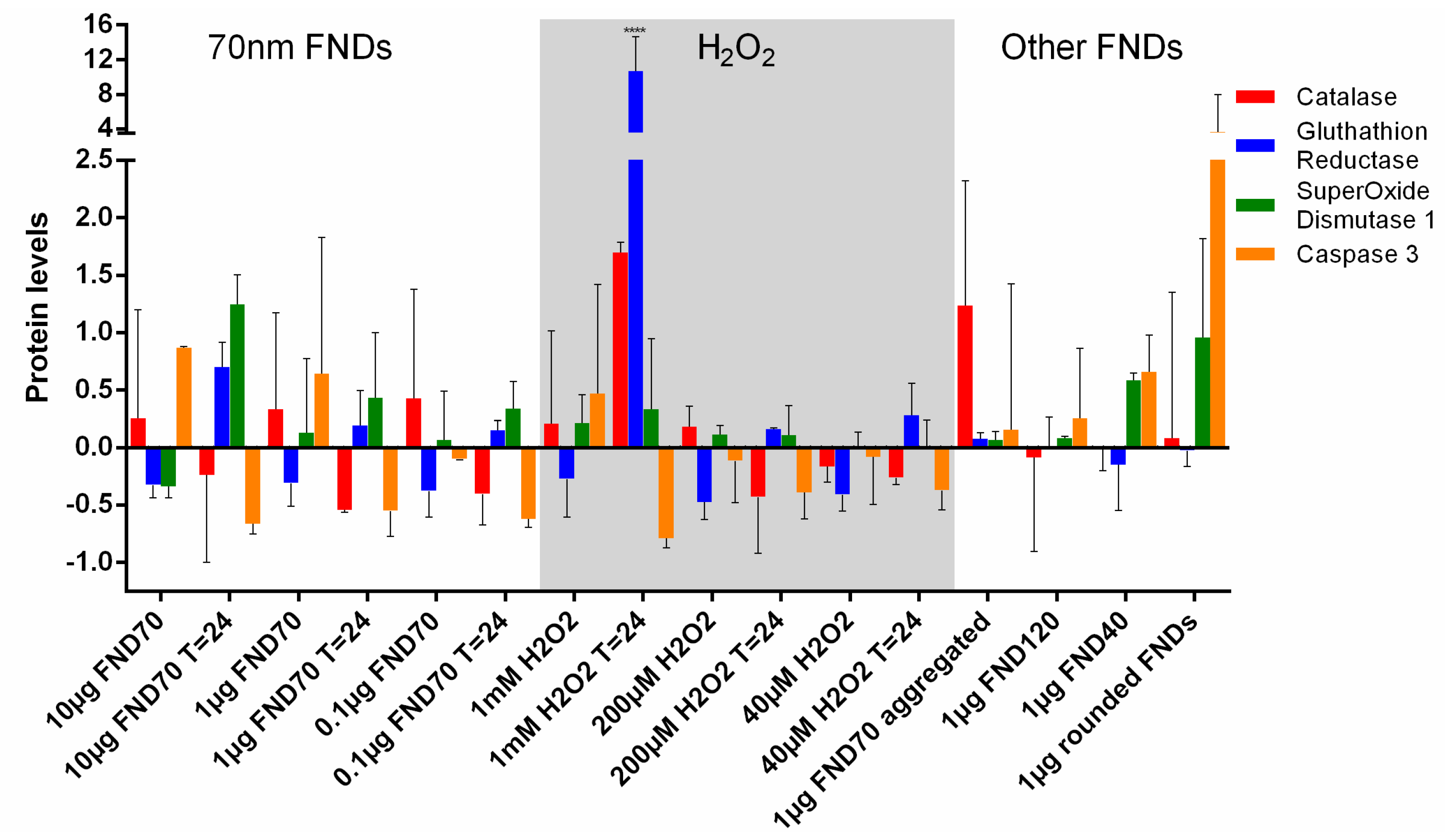
3.5. Protein Transcription
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aramesh, M.; Cervenka, J.; Roberts, A.; Djalalian-Assl, A.; Rajasekharan, R.; Fang, J.; Ostrikov, K.; Prawer, S. Coupling of a single-photon emitter in nanodiamond to surface plasmons of a nanochannel-enclosed silver nanowire. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 15530–15541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, J.R.; Koehl, W.F.; Varley, J.B.; Janotti, A.; Buckley, B.B.; Van de Walle, C.G.; Awschalom, D.D. Quantum computing with defects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 8513–8518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grinolds, M.S.; Hong, S.; Maletinsky, P.; Luan, L.; Lukin, M.D.; Walsworth, R.L.; Yacoby, A. Nanoscale magnetic imaging of a single electron spin under ambient conditions. Nat. Phys. 2013, 9, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamin, H.J.; Kim, M.; Sherwood, M.H.; Rettner, C.T.; Ohno, K.; Awschalom, D.D.; Rugar, D. Nanoscale nuclear magnetic resonance with a nitrogen-vacancy spin sensor. Science 2013, 339, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doherty, M.W.; Struzhkin, V.V.; Simpson, D.A.; McGuinness, L.P.; Meng, Y.; Stacey, A.; Karle, T.J.; Hemley, R.J.; Manson, N.B.; Hollenberg, L.C.L.; et al. Electronic properties and metrology applications of the diamond NV- Center under pressure. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta, V.M.; Bauch, E.; Ledbetter, M.P.; Waxman, A.; Bouchard, L.S.; Budker, D. Temperature dependence of the nitrogen-vacancy magnetic resonance in diamond. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Oort, E.; Glasbeek, M. Electric-field-induced modulation of spin echoes of N-V centers in diamond. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1990, 168, 529–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirhagl, R.; Chang, K.; Loretz, M.; Degen, C.L. Nitrogen-vacancy centers in diamond: nanoscale sensors for physics and biology. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2014, 65, 83–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, R.; Ho, D. Nanodiamonds as vehicles for systemic and localized drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2009, 6, 883–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhaddad, A.; Durieu, C.; Dantelle, G.; Le Cam, E.; Malvy, C.; Treussart, F.; Bertrand, J.R. Influence of the Internalization Pathway on the Efficacy of siRNA Delivery by Cationic Fluorescent Nanodiamonds in the Ewing Sarcoma Cell Model. PLoS ONE 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, C.-C.; Lee, H.-Y.; Chen, K.; Lim, T.-S.; Wu, H.-Y.; Lin, P.-K.; Wei, P.-K.; Tsao, P.-H.; Chang, H.-C.; Fann, W. Characterization and application of single fluorescent nanodiamonds as cellular biomarkers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemelaar, S.R.; de Boer, P.; Chipaux, M.; Zuidema, W.; Hamoh, T.; Martinez, F.P.; Nagl, A.; Hoogenboom, J.P.; Giepmans, B.N.G.; Schirhagl, R. Nanodiamonds as multi-purpose labels for microscopy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemelaar, S.R.; Nagl, A.; Bigot, F.; Rodríguez-García, M.M.; de Vries, M.P.; Chipaux, M.; Schirhagl, R. The interaction of fluorescent nanodiamond probes with cellular media. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perevedentseva, E.; Hong, S.F.; Huang, K.J.; Chiang, I.T.; Lee, C.Y.; Tseng, Y.T.; Cheng, C.L. Nanodiamond internalization in cells and the cell uptake mechanism. J. Nanopart. Res. 2013, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuinness, L.P.; Yan, Y.; Stacey, A.; Simpson, D.A.; Hall, L.T.; Maclaurin, D.; Prawer, S.; Mulvaney, P.; Wrachtrup, J.; Caruso, F.; et al. Quantum measurement and orientation tracking of fluorescent nanodiamonds inside living cells. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, C.; Fang, C.-Y.; Rehor, I.; Cigler, P.; Chang, H.-C.; Lin, G.; Liu, R.; et al. Unambiguous observation of shape effects on cellular fate of nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.-J.; Tzeng, Y.-K.; Chang, W.-W.; Cheng, C.-A.; Kuo, Y.; Chien, C.-H.; Chang, H.-C.; Yu, J. Tracking the engraftment and regenerative capabilities of transplanted lung stem cells using fluorescent nanodiamonds. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2013, 8, 682–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemelaar, S.R.; Van Der Laan, K.J.; Hinterding, S.R.; Koot, M.V.; Ellermann, E.; Perona-Martinez, F.P.; Roig, D.; Hommelet, S.; Novarina, D.; Takahashi, H.; et al. Generally Applicable Transformation Protocols for Fluorescent Nanodiamond Internalization into Cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.J.; Kang, M.W.; Chang, H.C.; Chen, K.M.; Yu, Y.C. Bright fluorescent nanodiamonds: No photobleaching and low cytotoxicity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 17604–17605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lien, Z.-Y.; Hsu, T.-C.; Liu, K.-K.; Liao, W.-S.; Hwang, K.-C.; Chao, J.-I. Cancer cell labeling and tracking using fluorescent and magnetic nanodiamond. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 6172–6185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paget, V.; Sergent, J.A.; Grall, R.; Altmeyer-Morel, S.; Girard, H.A.; Petit, T.; Gesset, C.; Mermoux, M.; Bergonzo, P.; Arnault, J.C.; et al. Carboxylated nanodiamonds are neither cytotoxic nor genotoxic on liver, kidney, intestine and lung human cell lines. Nanotoxicology 2014, 8, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaijayanthimala, V.; Cheng, P.Y.; Yeh, S.H.; Liu, K.K.; Hsiao, C.H.; Chao, J.I.; Chang, H.C. The long-term stability and biocompatibility of fluorescent nanodiamond as an in vivo contrast agent. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 7794–7802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Wang, X.; Jia, G.; Liu, J.H.; Wang, T.; Gu, Y.; Yang, S.T.; Zhen, S.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y. Pulmonary toxicity and translocation of nanodiamonds in mice. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2010, 19, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, S.; Gispert, J.D.; Martín, R.; Abad, S.; Menchón, C.; Pareto, D.; Víctor, V.M.; Álvaro, M.; García, H.; Herance, J.R. Biodistribution of amino-functionalized diamond nanoparticles. in vivo studies based on 18F radionuclide emission. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 5552–5559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, L.W.; Lin, Y.C.; Perevedentseva, E.; Lugovtsov, A.; Priezzhev, A.; Cheng, C.L. Nanodiamonds for medical applications: Interaction with blood in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Yin, J.; Kang, C.; Li, J.; Zhu, Y.; Li, W.; Huang, Q.; Zhu, Z. Biodistribution and toxicity of nanodiamonds in mice after intratracheal instillation. Toxicol. Lett. 2010, 198, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, L.; Yang, J.; Lan, T.T.H.; Osawa, E.; Lee, D.K.; Johnson, W.D.; Xi, J.; Chow, E.K.H.; Ho, D. Biocompatibility Assessment of Detonation Nanodiamond in Non-Human Primates and Rats Using Histological, Hematologic, and Urine Analysis. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 7385–7400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solarska, K.; Gajewska, A.; Kaczorowski, W.; Bartosz, G.; Mitura, K. Effect of nanodiamond powders on the viability and production of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species by human endothelial cells. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2012, 21, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, D.G.; Kim, K.H.; Kang, E.; Lim, S.H.; Ricci, J.; Sung, S.K.; Kwon, M.T.; Jeong, S.H. Comprehensive evaluation of carboxylated nanodiamond as a topical drug delivery system. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 2381–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.-K.; Zheng, W.-W.; Wang, C.-C.; Chiu, Y.-C.; Cheng, C.-L.; Lo, Y.-S.; Chen, C.; Chao, J.-I. Covalent linkage of nanodiamond-paclitaxel for drug delivery and cancer therapy. Nanotechnology 2010, 21, 315106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, E.K.; Zhang, X.-Q.; Chen, M.; Lam, R.; Robinson, E.; Huang, H.; Schaffer, D.; Osawa, E.; Goga, A.; Ho, D. Nanodiamond therapeutic delivery agents mediate enhanced chemoresistant tumor treatment. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 73ra21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, V.; Halloran, B.A.; Ambalavanan, N.; Catledge, S.A.; Vohra, Y.K. In vitro studies on the effect of particle size on macrophage responses to nanodiamond wear debris. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 1939–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, L.; Grobárová, V.; Shen, H.; Man, H.B.; Míčová, J.; Ledvina, M.; Štursa, J.; Nesladek, M.; Fišerová, A.; Ho, D. Comprehensive interrogation of the cellular response to fluorescent, detonation and functionalized nanodiamonds. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 11712–11721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.-A.; Kao, C.-W.; Liu, K.-K.; Huang, H.-S.; Chiang, M.-H.; Soo, C.-R.; Chang, H.-C.; Chiu, T.-W.; Chao, J.-I.; Hwang, E. The effect of fluorescent nanodiamonds on neuronal survival and morphogenesis. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diplock, A.T.; Charleux, J.L.; Crozier-Willi, G.; Kok, F.J.; Rice-Evans, C.; Roberfroid, M.; Stahl, W.; Viña-Ribes, J. Functional food science and defence against reactive oxidative species. Br. J. Nutr. 1998, 80 (Suppl. 1), S77–S112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, N.; Chen, C.S.; Hsieh, H.H.; Wu, Y.C.; Chang, H.C. In vivo imaging and toxicity assessments of fluorescent nanodiamonds in caenorhabditis elegans. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 3692–3699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrano, A.A.; Blechinger, J.; Osseforth, C.; Argyo, C.; Reller, A.; Bein, T.; Michaelis, J.; Bräuchle, C. A fast analysis method to quantify nanoparticle uptake on a single cell level. Nanomedicine 2013, 8, 1815–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nargi, F.E.; Yang, T.J. Optimization of the L-M cell bioassay for quantitating tumor necrosis factor α in serum and plasma. J. Immunol. Methods 1993, 159, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, S.Y.; Chipaux, M.; Nagl, A.; Schirhagl, R. Shape and crystallographic orientation of nanodiamonds for quantum sensing. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posakony, J.W.; England, J.M.; Attardi, G. Mitochondrial growth and division during the cell cycle in HeLa cells. J. Cell Biol. 1977, 74, 468–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jersmann, H.P.; Rathjen, D.A.; Ferrante, A. Enhancement of lipopolysaccharide-induced neutrophil oxygen radical production by tumor necrosis factor alpha. Infect. Immun. 1998, 66, 1744–1747. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pelka, J.; Gehrke, H.; Esselen, M.; Türk, M.; Crone, M.; Bräse, S.; Muller, T.; Blank, H.; Send, W.; Zibat, V.; et al. Cellular uptake of platinum nanoparticles in human colon carcinoma cells and their impact on cellular redox systems and DNA integrity. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2009, 22, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lake, M.P.; Bouchard, L.S. Targeted nanodiamonds for identification of subcellular protein assemblies in mammalian cells. PLoS ONE 2017, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, M.S.; Liu, L.S.; Leung, H.M.; Lo, P.K. Cancer-Cell-Specific Mitochondria-Targeted Drug Delivery by Dual-Ligand-Functionalized Nanodiamonds Circumvent Drug Resistance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 11780–11789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Laan, K.J.; Hasani, M.; Zheng, T.; Schirhagl, R. Nanodiamonds for in vivo applications. Small 2018, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, C.; Prakash, D.; Gupta, S. Cancer treatment with nano-diamonds. Front. Biosci. 2017, 9, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, D.; Wang, C.-H.K.; Chow, E.K.-H. Nanodiamonds: The intersection of nanotechnology, drug development, and personalized medicine. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1500439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augustine, S.; Singh, J.; Srivastava, M.; Sharma, M.; Das, A.; Malhotra, B.D. Recent advances in carbon based nanosystems for cancer theranostics. Biomater. Sci. 2017, 5, 901–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, W.; Toh, T.B.; Abdullah, L.N.; Yvonne, T.W.Z.; Lee, K.J.; Guenther, I.; Chow, E.K.H. Nanodiamond–Manganese dual mode MRI contrast agents for enhanced liver tumor detection. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2017, 13, 783–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manus, L.M.; Mastarone, D.J.; Waters, E.A.; Zhang, X.Q.; Schultz-Sikma, E.A.; MacRenaris, K.W.; Ho, D.; Meade, T.J. Gd(III)-nanodiamond conjugates for MRI contrast enhancement. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, Y.; Hsu, T.Y.; Wu, Y.C.; Chang, H.C. Fluorescent nanodiamond as a probe for the intercellular transport ofproteins invivo. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 8352–8360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
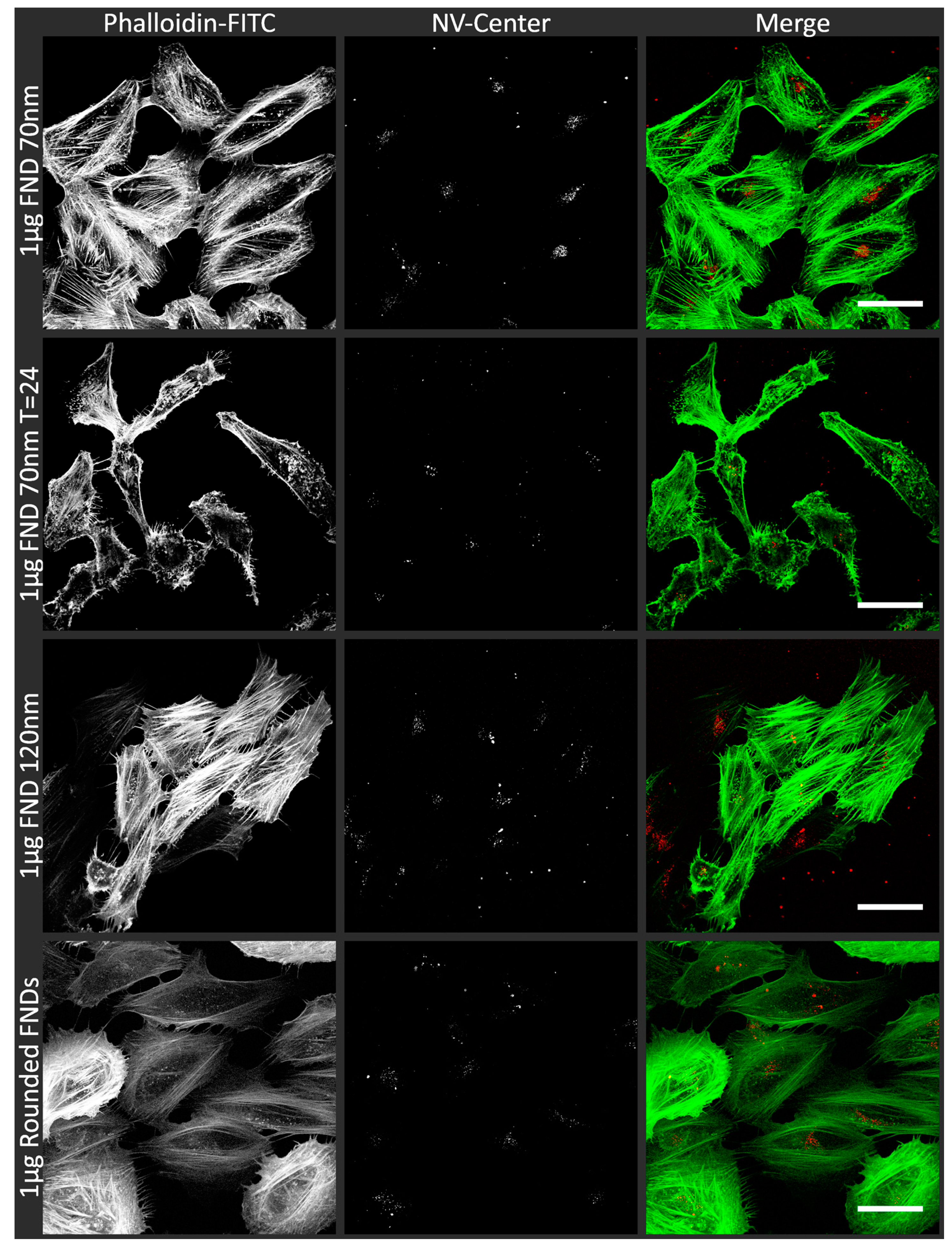


| Name | NV-Centres | Average Diameter | Concentration/Condition Used | Surface Termination | Surface Potential |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FND120 | >1000 NV/particle | 120 nm | 1 µg/mL | Carboxylated-COOH | −20 mV |
| FND70 | >300 NV/particle | 70 nm | 10 µg/mL, 1 µg/mL, 0.1 µg/mL, 1 µg/mL aggregated | Carboxylated-COOH | −40 mV |
| FND40 | 10–15 NV/particle | 40 nm | 1 µg/mL | Carboxylated-COOH | −45 mV |
| Rounded FNDs | 25 nm | Carboxylated-COOH | −23 mV |
| Target cDNA | Primer Sequence 5’->3’ | Product Size, bp | Tm |
|---|---|---|---|
| Catalase | CGCAGAAAGCTGATGTCCTG | 20 | 60.5 °C |
| Glutathion Reductase | TCAACGAGCTTTACCCCGAT | 20 | 60.4 °C |
| SuperOxide Dismutase 1 | ACAGCAGGCTGTACCAGTGC | 20 | 59.9 °C |
| Caspase-3 | GGGATCGTTGTAGAAGTCTAACTG | 24 | 57.1 °C |
| 18S | AAGGAGACTCTGGCATGCTAAC | 22 | 58.5 °C |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hemelaar, S.R.; Saspaanithy, B.; L’Hommelet, S.R.M.; Perona Martinez, F.P.; Van der Laan, K.J.; Schirhagl, R. The Response of HeLa Cells to Fluorescent NanoDiamond Uptake. Sensors 2018, 18, 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18020355
Hemelaar SR, Saspaanithy B, L’Hommelet SRM, Perona Martinez FP, Van der Laan KJ, Schirhagl R. The Response of HeLa Cells to Fluorescent NanoDiamond Uptake. Sensors. 2018; 18(2):355. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18020355
Chicago/Turabian StyleHemelaar, Simon R., Babujhi Saspaanithy, Severin R. M. L’Hommelet, Felipe P. Perona Martinez, Kiran J. Van der Laan, and Romana Schirhagl. 2018. "The Response of HeLa Cells to Fluorescent NanoDiamond Uptake" Sensors 18, no. 2: 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18020355
APA StyleHemelaar, S. R., Saspaanithy, B., L’Hommelet, S. R. M., Perona Martinez, F. P., Van der Laan, K. J., & Schirhagl, R. (2018). The Response of HeLa Cells to Fluorescent NanoDiamond Uptake. Sensors, 18(2), 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18020355





