Abstract
The critically endangered Vietnamese Pond Turtle (Mauremys annamensis), an endemic species occurring in a small lowland area in central Vietnam, has been virtually extirpated from its natural range. As a result, reintroduction of held individuals worldwide, especially from Europe, the United States, and Vietnam, will play a vital role in species recovery programs. Nevertheless, the discordance between different molecular markers in inferring the placements of two closely related species, M. annamensis and M. mutica, and the existence of two distinct mitochondrial lineages within M. annamensis, have hindered conservation strategies to properly maintain the genetic integrity of held populations to release individuals back to their natural habitat in the future. In this study, we sequenced 732 bps of a mitochondrial gene (ND4) and 1038 bps of an intron fragment of the RNA fingerprint protein 35 (R35) gene for 18 samples collected from the local trade in five provinces in Vietnam and 20 samples from founders in the Turtle Conservation Centre, Cuc Phuong National Park, Vietnam. DNA sequences analyzed by Bayesian Inference, Maximum Likelihood, and NeighborNet methods show that the Vietnamese Pond Turtle is a well-defined species and that the population of M. mutica from Hainan Island likely evolved through introgression between a lineage distantly related to true M. mutica and M. annamensis and a lineage closely related to the two mitochondrial haplotypes of M. annamensis. Interestingly, our analyses of samples collected from the local trade and those with known localities reveal that the two extant mitochondrial lineages within M. annamensis are geographically isolated and evolutionarily significant. Based upon the new findings, we recommend genetic screening for all held populations in Vietnam and elsewhere and that animals with different genetic histories be managed separately. In addition, it is important to use other molecular markers, such as microsatellites and single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), to determine potential hybrids between the two mitochondrial haplotypes and remove them from conservation breeding programs before releasing the turtles back to their natural habitat.
1. Introduction
The Vietnamese Pond Turtle, Mauremys annamensis, was first described by Siebenrock in 1903 based on a juvenile specimen from Phuc Son or Phuoc Son southwest of Tourane (now known as the city of Da Nang). Another adult specimen was collected at or near “Fai-Fo” (Hoi An Town, Quang Nam Province) by Bourret about 50 km northeast of Phuoc Son [1]. For a long time, this species was believed to occur in a very restricted area of central Vietnam [2,3]. To date, data obtained from numerous field and interview surveys have expanded the range of this species to include Da Nang City [4], Quang Nam Province [1,5], Binh Dinh Province [3], Quang Ngai Province [6], Gia Lai Province [7], Phu Yen Province, and Dak Lak Province [5] (Figure 1). However, despite intense survey efforts, this species has only been recorded a handful of times in the wild. Most recently, a team of the Asian Turtle Program (ATP) in Vietnam caught an individual in Dien Ban District, Quang Nam Province, in 2006 [6]. It was only the second time in 65 years the species was recorded in the wild by scientists since first reported by Bourret [1].
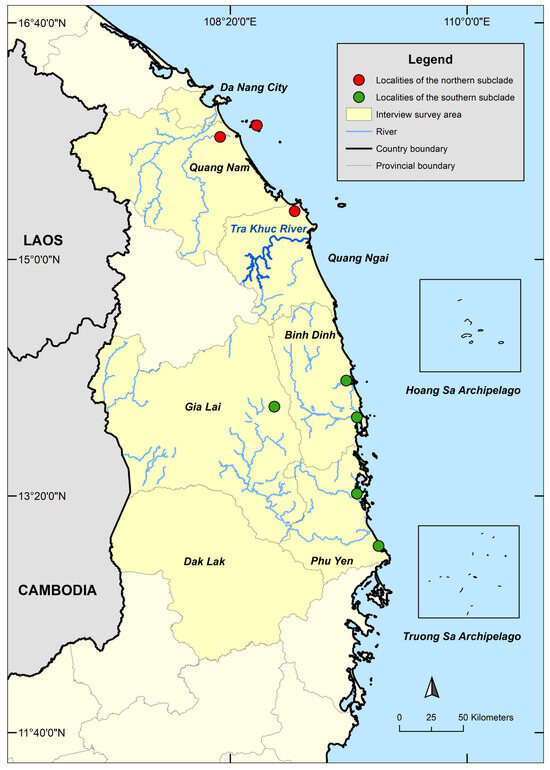
Figure 1.
Interview survey area in central Vietnam. Localities of local traded specimens are shown with red and green dots. The Tra Khuc River is the potential natural barrier separating the northern and southern subclades of the Vietnam Pond Turtle.
The Vietnamese Pond Turtle is particularly vulnerable to hunting pressure and habitat loss as it is confined to lowland wetlands across one municipality and six provinces in central Vietnam [3,5]. Much of its habitat, especially around towns and cities, has been converted to agricultural use, which is no longer suitable for the species [5]. In addition, after years of overexploitation, this species has become extremely rare or considered functionally extinct in the wild [5,8,9]. The species has been categorized in the IUCN Red List as Critically Endangered since 2000 [10], included in Appendix II of the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES) since 2003, and considered one of the top 25 most endangered tortoises and freshwater turtles in the world [9]. In Vietnam, this species is protected under Decree 64/2019/ND-CP and Decree 06/2019/ND-CP, where it is listed in Group IB, the highest level of protection for wild fauna, and as Critically Endangered in the Vietnam’s Red Data Book [11]. Fortunately, there are a number of healthy populations that breed well in captivity, currently maintained in Europe [12], the United States [9,13], Japan, and Vietnam [5]. Zoos and holding facilities have started a coordinated effort for ex situ conservation breeding of this species with a goal of releasing them to the wild once an appropriate protected area is established in its range [14].
Nonetheless, the status of animals in conservation breeding programs around the world is complicated by the propensity of hybridization between closely related species, i.e., Mauremys annamensis, M. mutica, M. nigricans, M. sinensis, Cuora amboinensis, and C. trifasciata [15,16,17,18]. All individuals of M. annamensis in human holdings, except one in the Columbus Zoo, USA, are of unknown origin and might come from farms where hybrids have been produced either intentionally or unintentionally [16,17,19,20]. Genetic distinction between the Vietnamese Pond Turtle, M. annamensis, and its sister species, the Yellow Pond Turtle, M. mutica, is further problematic by the discordance between nuclear and mitochondrial genes in recovering the phylogenetic relationships between the two taxa. According to analyses of the mitochondrial NADH dehydrogenase subunit 4 (ND4) and Cytochrome C oxidase subunit (COI) genes, M. mutica from Hainan and Vietnam are imbedded within M. annamensis, while the results based on the RNA fingerprint protein 35 gene (R35) show that the two forms of M. mutica are distantly related to M. annamensis [19,20,21,22]. Zhao et al. [22] even suggested that M. annamensis is a potential hybrid species because of its high level of genetic similarity with M. mutica based on the mitochondrial COI gene.
Moreover, traded and held individuals of the Vietnamese Pond Turtle in Europe and Vietnam contain at least two distinct mitochondrial haplotypes [14,20,21]. To release animals from the holdings to their native natural habitats, we need to clarify the genetic profile of M. annamensis, especially in relation to M. mutica from Hainan, using samples with reliable origins. To improve the likelihood of obtaining samples of known provenance, in this study, we focused on interviewing people involved in the local trade of M. annamensis across its range. Samples were taken from locally traded animals and used as reference because they have been shown to be valuable in tracking origins of turtles from unknown sources, especially for endangered species with very limited access to field-collected samples [23]. We also genetically screened founder individuals currently maintained at the Cuc Phuong Turtle Conservation Centre (TCC) in Vietnam. We sequenced one mitochondrial (ND4) and one nuclear (R35) gene from the new samples and analyzed the newly generated data along with data from previous studies using phylogenetic and network approaches to determine the genetic diversity, phylogeographic pattern, and evolutionary history of natural populations in Vietnam and better understand the genetic profiles of held animals at the TCC. The data will then be used to develop a breeding strategy to maintain genetic integrity of the turtles held in conservation facilities and ensure that they are released to their native habitat in the future.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Interviews
Interviews were conducted in Vietnamese in local communities of Da Nang City and six provinces (Quang Nam, Quang Ngai, Binh Dinh, Phu Yen, Dak Lak, and Gia Lai) (Figure 1) from 2003 to 2015 to determine species presence within those areas. We used a semi-structured survey technique and respondent-driven sampling [24]. The targeted interviewees were local hunters, local traders, local rangers, and other members of local communities near the wetland habitat of the species. Information was also collected on economic value, abundance, hunting pressure, trade and volume of trade, and, especially, areas of species occurrence in the study area. For the purposes of this study, only information related to localities of collected samples was included. Other data obtained from the interview surveys will be provided in future publications. When specimens were encountered, tissue samples (nail or tail tip) were collected whenever possible, and a standard field record form was completed for each sample. Interview protocols were conducted in accordance with international ethical standards and following relevant Vietnamese laws and regulations. See Supplementary Data S1 for more details on interview questions (translated to English) and the standard field record form.
2.2. Taxonomic Sampling
In total, 38 samples of M. annamensis were sequenced, including 18 samples collected from different locations in the central part of Vietnam guided by interview responses and 20 samples from founders in the TCC, Cuc Phuong National Park (Table 1 and Figure 1). Tail or skin tissue was taken from each animal and immediately preserved in 70% ethanol (Merck, Germany). Samples were transported to the VNU University of Science, Vietnam National University, Hanoi, and were stored at −20 °C until extracted.

Table 1.
GenBank accession numbers and associated voucher specimens/tissues that were used in this study.
2.3. Molecular Data
We sequenced the ND4 mitochondrial gene and nuclear R35 intron for each sample of M. annamensis. These two genes were selected because they were successfully used in previous studies to investigate phylogenetic relationships and detect hybridization between closely related species within this species complex [18,20,21]. From GenBank, we retrieved 33 sequences of M. mutica and M. annamensis, prioritizing sequences originating from specimens with known localities, and three outgroups, selected following Spinks et al. [25], Cuora amboinensis, C. galbinifrons, and M. sinensis (Table 1). Data from Somerová et al. [14] were inaccessible, and we did not include sequences of M. mutica from Vietnam because they came from traded animals with unknown origin.
Total genomic DNA was extracted using the DNeasy Blood and Tissue Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) following the manufacturer’s instructions for animal tissue. Genomic extraction was checked by electrophoresis. A negative control was used for every extraction. We amplified DNA samples collected from central Vietnam using HotStar Taq Master Mix (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). Amplification of DNA samples collected from Cuc Phuong Turtle Conservation Center was performed using Dream Taq PCR Master Mix (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Vilnius, Lithuania). Standard PCRs were carried out using the following conditions: 95 °C for 15 min with HotStarTaqTM Master Mix (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) or 95 °C for 5 min with DreamTaq PCR Mastermix (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Vilnius, Lithuania), 35 cycles at 95 °C for 30 s, 45 °C for 45 s, 72 °C for 60 s; a final extension at 72 °C for 6 min. PCR volume consisted of 2 µL of each primer at 10 pmol/µL, 5 µL of distilled water, 10 µL of Taq master mix, and 1–4 µL DNA template, depending on the quantity of DNA. All the primers used in this study are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Primers used in this study.
A negative control was used for every PCR reaction. To confirm the size and presence of PCR products, 5 µL of each PCR product was run on a 1% agarose gel, 1X TBE buffer, stained with 2 pg/µL bromide, and photographed under UV light. Successful PCR products were cleaned using Gene Jet PCR Purification Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Lithuania) following the manufacturer’s instructions. Cleaned products were sent to First Base (Malaysia) for sequencing.
2.4. Phylogenetic and Network Analyses
The newly generated sequences were edited using Sequencher v5.4 (Gene Codes Corp, Ann Arbor, MI, USA), and then all sequences were aligned using ClustalX v2.1 [29] with default settings. The data were analyzed by three methods: Bayesian inference (BI), as implemented in MrBayes v3.2.1 [30]; Maximum Likelihood (ML), as implemented in IQ-TREE v1.6.7.1 [31]; and NeighborNet, as implemented SplitsTree v4.14.2 [32]. A similar approach has been successfully implemented in previous studies [20,21,23].
We ran BI and ML analyses using both single-model and partitioned datasets based on the concatenated matrix to examine the robustness of tree topology [33,34]. For the single-model analysis, we determined the optimal model for the combined datasets using jmodelTest v2.1.4 [35]. For partitioned analyses, we divided the data into four sets, including three partitions for the mitochondrial marker, ND4, based on codon position (first, second, and third) and one partition for the nuclear gene, R35. The optimal model of molecular evolution for each partition was selected using the AIC (Akaike information criterion) in PartitionFinder v2.1.1 [36]. Both single-model and partitioned BI analyses were performed with a random starting tree, run for 1 × 107 generations, four Markov chains (one cold, three heated) with default heating values, and sampled every 1000 generations. Sample points were plotted against the number of generations to detect stationarity of the Markov chains. Trees generated prior to stationarity were discarded from the final analyses using the burn-in function. Two independent analyses were performed simultaneously. Posterior probability (PP) values for all nodes in the final majority rule consensus tree were provided. Parameters were inferred independently for each data partition in the partitioned Bayesian analysis using the UNLINK command. For the ML analyses, data were analyzed using with 10,000 ultrafast bootstrap (UFB) pseudo-replicates [37]. We regard UFB and PP values of ≥95% as strong support and values of <95% as weak support [30,37]. To detect discordance between the mitochondrial and nuclear genes and potential introgression/hybridization, we also ran separate single-model ML and BI analyses for each marker using the same procedure employed for the concatenated dataset. Uncorrected pairwise genetic distances between different mitochondrial subclades of M. annamensis and Hainan’s population of M. mutica were calculated based on ND4 data using the software package PAUP*4.0b10 [38].
For the NeighborNet analysis, the final matrix included 59 ND4 sequences of M. annamensis and M. mutica from Hainan. This final matrix was imported into the SplitsTree v4.14.2 [32] to create a distance-based unrooted tree diagram by means of the neighbor-joining algorithm [39]. Alternative interspecific relationships were visualized with the NeighborNet algorithm [40] as implemented in SplitsTree with the following settings: edge fitting as ordinary least squares, equal angle as the chosen splits transformation, least squares to modify weights, and four maximum dimensions as the filtering option. The generated split graph yielded a visual representation of conflicting signals in the data as a series of parallel edges. The program computed the least squares fit (LSfit) between the pair-wise distances from the graph and the distances from the matrix. Internal node support values were estimated by 10,000 bootstrap pseudo-replicates [41]. We regard bootstrap values of ≥95% as strong support and values of <95% as weak support.
3. Results
During 234 days of surveys, more than 1800 interviews were carried out and 116 field records from Binh Dinh, Gia Lai, Phu Yen, Quang Nam, and Quang Ngai provinces were reported. Little information of this species was collected in Da Nang City, and its occurrence in the lowland of Dak Lak Province was unconfirmed. A total of 18 DNA samples were collected from local households in five provinces (Binh Dinh, Gia Lai, Phu Yen, Quang Nam, and Quang Ngai). One sample was obtained from Hon Lao Island, Cu Lao Cham Archipelago, around 16 km offshore from Hoi An City, Quang Nam Province. The specimen was reportedly caught approximately 1 km from a local household and kept as pet since then. This is the first time the species was reported from the island (Nguyen et al.) [42]. Other results obtained from the interview surveys are not presented in this study but will be published in a future paper.
We successfully sequenced 18 samples collected from local interviews and 20 samples collected from founders in the TCC (Table 1). The final concatenated matrix consisted of 74 terminals, including 38 from this study and 36 from previous studies, including three outgroups with a total of 1887 aligned characters (ND4: 743 characters; R35: 1144 characters). We ran single-model Bayesian and ML analyses based on the combined matrix using the HKY + I + G model of molecular evolution as selected by jModelTest. TIM + I, TRN, and K81UF + G were the best-fit models of nucleotide evolution for first, second and third codon position of ND4, respectively, and HKY + I + G was the best-fit model for R35 (Table 3). In the single-model and the partitioned Bayesian analyses, -lnL scores reached the equilibrium after 39,000 and 40,000 generations, respectively (Table 3).

Table 3.
Models used in Bayesian and maximum likelihood analyses.
For the concatenated dataset, under both single-model and partitioned schemes, the topologies generated by BI and ML analyses were identical. All major nodes received strong support values from all analyses, except for four nodes weakly corroborated by the mixed-model ML analysis. In general, our phylogenetic estimates based on the concatenated matrix recovered the true M. mutica (the clade with a specimen from the type locality and others from eastern China), M. mutica from Hainan, and two subclades of M. annamensis from Vietnam (Supplementary Data S2). The ND4 tree, based on congruent BI and ML topologies, shows that the relationships between M. annamensis’s Subclade 1 and Subclade 2 and M. mutica from Hainan were unresolved in our analyses, whereas Subclade 1 and M. mutica from Hainan formed a monophyletic group with low statistical support values from all analyses in the previous studies. Overall, a major difference between the tree based on ND4 and R35 and that derived from ND4 alone is M. mutica from Hainan is sister to the two M. annamensis subclades with strong support from both BI and ML analyses (Figure 2).
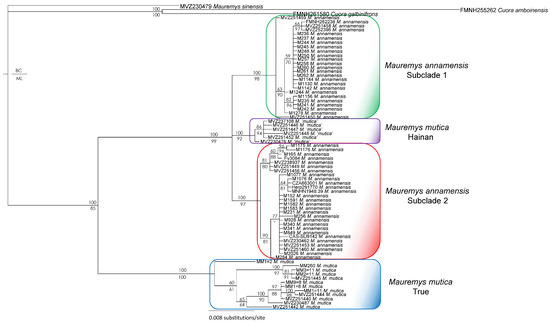
Figure 2.
Bayesian phylogram based on the ND4 gene. Numbers above branches are Bayesian single-model posterior probability (PP), while numbers below branches are ML ultrafast bootstrap (UFB) values. Hyphens denote value < 50%. Additional information on subclade assignment can be found in Table 1.
The tree generated from R35 demonstrates that both M. annamensis and M. mutica from Hainan were recovered as monophyletic in our ML and BI analyses with high nodal values from the latter, while the true M. mutica was paraphyletic with regard to M. annamensis. The two clades in turn formed a monophyletic group with significant support values from the BI analysis (Figure 3). The sets of relationships also show that the true M. mutica was monophyletic with low support values from all analyses.
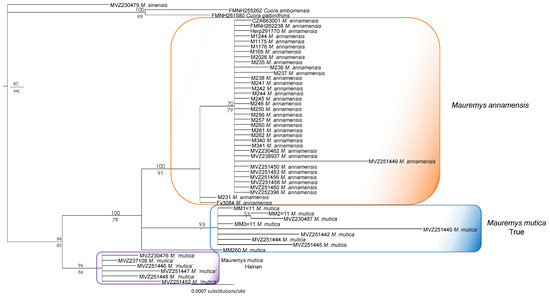
Figure 3.
Bayesian phylogram based on the R35 gene. Numbers above branches are Bayesian single-model PP values, while numbers below branches are ML UFB values. Hyphens denote values < 50%.
Since the major discrepancy between nuclear and mitochondrial trees was related to the placement of M. mutica from Hainan, we reran all analyses after removing these samples to check the stability of the remaining clades using the same procedures. The combined tree based on both markers showed two subclades within M. annamensis and the true M. mutica as the sister taxon to the species. All major nodes received strong statistical support values from at least three analyses (Figure 4). The ND4 tree had virtually the same topology as that of the combined one, whereas the R35 tree supported the monophylies of M. annamensis and the true M. mutica (Figure 5 and Figure 6), with high nodal values from both analyses only found for the M. annamensis clade (Figure 6).
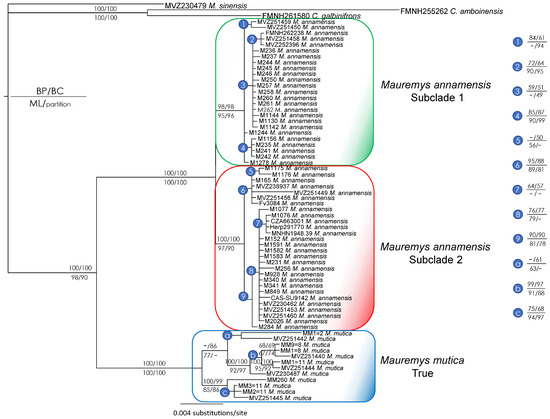
Figure 4.
Bayesian phylogram based on the combined matrix of ND4 and R35 genes (without data of Mauremys mutica from Hainan Island). Numbers above branches are Bayesian partitioned PP and Bayesian single-model PP values, while numbers below branches are ML and partitioned analysis UFB values. Hyphens denote values < 50%. Additional information on subclade assignment can be found in Table 1.
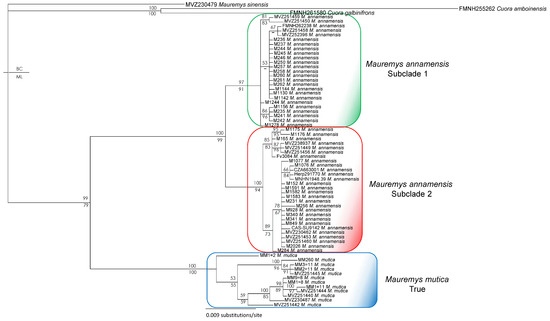
Figure 5.
Bayesian phylogram based on the ND4 gene (without data of Mauremys mutica from Hainan Island). Numbers above branches are Bayesian single-model PP values, while numbers below branches are ML UFB values. Hyphens denote values < 50%. Additional information on subclade assignment can be found in Table 1.
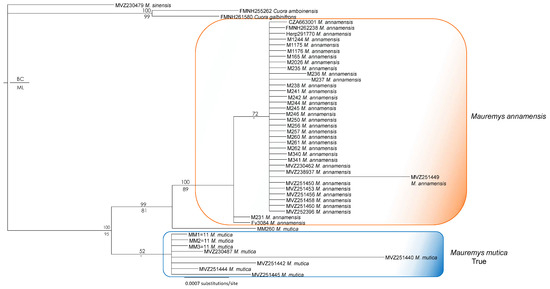
Figure 6.
Bayesian phylogram based on the R35 gene (without data of Mauremys mutica from Hainan Island). Numbers above branches are Bayesian single-model PP, while numbers below branches are ML UFB values. Hyphens denote values < 50%.
The main discordance between R35 and ND4 trees was the placement of the putative true M. mutica sample from Hualien Country, Taiwan (MM260). This sample clustered with the true M. mutica clade in both ND4 and combined analyses, but it was recovered as a sister taxon to the M. annamensis clade based on R35 with a high nodal value from the Bayesian analysis.
Similarly, we recovered three mitochondrial clusters in the NeighborNet. One cluster contained 18 sequences of M. annamensis from Quang Nam and Quang Ngai Provinces and the TCC. The other consisted of 20 samples from Binh Dinh, Gia Lai, and Phu Yen Provinces and the TCC with BP values of 95 and 99, respectively (Figure 7). The remaining cluster, which received a BP value of 96, comprised all sequences of M. mutica from Hainan. Uncorrected p-distance between the Hainan’s population and Subclade 1 and Subclade 2 was 1.1–2.6% and 1.1–2.3%, respectively, and Subclade 1 and Subclade 2 had 1.1–2.6% divergence, while the p-distance between the Hainan’s population, Subclade 1 and Subclade 2 and the true M. mutica was 6.2–8.0%, 3.5–8.2%, and 6.2–8.2%, respectively, based on the fragment of ND4 (Supplementary Data S3).
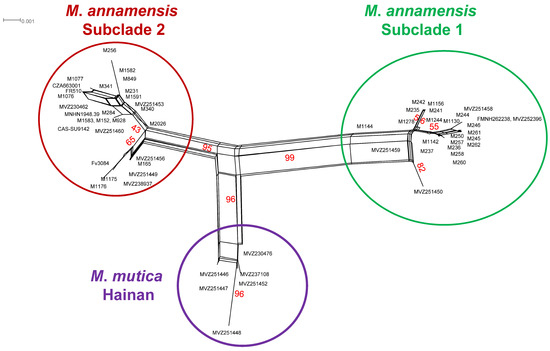
Figure 7.
Split tree network based on 59 ND4 sequences of Mauremys annamensis and M. mutica from Hainan Island. Red numbers represent bootstrap values (10,000 replications) in percentage. Additional information on subclade assignment can be found in Table 1.
4. Discussion
Our long-term, comprehensive interview surveys confirm the occurrence of the Vietnam Pond Turtle in five provinces in south-central Vietnam. Although the species was recorded in Da Nang City, it might have been extirpated in the highly developed areas surrounding the municipality. Similarly, the species could have occurred in the lowlands of Dak Lak Province, but our surveys were unable to verify its presence there. Interestingly, a sample of M. annamensis was collected for the first time from Cu Lao Cham Archipelago, which has been designated as a Biosphere Reserve by UNESCO (the United Nations Education, Scientific and Cultural Organization) since 2009. More studies should be conducted to assess the population status of the species on the island (Nguyen et al. in press) [42].
Our results from separate analyses of mitochondrial (ND4) and nuclear (R35) genes are highly similar to those reported by Fong et al. [20,21] and Somerová et al. [14] (Figure 2 and Figure 3). Two independent and reciprocally monophyletic mitochondrial clades of Mauremys annamensis are consistently recovered with high statistical support in nearly all analyses. Similarly, the monophyly of the true M. mutica clade is largely corroborated by separate analyses of both ND4 and R35, except for the sample MM260 from Taiwan (see below for more detail). In contrast, the placements of M. mutica from Hainan vary substantially between ND4 and R35 phylogenies (Figure 2 and Figure 3). In the former, the Hainan population groups with two other mitochondrial subclades of M. annamensis with strong support, while, in the latter, it forms a clade distantly related to M. annamensis. In our combined tree, the Hainan population is, however, recovered as a sister taxon to M. annamensis with high statistical values from all analyses (Supplementary Data S2). This novel relationship shows that this population probably represents a distinct species, for which Fong et al. [21] recommended the name M. schmackeri [43] because the type specimen (SMF 7584) was collected from Hainan.
On the other hand, the conflicting placements of the M. mutica from Hainan in the trees based on the nuclear marker results and a distinct mitochondrial clade within M. annamensis suggest that M. mutica from Hainan seems to have a hybrid origin between a sister lineage related to both the true M. mutica and M. annamensis (Figure 2 and Figure 3). In addition, our analyses without sequences of the population from Hainan confirm the congruence between mitochondrial and nuclear phylogenies, except for sample MM260 from Hualien Country, Taiwan (Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6). The conflicting placements of the sample in the two trees suggest that it might be a recent hybrid between the true M. mutica and M. annamensis. If true, it is likely that human-mediated hybridization between the two species has occurred in Taiwan, as also reported in other turtle species [18]. The issue should be further investigated in future studies.
This hypothesis contradicts the possibility raised by Zhao et al. [22] that M. annamensis could be a hybrid species because of its high level of similarity in the mitochondrial COI to M. mutica from Hainan. Nonetheless, as the results from Zhao et al. [22] were only based on a mitochondrial gene, the conclusion is likely drawn from an incomplete picture of the biological processes influencing the evolution of this complicated group of turtles.
Hybridization or introgression speciation was once thought to be rare in animals, but this phenomenon has been increasingly recognized by recent work [44,45,46]. Introgression speciation has been observed in other turtle species in both suborders Cryptodira and Pleurodira [47,48,49]. Despite numerous cases of artificially produced hybrid forms reported in previous studies [15,16,17], M. mutica from Hainan seems to represent a species naturally evolved through introgressive hybridization, because both nuclear and mitochondrial genotypes of the population are distinct from those found in the extant true M. mutica and M. annamensis. This hypothesis implies that different lineages of the species complex might have once co-occurred in the same region where genetic exchange between them were facilitated, especially considering the low genetic divergence between the two extant mitochondrial subclades of M. annamensis and that of M. mutica from Hainan Island. Subsequent dispersal and isolation by geographic barriers, such as mountain passes and the sea, resulted in the current distribution pattern of extant lineages within the complex.
The origin of M. mutica from Vietnam is, however, still unclear. Zhao et al. [22] reported that M. mutica from Hainan and Vietnam share the same mitochondrial haplotype with M. annamensis, whereas Fong et al. [20] showed that M. mutica collected from the trade in Vietnam has two distinct mitochondrial haplotypes, one clustering with Subclade 1 of M. annamensis and the other embedded within the clade of Hainan’s M. mutica. The discrepancy between the results from the two studies could just be down to the use of two different mitochondrial markers. The barcoding gene, COI, which is potentially not informative at the population level [50], was, as a result, unable to assign the samples to specific mitochondrial clades. It is also possible that Zhao et al. [22] did not include samples from all mitochondrial clades in their study. Fong et al. [20], on the other hand, found that the forms of M. mutica from Hainan and Vietnam are recovered in the same clade in the phylogeny based on R35. The finding seems to suggest that there were multiple hybridization events between Subclade 1 of M. annamensis and Hainan and Vietnam’s M. mutica in the past. However, since all samples of M. mutica from Vietnam used in the studies originated from the trade with unknown origin, this hypothesis needs to be verified with known-locality samples.
Phylogenetic and network analyses of samples collected from the local trade throughout the species range reveal that the two subclades of M. annamensis are geographically isolated. While Subclade 2 is found in the northern part, Subclade 1 occurs in the southern part of the species range (Figure 1). Four known-locality samples, CAS-SU9142 and MNHN 1948.39 (Hoi An City, Quang Nam Province), CZA663001 (Da Nang City), and Herp291770 (Dien Ban District, Quang Nam Province), originated from Quang Nam Province and Da Nang City and cluster with other samples collected from the local trade in Quang Nam and Quang Ngai provinces. Other samples obtained from more southern provinces, including Binh Dinh, Gia Lai, and Phu Yen, were placed in Subclade 1 (Figure 2 and Figure 4). As Tra Khuc River is the largest geographic feature present in the area between the two subclades, we hypothesize that it forms a natural barrier amid two haplotypes (Figure 1). Within Subclade 2, two additional mitochondrial lineages were recovered, but their nodal support is low, and pairwise genetic distance is negligible (Figure 3, Supplementary Data S3). Nonetheless, it is important to continue to investigate potential factors causing the genetic split. The sample collected from Hon Lao Island, Cu Lao Cham Archipelago is placed within Subclade 2 with other samples from the northern part of the region and shows little genetic divergence from the others. It is likely that the species recently dispersed to the island.
5. Recommendations
The results of our study based on locally traded and known-locality samples illustrate that the Vietnam Pond Turtle is a well-defined species with two geographically distinct mitochondrial lineages. Morphological research also confirms differences in carapace and plastron shape between individuals of the two mitochondrial lineages [51], supporting the evolutionary significance of the two subclades. To avoid genetic mixture between the two lineages in human holdings, we recommend genetic screening be conducted for founders with unknown origin to determine their genetic identity, as hybridization between them can compromise genetic distinctiveness of the two populations. Founders in Europe, the United States, and Vietnam, which have been found to contain both haplotypes [14,51], need to be separated based on available genetic assignments. Moreover, other markers, such as microsatellites and single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), should also be applied to determine potential hybrids between the two mitochondrial lineages in F1 and F2 generations in breeding programs around the world.
As the species is virtually extinct in the wild, reintroduction of held animals, genetically screened for their provenance, to its natural habitat seems to be the only viable solution to recover its populations. To this end, good assurance colonies have been maintained in Europe, Japan, the United States, and Vietnam [5,9,52]. Since 2006, 35 individuals from Hong Kong and 71 from Europe have been donated to the TCC in Cuc Phuong National Park, Vietnam, to strengthen the colony [52]. In addition, as one of the flagship species of the Vietnamazing conservation campaign sponsored by the European Association of Zoo and Aquaria (EAZA), more support will be allocated to genetic screening and restocking activities of the Vietnamese Pond Turtle (Ziegler et al. 2024) [53]. However, to date, no protected area has been established for the species in its range in central Vietnam. Our discovery of the species in the Cu Lao Cham Biosphere Reserve (Nguyen et al. 2025) [42] indicates that this could be the first known protected area where the species occurs, and held animals from the northern mitochondrial clade could be released to the island in the future. However, there is a need to set up another site in the southern part of its range where a suitable habitat is available to conserve the remaining lineage of this critically endangered and endemic species.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/d17040260/s1, Data S1: Interview questionnaire; Data S2: Bayesian phylogram based on the combined matrix of ND4 and R35 genes.; Data S3: Genetic distance table.
Author Contributions
Methodology, M.D.L. and H.T.N.; formal analysis, H.T.N. and M.D.L.; resources, T.E.M.M., T.Z., M.E.B., H.V.H., L.T.N., H.T.D., V.T.H.N., H.L.T.T. and T.T.N.; writing—original draft preparation, M.D.L., H.T.N. and H.V.H.; writing—review and editing, all authors. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Rotterdam Zoo, the Cleveland Metroparks Zoo, the Cologne Zoo, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service (USFWS-F22AP01784), the Critical Ecosystem Partnership Fund (CEPF-111987) and USAID-PEER Science [project no. 3-149].
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Central Institute for Natural Resources and Environmental Studies (date of approval: 28 March 2024).
Data Availability Statement
Sequences of all samples were uploaded to NCBI GenBank with accession numbers PV388581-PV388641.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Phong Dang Bui, Thuan Xuan Nguyen, Hang Thi Tran, and Thong Van Pham for assistance in the field and at the Turtle Conservation Centre (TCC). Cuc Phuong National Park (CPNP) and TCC facilitated sample collections. Six provinces and CPNP provided permits to carry out the study. We thank Nguyen Van Thanh, Duong Thuy Ha, and Cao Thi Huong Giang for laboratory assistance and helpful discussions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Bourret, R. Les tortues de l’Indochine; Institut Océanographique Indochine: Nha Trang, Vietnam, 1941; pp. 1–235. [Google Scholar]
- Iverson, J.B. A Revised Checklist with Distribution Maps of the Turtles of the World; Privately Printed: Richmond, IN, USA, 1992; pp. 1–359. [Google Scholar]
- Le, M.; Hoang, T.; Le, D. Trade data and some comments on the distribution of Mauremys annamensis (Siebenrock, 1903). Asiat. Herpetol. Res. 2004, 10, 110–113. [Google Scholar]
- Dawson, J.E.; Hatcher, R.E.; Calloway-Burke, G.E. Mauremys annamensis: Locality and longevity. Herpetol. Rev. 2013, 44, 91–93. [Google Scholar]
- McCormack, T.E.M.; Dawson, J.E.; Hendrie, D.B.; Ewert, M.A.; Iverson, J.B.; Hatcher, R.E.; Goode, J.M. Mauremys annamensis (Siebenrock 1903)—Vietnamese Pond Turtle, Annam Pond Turtle, Rùa Trung Bộ. In Conservation Biology of Freshwater Turtles and Tortoises; Rhodin, A.G.J., Pritchard, P.C.H., van Dijk, P.P., Saumure, R.A., Buhlmann, K.A., Iverson, J.B., Mittermeier, R.A., Eds.; A Compilation Project of the IUCN/SSC Tortoise and Freshwater Turtle Specialist Group; Chelonian Research Monographs; IUCN Species Survival Commission: Gland, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 57, pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormack, T.; Hendrie, D.; Nguyen, X.T. Rediscovery after 67 years of the critically endangered Vietnamese Pond Turtle, Mauremys annamensis, in central Vietnam. In Program and Abstracts of the Fifth Annual Symposium on the Conservation and Biology of Tortoises and Freshwater Turtles; Schaffer, C., Ed.; Turtle Survival Alliance: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Parham, J.F.; Stuart, B.L.; Orlov, N.L. Geographic distribution: Mauremys annamensis. Herpetol. Rev. 2006, 37, 239. [Google Scholar]
- CRES (Centre for Natural Resources and Environmental Studies). CEPF Final Project Completion Report; CRES: Hanoi, Vietnam, 2016; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Stanford, C.B.; Rhodin, A.G.J.; van Dijk, P.P.; Horne, B.D.; Blanck, T.; Goode, E.V.; Hudson, R.; Mittermeier, R.A.; Currylow, A.; Eisemberg, C.; et al. Turtles in Trouble: The World’s 25+ Most Endangered Tortoises and Freshwater Turtles—2018; Hemlock Printers: Ojai, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- McCormack, T.; van Dijk, P.P.; Roberton, S.; Dawson, J.E. Mauremys annamensis (Amended Version of 2020 Assessment). In The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020. e.T12876A182354172. Available online: https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T12876A182354172.en (accessed on 30 March 2025).
- Tran, K.; Ho, C.T.; Nguyen, S.V.; Pham, T. [Reptiles and amphibians]. Part 1. Animals. In Vietnam Red Data Book; Dang, N.T., Tran, K., Dang, H.H., Nguyen, C., Nguyen, T.N., Nguyen, Y.N., Dang, D.T., Eds.; Science and Technics Publishing House: Hanoi, Vietnam, 2007; pp. 219–276. (In Vietnamese) [Google Scholar]
- Raffel, M.; Meier, E. Best Year Ever at the International Centre for the Conservation of Turtles (IZS) at Muenster Zoo; Turtle Survival—A Publication of the Turtle Survival Alliance: Forth Worth, TX, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Shaffer, C. Vietnamese Pond Turtle program. Turt. Tortoise Newsl. 2006, 9, 13–14. [Google Scholar]
- Somerová, B.; Rehák, I.; Velenský, P.; Palupčíková, K.; Protiva, T.; Frynta, D. Haplotype variation in founders of the Mauremys annamensis population kept in European zoos. Acta Herpetol. 2015, 10, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parham, J.F.; Simison, W.B.; Kozak, K.H.; Feldman, C.R.; Shi, H. New Chinese turtles: Endangered or invalid? A reassessment of two species using mitochondrial DNA, allozyme electrophoresis and known-locality specimens. Anim. Conserv. 2001, 4, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Parham, J.F. Preliminary observations of a large turtle farm in Hainan Province, People’s Republic of China. Turt. Tortoise Newsl. 2001, 3, 4–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.; Blanck, T.; McCord, W.P.; Li, P.P. Tracking Cuora mccordi Ernst, 1988: The first records of its natural habitat; a re-description; with data on captive populations and its vulnerability. Hamadryad 2008, 32, 57–69. [Google Scholar]
- Fong, J.J.; Chen, T.H. DNA evidence for the hybridization of wild turtles in Taiwan: Possible genetic pollution from trade animals. Conserv. Genet. 2010, 11, 2061–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, C.R.; Parham, J.F. Molecular systematics of Old World Stripe-Necked Turtle (Testudines: Mauremys). Asiat. Herpetol. Res. 2004, 10, 28–37. [Google Scholar]
- Fong, J.J.; Parham, J.F.; Shi, H.; Stuart, B.L.; Carter, R.L. A genetic survey of heavily exploited, endangered turtles: Caveats on the conservation value of trade animals. Anim. Conserv. 2007, 10, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, J.J.; Stuart, B.L.; McCormack, T.E.M.; Parham, J.F. First genetic data of the critically endangered Vietnamese Pond Turtle (Mauremys annamensis) from known-locality specimens. Curr. Herpetol. 2019, 38, 140–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, W.; Wen, P.; Zhang, D.; Zhu, X. Genetic diversity and relationship of Mauremys mutica and M. annamensis assessed by DNA barcoding sequences. Mitochondrial DNA Part A 2015, 27, 3507–3510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, M.D.; McCormack, T.E.M.; Hoang, H.V.; Duong, H.T.; Nguyen, T.Q.; Ziegler, T.; Nguyen, H.D.; Ngo, H.T. Threats from wildlife trade: The importance of genetic data in safeguarding the endangered Four-eyed Turtle (Sacalia quadriocellata). Nat. Conserv. 2020, 41, 91–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creswell, J.W.; Poth, C.N. Qualitative Inquiry Research Design: Choosing Among Five Approaches; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Spinks, P.Q.; Shaffer, H.B.; Iverson, J.B.; McCord, W.P. Phylogenetic hypotheses for the turtle family Geoemydidae. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2004, 32, 164–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engstrom, T.N.; Shaffer, H.B.; McCord, W.P. Phylogenetic diversity of endangered and critically endangered southeast Asian softshell turtles (Trionychidae: Chitra). Biol. Conserv. 2002, 104, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arévalo, E.; Davis, S.K.; Sites, J.W. Mitochondrial DNA sequence divergence and phylogenetic relationships among eight chromosome races of the Sceloporus grammicus complex (Phrynosomatidae) in central Mexico. Syst. Biol. 1994, 43, 387–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, M.K.; Engstrom, T.N.; Starkey, D.E.; Shaffer, H.B. Turtle phylogeny: Insights from a novel nuclear intron. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2004, 31, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.D.; Gibson, T.J.; Plewniak, F.; Jeanmougin, F.; Higgins, D.G. The ClustalX windows interface: Flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 4876–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; van der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Bui, M.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huson, H.D.; Bryant, D. Application of Phylogenetic Networks in Evolutionary Studies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2006, 23, 254–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nylander, J.A.A.; Ronquist, F.; Huelsenback, J.P.; Nieves-Aldrey, J.L. Bayesian phylogenetic analysis of combined data. Syst. Biol. 2004, 53, 47–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandley, M.C.; Schmitz, A.; Reeder, T.W. Partitioned Bayesian analyses, partition choice, and the phylogenetic relationships of scincid lizards. Syst. Biol. 2005, 54, 373–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posada, D.; Crandall, K.A. MODELTEST: Testing the model. Bioinformatics 1998, 14, 817–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanfear, R.; Calcott, B.; Ho, S.Y.W.; Guindon, S. PartitionFinder: Combined selection of partitioning schemes and substitution models for phylogenetic analyses. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 29, 1695–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, B.Q.; Nguyen, M.A.T.; von Haeseler, A. Ultrafast approximation for phylogenetic bootstrap. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 1188–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swofford, D.L. PAUP*. Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (* and Other Methods), Version 4.0b10; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The neighbour-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryant, D.; Moulton, V. Neighbor-Net: An Agglomerative Method for the Construction of Planar Phylogenetic Networks. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2004, 21, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felsenstein, J. Confidence limits on phylogenies: An approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 1985, 39, 783–791. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Tran, T.-D.T.; Phan, S.C.; Ziegler, T.; Le, M.; McCormack, T.E.M. First offshore island record of Mauremys annamensis (Siebenrock, 1903) (Testudines, Geoemydidae) in Vietnam. Check List 2025, 21, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Boettger, O. Materialien zur herpetologi-schen fauna von China III. I. liste der von der insel Hainan bekannten kriechtiere. In Bericht der Senckenbergischen Naturforschenden Gesell-Schaft in Frankfurt am Main; Die Gesellschaft: Frankfurt, Germany, 1894; Volume 25, pp. 129–136. [Google Scholar]
- Mallet, J. Hybrid speciation. Nature 2007, 446, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, R.; Albach, D.; Ansell, S.; Arntzen, J.W.; Baird, S.J.E.; Bierne, N.; Boughman, J.; Brelsford, A.; Buerkle, C.A.; Buggs, R.; et al. Hybridization and speciation. J. Evol. Biol. 2013, 26, 229–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, R.; Schumer, M.; Kruesi, K.; Walter, R.; Andolfatto, P.; Rosenthal, G.G. Phylogenomics reveals extensive reticulate evolution in Xiphophorus fishes. Evolution 2013, 67, 2166–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spinks, P.Q.; Shaffer, H.B. Conflicting mitochondrial and nuclear phylogenies for the widely disjunct Emys (Testudines: Emydidae) species complex, and what they tell us about biogeography and hybridization. Syst. Biol. 2009, 61, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, R.C.; Spinks, P.Q.; Shaffer, H.B. Molecular phylogeny and divergence of the map turtles (Emydidae: Graptemys). Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2018, 121, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehlmaier, C.; Zhang, X.; Georges, A.; Campbell, P.D.; Thomson, S.; Fritz, U. Mitogenomics of historical type specimens of Australasian turtles: Clarification of taxonomic confusion and old mitochondrial introgression. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbert, P.D.N.; Cywinska, A.; Ball, S.L.; deWaard, J.R. Biological identifications through DNA barcodes. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2003, 270, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protiva, T. Genetic and shell shape variability in Mauremys annamensis. Turt. Surviv. Mag. 2015, 15, 56. [Google Scholar]
- Zwartepoorte, H.; Becker, H.; Meier, E.; Raffel, M.; McCormack, T. Captive breeding critical to saving the highly endangered Vietnamese Pond Turtle (Mauremys annamensis). Turt. Surviv. Mag. 2015, 15, 54–55. [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler, T.; Nguyen, T.Q.; Le, M.D.; Dieckmann, R.; Haase, C.; Haizak, C.; Heckel, J.-O.; Lefaux, B.; Mager, C.; Michel, V.; et al. The ‘VIETNAMAZING’ EAZA conservation campaign 2024–2025. WAZA News 2024, 1, 42–47. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).