Abstract
Despite the importance of Nile tilapia as a main aquaculture species in Uganda, limited research has been conducted concerning its genetic diversity, particularly in farmed populations. This gap has hindered the development of a systematic breeding program for this species. Successful aquaculture development, especially for genetic improvement, relies on the diversity and purity of wild and farmed populations as germplasm sources for selective breeding. Using microsatellite markers, the current study evaluated the genetic diversity of 480 samples collected from 20 populations of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) in Uganda. All the populations exhibited a higher expected heterozygosity (0.50 ± 0.01) than observed heterozygosity (0.42 ± 0.01), although this was not significantly different. Populations from ponds showed lower FST values (<0.001), an indication of lower genetic differentiation. The populations formed four main clusters; the first comprising of mainly cages (Pal and Busana), the second with cages: Katosi and SON in addition to Rocks hatchery, the third comprised of Bawe cage fish farm and Tendo hatchery, and the fourth were populations from ponds and beaches on Lake Victoria. Given the higher genetic diversity and genetic differentiation of Tendo and Rocks populations, these farms would provide potential candidates for the development of local strains in Uganda. These results provide more insights into the management of local Nile tilapia strains towards reduction of inbreeding levels.
1. Introduction
Aquaculture is one of the world’s fastest-growing food production sectors [1]. In 2022, it recorded 130.9 million tonnes in live weight at a total farm gate sale value of USD 312.8 billion [2]. The increased global aquaculture production makes the sector a suitable alternative for enhancing fish production to meet the demand-supply gap arising from the continual decline in capture fisheries [2,3]. Despite the global growth of aquaculture, African countries still contribute a relatively small share, estimated at 1.9% [2]. The FAO fisheries and aquaculture report [2] indicates that Egypt (67.0%), Nigeria (11.2%), Ghana (5.7%), and Uganda (4.4%) are the main contributors to aquaculture production in Africa. For Uganda, aquaculture production started in 1941 as a subsistence activity to provide cheap animal protein for rural households [4]. The transition to commercial aquaculture in Uganda gained momentum between 2005 and 2006 with the establishment of cage fish farming technology [4]. The increase in fish productivity, coupled with the vast surface area of inland water bodies and the suitability of native Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) species, offers significant potential for the success of aquaculture in Uganda, especially utilizing cage production facilities [3,5]. With the increased investment in cage aquaculture, Lake Victoria (L. Victoria) which is the main water body in Uganda has over 50 cage farm installations on its Northern shores [3].
Nile tilapia (O. niloticus henceforth) and the African catfish (Clarias gariepinus) are the main species farmed in Uganda [4]. With the recent growth of commercial cage aquaculture [6], the Ugandan culture of O. niloticus has increased greatly in the last two decades [3]. Oreochromis niloticus is an important source of proteins for most Ugandans. According to available statistics, fish in Uganda (especially O. niloticus and Lates niloticus) accounts for over 63% of the locally consumed proteins, with an annual per capita consumption of 12.5 kg [7]. Although O. niloticus is native to Uganda, there are differences in the growth rates in its aquaculture compared to most of the improved strains elsewhere in the continent [8,9,10,11]. This is partly attributed to seasonal procurement of O. niloticus fry from different hatcheries based on recommendations from fellow farmers. However, the inbreeding levels of such hatcheries are largely unknown. In addition, some aquaculturists and hatcheries obtain their brood stock from wild populations with unknown genetic backgrounds [12]. Such practices contribute to discrepancies in the lengths of production cycles between fish stocks sourced from different hatcheries among farmers. In Uganda, these hatchery practices arise from the absence of clear selective breeding programs among farmers, resulting into reduced genetic diversity [13].
Genetic diversity is key in enhancing stock during selective breeding programs. Most studies on genetic diversity among species in Uganda are usually to develop a good management strategy for the maintenance of the genetic quality of species, that is, genetically productive stocks [12,13]. Thus, they often involve the analysis of wild populations from various water bodies or comparisons between wild and farmed populations, using either phenotypic [8,14] or molecular techniques or both [12,15]. Earlier studies employed traditional genetic markers like allozymes and restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) to differentiate the genetic diversity of Oreochromis species in East African freshwater bodies [16]. These traditional markers have low resolving power and thus cannot characterize the variations within and between populations [17]. The application of microsatellite genotyping using next-generation sequencing has proven to be the most effective approach, as it minimizes size homoplasy (i.e., when different DNA sequences result in the same fragment size during analysis, leading to misinterpretation of genetic relationships). Size homoplasy is one of the limitations of traditional methods that relies solely on measuring the fragment length of simple sequence repeats (SSRs) [18].
As Uganda strives towards having a streamlined selective breeding program for O. niloticus, few studies have been done to provide essential baseline data [12,13,14,15]. While characterizing farmed O. niloticus using morphometric traits, three main clusters were observed, which could be attributed to the differences in the source of the fish seed [14]. The study by Tibihika et al. [12] revealed higher levels of admixture among the farmed populations. In this study, only a few farms (three) were considered which could have not captured the full range of genetic diversity present in the broader O. niloticus population in Uganda. With the limitations of phenotypic techniques and the use of few fish farms in the foregoing studies [12,14], there remain gaps related to the assessment of the genetic diversity of cultured O. niloticus strains, especially those from Ugandan hatcheries, ponds and cages. Since hatcheries often serve as the initial source of fish stocks for many farms, including samples from them in the current study was sought to establish a genetic baseline and provide insights into the original genetic diversity and differentiation of farmed O. niloticus populations. Currently, there are many cage farms established on L. Victoria, and it is important to characterize O. niloticus farmed in these cages in comparison with wild stocks. This is further supported by the fact that fish escapes are unavoidable during farm operations. The current study employed microsatellite markers based on next-generation sequencing (NGS) to determine the genetic variation within the farmed O. niloticus strain. Specifically, the study aimed to (1) characterize O. niloticus from hatcheries, ponds, and cages; (2) compare the identified genetic profiles of these farmed populations with wild populations; and (3) use the generated information as a tool to improve the management of domesticated farmed strains in Uganda. The information from this study will help to document and monitor cultured stocks for the possible emergence of other local strains or the introduction of exotic strains.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of Sampling Sites
This study was conducted in 20 sites inclusive of five cage farms (Bawe, Pal, Katosi, Busana, and SON), six pond farms (Lusalosalo, Mapema, Kabonera, KAF, Rural Aqua Devt, Kambuga, and Rukikaire), and four hatcheries (KachVic and Kachkyo (located at Kyanamira), Rocks, Tendo, and Kawuku) (Figure 1). The cage farms are among the commercial farms located on L. Victoria while the pond farms are distributed in Western and Central Uganda. Specifically, Rural Aqua Devt, Kambuga, and Rukikaire are located in Southwestern Uganda, while Lusalosalo and Kabonera are located in Central Uganda. For hatcheries, the Kyanamira aquaculture fish facility, located in the Kabale district, is a government facility under Kachwekano Zonal Agricultural Research and Development Institute (KaZARDI) of the National Agricultural Research Organization. Most pertinently, the fish populations at the Kyanamira aquaculture facility were stocked and raised in independent pond systems with the native broodstock originating from lakes; Victoria, and Kyoga. The other hatcheries (Kawuku, Tendo, and Rocks) are among the commercial hatcheries that are known to supply O. niloticus fry to the whole country. Additionally, three populations from Gaba, Garuga, and Kashenyi beaches on L. Victoria were collected and included in the study.
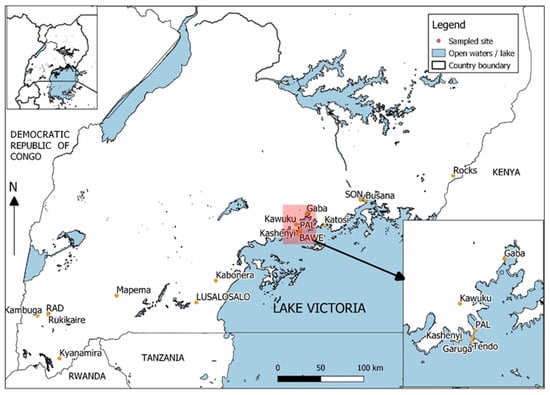
Figure 1.
Map showing the sampling sites in Uganda. KachVic and KachKyo are both located at Kyanamira, while KKN and KAF are located at Kabonera. Details are provided in Table 1.
2.2. Sample Collection
A total of 520 Oreochromis niloticus samples were collected from various sites, including 450 from farmed populations and 70 from wild populations (Table 1). All the samples were obtained either directly from the farms, farm sales outlets, or from boats landed on harvest days using a random sampling technique. For the wild populations, the samples were obtained from local fishermen when freshly killed. In cases where the fish was caught alive, individuals were promptly euthanized in an overdose of clove oil and a fin clip extracted. Sampling was done between March 2023 and June 2023, and each sample site was geo-referenced using a handheld GPS receiver. From each fish, a fin clip was cut from the caudal fin using a sterilized blade and capped into a collection tube filled with 95% ethanol for subsequent genotyping at the Institute of Integrative Nature Conservation Research (INF), BOKU University, Vienna, Austria. After quality check and trimming, the data resulted into 480 samples that were subsequently used for data analysis.

Table 1.
Location, sample sizes and geographical positioning system of the sampling sites.
2.3. Genotyping of Samples
The DNA extraction followed the protocol of Tibihika et al. [17] using magnetic beads (MagSi-DNA beads-Magna Medics) and a magnetic separator SL-MagSep96 (Stein Brenner, Germany). DNA quality was verified using 1.5% agarose gel and later visualized using a trans-illuminator system before amplification. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) amplification was carried out using 43 previously developed microsatellites (SSR) for O. niloticus populations from East Africa [17]. The selected primers were then divided into four multiplexes and used to prepare SSR genotyping by amplicon sequencing libraries (SSR-GBAS) based on the procedures by Kariuki et al. [19] with slight modifications [14]. The PCR products were pooled sample-wise, cleaned using AMPure magnetic beads, and subsequent indexing was performed as described by Tibihika et al. [17]. The individually indexed samples were pooled and used for a paired-end 300 bp sequencing run on an Illumina MiSeq at the Genomics Service Unit, Ludwig Maximilian Universität, München, Germany.
The PCR per sample contained a total volume of 5.0 μL including 2.0 μL of the genomic DNA, 0.25 μL of each primer (100 nM), 2.5 μL of Master mix (Qiagen Multiplex PCR Kit; Qiagen; Netherlands), and 0.25 μL of autoclaved water. The PCR conditions were as follows: initialization at 95 °C for 15 min, followed by denaturation for 30 cycles at 95 °C for 30 s, annealing at 55 °C for 1 min, and elongation for 1 min at 72 °C and the last extension steps at 72 °C for 10 min. The remaining amplicon library preparation and sequencing steps followed the same protocol of SSR-GBAS described above.
2.4. Sequence Analysis, Genotyping, and Allele Calling
Illumina sequencing data were quality-checked using FastQC (version 0.11.9, Babraham Bioinformatics, Cambridge, UK) and trimmed using Trimmomatic (version 0.39) [20] to remove adapters and poor-quality regions as described in Curto et al. [21]. Further steps, including merging, demultiplexing, and allele calling were done using Python scripts described previously [21].
2.5. Population Genetics
The SSR codominant matrix was analyzed using GenAlEx v. 6.503 [22] to evaluate genetic diversity and differentiation patterns at population levels. Genetic diversity was assessed based on the average number of alleles per locus (Na), effective number of alleles (Ne), observed heterozygosity (Ho), expected heterozygosity (He), and fixation index (F). Genetic differentiation was primarily evaluated using paired-wise FST values across all populations. Nei’s genetic distance calculated in GenAlEx v. 6.503 was used to compute a principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) allowing the visualization of genetic structure patterns. This was further explored in two approaches; Firstly, Nei’s genetic distances among populations [23] were visualized using an unweighted pair group method with an arithmetic mean (UPGMA) dendrogram generated by Populations v.1.2.32 [24]. Support values were obtained by executing 1000 bootstrap replicates over loci. Secondly, using STRUCTURE v2.3.4 [25] program to analyze genetic clustering among samples. The procedure involved 15 iterations with K set from 1 to 15 and 100,000 generations after a burn-in period of 10,000 using the admixture model and considering allele frequencies as independent. This was done for datasets consisting of all populations. Optimal K values were chosen based on the Evano method as implemented in Structure Selector [26].
3. Results
3.1. Genetic Diversity of the O. niloticus Populations
All the O. niloticus populations exhibited a higher expected heterozygosity than observed (Table 2, Figure 2). Samples from hatcheries and cages showed moderately higher values of heterozygosity measures while ponds and wild populations had the least values (Figure 2). Populations from Tendo (Ho; 0.58 ± 0.04, He; 0.67 ± 0.03) and Bawe (Ho; 0.52 ± 0.04, He; 0.65 ± 0.04) showed the highest value of heterozygosity measures (expected and observed) followed by Pal (Ho; 0.47 ± 0.05, He; 0.57 ± 0.05) and KachVic (Ho; 0.44 ± 0.04, He; 0.57 ± 0.04) while Katosi had the least value (Ho; 0.30 ± 0.05, He; 0.36 ± 0.06) (Table 2). Both populations from ponds and wild showed lower heterozygosity measures (Table 2).

Table 2.
Heterozygosity by population for codominant data for populations of O. niloticus from Uganda.
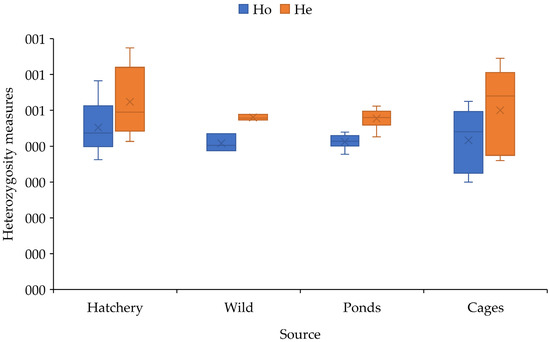
Figure 2.
Boxplot showing the heterozygosity measures among the O. niloticus populations.
The number of effective alleles (Ne) was higher among the samples from Tendo (3.94 ± 0.28) and Bawe (3.80 ± 0.30) followed by Pal (3.40 ± 0.39) while SON (2.28 ± 0.37) and Katosi (2.22 ± 0.30) had the lowest values. Among the wild populations, the heterozygosity measures were almost the same with populations from Gaba having the higher value (Ho; 0.44 ± 0.05 He; 0.49 ± 0.05) while Kashenyi had the lowest value (Ho; 0.39 ± 0.05, He; 0.47 ± 0.05).
3.2. Population Differentiation and Hierarchical Clustering
Pairwise genetic differentiation (FST values) among the O. niloticus populations were investigated (Table 3). Populations from cages (Pal, Katosi, SON, and Busana) were more differentiated. For example, Katosi and Mapema (FST = 0.45), SON and KAF (FST = 0.46), Katosi and KAF (FST = 0.47) (Table 3). Populations from ponds and the wild had the lowest FST values. These included Kawuku and Rukikaire (FST = 0.01), Bawe and Tendo (FST = 0.02), and Rukikaire and Kambuga (FST = 0.02). Comparisons between wild populations showed the lowest FST values, specifically Garuga and Gaba (FST = 0.01) and Kashenyi and Gaba (FST = 0.02). A comparison involving Garuga and KachVic showed a lower genetic differentiation (FST = 0.03). The comparison between KachVic and KachKyo, both collected from the same farm but stocked in different ponds, showed a lower FST value of 0.04 (Table 3).

Table 3.
Pairwise population FST values of the different populations of O. niloticus from Uganda.
Analysis of molecular variance suggested that the highest variance within individuals (55%) followed by among populations (27%) while the least was among individuals (18%) (Figure 3). The UPGMA dendrogram showed four main clades under study (Figure 4). Although, the first and second are closer to each other, the first clade contains mainly samples from cage fish farms (Pal and Busana) both located on L. Victoria while the second were samples from cages (SON and Katosi) and hatchery (Rocks). The third clade consists of populations from BAWE cage fish and Tendo hatchery. All other populations form the fourth clade. In this clade, the wild populations (Garuga, Kashenyi and Gaba) are clearly closer to each other, Samples from the Kawuku hatchery located in Central Uganda are closer to RAD pond farm found in South Western Uganda. A similar closeness is observed between Lusalo and Mapema pond fish farms both located in Central Uganda (Figure 4).
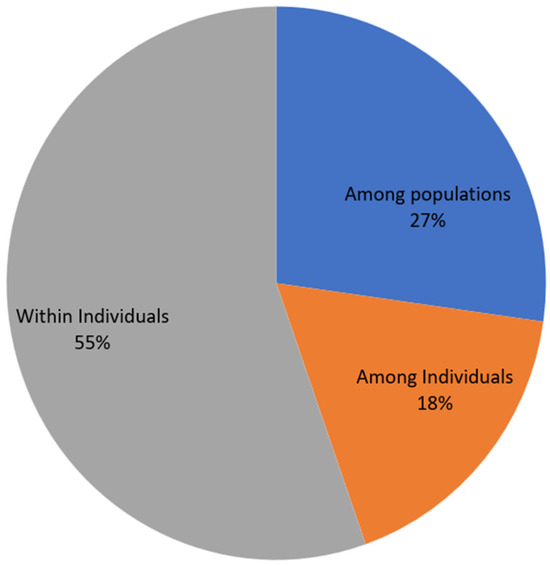
Figure 3.
Pie chart showing analysis of molecular variance within and among O. niloticus individuals and populations.
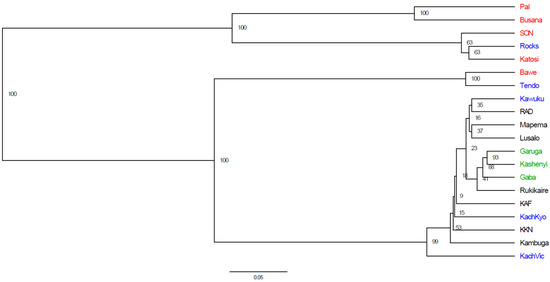
Figure 4.
UPGMA dendrogram of the different populations of O. niloticus constructed using Nei’s genetic distance. Support is given by bootstrap values. Red: Cages, Blue: Hatcheries, Green: Wild and Black: Ponds.
The Neighbor-Joining tree topology revealed a major divergence between Katosi, Pal, Busana, and SON and the remaining localities (Figure 5A). Among the samples from the cages, the populations from Busana and Pal showed a longer divergence than their counterparts. SON and Katosi cage fish farms are closer to the Rocks hatchery populations (Figure 5A).
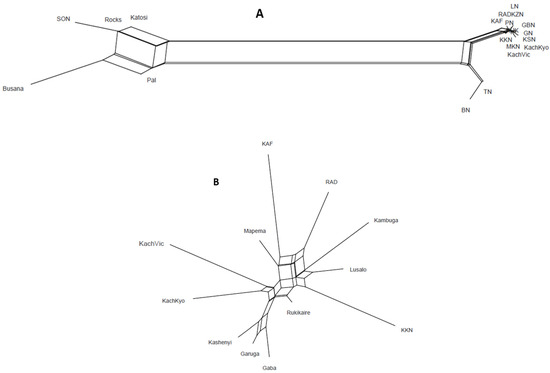
Figure 5.
Genetic structure based on unrooted network tree illustrating population relationships that are depicted on genetic distance (A) All populations, and (B) Populations from the wild and ponds.
Regarding the second group of populations, Tendo hatchery and Bawe cage fish farm diverge from the remaining sampling sites that are mostly composed by ponds and beaches on L. Victoria (Figure 5A). To clearly show the divergence between the wild and pond populations, a separate analysis involving them was conducted. The wild populations (Garuga, Kashenyi, and Gaba) are clearly closer to each other, as are KachVic and KachKyo. Although KAF and KKN were collected from the same farm but different ponds, they are unexpectedly very divergent from each other (Figure 5B).
The PCoA analysis showed a similar segregation pattern as depicted from the UPGMA and NJ among the populations where four main clusters are observed at both axes (Figure 6A): 1st the populations from the Tendo hatchery and Bawe fish farm; 2nd the populations from Busana and Pal; 3rd, populations from Katosi, Rocks, and SON; and 4th the remaining populations (Figure 6A). The wild populations from Gaba, Kashenyi, and Garuga did not show any clear clustering at both axes (Figure 6B). Within the cage populations, the above mentioned three clusters are observed (Figure 6C). Among the populations from ponds, Kabonera and Lusalosalo are clustered together and closer to a population of KKN that forms a slightly differentiated cluster from the remaining populations (Figure 6D).
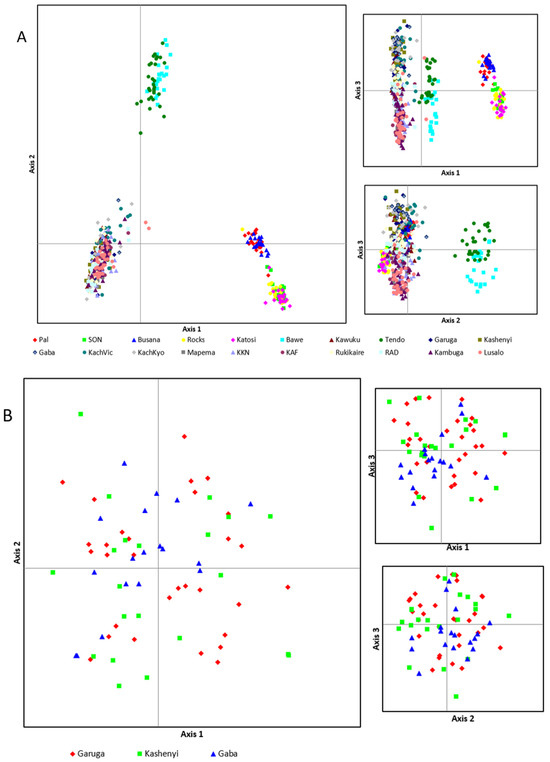
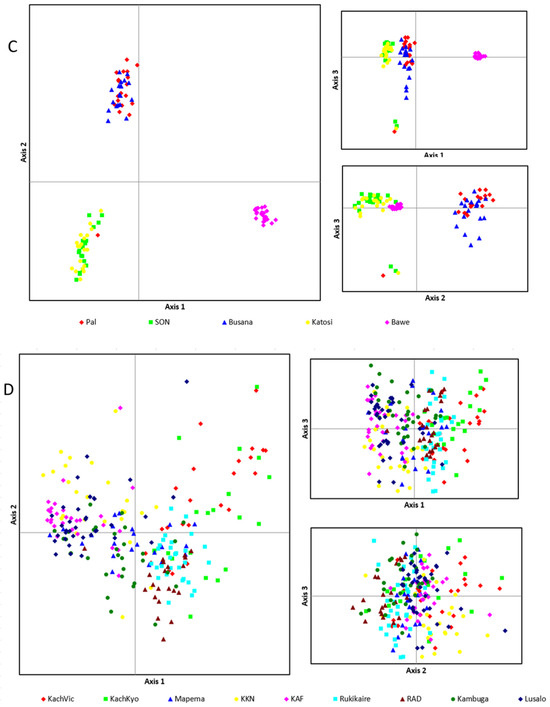
Figure 6.
Genetic structure as visualized through scatter plots based on PCoA for different populations. (A) All populations, (B) Wild populations, (C) Cage populations, and (D) Pond populations.
3.3. Genetic Structure and Signs of Admixture Among the Farmed O. niloticus Populations
Based on delta K (ΔK) values, K = 2 was considered the best fit for the data for all populations. STRUCTURE SELECTOR results also suggested K = 4 and K = 12 as the second and third-best fit for all populations’ data (Figure 7A). Generally, all the STRUCTURE outputs for different populations are congruent with the UPGMA, neighbor-joining network, and PCoA analyses in Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6. Further, K2 separates Busana, Pal Katosi, Rocks, and SON from the remaining populations. At K4, the grouping of Bawe and Tendo (blue) becomes evident. Although a substantial degree of admixture was observed at K12, individuals from the wild (Garuga, Kashenyi, and Gaba) are assigned to an independent cluster (dark green) to the remaining populations from ponds. Also, individuals from the Kawuku hatchery are assigned together with pond populations from RAD, Kambuga, Kachvic, and Lusalo (Figure 7A). The wild populations indicated K3 as the best fit for the data while K5 and K10 are the second and third respectively with no genetic structure among them (Figure 7B).
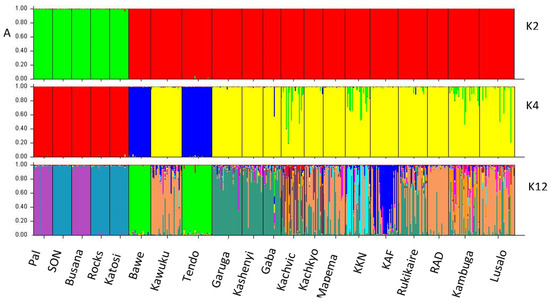
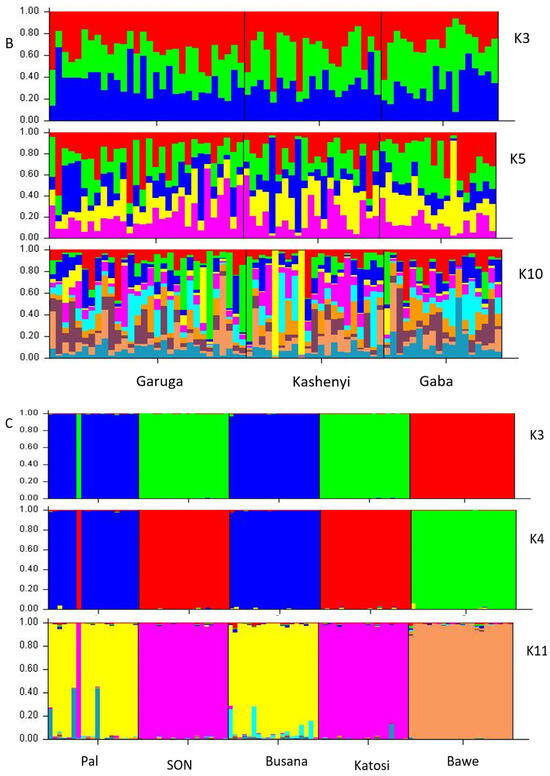
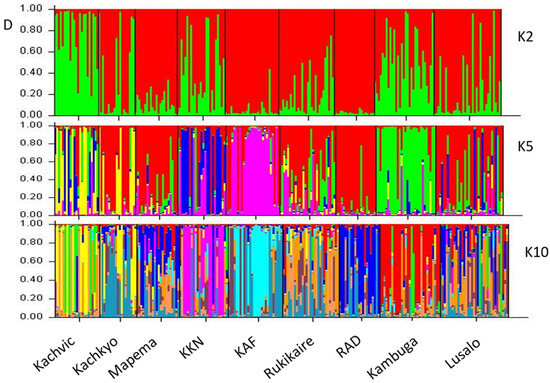
Figure 7.
Bayesian structure analysis showing the clustering of different populations (A) All populations, (B) Wild populations, (C) Cage populations, and (D) Pond populations.
Samples from the cages show K3 as the best fit for the data followed by K11 and 4 as second and third. It was observed that individuals from Pal and Busana are assigned together as are SON and Katosi (Figure 6C). One individual from Pal showed a similar assignment with SON and Katosi. Bawe is assigned independently (Figure 7C). Among the pond populations, K10 was considered the best fit for data while K5 and K2 were the second and third, respectively. Although with high degree of admixture, at K2 only Kachviv population is mostly assigned to an independent cluster, and at K5 and K10 independent cluster assignment patterns are found for the remaining populations (Figure 7D).
4. Discussion
Understanding genetic diversity within and among populations is crucial for ensuring that the most genetically diverse populations are incorporated into selective breeding aquaculture programs. Most genetic studies on O. niloticus have been mainly focused on estimating the variations among the wild populations [10,12,15] with less focus on farmed populations. The current study used SSR based on NGS to investigate the genetic diversity and population differentiation among cultured populations of O. niloticus in Uganda. This is crucial for guiding the selection and conservation of O. niloticus in Uganda. Although our study employed SSR markers, the results are consistent with trends reported in recent SNP-based studies. For example, Robledo et al. [15] identified higher heterozygosity in specific farmed populations in Uganda, with observed admixture among farmed and wild populations. It is incontestable that SNP markers provide greater resolution for fine-scale genetic differences, but SSR markers have demonstrated reliability in assessing broad patterns of genetic diversity and structure, especially where access to SNP genotyping technology is limited [27,28]. For instance, Mamoon et al. [29] recently utilized SSR markers and observed that variations in body length and weight among O. niloticus populations in an Egyptian fish farm correlated with differences in allele frequencies.
4.1. Genetic Diversity of the Farmed O. niloticus Populations
Heterozygosity (observed and expected heterozygosity) is a common measure for comparing genetic diversity within different populations [30]. The current results obtained a higher expected heterozygosity than observed among the different populations. Previous studies observed similar higher expected heterozygosity than observed heterozygosity among O. niloticus populations [15,27,31,32]. Robledo et al. [15], for example, in their characterization of the genetic diversity and population structure of farmed and wild O. niloticus in Uganda using SNPs obtained a higher expected heterozygosity for some hatchery populations. Elsewhere, Gu et al. [32] observed a higher expected heterozygosity (He = 0.709) than observed heterozygosity (Ho = 0.448). Similarly, Hassanien and Gilbey [27] obtained higher expected heterozygosity (He = 0.88) than observed heterozygosity (Ho = 0.82) in O. niloticus populations. In another study, Geletu et al. [33] found that the genetic diversity metrics of O. niloticus from Ethiopia (He = 0.24, Ho = 0.25) suggested a moderate level of genetic diversity. The authors linked this to potential factors such as gene flow or hybridization in the cultured O. niloticus populations. Recently, Ahmed et al. [34] reported that the expected heterozygosity and observed heterozygosity for O. niloticus from Ethiopia varied between 0.10–0.50 and 0.115–0.265, respectively. Taken together, high levels of genetic diversity are only to be expected in genetically improved strains developed through well-designed breeding programs that incorporate individuals from diverse genetic backgrounds into the founding population [33,35,36,37].
The observed heterozygosity (Ho) values were generally close to the expected heterozygosity (He) values, and these were not statistically different (Table 2, Figure 2). This indicates that the population may not deviate significantly from Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium in most cases, and factors such as the Wahlund effect, inbreeding, or selection might not strongly influence the genetic structure or their effects are not pronounced enough to show statistically significant differences. In Uganda, the lack of clear selective breeding programs makes farmers to source fry from multiple farms and hatcheries. Consequently, the repeated use of the same broodstock across several breeding cycles reduces genetic diversity in ponds, particularly among subsistence farmers. Furthermore, some populations in the current study had a lower number of samples and this might have contributed to lower genetic diversity. Smaller sample sizes (<20) can increase the likelihood of inbreeding, reducing heterozygosity and increasing the prevalence of homozygosity, which may lead to inbreeding depression [38]. Similar low levels of observed heterozygosity as in the present study were previously observed by Yoshida et al. [39] while estimating the population structure and genetic differentiation of O. niloticus breeding populations in Latin America using SNPs. They attributed this to the founder effect or effective population size, both of which are known to lower genetic diversity [40,41].
The moderate genetic diversity exhibited by KachVic populations suggests somehow proper broodstock management of these strains at the Kyanamira fish facility. These samples were collected from the Kyanamira aquaculture facility where good farm management practices are always followed since it is a research facility. This shows that the effective number of individuals contributing to the population has not declined, thus a higher genetic diversity [42]. A similar explanation applies to the Tendo which are commercial hatcheries engaged in some breeding and fry production, and later supply to other farmers. Therefore, as Uganda works toward establishing a robust breeding program, these populations require special attention within the framework.
The sources of broodstocks for Kambuga, Lusalosalo, and Kabonera populations were unknown at the time of sample collection. This uncertainty may influence estimates of genetic variation, especially in cases where inbreeding is higher due to poor farm management practices [43].
The wild populations from L. Victoria (Gaba, Garuga, and Kashenyi beaches) showed more or less the same level of expected and observed heterozygosity, an indication that there are chances of random mating among these populations. The close connectivity between these beaches and the lack of physical barriers between them beaches is key in enhancing the chances of admixtures among the populations. Also, the chances of unregulated fish transfers as previously cited by Tibihika et al. [12] could contribute to the heterozygosity measures.
4.2. Population Structure and Differentiation Patterns
Genetic differentiation is usually estimated using FST values, which conventionally lies between 0 and 1 [44]. As a general rule, values ranging from 0 to 0.049 show lower genetic differentiation, 0.05 to 0.25 show moderate differentiation, and above 0.25 show a higher genetic differentiation [45]. In the current study, most of the population comparisons especially for the ponds and the wild showed lower genetic differentiation, suggesting higher gene flow. The lower genetic differentiation between O. niloticus populations from the L. Victoria beaches (Gaba, Kashenyi, and Garuga) could be a result of the proximity of these beaches (≤20 km) and their connection to the same water body (L. Victoria). Such short distances between sites increases the likelihood of fish transfer, which can lead to greater genetic admixture. Similar lower levels of genetic differentiation were previously documented [46]. Low-moderate levels of differentiation (FST = 0.074) have been reported between wild O. niloticus from Lake Volta and the improved Akosombo strains in Ghana [46].
Lower genetic differentiation was observed between wild populations and KachVic. It is to be noted that the brood stock of KachVic was originally collected from L. Victoria, and thus shares the same genetic background. Moreover, the assignment of wild populations (Garuga, Kashenyi, and Gaba) and KachVic in the same cluster according to multivariate analysis (PCoA and NJ) supports the hypothesis above. Similarly, the lower FST values between Bawe and Tendo indicate lower genetic differentiation among these populations. Since Tendo is a hatchery near Bawe fish farm (10 km), Bawe likely got its stock from Tendo hatchery, thus sharing the same genetic background. This is also supported by PCoA and NJ results where these populations are clustered together. Higher genetic differentiation and genetic diversity among the KachKyo populations could result from genetic drift which appears after breeding selections from a small number of founder individuals [31]. The founder populations for KachVic and Kachkyo were sourced 8 years ago from L. Victoria and Lake Kyoga, respectively. This time is long enough to enhance the divergence, and thus the observed genetic differentiation.
The current study used Multiple approaches (UPGMA, NJ, and PCoA) and Bayesian clustering algorithms (STRUCTURE) to derive the underlying genetic structure patterns among the sampled populations. These analyses observed four main clusters i.e., first; Bawe and Tendo, second; Pal and Busana (cages), third; SON, Rocks and Katosi, and the fourth encompassed all other populations, inclusive of pond and wild samples. The genetic clustering of Katosi and SON cage fish farms with Rocks indicates that these populations share the same genetic background. Rocks is a commercial hatchery that supplies fry to fish farms, and it is possible that Katosi and SON cage fish farms might have obtained their broodstock from Rocks. A similar explanation can be advanced for the close clustering between BAWE and Tendo populations because the latter is a hatchery and former is a grow-out fish farm.
The close clustering among the pond populations could result from factors such as government initiatives and farm management practices. Many farms source their broodstock from the same hatchery or farms, often based on recommendations from fellow farmers about the hatchery’s good quality seed [8]. The Ugandan government has taken many initiatives, especially Operation Wealth Creation (OWC) aimed at boosting the livelihoods of different farmers. The OWC was launched by the President of the Republic of Uganda in 2013 as an intervention to efficiently facilitate national socio-economic transformation, with a focus on raising household incomes and wealth creation by transforming subsistence farmers into commercial farmers [47]. The program involves supporting farmers by providing them with inputs like fry/fingerings to stock their respective farms. In this program, many farmers are supplied by a single hatchery across an entire district or sometimes a region, indicating that there is a high possibility of these populations originating from the same source and, thus, having a similar genetic composition. Using morphometric characteristics, Kwikiriza et al. [14] recently reported similar findings while characterizing different strains of O. niloticus cultured in ponds.
In all the analyses, populations from the wild and ponds shared the same genetic groupings. Because there is no clear selective breeding program in Uganda, these farms might be collecting the broodstock directly from the wild (L. Victoria) [13]. The wild populations from Gaba, Kashenyi, and Garuga did not show any clear clustering, an indication of admixtures between these populations. This may be explained by the shorter geographical distances between these beaches and lack of barriers coupled with chances of fish transfers by fishermen. Similar results were obtained by Fagbémi et al. [48] while characterizing the genetic structure of wild and farmed O. niloticus populations in Benin.
In addition to exhibiting a higher genetic differentiation, populations from cages (Pal and Busana) showed higher divergence from other samples. Since these populations did not show any clustering from L. Victoria, it is likely that they were either sourced from other Ugandan lakes (such as Lake Albert and Lake Kyoga) or outside the country. The speculated uncontrolled movement of fish between different locations in and outside Uganda, maybe from Kenya, Thailand, Egypt, and Burundi could explain the observed population divergence. Recent studies have shown that Genetically Improved Farmed Tilapia (GIFT) strain introductions have occurred in neighboring countries, specifically Tanzania [9]. Uganda may not be exempt from this trend, with the increase in the number of commercial fish farms. Unfortunately, we have no precise information on the origin of the Pal and Busana populations. Therefore, given the minimal restrictions on border crossings between these countries and Uganda, it is expected that this strain could be circulating in Uganda’s O. niloticus aquaculture industry.
Populations from the fish ponds showed higher levels of admixtures, which could be attributed to factors like management practices, weather conditions, and general farm design [49]. Particularly, generations from KachVic and KachKyo had mixed assignments. These samples were collected from the same farm but in different ponds. The brood stocks of KachVic and KachKyo were initially sourced from L. Victoria and L. Kyoga, and later stocked at the Kyanamira fish facility. In 2019, heavy flooding of the Rwabakazi stream caused the ponds to overflow, leading to the mixing of fish from different ponds. Since these ponds are close to each other, the likelihood of fish transferring from one pond to another increased, leading to mating and eventual admixture. Additionally, escapees during sampling and sorting are inevitable in such farms due to the closeness of the ponds. For the case of KAF and Kabonera, the admixtures could have resulted from poor farm management practices like inconsistencies in stockings where fish from different sources are added to the pond without prior genetic compatibility. In this farm, it was clear that good management practices were not followed and chances of fish mixing from one pond to another were inevitable. Previous studies have indicated that poor farm management practices promote fish escapism which results into random mating [12,31,50]. Therefore, proper farm management is key to the success of a good selective breeding program.
5. Conclusions
The current study indicated that different groups had varied genetic diversity. Populations from the cages and hatcheries had a higher genetic diversity than samples from the ponds and L. Victoria beaches. Factors such as farm management practices including sourcing seed from farm to farm or wild to farm, are the likely contributors to these variations. Samples from cages exhibited a higher genetic differentiation compared to those from ponds and the wild. Lower genetic differentiation among the wild populations could be attributed to the closeness of these beaches with no physical barriers. Government programs are key in contributing to the lower genetic differentiation and admixtures observed among the pond populations. Based on the obtained results, this study characterized the populations into four main groups: (1) Bawe and Tendo, (2) Pal and Busana, (3) SON, Rocks and Katosi and (4) populations from ponds and the wild. Therefore, the results from this study could be used as a guide for future breeding programs and genetic improvement of local O. niloticus in Uganda.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and methodology. G.K. and H.M.; software, G.K., M.C. and H.M.; validation, I.A., P.D.T., N.K., A.M. and H.M.; formal analysis, G.K., A.A.I., F.A. and M.C.; investigation, F.A.; resources, H.M.; data curation, G.K. and M.C.; writing—original draft preparation, G.K., A.A.I. and F.A.; writing—review and editing, I.A., P.D.T., T.O., J.K.N., N.K., M.C., A.M. and H.M.; visualization, G.K., I.A., P.D.T., J.K.N., N.K. and M.C.; supervision, P.D.T., J.K.N., M.C., A.M. and H.M.; project administration, H.M.; funding acquisition, G.K. and H.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study received financial support from the Austrian Partnership Programme in Higher Education and Research for Development (APPEAR), under grant number MPC-2021-01836. APPEAR is an Austrian Development Cooperation (ADC) program implemented by the Austrian Agency for International Cooperation in Education and Research (OeAD-GmbH), OEZA Project No. 0894-01/2020. The article processing charge for this article was in part supported by BOKU University through its Institutional Open Access Program with the publisher (No:3446568).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study because field excursions were conducted together with respective authorities per district and therefore no special permission was required. Throughout the sampling regimes, fish were always bought from the farmers; thus, no special treatment for the animals was administered in the process.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available upon reasonable request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge farmers who provided the samples used in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Guillen, J.; Asche, F.; Borriello, A.; Carvalho, N.; Druon, J.-N.; Garlock, T.; Llorente, I.; Macias, D. What is happening to the European Union aquaculture production? Investigating its stagnation and sustainability. Aquaculture 2025, 596, 741793. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2024. Blue Transformation in Action. Rome. Available online: https://doi.org/10.4060/cd0683en (accessed on 8 January 2024).
- Musinguzi, L.; Lugya, J.; Rwezawula, P.; Kamya, A.; Nuwahereza, C.; Halafo, J.; Kamondo, S.; Njaya, F.; Aura, C.; Shoko, A.P.; et al. The extent of cage aquaculture, adherence to best practices and reflections for sustainable aquaculture on African inland waters. J. Great Lakes Res. 2019, 45, 1340–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutaisire, J.; Nandi, S.; Sundaray, J.K. A review of Uganda and India’s freshwater aquaculture: Key practices and experience from each country. J. Ecol. Nat. Environ. 2017, 9, 15–29. [Google Scholar]
- Abaho, I.; Kwikiriza, G.; Atukwatse, F.; Izaara, A.A.; Ekwangu, J.; Baguma, S.D.; Kubiriba, J.; Kasozi, N. Selective Breeding for Genetic Improvement of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus Linnaeus, 1758) in Uganda: Current Status, Challenges, and Future Perspectives. Animals 2025, 15, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelos-Castro, R.M.; Aparicio-Simón, B.; García-Morales, R.; Cruz-Hernández, P.; Campos-Ramos, R.; Espinosa-Chaurand, D.; Garza-Torres, R.; Maeda-Martínez, A.N. Exploring the presence of tilapia species in a central western Mexican reservoir using mitochondrial DNA control region sequencing. Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res. 2024, 52, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obiero, K.; Meulenbroek, P.; Drexler, S.; Dagne, A.; Akoll, P.; Odong, R.; Kaunda-Arara, B.; Waidbacher, H. The Contribution of Fish to Food and Nutrition Security in Eastern Africa: Emerging Trends and Future Outlooks. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthew, M.T.; Godfrey, K.; Phyllis, A.; James, K.; Michael, S.M.; Victoria, N. Growth performance evaluation of four wild strains and one current farmed strain of Nile tilapia in Uganda. Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Stud. 2016, 4, 594–598. [Google Scholar]
- Moses, M.; Chauka, L.J.; de Koning, D.J.; Palaiokostas, C.; Mtolera, M.S. Growth performance of five different strains of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) introduced to Tanzania reared in fresh and brackish waters. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lind, C.E.; Agyakwah, S.K.; Attipoe, F.Y.; Nugent, C.; Crooijmans, R.P.M.A.; Toguyeni, A. Genetic diversity of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) throughout West Africa. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanda, M.K. Genetic Variation in Wild and Farmed Tilapia and Catfish in Nigeria. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Glasgow, Glasgow, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Tibihika, P.D.; Curto, M.; Alemayehu, E.; Waidbacher, H.; Masembe, C.; Akoll, P.; Meimberg, H. Molecular genetic diversity and differentiation of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus, L. 1758) in East African natural and stocked populations. BMC Evol. Biol. 2020, 20, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mwanja, M.; Ondhoro, C.; Sserwada, M.; Achieng, P.; Ddungu, R.; Mwanja, W. Morphological variation of Nile tilapia populations from major water bodies of Uganda. Uganda J. Agric. Sci. 2016, 17, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwikiriza, G.; Yegon, M.J.; Byamugisha, N.; Beingana, A.; Atukwatse, F.; Barekye, A.; Nattabi, J.K.; Meimberg, H. Morphometric Variations of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) (Linnaeus, 1758) Local Strains Collected from Different Fish Farms in South Western Highland Agro-Ecological Zone (SWHAEZ), Uganda: Screening Strains for Aquaculture. Fishes 2023, 8, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robledo, D.; Ogwang, J.; Byakora, E.; Nascimento-Schulze, J.C.; Benda, K.K.; Fraslin, C.; Salisbury, S.; Solimo, M.; Mayega, J.F.; Peter, B.; et al. Genetic diversity and population structure of farmed and wild Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) in Uganda: The potential for aquaculture selection and breeding programs. Genomics 2024, 116, 110781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnèse, J.F.; Adépo-Gourène, B.; Abban, E.K.; Fermon, Y. Genetic differentiation among natural populations of the Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus (Teleostei, Cichlidae). Heredity 1997, 79, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tibihika, P.D.; Curto, M.; Dornstauder-Schrammel, E.; Winter, S.; Alemayehu, E.; Waidbacher, H.; Meimberg, H. Application of microsatellite genotyping by sequencing (SSR-GBS) to measure genetic diversity of the East African Oreochromis niloticus. Conserv. Genet. 2019, 20, 357–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlötterer, C. Evolutionary dynamics of microsatellite DNA. Chromosoma 2000, 109, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kariuki, J.; Tibihika, P.D.; Curto, M.; Alemayehu, E.; Winkler, G.; Meimberg, H. Application of microsatellite genotyping by amplicon sequencing for delimitation of African tilapiine species relevant for aquaculture. Aquaculture 2021, 537, 736501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curto, M.; Winter, S.; Seiter, A.; Schmid, L.; Scheicher, K.; Barthel, L.M.; Plass, J.; Meimberg, H. Application of a SSR-GBS marker system on investigation of European Hedgehog species and their hybrid zone dynamics. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 2814–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peakall, R.O.D.; Smouse, P.E. GENALEX 6: Genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2006, 6, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, S.; Roessli, D.; Excoffier, L. Arlequin Ver. 2.000. A Software for Population Genetics Data Analysis; Genetics and Biometry Laboratory, University of Geneva: Geneva, Switzerland, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Langella, O. Populations 1.2. 28: A Population Genetic Software. Available online: http://www.pge.cnrs-gif.fr/bioinfo/populations/index.php (accessed on 20 November 2024).
- Hubisz, M.J.; Falush, D.; Stephens, M.; Pritchard, J.K. Inferring weak population structure with the assistance of sample group information. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2009, 9, 1322–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.L.; Liu, J.X. Structure Selector: A web-based software to select and visualize the optimal number of clusters using multiple methods. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2018, 18, 176–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanien, H.A.; Gilbey, J. Genetic diversity and differentiation of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) revealed by DNA microsatellites. Aquac. Res. 2005, 36, 1450–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milano, I.; Babbucci, M.; Cariani, A.; Atanassova, M.; Bekkevold, D.; Carvalho, G.R.; Espiñeira, M.; Fiorentino, F.; Garofalo, G.; Geffen, A.J.; et al. Outlier SNP markers reveal fine-scale genetic structuring across European hake populations (Merluccius merluccius). Mol. Ecol. 2014, 23, 118–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamoon, A.; Ismail, M.; Awad, S.T.; Ali, F.S. Investigating Nuclear DNA Microsatellites in the Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus): Insights into Association Genetics. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2024, 28, 661–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allendorf, F.W. Genetic drift and the loss of alleles versus heterozygosity. Zoo Biol. 1986, 5, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajungiro, R.A.; Palaiokostas, C.; Pinto, F.A.L.; Mmochi, A.J.; Mtolera, M.; Houston, R.D.; De Koning, D.J. Population structure and genetic diversity of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) strains cultured in Tanzania. Front Genet. 2019, 10, 450642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.E.; Luo, D.; Xu, M.; Ma, G.M.; Mu, X.D.; Luo, J.R.; Hu, Y.C. Species diversity defends against the invasion of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2014, 414, 07. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geletu, T.T.; Tang, S.; Zhao, J. Genetic diversity and differentiation of cultured Nile tilapia populations from Ethiopia revealed by ddRAD-seq: Implications for better hatchery management. Aquat. Living Resour. 2025, 38, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.M.; Hordofa, B.; Meressa, B.H.; Tamiru, M. Population structure and genetic diversity of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) using microsatellite markers from selected water bodies in southwest Ethiopia. Vet. Med. Sci. 2023, 9, 2095–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moses, M.; Mtolera, M.S.P.; Chauka, L.J.; Lopes, F.A.; De Koning, D.J.; Houston, R.D.; Palaiokostas, C. Characterizing the genetic structure of introduced Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) strains in Tanzania using double digest RAD sequencing. Aquac. Int. 2020, 28, 477–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva, B.; Fernández, A.; Peiró-Pastor, R.; Peñaloza, C.; Houston, R.D.; Sonesson, A.K.; Tsigenopoulos, C.S.; Bargelloni, L.; Gamsız, K.; Karahan, B.; et al. Population structure and genetic variability in wild and farmed Mediterranean populations of gilthead seabream and European seabass inferred from a 60K combined species SNP array. Aquac. Rep. 2022, 24, 101145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diyie, R.L.; Agyarkwa, S.; Armah, E.; Amonoo, N.A.; Owusu-Frimpong, I.; Osei-Atweneboana, M.Y. Genetic variations among different generations and cultured populations of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) in Ghana: Application of microsatellite markers. Aquaculture 2021, 544, 737070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megahed, M.E. Genetic selection for improved disease resistance in aquaculture with special reference to shrimp and tilapia breeding programs in Egypt. J. Appl. Aquac. 2020, 32, 291–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, G.M.; Barria, A.; Correa, K.; Cáceres, G.; Jedlicki, A.; Cadiz, M.I.; Lhorente, J.P.; Yáñez, J.M. Genome-wide patterns of population structure and linkage disequilibrium in farmed Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kliman, R.; Sheehy, B.; Schultz, J. Genetic Drift and Effective Population Size. Nat. Educ. 2008, 1, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Bernos, T.A.; Avlijaš, S.; Hill, J.; Morissette, O.; Ricciardi, A.; Mandrak, N.E.; Jeffries, K.M. Genetic diversity and structure of a recent fish invasion: Tench (Tinca tinca) in eastern North America. Evol. Appl. 2022, 16, 173–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allendorf, F.W.; Hössjer, O.; Ryman, N. What does effective population size tell us about loss of allelic variation? Evol. Appl. 2024, 17, e13733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbiru, M.; Limbu, S.M.; Chenyambuga, S.W.; Lamtane, H.A.; Tamatamah, R.; Madalla, N.A.; Mwandya, A.W. Comparative performance of mixed-sex and hormonal-sex-reversed Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus and hybrids (Oreochromis niloticus × Oreochromis urolepis hornorum) cultured in concrete tanks. Aquac. Int. 2016, 24, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holsinger, K.E.; Weir, B.S. Genetics in geographically structured populations: Defining, estimating and interpreting FST. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’connell, M.; Wright, J.M. Microsatellite DNA in fishes. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 1997, 7, 331–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mireku, K.K.; Kassam, D.; Changadeya, W.; Attipoe, F.Y.; Adinortey, C.A. Assessment of genetic variations of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus L.) in the Volta Lake of Ghana using microsatellite markers. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2016, 16, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mpangwire, V.; Musiita, B.; Akisimire, R. The Role of Operation Wealth Creation (OWC) Program on Diary Farmers in Mbarara District-A Descriptive Perspective. J. Econ. Behav. Stud. 2023, 15, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagbémi, M.N.A.; Pigneur, L.M.; André, A.; Smitz, N.; Gennotte, V.; Michaux, J.R.; Mélard, C.; Lalèyè, P.A.; Rougeot, C. Genetic structure of wild and farmed Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) populations in Benin based on genome wide SNP technology. Aquaculture 2021, 535, 736432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, A.F.M. On-farm feed management practices for Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) in Egypt. In On-Farm Feeding and Feed Management in Aquaculture; Hasan, M.R., New, M.B., Eds.; FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Technical Paper No. 583; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2013; pp. 101–129. [Google Scholar]
- McKinna, E.M.; Nandlal, S.; Mather, P.B.; Hurwood, D.A. An investigation of the possible causes for the loss of productivity in genetically improved farmed tilapia strain in Fiji: Inbreeding versus wild stock introgression. Aquac. Res. 2010, 41, e730–e742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
