Abstract
Even though spring ecosystems are ecologically unique and socio-culturally important worldwide, they hardly attract research attention. The aims of this study were to evaluate the environmental status of water quality, and to inventory the species diversity of aquatic animals in 65 springs in Taiwan from 2012 to 2017, of which seven springs were unable to be sampled due the fact that they were dried or sealed up. The environmental status of 58 springs with complete water quality data was assessed by the River Pollution Index (RPI). Based on the RPI, the water quality of these 58 sampled springs was mainly non-/mildly polluted (26 springs, 44.8%) and lightly polluted (23 spring, 39.6%), and nine (15.5%) springs were moderately polluted. However, when applied to springs, the RPI may intensify the pollution rankings because dissolved oxygen is an assessing factor, and hypoxia may naturally be observed in the springs. To avoid this concern, we suggest choosing the concentration of coliform instead of dissolved oxygen content in the RPI when it is applied to springs. During the 6 years of the study period, we collected 48 fish species in 44 springs, 24 gastropoda and bivalve species in 46 springs, 16 shrimp species in 34 springs, and 14 crab species in 18 springs. Within the species collected, 31 fish, 20 gastropoda and bivalves, 12 shrimps, and 14 crabs are native species of Taiwan. They totaled 27.2 to 35% of the known aquatic native species of the island. Thus, springs in Taiwan may be considered to be a conservation hotspot of aquatic animals. Other than native species, exotic aquatic animals also represent threats, as seventeen fishes (35.4%), four gastropoda and bivalves (16.6%), and two shrimps (12.5%) were found in the springs of Taiwan. The springs in Taiwan show diverse and vital ecosystem services, such as delivering social, cultural, and economic value, conserving native and endangered freshwater animals, developing new academic theories, and supplying habitat refugees from climate change. Unfortunately, springs in Taiwan currently are also threatened by multiple anthropogenic disturbances, such as the overconsumption of groundwater by land development and urbanization, deterioration of water quality by agricultural, domestic, and industrial pollution, and inappropriate tourism and management tactics. To restore and sustain the springs in Taiwan, effective strategies and practical measures are urgently required to minimize human-caused threats and revitalize social awareness of springs.
1. Introduction
Springs have long been recognized for their physical, chemical, and biological diversity [1,2,3]. Because of nourishing by aquifers, springs are unique for their stable flow, water temperature, nutrient cycling, and physicochemical characteristics that constitute different types of waters than other freshwater ecosystems [4]. Moreover, springs function as ecoclines among subterranean and fluvial aquatic ecosystems [5], and are also used as ecotones between the aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems [6]. Additionally, springs have significant ecological and socio-cultural value worldwide [7], and serve as economically important water sources for drinking, agriculture, industry, and recreation [8]. The European Commission, Australia, Japan, New Zealand, Finland, and many other countries have determined to conserve and protect springs for their substantial contributions to human societies [9,10,11].
Despite their ecological significance, spring research hardly attracted the interest of aquatic scientists until 1990 [12]. During the 1990s’ in Europe, North America, and Australia, the biological groups which were most frequently studied in springs were diatoms and aquatic invertebrates, due to the relatively profound knowledge of their taxonomy and the appeal of using them as bioindicators [13,14,15,16]. However, complete biota inventories of springs’ ecosystems were scarcely present until recent studies like that of Pascual et al. [17], who recorded the biological richness of Mediterranean springs.
Springs are commonly threatened by diverse anthropogenic impacts, including groundwater depletion and pollution, habitat modifications, and management issues [5,12]. Due to its ecological importance and ecosystem services, research focusing on the biodiversity of springs is necessary worldwide. In response to this need, we visited 65 springs in Taiwan from 2012 to 2017 to achieve the following aims: (1) to assess the current status of water quality in the sampled springs, and (2) to inventory the diversity of species of aquatic animals (macrofauna) in the sampled springs of Taiwan.
2. Methods
2.1. Spring Selections and Sampling Frequency
From 2012 to 2017, we visited and conducted a six-year survey of the water quality assessment and species diversity of the aquatic animals of 65 springs in Taiwan (Figure 1). Springs identified were based on information from governmental documents, research reports, citizen guidance, and country legends.
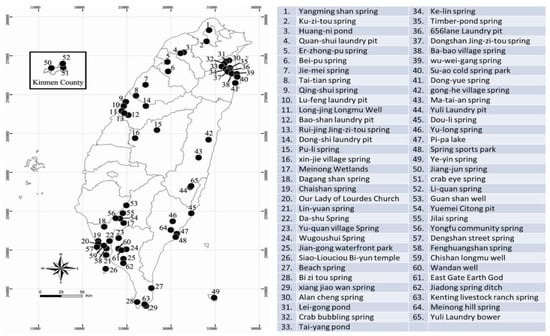
Figure 1.
Locations of 65 visited springs in Taiwan.
Among the 65 visited springs, seven springs were unable to be sampled because they were dried or sealed up. Thus, 58 springs were sampled for water quality and aquatic animals. Each spring was surveyed twice over the sampling period, and the two sampling times were arranged separately in the dry season (October to March) and in the wet season (April to September).
Ecosystem services provided by the springs in Taiwan include drinking, swimming, laundry, recreation, irrigation, wood storage, and conservation by springs and spring-fed lotic and lentic water bodies. Thus, the sampling sites we made in the springs were both on the spring outlet and on the outlet-fed streams, ponds, pools, and laundry pits.
2.2. Water Quality Assessment and River Pollution Index (RPI)
The River Pollution Index (RPI), an index developed by the Environmental Protection Agency of Taiwan, was used to assess the current status of springs’ water quality. [18]. We collected two water samples from each of the 58 springs to record water quality and to calculate the RPI scores.
The RPI includes four variables: dissolved oxygen (DO), biochemical oxygen demand (BOD5), suspended solids (SS), and ammonia nitrogen (NH3-N). The dissolved oxygen was measured in the field sites with a YSI 556 Handheld Multiparameter Instrument, while the other three measurements of water quality were conducted in a laboratory following the standard protocols of the Environmental Protection Administration of Taiwan [18].
To determine the RPI score, each variable of water quality was first converted to one of 4 index values (Si = 1, 3, 6, or 10); then, the arithmetic average of these index values was calculated as the RPI (Table 1):
RPI = 1/4 (Σ Si)

Table 1.
Definition of River Pollution Index (RPI).
Si: the index scores based on Table 1.
The RPI score ranges from 1 to 10, and four pollution classifications are listed as unpolluted, negligibly polluted, moderately polluted, and severely polluted (Table 1) [18].
2.3. Species Inventory of Aquatic Animals
The applications of sampling methods in each spring to collect aquatic animals were based on the habitat complexity of the flow regime, water depth, and aquatic vegetation.
2.3.1. Fish Sampling
Three kinds of sampling gears were used in springs to collect fishes. In the springs with limited outlets, four fish traps (radius × length: 16 cm × 36 cm) with commercial lures were placed at least 3 m apart for over 72 h for fish sampling. For those lentic-type springs such as pools, ponds, or laundry pits, a long and square fyke net (opening size: 8 cm × 12 cm, length: 5 m, width: 30 cm, mesh size: 1 cm) with baits was set for at least 12 h overnight to catch fishes. For those lotic-type springs such as spring-fed streams, when the above two fishing gears were not seemingly applicable, 30 min electrofishing was chosen to sample. After sample identification and counting, collected fishes were released to the springs except for those exotic species.
2.3.2. Samplings of Benthic Animals
The benthic animals in springs included gastropoda, bivalves, shrimps, and crabs. Handpicking was the main collection method for gastropoda and bivalves. For the collection of shrimps and crabs, four traps (radius × length: 16 cm × 36 cm) with baits were placed at least 3 m apart for over 72 h in the spring outlets and lotic-type springs. In those lentic-type springs, a long and square fyke net (opening size: 8 cm × 12 cm, length: 5 m, width: 30 cm, mesh size: 1 cm) with baits was placed for at least 12 h overnight to collect benthic animals.
After species identification and counting, benthic animals were released on site. Unidentified individuals were carried back to the laboratory for species taxonomy.
2.4. Species Identification
Species identification of gastropoda and bivalves followed the Taiwan Malacofauna Database [19], established by the Academia Sinica. Fish taxonomy was based on the Fish Database of Taiwan [20] which was also developed by the Academia Sinica. Shrimp and crab classification was based separately by Shi and You [21] and Shi and Lee [22].
2.5. Data Analyses
The number of springs grouped into four pollution levels of the RPI was estimated to evaluate the current status of water quality in 58 sampled springs in Taiwan. Occurrence frequencies of sampled springs in each index score (Si) of 4 water quality measurements in 58 sampled springs were also analyzed.
Collected aquatic animals were identified by species. Each species was grouped into ethnic groups of native and exotic species based on taxonomy reference [19,20,21,22], and endemic species were also recognized. In this study, a native species is recognized as an organism that is currently existing in Taiwan due to natural occurrence without any human involvement. The exotic species is introduced to Taiwan where it does not occur naturally [19,20,21,22]. Endemic species are organisms that exist only in Taiwan, and also are grouped into native species in this study.
The total number of recorded species, native species, endemic species, and exotic species was counted for each spring, with occurrence frequency in the 58 sampled springs calculated for each species. Spearman’s rank-order correlation was performed to assess the association between the RPI with total recorded species, native species, exotic species, and endemic species, and separately for fish, gastropoda and bivalves, shrimps, and crabs.
3. Results
3.1. Water Quality Assessment and RPI
In the 58 sampled springs, the dissolved oxygen ranged from 0.27 to 13.4 mg/L, with an average of 5.2 ± 2.9 mg/L. The average BOD measurement of sampled springs was 2.7 ± 4.4 mg/L, ranging from 0 to 22.4 mg/L. The mean suspended solid values of springs were 4.6 ± 9.1 mg/L, varying from 0 to 44.5 mg/L. Low NH3-N values were found between 0 to 1.38 mg/L (mean ± SE: 0.09 ± 0.19 mg/L) in sampled springs.
For the 58 springs with RPI scores, 26 were grouped as non-/mildly polluted, 23 were classified as lightly polluted, and 9 were ranked as moderately polluted. No springs were categorized as severely polluted (Table 2, Figure 2).

Table 2.
The occurrence and frequency of sampled springs in each index score (Si) of four water quality measurements were calculated for the 58 sampled springs. A higher index score indicated a greater polluted status as shown in Table 1.
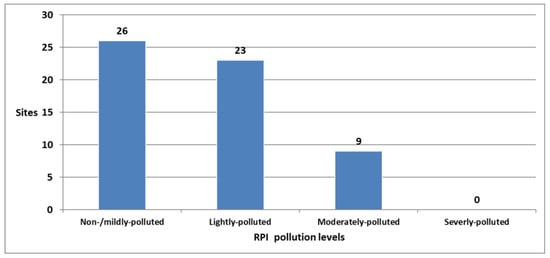
Figure 2.
Number of springs grouped into four pollution levels based on the River Pollution Index.
The occurrence and frequency of sampled springs were calculated for each index score of four water quality measurements (Table 2). The DO in 30 sampled springs was below 4.5 mg/L, as their index scores were lower than 6 points. For the BOD, 5 sampled springs were grouped into moderately polluted, and 53 springs are placed into negligibly polluted or unpolluted. For the SS and NH3-N, almost all sampled springs were classified as unpolluted.
3.2. Fishes
A total of 48 fish species, belonging to 12 families, were collected from the 58 sampled springs (Table 3). Among the 48 fish species, 17 were exotics, and 31 were natives, which included 11 endemics. The Cyprinidae, with 20 fish species, was the largest family collected. Nine species of two families, including three species of Poeciliidae and six species of Cichlidae, were all exotic fishes.

Table 3.
The Taiwan conservation status and occurrence and frequency of recorded fish species in 58 sampled springs of Taiwan. The Taiwan conservation status are based on Yang et al. [23]. (Conservation status: NVU: Nationally Vulnerable, NEN: Nationally Endangered, NCR: Nationally Critical, NNT: Nationally Near-Threatened) (Ethnic groups: Exotic species (EX)/Native species (NA)/Endemic species (NA*)).
The total number of recorded fish species collected in springs ranged from 0 to 20, and the highest was recorded in Wugoushui Spring (Table 4). The mean total recorded fish species in the springs is 3.4 ± 4.0 species (Table 4). In 44 of the 58 sampled springs fishes were collected, but in 14 no fish were found. The existing fishes in 44 of the 58 sampled springs varied from 1 to 20 species, with 22 springs (50%) containing fewer than 3 species (Figure 3, Table 3).

Table 4.
Range and mean values of total recorded species, native species, endemic species, and exotic species of collected fishes, gastropoda and bivalves, shrimps, and crabs in the 58 sampled springs in Taiwan.
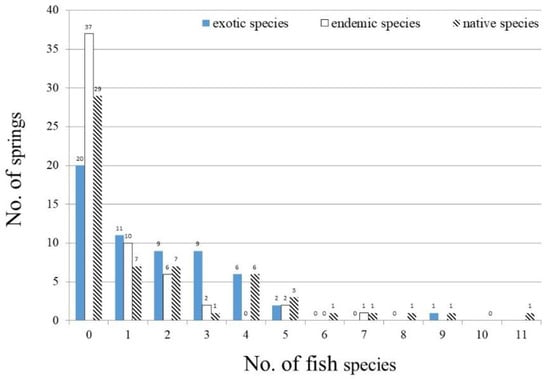
Figure 3.
Occurrence frequency of 58 sampled springs for exotic, endemic, and native fish species.
Native fishes were present in 29 springs, and endemic species appeared in 21 springs (Figure 3). The native fish species of springs varied from 0–11 species with a mean of 1.8 ± 2.5 species (Table 4). Among the 29 native fishes, six species were found over seven springs, i.e., Rhinogobius giurinus (9), Carassius auratus auratus (8), as well as other four endemic fishes, Opsarichthys pachycephalus (9), Acrossocheilus paradoxus (8), Candidia barbata, (7) and Tanakia himantegus (7).
Endemic fish species in the springs ranged from 0 to 7 species (Table 4). The mean endemic fish species in the springs were 0.8 ± 1.4 species. Five endemic fish, such as Metzia formosae, Onychostoma alticorpus, Rhinogobius candidianus, Rhinogobius gigas, and Rhinogobius lanyuensis, were found only in a single spring (Table 3).
Exotic fishes existed in 38 springs, and ranged from 0 to 9 with a mean of 1.7 ± 4.0 species (Figure 3, Table 4). Among the 17 exotic fishes, Gambusia affinis, present in 30 springs, and Oreochromis niloticus, found in 21 springs, were the top two most widely distributed exotics species (Table 2). Three exotic fishes, including Poecilia reticulate (8), Tilapia zillii (8), and Channa striata (9), were collected in more than eight springs. Twelve other exotics were found in fewer than four sites.
3.3. Gastropoda and Bivalves
Gastropoda and bivalve species were collected in 46 of the 58 sampled springs (Figure 4). Among the 46 springs, 24 gastropoda (22 species) and bivalves (two species) of 11 families were sampled (Table 5). Among the 24 gastropoda and bivalve species, four exotics (16.6%) and 20 natives (83.3%), including two endemics, were recorded. Native species appeared in 46 springs; endemic species were found in 3 springs; and exotics were present in 33 springs. The total recorded gastropoda and bivalve species of the springs varied between 0 to 12 species with a mean of 4.1 ± 3.4 species (Table 4).
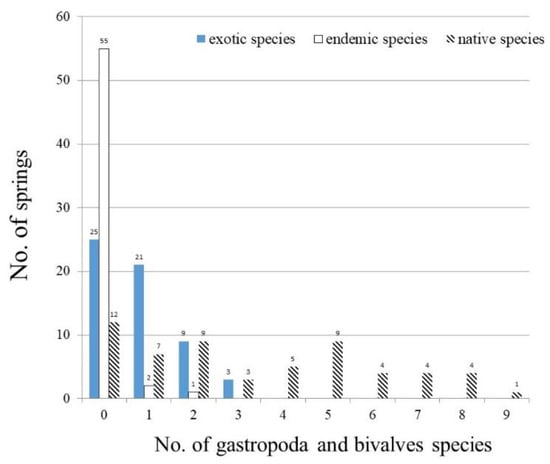
Figure 4.
Occurrence frequency of 58 sampled springs for exotic, endemic and native gastropoda and bivalve species.

Table 5.
The occurrence and frequency of recorded gastropods and bivalves in the 58 sampled springs of Taiwan (Ethnic groups: Exotic species (EX)/Native species (NA)/Endemic species (NA*)).
Native gastropoda and bivalve species in springs ranged from 0 to 9 species (mean: 3.1 ± 2.8 species), and endemic species showed within 0–2 species (mean: 0.1 ± 0.3 species) (Table 4). Melanoides tuberculatus appeared in 33 springs and was the most common native gastropoda (Table 5). Five other native gastropoda present in over ten springs were listed accordingly as Tarebia granifera (27), Stenomelania plicaria (23), Sinotaia quadrata (23), Austropeplea ollula (19), and Thiara scabra scabra (14). A native bivalve, Corbicula fluminea, was sampled in 10 springs. Endemic species of two gastropoda, Melanoides formosensis and Stenothyra formosana, were both found in a number of springs equal to or fewer than two.
Recorded exotic species in each spring fluctuated within 0–3 species with a mean of 0.8 ± 0.9 species (Table 4). Four exotics were sampled, i.e., Pomacea canaliculata was widely dispersed in 26 springs; physella acuta was found in 16 springs; Pomacea scalaris was present in seven springs; and Indoplanorbis exustus appeared only in one single spring (Table 5).
3.4. Shrimps
Sixteen shrimp species belonging to three families were collected in thirty-four of fifty-eight sampled springs (Table 6). Along with two species, the ethnic groupings of which we were unable to determine, we found two exotic shrimps and 12 native species, which included three endemics. Native shrimps appeared in 34 springs with endemics shown in 10 springs, while exotic species were found in 3 sites. The total recorded shrimp species in springs ranged from 0 to 4 species with a mean of 1.1 ± 1.2 species (Table 4).

Table 6.
The occurrence and frequency of recorded shrimp and crab species in 58 sampled springs of Taiwan (Ethnic groups: Exotic species (EX)/Native species (NA)/Endemic species (NA*)).
The total number of native shrimps in the springs varied in 0–4 species (mean: 1.1 ± 1.1 species), and the total number of endemic shrimps in the springs changed within 0–2 species (mean: 0.1 ± 0.3 species) (Figure 5, Table 4). Native shrimps appeared in more than nine springs, including Neocaridina denticulate (18), Macrobrachium asperulum (13), and Macrobrachium lar (9) (Table 6). Endemic shrimps of Caridian pseudodenticulata appeared in eight springs, but Neocaridina sacca and Caridina formosae were only recorded in two springs and one spring, respectively.
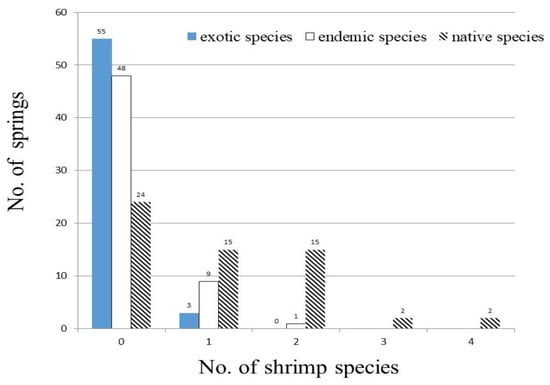
Figure 5.
Occurrence frequency of 58 sampled springs for exotic, endemic, and native shrimp species.
3.5. Crabs
A total of 14 crab species were sampled in 18 of 58 samples springs, with 14 native species and no exotic species (Table 6). Among the 14 native species, 10 species were endemic crabs. The total number of crabs recorded in the springs changed from 0 to 4 species, and averaged 0.4 ± 0.9 species (Table 4).
The total number of native crabs in the springs ranged from 0 to 4 species (mean: 0.4 ± 0.9 species), and the total number of endemic crabs in the springs fluctuated between 0 to 3 species (mean: 0.3 ± 0.7 species) (Table 4). Given that there were no exotic species, Candidiopotamon rathbunae, a native and endemic crab recorded in seven springs, was the most common crab (Figure 6). Among the other eight endemic crabs, Geothelphusa tsayae was found in three springs, Geothelphusa miyazakii and Geothelphusa olea were collected in two springs, and five other endemic crabs were present in a single site.
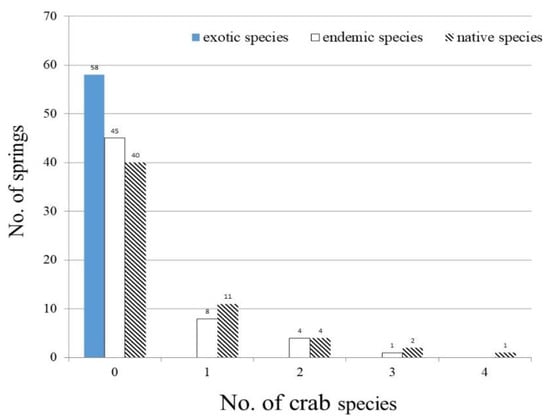
Figure 6.
Occurrence frequency of sampled springs for exotic, endemic, and native crab species.
3.6. Correlations of RPI and Biological Variables
The RPI scores were individually correlated with the number of total recorded species, exotic species, native species, endemic species for fish, gastropoda and bivalves, shrimps, and crabs, using Spearman’s correlation. A total of 15 correlations were performed (no exotic crabs were collected), but a significant negative correlation was only identified between the RPI score and endemic species of gastropoda and bivalves (ρ = −0.17, n = 58). This result showed that the greater RPI score and lower water quality would generate lower endemic species of gastropoda and bivalves.
4. Discussion
4.1. Water Quality Assessment and RPI
Based on the RPI, the water quality of 58 sampled springs was mainly grouped as non-/mildly polluted (26, 44.8%) and lightly polluted (23, 39.6%), while the other 9 springs were placed into the category of moderately polluted. However, for assessing the pollution status of springs, the RPI is not an adequate water quality index. According to the occurrence frequencies of sampled springs in index scores of four water quality measurements, the dissolved oxygen is the main determinant in assigning the environmental status for sampled springs. Generally speaking, higher dissolved oxygen in surface waters indicates a better environmental quality [24]. However, freshwater springs are naturally found deoxygenated around the world because their water flows from aquifers [24,25]. Judging from the occurrence frequency of the index scores of BOD, SS, and NH3-N in the RPI, the pollution status of sampled springs would be greatly improved if the current evaluation of the assessing factor of dissolved oxygen is replaced by another water quality measurement, one which will properly reflect the environmental quality of springs.
The Surface Water Classification and Water Quality Criteria (SWCWQC) of Taiwan was revised in 2017 and currently serves as a major environmental assessment standard for surface waters [26]. Dissolved oxygen was included in the SWCWQC as a water quality criterion to categorize surface water bodies for public water (DO > 6.5 ppm), swimming (DO > 6.5 ppm), aquaculture (DO > 5.5 ppm), irrigation and industrial use (DO > 4.5 ppm), and environmental conservation (DO > 2.0 ppm). As hypoxia is naturally present, the SWCWQC is also not an appropriate assessment and classification tool for springs in Taiwan for evaluating its environmental status, nor for determining its management tendency.
Reflected by the index scores of BOD in this study, organic pollutants from domestic sewage may be the major pollutant in the springs of Taiwan [27]. For assessing the environmental status of the springs in Taiwan, developing a dedicated water quality index or readjusting the RPI by selecting another water quality measurement to replace dissolved oxygen is suggested. Alluvial groundwater from springs and bore wells display high concentrations of fecal coliform and fecal streptococcus from the anthropogenic pollutions of semi-urban settlements as shown in a study done in Douala, Cameroon, Western Africa [28]. Considering that spring water is a major source for drinking, tea brewing, and other domestic purposes in Taiwan and worldwide, the concentration of fecal coliform, a water quality measurement for drinking water standard in Taiwan, is suggested to replace dissolved oxygen content in the water quality index to assess the environmental status of springs.
4.2. Species Diversity of Aquatic Animals
Springs in Taiwan are renowned conservation hotspots for the species diversity of freshwater animals because more than 25% of native species of each and every category of freshwater animals, including fishes, gastropod and bivalves, shrimps, and crabs, are often found in Taiwan. Taxonomy books and field guides of freshwater animals in Taiwan reported 95 fishes [23], 60 gastropoda and bivalves [29], 44 shrimps [30] (Chou et al., 2021), and 40 crabs [22] in Taiwan. In the 58 sampled springs, we collected freshwater native species of 31 fishes (31/95 = 32.6%), 20 gastropoda and bivalves (20/60= 33.3%), 12 shrimps (12/44 = 27.2%), and 14 crabs (14/40 = 35%). Despite many native species present, the invasion of exotic species, especially freshwater fishes, has posed diverse threats to the freshwater biodiversity of springs in Taiwan.
4.3. Fishes
Many threatened native fishes are present in the springs of Taiwan. Among the 31 native fish species of the 58 sampled springs, Metzia formosae is listed in the 2021 National Conservation Species List of Council of Aquaculture, Taiwan [31]. According to life history classification and 2012 IUCN criteria, Yang et al. [23] counted 95 freshwater fishes in Taiwan, and categorized 25 as nationally threatened, and 11 as nationally near-threatened species. Based on the conservation status of Yang et al. [23], six collected species (6/25 = 24.0%) are listed as nationally threatened species, including Rhinogabius lanyuensis, Distoechodon tumirostris, Oryzias latipes, Channa asiatica, Metzia formosae, and Puntius semifasciolatus, and four (4/11 = 36.3%) species are placed as nationally near-endangered, including Rhodeus ocellatus ocellatus, Onychostoma alticorpus, Silurus asotus, and Macropodus opercularis.
Exotic fishes are also widely distributed and abundant in the springs of Taiwan. Among the 48 collected fishes, 17 species (35.4%) were exotic fishes. Eleven species in three families, such as Loricariidae, Poeciliidae, and Cichlidae, were completely composed of exotic fishes. This situation indicates that exotic fishes have become a serious threat, and will continue to cause numerous negative impacts on the aquatic biodiversity in the springs of Taiwan.
The most widely distributed exotic fishes, Gambusia affinis (30 springs), appear in the IUCN/SSC 100 of the World’s Worst Invasive Alien Species [32]. Other than Gambusia affinis, several worldwide and notorious invasive exotic fishes, including two species of armored catfish (Loricariidae), six species of tilapia (Cichlidae), and striped snakehead Channa striata, are also present. Since the 1970s, armored catfish, Liposarcus multiradiatus, invaded Taiwan, and were suspected to have a negative impact on those endemic fishes with bottom/attached eggs and benthic algae/detritus feeders [33]. Additionally, in the Blue Spring of Florida, U.S., the armored catfish, Pterygoplichthys disjunctivus, not only significantly alter nutrient availability for algae with its fecal leachate [34], but also disturbs manatee behavior by attached to and grazing on the algae on their bodies [35]. Tilapia has generated competition and predation with endemic fishes since it was introduced for aquaculture during the early 1960s [33]. Except the Cichlasoma managuen and an unidentified Cichlasoma species, four other tilapia species were listed in Taiwan before 2010 [36,37]. Tilapia fishes in Taiwan are famous for their high tolerance to survive in low-oxygen and turbid waters, their predation on macroinvetebrate and larvae, young, and small-size endemic fishes, and their competition over breeding sites and food sources with native fishes [36,37]. The chevron snakehead, Channa striata, has invaded Taiwan for over 30 years, and has caused great negative impacts to the biodiversity of native aquatic organisms due to its strong environmental adaptability and carnivore diet [38]. Above examples provide strong support to restrain and control the exotic fishes in springs to preserve the artesian biodiversity in Taiwan.
4.4. Gastropods and Bivalves
Springs could be identified as the conservation oasis for freshwater gastropods and bivalves in Taiwan. Of the 60 freshwater gastropods and bivalves in Taiwan, 20 natives (1/3 = 33.3%) are present in the 58 sampled springs [29]. With greater collection efforts and more sampled springs, more native gastropods and bivalves would exist.
Threats from exotic gastropods and bivalves are present and potentially expanding in the future. Four exotic gastropods and bivalves existed in the fifty-eight sampled springs, including Pomacea canaliculata, Pomacea scalaris, and Physella acuta, and Indoplanorbis exustus. Pomacea, the largest of nine genera in the family of apple snails (Ampullariidae), is native to South America [39] (Hayes et al., 2008). Pomacea spp., especially Pomacea canaliculate, listed among the World’s 100 Worst Invasive Alien Species, was introduced to Asia around 1980, initially introduced to Taiwan for commercial purposes, and subsequently introduced to numerous countries of Southern and Eastern Asia [39,40]. Pomacea canaliculata was developed as a serious agricultural pest of wetland rice and other crops, causing massive economic damages, e.g., US$40 million per year in the Philippines [41,42]. Moreover, Pomacea spp. has created negative ecological impacts, including the decline of native ampullariids [43], local extirpation of freshwater bryozoans [44], and the loss and alteration of macrophytes in natural wetlands [45].
Physella acuta was recorded in 16 springs. P. acuta, a small air-breathing snail in the family Physidae, is an effective and spectacular invader among freshwater snails worldwide [46]. Of New World origin, the earliest reliable records of P. acuta in the Old World can be dated to 1742 and were first described in 1805 in France [46]; Bousset et al. [47] cited that P. acuta was an excellent biological model for geographically investigating biological invasion.
Native mussels in Taiwan also exhibited an invasion crisis and altered freshwater ecosystems around the world. Anodonta woodiana, a native unionid mussel of Taiwan, has an obligatory parasitic stage (glochidium) and must encyst on host fish [48]. Because A. woodiana is a broad host generalist and shows no reproduction limitation by ambient water temperature, future increase in its invasion speed, range, and establishment worldwide is expected [48,49].
4.5. Shrimp
A total of 16 shrimp species, including 12 native species, 2 exotic species, and 2 undetermined species are identified in the 58 sampled springs. There are 44 shrimps in Taiwan, and over a quarter of them (12/44 = 27.2%) could be found in springs [30]. Among the twelve native species, four species, Macrobrachium gracilirostre, Macrobrachium hirtimanus, Caridina formosae, and Neocaridina saccam, are listed as having a rare status by Lin et al. [50] and Chou et al. [30], while two species, Macrobrachium nipponense and Palaemon concinnus, are suggested for ornamental value [30].
Despite its limited distribution, the exotic shrimp of North American crayfish, Procambarus clarkii, is one of the most extensively introduced freshwater shrimp in the world due to its high economic value [51]. To successfully colonize a wide range of regions is a consequence of the biological characteristics of Procambarus clarkii, such as rapid growth rate, early maturity, high offspring number, and opportunistic feeding habits [51,52]. After invasion, Procambarus clarkii will cause diverse negative impacts, including altering the whole functioning of the ecosystem [53], replacing indigenous crayfishes [52], vectoring the crayfish plague of Aphanomyces astaci [54], and generating economic loss in agriculture, forestry, and fishery [51].
4.6. Crab
Springs serve as both an important habitat and a gene bank for preserving the endemic crabs in Taiwan. High endemic crab species and no exotic species were found in the 58 sampled springs. Of the 40 recorded crab species in Taiwan, at least 14 (14/40 = 35%) native crab species were collected in the 58 sampled springs [22]. Among the 14 collected crabs, 10 endemic species (10/14 = 71.4%) were listed. Shih and Ng [55] analyzed the diversity and biogeography of Potamidae and Gecarcinucidae found in freshwater in East Asia. They found that Taiwan has the highest species richness (42 species) of the island system in East Asia, and that the warmer climate, more diverse habitat, and a long history of cladogenesis generally may contribute to this observation. This study revealed that nine species of Potamidae collected from springs were all endemic species. This high endemism of freshwater crabs in the springs of Taiwan demands further investigation.
4.7. Correlation between Species Diversity with Environmental Measurements
One of fifteen correlations between water quality measurements and species diversity of aquatic animals is present in this study. No collection of aquatic animals in many springs and environmental features in springs different from regular lotic and lentic ecosystems, such as oxygen concentration, may both contribute to this finding [25]. Intense environmental alternations by anthropogenic interference over the years may also subsidize for failing to identify the statistical correlation between environmental factors and species diversity in springs.
4.8. Threats and Conservation for Springs in Taiwan
In addition to the invasion of aquatic animals, the existence springs in Taiwan are currently threatened by several environmental alternations (Figure 7). These environmental alternations include overconsumption and depletion of groundwater by land development and urbanization, deterioration of water quality by agricultural, industrial, and domestic pollutions, increasing paved roads due to tourism development, and inappropriate land use and management of cementation for swimming pools and laundry pits [26]. All these environmental alterations combined with higher tap water coverage gradually decrease the domestic reliability of the daily water use of spring water by general public, and eventually decrease the appreciation and awareness of the importance and sustainability of springs by the citizens and administration agencies. Societal ignorance of the importance of springs generates a negative administrative strategy regarding the spring management in Taiwan; for example, a spring in Jinshan, New Taipei City was completely sealed up by Forestry Bureau, Council of Agriculture in 2014 without consulting the opinions of local residents [56]. To restore and sustain the springs in Taiwan, critical measures to minimize these threated factors and to raise the societal awareness of the springs are urgent and essential.
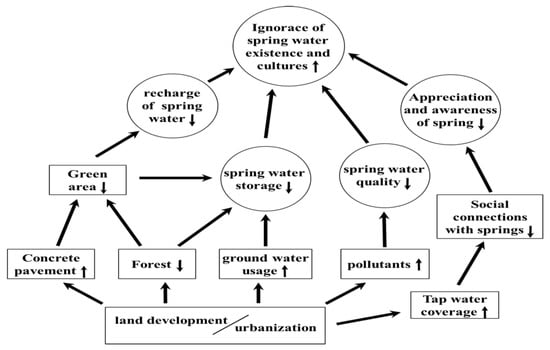
Figure 7.
Threatened factors and their consequence effects in the springs of Taiwan (square: threatened factors, circle: consequence effect, ↑: increase, ↓: decrease).
5. Conclusions
The environmental status of water quality in 49 (84.4%) of 58 sampled springs was majorly placed as non-/mildly polluted (26 springs) and lightly polluted (23 springs) based on the RPI. However, hypoxia may naturally occur in the springs as a result of their water flowing from aquifers, and lower dissolved oxygen values would intensify the pollution status when the RPI was applied in the springs [24,25]. This observation indicated that the RPI was not a suitable index to evaluate the status of the water quality of the springs. Instead, our suggestion was to select the concentration of fecal coliform as a replacement measurement for dissolved oxygen in the RPI, because the general public in Taiwan still prefers spring water for drinking, brewing tea, and other daily uses. Another option is to select meiofauna to assess the water quality of groundwater as in Europe and worldwide, though currently it is poorly adopted in Taiwan due to the existing limited studies [57].
Although springs are threatened by biological invasion and anthropogenic disturbances, the results of this study indicate that many native and endemic aquatic animals are present in the springs and spring-fed waters of Taiwan. Lusardi et al. [58] reviewed the existing literature on spring-fed rivers and a decade of research on the volcanic spring-fed rivers of northern California. They reported that the environmental condition of springs and spring-fed waters differed from surface runoff rivers with unique nutrient cycling, stable temperature, water volume, and water quality, and that hypoxia may exist due to its hydrogeological processes [25]. They also indicated that traditional stream academic theories, such as the River Continuum Concept and Flood Pulse Concept for providing conceptual frameworks to realize riverine processes, have hardly applied to spring-fed streams and systems [56]. In the future, climate change may generate radical shifts in stream discharge and temperature regimes, and these changes are projected to further imperil aquatic biodiversity worldwide. Thus, new academic theories and findings will be developed and revealed if interdisciplinary studies are carried out to understand the interactions of the hydrogeological background, habitat characteristics, biological composition, and processes of springs and spring-fed waters in Taiwan [7,8]. Additionally, because of its stability in water volume and temperature, springs and spring-fed systems in Taiwan will provide a habitat refuge for aquatic organisms as the power of climate change becomes more intense. To restore and sustain springs in Taiwan, effective strategies and practical measures, such as stronger law enforcement, wider education coverage, and more research on springs are urgently required in order to minimize human-caused threats and raise social awareness for endangering springs.
Author Contributions
Y.-W.C. and S.-H.L. formulated the idea. Y.-W.C., S.-H.L., D.-J.H., B.-S.S., Y.-C.G., Y.-C.C. and C.-H.J. built the sampling design, collected the data, and identified the aquatic animals. B.-S.S. and S.-H.L. performed the statistical analysis. S.-H.L. wrote the manuscript with collaboration from L.-L.L., S.-H.L. and B.-S.S. reviewed the manuscript and contributed to the discussion of the results. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Forestry Bureau, Council of Agriculture, and Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST 108-2621-B-017-001-MY3) of Taiwan.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Datasets are accessible from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Forestry Bureau, Council of Agriculture, and Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan via a research grant (MOST 108-2621-B-017-001-MY3) to Shih-hsiung Liang. We are highly grateful to anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments on the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
References
- Odum, H.T. Trophic structure and productivity of Silver Springs, Florida. Ecol. Monogr. 1957, 27, 55–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hershler, R.; Liu, H.-P.; Howard, J. Springsnails: A new conservation focus in western North America. BioScience 2014, 64, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, J.M.; Lima, R.E.; Springer, A.E. Can environmental attributes influence protected area designation? A case study valuing preferences for springs in Grand Canyon National Park. Land Use Policy 2017, 63, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odum, E.P. Fundamentals, of Ecology; WB Saunders: Philadelphia, PE, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, D.D. The springs as an interface between groundwater and lotic faunas and as a tool in assessing groundwater quality. Verh. Int. Ver. Theor. Angew. Limnol. 1991, 24, 1621–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibert, J.; Dole-Oliver, M.J.; Marmonier, P.; Vervier, P. Surface Water-Groundwater Ecotones. In The Ecology and Management of Aquatic-Terrestrial Ecotones; United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization: Paris, France, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Cuthbert, M.O.; Ashley, G.M. A spring forward for hominin evolution in East Africa. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreamer, D.K.; Stevens, L.E.; Ledbetter, J.D. Groundwater dependent ecosystems—Science, challenges, and policy. In Groundwater; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Onete, M.; Ion, R.; Bodescu, F.P. Description and threats to Natura 2000 habitat 7220* Petrifying springs with tufa formations (Cratoneurion). A review. Marisia Stud. Mat. St. Nat. 2014, XXXIII–XXXIV, 71–79. [Google Scholar]
- Cantonati, M.; Stevens, L.E.; Segadelli, S.; Springer, A.E.; Goldscheider, N.; Celico, F.; Filippini, M.; Ogata, K.; Garginin, A. Ecohydrogeology: The interdisciplinary convergence needed to improve the study and stewardship of springs and other groundwater dependent habitats, biota, and ecosystems. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 110, 105803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantonati, M.; Fensham, R.J.; Stevens, L.E.; Gerecke, R.; Glazier, D.S.; Goldscheider, N.; Knight, R.L.; Richardson, J.S.; Springer, A.E.; Tockner, K. Urgent plea for global protection of springs. Conserv. Biol. 2021, 35, 378–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, L.E.; Schenk, E.R.; Springer, A.E. Springs ecosystem classification. Ecol. Appl. 2020, 31, e002218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, D.W.; Wetzel, M.J.; Phillippe, L.R.; Reed, P.C.; Young, T.C. Aquatic biodiversity in Illinois springs. J. Kans. Entomol. Soc. 1995, 68, 93–107. [Google Scholar]
- Aboal, M.; Puig, A.M.; Prefasi, M. Diatom assemblages in springs in Castellón province, Eastern Spain. Algol. Stud. 1998, 90, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatton, T.; Evans, R. Dependence of Ecosystems on Groundwater and Its Significance to Australia; Occasional Paper No 12/98; Land and Water Resources Research and Development Corporation: Canberra, Australia, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, G.G.; Padedda, B.M.; Wetzel, C.E.; Lugile, A.; Sechi, N.; Ector, L. Epilithic diatom assemblages and environmental quality of the Su Gologone karst spring (centraleastern Sardinia, Italy). Acta. Bot. Croat. 2016, 75, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, R.; Nebra, A.; Gomà, J.; Pedrocchi, C.; Cadiach, O.; García, G.; Solé, J. First data on the biological richness of Mediterranean springs. Limnetica 2020, 39, 121–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environmental Protection Administration. Available online: https://wq.epa.gov.tw/EWQP/en/Encyclopedia/NounDefinition/Pedia_37.aspx. (accessed on 27 March 2022).
- Taiwan Malacofauna Database. Available online: https://shell.sinica.edu.tw/ (accessed on 22 January 2022).
- The Fish Database of Taiwan. Available online: https://fishdb.sinica.edu.tw/ (accessed on 10 January 2022).
- Shi, J.Y.; You, S.P. Freshwater shrimps of Taiwan; National Museum of Marine Biology and aquarium, Ministry of Education: Taipei, Taiwan, 1998. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.Y.; Lee, P.W. Freshwater crabs of Taiwan; Morning Star Publ.: Taichung, Taiwan, 2009. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.H.; Tseng, T.J.; Lin, R.S.; Tzeng, C.S.; Liao, T.Y. The Red List of Freshwater Fishes of Taiwan, 2017; Endemic Species Research Institute, Forestry Bureau, Council of Agriculture: Taipei, Taiwan, 2017. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- McKinsey, D.M.; Chapman, L.J. Dissolved oxygen and fish distribution in a Florida spring. Environ. Biol. of Fishes 1998, 53, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, M.A.; Thornton, A.; Pasko, S.; Crater, A. Patterns of air-breathing behavior in juvenile armored catfish, Pterygoplichthys sp. (Gill 1858). Environ. Biol. of Fishes 2021, 104, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law & Regulation Database. Available online: https://law.moj.gov.tw/Eng/ (accessed on 12 January 2022).
- Liang, S.H.; Chiu, Y.W.; Huang, D.J. Development of Sustainable Model and Assessment of Habitat Quality of Springs in Taiwan; Council of Aquaculture: Taipei, Taiwan, 2017. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Takem, G.E.; Chandrasekharam, D.; Ayonghe, S.N.; Thambidurai, P. Pollution characteristics of alluvial groundwater from springs and bore wells in semi-urban informal settlements of Douala, Cameroon, Western Africa. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 61, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.D. Freshwater Molluscs of Taiwan; National Museum of Marine Biology and Aquarium, Ministry of Education: Taipei, Taiwan, 2011. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chou, M.T.; Gao, R.Q.; Chang, R.Z.; Liao, G. The Freshwater, Estuarine Fish and Shrimp of Taiwan; Morning Star Publ.: Taichung, Taiwan, 2021. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Council of Aquaculture. Available online: https://conservation.forest.gov.tw/0002021 (accessed on 31 January 2022).
- GLOBAL INVASIVE SPECIES DATABASE. Available online: http://www.iucngisd.org/gisd/100_worst.php (accessed on 31 January 2022).
- Liang, S.H.; Wu, H.P.; Shieh, B.S. Size structure, reproductive phenology, and sex ratio of an exotic armored catfish (Liposarcus multiradiatus) in the Kao-ping River of southern Taiwan. Zool. Stud. 2005, 44, 252–259. [Google Scholar]
- Rubio, V.Y.; Gibbs, M.A.; Work, K.A.; Bryan, C.E. Abundant feces from an exotic armored Catfish, Pterygoplichthys Disjunctivus (Weber, 1991), create nutrient hotspots and promote algal growth in a Florida Spring. Aquat. Invasions 2016, 11, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, M.; Futral, T.; Mallinger, M.; Martin, D.; Ross, M. Disturbance on the Florida Manatee by an Invasive Catfish. Southeast Nat. 2010, 9, 635–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, I.S.; Huang, S.B.; Liu, J.C. Indicator Species of Riverine Fishes in Taiwan. Volume 1. Primary Freshwater Fishes; National Taiwan Marine University: Keelung, Taiwan, 2010. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, I.S.; Huang, S.P.; Liu, C.C. Alien, Invasive Freshwater Fishes in Taiwan; National Taiwan Ocean University: Keelung, Taiwan, 2010. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.C.; Shieh, B.S.; Chiu, Y.W.; Huang, D.J.; Liang, S.H. Growth, diet composition and reproductive biology of the invasive freshwater fish Chevron snakehead Channa striata on a subtropical island. Zool. Stud. 2017, 55, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, K.A.; Joshi, R.C.; Thiengo, C.; Cowie, R.H. Out of South America: Multiple origins of non-native apple snails in Asia. Divers. Distrib. 2008, 14, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowie, R.H.; Hayes, K.A.; Strong, E.E.; Thiengo, S.C. Non-Native Apple Snails: Systematics, Distribution, Invasion History a Reasons for Introduction. Biology and Management of Invasive Apple Snails; Philippine Rice Research Institute (PhilRice), Maligaya: Science City of Muñoz, Nueva Ecija, Phillippine, 2017; Volume 3119, pp. 3–32. [Google Scholar]
- Naylor, R. Invasions in agriculture: Assessing the cost of the golden apple snail in Asia. Ambio 1996, 25, 443–448. [Google Scholar]
- Cowie, R.H. Apple snails (Ampullariidae) as agricultural pests: Their biology, impacts and management. In Molluscs as Crop Pests; CAB-International: Wallingford, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Halwart, M. The golden apple snail Pomacea canaliculata in Asian rice farming systems: Present impact and future threat. Int. J. Pest Manag. 1994, 40, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, T.; Anurakpongsatorn, P.; Chaichana, R.; Mahujchariyawong, J.; Satapanajaru, T. Predation on freshwater bryozoans by the apple snail, Pomacea canaliculata, Ampulariidae [sic], an invasive species in Southeast Asia: A summary report. Denisia 2005, 16, 283–286. [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson, N.O.L.; Bronmark, C.; Hansson, L.-A. Invading herbivory: The golden apple snail alters ecosystem functioning in Asian wetlands. Ecology 2004, 85, 1575–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinarski, M.V. The history of an invasion: Phases of the explosive spread of the physid snail Physella acuta through Europe, Transcaucasia and Central Asia. Biol. Invasion 2017, 19, 1299–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousset, L.; Pointier, J.P.; David, P.; Jarne, P. Neither variation loss, nor change in selfing rate is associated with the worldwide invasion of Physa acuta from its native North America. Biol. Invasions 2014, 16, 1769–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douda, K.; Vrtilek, M.; Slavik, O.; Reichard, M. The role of host specificity in explaining the invasion success of the freshwater mussel Anodonta woodiana in Europe. Biol. Invasion 2012, 14, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichard, M.; Polacik, M.; Tarkan, A.S.; Spence, R.; Gaygusuz, O.; Ercan, E.; Ondrackova, M.; Smith, C. The bitterling mussel coevolutionary relationship in areas of recent and ancient sympatry. Evolution 2010, 64, 3047–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.G. A Field Guide to Freshwater Fish and Shrimps in Taiwan; Big Tree Publ.: Taipei, Taiwan, 2017; Volume 2. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Loureiro, T.G.; Anastacio, P.M.S.G.; Araujo, P.B.; Souty-Grosser, G.; Almerao, M.P. Red swamp crayfish: Biology, ecology and invasion–an overview. Nauplius 2015, 23, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherardi, F. Crayfish invading Europe: The case study of Procambarus clarkii. Mar. Freshw. Behav. Physiol. 2006, 39, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, M.J.; Segurado, P.; Sousa, M.; Rebelo, R. Collapse of the amphibian community of the Paul do Boquilobo Natural Reserve (central Portugal) after the arrival of the exotic American crayfish Procambarus clarkii. J. Herpeto. 2008, 18, 197–204. [Google Scholar]
- Holdich, D.M.; Reynolds, J.D.; Souty-Grosset, C.; Sibley, P.J. A review of the ever increasing threat to European crayfish from non-indigenous crayfish species. Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2009, 11, 394–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, H.T.; Ng, P.K.L. Diversity and biogeography of freshwater crabs (Crustacea: Brachyure: Potamidae, Gecarcinucidae) from East Asia. System. Biodivers. 2011, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orient Daily. 2015/04/20. Available online: https://hk.on.cc/tw/bkn/cnt/news/20150420/bkntw-20150420082047492-0420_04011_001.html (accessed on 21 March 2022).
- Epure, L.; Borda, D.R. Groundwater contamination and the relationship between water chemistry and biotic components in a karst system (Bihor Mountains, Romania). Trav. Inst. Speol. 2014, 53, 69–84. [Google Scholar]
- Lusardi, R.A.; Nichols, A.L.; Willis, A.D.; Jeffres, C.A.; Kiers, A.H.; Van Nieuwenhuyse, E.E.; Dahlgren, R.A. Not all rivers are created equal: The importance of spring-fed rivers under a changing climate. Water 2021, 13, 1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).