Abstract
Rhodolith beds are biogenic benthic habitats mainly formed by unattached, non-geniculate coralline algae, which can be inhabited by many associated species. The Brazilian continental shelf encompasses the largest continuous rhodolith bed in the world. This study was based on samples obtained from seven sites and videos taken by a Remotely Operated Vehicle (ROV) at four transects off the Sergipe-Alagoas Coast on the northeast Brazilian shelf. ROV operations and bottom trawl sampling revealed the occurrence of rhodolith beds between 25 and 54 m depths. At the shallower depths, fruticose (branching) rhodoliths (maërl) appear in troughs of ripples, and other non-branching rhodoliths occur associated with corals and sponge patches surrounded by bioclastic sand. Rhodoliths also occur in patches from 30 to 39 m depth; some are fused, forming larger, complex tridimensional structures. At deeper depths, from 40 to 54 m, the abundance of rhodoliths increases and occur associated with fleshy macroalgae on a smooth seafloor; some rhodoliths are fused into complex structures, locally some are fruticose (maërl), and others are partially buried by fine-grained sediment. The collected rhodoliths vary from fruticose in two sites to encrusting to lumpy, concentric and boxwork nodules in the rest; their size ranges from small (<1.5 cm) to large (~6 cm) and are mostly sub-spheroidal to spheroidal. A total of 16 red algal morpho-taxa were identified in the study sites. Two phases of growth can be distinguished in some rhodoliths by changes in color. The brownish inner cores yielded ages of 1600–1850 cal years before the present, whereas outer layers were much younger (180–50 years BP old). Growth layers appeared to have been separated by a long period of burial in the seafloor sediment. Other rhodoliths have ages of hundreds of years.
1. Introduction
Throughout their evolutionary history, non-geniculate coralline algae have been present in carbonate platforms as well as siliciclastic and mixed carbonate-siliciclastic systems [1]. Living and fossil non-geniculate coralline algae occur as crusts of varying thickness on both hard and soft substrates and free-living (unattached) nodules, also called rhodoliths and maërl, which can occur in large concentrations on the seafloor, known as rhodolith beds [2]. The rhodoliths occur worldwide from polar to tropical seas in a wide depth range on marine shelves [3,4] and are generally found where light is weak but sufficient for non-geniculate coralline algal growth and water motion and/or bioturbation are sufficient to move the rhodoliths [5]. Rhodoliths develop, in many cases, around a nucleus (bioclast or rock fragment) and can be composed of one or several non-geniculate coralline algal species, which can be intergrown with other encrusting organisms, such as bryozoans, gastropods, serpulids and encrusting foraminifera [6]. The rhodolith beds form three-dimensional complex biogenic benthic habitats [5] inhabited by a diverse biota of macroalgae and invertebrates [7,8,9], in particular crustaceans, polychaetes [10], cnidarians and chitons [11]. Some species of the associated fauna seem to be rhodolith-specific [12], influenced by rhodolith-forming species and rhodolith morphologies [13,14]. Furthermore, the phytobenthic community from the Sergipe-Alagoas (SEAL) Basin was characterized by a rich flora with a predominance of red algae (Rhodophyta) [15], showing an increasing gradient from the coast to the deepest regions, with lower values in the coastal areas under the influence of the São Francisco, Sergipe and Vaza-Barris rivers, and higher values in the deeper areas, characterized by the occurrence of more stable sediments [15], consisting of rhodolith beds.
Analyses of growth forms (e.g., lumpy, warty or encrusting) and the taxonomic composition of the non-geniculate coralline algae from the nucleus to the surface of the rhodoliths can provide valuable information on paleoenvironmental conditions during their development [1]. Rhodoliths and rhodolith beds do not grow continuously, as their growth could be interrupted by burial [16], sometimes making paleoenvironmental inferences from their growth record difficult [1].
The Brazilian continental shelf encompasses the largest continuous rhodolith beds in the world [17]. The fauna associated with rhodolith beds indicates high diversity of species across extensive areas of the continental shelf, but the main geographical gap of knowledge about rhodolith beds in Brazil is the northeast coast, specifically the continental shelf between Sergipe and Pernambuco, including the region of the São Francisco River mouth [18]. The marine sedimentation of the Sergipe-Alagoas continental shelf was analyzed in some studies that characterized Holocene sedimentation [19,20]. These studies show the spatial distribution of the main carbonate and siliciclastic components of the seabed [20,21] and their contributions to the formation of superficial sediment, comparing biotic and abiotic characteristics [22,23].
In this study, we aimed to (a) determine the distribution, structure and composition of rhodolith beds from the middle and outer shelf of the Sergipe-Alagoas Basin and (b) know their temporal evolution by establishing rhodolith ages obtained at different depths through carbon radiometric dating.
2. Study Area
The SEAL Basin on the northeast shelf of Brazil is subdivided into the Alagoas sub-basin, Sergipe sub-basin, Cabo sub-basin and Jacuípe sub-basin [24]. The study area (35° to 37° W and 10° to 11° S) is located within the Sergipe sub-basin and northern Jacuípe sub-basin, between the mouths of the Coruripe and Piaui-Real rivers (Figure 1). The Sergipe and south Alagoas continental shelf is considered shallow and narrow, with an average depth of 45 m and an average width of 28 km in Alagoas, 33 km in north Sergipe and 22 km in south Sergipe [23,25], with the shelf break beginning between 36 and 51 m depth in the center of the study area. It presents a gentle slope of approximately 1:570 and is characterized by a series of incised-shelf valleys, which have a northwest–southeast direction [23]. The main hydrographic basins of the study area are Coruripe, São Francisco, Japaratuba, Sergipe, Vaza Barris, Piauí and Real [26]. The continental shelf has different geomorphological settings along its 380 km length. These include five different areas, namely smooth areas or areas with little roughness, rough areas, canyons, incised valleys and aligned banks [27]. Rough areas are located south of Alagoas, between the São Francisco and Japaratuba rivers and south of Sergipe and correspond to the carbonate domain with calcareous algae [27]. We subdivided the carbonate domain into north, central and south sectors (Figure 1), which are separated by the two largest canyons, formed by the influence of the São Francisco and the Japaratuba rivers. The outer shelf of the north sector shows a reduced width and a soft and smooth relief in the southern part and a rugged and steeper relief in the northern one. The outer zone starts at the 30 m isobath and continues until the shelf break [23]. The incised valleys were partially filled with fine sediments, and carbonate deposition at the outer edge of the shelf is segmented by muddy zones adjacent to the river mouths. During the last deglaciation, the continental shelf of the SEAL was quickly flooded by the rapid rise in sea level. The shelf flooding started around 10,000 years BP and was completed 3000 years later [28,29]. The presence of sediments deposited over a geological history that extends from the penultimate marine regression represents the last marine transgression and records the stage of the current marine regression [21].
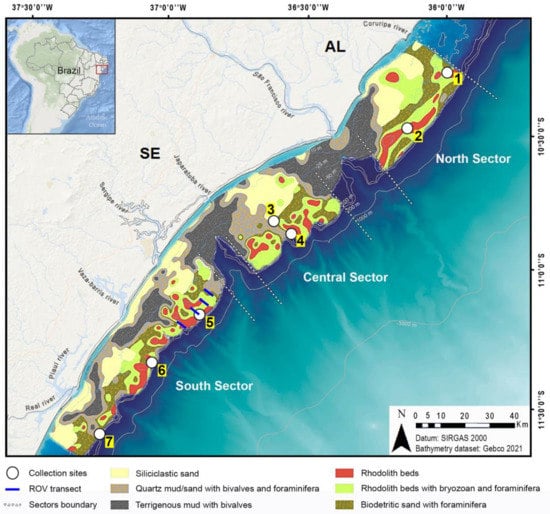
Figure 1.
Sergipe-Alagoas (SEAL) Basin and collection sites (white circles with numbers 1–7) along the three carbonate domain sectors (North, Central and South) on the middle/outer shelf collected in 2011 and transects surveyed by a remotely operated vehicle (ROV) from the south sector obtained in 2014 (blue lines) with biofacies data [21] and the bathymetry dataset [22].
The tidal regime in the study area is semi-diurnal, with amplitude between 1.0 to 3.0 m [26], and the wave regime is high energy, predominating from NE and E in January to May (summer–autumn) and September to November (spring), and SE waves occur from March to August [26,30]. The normal sea surface temperature (SST) values vary between 25 and 28 °C and show a discrete decrease from north to south [26]. The SST in the summer and winter periods oscillates around 27–28 °C and 25–26 °C, respectively. Salinity (36–37‰) increases in the north and south, from the coastal region to the outer shelf, except near the river mouths, where salinity can reach values as low as 32–33‰ [26]. The primary productivity varies from 1.6–2.0 mg C/m2/day, and surface chlorophyll A concentrations vary from 0.7 and 5 mg/m3, with the highest values recorded in the coastal zone, which presented the potential of effective littoral drift with a predominant direction to the south [30]. The São Francisco River Basin discharges at the border between Sergipe and Alagoas and is the largest drainage basin in the Brazilian territory [29]. It is also one of the most regulated rivers in the country, and the discharge of the São Francisco River was drastically altered by the construction of six large dams built to generate energy and regulate flow [29]. Its average annual flow of more than 3000 m3/s declined by 80%. Its natural seasonal pulsation has been regulated to an almost constant flow of ~600 m3/s [25], and approximately 95% of the river’s total solids in suspension (TSS) are retained within the dam reservoirs [22,29,30]. The impact of the dams has considerably modified the main estuarine processes and sediment transportation; coastal erosion has also been drastically increased [31,32,33,34]. The São Francisco River and its delta have been featured in global compilations on the effects of sediment retention in dams and the risks represented by climate change [35]. Since 1960, rainfall has declined by approximately 27%, and average annual precipitation is projected to decrease up to 35% by 2080, compared to the average of 1961–1990, using the A1B scenario of the IPCC [35].
Currently, the continental shelf is characterized by low fluvial input and greater influence of the tropical surface waters (TSW) of the South Equatorial Current (SEC) that flows from east to west across the Atlantic Ocean [26,30]. In the proximity of the São Francisco and Japaratuba canyons during the summer months (December), there are lower temperatures and nutrient-rich waters due to the seasonal upwelling of the South Atlantic Central Water [26]. These environmental conditions promote the predominance of carbonate features from 30 m to 60 m depth, dominated by gravel and biogenic carbonate components [19,21,36] with an associated biota [19].
Coastal sediment transport along the Sergipe coast is 790,000 m3/year, with about 658,000 m3/year in the NE–SW direction and 132,000 m3/year in the opposite direction [37]. These processes influence the coastal region, either through coastal erosion in certain places or through deposition in others, as observed on the coast of the Sergipe State [38]. Large areas of smooth mud surfaces have been identified in front of the mouths of the São Francisco and Japaratuba rivers [39]. The middle and outer shelf, ca. 10,000 km2 of the Sergipe–Alagoas shelf, are mainly characterized by carbonate deposits [39]. In southern Alagoas, these carbonate sediments are also found near the coastline [27]. Rough surfaces were found in the north sector, in the central sector, between the mentioned rivers, and in a larger area in the south sector. Siliciclastic components (quartz and rock fragments) are present along the inner shelf, up to 30 m depth, while carbonate contents that are predominate on the middle to outer shelf consist of rhodolith beds (Figure 1) that comprise non-geniculate coralline algae, foraminifera, bivalves and bryozoans (82%), while green algae Halimeda sp., echinoderms (spines and tests of urchins), spicules of sponges, fragments of crustaceans, gastropods, scaphopods, serpulids and corals are minor components, representing the remaining 18% [19,21].
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sampling
Data were collected within the framework of the SEAL Basin Regional Characterization Project carried out by Petrobras (Brazilian Petroleum S.A., Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brazil) and the Federal University of Sergipe (UFS) from 2008 to 2018. A total of 53 high-definition video images, comprising 33 h of video inspections, was recorded from February to March 2014 [40] with a remotely operated vehicle (ROV) along four transects with a length of 4 km per transect, ranging from 25 to 46 m depth in the south sector of the study area (Figure 1, Supplementary Material Table S1 and Video S1). The cover percentage of rhodoliths was estimated by the proportion of the total video time spent on rhodolith concentrations.
Due to the high facies complexity of the continental margin of the Sergipe and Alagoas shelf and the distribution patterns of the biota along environmental gradients, the strategy for selecting the collection sites considered longitudinal, latitudinal and bathymetric gradients [41]. Rhodolith samples (404 rhodoliths) were obtained from two expeditions: the first carried out from 29 January to 6 February 2011 aboard the R/V Luke Thomas and the second from 24 June to 3 July 2011 aboard the R/V Seward Johnson, using a trawl [41]. The samples were stored in the Laboratory of Benthos from UFS and later ceded to the Instituto de Pesquisas Jardim Botânico do Rio de Janeiro (IPJBRJ). Rhodolith sampling sites and ROV video transects are shown in Figure 1. A total of seven sites between 27 and 54 m in depth were sampled along the middle and outer shelf of the SEAL Basin (Figure 1 and Table 1). The geomorphological features of the shelf evaluated by high-resolution mapping in other studies [21,22], combined with the biofacies classes, sedimentological data [21] and the bathymetry dataset [22], were incorporated into a geographic information system (GIS) environment on the QGIS platform to produce the map in Figure 1.

Table 1.
Sampling site locations, water depth and number (n = 404) of samples collected and analyzed in the present study. Coordinates are in SIRGAS 2000 Datum.
3.2. Sample Characterization
The non-geniculate coralline algal growth forms were classified based on their morphology as encrusting, encrusting warty, lumpy and fruticose, according to [42,43]. The latter are monospecific rhodoliths lacking a macroscopic nucleus and characterized by a high prevalence of protuberances [44]. Based on their longest axes, rhodoliths were divided into large (d > 3 cm), medium (d = 1.5–3 cm) and small (d < 1.5 cm) size classes. Rhodolith sphericity was determined by measuring the longest, intermediate and shortest axes [45,46], and the triangular diagram plotting spreadsheet (TRI-PLOT) was used to separate ellipsoidal, discoidal or spheroidal shapes [46]. Species identification of crusts on the outermost surface of rhodoliths was conducted solely through the morpho-anatomical observation of histological sections (Supplementary Material Figure S1) of fertile material [44,47,48,49,50]. A permutational multivariate analysis of variance (PERMANOVA) with the software Primer (v.6) + PERMANOVA was used to evaluate possible significant differences in rhodolith size between the different sites and depths. Images of fruticose (branching) rhodoliths were used to derive a morphological parameter, the mean solidity index (degree of complexity of the thalli, which is reflected as values between 0—fully complex shape—and 1—no ramifications) of the thalli, corresponding to the surface of a given thallus of the fruticose rhodoliths on the image plane divided by its convex surface [51]. These analyses were performed using ImageJ 1.53 free software [51].
To characterize the inner structure of rhodoliths, 15 samples were selected and sectioned along their longest axis with a tungsten handsaw (Dremel 3000, Dremel, Bosch Power Tools). Both halves of the rhodoliths were then photographed using a digital camera (Nikon D7000, Nikon). The inner structure was defined as a boxwork, asymmetrical or concentric arrangement [42]. Small blocks (3 × 3 cm) were cut from 10 selected samples and were sent to the National Petrographic Service Inc. (Rosenberg, TX, USA) to make thin sections. The carbonate texture [52,53] was identified, and the Bioerosion Index (BI) was determined [54] to estimate the extent to which the primary features were bioeroded. Fossil marine macroinvertebrates, foraminifera and borings were identified to the most precise taxonomic level possible. The average proportions (%) of the main rhodolith components, trace fossils, voids and sediment were estimated by counting on images taken from each thin section (10 images per sample (n = 10), with 50 points randomly distributed on each image) using the CoralNet program ([55], https://coralnet.ucsd.edu/; accessed on 12 March 2021). Voids include constructional voids (intraskeletal and spaces among encruster skeletons) and bioerosion [56]. Voucher specimens of algae were deposited in the Herbarium of the Rio de Janeiro Botanical Garden (RB) (Supplementary Material Table S2).
To determine the radiocarbon age, eight subsamples of fossils in rhodoliths were selected. About 10–20 mg of carbonate powder was obtained from each subsample with a tungsten handsaw (Dremel 3000, Bosch Power Tools) and then chemically pretreated with HCl. They were analyzed at the Center for Applied Isotope Studies (University of Georgia, Athens, GA, USA) using an Accelerator Mass Spectrometer (AMS, nuPlasma II multi-collector). All conventional radiocarbon ages (between 603 and 50,779 years before present (BP)) were recalibrated using the software CALIB 8.2 ([57], http://calib.org/; accessed on 28 August 2020), using the Marine20 calibration curve [58] and a global reservoir effect. Dates are reported as calendar years before present (cal year BP; “present” = 1950 CE) with a 2-sigma confidence interval.
4. Results
4.1. Seabed Characterization in the Examined ROV Transect Lines
In the south sector (around site 5), living rhodoliths were always associated with fleshy macroalgae and were recorded along the four ROV transects (totaling 16 km in length, 4 km per transect). At the shallower depths (25–30 m) in this sector, fruticose (branching) rhodoliths (maërl) appeared in troughs of ripples on bioclastic sands (1.6 km; 10% of ROV transect length, Figure 2A,B). At the same depth range, patches of encrusting to lumpy rhodoliths (Figure 2C,D) were associated with corals, sponges and macroalgae (Figure 3A,C,D) and were surrounded by bioclastic sand occupying another 1.6 km (10%) of the transect length (Figure 2C,D). At depths between 30 and 39 m, rhodoliths patches extended for 4.8 km (30%) of the transect length and included small fused rhodoliths creating larger complex 3D structures together with corals and sponges (Figure 2E) associated with fleshy macroalgae (Figure 3B). From 40 to 54 m, the abundance of rhodoliths increased. They occurred in association with fleshy macroalgae on a smooth seafloor (6.4 km; 40% of transect length, Figure 2F), and some include fused rhodolith structures (Figure 2G). At this depth interval, 5% (0.8 km) of the transect length was occupied by rhodoliths partially buried by fine-grained sediment (Figure 2H). Fruticose (branching) rhodoliths (maërl) also occurred locally at 47 m. A reef fish community was observed associated with rhodolith patches between 36 and 44 m depth, including Holocentrus adscensionis, Gymnothorax moringa and Cephalopholis fulva (Figure 2E, and Figure 3B,E,F) as the main species. Massive sponge species were recorded attached to rhodoliths, including Aplysina sp. and Ircinia strobilina (Figure 2D and Figure 3C). The videos showed differences in rhodolith distribution between the northeast (green colour in Figure 1) and southwest (red colour in Figure 1). Rhodoliths were sparsely grouped, and some of them fused (Figure 2A–D) in the former transect, whereas rhodolith patches were larger with larger aggregates of fused rhodoliths (Figure 2E–H) in the latter.

Figure 2.
In situ images of the explored sites on the middle and outer shelf of the south sector of the SEAL Basin: (A) Zoom-out of fruticose rhodoliths on ripple troughs (darker colours) at 30 m depth; (B) Zoom-in of the seafloor dominated by living fruticose rhodoliths at 30 m depth (vinaceous colours); (C,D) Rhodolith patches at 30 m depth, depicting the sponge Aplysina sp.; (E) Reef formed by fused rhodoliths associated to corals (Montastraea cavernosa), macroalgae and encrusting sponges (Monanchora arbuscula) at 32 m depth; (F,G) Coalescent rhodoliths forming complex three-dimensional structures covered by macroalgae, at 41 and 43 m depths, respectively; (H) Rhodoliths partially buried by fine-grained sediment with living coralline algae covered by green macroalgae at 43 m depth. Scale bars = ~5 cm.

Figure 3.
In situ images of the benthic community associated with the rhodolith beds on the south sector of the SEAL Basin: (A,C,D) Fleshy macroalgae, corals (Montastraea cavernosa) and sponges (Aplysina sp. and Ircinia strobilina) occur from 25 m to 30 m depth; (B,E,F) A reef fish community (Aulostomus maculatus, Holocentrus adscensionis, Gymnothorax moringa and Cephalopholis fulva) occurs from 36 to 44 m depth. Scale bars = ~5 cm.
4.2. North Sector
The rhodoliths collected in the middle shelf at 30 m depth from site 1 were large (5.7–20.4 cm at the longest axis and mean diameter that ranged from 4.2–14.3 cm; Figure 4A and Figure 5A), encrusting and encrusting warty with mostly sub-discoidal (42.8%) to sub-spheroidal (28.5%) shapes (Figure 5B and Table 2). The rhodoliths examined from this site had living encrusting coralline algae (Harveylithon sp., Sporolithon sp.) and sponges partially covering their surfaces (Figure 4A). The nuclei consisted of coral fragments (Figure 6A) or other bioclasts. Coralline algae intergrown with bryozoans, corals and serpulids formed an asymmetrical cover with a boxwork structure. Coralline algae included Mesophyllum sp., Lithophyllum sp., Harveylithon gr. catarinense (I.O.Costa, P.A.Horta & J.M.C.Nunes 2019) and an unidentified Hapalidiales species (Figure 6C and Table 2). The three rhodoliths examined were heavily bored (Bioerosion Index is 4) by sponges (Entobia) and bivalves (Gastrochaenolites). Constructional voids and bioerosion traces varied from empty to partially filled by wackestone rich in sponge spicules and micrite-rich packstone. Geniculate coralline algae, benthic and planktonic foraminifera, and solitary corals appeared in the fillings (Figure 6B and Table 3). Radiocarbon dating of a coral in the innermost part of a rhodolith sample yielded an age of 789 cal yr BP (Figure 7A), and a non-geniculate coralline algae in the outermost part of another rhodolith sample yielded an age of 180 cal yr BP (Figure 7B and Table 4).

Figure 4.
Surface and inner portion of rhodoliths analyzed in this study (upper and lower images, respectively): North sector: (A) rhodolith from site 1; (B) rhodolith from site 2; Central sector: (C) rhodolith from site 3; South sector: (D) rhodolith from site 5; (E) rhodolith from site 6; (F) rhodolith from site 7. Non-geniculate coralline algae (green asterisks), bryozoan (red asterisks), coral (red arrows), sponge Cliona cf. schmidtii (yellow arrows), gastropod (blue arrows). Scale bars = 1 cm.
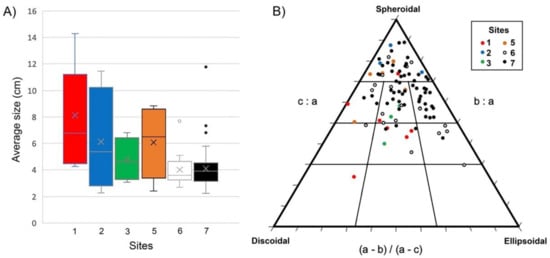
Figure 5.
Graphical analyses of rhodolith (n = 94) size and shape: (A) Box plot showing average size range of rhodoliths (average axes value), considering them as ellipsoidal structures (with long, intermediate and short axes); (B) Shape classification of rhodoliths using a TRIPLOT diagram [40,41]: Long (a), intermediate (b) and short (c) axes of rhodoliths. Hence, branching rhodoliths were not considered for size and sphericity measurements.

Table 2.
Rhodolith size, coralline algal growth-form, rhodolith shape (%) and rhodolith-forming coralline algal species from the SEAL Basin. Surface (x-blue); outermost portion (x-green); innermost portion (x-red).
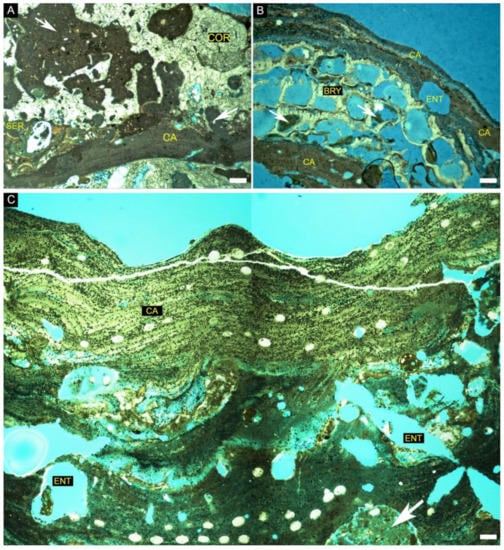
Figure 6.
Thin-section images of rhodoliths from site 1 of the north sector of the SEAL Basin (30 m depth). (A) Innermost portion of rhodolith sample 1 composed of coral (COR), coralline algae (CA) and serpulid (SER) with borings filled by micrite (white arrow) and siliciclastic grains (quartz-white grains); (B) Outermost portion of rhodolith sample 2 composed mainly by coralline algae (CA) intergrown with bryozoans (BRY) with sponge borings (Entobia-ENT), some filled by packstone (white arrow); (C) Middle to outermost portion of rhodolith sample 3 with dominance of Harveylithon gr. catarinense (CA) and sponge borings (Entobia-ENT), some filled by packstone (white arrow). Scale bars = 200 µm.

Table 3.
Main components (%) in ten analyzed rhodolith samples from the SEAL Basin. 1gp = first growth phase (innermost portion); 2gp = second growth phase (outermost portion).
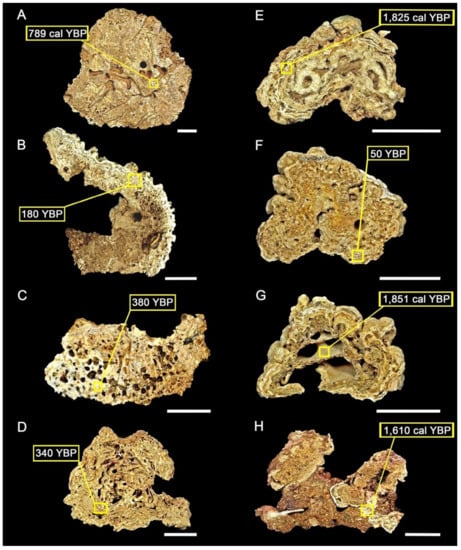
Figure 7.
Radiocarbon dated samples collected in different sectors of the SEAL Basin. The yellow squares indicate location of the dated fossils in the sample: North sector: (A) Coral from site 1 (30 m depth); (B) Coralline algae from site 1 (30 m depth); Central sector: (C) Coral from site 3 (27 m depth); South sector: (D) Coralline algae from site 5 (47 m depth); (E) Coralline algae from site 6 (54 m depth); (F) Coralline algae from site 7 (50 m depth); (G) Gastropod shell from site 7 (50 m depth); (H) Bryozoan from site 7 (50 m depth). Scale bars = 2 cm.

Table 4.
Radiocarbon age of different components in rhodoliths collected at different sites from 3 sectors (N, North; C, Central; and S, South) of the SEAL Basin. Coordinates are in SIRGAS 2000 Datum. * Values < 433 yr BP cannot be calibrated at the curve Marine20; BP = before present.
Rhodoliths from site 2 were mostly fruticose (branching) less than 2 cm in length (Figure 8A). They exhibited complex shapes with branches varying from small to medium (Solidity Index = 0.386–0.937). Together with bryozoans, specimens of Harveylithon gr. rupestre, Roseolithon sp., Lithothamnion sp., Lithophyllum sp., Melyvonnea gr. erubescens and Mesophyllum sp. were identified at the rhodolith surfaces (Figure 8A and Table 2). Larger rhodoliths with asymmetrical boxwork to the concentric inner arrangement also occurred. They were medium to large (2.1–13.7 cm; Figure 4B and Figure 5A), encrusting and lumpy with mostly spheroidal (75%) shapes (Figure 5B and Table 2). Rhodolith were formed mainly by non-geniculate coralline algae with bryozoans and corals as secondary components.

Figure 8.
Fruticose (maërl) and small encrusting rhodoliths with associated shells: (A) from site 2 of the north sector, at 30 m depth; (B) from site 4 of the central sector, at 47 m depth. Scale bars = 1 cm.
4.3. Central Sector
Rhodoliths from site 3 at 27 m depth were large in size (4–9.5 cm at the longest axis and mean diameter that ranged from 3.0-6.8 cm; Figure 4C and Figure 5A), encrusting with sub-spheroidal (50%) and sub-discoidal (50%) shapes (Figure 5B and Table 2). Four rhodoliths examined had surfaces partially covered by red algae (Spongites sp., Peyssonnelia sp.). They were characterized by a highly asymmetrical boxwork inner arrangement, with nuclei formed mostly by corals. The covers consist of non-geniculate coralline algae, serpulids, bryozoans and encrusting foraminifers (Figure 9A,B and Table 3). Both nuclei and covers are bored by sponges (Entobia), and the Bioerosion Index is 3. The borings were partially filled by wackestone and packstone rich in micrite, with bioclasts of echinoids and mollusks, sponge spicules, and siliciclastic grains, mainly quartz (Figure 9C). Radiocarbon dating of a coral nucleus of a rhodolith yielded an age of 380 yr BP (Figure 7C and Table 4).
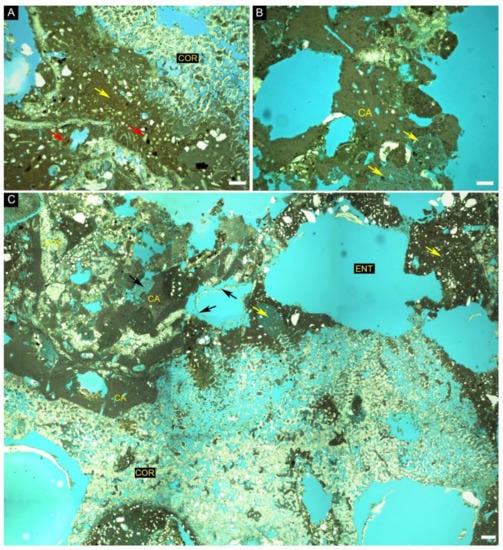

Figure 9.
Thin-section images of rhodolith sample 4 from site 3 of the central sector of the SEAL Basin (27 m depth). (A) Middle portion of a rhodolith with coral (COR) with borings partially filled by packstone (yellow arrow) and siliciclastic grains, mainly quartz (white color) and bioclasts of echinoids (red arrow); (B) Outermost portion of a rhodolith with coralline algae (CA) with some voids filled by wackestone (yellow arrow); (C) Rhodolith with coral (COR) nucleus overgrown by coralline algae (CA), with boring and intraskeletal voids partially filled by wackestone (yellow arrow), siliciclastic grains (white) and sponge spicules (black arrows). Borings are attributed to Entobia borings (ENT). Scale bars = 200 µm.
The rhodoliths collected in the outer shelf at 47 m depth from site 4 were mainly fruticose, and a few were small encrusting warty. Fruticose rhodoliths were less than 3 cm in size (Figure 8B), with low complexity, i.e., exhibit medium branches and no branching (Solidity Index = 0.614–1.000). They were mainly made up of Lithothamnion sp. and Lithophyllum sp., whereas bryozoans were secondary components. Sporolithon sp. was identified at the surface of small encrusting warty rhodoliths (Figure 8B).
4.4. South Sector
Rhodoliths from site 5 at 47 m depth were medium to large (2.7–10.3 cm at the longest axis and mean diameter that ranged from 2.4-8.8 cm; Figure 4D and Figure 5A), encrusting, encrusting warty, and lumpy with mostly spheroidal (60%) shapes (Figure 5B and Table 2). The rhodolith surfaces were partially covered by living encrusting red algae (Harveylithon gr. rupestre, Harveylithon sp., Pneophyllum gr. fragile, Sporolithon franciscanum, Sporolithon sp. and Peyssonneliaceans, Figure 4D) and Cliona cf. schmidtii sponges. The rhodoliths had an asymmetrical boxwork inner arrangement, formed mostly by non-geniculate coralline algae, bryozoans, encrusting foraminifera and serpulids. Lithothamnion sp. and unidentifiable Hapalidiales, Harveylithon sp., Lithophyllum gr. pustulatum, thin unidentifiable laminar thalli, Sporolithon sp. and Peyssonneliaceans are the algal components (Table 2). The skeletal framework was heavily bored by sponges (Entobia), and the Bioerosion Index is 4. Intraskeletal and constructional voids, as well as sponge borings (Figure 10A and Table 3), varied from empty to partially filled by wackestone to packstone. Geniculate coralline algae, benthic and planktonic foraminifera appear with echinoid and mollusk fragments and siliciclastic grains, mainly quartz, in the fillings. Sponge spicules are common in the empty spaces in the outer part. Radiocarbon dating of non-geniculate coralline algae in the middle part of a rhodolith yielded an age of 340 yr BP (Figure 7D and Table 4).
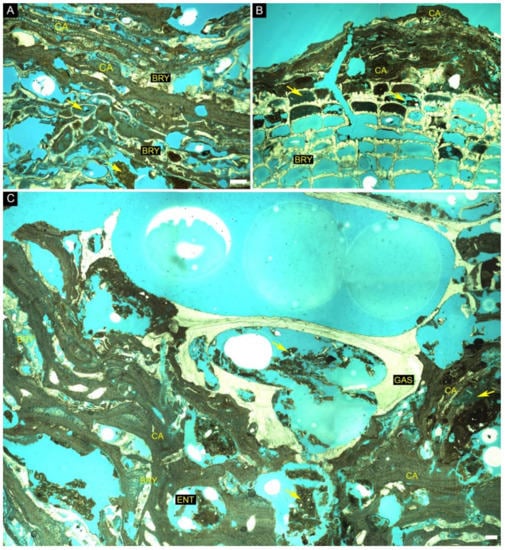
Figure 10.
Thin-section images of rhodoliths from the south sector of the SEAL Basin. (A) Inner portion of a rhodolith sample 5 from site 5 (at 47 m depth) formed by coralline algae (CA) and bryozoans with some voids filled by micrite (yellow arrow); (B) Outer portion of a rhodolith sample 7 from site 6 (at 54 m depth) with bryozoan (BRY) in the nucleus covered by coralline algae (CA) with some voids filled by packstone rich in micrite (yellow arrow); (C) Rhodolith sample 10 from site 7 (at 50 m depth) with gastropod shell (GAS) in the nucleus covered by coralline algae (CA) and bryozoan (BRY) with some voids partially filled by wackestone (yellow arrow). Scale bars = 200 µm.
Rhodoliths from site 6 at 54 m depth were large (3.3–13.8 cm at the longest axis and mean diameter that ranged from 2.6–7.6 cm; Figure 4E and Figure 5A), encrusting, encrusting warty, and lumpy with sub-spheroidal (38%) and spheroidal (22%) shapes (Figure 5B and Table 2). The surfaces were partially covered by Peyssonneliaceans, Roseolithon sp. and thin unidentifiable non-geniculate coralline algae. The examined rhodoliths consist of brownish bioclastic nuclei, commonly bryozoan nodules or gastropod shells (Figure 4D, Figure 7E,G and Figure 10B,C), and covers made of non-geniculate coralline algae intergrown with bryozoans with an asymmetrical concentric arrangement. Serpulids and encrusting foraminifers were secondary framework builders. Roseolithon sp., Lithothamnion sp., Spongites sp., Harveylithon sp., Lithoporella sp., Lithophyllum gr. pustulatum, Lithophyllum sp., Sporolithon sp., unidentifiable thin laminar thalli and Peyssonneliaceans are the algal components (Table 2). The rhodoliths were slightly bioeroded (Bioerosion Index is 2) by sponges and worms. Most intraskeletal and constructional voids and borings are empty (Figure 10B), with a small proportion partially filled by wackestone and packstone rich in micrite with siliciclastic grains, mainly quartz (Table 3). Radiocarbon dating of non-geniculate coralline algae in the middle part of a rhodolith yielded an age of 1825 cal yr BP (Figure 7E and Table 4).
Rhodoliths from site 7 at 50 m depth were medium to large (3.4–14.5 cm at the longest axis and mean diameter that ranged from 2.3–11.7 cm; Figure 4F and Figure 5A), encrusting, encrusting warty, and lumpy with mostly sub-spheroidal (53%) shapes (Figure 5B and Table 2). The surfaces are partially covered by thin crusts of Melyvonnea gr. erubescens, Lithothamnion sp., Lithophyllum gr. pustulatum and Peyssonneliaceans (Table 2). Most rhodoliths show two distinct phases of growth. The inner phases, brownish in color, are made of bioclastic nuclei, such as gastropod shells and bryozoan fragments, or frameworks of bryozoans, serpulids and small oysters with a small proportion of non-geniculate coralline algae, including Lithophyllum sp. and Lithoporella sp. (Figure 10C and Table 3). These inner phases are bored by sponges. Borings and intraskeletal voids are partially filled by mudstone to packstone. The outer phases consist of non-geniculate coralline algae intergrown with bryozoans and minor serpulids and encrusting foraminifers with an asymmetrical concentric arrangement. Roseolithon sp., Lithothamnion sp., unidentifiable Hapalidiales, Spongites sp., Harveylithon sp., Lithoporella sp., Lithophyllum gr. pustulatum, Lithophyllum sp., Sporolithon sp., unidentifiable thin laminar thalli and Peyssonneliaceans are the algal components (Table 2). The outer and inner phases, including the boring fillings, are bioeroded by sponges, and most of the voids are empty. A gastropod shell and a bryozoan in the inner phases of two rhodoliths were dated as 1851 and 1610 cal yr BP, respectively. Radiocarbon dating of non-geniculate coralline algae from the outer phase of another rhodolith yielded an age of 50 years BP (Figure 7F–H and Table 4).
4.5. Comparison of Rhodolith Distribution and Characteristics among Sectors
According to the biofacies distribution at SEAL (See Section 2 Figure 1), the different bottom features of the rhodolith beds in the south sector of the SEAL Basin, observed in ROV video, extend to the middle and outer shelf of the north and central sectors.
The size of rhodoliths differs among sites (PERMANOVA; F = 6.8764; p = 0.0002). A posteriori test, pairwise, showed that rhodoliths of site 1 were larger than those of deeper sites 6 (p = 0.0014) and 7 (p = 0.0002) (Figure 5A). Small fruticose rhodoliths (maërl) occurred both in ripple troughs in shallow settings in the south sector and the deeper sampling sites in the north and central sectors. The rest of the rhodoliths exhibited concentric and boxwork inner arrangements made up of encrusting to lumpy coralline algae in all sites. In the south sector, however, the proportion of constructional void is higher, and a concentric arrangement was prevalent in rhodoliths at the two deepest sampling sites. In these sites, a two-phase development of analyzed rhodoliths was observed. The nuclei of shallowest rhodoliths are commonly formed by corals, which are absent in deeper rhodoliths from the south sector.
The number of coralline morpho-taxa involved in rhodolith formation was higher in the south sector than in the other two. The nuclei of rhodoliths in the north and central sectors include coral fragments, which are absent in the south sector, where the nuclei are formed either by mollusk shells or bryozoan skeletons.
5. Discussion
The rhodoliths analyzed in this study started to grow between 1.9 and 1.8 ka cal BP, a long time after the Holocene flooding of the SEAL shelf [35]. The bathymetry of the investigated rhodolith beds lies within the large range of rhodolith beds in Brazil, which occur between 12 and 95 m depth [59,60,61,62,63,64,65]. Temperature, nutrients, sedimentation and water current velocity are considered the main environmental drivers of rhodolith development in the Brazilian ecoregions [65]. Specifically, sediment influx depends on discharge from large rivers and directly influences the distribution of bottom sediments and rhodolith beds [59]. On the inner SEAL shelf, rhodolith growth is inhibited by riverine sediment influx (mud/sand siliciclastic sediments), but rhodolith beds can occur locally (See Section 2 Figure 1). Rhodolith beds on the SEAL shelf were concentrated north and south of the São Francisco river mouth. A similar distribution can be observed in the Rio Doce shelf, where rhodoliths are most abundant in two discontinuous areas at depths between 45 and 65 m. The area south of the Rio Doce mouth is larger and shows higher rhodolith cover, while the area north of the mouth shows very low rhodolith cover (<10%), which was interpreted as a consequence of long-term deposition of fine sediments [59].
Rhodolith beds on the SEAL shelf are widespread in the middle-outer shelf, following the same trend observed along the Brazilian margin, but their distribution is interrupted by the presence of shelf-incised valleys and canyons, such as the Sao Francisco canyon, and minor incisions dissecting the shelf (Figure 1). In narrow mixed continental shelves, such as the SEAL shelf, transitions from terrigenous sediments to carbonates occur laterally due to lateral variation in environmental controls, such as sediment input and carbonate production [66]. Moreover, the presence of canyon systems in narrow shelves favor the possibility of discontinuities in sediment distribution even during high stands [67]. Shelf-incised valleys, canyons and riverine plumes led to the patchy distribution in large-scale rhodolith beds on the SEAL shelf (Figure 1). On wider shelves, such as the Abrolhos shelf, which also has low sediment input, rhodolith beds are extensive and more continuous [63,66]. At a smaller scale, within individual rhodolith beds mapped on the SEAL shelf (Figure 1), the distribution of rhodoliths is patchy with varying rhodolith density. This uneven distribution has been reported for deep rhodolith beds and seems to be mainly related to seafloor morphology and/or bottom currents [59,68,69,70].
The video surveys confirmed the occurrence of patches of fused rhodoliths in depths between 30 and 50 m, creating complex large three-dimensional structures with up to 10% of cover (Figure 2F and Figure 3F). Similar structures occur in deeper waters in other regions in Brazil, i.e., from around 50 to 80 m depths on the Rocas Atoll shelf [69] and from 65 to 105 m on the Doce River shelf [59]. On the latter shelf, carbonate concretions, including rhodoliths, occur in areas with a high density of rhodoliths, suggesting that the concretions were formed by rhodolith fusions, later overgrown by coralline algae and other encrusters, mainly bryozoans [59]. In the Mediterranean Sea, the so-called coralligenous de plateau (tridimensional build-ups of calcareous encrusting algae growing on flat surfaces) are common on almost all shelves, at low irradiance levels and in relatively calm waters [71,72]. In some cases, they were interpreted as frameworks developed from a coalescence of rhodoliths [71,73,74], and, therefore, the patches of fused rhodoliths on the SEAL shelf can be considered initial steps of the formation of frameworks similar to coralligenous banks. However, fossil examples from the early Miocene in Sardinia [75] and the late Miocene in SE Spain [76] showed that fused rhodoliths do not necessarily promote further development of coralline algal frameworks.
The shallowest rhodoliths (27 m depth) in the north and central sectors commonly have large nuclei of coral fragments, which is in accordance with the occurrence of corals in the rhodolith patches observed by the ROV between 25 and 30 m depth. Similar nuclei characterize the rhodoliths collected at 20 m depth in the Queimada Grande Island [64] and at 23 m depth in the southern zone of the Amazon continental margin, which has the lowest riverine influx in the region off the Amazon mouth [62]. In the north sector of the SEAL shelf, the coral nuclei have an age of nearly 800 years BP, while the dated coralline algae cover is only a few hundred years old.
Beds of small fruticose rhodoliths (maërl) are uncommon on the Brazilian shelf. The fruticose rhodoliths in sites 2 and 4 exhibit low to medium branching or no ramification in some cases, which corresponds to low habitat complexity. The development and distribution of maërl are controlled by various environmental factors that remain difficult to discern [77,78]. Maërl beds can be shaped by the swell to form megaripples, but wave energy can rapidly limit the vitality of the maërl-forming species in contrast to encrusting coralline algae that can live in highly hydrodynamic environments [78]. The mobility of branching rhodoliths depends on wave agitation and currents, and they may only move occasionally due to bioturbation and severe storms [79]. If hydrodynamic conditions are too low, fine sediment particles can stifle algal growth [80], whereas under strong energy, the fine sediments are re-suspended, inhibiting photosynthetic activity, and coarser particles such as sand or broken shells bury the thalli [78]. Well-developed maërl beds occur in areas swept by currents, preventing the burial of rhodoliths by fine-grained sediment [42,81], although they also occur in areas with no significant energy but with reduced sediment influx [82]. Maërl beds are consequently very sensitive to sediment input and sediment mobility. On the north Atlantic coasts, maërl beds usually occur in shallow and sheltered bays [77,78]. In contrast, in the Spencer Gulf in South Australia, fruticose rhodolith pavements develop at depths of several tens of meters under the influence of moderate to high-energy currents of tidal origin that remove fine sediments [83]. In the Mediterranean Sea, fruticose rhodoliths are found in deeper settings, from 30 to 100 m [81,84,85,86]. In fossil examples, fruticose rhodoliths also tend to occur in paleoenvironments deeper than those of nodules formed by encrusting to lumpy thalli [87]. The occurrence of the two beds of maërl in the deeper sites of the north and central sectors of the SEAL seems to be favored by calm conditions in deep shelf settings sheltered from sediment influx. In the south sector, however, fruticose rhodoliths occur in higher energy areas in the troughs of ripples.
The concentric arrangement and high proportions of constructional void in rhodolith covers in sites of the south sector of the SEAL shelf are common in shallow-water rhodoliths in the south Espirito Santo and Rio Doce shelves [59,63]. High proportions of constructional voids were interpreted as reflecting low energy conditions [63], whereas concentric arrangements with little destruction by bioerosion indicate relatively short residence times of rhodoliths on the seafloor before burial. In the deepest sites of the south sector, a two-phase development of rhodoliths was observed. Nuclei are highly bored by sponges, whilst bioerosion in the covers is very low. In these rhodoliths, there is a large difference in age between growth phases: the inner phases yielded ages of 1600–1850 cal years BP, whereas the dated outer phase was only 50 years BP. The difference in bioerosion density and age can be explained by two phases of growth separated in time by a long period of burial in the seafloor sediment. Such a burial of rhodoliths by fine-grained sediments was recently observed in the ROV transects at site 5, between 40 and 46 m depths. A similar two-phase development of rhodoliths was observed in the central zone of the Amazon River mouth, at 50–55 m depth [62]. In this location, the growing gap was much shorter, about 400 years from the oldest age of the darkened interior [62]. The burial by sediment, subsequent exhumation and regrowth are probably related to variations in riverine discharge to the shelf [62]. Some deep-water rhodoliths of the Abrolhos Continental Shelf also show multiphasic growth with growth gaps of thousands of years caused by temporary burial and exhumation [63]. Rhodoliths with well-differentiated growth phases have also been described in different regions [88,89,90,91,92], with time gaps between growth phases of several hundred years. Multistory rhodoliths with two to several growth phases have also been described in the fossil records [1,93], suggesting that temporary burial is a common phenomenon in rhodolith beds.
The 15 rhodolith-forming coralline taxa recorded in this study are commonly found in the beds of northeast and southeast Brazil [18,59]. Among the identified taxa, the multispecific genus Roseolithon (previously recognized as the single species Lithothamnion crispatum in Brazil) occurs on surfaces and inner portions of rhodoliths from sites in the north and south sectors of the SEAL Basin. This is considered one of the main rhodolith-forming non-geniculate coralline algae of the Brazilian continental shelf [17,18,94]. The number of morphoanatomically identified taxa in the SEAL shelf is similar to that of the Abrolhos continental shelf (14 taxa) but substantially higher than numbers recorded in the Rio Doce shelf (10 taxa), Campos Basin (2 taxa), Amazon continental margin (6 taxa) and Fernando de Noronha Archipelago (6 taxa) [17,18,48,62,95]. However, all these taxon accounts based on morpho-anatomical identifications do not reflect the higher richness of phylogenetic species of coralline algae delimited in the different ecoregions of the Brazilian shelf by DNA-based methods [65]. In particular, in the northeastern Brazil ecoregion to which the SEAL shelf belongs, 23 phylogenetic species of coralline algae have been identified [65].
The extension and composition of the SEAL rhodolith beds show the importance of these ecosystems on the Brazilian continental shelf. This region has great economic importance due to its extensive areas of carbonate accumulation [22] and is subjected to multiple disturbances as direct and indirect consequences of human activities, such as mineral extraction of calcium carbonate for commercial use, bottom trawl fishing, and oil and gas extraction [21,96]. Knowledge about rhodolith beds is becoming even more urgent to support local conservation and management actions and assess the environmental impacts that the exploitation of its resources can generate on this rich marine ecosystem.
6. Conclusions
Rhodolith beds on the SEAL shelf mainly occur on the middle-outer shelf, at depths between 25 and 55 m. Sediment influx from the major rivers in the area and incision of the shelf by submarine canyons determine the large-scale areal distribution of rhodolith beds on the shelf. The spatial variability of rhodolith beds reveals living rhodoliths grouped in patches interspersed with bioclastic sediments and associated with fleshy macroalgae and a reef fish community; some rhodoliths are fused, forming coralline algal concretions; fruticose rhodoliths (maërl) occur both in ripple troughs in shallow waters and deeper sites of the north and central sectors. Coralline algal identification recorded a total of 15 taxa in the study sites, where some sites supported up to 11 different morphospecies; some species occur at five sites along the three sectors of the SEAL shelf. The rhodoliths from the north and central sectors commonly have large nuclei of coral fragments hundreds of years old. In the south sector, the rhodoliths have old nuclei (about 1800–1600 cal years BP) of gastropod and bryozoan fragments or coralline algae-bryozoan-serpulid boundstones. In this sector, rhodoliths show two growth phases with a difference in age of more than 1500 years, which can be explained by a long period of burial in the seabed sediment and later exhumation and resuming of growth. Increased knowledge about the role of these rhodolith beds in the benthic ecosystems is important to provide support for marine spatial planning programs, which could lead to more sustainable use of these habitats.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/d14040282/s1; Figure S1: External morphology and the anatomy of identified coralline algae species; Table S1: Remotely operated vehicle (ROV) log sheet at different depths on the south sector of the SEAL shelf; Table S2: Voucher samples of the coralline algae deposited in the Herbarium of the Rio de Janeiro Botanical Garden (RB); Video S1: Video obtained from ROV surveys on the middle to outer shelf of the SEAL shelf (south sector).
Author Contributions
N.F.L.V.: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing—Original Draft, Visualization. J.C.B.: Investigation, Writing—Review & Editing, Supervision. A.C.B.: Formal analysis, Writing—Review & Editing, Supervision. F.C.M.: Review & Editing, Visualization. C.S.K.: Formal analysis, Writing—Review & Editing, Visualization. R.G.B.: Formal analysis, Review & Editing, Visualization. L.A.L.: Formal analysis, Visualization. R.C.P.: Formal analysis, Visualization. G.M.A.-F. (in memoriam): Conceptualization, Investigation, Supervision. L.T.S.: Writing—Review & Editing, Visualization, Supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the Coordenacão de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES-Finance Code 001) and Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro- Jovem Cientista do Nosso Estado (FAPERJ/JCNE-Fellow to Leonardo T. Salgado).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data produced as part of this research is included in the manuscript and Supplementary Material.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Maria Eulália R. Carneiro (Petrobras) and the Federal University of Sergipe for providing the samples and for the collaboration with the IPJBRJ and the three reviewers for their comments that improved the final version of the manuscript. We dedicate this work to the memory of our dear leader, Gilberto M. Amado-Filho.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Aguirre, J.; Braga, J.C.; Bassi, D. Rhodoliths and rhodolith beds in the rock record. In Rhodolith/Maërl Beds: A Global Perspective; Riosmena-Rodríguez, R., Nelson, W., Aguirre, J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Geerbestrasse, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 15, pp. 105–138. [Google Scholar]
- Basso, D.; Babbini, L.; Kaleb, S.; Bracchi, V.; Falace, A. Monitoring deep Mediterranean rhodolith beds. Aquat. Conserv. 2016, 26, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, M.S. Rhodoliths: Between rocks and soft places—Minireview. J. Phycol. 2001, 37, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamenos, N.A.; Heidi, L.B.; Darrenougue, N. Coralline algae as recorders of past climatic and environmental conditions. In Rhodolith/Maërl Beds: A Global Perspective; Riosmena-Rodríguez, R., Nelson, W., Aguirre, J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Geerbestrasse, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 15, pp. 27–53. [Google Scholar]
- Foster, M.S.; Amado-Filho, G.M.; Kamenos, N.A.; Riosmena-Rodriguez, R.; Steller, D.S. Rhodolith and rhodolith beds. In Contribution of SCUBA Diving to Research and Discovery in Marine Environments; Lang, M.O., Ed.; Smithsonian Institution Scholarly Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; pp. 143–156. [Google Scholar]
- Harvey, A.S.; Woelkerling, W.J. A guide to non-geniculate coralline red algal (Corallinales, Rhodophyta) rhodolith identification. Cienc. Mar. 2007, 33, 411–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hily, C.; Potin, P.; Floch, J.Y. Structure of subtidal algal assemblages on soft bottom sediments: Fauna/flora interactions and role of disturbances in the Bay of Brest, France. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1992, 85, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkett, D.A.; Maggs, C.; Dring, M.J. Maërl: An overview of dynamic and sensitivity characteristics for conservation management of marine SACs. Scott. Assoc. Mar. Sci. 1998, 5, 1–90. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, W.A.; Neill, K.; Farr, T.; Barr, N.; D’Archino, R.; Miller, S.; Stewart, R. Rhodolith Beds in Northern New Zealand: Characterization of associated biodiversity and vulnerability to environmental stressors. N. Z. Aquat. Environ. Biodivers. Rep. 2009, 99, 102. [Google Scholar]
- Harvey, A.S.; Bird, F.L. Community structure of a rhodolith bed from cold temperate waters (southern Australia). Aust. J. Bot. 2008, 56, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konar, B.; Riosmena-Rodriguez, R.; Iken, K. Rhodolith bed: A newly discovered habitat in the North Pacific Ocean. Bot. Mar. 2006, 49, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steller, D.L.; Riosmena-Rodriguez, R.; Foster, M.S.; Roberts, C. Rhodolith bed diversity in the Gulf of California: The importance of rhodolith structure and consequences of anthropogenic disturbances. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2003, 13, S5–S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinojosa-Arango, G.; Riosmena-Rodriguez, R. Influence of rhodolith-forming species and growth-form on associated fauna of rhodolith beds in the central-west Gulf of California, México. Mar. Ecol. 2004, 25, 109–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sañé, E.; Chiocci, F.L.; Basso, D.; Martorelli, E. Environmental factors controlling the distribution of rhodoliths: An integrated study based on seafloor sampling, ROV and side scan sonar data, offshore the W-Pontine Archipelago. Cont. Shelf Res. 2016, 129, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concentino, A.L.M.; Vieira, I.B.; Reis, T.N.V.; Vasconcelos, E.R.T.P.P.; Paes, E.T. Fitobentos da Plataforma Continental de Sergipe e de Alagoas. In Plataforma Continental de Sergipe e Alagoas: Geoquímica Sedimentar e Comunidade Bêntica; de Lara Palmeira de Macedo Arguelho, M.E.R.C.e.M., Ed.; Editora UFS; Coleção Projeto MARSEAL: São Cristóvão, Brazil, 2018; Volume 2, pp. 196–220. [Google Scholar]
- Figueiredo, M.A.O.; Eide, I.; Reynier, M.; Villas-Bôas, A.B.; Tâmega, F.T.S.; Ferreira, C.G.; Nilssen, I.; Coutinho, R.; Johnsen, S. The effect of sediment mimicking drill cuttings on deep-water rhodoliths in a flow-through system: Experimental work and modeling. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 95, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amado-Filho, G.M.; Moura, R.L.; Bastos, A.C.; Salgado, L.T.; Sumida, P.Y.G.; Guth, A.Z.; Francini-Filho, R.B.; Pereira-Filho, G.H.; Abrantes, D.P.; Brasileiro, P.S.; et al. Rhodolith beds are major CaCO3 bio-factories in the tropical South West Atlantic. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amado-Filho, G.M.; Bahia, R.G.; Pereira-Filho, G.H.; Longo, L.L. South Atlantic rhodolith beds: Latitudinal distribution, species composition, structure and ecosystem functions, threats and conservation status. In Rhodolith/Maërl Beds: A Global Perspective; Riosmena-Rodríguez, R., Nelson, W., Aguirre, J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Geerbestrasse, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 15, pp. 299–317. [Google Scholar]
- Guimarães, C.R.P. Composição e distribuição dos sedimentos superficiais e da fauna bêntica na plataforma continental de Sergipe. Ph.D. Thesis, Instituto de Geociências, Universidade Federal da Bahia, Salvador-Bahia, Brazil, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Nascimento, A.A. Sedimentação holocênica na plataforma continental de Sergipe, nordeste do Brasil. Master’s Thesis, Instituto de Geociências, Universidade Federal da Bahia, Salvador–Bahia, Brazil, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Fontes, L.C.S.; Santos, J.R.; Santos, L.A.; Mendonça, J.B.S.; Santos, M.S. Sedimentos superficiais da plataforma continental de Sergipe-Alagoas. In Geologia e Geomorfologia da Bacia de Sergipe-Alagoas; Carneiro, M.E.R., Ed.; Editora UFS; Coleção Projeto MARSEAL: São Cristóvão, Brazil, 2017; Volume 1, pp. 64–96. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, J.R.; Souza, R.M.; Andrade, E.; Fontes, L.C.S. Biogenic components as environmental indicators of the Continental Platform of the state Sergipe and south of Alagoas. Geociências 2019, 38, 409–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.S.; Santos, L.A.; Fontes, L.C.S. Geomorphological and sedimentary mapping of paleo-lines of coast in the continental platform South of Alagoas. GeoNordeste J. 2019, 1, 60–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza-Lima, W.; Andrade, A.J.; Bengtson, P.; Galm, P.C. A Bacia de Sergipe-Alagoas: Evolução geológica, estratigrafia e conteúdo fóssil. Fund. Paleontológica Phoenix Aracaju 2002, 1, 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Coutinho, P.N. Geologia Marinha da Plataforma Continental Alagoas-Sergipe. Ph.D. Thesis, Centro de Tecnologia, Universidade Federal de Pernambuco, Recife, Brazil, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, J.R. Feições morfológicas e biofacies como indicadores evolutivos da Plataforma Continental de Sergipe e sul de Alagoas. Ph.D. Thesis, Centro de Tecnologia, Universidade Federal de Sergipe, Recife, Brazil, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Knoppers, B.A.; Carneiro, M.E.R.; Fontes, L.C.S.; Souza, W.F.L.; Medeiros, P.R.P. Plataforma Continental de Sergipe e Alagoas. In Plataforma Continental de Sergipe e Alagoas: Geoquímica Sedimentar e Comunidade Bêntica; de Lara Palmeira de Macedo Arguelho, M.E.R.C.e.M., Ed.; Editora UFS; Coleção Projeto MARSEAL: São Cristóvão, Brazil, 2018; Volume 2, pp. 11–38. [Google Scholar]
- Bezerra, F.H.R.; Barreto, A.M.F.; Suguio, K. Holocene sea level history on the Rio Grande do Norte State Coastal, Brazil. Mar. Geol. 2003, 196, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldas, L.H.O.; Stattegger, K.; Vital, H. Holocene sea-level history and coastal evolution: Evidences from coastal sediments of the northern Rio Grande do Norte coast, NE Brazil. Mar. Geol. 2006, 228, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, P.R.P.; Knoppers, B.A.; Santos, R.C.; Souza, W.F.L. Aporte fluvial e dispersão de matéria particulada em suspensão na zona costeira do rio São Francisco (SE/AL). Geochim. Bras. 2007, 21, 212–231. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, E.N.; Knoppers, B.A.; Lorenzzetti, J.A.; Medeiros, P.R.P.; Carneiro, M.E.; Souza, W.F.L. A satellite view of riverine turbidity plumes on the NE-E Brazilian coastal zone. Braz. J. Oceanogr. 2012, 60, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Knoppers, B.; Medeiros, P.R.P.; Souza, W.F.L.; Jennerjahn, T. The São Francisco Estuary, Brazil. In Estuaries, Pollution; Wangersky, P., Ed.; Springer Handbook of Environmental Chemistry: Berlin, Germany, 2006; Volume 5, pp. 51–70. [Google Scholar]
- Bittencourt, A.C.S.P.; Dominguez, J.M.L.; Fontes, L.C.S.; Sousa, D.L.; Silva, I.R.; Silva, F.R. Wave refraction, river damming and episodes of severe shoreline erosion: The Sao Francisco River Mouth, Northeastern Brazil. J. Coast. Res. 2007, 23, 930–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, P.R.P.; Knoppers, B.; Souza, W.F.L.; Oliveira, E.N. Aporte de material em suspensão no Baixo Rio São Francisco (SE/AL), em diferentes condições hidrológicas. Braz. J. Aquat. Sci. Technol. 2011, 15, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, J.M.L.; Guimarães, J.K. Effects of Holocene climate changes and anthropogenic river regulation in the development of a wave-dominated delta: The São Francisco River (Eastern Brazil). Mar. Geol. 2021, 435, 106456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutinho, P.N. Oceanografia Geológica. In Levantamento do Estado da Arte da Pesquisa dos Recursos Vivos Marinhos do Brasil (Programa REVIZEE); Coutinho, P.N., Ed.; Ministério do Meio Ambiente dos Recursos Hídricos e da Amazônia Legal, Secretaria de Coordenação dos Assuntos do Meio Ambiente: Brasília, Brazil, 2000; p. 75. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, M.B. Caracterização Integrada da Linha de Costa do Estado de Sergipe–Brasil. Master’s Thesis, Instituto de Geociências, Universidade Federal da Bahia, Salvador, Brazil, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Bittencourt, A.C.S.P.; Oliveira, M.B.; Dominguez, J.M.L. Erosão e Progradação do Litoral Brasileiro–Sergipe. In Erosão e Progradação do Litoral Brasileiro; Muehe, D., Ed.; Ministério do Meio Ambiente: Brasília, Brazil, 2006; Volume 2, pp. 213–218. [Google Scholar]
- Fontes, L.C.S.; Santos, J.R.; Santos, L.A.; Mendonça, J.B.S.; Santos, M.S. Geomorfologia da Plataforma Continental de Sergipe-Alagoas. In Geologia e Geomorfologia da Bacia de Sergipe-Alagoas; Fontes, L.C.S., Kowsmann, R.O., Puga-Bernabéu, A., Eds.; Editora UFS: São Cristóvão, Brazil, 2017; Volume 1, pp. 25–61. [Google Scholar]
- PETROBRAS. Projeto de Caracterização Regional da Bacia de Sergipe-Alagoas, Relatório IBAMA; Etapa 3; Volume 3, Algas Calcárias, Corais e Moluscos da Bacia Sergipe-Alagoas; PETROBRAS: Rio de Janeiro, Brasil, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Carneiro, M.E.R.; Moreira, D.L.; Oliveira, P.; Omena, E.; Garcia, C.A.B.; Alexandre, M.R.; Carreira, R.; Santos, N.C.; Politano, A.T. Delineamento amostral, métodos de campo e análise dos dados. In Plataforma Continental de Sergipe e Alagoas: Geoquímica Sedimentar e Comunidade Bêntica; de Lara Palmeira de Macedo Arguelho, M.E.R.C.e.M., Ed.; Editora UFS; Coleção Projeto MARSEAL: São Cristóvão, Brazil, 2018; Volume 2, pp. 40–59. [Google Scholar]
- Basso, D. Deep rhodolith distribution in the Pontian Islands, Italy: A model for the paleoecology of a temperate sea. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclim. Palaeoecol. 1998, 137, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woelkerling, W.J.; Irvine, L.M.; Harvey, A.S. Growth-forms in non-geniculate coralline red algae (Corallinales, Rhodophyta). Aust. Syst. Bot. 1993, 6, 277–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basso, D.; Nalin, R.; Nelson, C.S. Shallow-water Sporolithon rhodoliths from North Island (New Zealand). Palaios 2009, 24, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosence, D.W.J. Description and classification of rhodoliths (rhodoids, rhodolites). In Coated grains; Peryt, T.M., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1983; pp. 217–224. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, D.J.; Midglay, N.G. Graphical representation of a particle shape using triangular diagrams: An Excel spread sheet method. Earth Surf. Processes Landf. 2000, 25, 1473–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maneveldt, G.W.; Van Der Merwe, E. Heydrichia cerasina sp. nov. (Sporolithales, Corallinophycidae, Rhodophyta) from the southernmost tip of Africa. Phycologia 2012, 51, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahia, R.G. Algas Coralináceas Formadoras de Rodolitos da Plataforma Continental Tropical e Ilhas Oceânicas do Brasil: Levantamento florístico e taxonomia. Ph.D. Thesis, Escola Nacional de Botânica Tropical, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Leão, L.A.S.; Bahia, R.G.; Jesionek, M.B.; Adey, W.H.; Johnson, G.; Salgado, L.T.; Pereira, R.C. Sporolithon franciscanum sp. nov. (Sporolithales, Rhodophyta), a New Rhodolith-Forming Species from Northeast Brazil. Diversity 2020, 12, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, I.O.; Jesus, P.B.; Jesus, T.S.; Souza, P.S.; Horta, P.A.; Nunes, J.M.D.C. Reef-building coralline algae from the Southwest Atlantic: Filling gaps with the recognition of Harveylithon (Corallinaceae, Rhodophyta) on the Brazilian Coast. J. Phycol. 2019, 55, 1370–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, G.; Romero-Ramirez, A.; Tauran, A.; Pantalos, M.; Deflandre, B.; Grall, J.; Grémare, A. Declining maerl vitality and habitat complexity across a dredging gradient: Insights from in situ sediment profile imagery (SPI). Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunham, R.J. Classification of carbonate rocks according to depositional texture. In Classification of Carbonate Rocks; Ham, W.E., Ed.; AAPG Mem: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1962; pp. 108–121. [Google Scholar]
- Embry, A.F.; Klovan, J.E. Absolute water depth limits of late Devonian paleoecological zones. Geol. Rundsch. 1972, 61, 672–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassi, D.; Iryu, Y.; Humblet, M.; Matsuda, H.; Machiyama, H.; Sasaki, K.; Matsuda, S.; Arai, K.; Inoue, T. Recent macroids on the Kikai-jima shelf, Central Ryukyu Islands, Japan. Sedimentology 2012, 59, 2024–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beijbom, O.; Edmunds, P.J.; Roelfsema, C.; Smith, J.; Kline, D.I.; Neal, B.; Dunlap, M.J.; Moriarty, V.; Fan, T.-Y.; Tan, C.-J.; et al. Towards automated annotation of benthic survey images: Variability of human experts and operational modes of automation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitsch, F.; Nebelsick, J.H.; Bassi, D. Constructional and Destructional patterns—Void classification of rhodoliths from Giglio Island, Italy. Palaios 2015, 30, 680–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuiver, M.; Reimer, P.J.; Reimer, R.W. CALIB 8.2. 2020. Available online: http://calib.org (accessed on 28 August 2020).
- Heaton, T.J.; Köhler, P.; Butzin, M.; Bard, E.; Reimer, R.W.; Austin, W.E.N.; Bronk Ramsey, C.; Hughen, K.A.; Kromer, B.; Reimer, P.J.; et al. Marine20-the marine radiocarbon age calibration curve (0–55,000 cal BP). Radiocarbon 2020, 62, 779–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holz, V.L.; Bahia, R.G.; Karez, C.S.; Vieira, F.V.; Moraes, F.C.; Vale, N.F.; Sudatti, D.B.; Salgado, L.T.; Moura, R.L.; Amado-Filho, G.M.; et al. Structure of Rhodolith Beds and Surrounding Habitats at the Doce River Shelf (Brazil). Diversity 2020, 12, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelzer, P.S.; Mazzuco, A.C.A.; Gomes, L.E.; Martins, J.; Netto, S.; Bernardino, A.F. Taxonomic and functional diversity of benthic macrofauna associated with rhodolith beds in SE Brazil. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, R.L.; Amado-Filho, G.M.; Moraes, F.C.; Brasileiro, P.S.; Salomon, P.S.; Mahiques, M.M.; Bastos, A.C.; Almeida, M.G.; Silva, J.M.; Araujo, B.F.; et al. An extensive reef system at the Amazon River mouth. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vale, N.F.L.; Amado-Filho, G.M.; Braga, J.C.; Brasileiro, P.S.; Karez, C.S.; Moraes, F.C.; Bahia, R.G.; Bastos, A.C.; Moura, R.L. Structure and composition of rhodoliths from the Amazon River mouth, Brazil. J. South Am. Earth Sci. 2018, 84, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasileiro, P.S.; Braga, J.C.; Amado-Filho, G.M.; Leal, R.N.; Bassi, D.; Franco, T.; Bastos, A.C.; Moura, R.L. Burial rate determines Holocene rhodolith development on the Brazilian Shelf. Palaios 2018, 33, 464–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira-Filho, G.H.; Shintate, G.S.; Kitahara, M.V.; Moura, R.L.; Amado-Filho, G.M.; Bahia, R.G.; Moraes, F.C.; Neves, L.M.; Francini, C.L.B.; Gibran, F.Z.; et al. The southernmost Atlantic coral reef is off the subtropical island of Queimada Grande (24° S), Brazil. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2019, 95, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sissini, M.N.; Koerich, G.; de Barros-Barreto, M.B.; Coutinho, L.M.; Gomes, F.P.; Oliveira, W.; Costa, I.O.; Nunes, J.M.C.; Henriques, M.C.; Vieira-Pinto, T.; et al. Diversity, distribution, and environmental drivers of coralline red algae: The major reef builders in the Southwestern Atlantic. Coral Reefs 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, F.V.; Bastos, A.C.; Quaresma, V.S.; Leite, M.D.; Costa, A., Jr.; Oliveira, K.S.S.; Dalvi, C.F.; Bahia, R.G.; Holz, V.L.; Moura, R.L.; et al. Along-shelf changes in mixed carbonate-siliciclastic sedimentation patterns. Cont. Shelf Res. 2019, 187, 103964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, R.F.; Dominguez, J.M.L.; Santos, A.A.; Rangel, A.G.A.N. Continuous canyon-river connection on a passive margin: The case of São Francisco Canyon (eastern Brazil). Geomorphology 2021, 375, 107549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira-Filho, G.H.; Veras, P.C.; Francini-Filho, R.B.; Moura, R.L.; Pinheiro, H.T.; Gibran, F.Z.; Matheus, Z.; Neves, L.M.; Amado-Filho, G.M. Effects of the sand tilefish Malacanthus plumieri on the structure and dynamics of a rhodolith bed in the Fernando de Noronha Archipelago, tropical West Atlantic. Mar. Ecol. Progr. Ser. 2015, 541, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amado-Filho, G.M.; Moura, R.L.; Bastos, A.C.; Francini-Filho, R.B.; Pereira-Filho, G.H.; Bahia, R.G.; Moraes, F.C.; Motta, F.S. Mesophotic ecosystems of the unique South Atlantic atoll are composed by rhodolith beds and scattered consolidated reefs. Mar. Biodiv. 2016, 46, 933–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prager, E.J.; Ginsburg, R.N. Carbonate nodule growth on Florida’s outer shelf and its implications for fossil interpretations. Palaios 1989, 4, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérès, J.; Picard, J.M. Nouveau manuel de bionomie benthique de la mer Méditerranée. Recl. Trav. Stn. Mar. Endoume 1964, 31, 1–131. [Google Scholar]
- Ballesteros, E. Mediterranean coralligenous assemblages: A synthesis of present knowledge. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Annu. Rev. 2006, 44, 123–195. [Google Scholar]
- Nalin, R.; Basso, D.; Massari, F. Pleistocene coralline algal build-ups (coralligène de plateau) and associated bioclastic deposits in the sedimentary cover of Cutro marine terrace (Calabria, southern Italy). In Cool-Water Carbonates: Depositional Systems and Palaeoenvironmental Controls; Pedley, H.M., Carannante, G., Eds.; Geological Society, Special Publications: London, UK, 2006; Volume 255, pp. 11–22. [Google Scholar]
- Basso, D.; Nalin, R.; Massari, F. Genesis and composition of the Pleistocene Coralligène de plateau of the Cutro Terrace (Calabria, southern Italy). Neues Jahrbuch für Geologie und Paläontologie–Abhandlungen 2007, 244, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benisek, M.F.; Marcano, G.; Betzler, C.; Mutti, M. Facies and stratigraphic architecture of a Miocene warm-temperate to tropical fault-block carbonate platform, Sardinia (Central Mediterranean Sea). In Carbonate Systems during the Oligocene-Miocene Climatic Transition; Mutti, M., Piller, W.E., Betzler, C., Eds.; IAS Special Publications: Gent, Belgium, 2010; Volume 42, pp. 129–148. [Google Scholar]
- Braga, J.C.; Martín, J.M. Neogene coralline-algal growth-forms and their palaeoenvironments in the Almanzora River Valley (Almeria, S.E. Spain). Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclim. Palaeoecol. 1988, 67, 285–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.; Blake, C.; Berges, J.A.; Maggs, C.A. Environmental tolerances of free-living coralline algae (maerl): Implications for European marine conservation. Biol. Conserv. 2004, 120, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrhold, A.; Jouet, G.; Le Roy, P.; Jorry, S.J.; Grall, J.; Reixach, T.; Lambert, C.; Gregoire, G.; Goslin, J.; Roubi, A.; et al. Fossil maerl beds as coastal indicators of late Holocene palaeo-environmental evolution in the Bay of Brest (Western France). Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclim. Palaeoecol. 2021, 577, 110525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, C.; Guillemin, M.L.; Pena, V.; Bárbara, I.; Valero, M.; Barreiro, R. Local coastal configuration rather than latitudinal gradient shape clonal diversity and genetic structure of Phymatolithon calcareum maerl Beds in north European Atlantic. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steller, D.L.; Hernandez-Ayon, J.M.; Riosmena-Rodriguez, R.; Cabello-Pasini, A. Effect of temperature on photosynthesis, growth and calcification rates of the free- living coralline alga Lithophyllum margaritae. Cienc. Mar. 2007, 33, 441–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toscano, F.; Vigliotti, M.; Simone, L. Variety of coralline algal deposits (rhodalgal facies) from the Bays of Naples and Pozzuoli (northern Tyrrhenian Sea, Italy). In Cool-Water Carbonates: Depositional Systems and Paleoenvironmental Controls; Pedley, H.M., Carannante, G., Eds.; Geological Society, Special Publications: London, UK, 2006; Volume 225, pp. 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, K.R.; Gagnon, P. Mechanisms of stability of rhodolith beds: Sedimentological aspects. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2018, 594, 65–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, L.G.; James, N.P.; Doubell, M.; Middleton, J.F.; Luick, J.; Currie, D.R.; Bone, Y. Oceanographic controls on shallow-water temperate carbonate sedimentation: Spencer Gulf, South Australia. Sedimentology 2016, 63, 105–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basso, D. Study of living calcareous algae by a paleontological approach: The non-geniculate Corallinaceac (Rhodophyta) of the soft bottoms of the Tyrrhenian Sea (Western Mediterranean). The genera Phymamlitum Foslie and Mesophyllum Lemoine. Rivista Italiana di Paleontologia e Stratigrafia 1994, 100, 575–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basso, D. Living calcareous algae by a paleontological approach: The genus Lithothamnion Heydrich nom. cons. from the soft bottoms of the Tyrrhenian Sea (Mediterranean). Rivista Italiana di Paleontologia e Stratigrafia 1995, 101, 349–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Geronimo, R.; Giaccone, G. Le alghe calcaree nel Detritico Costiero di Lampedusa (lsole Pelagie). Boll. Acc. Gioenia Sci. Nat. 1994, 27, 5–25. [Google Scholar]
- Braga, J.C. Neogene rhodoliths in the Mediterranean Basins. In Rhodolith/Maërl Beds: A Global Perspective; Riosmena-Rodríguez, R., Nelson, W., Aguirre, J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Geerbestrasse, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 15, pp. 169–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMaster, R.W.; Conover, J.P. Recent algal stromatolites from the Canary Islands. J. Geol. 1966, 74, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Focke, J.W.; Gebelein, C.D. Marine lithification of reef rock and rhodolites at a fore-reef slope locality (−50m) off Bermuda. Geol. Mijnb. 1978, 57, 163–171. [Google Scholar]
- Reid, R.P.; Macintyre, I.G. Foraminiferal-algal nodules from the Eastern Caribbean: Growth history and implications on the value of nodules as paleoenvironmental indicators. Palaios 1988, 3, 424–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minnery, G.A. Crustose coralline algae from the Flower Garden Banks, northwestern Gulf of Mexico: Controls on distribution and growth morphology. J. Sed. Petrol. 1990, 60, 992–1007. [Google Scholar]
- Littler, M.M.; Littler, D.S.; Hanisak, M.D. Deep-water rhodolith, productivity, and growth history at sites of formation and subsequent degradation. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1991, 150, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Checconi, A.; Bassi, D.; Carannante, G.; Monaco, P. Re-deposited rhodoliths in the middle Miocene hemipelagic deposits of vitulano (Southern Apennines, Italy): Coralline assemblage characterization and related trace fossils. Sediment. Geol. 2010, 225, 50–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutinho, L.M.; Gomes, F.P.; Sissini, M.N.; Vieira-Pinto, T.; de Oliveira Henriques, M.C.M.; Oliveira, M.C.; Horta, P.A.; de Barros Barreto, M.B.B. Cryptic diversity in non-geniculate coralline algae: A new genus Roseolithon (Hapalidiales, Rhodophyta) and seven new species from the Western Atlantic. Eur. J. Phycol. 2021, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tâmega, F.T.S.; Bassi, D.; Figueiredo, M.A.; Cherkinsky, A. Deep-water rhodolith bed from central Brazilian continental shelf, Campos Basin: Coralline algal and faunal taxonomic composition. J. Coral Reef Stud. 2014, 16, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.; Hall-Spencer, J.M. Effects of Ocean Warming and Acidification on Rhodolith/Maërl Beds. In Rhodolith/Maerl Beds: A Global Perspective; Riosmena-Rodrigues, R., Nelson, W., Aguirre, J., Eds.; Coastal Research Library, Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 15, pp. 55–85. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
