The Young Stages of the Cannonball Jellyfish (Stomolophus sp. 2) from the Central Gulf of California (Mexico)
Abstract
1. Introduction
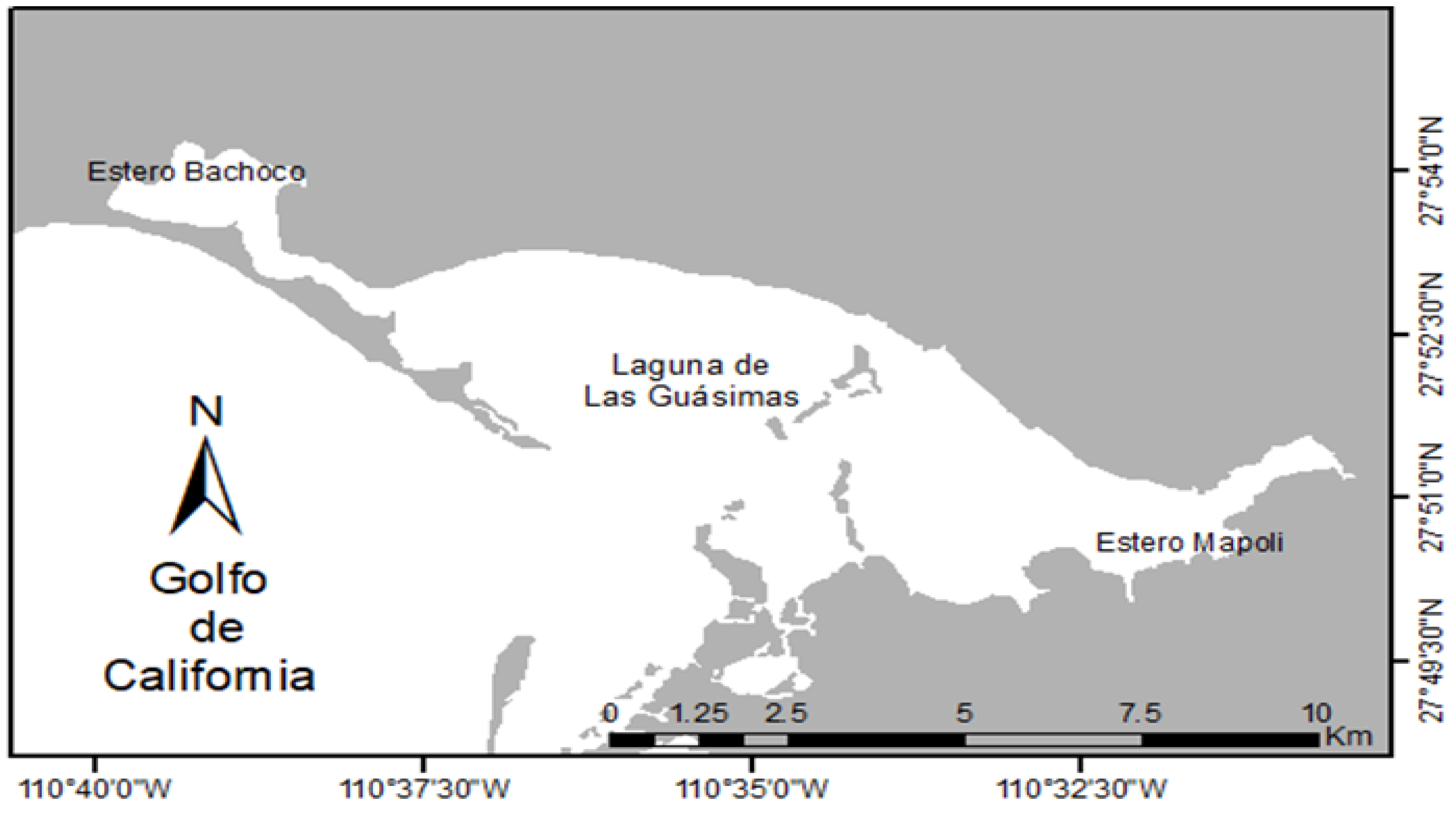
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
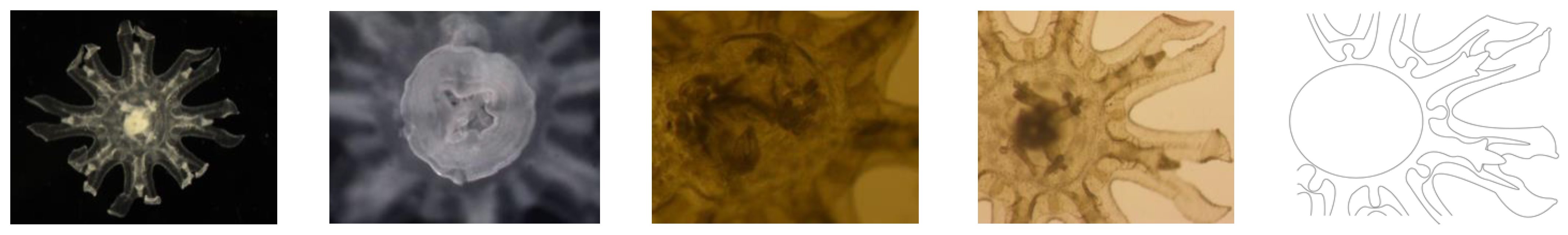
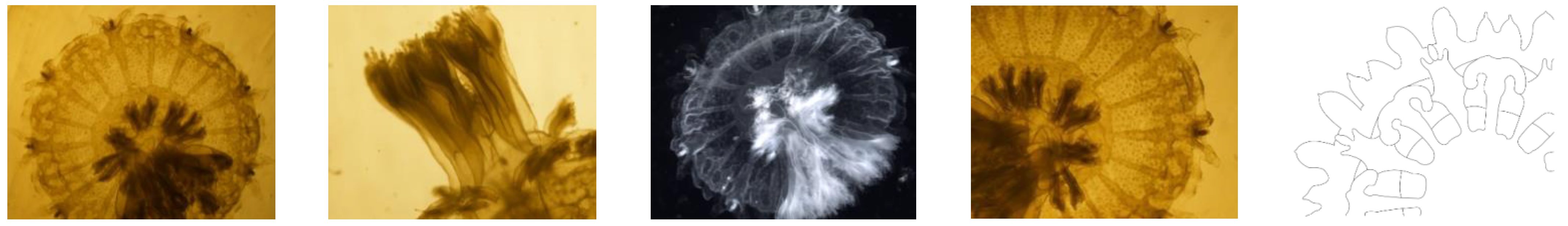
3.1. Features of the Ephyrae of Stomolophus sp. 2
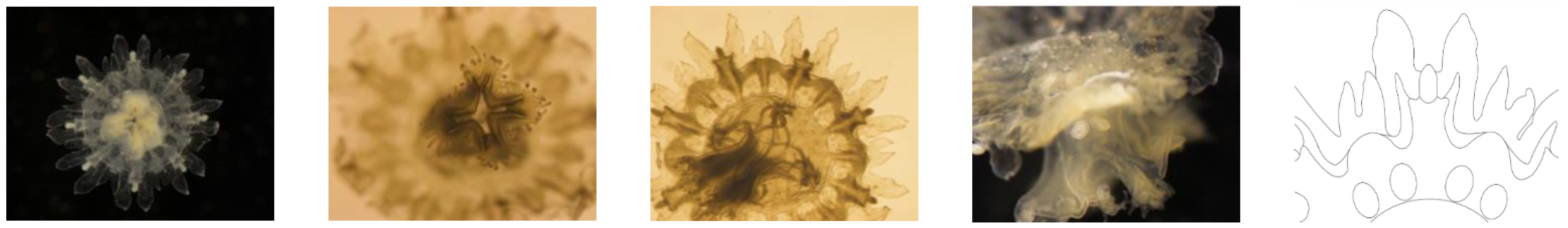
3.2. Different Stages of the Development of Stomolophus sp. 2
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Purcell, J.E.; Uye, S.I.; Lo, W.T. Anthropogenic causes of jellyfish blooms and their direct consequences for humans: A review. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 350, 153–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brotz, L. Changing Jellyfish Populations: Trends in Large Marine Ecosystems. Master’s Thesis, The University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Seo, J.; Yoon, W.; Suh, Y. Estimating the economic damage caused by jellyfish to fisheries in Korea. Fish. Sci. 2012, 78, 1147–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, J.E. Jellyfish and Ctenophore Blooms Coincide with Human Proliferations and Environmental Perturbations. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2012, 4, 209–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.-H.P.; Rudloe, J. Potential of utilizing jellyfish as food in Western countries. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1994, 5, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omori, M.; Nakano, E. Jellyfish fisheries in southeast Asia. Hydrobiologia 2001, 451, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hsieh, Y.-H.P. Traditional Chinese food technology and cuisine. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 13, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kitamura, M.; Omori, M. Synopsis of edible jellyfishes collected from Southeast Asia, with notes on jellyfish fisheries. Plankton Benthos Res. 2010, 5, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.-H.P.; Leong, F.-M.; Rudloe, J. Jellyfish as food. Hydrobiologia 2001, 451, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Martínez, J.; Álvarez-Tello, J. The jellyfish fishery in Mexico. Agric. Sci. 2013, 4, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brotz, L.; Schiariti, A.; López-Martínez, J.; Álvarez-Tello, J.; Peggy Hsieh, Y.H.; Jones, R.P.; Quiñones, J.; Dong, Z.; Morandini, A.C.; Preciado, M.; et al. Jellyfish fisheries in the Americas: Origin, state of the art, and perspectives on new fishing grounds. Rev. Fish Biol Fish. 2017, 27, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torri, L.; Tuccillo, F.; Bonelli, S.; Piraino, S.; Leone, A. The Attitudes of Italian Consumers towards Jellyfish as Novel Food. Food Qual. Prefer. 2020, 79, 103782. Available online: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0950329318310346 (accessed on 27 August 2019). [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Liu, D.; Keesing, J.K. Contrasting Trends in Populations of Rhopilema esculentum and Aurelia aurita in Chinese Waters. In Jellyfish Blooms; Pitt, K., Lucas, C., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, Holland, 2014; pp. 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramp, P.L. Zoogeographical studies on Rhizostomeae. Vidensk. Medd. Fra Dansk Naturh. Foren. 1970, 133, 7–30. [Google Scholar]
- Jarms, G.; Morandini, A.C. World Atlas of Jellyfish; Dölling und Galitz Verlag: Hamburg, Germany, 2019; p. 816. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, A.G. Medusae of the world III: The Scyphomedusae. Publ. Carnegie Inst. Wash. 1910, 109, 499–735. [Google Scholar]
- Kramp, P.L. A revision of Ernst Haeckel’s determinations of a collection of medusae belonging to the Zoological Museum of Copenhagen. Deep Sea Res. 1955, 3, 149–168. [Google Scholar]
- Kramp, P.L. Synopsis of the medusae of the world. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 1961, 40, 7–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, T. Some medusae of the central Pacific. J. Fac. Sci. Hokkaido Univ. Ser. 6 Zool. 1947, 9, 297–319. [Google Scholar]
- Mianzan, H.W.; Cornelius, P.F.S. Cubomedusae and Scyphomedusae. In South Atlantic Zooplankton; Boltovskoy, D., Ed.; Backhuys Publishers: Leiden, Holland, 1999; Volume 1, pp. 513–559. [Google Scholar]
- Banha, T.N.S.; Morandini, A.C.; Rosário, R.P.; Martinelli Filho, J.E. Scyphozoan jellyfish (Cnidaria, Medusozoa) from Amazon coast: Distribution, temporal variation and length–weight relationship. J. Plankton Res. 2020, 42, 767–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Daglio, L.; Dawson, M.N. Species richness of jellyfishes (Scyphozoa: Discomedusae) in the Tropical Eastern Pacific: Missed taxa, molecules, and morphology match in a biodiversity hotspot. Invertebr. Syst. 2017, 31, 635–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getino Mamet, L.N.; Gómez-Daglio, L.; García-De Léon, F.J. High genetic differentiation in the edible cannonball jellyfish (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa: Stomolophus spp.) from the Gulf of California, Mexico. Fish. Res. 2019, 219, 105328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Martinez, J.; Arzola-Sotelo, E.A.; Nevarez-Martinez, M.O.; Alvarez-Tello, F.J.; Morales-Bojorquez, E. Modeling growth on the cannonball jellyfish Stomolophus meleagris based on a multi-model inference approach. Hydrobiologia 2020, 847, 1399–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boero, F.; Bouillon, J.; Gravili, C.; Miglietta, M.; Parsons, T.; Piraino, S. Gelatinous plankton: Irregularities rule the world (sometimes). Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 18, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, M.; Boero, F.; Brotz, L. We should not assume that fishing jellyfish will solve our jellyfish problem. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2016, 73, 1012–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straehler-Pohl, I.; Jarms, G. Identification key for young ephyrae: A first step for early detection of jellyfish blooms. Hydrobiologia 2010, 645, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holst, S. Morphology and development of benthic and pelagic life stages of North Sea jellyfish (Scyphozoa, Cnidaria) with special emphasis on the identification of ephyra stages. Mar. Biol. 2012, 159, 2707–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calder, D.R. Life history of the cannonball jellyfish, Stomolophus meleagris L. Agassiz, 1860 (Scyphozoa, Rhizostomida). Biol. Bull. 1982, 162, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Aguirre, S. Larva éfira y diferenciación de Stomolophus meleagris (Scyphozoa Rhizostomeae) en plancton de lagunas costeras de Tabasco, México. An. Inst. Biol. Univ. Nac. Autón. México Ser. Zool. 1991, 62, 383–389. [Google Scholar]
- Stiasny, G. Papers from Dr. Th. Mortensen’s Pacific Expedition 1914-16. XII. Zur Kenntnis der Entwicklung von Stomolophus meleagris L. Agassiz. Vidensk Medd Fra Dansk Naturh Foren 1922, 73, 499–511. [Google Scholar]
- Burrola-Sánchez, M.S.; López-Martínez, J.; Padilla-Arredondo, G.; Urias-Laborin, D.; Padilla-Serrato, J.G. Influencia de los procesos costeros sobre la distribución de la medusa bola de cañón Stomolophus melegris (Agassiz, 1860) en el Golfo de California. In La Variabilidad Ambiental y Las Pesquerías De México; López-Martínez, J., Ed.; Comisión Nacional de Acuacultura y Pesca: Mazatlán, México, 2008; pp. 156–177. [Google Scholar]
- López-Martínez, J.; Rodríguez-Romero, J. Primer registro de la asociación del jurelillo negro Hemicaranx zelotes Gilbert (Pisces: Carangidae) con la medusa bala de cañón Stomolophus meleagris Agassiz (Scyphozoa: Rhizostomatidae) en Bahía de Kino, Golfo de California. Hidrobiológica 2008, 18, 173–176. [Google Scholar]
- Nevárez-López, C.A.; Váldez-Holguín, J.E.; Hernández-Saavedra, N.Y. Caracterización Genética de los fenotipos de la medusa “Bola de (Stomolophus meleagris, L. AGASSIZ 1862) en las Guásimas, Sonora. In Biotecnología Marina; XII Congreso Nacional de Biotecnología y Bioingeniería y VII Simposio Internacional de Producción de Alcoholes y Levaduras: Acapulco, Guerrero, México, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho-Saucedo, L.; García-Domínguez, F.; Rodriguez-Jaramillo, C.; López-Martínez, J. Variación lipídica en los ovocitos de la medusa Stomolophus meleagris (Scyphozoa: Rhizostomeae), durante el desarrollo gonádico, en la laguna Las Guásimas, Sonora, México. Rev. Biol. Trop. 2010, 58, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Tello, J.; López-Martínez, J.; Lluch-Cota, D. Trophic spectrum and feeding pattern of cannonball jellyfish Stomolophus meleagris (Agassiz, 1862) from central Gulf of California. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2015, 6, 1217–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straehler-Pohl, I.; Widmer, C.L.; Morandini, A.C. Characterizations of juvenile stages of some semaeostome Scyphozoa (Cnidaria), with recognition of a new family (Phacellophoridae). Zootaxa 2011, 2741, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, F.S. The Medusae of the British Isles II, Pelagic Scyphozoa with a Supplement to the First Volume on Hydromedusae; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1970; pp. 1–284. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Z.; Shibata, M.; Makake, R.; Ikeda, H.; Uye, S. Body size reduction under starvation, and the point of no return, in ephyrae of the moon jellyfish Aurelia aurita. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2014, 510, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaverano, L.M.; Graham, W.M. Morphological plasticity in Aurelia polyps, with subsequent effects on asexual fecundity and morphology of young medusae. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2017, 582, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morandini, A.C.; Silveira, F.L.; Jarms, G. The life cycle of Chrysaora lactea Eschscholtz, 1829 (Cnidaria, Scyphozoa) with notes on the scyphistoma stage of three other species. Hydrobiologia 2004, 530/531, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widmer, C.L. Life cycle of Chrysaora fuscescens (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa) and a key to sympatric ephyrae. Pac. Sci. 2008, 62, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
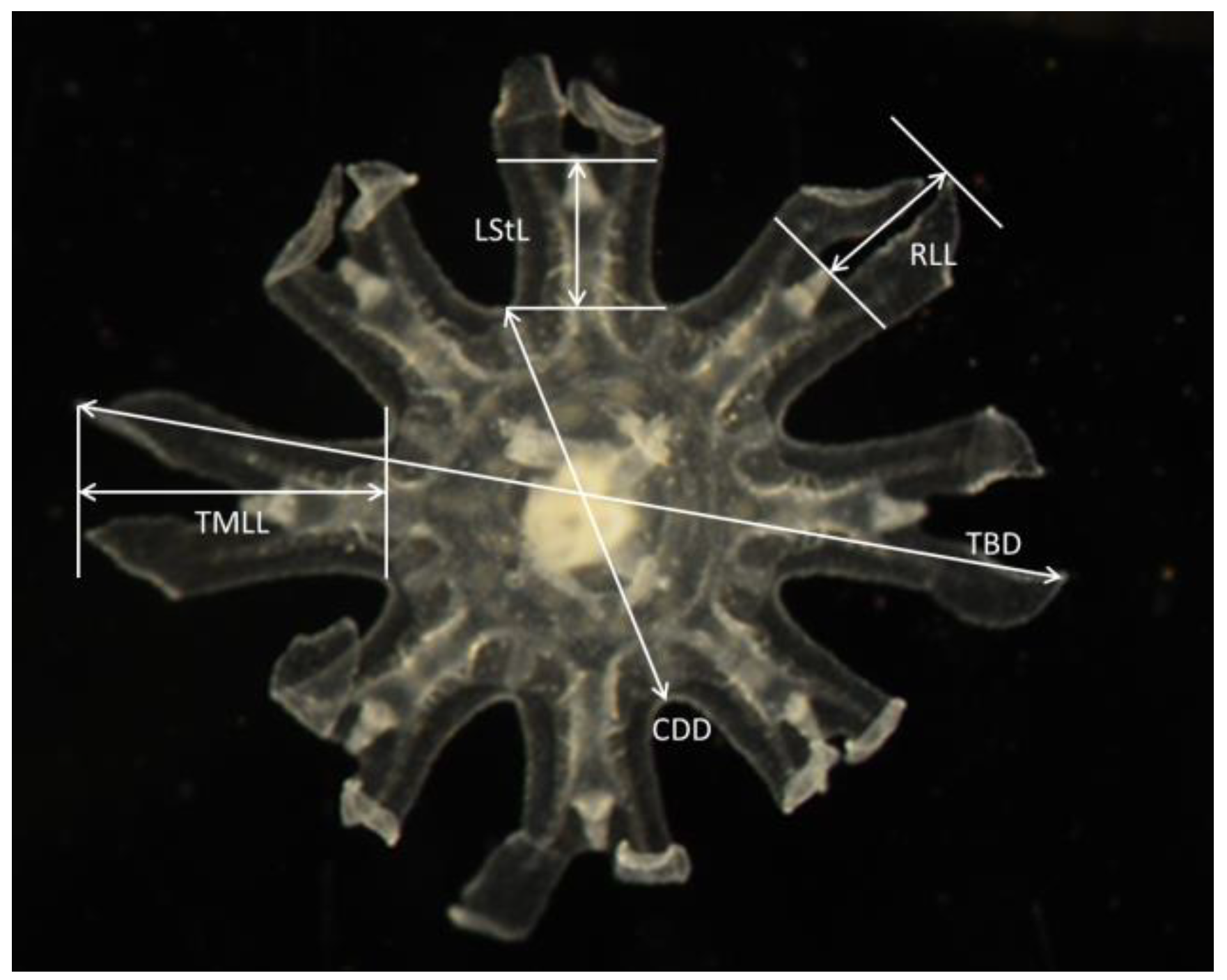
| Specimen | CDD/TBD × 100 | TMLL/TBD × 100 | RLL/TMLL × 100 | LStL/TMLL × 100 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 41.66 | 29.58 | 60.46 | 50.55 |
| 2 | 48.41 | 29.30 | 51.93 | 52.80 |
| 3 | 37.71 | 33.72 | 54.70 | 49.91 |
| 4 | 54.29 | 26.87 | 53.59 | 57.13 |
| 5 | 53.54 | 29.67 | 50.33 | 46.63 |
| 6 | 44.78 | 26.45 | 65.66 | 68.67 |
| 7 | 45.05 | 32.57 | 53.52 | 57.78 |
| 8 | 48.01 | 30.56 | 51.57 | 48.43 |
| 9 | 39.46 | 29.84 | 47.18 | 42.91 |
| 10 | 48.75 | 27.87 | 62.19 | 48.06 |
| 11 | 41.58 | 32.42 | 57.94 | 47.84 |
| 12 | 49.19 | 30.98 | 55.57 | 46.78 |
| 13 | 42.32 | 28.39 | 52.66 | 45.94 |
| 14 | 44.24 | 28.61 | 57.89 | 42.83 |
| 15 | 38.31 | 32.18 | 54.68 | 43.53 |
| 16 | 45.68 | 27.98 | 57.20 | 49.69 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gómez-Salinas, L.C.; López-Martínez, J.; Morandini, A.C. The Young Stages of the Cannonball Jellyfish (Stomolophus sp. 2) from the Central Gulf of California (Mexico). Diversity 2021, 13, 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13060229
Gómez-Salinas LC, López-Martínez J, Morandini AC. The Young Stages of the Cannonball Jellyfish (Stomolophus sp. 2) from the Central Gulf of California (Mexico). Diversity. 2021; 13(6):229. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13060229
Chicago/Turabian StyleGómez-Salinas, Laura Cristina, Juana López-Martínez, and André Carrara Morandini. 2021. "The Young Stages of the Cannonball Jellyfish (Stomolophus sp. 2) from the Central Gulf of California (Mexico)" Diversity 13, no. 6: 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13060229
APA StyleGómez-Salinas, L. C., López-Martínez, J., & Morandini, A. C. (2021). The Young Stages of the Cannonball Jellyfish (Stomolophus sp. 2) from the Central Gulf of California (Mexico). Diversity, 13(6), 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13060229






