Diversity of Brazilian Troglobitic Fishes: Models of Colonization and Differentiation in Subterranean Habitats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Taxonomic Considerations
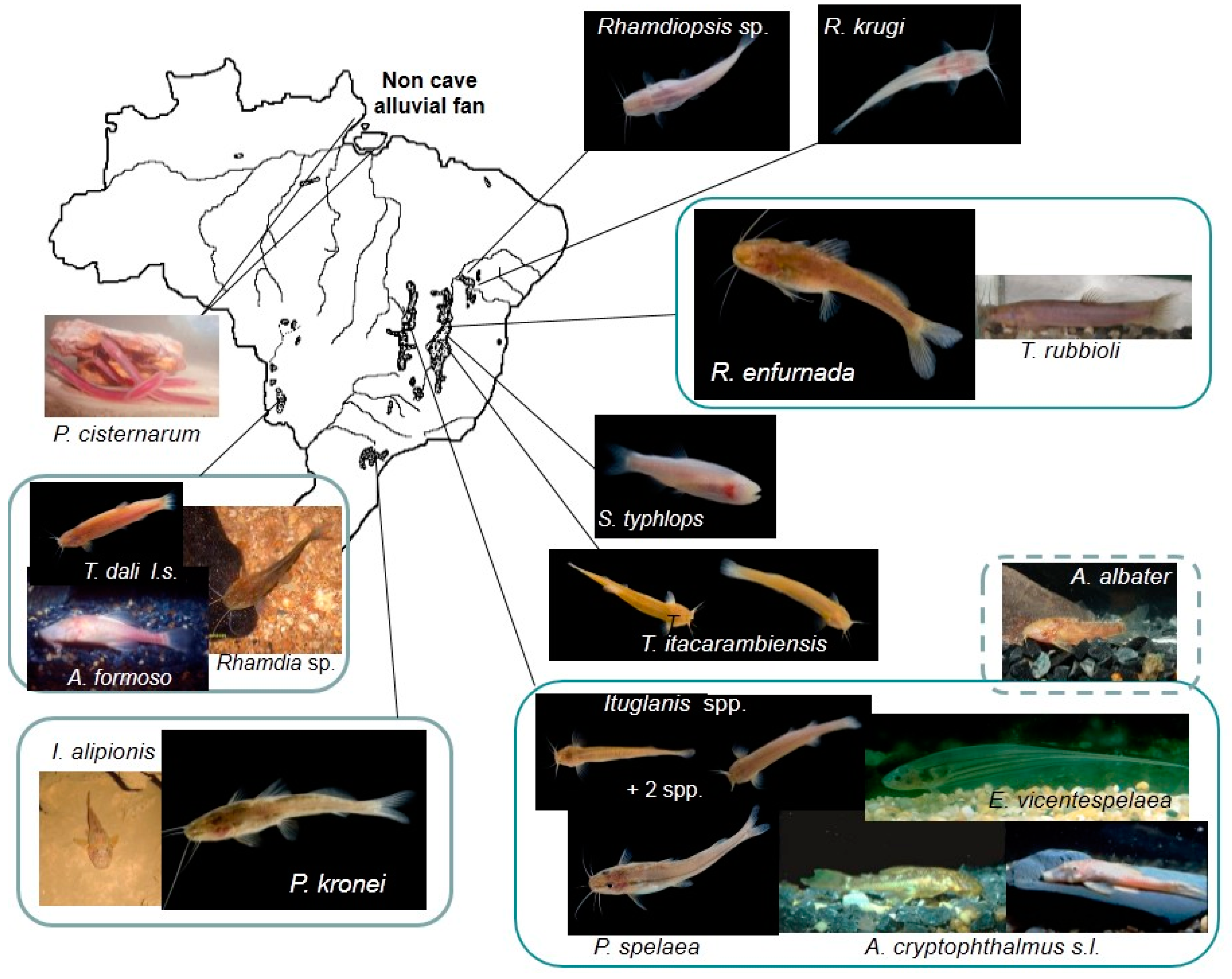
3. Diversity among Brazilian Subterranean Fishes
3.1. Taxonomic Diversity (Species Richness) and Distribution
3.2. Habitat, Morphology and Adaptations to a Subterranean Life
3.3. Hidden Diversity
4. Origin and Evolution of Subterranean Fishes in Brazil
4.1. The Challenge of Colonizing Subterranean Habitats: The Establishment of Troglophilic Populations
4.2. Modes and Models of Isolation and Differentiation in Subterranean Habitats: Origin of Troglobites
4.3. Stream Dwellers: (Sub)Horizontal Colonization through Sinkholes and Resurgences, Eventually Followed by Isolation
4.4. Transition from Lotic to Lentic Waters: Adaptation to Phreatic Waters
4.4.1. Stygichthys Typhlops
4.4.2. Flooded Caves: Troglobitic Fishes in Serra da Bodoquena Karst Area
4.4.3. Trichomycterus Rubbioli: The Problem of Sink Populations
4.5. Multiple-Step Model of Colonization and Differentiation in Subterranean Habitats: The Way through the Hyporheic Zone and Epikarst
4.5.1. Rhamdiopsis spp. from Semiarid Bahia
4.5.2. Ituglanis Catfishes from the São Domingos Karst Area
4.5.3. The Amazon Basin: Phreatobius spp.
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trajano, E.; Carvalho, M.R. Towards a biologically meaningful classification of subterranean organisms: A critical analysis of the Schiner-Racovitza system from a historical perspective, difficulties of its application and implications for conservation. Subterr. Biol. 2017, 22, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattox, G.M.T.; Bichuette, M.E.; Secutti, S.; Trajano, E. Surface and subterranean ichthyofauna in the Serra do Ramalho karst area, northeastern Brazil, with updated lists of Brazilian troglobitic and troglophilic fishes. Biota Neotrop. 2008, 8, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gallão, J.E.; Bichuette, M.E. Brazilian obligatory subterranean fauna and threats to the hypogean environment. Zookeys 2018, 746, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giachino, P.M.; Vailati, D. The Subterranean Environment; WBA Handbooks: Verona, Italy, 2010; Volume 3, pp. 1–132. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, J. Cavefish of China. In Encyclopedia of Caves, 2nd ed.; White, W., Culver, D.C., Pipan, T., Eds.; Academic Press: Waltham, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 237–254. [Google Scholar]
- Proudlove, G.S. Biodiversity and Distribution of the Subterranean Fishes of the World. In Biology of Subterranean Fishes; Trajano, E., Bichuette, M.E., Kapoor, B.G., Eds.; Science Publ.: Enfield, UK, 2010; Chapter 2; pp. 41–63. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkens, H. Regressive evolution and phylogenetic age: The history of colonization of freshwaters of Yucatan by fish and Crustacea. Assoc. Mex. Cave Stud. Bull. 1982, 8, 237–243. [Google Scholar]
- Arai, M. Aptian/Albian (Early Cretaceous) paleogeography of the South Atlantic: A paleontological perspective. Braz. J. Geol. 2014, 44, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trajano, E. Populational ecology of Pimelodella kronei, troglobitic catfish from southeastern Brazil (Siluriformes, Pimelodidae). Environ. Biol. Fishes 1991, 30, 407–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trajano, E. Agonistic behaviour of Pimelodella kronei, a troglobitic catfish from Southeastern Brazil (Siluriformes, Pimelodidae). Behav. Process. 1991, 23, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trajano, E. Comparative study on the brain and olfactory organ of the troglobitic catfish, Pimelodella kronei (Ribeiro, 1907), and its putative ancestor, P. transitoria (Ribeiro, 1912) (Siluriformes, Pimelodidae). Trop. Zool. 1994, 7, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trajano, E.; Ueno, J.C.H.; Menna-Barreto, L. Evolution of time-control mechanisms in subterranean organisms: Cave fishes under light-dark cycles (Teleostei: Siluriformes, Characiformes). Biol. Rhythm. Res. 2012, 43, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trajano, E. Ecology and ethology of subterranean fishes. In Catfishes; Arratia, G., Kapoor, B.C., Chardon, M., Diogo, R., Eds.; Science Publ.: Enfield, UK, 2003; Volume 2, pp. 601–635. [Google Scholar]
- Trajano, E. Ecology of subterranean fishes: An overview. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2001, 62, 133–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trajano, E.; Bichuette, M.E. Subterranean Fishes of Brazil. In Biology of Subterranean Fishes; Trajano, E., Bichuette, M.E., Kapoor, B.G., Eds.; Science Publ.: Enfield, UK, 2010; Chapter 9; pp. 331–355. [Google Scholar]
- Cordeiro, L.M. Distribuição, Ecologia e Filogeografia dos Bagres Troglóbios do Gênero Trichomycterus na Área Cástica Da Serra da Bodoquena, MS. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bichuette, M.E.; Trajano, E. Population density and habitat of an endangered cave ifsh Eigenmannia vicentespelaea Triques, 1996 (Ostariophysi: Gymnotiformes) from a karst area in central Brazil. Neotrop. Ichthyol. 2015, 13, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bichuette, M.E.; Trajano, E. Biology and behavior of Eigenmannia vicentespelaea, a troglobitic electric fish from Brazil (Teleostei: Gymnotiformes: Sternopygidae): A comparison to the epigean species, E. trilineata, and the consequences of cave life. Trop. Zool. 2017, 30, 68–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, T.C. Cave ecology and the evolution of troglobites. Evol. Biol. 1968, 2, 35–102. [Google Scholar]
- Trajano, E.; Britski, H.A. Pimelodella kronei (Ribeiro,1907) e seu sinônimo Caecorhamdella brasiliensis Borodin, 1927: Morfologia externa, taxonomia e evolução (Teleostomi, Siluriformes). Bol. Zool. 1992, 12, 53–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bichuette, M.E.; Rantin, B.; Zingst-Zaher, E.; Trajano, E. Geometric morphometrics throws light on evolutionof the subterranean catfish Rhamdiopsis krugi (Teleostei: Siluriformes: Heptapteridae) in eastern Brazil. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2015, 114, 136–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trajano, E.; Reis, R.E.; Bichuette, M.E. Pimelodella spelaea, a new cave catfish from Central Brazil, with data on ecology and evolutionary considerations (Siluriformes: Heptapteridae). Copeia 2004, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bichuette, M.E.; Trajano, E. Three new subterranean species of Ituglanis from Central Brazil (Siluriformes: Trichomycteridae). Ichthyol. Explor. Freshw. 2004, 15, 243–256. [Google Scholar]
- de Queiroz, K. Species concepts and species delimitation. Syst. Biol. 2007, 56, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trajano, E. The challenge of estimating the age of subterranean lineages: Examples from Brazil. Acta Carsol. 2007, 36, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, R.E.; Trajano, E.; Hingst-Zaher, E. Shape variation in surface and cave populations of the armoured catfish Ancistrus (Siluriformes: Loricariidae) from the São Domingos karst area, Upper Tocantins River, Brazil. J. Fish Biol. 2006, 68, 414–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moller, D.; Parzefall, J. Single or multiple origin of the subterranean catfish, Ancistrus cryptophthalmus. What we can learn from molecular data. Brazil ISB 2001, 1, 38. [Google Scholar]
- Gallão, J.E.; Bichuette, M.E. A Lista de Fauna Ameaçada de Extinção e os entraves para a inclusão de espécies-o exemplo dos peixes troglóbios brasileiros. Nat. Conserv. 2012, 10, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, J.M.F.L. Biodiversidade e Sistemática Molecular de Phreatobiidae (Ostariophysi, Siluriformes)—Com Uma Proposta Sobre sua Posição Filogenética em Siluriformes e uma Discussão Sobre a Evolução do Hábito Subterrâneo. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ohara, W.M.; Costa, I.D.; Fonseca, M.L. Behaviour, feeding habits and ecology of the blind catfsh Phreatobius sanguijuela (Ostariophysi: Siluriformes). J. Fish Biol. 2016, 89, 1285–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, D.; Williams, P. Karst Hydrology and Geomorphology; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2007; 562p. [Google Scholar]
- Howarth, F.G. Ecoloy of cave arthropods. Ann. Rev. Entomol. 1983, 28, 365–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibert, J.; Stanford, J.A.; Dole-Olivier, M.-J.; Ward, J.V. Basic attributes of groundwater ecosystems and prospects for research. In Groundwater Ecology; Danielopol, D.L., Stanford, J.A., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1994; pp. 7–40. [Google Scholar]
- Rizzato, P.P.; Costa, E.P., Jr.; Trajano, E.; Bichuette, M.E. Trichomycterus dali: A new highly troglomorphic catfish (Silurifomes: Trichomycteridae), from Serra da Bodoquena, Mato Grosso do Sul State, Central Brazil. Neotrop. Ichthyol. 2011, 9, 477–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, L.; Bichuette, M.E. A new cave dwelling species of Ituglanis from heSão Domingos karst, Cenral Brazil (Siluriformes: Trichomycteridae). Ichhyol. Explor. Feshw. 2002, 13, 273–278. [Google Scholar]
- Shibatta, O.K.; Muriel-Cunha, J.; de Pinna, M.C.C. A new subterranean species of Phreatobius Goeldi, 1905 (Siluriformes, incertae sedis) from the Southwestern Amazon basin. Pap. Avulsos Zool. 2007, 47, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichel, M. Étude anatomique de Phreatobius cisternarum Goeldi, Silure aveugle do Brésil. Rev. Suisse Zool. 1927, 34, 28–401+6 plates. [Google Scholar]
- Sabino, J.; Trajano, E. A new species of blind armoured catfish, genus Ancistrus, from caves of Bodoquena region, Mato Grosso do Sul, southwestern Brazil (Siluriformes, Loricariidae, Ancistrinae). Rev. Fr. Aquariol. 1998, 24, 73–77. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann, B.L.; Campos-Filho, I.S.; Araujo, P.B. Integrative taxonomy reveals a new genus and new species of Philosciidae (Crustacea: Isopoda: Oniscidea) from the Neotropical region. Can. J. Zool. 2018, 96, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trajano, E.; Souza, A.M. The behaviour of Ancistrus cryptophthalmus, an armoured blind catfish from caves of Central Brazil, with notes on syntopic Trichomycterus sp. (Siluriformes: Loricariidae, Trichomycteridae). Mém. Biospéol. 1994, 21, 151–159. [Google Scholar]
- Bessa, E.; Trajano, E. Light reation and cryptobiotic habits in armoured catfishes, genus Ancistrus, from caves in central and northeastern Brazil (Siluriformes: Loricariidae). Mém. Biospéol. 2002, 28, 29–37. [Google Scholar]
- Mendes, I.S.; Prosdocimi, F.; Schomaker-Bastos, A.; Furtado, C.; Ferreira, R.L.; Pompeu, P.S.; Carvalho, D.C. On the evolutionary origin of Neotropical cavefish Ancistrus cryptophthalmus (Siluriformes, Loricariidae) based on the mitogenome and genetic structure of cave and surface populations. Hydrobiologia 2019, 842, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secutti, S.; Trajano, E. Reproductive behavior, development and eye regression in the cave armored catfish, Ancistrus cryptophthalmus Reis, 1987 (Siluriformes: Loricariidae), breed in laboratory. Neotrop. Ichthyol. 2009, 7, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genthner, C.; Ferrari, J.A.; Karmann, I. Identificação das áreas de recarga de fontes cársticas com o uso do traçador Rodamina FWT (Área Carbonática Lajeado—Bombas, Iporanga-SP). Rev. Inst. Geol. 2003, 24, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavan, C. Os peixes cegos das cavernas de Iporanga e a evolução. Bol. Fac. Fil. Ciênc. Let. 1945, 79, 9–104. [Google Scholar]
- Hoenen, S. Comparative field ecology and morphology of two populations of the troglobitic catfish Pimelodellla kronei (Siluriformes: Pimelodidae) from southeastern Brazil. Pap. Avulsos Zool. 1998, 40, 323–335. [Google Scholar]
- Trajano, E.; Bockmann, F.A. Evolution of ecology and behaviour in Brazilian cave Heptapterinae catfishes, based on cladistic analysis (Teleostei: Siluriformes). Mém. Biospéol. 1999, 26, 123–129. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, R.W.; Russell, W.H.; Elliott, W.R. Mexican eyeless characin fishes, genus Astyanax: Environment, distribution, and evolution. Spec. Publ. Mus. Tex. Tech. Univ. 1977, 12, 1–89. [Google Scholar]
- Trajano, E. Ecological classification of subterranean organisms. In Encyclopedia of Caves; White, W.B., Culver, D.C., Eds.; Academic Press: Waltham, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Trajano, E. Evolution of tropical troglobites: Applicability of the model of Quaternary climatic fluctuations. Mém. Biospéol. 1995, 22, 203–209. [Google Scholar]
- Buss, D.M.; Haselton, M.G.; Shackelford, T.K.; Bleske, A.L.; Wakefield, J.C. Adaptations, Exaptations, and Spandrels. Am. Psychol. 1998, 53, 533–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmann, I. Evolução e Dinâmica Atual do Sistema Cárstico do Alto Vale do Rio Ribeira de Iguape, Sudeste do Estado de São Paulo. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, CA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Bosák, P. Karst processes from the beginning to the end: How can they be dated¿. In Evolution of Kars: From Prekarst to Cessation; Gabrovšek, F., Ed.; Inštitut za raziskovanje krasa, ZRC SAZU, Zalošba: Postojna-Ljubljana, Slovenija, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Moreira, C.R.; Bichuette, M.E.; Oyakawa, O.T.; Pinna, M.C.C.; Trajano, E. Rediscovery and redescription of the unusual subterranean characiform Stygichthys typhlops, with notes on its life history. J. Fish Biol. 2010, 76, 1815–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallun-Filho, W.; Karmann, I.; Wang, X.; Edwards, R.L.; Cheng, H.; Asmeromd, Y.; Polyak, V.J. Neotectônica vs. clima na submersão de cavernas no carste da Serra da Bodoquena (MS). In XLIII Congresso Brasileiro de Geologia; Anais, ST06:AO-462: Aracaju, Brazil, 2006; p. 122. [Google Scholar]
- Fong, D.W. Intermittent pools at headwaters of subterranean drainage basins as sampling sites for epikarst fauna. In Epikarst; Jones, W.K., Culver, D.C., Herman, J.S., Eds.; Karst Waters Institute Special Publication: Chales Town, WV, USA, 2004; Volume 9, pp. 114–188. [Google Scholar]
- Trajano, E.; Moreira, C.S. Stygichthys typhlops Brittan & Böhlke, 1965 (Teleostei:Characiformes), a phreatobic fish from eastern Brazil: Comments on Sampaio et al. (2012). Speleobiol. Notes 2014, 6, 33–41. [Google Scholar]
- Passow, C.N.; Greenway, R.; Arias-Rodriguez, L.; Jeyasingh, P.D.; Tobler, M. Reduction of Energetic Demands through modification of body size and routine metabolic rates in extremophile fish. Physiol. Biochem. Zool. 2015, 88, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacioglu, O. Ecology of the hyporheic zone: A review. Cave Karst Sci. 2010, 36, 69–76. [Google Scholar]
- Moldovan, O.T.; Levei, E. Temporal variability of fauna and the importance of sampling frequency in the hyporheic zone. Hydrobiologia 2015, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Auler, A.S.; Edwards, R.L.; Cheng, H.; Cristalli, P.S.; Smart, P.L.; Richard, D.A.; Shen, C.-C. Wet periods in northeastern Brazil over the past 210 kyr linked to distant climate anomalies. Nature 2004, 432, 740–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bockmann, F.A.; Castro, R.M.C. The blind catfish from the caves of Chapada Diamantina, Bahia, Brazil (Siluriformes: Heptapteridae): Description, anatomy, phylogenetic relationships, natural history, and biogeography. Neotrop. Ichthyol. 2010, 8, 673–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, A.V.; Leal, L.R.B.; Gomes, D.F. Anfípode subterrâneo do gênero Spelaeogammarus como um indicador de conectividade em um aquífero cárstico da bacia do rio Salitre, centro norte do Estado da Bahia. In Proceedings of the Anais do XIX Congresso Brasileiro de Aguas Subterrâneas, Campinas, Brazil, 20–23 September 2016; Associação Brasileira de Águas Subterrâneas: São Paulo, Brazil, 2016. 11p. [Google Scholar]
- Bichuette, M.E. Distribuição, Biologia, Ecologia Populacional e Comportamento de Peixes Subterrâneos Gêneros Ituglanis (Siluriformes: Trichomycteridae) e Eigenmannia (Gymnotiformes: Sternopygidae) da Área Cárstica de São Domingos Nordeste de Goiás. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Hoorn, C.; Wesselingh, F.P.; ter Steege, H.; Bermudez, M.A.; Mora, A.; Sevink, J.; Sanmartín, I.; Sanchez-Meseguer, A.; Anderson, C.L.; Figueiredo, J.P.; et al. Amazonia Through Time: Andean Uplift, Climate Change, Landscape Evolution, and Biodiversity. Science 2010, 330, 927–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Species | Distribution—Karst Area | Habitat | Troglom. Degree |
|---|---|---|---|
| Order Siluriformes | |||
| HEPTAPTERIDAE | |||
| Pimelodella kronei Ribeiro 1907 [at least two divergent lineages—Pavan 1945, among others] | Alto Ribeira/SP | Lotic—Base-level streams | ++ |
| P. spelaea Trajano, Reis and Bichuette 2004 | São Domingos/GO | Lotic—Vadose tributary | + |
| Rhamdia enfurnada Bichuette and Trajano 2005 | Serra do Ramalho/BA | Lotic—Base-level stream | ++ |
| Rhamdia undesc. sp. (Gruta das Fadas) [Borghezan 2013] | Serra da Bodoquena/MS | Lotic—Base-level stream | ++ |
| Rhamdiopsis krugi Bockmann and Castro 2010 [two lineages—Bichuette et al. 2015)] | Chapada Diamantina/BA | Lentic—Upper phreatic zone | +++ |
| Rhamdiopsis undesc. sp. (Toca do Gonçalo) [Trajano and Bichuette 2010] | Campo Formoso/BA | Lentic—Upper phreatic zone * | ++++ |
| Rhamdiopsis undesc. sp. (Gruta do Salitre) [Trajano and Bichuette 2010] | Cordisburgo/MG | Base-level stream | + |
| TRICHOMYCTERIDAE | |||
| Trichomycterus dali Rizzato, Costa-Jr., Trajano and Bichuette 2011 [three lineages—Cordeiro 2014] | S. Bodoquena/MS | Upper and deep phreatic zones; vadose tributary | +++/++++ |
| T. rubbioli Bichuette and Rizzato 2012 | Serra do Ramalho/BA | Vadose tributary; phreatic | +++ |
| T. itacarambiensis Trajano and Pinna 1996 | Peruaçu/MG | Lotic—Base-level streams | ++ |
| Ituglanis bambui Bichuette and Trajano 2004 | São Domingos/GO | Vadose tributary | ++ |
| I. epikarsticus Bichuette and Trajano 2004 | Epikarst | ++ | |
| I. ramiroi Bichuette and Trajano 2004 | Vadose tributary/epikarst | ++ | |
| I. passensis Fernández and Bichuette 2002 | Base-level stream | ++ | |
| I. mambai Bichuette and Trajano 2008 | Mambaí/GO | Base-level streams | + |
| I. boticario Bichuette and Rizzato 2012 | + | ||
| Glaphyropoma spinosum Bichuette, Pinna and Trajano 2008 | Chapada Diamantina/BA—sandstones | Base-level streams | ++ |
| Copionodon sp. Gruna dos Torras [Bichuette et al. 2008] | + | ||
| LORICARIIDAE | |||
| Ancistrus formoso Sabino and Trajano 1997 | Serra da Bodoquena/MS | Flooded cave system | ++++ |
| Ancistrus sp. G. Fadas [Borghezan 2013] | Base-level stream | ++ | |
| A. cryptophthalmus Reis 1987 [2+ differentiated lineages—Reis et al 2006] | São Domingos/GO | Lotic—Base-level streams | ++ |
| Isbrueckerichthys alipionis from Santana Cave | Alto Ribeira/SP | Upper vadose tributary | - |
| CALLYCHTHYIDAE | |||
| Aspidoras albater cave form [Secutti et al. 2011] | Mambaí/GO | Base-level stream | + |
| PHREATOBIIDAE (sensu Cunha 2008) | |||
| Phreatobius cisternarum Goeldi 1904 | Amazonas River delta and Marajó Is. | Non-karst phreatic waters (accessible through artificial wells) | ++ |
| P. dracunculus Shibata, Muriel-Cunha and Pinna 2007 | Rio Branco drainage/RO | +++ | |
| P. sanguijuela Fernandéz, Saucedo, Carvajal-Vallejos and Schaeffer 2007 | Rio Guaporé drainage/RO (also in Bolivia) | ||
| Order Gymnotiformes | |||
| STERNOPYGIDAE | |||
| Eigenmannia vicentespelaea Triques 1996 | São Domingos/GO | Base-level stream | + |
| Order Characiformes | |||
| CHARACIDAE | |||
| Stygichthys typhlops Brittan and Böhlke 1965 | Jaíba/MG | Phreatic | ++++ |
| Species | Step 1 | Step 2 | Step 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rhamdiopsis krugi | Colonization of the hyporheic zone | Colonization of the subterranean habitat beneath the hyporheic zone | Genetic isolation | ------- |
| Rhamdiopsis sp. CF | Transition from upper to deep phreatic zone | |||
| Ituglanis bambui, I. epikarsticus, I. ramaroi | Colonization of epikarsts | Sink populations in vadose streams and the main river channel | ||
| I. passensis | Secondary adaptation to a lotic habitat due to the opening of large entrances | |||
| Phreatobius spp. | Colonization of sedimentary layers beneath the hyporheic zone | -------- |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trajano, E. Diversity of Brazilian Troglobitic Fishes: Models of Colonization and Differentiation in Subterranean Habitats. Diversity 2021, 13, 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13030106
Trajano E. Diversity of Brazilian Troglobitic Fishes: Models of Colonization and Differentiation in Subterranean Habitats. Diversity. 2021; 13(3):106. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13030106
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrajano, Eleonora. 2021. "Diversity of Brazilian Troglobitic Fishes: Models of Colonization and Differentiation in Subterranean Habitats" Diversity 13, no. 3: 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13030106
APA StyleTrajano, E. (2021). Diversity of Brazilian Troglobitic Fishes: Models of Colonization and Differentiation in Subterranean Habitats. Diversity, 13(3), 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13030106






