Abstract
One novel molecular emissive probe L has been synthesized by classical Schiff-base reaction between 1H-indazole-6-carboxaldehyde and tetraethylenepentamine. The structure of compound L was confirmed by melting point, elemental analysis, ESI-MS spectrometry and by IR and 13C-NMR and 1H-NMR spectroscopy.
Indazole ring systems have an interesting chemistry, which has been used in biology, catalysis, and medicinal chemistry [1]. Although rare in nature [2], indazoles exhibit a variety of biological activities such as HIV protease inhibition [3,4,5], antiarrhythmic and analgesic activities [6], antitumor activity [7,8], and antihypertensive properties [9]. Furthermore, antimicrobial and antineoplastic activities have also been shown to be associated with certain indazole derivatives [10].
As a part of our ongoing research into the design and synthesis of novel organic molecular probes, luminescent materials and MALDI-TOF-MS matrices [11,12,13,14], here we report the synthesis and characterization of a new Schiff-base compound L containing two indazole units linked by a flexible polyethylene bridged (See scheme 1).
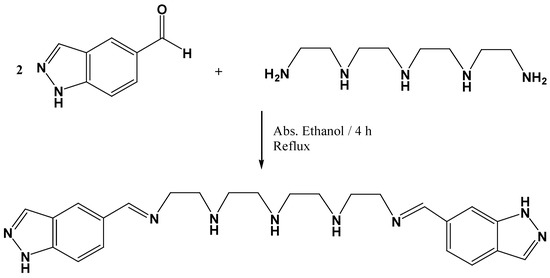
Scheme 1.
Schematic representation of compound L.
Experimental
A solution of 1H-indazole-6-carboxaldehyde (0.254 g, 1.718 mmol) in absolute ethanol (10 mL) was added dropwise to a refluxing solution of tetraethylenepentamine (0.162 g, 0.859 mmol) in the same solvent (30 mL) (See scheme 1). The resulting solution was gently refluxed with magnetic stirring for ca. 4 h. The colour changed from yellow to brown. After that time, the mixture was allowed to cool to room temperature and a brown powder precipitate was formed; this was then filtered off, washed with cold absolute ethanol and cold diethyl ether and dried under vacuum. The resulting compound was characterized as L follow purification by column chromatography.
Melting point: 163–165 °C.
Yield: 382 mg (L) (93%).
ESI-MS: m/z (rel. int%): 446.27 (100) ([L+H]+.
1H-NMR (CDCl3) (L): δ = 12.1 (s, 2H, N–H); 8.4 (s, 2H, N=C–H); 8.2–7.0 (m, 6H, C-Har); 3.9–2.1 (m, 16H, CH2); 1.5 (s, 3H, NH) ppm.
13C-NMR (CDCl3) (L): δ = 160.5; 150.3; 147.2; 133.6; 131.2; 127.9; 126.1; 125.0; 124.2; 119.7; 112.3; 110.4; 56.2; 50.6; 49.8.
IR (cm−1) (L): 3051 (C–H, Ar), 1638 (C=N, Imine), 1618, 1593, 1562 and 1509 (C=C, Ar).
Elemental analysis: Calcd for C24H37N9O3: C, 57.70; H, 7.45; N, 25.25. Found (L): C, 58.00; H, 7.15; N, 25.00.
Uv-vis (CHCl3), [L] = 1.00 × 10−5 M, λmax 275 and 324 nm.
Fluorescence Emission (CHCl3); [L] = 1.00 × 10−5): λmax 427 nm.
Supplementary materials
Supplementary File 1Supplementary File 2Supplementary File 3Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Xunta de Galicia (Spain) for projects 09CSA043383PR and 10CSA383009PR (Biomedicine) and to the Scientific Association ProteoMass for financial support. C.N. thanks the Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia/FEDER (Portugal/EU) programme postdoctoral contract SFRH/BPD/65367/2009. J.F.L. thanks Xunta de Galicia (Spain) for a research contract by project 09CSA043383PR in Biomedicine. J.L.C. and C.L. thank Xunta de Galicia for the Isidro Parga Pondal Research program.
References and Notes
- Sather, A.C.; Berryman, O.B.; Rebek, J., Jr. Synthesis of Fused Indazole Ring Systems and Application to Nigeglanine Hydrobromide. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 1600–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, Z.; Ferreira, D.; Carvalho, P.; Avery, M.A.; Khan, I.A. Nigellidine-4-O-sulfite, the First Sulfated Indazole-Type Alkaloid from the Seeds of Nigella sativa. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1111–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, W.; Pelletier, J.C.; Hodge, C.N. Tricyclic ureas: A new class of HIV-1 protease inhibitor. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1998, 8, 3615–3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.; Rodgers, J.D.; McHugh, R.J., Jr.; Johnson, B.L.; Cordova, B.C.; Klaba, R.M.; Bacheler, L.T.; Erickson-Viitanen, S.; Ko, S.S. Unsymmetrical cyclic ureas as HIV-1 protease inhibitors: Novel biaryl indazoles as P2/P2′ substituents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1999, 9, 3217–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.-H.; Teleha, C.A.; Yan, J.-S.; Rodgers, J.D.; Nugiel, D.A. Efficient Synthesis of 5-(Bromomethyl)- and 5-(Aminomethyl)-1-THP-Indazole. J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 5627–5629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosti, L.; Menozzi, G.; Fossa, P.; Filippelli, W.; Gessi, S.; Rinaldi, B.; Falcone, G. Synthesis and preliminary biological evaluation of novel N-substituted 1-amino-3-[1-methyl(phenyl)-1H-indazol-4-yloxy]-propan-2-ols interesting as potential antiarrhythmic, local anaesthetic and analgesic agents. Arzneimittelforschung 2000, 50, 963–972. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jakupec, M.A.; Reisner, E.; Eichinger, A.; Pongratz, M.; Arion, V.B.; Galanski, M.; Hartinger, C.G.; Keppler, B.K. Redox-Active Antineoplastic Ruthenium Complexes with Indazole: Correlation of in Vitro Potency and Reduction Potential. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 2831–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Showalter, H.D.H.; Angelo, M.M.; Berman, E.M.; Kanter, G.D.; Ortwine, D.F.; Ross-Kesten, S.G.; Sercel, A.D.; Turner, W.R.; Werbel, L.M.; Worth, D.F.; et al. Benzothiopyranoindazoles, a New Class of Chromophore Modified Anthracenedione Anticancer Agents. Synthesis and Activity against Murine Leukemias. J. Med. Chem. 1988, 31, 1527–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, K.B.; Cui, H.; Dowdell, S.E.; Gaitanopoulos, D.E.; Ivy, R.L.; Sehon, C.A.; Stavenger, R.A.; Wang, G.Z.; Viet, A.Q.; Xu, W.; et al. Development of Dihydropyridone Indazole Amides as Selective Rho-Kinase Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raffa, D.; Daidone, G.; Maggio, B.; Schillaci, D.; Plescia, F. Synthesis and Antiproliferative Activity of Novel 3-(Indazol-3-yl)-quinazolin-4(3H)-one and 3-(Indazol-3-yl)-benzotriazin-4(3H)-one Derivatives. Arch. Pharm. Pharm. Med. Chem. 1999, 332, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodeiro, C.; Pina, F. Luminescent and chromogenic molecular probes based on polyamines and related compounds. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2009, 253, 1353–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodeiro, C.; Capelo, J.L.; Mejuto, J.C.; Oliveira, E.; Santos, H.M.; Pedras, B.; Nuñez, C. Light and colour as analytical detection tools: A journey into the periodic table using polyamines to bio-inspired systems as chemosensors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 2948–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastista, R.M.F.; Oliveira, E.; Costa, S.P.G.; Lodeiro, C.; Raposo, M.M.M. Imidazo-benzo-15-crwon-5 ethers bearing arylthienyl and bithienyl moieitis as novel fluorescent chemosensor for Pd(II) and Cu(II). Tetrahedron 2011, 67, 7106–7113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Lodeiro, J.; Nuñez, C.; Carreira, R.; Santos, H.M.; López, C.S.; Mejuto, J.C.; Capelo, J.L.; Lodeiro, C. Novel versatile imine-enamine chemosensor based on 6-nitro-4-oxo-4H-chromene for ion detection in solution, solid and gas phase: Synthesis, emission, computational and MALDI-TOF-MS studies. Tetrahedron 2011, 67, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).