Abstract
The title compound, 3-chloro-N'-(2-hydroxy-4-pentadecylbenzylidene)benzo[b]thiophene-2-carbohydrazide has been synthesized by reaction of 2-hydroxy-4-pentadecylbenzaldehyde with 3-chloro-1-benzo[b]thiophene-2-carboxylic acid hydrazide in the presence of acetic acid in ethanol. The structure of this new compound was confirmed by elemental analysis, IR, 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR and mass spectral analysis.
Heterocyclic compounds containing nitrogen and sulphur exhibit a wide variety of biological activities such as antibacterial [1], antifungal [2], antitumor [3], or anti-HIV activity [4]. The thiophene ring dramatically increases the diversity of certain biological properties such as antibacterial [5], antiviral [6], and antitubercular [7] activities. In this paper, we report the synthesis of a novel compound by condensation of 2-hydroxy-4-pentadecylbenzaldehyde and 3-chloro-1-benzo[b]thiophene-2-carboxylic acid hydrazide.
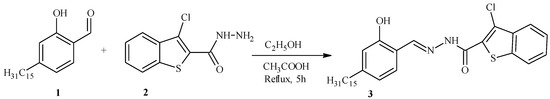
Scheme 1.
Synthesis of 3-chloro-N'-(2-hydroxy-4-pentadecylbenzylidene)benzo[b]thiophene-2-carbohydrazide.
Experimental
Melting points were determined in open capillary and are uncorrected. FT-IR spectra were recorded on a Nicolet Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrophotometer: Impact 410 (Nicolet Instrument Technologies, Inc. WI, USA). 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR were obtained in DMSO-d6 at 400 MHz for 1H nuclei and 100 MHz for 13C nuclei (Varian Company, USA). All chemical shifts were reported in parts per million (ppm) using residual proton or carbon signal in deuterated solvents as internal references. Mass spectra were obtained using matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF) by using dithranol as a matrix. Elemental analysis (C, H, N and S) was performed on a Perkin Elmer 2400 analyzer. The purity of the compound was checked by TLC on silica gel and further purification was performed through column chromatography (silica gel, 60–120 mesh).
A mixture of 2-hydroxy-4-pentadecylbenzaldehyde 1 (1.10 g, 0.003 mol), 3-chloro-1-benzothiophene-2-carboxylic acid hydrazide 2 (0.75 g, 0.003 mol) in the presence of acetic acid in absolute ethanol (30 mL) was refluxed for 5 h. The completion of the reaction was monitored by TLC. The reaction mixture was allowed to cool down to room temperature, and then poured into crushed ice. The precipitate was filtered, dried and recrystallized from absolute ethanol. The resulting solid was further purified by column chromatography [silica, petroleum ether/ethyl acetate (80:20)], leading to pure compound 3 as light yellowish solid.
Yield: 0.95 g (86%).
Melting point: 281–282 °C.
MS: m/z = 540.98 (M++1).
IR (KBr): νmax (cm−1): 3280 (NH), 1650 (C=O).
1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ ppm: 12.13 (s, 1H, OH), 10.96 (s, 1H, NH), 8.62–6.61 (m, 7H, Ar-CH and CH=N), 2.51 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H, Ar-CH2), 1.55–1.01 (m, 26H, (CH2)13), 0.85 (t, J = 6.8 Hz, 3H, CH3).
13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ ppm: 161.8, 157.4, 156.7, 149.4, 147.0, 137.5, 136.8, 135.7, 129.2, 127.7, 126.1, 123.5, 122.6, 119.8, 116.1, 116.0, 35.1, 31.2, 30.3, 28.9, 28.9, 28.9, 28.7, 28.6, 28.5, 22.0, 13.9.
Elemental analysis: Calculated for C31H41ClN2O2S: C, 68.80%; H, 7.64%; N, 5.18%; S, 5.92%; found: C, 69.09%; H, 8.07%; N, 5.39%; S, 6.20%.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary File 1Supplementary File 2Supplementary File 3Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Higher Education Research Promotion and National Research University Project of Thailand, Office of the Higher Education Commission (Project No: AM1079B). The post doctoral fellowship grant from the Ratchadapisakesompote Endownment Fund, Chulalongkorn University (to G.N.) was gratefully acknowledged.
References
- Przybylski, P.; Pyta, K.; Stefanska, J.; Ratajczak-Sitarz, M.; Katrusiak, A.; Huczynski, A.; Brzezinski, B. Synthesis, crystal structures and antibacterial activity studies of aza-derivatives of phytoalexin from cotton plant–gossypol. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 4393–4403. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ramesh, R.; Maheswaran, S. Synthesis, spectra, dioxygen affinity and antifungal activity of Ru(III) Schiff base complexes. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2003, 96, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Silveira, V.C.; Luz, J.S.; Oliveira, C.C.; Graziani, I.; Ciriolo, M.R.; Ferreira, A.M.C. Double-strand DNA cleavage induced by oxindole-Schiff base copper(II) complexes with potential antitumor activity. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2008, 102, 1090–1103. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pandeya, S.N.; Sriram, D.; Nath, G.; Clercq, E. Synthesis, antibacterial, antifungal and anti-HIV activities of Schiff and Mannich bases derived from isatin derivatives and N-[4-(4′-chlorophenyl)thiazol-2-yl]thiosemicarbazide. Eur. J. Pharma. Sci. 1999, 9, 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Holla, B.S.; Malini, K.V.; Rao, V.S.; Sarojini, B.K.; Kumari, N.S. Synthesis of some new 2,4-disubstituted thiazoles as possible antibacterial and anti-inflammatory agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 38, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sabbagh, O.I.; Baraka, M.M.; Ibrahim, S.M.; Pannecouque, C.; Andrei, Graciela; Snoeck, R.; Balzarini, J.; Rashad, A.A. Synthesis and antiviral activity of new pyrazole and thiazole derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 3746–3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallikarjuna, B.P.; Sastry, B.S.; Kumar, G.V.S.; Rajendraprasad, Y.; Chandrashekar, S.M.; Sathisha, K. Synthesis of new 4-isopropylthiazole hydrazide analogs and some derived clubbed triazole, oxadiazole ring systems–A novel class of potential antibacterial, antifungal and antitubercular agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 4739–4746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).