Abstract
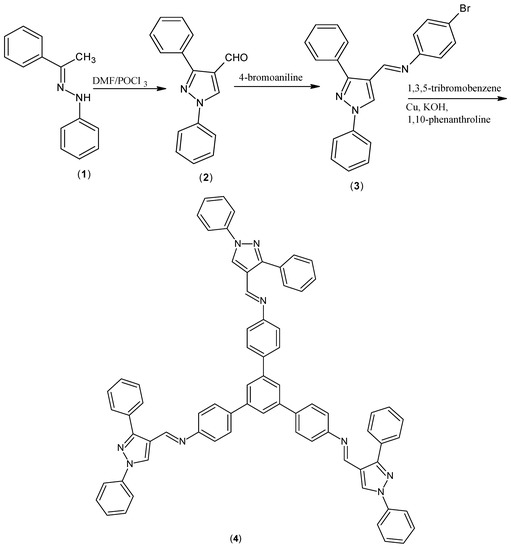
1,3,5-Tris{[N-(1,3-diphenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)methylene]-4-aminophenyl}-benzene was synthesised from N-(4-bromophenyl)-N-[(1,3-diphenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-methylene]amine and 1,3,5-tribromobenzene by an Ullman coupling reaction. The synthesized compound was charecterised by NMR, IR, MS and elemental analysis.
The title compound, 1,3,5-tris{[N-(1,3-diphenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)methylene]-4-aminophenyl}-benzene, is a highly conjugated pyrazole derivative. Due to this extensive conjugation, the above compound can be potentially used as hole transporting material in photoelectric conversion devices such as solar cells. Usually used hole transporting materials are arylamines [1].
1,3-Diphenyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxaldehyde (2) was prepared according to the known procedure [2]. The yield of the product was 72% and its m.p. was found to be 135 °C. The aldimine derivative, N-(4-bromophenyl)-N-[(1,3-diphenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)methylene]amine (3) [2,3] was obtained from 1,3-diphenyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carbox-aldehyde and 4-bromoaniline and it was recrystallised from ethyl acetate. The yield of the product was 60% with m.p. 127 °C. The aldimine derivative (3) (0.3 mmol) and 1,3,5-tribromobenzene (0.1 mmol) were dissolved in DMF. To this solution, 0.1 g of electrolytic copper, 0.01 g of KOH and 0.001 g of 1,10-phenanthroline were added and the reaction mixture was heated for 15 h at 140 °C to get the title compound (4). The hot solution was filtered to remove the copper compounds and the base [4,5]. The solvent DMF was evaporated under vacuum and the solid was triturated with ethyl acetate, filtered and further purified by chromatography on silica gel using ethyl acetate-hexane (1:3) as eluent. According to a theoretical calculation, the formed compound may be the E isomer (least steric hindrance). Furthermore, the 1H NMR spectral data indicate that there is only one product formed.
Yield: 60%.
M.p. 149 °C.
IR (KBr) cm-1: 3019.2 (Ar C-Hstr), 1026.9 (Ar C-Hdef), 1422.3 (Ar C=Cstr), 1599.7 (C=Nstr), 1338.4 (Ph-Nstr).
1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm: 10.07 (s, 3H, pyrazole 5-H), 8.56 (s, 3H, HC=N), 7.85-7.80 (m, 12H, N-Ph-), 7.55-7.35 (m, 30 H, Ph), 7.27 (s, 3H, Ph).
13C NMR (75 MHz, DMSO-d6): 163.7, 158.0, 147.9, 137.6, 136.5, 135.0, 129.1, 129.0, 128.7, 128.5, 128.1, 127.0, 126.0, 125.2, 122.5, 118.8, 108, 99.7.
MS: m/z (ES), 1042 [(M+1)+].
Elemental analysis calculated for C72H51N9 (1042.24): C, 82.97%; H, 4.93%; N, 12.10%. Found: C, 83.00%; H, 4.90%; N, 12.10%.
Supplementary materials
Supplementary File 1Supplementary File 2Supplementary File 3Acknowledgments
Thanks are due to NMR research centre, IIT, Chennai for recording the NMR spectra.
References
- Thelakkat, M.; Schmitz, C.; Hohle, C.; Strohriegl, P.; Schmidt, H.-W.; Hofmann, U.; Schloter, S.; Haarer, D. Novel functional materials based on triarylamines-synthesis and application in electroluminescent devices and photorefractive systems. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 1999, 1, 1693–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohite, S.K.; Magdum, C.S. Novel synthesis of functionally substituted N-{[3-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl]methylene}anilines and their pharmacological screening. Int. J. Chem. Sci. 2006, 4, 980–988. [Google Scholar]
- Rathelot, P.; Azas, N.; El-Kashef, H.; Delmas, F.; Di Giorgio, C.; Timon-David, P.; Maldonado, J.; Vanelle, P. 1,3-Diphenylpyrazoles: Synthesis and antiparasitic activities of azomethine derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 37, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodbrand, H.B.; Hu, N.-X. Ligand-accelerated catalysis of the Ullmann condensation: Application to hole conducting triarylamines. J. Org. Chem. 1999, 64, 670–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, D.; Liebeskind, L.S. Ambient temperature, Ullmann-like reductive coupling of aryl, heteroaryl, and alkenyl halides. J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 2312–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2009 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).