Pancreatic Cancer and Diabetes: Insights, Hypotheses, and Next Steps
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Epidemiology, Clinicopathologic Risk, Perioperative Therapy, and Metabolic Surveillance in PDAC
2.1. Overview
2.2. Recent Trends in Epidemiology
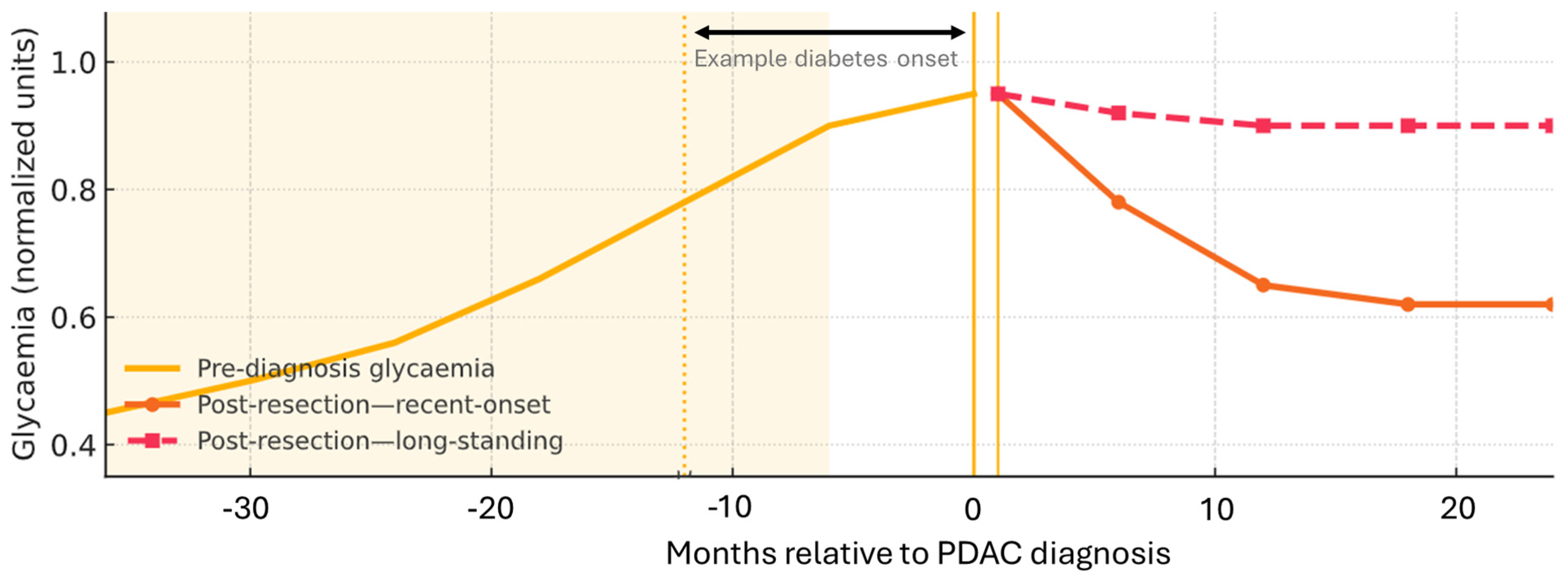
- Diabetes diagnosed within the prior 6–36 months (with highest risk within the first 12 months).
- Unintentional weight loss ≥5% over 6–12 months.
- Rapid HbA1c rise (e.g., ≥1.5% within 3–6 months) or early insulin/therapy escalation.
- Glycaemic deterioration out of proportion to lifestyle changes.
- Action: When ≥2 features cluster, consider pancreatic imaging ±CA19-9, recognising CA19-9 limitations (e.g., cholestasis; Lewis-antigen-negative) (summarises Section 2.2 and Section 2.3).
2.3. The Challenges in Phenotyping PDAC-DM in the Clinical Setting
2.4. Pancreatic Cancer Margins and Pathology Reporting
2.5. Perineural and Intraneural Invasion (PNI/INI)
2.6. Adjuvant Systemic Therapy After Resection
2.7. Neoadjuvant and Perioperative Approaches
2.8. Diabetes Dynamics and Changes After Resection
2.9. Deterioration and Recurrence
2.10. Therapeutics: Metformin, Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists (GLP-1 RAs), and Sodium–Glucose Cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors
3. Mechanisms Linking PDAC to Dysglycaemia
3.1. Overview and Scope
3.2. Tumour-Intrinsic Programmes and Metabolic Rewiring
3.3. Systemic Insulin Resistance: Cytokines and EVs
3.3.1. Cytokines
3.3.2. Extracellular Vesicles
3.3.3. β-Cell Stress and Identity
3.3.4. Modulating Systems (Incretins, Autonomic Input, Cachexia)
3.4. Fibrosis and a Model for Insulin Dysfunction
3.4.1. Matrix and Perfusion
3.4.2. Mechanotransduction
3.4.3. Immune–Matrix Crosstalk
3.4.4. Islet-Adjacent Pathology
4. Toward a Hypothesis-Driven Model of PDAC-Associated Dysglycaemia: Islet, Vascular, and ECM Mechanisms
4.1. Overview
4.2. β-Cell Stimulus Secretion and Identity
4.3. α-Cell Disinhibition and Paracrine Control
4.4. δ-Cell Somatostatin Gating
4.5. Microvasculature, Basement Membrane, and ECM Mechanics
5. Gaps/Limitations and Future Directions
5.1. Gaps and Limitations
5.2. Future Directions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AKT | Protein kinase B |
| AMP | Adenosine monophosphate |
| ATP | Adenosine triphosphate |
| ATP/ADP | ATP to ADP ratio |
| CA19-9 | Carbohydrate antigen 19-9 |
| CAF | Cancer-associated fibroblast |
| CD8 | Cluster of Differentiation 8 (cytotoxic T cell) |
| CDKN2A | Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| CONKO | Charité Onkologie trial group (e.g., CONKO-001) |
| CXCL12 | C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 12 |
| CXCR4 | C-X-C chemokine receptor 4 |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| EHR | Electronic health record |
| ER | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| ERK/MAPK | Extracellular signal-regulated kinase/mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway |
| ESPAC | European Study Group for Pancreatic Cancer |
| EV | Extracellular vesicle |
| FAK | Focal adhesion kinase |
| FOLFIRINOX | FOLFIRINOX regimen variant (oxaliplatin, irinotecan, leucovorin, 5-FU) |
| FU | Fluorouracil (5-FU) |
| GABA | Gamma-aminobutyric acid |
| GCG | Glucagon (gene/protein) |
| GIP | Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide |
| GLP-1 RA | Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist |
| HR | Hazard ratio |
| IL | Interleukin |
| IL-1 | Interleukin-1 |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| INI | Intraneural invasion |
| INS | Insulin |
| IRS | Insulin receptor substrate |
| JAK | Janus kinase |
| KATP | Potassium ATP |
| KRAS | KRAS proto-oncogene, GTPase |
| MAFA | Beta-cell transcription factor MAFA |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| NADPH | Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (reduced) |
| NKX6 | NKX6 homeobox (e.g., NKX6.1) transcription factor |
| NOD | New-onset diabetes |
| PDAC | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma |
| PDX1 | Pancreatic and duodenal homeobox 1 |
| PEGPH20 | Pegylated recombinant human hyaluronidase PH20 |
| PH20 | Hyaluronidase PH20 |
| PI3K | Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase |
| PIEZO1 | Piezo-type mechanosensitive ion channel component 1 |
| PNI | Perineural invasion |
| PNI/INI | Perineural/intraneural invasion |
| SGLT2 | Sodium–-glucose cotransporter 2 |
| SMAD4 | Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 4 |
| SNARE | Soluble NSF attachment protein receptor |
| SOCS | Suppressor of cytokine signallingubstrate |
| SST | Somatostatin |
| SSTR2 | Somatostatin receptor 2 |
| STAT3 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 |
| TAZ | Transcriptional co-activator with PDZ-binding motif |
| TEAD | TEA domain family member |
| TGF | Transforming growth factor |
| TNFTGF | Tumour necrosis factorTransforming growth factor |
| TP53TNF | Tumour protein p53Tumour necrosis factor |
| UCN3-CRHR2TP53 | Urocortin-3 and corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor-2 axisTumour protein p53 |
| UPRUCN3-CRHR2 | Unfolded protein responseUrocortin-3 and corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor-2 axis |
| YAPUPR | Yes-associated proteinUnfolded protein response |
| YAP | Yes-associated protein |
References
- Gallo, M.; Gentile, L.; Arvat, E.; Bertetto, O.; Clemente, G. Diabetology and oncology meet in a network model: Union is strength. Acta Diabetol. 2016, 53, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodmansey, C.; McGovern, A.P.; McCullough, K.A.; Whyte, M.B.; Munro, N.M.; Correa, A.C.; Gatenby, P.A.C.; Jones, S.A.; de Lusignan, S. Incidence, Demographics, and Clinical Characteristics of Diabetes of the Exocrine Pancreas (Type 3c): A Retrospective Cohort Study. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 1486–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, P.A.; Bellin, M.D.; Andersen, D.K.; Bradley, D.; Cruz-Monserrate, Z.; Forsmark, C.E.; Goodarzi, M.O.; Habtezion, A.; Korc, M.; Kudva, Y.C.; et al. Type 3c (pancreatogenic) diabetes mellitus secondary to chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 1, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewald, N.; Bretzel, R.G. Diabetes mellitus secondary to pancreatic diseases (Type 3c)—Are we neglecting an important disease? Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2013, 24, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrov, M.S. Diabetes of the exocrine pancreas: American Diabetes Association-compliant lexicon. Pancreatology 2017, 17, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannala, R.; Leirness, J.B.; Bamlet, W.R.; Basu, A.; Petersen, G.M.; Chari, S.T. Prevalence and Clinical Profile of Pancreatic Cancer–Associated Diabetes Mellitus. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 981–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sah, R.P.; Nagpal, S.J.S.; Mukhopadhyay, D.; Chari, S.T. New insights into pancreatic cancer-induced paraneoplastic diabetes. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, F.G.S.; Li, Y.; Wang, F.; Bellin, M.D.; Brand, R.; Cusi, K.; Fisher, W.; Kudva, Y.C.; Park, W.G.; Saeed, Z.I.; et al. Pancreatic cancer-related diabetes and type 2 diabetes differ in multiple aspects of glucose homeostasis. Diabetologia 2025, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ose, D.J.; Viskochil, R.; Holowatyj, A.N.; Larson, M.; Wilson, D.; Dunson, W.A.; Deshmukh, V.G.; Butcher, J.R.; Taylor, B.R.; Svoboda, K.; et al. Understanding the Prevalence of Prediabetes and Diabetes in Patients with Cancer in Clinical Practice: A Real-World Cohort Study. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2021, 19, 709–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setiawan, V.W.; Stram, D.O.; Porcel, J.; Chari, S.T.; Maskarinec, G.; Le Marchand, L.; Wilkens, L.R.; Haiman, C.A.; Pandol, S.J.; Monroe, K.R. Pancreatic Cancer Following Incident Diabetes in African Americans and Latinos: The Multiethnic Cohort. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2019, 111, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batabyal, P.; Vander Hoorn, S.; Christophi, C.; Nikfarjam, M. Association of Diabetes Mellitus and Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: A Meta-Analysis of 88 Studies. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 21, 2453–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brewer, M.J.; Doucette, J.T.; Bar-Mashiah, A.; Glickman, J.W.; Kessel, E.; Aronson, A.; Lucas, A.L. Glycemic Changes and Weight Loss Precede Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma by up to 3 Years in a Diverse Population. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, 1105–1111.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boursi, B.; Finkelman, B.; Giantonio, B.J.; Haynes, K.; Rustgi, A.K.; Rhim, A.D.; Mamtani, R.; Yang, Y.X. A Clinical Prediction Model to Assess Risk for Pancreatic Cancer Among Patients with New-Onset Diabetes. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 840–850.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, R.C.; Shim, B.; Pandya, D.; Krebs, T.; Ma, C.; Labow, D.; Denowitz, J.; Anand, N.; Krumholtz, P.; Sullivan, K.; et al. Pancreatic Cancer Screening in New-onset and Deteriorating Diabetes: Preliminary Results from the PANDOME Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2025, dgaf319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, D.-H.; Han, K.-D.; Park, C.-Y. The Incremental Risk of Pancreatic Cancer According to Fasting Glucose Levels: Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 4594–4599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, S.; Brown, K.; Miksza, J.K.; Howells, L.; Morrison, A.; Issa, E.; Yates, T.; Khunti, K.; Davies, M.J.; Zaccardi, F. Association of Type 2 Diabetes with Cancer: A Meta-analysis with Bias Analysis for Unmeasured Confounding in 151 Cohorts Comprising 32 Million People. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 2313–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Kar, S.; Carter, P.; Vithayathil, M.; Mason, A.M.; Burgess, S.; Larsson, S.C. Is Type 2 Diabetes Causally Associated With Cancer Risk? Evidence from a Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. Diabetes 2020, 69, 1588–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Babic, A.; Khalaf, N.; Nowak, J.A.; Brais, L.K.; Rubinson, D.A.; Ng, K.; Aguirre, A.J.; Pandharipande, P.V.; Fuchs, C.S.; et al. Diabetes, Weight Change, and Pancreatic Cancer Risk. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, e202948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Kartsonaki, C.; Guo, Y.; Bragg, F.; Yang, L.; Bian, Z.; Chen, Y.; Iona, A.; Millwood, I.Y.; Lv, J.; et al. Diabetes, plasma glucose and incidence of pancreatic cancer: A prospective study of 0.5 million Chinese adults and a meta-analysis of 22 cohort studies. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 140, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben, Q.; Xu, M.; Ning, X.; Liu, J.; Hong, S.; Huang, W.; Zhang, H.; Li, Z. Diabetes mellitus and risk of pancreatic cancer: A meta-analysis of cohort studies. Eur. J. Cancer 2011, 47, 1928–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milani, I.; Guarisco, G.; Chinucci, M.; Gaita, C.; Leonetti, F.; Capoccia, D. The Challenge of Type 3c Diabetes: From Accurate Diagnosis to Effective Treatment. JCEM Case Rep. 2025, 3, luaf109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, I.; Kleeff, J.; Bergmann, F.; Reiser, C.; Herpel, E.; Friess, H.; Schirmacher, P.; Büchler, M.W. Most Pancreatic Cancer Resections are R1 Resections. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2008, 15, 1651–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrasegaram, M.D.; Goldstein, D.; Simes, J.; Gebski, V.; Kench, J.G.; Gill, A.J.; Samra, J.S.; Merrett, N.D.; Richardson, A.J.; Barbour, A.P. Meta-analysis of radical resection rates and margin assessment in pancreatic cancer. Br. J. Surg. 2015, 102, 1459–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amit, M.; Na’ara, S.; Gil, Z. Mechanisms of cancer dissemination along nerves. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felsenstein, M.; Lindhammer, F.; Feist, M.; Hillebrandt, K.H.; Timmermann, L.; Benzing, C.; Globke, B.; Zocholl, D.; Hu, M.; Fehrenbach, U.; et al. Perineural Invasion in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (PDAC): A Saboteur of Curative Intended Therapies? JCM 2022, 11, 2367, Correction in JCM 2023, 12, 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12216947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovecek, M.; Dirimtekin, E.; Garajová, I.; Gasparini, G.; Crippa, S.; Giovannetti, E.; Sochorova, D.; Reyes, C.M.; Demir, I.E.; Uysal-Onganer, P.; et al. Perineural Invasion in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: Recapitulating Its Importance and Defining Future Directions. UEG J. 2025, ueg2.70118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Diaz, R.; Abdulreda, M.H.; Formoso, A.L.; Gans, I.; Ricordi, C.; Berggren, P.-O.; Caicedo, A. Innervation Patterns of Autonomic Axons in the Human Endocrine Pancreas. Cell Metab. 2011, 14, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampton, R.F.; Jimenez-Gonzalez, M.; Stanley, S.A. Unravelling innervation of pancreatic islets. Diabetologia 2022, 65, 1069–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oettle, H.; Neuhaus, P.; Hochhaus, A.; Hartmann, J.T.; Gellert, K.; Ridwelski, K.; Niedergethmann, M.; Zülke, C.; Fahlke, J.; Arning, M.B.; et al. Adjuvant Chemotherapy with Gemcitabine and Long-term Outcomes Among Patients with Resected Pancreatic Cancer: The CONKO-001 Randomized Trial. JAMA 2013, 310, 1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neoptolemos, J.P.; Palmer, D.H.; Ghaneh, P.; Psarelli, E.E.; Valle, J.W.; Halloran, C.M.; Faluyi, O.; O’Reilly, D.A.; Cunningham, D.; Wadsley, J.; et al. Comparison of adjuvant gemcitabine and capecitabine with gemcitabine monotherapy in patients with resected pancreatic cancer (ESPAC-4): A multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 1011–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conroy, T.; Hammel, P.; Hebbar, M.; Ben Abdelghani, M.; Wei, A.C.; Raoul, J.-L.; Choné, L.; Francois, E.; Artru, P.; Biagi, J.J.; et al. FOLFIRINOX or Gemcitabine as Adjuvant Therapy for Pancreatic Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2395–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nosrati, J.D.; Sidiqi, B.U.; Chitti, B.; Riegel, A.C.; Herman, J.M.; Tchelebi, L.T. Borderline resectable pancreatic cancer: A review of recent radiation therapy literature and clinical practice. Dig. Med. Res. 2023, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teoh, S.; Ooms, A.; George, B.; Owens, R.; Chu, K.-Y.; Drabble, J.; Robinson, M.; Parkes, M.J.; Swan, L.; Griffiths, L.; et al. Evaluation of hypofractionated adaptive radiotherapy using the MR Linac in localised pancreatic cancer: Protocol summary of the Emerald-Pancreas phase 1/expansion study located at Oxford University Hospital, UK. BMJ Open 2023, 13, e068906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleeff, J.; Costello, E.; Jackson, R.; Halloran, C.; Greenhalf, W.; Ghaneh, P.; Lamb, R.F.; Lerch, M.M.; Mayerle, J.; Palmer, D.; et al. The impact of diabetes mellitus on survival following resection and adjuvant chemotherapy for pancreatic cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 115, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groot, V.P.; Rezaee, N.; Wu, W.; Cameron, J.L.; Fishman, E.K.; Hruban, R.H.; Weiss, M.J.; Zheng, L.; Wolfgang, C.L.; He, J. Patterns, Timing, and Predictors of Recurrence Following Pancreatectomy for Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Ann. Surg. 2018, 267, 936–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizian, A.; Rühlmann, F.; Krause, T.; Bernhardt, M.; Jo, P.; König, A.; Kleiß, M.; Leha, A.; Ghadimi, M.; Gaedcke, J. CA19-9 for detecting recurrence of pancreatic cancer. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nong, M.Z.; Dove, D.; Fischer, D.A.; Hourdequin, K.C.; Ripple, G.H.; Amin, M.A.; McGrath, E.B.; Zaki, B.I.; Smith, K.D.; Brooks, G.A. Surveillance with Serial Imaging and CA 19-9 Tumor Marker Testing After Resection of Pancreatic Cancer: A Single-Center Retrospective Study. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 47, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Z.; Kan, H.; Sun, Z.; Xing, J.; Cheng, Y.; Bai, C. CA19-9 elevation as an indication to start salvage treatment in surveillance after pancreatic cancer resection. Pancreatology 2019, 19, 302–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoub, M.; Faris, C.; Juranovic, T.; Chela, H.; Daglilar, E. The Use of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Does Not Increase the Risk of Pancreatic Cancer: A U.S.-Based Cohort Study. Cancers 2024, 16, 1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Fan, H.-D.; Gong, J.-P.; Mao, Q.-S. The relationship between the use of metformin and the risk of pancreatic cancer in patients with diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2023, 23, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Li, T.; Liu, Z.; Gou, S.; Wang, C. The effect of metformin on survival of patients with pancreatic cancer: A meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dankner, R.; Murad, H.; Agay, N.; Olmer, L.; Freedman, L.S. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists and Pancreatic Cancer Risk in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e2350408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, L.C.; Falcetta, M.R.; Rados, D.V.; Leitão, C.B.; Gross, J.L. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and pancreatic cancer: A meta-analysis with trial sequential analysis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelniker, T.A.; Wiviott, S.D.; Raz, I.; Im, K.; Goodrich, E.L.; Bonaca, M.P.; Mosenzon, O.; Kato, E.T.; Cahn, A.; Furtado, R.H.M.; et al. SGLT2 inhibitors for primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cardiovascular outcome trials. Lancet 2019, 393, 31–39, Correction in Lancet 2019, 393, 30. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(18)33206-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scafoglio, C.; Hirayama, B.A.; Kepe, V.; Liu, J.; Ghezzi, C.; Satyamurthy, N.; Moatamed, N.A.; Huang, L.; Koepsell, H.; Barrio, J.R.; et al. Functional expression of sodium-glucose transporters in cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E4111–E4119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, P.; Chang, D.K.; Nones, K.; Johns, A.L.; Patch, A.-M.; Gingras, M.-C.; Miller, D.K.; Christ, A.N.; Bruxner, T.J.; Quinn, M.C.; et al. Genomic analyses identify molecular subtypes of pancreatic cancer. Nature 2016, 531, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanoudakis, D.; Frountzas, M.; Schizas, D.; Michalopoulos, N.V.; Drakaki, A.; Toutouzas, K.G. Significance of TP53, CDKN2A, SMAD4 and KRAS in Pancreatic Cancer. CIMB 2024, 46, 2827–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, H.; Kimmelman, A.C.; Lyssiotis, C.A.; Hua, S.; Chu, G.C.; Fletcher-Sananikone, E.; Locasale, J.W.; Son, J.; Zhang, H.; Coloff, J.L.; et al. Oncogenic Kras Maintains Pancreatic Tumors through Regulation of Anabolic Glucose Metabolism. Cell 2012, 149, 656–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, K.L.; Mancias, J.D.; Kimmelman, A.C.; Der, C.J. KRAS: Feeding pancreatic cancer proliferation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2014, 39, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, J.; Lyssiotis, C.A.; Ying, H.; Wang, X.; Hua, S.; Ligorio, M.; Perera, R.M.; Ferrone, C.R.; Mullarky, E.; Shyh-Chang, N.; et al. Glutamine supports pancreatic cancer growth through a KRAS-regulated metabolic pathway. Nature 2013, 496, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, J.; Kang, Y.; Zhao, R.; Xia, Q.; Lee, D.-F.; Chang, Z.; Li, J.; Peng, B.; Fleming, J.B.; Wang, H.; et al. KrasG12D-Induced IKK2/β/NF-κB Activation by IL-1α and p62 Feedforward Loops Is Required for Development of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Cell 2012, 21, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanconato, F.; Cordenonsi, M.; Piccolo, S. YAP/TAZ at the Roots of Cancer. Cancer Cell 2016, 29, 783–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, A.; Yao, W.; Ying, H.; Hua, S.; Liewen, A.; Wang, Q.; Zhong, Y.; Wu, C.J.; Sadanandam, A.; Hu, B.; et al. Yap1 Activation Enables Bypass of Oncogenic Kras Addiction in Pancreatic Cancer. Cell 2014, 158, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, C.J.; Massagué, J. Contextual determinants of TGFβ action in development, immunity and cancer. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 419–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flint, T.R.; Janowitz, T.; Connell, C.M.; Roberts, E.W.; Denton, A.E.; Coll, A.P.; Jodrell, D.I.; Fearon, D.T. Tumor-Induced IL-6 Reprograms Host Metabolism to Suppress Anti-tumor Immunity. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 672–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa-Silva, B.; Aiello, N.M.; Ocean, A.J.; Singh, S.; Zhang, H.; Thakur, B.K.; Becker, A.; Hoshino, A.; Mark, M.T.; Molina, H.; et al. Pancreatic cancer exosomes initiate pre-metastatic niche formation in the liver. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 17, 816–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petruzzelli, M.; Wagner, E.F. Mechanisms of metabolic dysfunction in cancer-associated cachexia. Genes Dev. 2016, 30, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammation, metaflammation and immunometabolic disorders. Nature 2017, 542, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donath, M.Y.; Böni-Schnetzler, M.; Ellingsgaard, H.; Ehses, J.A. Islet Inflammation Impairs the Pancreatic β-Cell in Type 2 Diabetes. Physiology 2009, 24, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, G.C.; Turner, N. FOX01 is the headline Akt regulating hepatic glucose metabolism. Endocrinology 2017, 158, 2436–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, E.; Flier, E.; Molle, D.; Accili, D.; McGraw, T.E. Hyperinsulinemia leads to uncoupled insulin regulation of the GLUT4 glucose transporter and the FoxO1 transcription factor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 10162–10167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, B.; Zheng, W.; Kang, M.; Chen, Q.; Qin, W.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, Y.; Wu, Y. Exosomes derived from pancreatic cancer cells induce insulin resistance in C2C12 myotube cells through the PI3K/Akt/FoxO1 pathway. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javeed, N.; Sagar, G.; Dutta, S.K.; Smyrk, T.C.; Lau, J.S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Truty, M.; Petersen, G.M.; Kaufman, R.J.; Chari, S.T.; et al. Pancreatic Cancer–Derived Exosomes Cause Paraneoplastic β-cell Dysfunction. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 1722–1733, Correction in Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 4495. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-15-1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Back, S.H.; Kaufman, R.J. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Type 2 Diabetes. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2012, 81, 767–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prentki, M.; Matschinsky, F.M.; Madiraju, S.R.M. Metabolic Signaling in Fuel-Induced Insulin Secretion. Cell Metab. 2013, 18, 162–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talchai, C.; Xuan, S.; Lin, H.V.; Sussel, L.; Accili, D. Pancreatic β Cell Dedifferentiation as a Mechanism of Diabetic β Cell Failure. Cell 2012, 150, 1223–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knop, F.K.; Vilsbøll, T.; Højberg, P.V.; Larsen, S.; Madsbad, S.; Holst, J.J.; Krarup, T. The insulinotropic effect of GIP is impaired in patients with chronic pancreatitis and secondary diabetes mellitus as compared to patients with chronic pancreatitis and normal glucose tolerance. Regul. Pept. 2007, 144, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perano, S.J.; Couper, J.J.; Horowitz, M.; Martin, A.J.; Kritas, S.; Sullivan, T.; Rayner, C.K. Pancreatic Enzyme Supplementation Improves the Incretin Hormone Response and Attenuates Postprandial Glycemia in Adolescents with Cystic Fibrosis: A Randomized Crossover Trial. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, 2486–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holst, J.J. The incretin system in healthy humans: The role of GIP and GLP-1. Metabolism 2019, 96, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baracos, V.E.; Martin, L.; Korc, M.; Guttridge, D.C.; Fearon, K.C.H. Cancer-associated cachexia. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provenzano, P.P.; Cuevas, C.; Chang, A.E.; Goel, V.K.; Von Hoff, D.D.; Hingorani, S.R. Enzymatic Targeting of the Stroma Ablates Physical Barriers to Treatment of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Cell 2012, 21, 418–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobetz, M.A.; Chan, D.S.; Neesse, A.; Bapiro, T.E.; Cook, N.; Frese, K.K.; Feig, C.; Nakagawa, T.; Caldwell, M.E.; Zecchini, H.I.; et al. Hyaluronan impairs vascular function and drug delivery in a mouse model of pancreatic cancer. Gut 2013, 62, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provenzano, P.P.; Hingorani, S.R. Hyaluronan, fluid pressure, and stromal resistance in pancreas cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laklai, H.; Miroshnikova, Y.A.; Pickup, M.W.; Collisson, E.A.; Kim, G.E.; Barrett, A.S.; Hill, R.C.; Lakins, J.N.; Schlaepfer, D.D.; Mouw, J.K.; et al. Genotype tunes pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma tissue tension to induce matricellular fibrosis and tumor progression. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, F.; Ege, N.; Grande-Garcia, A.; Hooper, S.; Jenkins, R.P.; Chaudhry, S.I.; Harrington, K.; Williamson, P.; Moeendarbary, E.; Charras, G.; et al. Mechanotransduction and YAP-dependent matrix remodelling is required for the generation and maintenance of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Nat. Cell Biol. 2013, 15, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachowski, D.; Cortes, E.; Pink, D.; Chronopoulos, A.; Karim, S.A.; P Morton, J.; Del Río Hernández, A.E. Substrate Rigidity Controls Activation and Durotaxis in Pancreatic Stellate Cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Hegde, S.; Knolhoff, B.L.; Zhu, Y.; Herndon, J.M.; Meyer, M.A.; Nywening, T.M.; Hawkins, W.G.; Shapiro, I.M.; Weaver, D.T.; et al. Targeting focal adhesion kinase renders pancreatic cancers responsive to checkpoint immunotherapy. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, W.J.; Do, O.H.; Cottle, L.; Ma, W.; Kosobrodova, E.; Cooper-White, J.; Bilek, M.; Thorn, P. Local Integrin Activation in Pancreatic β Cells Targets Insulin Secretion to the Vasculature. Cell Rep. 2018, 24, 2819–2826.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, E.P.; Casimir, M.; Schroer, S.A.; Luk, C.T.; Shi, S.Y.; Choi, D.; Dai, X.Q.; Hajmrle, C.; Spigelman, A.F.; Zhu, D.; et al. In Vivo Role of Focal Adhesion Kinase in Regulating Pancreatic β-Cell Mass and Function Through Insulin Signaling, Actin Dynamics, and Granule Trafficking. Diabetes 2012, 61, 1708–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noordstra, I.; Van Den Berg, C.M.; Boot, F.W.J.; Katrukha, E.A.; Yu, K.L.; Tas, R.P.; Portegies, S.; Viergever, B.J.; de Graaff, E.; Hoogenraad, C.C.; et al. Organization and dynamics of the cortical complexes controlling insulin secretion in β-cells. J. Cell Sci. 2022, 135, jcs259430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Barghouth, M.; Dou, H.; Luan, C.; Wang, Y.; Karagiannopoulos, A.; Jiang, X.; Krus, U.; Fex, M.; Zhang, Q.; et al. A critical role of the mechanosensor PIEZO1 in glucose-induced insulin secretion in pancreatic β-cells. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, C.G.; Holcomb, K.; Sela, A.; Morrall, S.; Park, D.; Farnsworth, N.L. Extracellular matrix stiffness mediates insulin secretion in pancreatic islets via mechanosensitive Piezo1 channel regulated Ca2+ dynamics. Matrix Biol. Plus 2024, 22, 100148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arous, C.; Halban, P.A. The skeleton in the closet: Actin cytoskeletal remodeling in β-cell function. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 309, E611–E620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar-Hmeadi, M.; Idevall-Hagren, O. Insulin granule biogenesis and exocytosis. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 1957–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rorsman, P.; Ashcroft, F.M. Pancreatic β-Cell Electrical Activity and Insulin Secretion: Of Mice and Men. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 117–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feig, C.; Jones, J.O.; Kraman, M.; Wells, R.J.B.; Deonarine, A.; Chan, D.S.; Connell, C.M.; Roberts, E.W.; Zhao, Q.; Caballero, O.L.; et al. Targeting CXCL12 from FAP-expressing carcinoma-associated fibroblasts synergizes with anti–PD-L1 immunotherapy in pancreatic cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 20212–20217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ene–Obong, A.; Clear, A.J.; Watt, J.; Wang, J.; Fatah, R.; Riches, J.C.; Marshall, J.F.; Chin-Aleong, J.; Chelala, C.; Gribben, J.G.; et al. Activated Pancreatic Stellate Cells Sequester CD8+ T Cells to Reduce Their Infiltration of the Juxtatumoral Compartment of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 1121–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, B.C.; Pentcheva-Hoang, T.; Carstens, J.L.; Zheng, X.; Wu, C.-C.; Simpson, T.R.; Laklai, H.; Sugimoto, H.; Kahlert, C.; Novitskiy, S.V.; et al. Depletion of Carcinoma-Associated Fibroblasts and Fibrosis Induces Immunosuppression and Accelerates Pancreas Cancer with Reduced Survival. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 719–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Öhlund, D.; Handly-Santana, A.; Biffi, G.; Elyada, E.; Almeida, A.S.; Ponz-Sarvise, M.; Corbo, V.; Oni, T.E.; Hearn, S.A.; Lee, E.J.; et al. Distinct populations of inflammatory fibroblasts and myofibroblasts in pancreatic cancer. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 579–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, J.L.E.; Leonard, E.; Parslow, D.; Hill, D.J. Gene Dysregulation and Islet Changes in PDAC-Associated Type 3c Diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goess, R.; Mutgan, A.; Çalışan, U.; Erdoğan, Y.; Ren, L.; Jäger, C.; Safak, O.; Stupakov, P.; Istvanffy, R.; Friess, H.; et al. Patterns and Relevance of Langerhans Islet Invasion in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chari, S.T.; Leibson, C.L.; Rabe, K.G.; Timmons, L.J.; Ransom, J.; De Andrade, M.; Petersen, G.M. Pancreatic Cancer–Associated Diabetes Mellitus: Prevalence and Temporal Association with Diagnosis of Cancer. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelaez-Luna, M.; Takahashi, N.; Fletcher, J.G.; Chari, S.T. Resectability of Presymptomatic Pancreatic Cancer and Its Relationship to Onset of Diabetes: A Retrospective Review of CT Scans and Fasting Glucose Values Prior to Diagnosis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 102, 2157–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cersosimo, E.; Pisters, P.W.T.; Pesola, G.; McDermott, K.; Bajorunas, D.; Brennan, M.F. Insulin secretion and action in patients with pancreatic cancer. Cancer 1991, 67, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chari, S.T.; Zapiach, M.; Yadav, D.; Rizza, R.A. Beta-cell function and insulin resistance evaluated by HOMA in pancreatic cancer subjects with varying degrees of glucose intolerance. Pancreatology 2005, 5, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.H.; Mcintyre, S.S.; Shah, H.; Veldhuis, J.D.; Hayes, P.C.; Butler, P.C. Direct Measurement of Pulsatile Insulin Secretion from the Portal Vein in Human Subjects. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 85, 4491–4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritzel, R.A.; Veldhuis, J.D.; Butler, P.C. Glucose Stimulates Pulsatile Insulin Secretion from Human Pancreatic Islets by Increasing Secretory Burst Mass: Dose-Response Relationships. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 742–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mari, A.; Tura, A.; Natali, A.; Laville, M.; Laakso, M.; Gabriel, R.; Beck-Nielsen, H.; Ferrannini, E.; RISC Investigators. Impaired beta cell glucose sensitivity rather than inadequate compensation for insulin resistance is the dominant defect in glucose intolerance. Diabetologia 2010, 53, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seino, S.; Shibasaki, T.; Minami, K. Dynamics of insulin secretion and the clinical implications for obesity and diabetes. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2118–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merrins, M.J.; Corkey, B.E.; Kibbey, R.G.; Prentki, M. Metabolic cycles and signals for insulin secretion. Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 947–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kailey, B.; Van De Bunt, M.; Cheley, S.; Johnson, P.R.; MacDonald, P.E.; Gloyn, A.L.; Rorsman, P.; Braun, M. SSTR2 is the functionally dominant somatostatin receptor in human pancreatic β- and α-cells. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 303, E1107–E1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauge-Evans, A.C.; King, A.J.; Carmignac, D.; Richardson, C.C.; Robinson, I.C.A.F.; Low, M.J.; Christie, M.R.; Persaud, S.J.; Jones, P.M. Somatostatin Secreted by Islet δ-Cells Fulfills Multiple Roles as a Paracrine Regulator of Islet Function. Diabetes 2009, 58, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, T.G.; Gao, R.; Benrick, A.; Kothegala, L.; Rorsman, N.; Santos, C.; Acreman, S.; Briant, L.J.; Dou, H.; Gandasi, N.R.; et al. Loss of electrical β-cell to δ-cell coupling underlies impaired hypoglycaemia-induced glucagon secretion in type-1 diabetes. Nat. Metab. 2024, 6, 2070–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Meulen, T.; Donaldson, C.J.; Cáceres, E.; Hunter, A.E.; Cowing-Zitron, C.; Pound, L.D.; Adams, M.W.; Zembrzycki, A.; Grove, K.L.; Huising, M.O. Urocortin3 mediates somatostatin-dependent negative feedback control of insulin secretion. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaça, J.; Weitz, J.; Rodriguez-Diaz, R.; Pereira, E.; Caicedo, A. The Pericyte of the Pancreatic Islet Regulates Capillary Diameter and Local Blood Flow. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 630–644.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaça, J.; Caicedo, A.; Landsman, L. Beta cell dysfunction in diabetes: The islet microenvironment as an unusual suspect. Diabetologia 2020, 63, 2076–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Incio, J.; Liu, H.; Suboj, P.; Chin, S.M.; Chen, I.X.; Pinter, M.; Ng, M.R.; Nia, H.T.; Grahovac, J.; Kao, S.; et al. Obesity-Induced Inflammation and Desmoplasia Promote Pancreatic Cancer Progression and Resistance to Chemotherapy. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 852–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, T.G.; Hill, D.J. The Importance of Intra-Islet Communication in the Function and Plasticity of the Islets of Langerhans during Health and Diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rorsman, P.; Renström, E. Insulin granule dynamics in pancreatic beta cells. Diabetologia 2003, 46, 1029–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aberer, F.; Hochfellner, D.A.; Sourij, H.; Mader, J.K. A Practical Guide for the Management of Steroid Induced Hyperglycaemia in the Hospital. JCM 2021, 10, 2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Hayashi, H.; Matsumura, K.; Uemura, N.; Shiraishi, Y.; Sato, H.; Baba, H. Biological and Clinical Impacts of Glucose Metabolism in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Cancers 2023, 15, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Yang, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Mu, J.; Zeng, Q.; Deng, S.; Zhou, H. Signaling pathways in cancer-associated fibroblasts and targeted therapy for cancer. Sig. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, A.M.Y.; Chu, K.H.; Daly, B.F.; Ruiter, T.; Dou, Y.; Yang, J.C.C.; de Winter, T.J.J.; Chhuor, J.; Wang, S.; Flibotte, S.; et al. Effects of hyperinsulinemia on pancreatic cancer development and the immune microenvironment revealed through single-cell transcriptomics. Cancer Metab. 2022, 10, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Class/Agent | Primary Glycaemic Effects | PDAC-Specific Oncologic Signals (Human) | Practical Selection in PDAC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metformin | ↓ Hepatic gluconeogenesis; insulin-sensitising | Observational survival associations reported; randomised add-on trials with chemotherapy have not shown consistent overall survival benefit | Useful when oral intake adequate; inexpensive |
| GLP-1 RAs | ↑ Glucose-dependent insulin; ↓ glucagon; slows gastric emptying; weight loss | Large cohorts/meta-analyses show no confirmed increase in PDAC risk; oncologic signal neutral | Consider if weight loss is controlled and intake maintained; monitor GI adverse events |
| SGLT2 inhibitors | ↑ Urinary glucose excretion | PDAC cells can express SGLTs (preclinical); no clinical anticancer benefit established | Consider with preserved renal function and adequate caloric intake |
| Axis | What is Documented in PDAC (Human/PDAC Models) | Mechanisms Suggested (Inferred from Islet/Oncology) |
|---|---|---|
| β-cell stimulus–secretion and identity |
|
|
| α-cell disinhibition and paracrine control |
|
|
| δ-cell somatostatin gating |
|
|
| Axis | What Is Documented in PDAC (Human/PDAC Models) | Mechanisms Suggested (Inferred from Islet/Oncology) |
|---|---|---|
| Microvasculature and perfusion |
|
|
| ECM stiffness and mechanotransduction |
|
|
| Cross-cutting paraneoplastic mediators |
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hill, J.L.E.; Hill, T.G.; Parslow, D.; Hill, D.J. Pancreatic Cancer and Diabetes: Insights, Hypotheses, and Next Steps. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10245. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110245
Hill JLE, Hill TG, Parslow D, Hill DJ. Pancreatic Cancer and Diabetes: Insights, Hypotheses, and Next Steps. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(21):10245. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110245
Chicago/Turabian StyleHill, Jessica L. E., Thomas G. Hill, Dominique Parslow, and David J. Hill. 2025. "Pancreatic Cancer and Diabetes: Insights, Hypotheses, and Next Steps" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 21: 10245. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110245
APA StyleHill, J. L. E., Hill, T. G., Parslow, D., & Hill, D. J. (2025). Pancreatic Cancer and Diabetes: Insights, Hypotheses, and Next Steps. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(21), 10245. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110245






