Lactiplantibacillus plantarum HY7718 Attenuates Renal Injury in an Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease Mouse Model via Inhibition of Inflammation and Apoptosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effect of HY7718 on Viaibility of H2O2-Treated HK2 Cells
2.2. Measurement of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Levels in H2O2-Treated HK2 Cells
2.3. Effect of HY7718 on Cell Viability of TNF+CHX-Treated HK2 Cells
2.4. The Effect of HY7718 on the Apoptosis Marker Caspase-3 in TNF+CHX-Treated HK2 Cells
2.5. Effects of HY7718 on Psysiological Indicators in CKD-Induced Mice
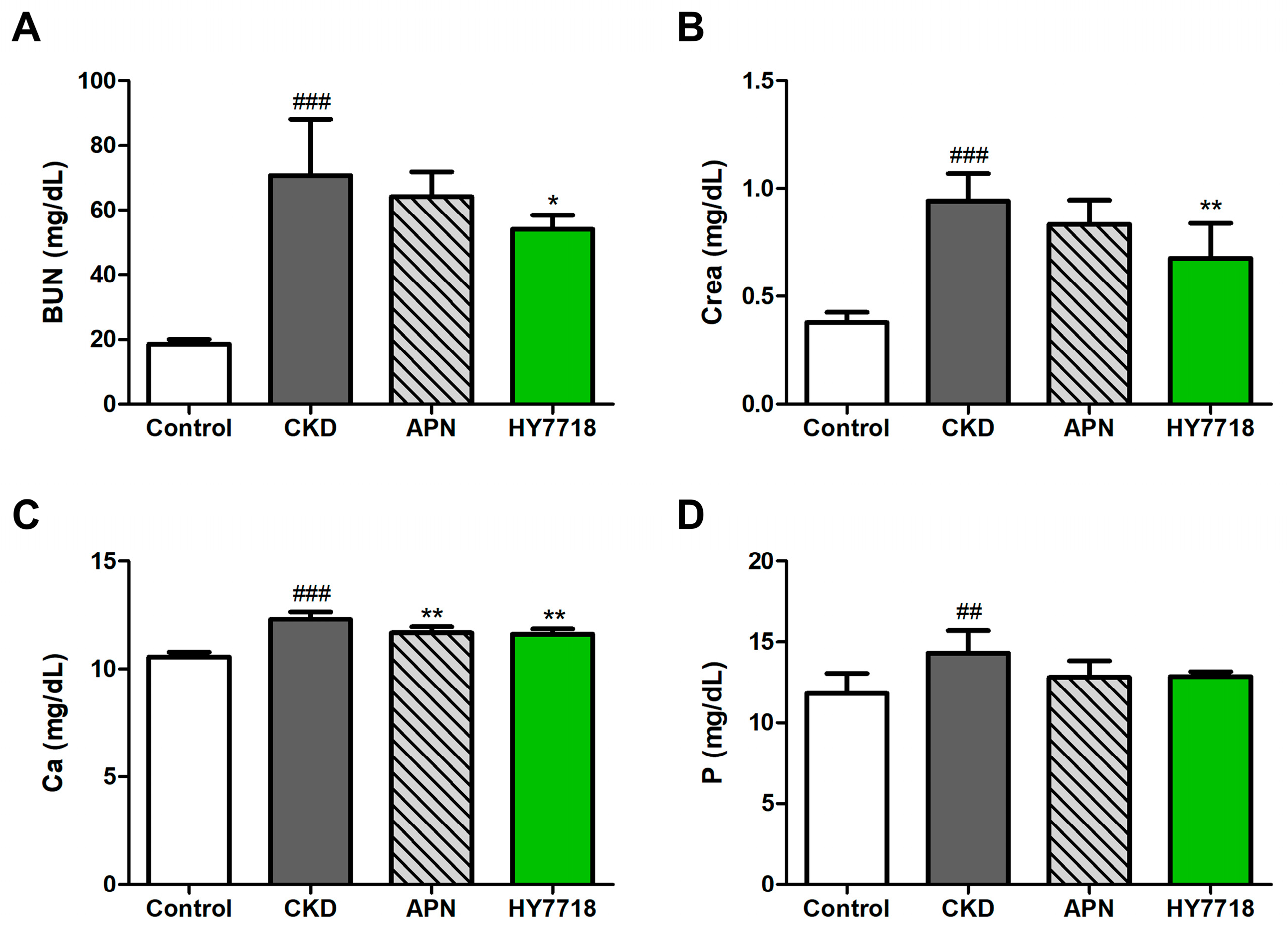
2.6. Effects of HY7718 on Blood Biochemistry in CKD-Induced Mice
2.7. Effects of HY7718 on Kidney Histopathology
2.8. Effects of HY7718 on Renal Inflammation-Related Gene Expression
2.9. Effect of HY7718 Apoptosis in Kidney Tissues
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strain Culture and Sample Preparation
4.2. Cell Culture of HK2 Cells and Sample Treatment
4.3. Cell Viability Assay
4.4. Cytotoxicity Assay
4.5. Secretion of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines
4.6. Measurement of Caspase-3 Activity and Cleaved Caspase-3
4.7. Animal Experiments Design
4.8. Serum Biochemical Analysis
4.9. Histopathological Examination
4.10. Detection of Apoptosis by the TUNEL Assay
4.11. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, C.; Yang, L.; Wei, W.; Fu, P. Efficacy of probiotics/synbiotics supplementation in patients with chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1434613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazidi, M.; Kengne, A.P.; Siervo, M.; Kirwan, R. Association of dietary intakes and genetically determined serum concentrations of mono and poly unsaturated fatty acids on chronic kidney disease: Insights from dietary analysis and Mendelian randomization. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoccali, C.; Vanholder, R.; Massy, Z.A.; Ortiz, A.; Sarafidis, P.; Dekker, F.W.; Fliser, D.; Fouque, D.; Heine, G.H.; Jager, K.J. The systemic nature of CKD. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 344–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, R.; Kanso, A.; Sedor, J.R. Chronic kidney disease and its complications. Prim. Care Clin. Off. Pract. 2008, 35, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Astor, B.C.; Lewis, J.; Hu, B.; Appel, L.J.; Lipkowitz, M.S.; Toto, R.D.; Wang, X.; Wright Jr, J.T.; Greene, T.H. Longitudinal progression trajectory of GFR among patients with CKD. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2012, 59, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.K.; Knicely, D.H.; Grams, M.E. Chronic kidney disease diagnosis and management: A review. JAMA 2019, 322, 1294–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, N.; Katz, R.; Bansal, N. ACE inhibitor/angiotensin receptor blocker use patterns in advanced CKD and risk of kidney failure and death. Kidney Med. 2020, 2, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mende, C.W. Chronic kidney disease and SGLT2 inhibitors: A review of the evolving treatment landscape. Adv. Ther. 2022, 39, 148–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gusev, E.; Solomatina, L.; Zhuravleva, Y.; Sarapultsev, A. The pathogenesis of end-stage renal disease from the standpoint of the theory of general pathological processes of inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Nam, B.Y.; Park, J.; Song, S.; Kim, W.K.; Lee, K.; Nam, T.W.; Park, J.T.; Yoo, T.H.; Kang, S.W. Lactobacillus acidophilus KBL409 reduces kidney fibrosis via immune modulatory effects in mice with chronic kidney disease. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2022, 66, 2101105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahl, H.; Sandblost, S.R.; Welland, N.L.; Sandnes, K.; Sekse, I.; Sæle, K.; Marti, H.-P.; Holst, L.; Dierkes, J. Medication prescription, common side-effects, and nutritional status are associated in patients with chronic kidney disease. J. Ren. Nutr. 2022, 32, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chafekar, D. Optimizing chronic kidney disease management: The potential of a multi-strain probiotic formulation. World J. Nephrol. 2025, 14, 101515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Gonzalez, N.; Battista, N.; Prete, R.; Corsetti, A. Health-promoting role of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum isolated from fermented foods. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echegaray, N.; Yilmaz, B.; Sharma, H.; Kumar, M.; Pateiro, M.; Ozogul, F.; Lorenzo, J.M. A novel approach to Lactiplantibacillus plantarum: From probiotic properties to the omics insights. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 268, 127289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, D.; Aryaee, H.; Mirdamadi, S.; Shirkhan, F. The Benefits and Applications of Lactobacillus plantarum in Food and Health: A Narrative Review. Iran. J. Public Health 2024, 53, 2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, B.; Kim, S.A.; Park, S.D.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, J.S.; Bae, C.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Nam, W.; Lee, J.L.; Sim, J.H. Regulatory effects of Lactobacillus plantarum HY7714 on skin health by improving intestinal condition. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, E.-J.; Lee, Y.-S.; Kim, S.M.; Park, G.-S.; Lee, Y.H.; Jeong, D.Y.; Kang, J.; Lee, H.-J. Beneficial effects of Lactobacillus plantarum strains on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in high fat/high fructose diet-fed rats. Nutrients 2020, 12, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, A.; Mandal, S.; Samanta, A.; Mondal, K.C.; Nandi, D.K. Therapeutic potential of probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum AD3 on acetaminophen induced uremia in experimental rats. Clin. Nutr. Exp. 2018, 19, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, W.; Wang, D.; He, J.; Li, X.; Jia, L.; Wang, Y. Modulatory effects of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum MA2 and its postbiotic on the adenine-induced chronic kidney disease. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2025, 14, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Su, S.; Luo, N.; Cao, G. Adenine-induced animal model of chronic kidney disease: Current applications and future perspectives. Ren. Fail. 2024, 46, 2336128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fillion, A.; Vichier-Guerre, S.; Arimondo, P.B. Adenine, a key player in biology and medicinal chemistry. Comptes Rendus. Chim. 2024, 27 (Suppl. S2), 143–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salati, L.M.; Gross, C.J.; Henderson, L.M.; Savaiano, D.A. Absorption and metabolism of adenine, adenosine-5’-monophosphate, adenosine and hypoxanthine by the isolated vascularly perfused rat small intestine. J. Nutr. 1984, 114, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokozawa, T.; Zheng, P.D.; Oura, H.; Koizumi, F. Animal model of adenine-induced chronic renal failure in rats. Nephron 1986, 44, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diwan, V.; Brown, L.; Gobe, G.C. Adenine-induced chronic kidney disease in rats. Nephrology 2018, 23, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamasaki, Y.; Doi, K.; Maeda-Mamiya, R.; Ogasawara, E.; Katagiri, D.; Tanaka, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Sugaya, T.; Nangaku, M.; Noiri, E. A 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor antagonist, sarpogrelate, reduces renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis by suppressing PAI-1. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2013, 305, F1796–F1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Yoo, M.-S.; Jeon, H.; Shim, J.-J.; Park, W.-J.; Kim, J.-Y.; Lee, J.-L. Probiotic properties and safety evaluation of Lactobacillus plantarum hy7718 with superior storage stability isolated from fermented squid. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-J.; Jeon, H.-J.; Kim, J.-Y.; Shim, J.-J.; Lee, J.-H. Lactiplantibacillus plantarum HY7718 improves intestinal integrity in a DSS-induced ulcerative colitis mouse model by suppressing inflammation through modulation of the gut microbiota. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, C.-H.; Sun, C.-K.; Leu, S.; Wallace, C.G.; Lin, Y.-C.; Chang, L.-T.; Chen, Y.-L.; Tsa, T.-H.; Kao, Y.-H.; Shao, P.-L. Continuing exposure to low-dose nonylphenol aggravates adenine-induced chronic renal dysfunction and role of rosuvastatin therapy. J. Transl. Med. 2012, 10, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, A.K.; Pareek, A.; Singla-Pareek, S.L. TUNEL assay to assess extent of DNA fragmentation and programmed cell death in root cells under various stress conditions. Bio-Protocol 2017, 7, e2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daenen, K.; Andries, A.; Mekahli, D.; Van Schepdael, A.; Jouret, F.; Bammens, B. Oxidative stress in chronic kidney disease. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2019, 34, 975–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, O.Y.A.; Wong, A.N.N.; Ho, C.Y.; Tse, K.W.; Chan, A.Z.; Leung, G.P.-H.; Kwan, Y.W.; Yeung, M.H.Y. Potentials of natural antioxidants in reducing inflammation and oxidative stress in chronic kidney disease. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanaoka, H.; Aoki, T.; Kosaka, T.; Yoshinaga, S.; Shibata, A.; Sakai, R.; Kurasawa, T.; Amano, K. Chronic kidney disease and inflammatory cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis: A potential pathogenic link. Immunol. Med. 2025, 48, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Lei, C.-T.; Zhang, C. Interleukin-6 signaling pathway and its role in kidney disease: An update. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lousa, I.; Reis, F.; Santos-Silva, A.; Belo, L. The signaling pathway of TNF receptors: Linking animal models of renal disease to human CKD. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakoshi, M.; Gohda, T.; Suzuki, Y. Circulating tumor necrosis factor receptors: A potential biomarker for the progression of diabetic kidney disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cai, J.; Tang, C.; Dong, Z. Mitophagy in acute kidney injury and kidney repair. Cells 2020, 9, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, A.B.; Sanchez-Niño, M.D.; Ramos, A.M.; Ortiz, A. Regulated cell death pathways in kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2023, 19, 281–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, S.; Yang, B.; Migneault, F.; Turgeon, J.; Bourgault, M.; Dieudé, M.; Cardinal, H.; Hickey, M.J.; Patey, N.; Hébert, M.-J. Caspase-3-dependent peritubular capillary dysfunction is pivotal for the transition from acute to chronic kidney disease after acute ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2021, 321, F335–F351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponder, K.G.; Boise, L.H. The prodomain of caspase-3 regulates its own removal and caspase activation. Cell Death Discov. 2019, 5, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadendla, E.K.; Tweedell, R.E.; Kasof, G.; Kanneganti, T.-D. Caspases: Structural and molecular mechanisms and functions in cell death, innate immunity, and disease. Cell Discov. 2025, 11, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polunovsky, V.A.; Wendt, C.H.; Ingbar, D.H.; Peterson, M.S.; Bitterman, P.B. Induction of endothelial cell apoptosis by TNFα: Modulation by inhibitors of protein synthesis. Exp. Cell Res. 1994, 214, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, A.; Thakar, C.V.; Amlal, H. Adenine at lower doses acts in the kidney as an aquaretic agent and prevents hyponatremia. Purinergic Signal. 2025, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, N.C.; Suassuna, J.H.R. The spleen size in patients undergoing hemodialysis. Braz. J. Nephrol. 2021, 43, 61–67, Erratum in J. Bras. Nefrol. 2021, 43, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sabra, M.S.; Hemida, F.K.; Allam, E.A. Adenine model of chronic renal failure in rats to determine whether MCC950, an NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitor, is a renopreventive. BMC Nephrol. 2023, 24, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, R.J.; Prior, C.; Puig, J.G. Efficacy and safety of allopurinol in patients with hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase deficiency. Metabolism 2007, 56, 1179–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diwan, V.; Small, D.; Kauter, K.; Gobe, G.C.; Brown, L. Gender differences in adenine-induced chronic kidney disease and cardiovascular complications in rats. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2014, 307, F1169–F1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Choi, M.-S.; Jeon, J.; Moon, J.; Lee, J.; Kong, E.; Lucia, S.E.; Hong, S.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, E.Y. In vivo longitudinal 920 nm two-photon intravital kidney imaging of a dynamic 2, 8-DHA crystal formation and tubular deterioration in the adenine-induced chronic kidney disease mouse model. Biomed. Opt. Express 2023, 14, 1647–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Frutos, S.; Luengo, A.; Garcia-Jerez, A.; Hatem-Vaquero, M.; Griera, M.; O’Valle, F.; Rodríguez–Puyol, M.; Rodríguez–Puyol, D.; Calleros, L. Chronic kidney disease induced by an adenine rich diet upregulates integrin linked kinase (ILK) and its depletion prevents the disease progression. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2019, 1865, 1284–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abass, N.M.; Yousef, A.M.; Sabet, E.A.; Kamal, Y.M.; El-Rashidy, M.H. Study of serum calcium and phosphorus levels in chronic kidney disease patients with acute coronary syndrome. Egypt. J. Intern. Med. 2024, 36, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, K.A.; Singh, R.D.; Croatt, A.J.; Adams, C.M. Heme proteins and kidney injury: Beyond rhabdomyolysis. Kidney360 2022, 3, 1969–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Achkar, T.M.; Wu, X.-R. Uromodulin in kidney injury: An instigator, bystander, or protector? Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2012, 59, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.-L.; Wei, M.-J.; Chen, M.-Y.; Chen, N. Relationship between mononuclear cells infiltration in renal interstitium and the prognosis of kidney disease. Chin. J. Contemp. Pediatr. 2005, 7, 131–133. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; He, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, C.; Pei, T.; Yan, S.; Yan, Y.; Wang, F.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, N. Caffeic acid alleviates skeletal muscle atrophy in 5/6 nephrectomy rats through the TLR4/MYD88/NF-kB pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 174, 116556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuji, K.; Uchida, N.; Nakanoh, H.; Fukushima, K.; Haraguchi, S.; Kitamura, S.; Wada, J. The gut–kidney axis in chronic kidney diseases. Diagnostics 2024, 15, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Gene Category | Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Assay ID |
|---|---|---|---|
| In vitro experiments (HK cells) | |||
| House-keeping gene | GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | Hs99999905_m1 |
| Pro-inflammatory cytokines | TNFα | Tumor necrosis factor-alpha | Hs00174128_m1 |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 | Hs00174131_m1 | |
| In vivo experiments (Mouse kidney tissues) | |||
| House-keeping gene | Gapdh | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | Mm99999915_g1 |
| Pro-inflammatory cytokines | Tnfα | Tumor necrosis factor-alpha | Mm00443258_m1 |
| Il-6 | Interleukin-6 | Mm00446190_m1 | |
| Il-1β | Interleukin 1 beta | Mm00434228_m1 | |
| Ccl2 (Mcp-1) | C-C motif chemokine ligand 2 | Mm00441242_m1 | |
| Inflammatory signaling pathway | Tlr4 | Toll-like receptor 4 | Mm00445273_m1 |
| Nfκb1 | Nuclear factor kappa B subunit1 | Mm00476361_m1 | |
| Apoptosis | Bax | BCL2 associated X, apoptosis regulator | Mm00432051_m1 |
| Bcl-2 | BCL2, apoptosis regulator | Mm00477631_m1 | |
| Casp3 | Caspase-3 | Mm01195085_m1 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, H.; Jeong, J.-W.; Jeong, H.; Lee, D.; Gwon, H.; Lee, K.; Kim, J.-Y.; Shim, J.-J.; Lee, J.-H. Lactiplantibacillus plantarum HY7718 Attenuates Renal Injury in an Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease Mouse Model via Inhibition of Inflammation and Apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10052. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010052
Kim H, Jeong J-W, Jeong H, Lee D, Gwon H, Lee K, Kim J-Y, Shim J-J, Lee J-H. Lactiplantibacillus plantarum HY7718 Attenuates Renal Injury in an Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease Mouse Model via Inhibition of Inflammation and Apoptosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(20):10052. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010052
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Hyeonji, Ji-Woong Jeong, Haeryn Jeong, Daehyeop Lee, Hyeonjun Gwon, Kippuem Lee, Joo-Yun Kim, Jae-Jung Shim, and Jae-Hwan Lee. 2025. "Lactiplantibacillus plantarum HY7718 Attenuates Renal Injury in an Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease Mouse Model via Inhibition of Inflammation and Apoptosis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 20: 10052. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010052
APA StyleKim, H., Jeong, J.-W., Jeong, H., Lee, D., Gwon, H., Lee, K., Kim, J.-Y., Shim, J.-J., & Lee, J.-H. (2025). Lactiplantibacillus plantarum HY7718 Attenuates Renal Injury in an Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease Mouse Model via Inhibition of Inflammation and Apoptosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(20), 10052. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010052






