Abstract
Current clinical approaches for managing inflammatory pain are frequently accompanied by adverse effects, significantly compromising patients’ quality of life. This study investigates the analgesic potential of Heat Shock Protein Family A Member 1A (HSPA1A) in alleviating Complete Freund’s Adjuvant (CFA)-induced inflammatory pain. The immunomodulatory mechanisms were elucidated through behavioral studies, flow cytometry, transcriptomics, proteomics, and cellular metabolic analyses. Findings indicate that HSPA1A mitigates CFA-induced mechanical allodynia, an effect independent of T or B lymphocytes and neutrophils but positively correlated with macrophage abundance. Transcriptomic RNA sequencing suggests involvement of inflammation-associated pathways. In vitro experiments demonstrate that HSPA1A suppresses the polarization of bone marrow-derived macrophages toward the pro-inflammatory M1 phenotype in an inflammatory model, with decreased mRNA expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines Interleukin-1β (Il1b) and Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF). Macrophage metabolism undergoes reprogramming, characterized by reduced glycolysis and enhanced oxidative phosphorylation. Proteomic pathway analysis reveals suppression of pro-inflammatory and glycolytic proteins, coupled with upregulation of anti-inflammatory and tricarboxylic acid cycle-related proteins. In summary, HSPA1A likely exerts its analgesic effects by inhibiting glycolysis in macrophages, providing novel insights into inflammatory pain management and highlighting potential therapeutic targets for future clinical drug development with substantial translational potential.
1. Introduction
Inflammatory pain represents a significant challenge in clinical management, with its pathogenesis involving complex interplay between cellular and non-cellular immune mechanisms []. This pain is characterized by heightened excitability in primary afferent neurons, manifesting as spontaneous pain, hyperalgesia, and allodynia. Peripheral sensitization constitutes its core pathological process: on one hand, inflammatory mediators can elicit abnormal pain responses to normal stimuli; on the other hand, responsiveness to inflammatory stimuli is significantly amplified following tissue injury []. Inflammatory pain is classified into acute and chronic types. Acute inflammation serves as a physiological defense response to trauma or disease, activating nociceptors to trigger protective behaviors and promote tissue repair []. Chronic inflammation, however, persists pathologically, accompanied by intractable pain. Chemical mediators mediating tissue inflammation act on peripheral nociceptive nerve terminals, lowering neuronal excitation thresholds and increasing afferent firing rates, thereby inducing allodynia and hyperalgesia, respectively [,]. Animal models provide crucial tools for dissecting the pathophysiological mechanisms of chronic inflammatory pain and offer reliable data support for the screening and validation of candidate analgesic drugs [,].
Nociceptors, as somatosensory neurons, are widely distributed in the skin, cornea, urogenital tract, gastrointestinal tract, joints, bone, muscle, and deep visceral tissues [,]. Their peripheral nerve endings express molecular sensors such as Transient Receptor Potential (TRP) channels and G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), capable of detecting noxious inflammatory stimuli. These stimuli include reactive chemicals, extreme temperatures (heat and cold), and mechanical damage, as well as immune mediators like ATP, bradykinin, histamine, and cytokines [,]. Studies indicate that neuro-immune interactions in pain exhibit bidirectional regulatory properties [,]. Cytokines, lipids, growth factors, and other substances released by immune cells can act on peripheral nociceptors and central nervous system (CNS) neurons, mediating pain sensitization. Conversely, nociceptors can actively release neuropeptides from their peripheral terminals, modulating the functional states of innate and adaptive immune cells. Specifically, molecules including Interleukin-1β (Il1b), Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF), Nerve Growth Factor (NGF), Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), Leukotriene B4 (LTB4), and bradykinin can bind to their cognate receptors on nociceptive terminals, triggering neuronal firing. In summary, the immune system plays a key role in pain by releasing molecular mediators that sensitize nociceptive neurons. Tissue injury and inflammation are closely associated with increased pain perception. Nociceptor peripheral nerve endings possess receptors and ion channels that detect molecular mediators released during inflammation. Upon activation, action potentials are transduced to the nociceptor cell bodies within the dorsal root ganglion (DRG) []. Furthermore, immune mediators can enhance channel function by promoting membrane trafficking or upregulating their transcriptional expression. The combined effects of these immune-mediated pathways ultimately lower the response threshold of nociceptors to mechanical or thermal stimuli, resulting in heightened pain sensitivity [].
Reports indicate that overexpression of Heat Shock Protein Family A Member 1A (HSPA1A) in joint tissues suppressed synovial inflammation, reduced chondrocyte apoptosis, and protected mice from osteoarthritis []. However, no study has definitively established the relationship between HSPA1A, immune cells, and inflammatory cytokines. Therefore, we will administer murine-derived HSPA1A protein to investigate its potential ameliorative effects on Complete Freund’s Adjuvant (CFA)-induced inflammatory pain and explore the underlying immune mechanisms.
2. Results
2.1. Effects of Different HSPA1A Doses on Inflammatory Pain Mouse Models
At 10 h post-CFA injection, paw withdrawal thresholds (PWTs) in C57BL/6 J mice decreased significantly to comparable levels, confirming successful establishment of CFA-induced inflammatory pain. Administration of 1 μg HSPA1A at 12 h and 20 h post-CFA significantly elevated PWTs (Figure 1A). Further investigation of HSPA1A dosing revealed that PWTs increased proportionally with higher HSPA1A doses, and the rate of PWT decline slowed as the administered dose increased (Figure 1B). Additionally, HSPA1A exerted consistent analgesic effects in both female and male mice, with no significant sex-based differences (Figure 1C).
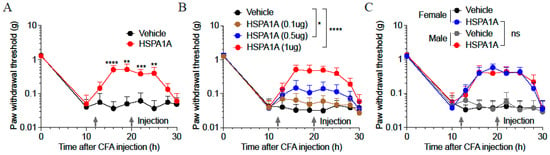
Figure 1.
Effects of HSPA1A on paw PWTs in CFA-induced inflammatory pain mouse models. (A): PWTs in CFA-induced mice after HSPA1A injection (n = 9). (B): PWTs in CFA-induced mice after different HSPA1A doses (n = 7). (C): PWTs in female and male mice after HSPA1A injection (n = 7). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001, ns: not significant (p > 0.05).
2.2. Transcriptomic RNA Analysis of HSPA1A-Induced Regulatory Changes
Transcriptomic RNA analysis identified 1947 upregulated and 1817 downregulated genes in HSPA1A-treated mice versus controls (Figure 2A). Further analysis of pro-inflammatory genes revealed significant downregulation of IL1a, IL6, CXCL1, and others (Figure 2B). Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment analysis demonstrated that downregulated genes were significantly enriched in biological processes including vascular development, cytokine–cytokine interaction, the IL-17 signaling pathway, RAF-independent MAPK1/3 activation, and regulation of the ERK1 and ERK2 cascade (Figure 2C).
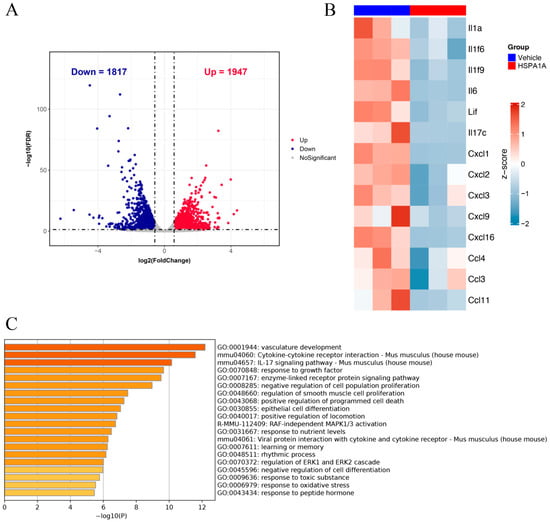
Figure 2.
Transcriptomic RNA analysis. (A): Volcano plot of differentially expressed genes. (B): Heatmap showing expression changes of pro-inflammatory mediators in plantar tissues after HSPA1A injection. (C): GO enrichment bar chart displaying altered pathways.
2.3. Impact of Different Immune Cells on HSPA1A-Mediated Analgesia
To determine whether immune cells influence HSPA1A efficacy, we compared inflammatory pain models in C57BL/6 J and NOD-SCID mice. NOD-SCID mice exhibit congenital immunodeficiency with minimal T and B cells (Figure 3A), yet HSPA1A retained its analgesic effect (Figure 3D). Neutrophil depletion in C57BL/6 J mice via anti-Gr1 antibody injection (Figure 3B) did not impair HSPA1A-mediated pain relief (Figure 3E). Conversely, macrophage depletion using clodronate liposomes (Figure 3C) significantly attenuated HSPA1A efficacy, resulting in lower PWTs versus controls (Figure 3F).
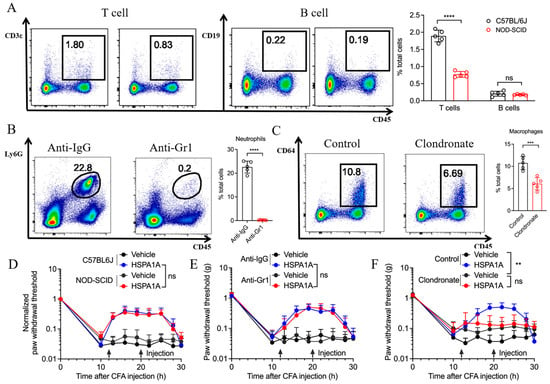
Figure 3.
Effects of immune cell depletion on HSPA1A function. (A–C): Flow cytometry quantification of immune cells (n = 5) in plantar skin, (A): T/B cells, (B): Neutrophils, (C): Macrophages. (D–F): PWT measurements (n = 7). (D): T/B lymphocyte group, (E): Neutrophil group, (F): Macrophage group. ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001, ns: not significant (p > 0.05).
2.4. In Vitro Validation of HSPA1A Effects on Macrophage Polarization
Flow cytometry revealed leftward peak shifts for CD80, CD86, and MHC-II (M1 markers) in HSPA1A-treated BMDMs (LPS/IFN-γ) versus positive controls, while CD163 and CD206 (M2 markers) remained unchanged, indicating suppressed M1 polarization without affecting M2 differentiation (Figure 4A). qPCR confirmed downregulated Il1b and Tnf mRNA levels (Figure 4B). Adoptive transfer of BMDMs (LPS/IFN-γ, 1 × 104 cells per mouse) into the paw elicited mechanical hyperalgesia, which was significantly attenuated by treating the cells with HSPA1A (Figure 4C). Metabolic analysis showed decreased ECAR and increased OCR in HSPA1A-treated BMDMs (LPS/IFN-γ) versus positive controls, indicating suppressed glycolysis and enhanced oxidative phosphorylation (Figure 4D).
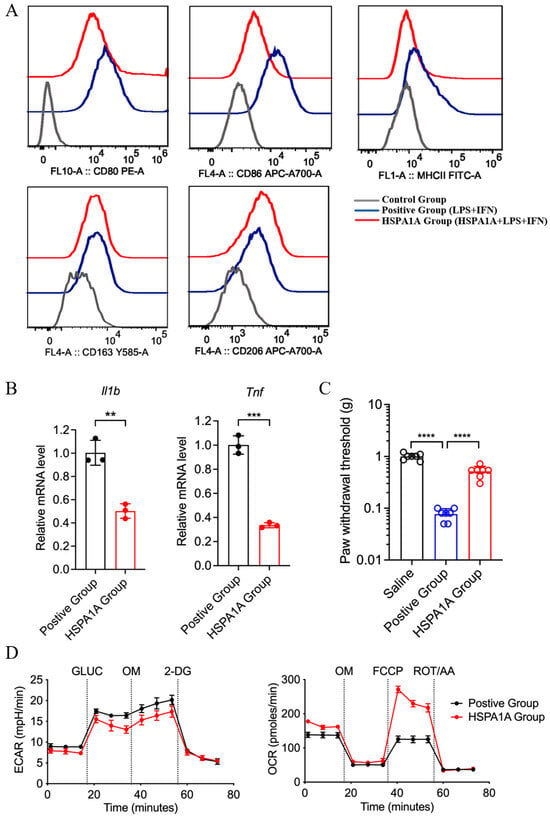
Figure 4.
In vitro effects of HSPA1A on M1-polarized BMDMs. (A): Flow cytometry analysis of M1 (CD80, CD86, MHCII) and M2 (CD163, CD206) surface markers. (B): qPCR of Il1b and Tnf mRNA (n = 3). (C): PWT measurements (n = 7). (D): ECAR and OCR assessments (n = 6). ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001, ns: not significant (p > 0.05).
2.5. Proteomic Profiling of DEPs and Enriched Pathways
Proteomic heatmaps identified differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) in HSPA1A-treated BMDMs, primarily involved in metabolic regulation and inflammation. Pro-inflammatory proteins (Cxcl2, CD80, NOS2, and TNF) were downregulated (Figure 5A), while anti-inflammatory proteins (Csf1r, CD36, Tgm2, and Bst2) were upregulated (Figure 5B). Glycolysis-related proteins (HK1, Gpi, Pfkl, and Pfkp) decreased (Figure 5C), whereas TCA cycle proteins (Suclg2, Suclg1, and Sdhb) increased (Figure 5D).
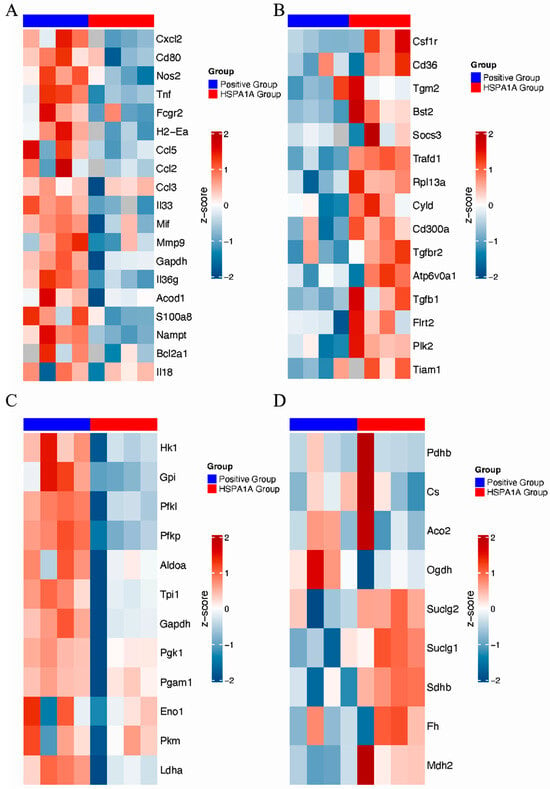
Figure 5.
Proteomic analysis of HSPA1A-induced protein alterations in BMDMs. (A): Pro-inflammatory proteins. (B): Anti-inflammatory proteins. (C): Glycolysis-related proteins. (D): TCA cycle-related proteins. Protein expressions are shown as row-wise Z-scores (red, high; blue, low).
3. Discussion
Pain affects over 20% of the global population, imposing significant health and economic burdens. Effective pain management is crucial for sufferers. However, current pain assessment and treatment methods fall short of clinical needs. Thanks to advances in neuroscience and biotechnology, neuronal circuits and molecular mechanisms critically involved in pain modulation have been elucidated [,]. Inflammation causes pain, and pain is one of the primary signs of inflammation [,]. Clinical observations undoubtedly aid in treating inflammatory diseases, yet most fundamental discoveries regarding inflammatory mechanisms originate from animal models [,,]. In vivo models help us clarify endogenous molecules involved in initiating and resolving inflammation and further improve our understanding of inflammatory pain. Moreover, animal models are essential for testing the efficacy and safety of new chemical entities with potential as novel anti-inflammatory analgesics. CFA is a conventional inducer for studying chronic inflammatory pain models in rodents. CFA injections induce production and release of various inflammatory mediators such as PGE2, nitric oxide, leukotriene B2, TNF-α, IL-2, and IL-17 [,]. These pro-inflammatory mediators can cause synovitis, polyarthritis, bone resorption, and periosteal bone proliferation and may lead to joint degeneration [,]. CFA is one of the superior models for studying inflammatory joint pain and is widely applied in research on skin inflammatory pain in mouse hind paws to investigate potential analgesic drugs. This study identified multiple inflammatory pain-related targets, all of which may provide new avenues for future pain treatment, offering theoretical foundations for clinically improving inflammatory pain management and addressing issues like opioid abuse and dependence.
Transcriptomic RNA analysis revealed that downregulated genes in HSPA1A-treated mice were enriched in pathways associated with the IL-17 signaling pathway, the MAPK signaling pathway, and the ERK signaling pathway. In temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis, M1 macrophage polarization has been shown to correlate with activation of the NF-κB/IL-17 pathway []. Meanwhile, RNA sequencing analysis in a model of LPS-pretreated cardiomyocyte-derived large extracellular vesicles (EVs) revealed significant enrichment of the MAPK pathway, suggesting its involvement in promoting M2-like polarization while suppressing the M1 phenotype []. Additionally, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-stimulated gene-6 (TSG6) has been reported to promote tumor-associated macrophage polarization by activating the TGFβR1/Smad and MAPK/ERK pathways through direct interactions between CD44 and TGFβR1 or EGFR []. Whether HSPA1A modulates macrophage polarization to alleviate inflammatory pain through these or related signaling pathways warrants further investigation.
Macrophages are among the most important cells in the innate immune system. They transform into two distinct subtypes under different microenvironmental stimuli, exhibiting completely different molecular phenotypes and functional characteristics. Macrophages typically exist in two distinct subpopulations: (1) classically activated, or M1, macrophages, which are pro-inflammatory and polarized by LPS alone or in combination with Th1 cytokines, producing pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β, IL-6, IL-12, IL-23, and TNF-α; (2) alternatively activated, or M2, macrophages, which have anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects, are polarized by Th2 cytokines like IL-4 and IL-13 and produce anti-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-10 and TGF-β [,]. Multiple studies indicate macrophages regulate inflammatory responses through different signaling pathways [,,]. Expression levels of most inflammation-related proteins showed downward trends, while most anti-inflammatory proteins were upregulated, indicating HSPA1A may inhibit pro-inflammatory phenotypes in macrophages. As previously demonstrated, activation of the HSPA1A reduces NLRP3 inflammasome activity and the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as Il1b [], supporting our observation. Metabolic reprogramming plays a key role in regulating macrophage function. Classically activated M1 macrophages favor glycolysis, producing lactate instead of metabolizing pyruvate to acetyl-CoA, and exhibit an interrupted TCA cycle at two points. M2 macrophages primarily utilize β-oxidation of fatty acids and oxidative phosphorylation to generate energy-rich molecules like ATP, participating in tissue repair and inflammation downregulation [,]. Song et al. found that Salvianolic Acid B attenuates liver fibrosis via suppression of glycolysis-dependent M1 macrophage polarization []. Whether metabolic reprogramming contributes to this HSPA1A-mediated polarization shift in inflammatory pain remains unclear. To explore this, we examined macrophage metabolism in vitro experiments and proteomics analysis and found that HSPA1A inhibits glycolysis while enhancing both oxidative phosphorylation and the tricarboxylic acid cycle, indicative of a metabolic reprogramming effect. These findings provide initial evidence that HSPA1A alleviates inflammation and pain through metabolic reprogramming of macrophages, offering new insights into the mechanisms behind its anti-inflammatory and analgesic actions.
Although our findings demonstrate that HSPA1A protein alleviates CFA-induced inflammatory pain by inhibiting glycolysis and suppressing M1 polarization of BMDMs, the specific binding receptors and activation states of related downstream signaling pathways remain unclear, which is a limitation of this study. In future studies, we will validate the expression of glycolysis-related proteins through in vivo and in vitro experiments and investigate glycolysis-associated signaling pathways in macrophages following HSPA1A treatment. Our study elucidated the mechanism through which HSPA1A regulates macrophage polarization by performing transcriptomic and proteomic sequencing of plantar tissues and BMDMs following HSPA1A treatment. Existing research indicates persistent increases in cytokines and chemokines in the central nervous system also promote chronic widespread pain affecting multiple body parts, and this modulation is associated with regulation of immune signals [,]. Therefore, to clarify the potential role of the CNS in the mechanism of HSPA1A action, future studies will investigate changes in the cerebrospinal fluid after HSPA1A administration. Furthermore, our findings demonstrate that HSPA1A downregulates the expression of the glycolytic enzymes HK1 and Pfkl in macrophages. Previous research has shown that demethylation of HK1 can modulate the glycolytic pathway [], while phosphorylation of Pfkl, a rate-limiting enzyme in glycolysis, can activate metabolic reprogramming in macrophages []. Whether metabolic enzyme activity involved in metabolic reprogramming affects metabolic gene expression through epigenetic modifications such as methylation and phosphorylation was not deeply explored in this study. These limitations provide directions for future research.
In summary, we show that mouse-derived HSPA1A alleviates CFA-induced inflammatory pain by modulating macrophage polarization via glycolysis inhibition. However, the precise mechanism through which HSPA1A regulates glycolysis has not been fully elucidated, highlighting an important area for future investigation. Future studies will further explore molecular targets, expand disease models, and enhance clinical translation feasibility to bridge basic research and clinical applications.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Synthesis of HSPA1A Proteins
Recombinant murine HSPA1A protein was prepared as previously described []. Briefly, mouse HSPA1A cDNA and its N-terminal nucleotide-binding domain (NBD) and substrate-binding domain (SBD) fragments were amplified by PCR. These fragments were directionally cloned into the pET-22b+ vector using specific primers and restriction enzymes (NdeI and XhoI), transformed into E. coli DH5α, and positive clones were verified by PCR and sequencing. For recombinant protein production and purification, the validated plasmid was transformed into E. coli BL21(DE3). A single colony was cultured until OD reached 0.8–1.0, induced with IPTG for 14–16 h, and bacterial cells were collected by centrifugation. After lysis, the supernatant was incubated with cobalt–agarose beads to bind the target protein. Following washing, bound protein was eluted with imidazole-containing buffer and dialyzed into HEPES buffer using centrifugal filters.
4.2. Isolation and Culture of Bone Marrow-Derived Macrophages (BMDMs)
Femurs and tibiae from C57BL/6 J mice were dissected, adherent tissues removed, and bone marrow cells flushed with sterile PBS. After centrifugation, cells were resuspended in DMEM with 10% fetal bovine serum. Macrophage colony-stimulating factor (Peprotech, Cranbury, NJ, USA) was added to induce differentiation. Cells were cultured at 37 °C under 5% CO2 for 7–10 days, with the medium replaced every 2–3 days. Mature BMDMs were used for subsequent experiments.
4.3. Induction and Treatment of M1 Macrophages
Differentiated BMDMs were cultured in complete DMEM containing LPS (100 ng/mL, Beyotime, Haimen, China) and IFN-γ (20 ng/mL, Peprotech, USA) for 24 h to obtain M1 macrophages. For the experimental group, 100 ng/mL HSPA1A was added during this process; controls received an equal volume of solvent.
4.4. Establishment and Treatment of Inflammatory Pain Models
Thirty-nine C57BL/6 J mice (male, weighing 20 ± 2 g) and twelve NOD-SCID mice (male, weighing 20 ± 2 g) were purchased from Guangdong Zhiyuan Biomedical Technology Co., LTD (Shenzhen, China). Animals were housed conventionally with free access to food and water on a 12-hour light/dark cycle. All animal experimental procedures were approved by the Laboratory Animal Ethics Committee of Lai’an Technology (Guangzhou, China) Co., LTD (Approval number: G2025065, approval date: 7 August 2025) and were carried out in compliance with the ARRIVE 2.0 guidelines (https://arriveguidelines.org) accessed on 7 August 2025 regarding the care and use of laboratory animals. Into the plantar surface of the mouse hind paw was injected 10 μL of 1:1 diluted CFA (Sigma, Darmstadt, Germany). At 12 h and 20 h post-injection, mice received HSPA1A or an equal volume of saline (control). For neutrophil depletion, C57BL/6 J mice were intraperitoneally injected with anti-Gr1 antibody (49.5 μg dissolved in a total of 200 μL saline solution) 48 h and 24 h before CFA injection; controls received IgG antibody. For macrophage depletion, clodronate liposomes (300 μL) were administered intraperitoneally 72 h and 24 h before CFA; controls received empty liposomes.
4.5. Quantitative PCR (qPCR)
Total RNA was extracted using the AMV One-step RT-PCR Kit (Sangon, Shanghai, China) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Reverse transcription was performed using the AMV First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (Sangon, CN). qPCR was conducted on a Roche LightCycler 96 system using 2 × SYBR Green Abstart PCR Mix (Sangon, CN), with primers listed in Table 1. Relative gene expression was calculated by the 2−ΔΔCt method, normalized to GAPDH.

Table 1.
Primer sequences.
4.6. Measurement of Mechanical Hypersensitivity
Before behavioral experiments, mice were exposed to the testing environment for 1–2 h daily for 2 days without stimulation. All mice were acclimated to the testing environment. Experimenters were blinded to group assignments during testing. Each mouse was placed individually in a plexiglass chamber for 30 min habituation. Calibrated Semmes-Weinstein von Frey filaments (0.008, 0.02, 0.04, 0.07, 0.16, 0.4, 0.6, 1.0, and 1.4 g) were applied to the plantar surface of the inflamed paw for 3–4 s, with 5-minute intervals between stimuli. Filament forces were adjusted stepwise based on the mouse’s response. A positive response was defined as rapid withdrawal of the hind paw. After the first observed response change, five additional stimuli were applied. Paw withdrawal thresholds (PWTs) were assessed 8 times within 30 h post-CFA injection using the up–down von Frey testing paradigm. Baseline PWTs differed between NOD-SCID and C57BL/6 J mice; thus, NOD-SCID data were normalized.
4.7. Analysis of Cell Bioenergetics
Glycolysis and tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle activity in HSPA1A-treated BMDMs were measured using a Seahorse XFe96 Analyzer (Seahorse, La Verne, CA, USA). Extracellular acidification rate (ECAR) and oxygen consumption rate (OCR) were used to evaluate metabolic levels. As described [], 25,000 BMDMs were seeded in XF-96 plates and treated. ECAR and OCR were measured using the XF-96 flux analyzer. Glycolytic parameters were calculated from ECAR changes after injections of glucose, oligomycin (OM), and 2-deoxyglucose (2-DG). Mitochondrial parameters were derived from OCR changes after injections of OM, FCCP, and rotenone + antimycin A (ROT + AA). ECAR and OCR data were normalized to DNA content measured by CyQuant.
4.8. Flow Cytometry
Plantar skin tissues were placed in cold PBS, minced, and digested with 0.2% collagenase at 37 °C for 30 min. Tissues were dispersed into single-cell suspensions, filtered through a cell strainer, and centrifuged at 1500 rpm for 5 min. The supernatant was discarded, and the pellet was resuspended in PBS. Cells were finally resuspended in PBS with 2% FBS at 1 × 106 cells/mL. Cell suspensions were stained with CD45 (BioLegend, San Diego, CA, USA) antibody at 4 °C for 15 min protected from light. Antibodies against B cells (CD19, BioLegend, USA), NK cells (CD161c, BioLegend, USA), neutrophils (Ly6G, BioLegend, USA), and macrophages (CD64, BioLegend, USA) were added, mixed gently, and incubated at 4 °C for 30 min protected from light. After two PBS washes, cells were resuspended in 500 μL PBS and analyzed on a Beckman Cytoflex S flow cytometer (Beckman, Indianapolis, IN, USA). Data were analyzed using FlowJo (v10.4).
4.9. Transcriptomic Sequencing and Analysis
Plantar tissues from HSPA1A-treated and control mice were collected. Total RNA was isolated, treated with DNase, and purified using columns. RNA concentration was measured and adjusted. RNA quality was confirmed using a fragment analyzer. Qualified samples were used for library preparation: mRNA was enriched with oligo-dT beads, fragmented, and cDNA was synthesized. Adapters were ligated and PCR-amplified. Libraries were sequenced (paired-end) on an Illumina platform (https://www.illumina.com/, accessed on 7 August 2025). Raw data (FASTQ format) underwent base calling and quality control. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified (threshold: |log2FC| > 0.58, adjusted p-value < 0.05). DEG heatmaps were generated using the pheatmap package, and volcano plots were created with ggplot2. Downregulated DEGs were analyzed for GO enrichment using Metascape (Fisher’s exact test, p < 0.05).
4.10. Proteomic Sequencing and Analysis
Samples were prepared as above and submitted to APTBIO (Shanghai, China). Proteins were extracted using SDS-containing buffer and quantified. Labeled peptides were mixed, vacuum-dried, separated on a C18 trap column, and analyzed by LC-MS/MS. Peptides were identified by parsimony principles and filtered to a defined false discovery rate. Quantification positively identified peptides. Proteins with |log2FC| > 1 and an adjusted p-value < 0.05 were defined as differentially expressed proteins (DEPs). DEP heatmaps were generated using pheatmap.
4.11. Statistical Analysis
GraphPad Prism 9.5.1 was used for analysis. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. For statistical comparison between groups, two-group comparisons were made using two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-tests or Welch’s t-tests (for unequal variances). For comparisons of two groups over time, two-way ANOVA with the Sidak post hoc test was used. p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
5. Conclusions
HSPA1A protein alleviates CFA-induced inflammatory pain, and this effect specifically depends on macrophages. HSPA1A suppressed the M1 polarization of BMDM and reduced the secretion of the inflammatory cytokines IL-1β and TNF-α. This effect was associated with HSPA1A-induced metabolic reprogramming in macrophages, particularly through the inhibition of glycolysis (Figure 6). Our findings provide new experimental evidence clarifying the mechanism by which HSPA1A regulates macrophage polarization and highlight the potential of HSPA1A as a novel analgesic agent.
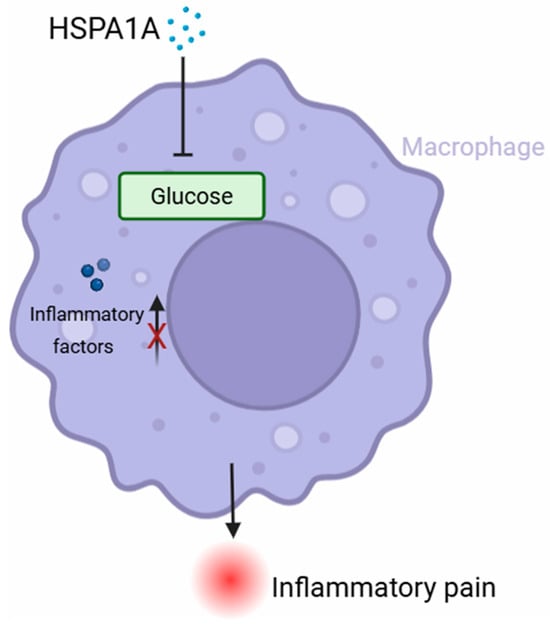
Figure 6.
Schematic diagram. The present study demonstrated that HSPA1A significantly ameliorated CFA-induced inflammatory pain. This protective effect was achieved through inhibition of macrophage M1 polarization and glycolysis. HSPA1A inhibited glycolysis, thereby reducing macrophage M1 polarization and the release of inflammatory factors.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.Z. and F.C.; methodology, W.Z. and F.C.; software, X.X. (Xiaojun Xie); validation, W.Z., X.X. (Xiaojun Xie) and X.X. (Xiaomin Xiong); formal analysis, W.Z., X.X. (Xiaojun Xie) and X.X. (Xiaomin Xiong); investigation, W.Z.; resources, X.X. (Xiaojun Xie); data curation, X.X. (Xiaomin Xiong); writing—original draft preparation, W.Z.; writing—review and editing, W.Z. and F.C.; visualization, X.X. (Xiaomin Xiong); supervision, W.Z.; project administration, F.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of Lai’an Technology (Guangzhou, China) Co., LTD (Approval number: G2025065, approval date: 7 August 2025).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The transcriptomic sequencing data generated in this study have been deposited in the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database under the accession number GSE304075, which is publicly accessible at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/, accessed on 7 August 2025. The proteomic datasets have been deposited in the iProX database with the accession number IPX0012817000 (available at https://www.iprox.cn/, accessed on 7 August 2025) and are also archived in the PRIDE database under the accession number PXD066909 (accessible at https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/, accessed on 7 August 2025). All other relevant data supporting the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Sekiguchi, F.; Tsubota, M.; Kawabata, A. Involvement of Voltage-Gated Calcium Channels in Inflammation and Inflammatory Pain. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 41, 1127–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, K.; Torres, R. Role of interleukin-1beta during pain and inflammation. Brain Res. Rev. 2009, 60, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Heinricher, M.M. Plasticity in the Link between Pain-Transmitting and Pain-Modulating Systems in Acute and Persistent Inflammation. J. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 2065–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Qadri, Y.J.; Serhan, C.N.; Ji, R.R. Microglia in Pain: Detrimental and Protective Roles in Pathogenesis and Resolution of Pain. Neuron 2018, 100, 1292–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.F.; Yang, H.W.; Yang, T.S.; Xie, W.; Hu, Z.H. TNF-α—mediated peripheral and central inflammation are associated with increased incidence of PND in acute postoperative pain. BMC Anesthesiol. 2021, 21, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudnik-Jansen, I.; Schrijver, K.; Woike, N.; Tellegen, A.; Versteeg, S.; Emans, P.; Mihov, G.; Thies, J.; Eijkelkamp, N.; Tryfonidou, M.; et al. Intra-articular injection of triamcinolone acetonide releasing biomaterial microspheres inhibits pain and inflammation in an acute arthritis model. Drug Deliv. 2019, 26, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, A.; Iliff, D.; Zaheer, K.; Gansau, J.; Laudier, D.M.; Zachariou, V.; Iatridis, J.C. Annulus Fibrosus Injury Induces Acute Neuroinflammation and Chronic Glial Response in Dorsal Root Ganglion and Spinal Cord-An In Vivo Rat Discogenic Pain Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basbaum, A.I.; Bautista, D.M.; Scherrer, G.; Julius, D. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of pain. Cell 2009, 139, 267–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares-Ferreira, D.; Shiers, S.; Ray, P.R.; Wangzhou, A.; Jeevakumar, V.; Sankaranarayanan, I.; Cervantes, A.M.; Reese, J.C.; Chamessian, A.; Copits, B.A.; et al. Spatial transcriptomics of dorsal root ganglia identifies molecular signatures of human nociceptors. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14, eabj8186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilger, D.; Masureel, M.; Kobilka, B.K. Structure and dynamics of GPCR signaling complexes. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2018, 25, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, F.; Bouma, E.M.; Hu, G.; Zhu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Smit, J.M.; Diamond, M.S.; Zhang, R. Colocalization of Chikungunya Virus with Its Receptor MXRA8 During Cell Attachment, Internalization, and Membrane Fusion. J. Virol. 2023, 97, e0155722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho-Ribeiro, F.A.; Verri WAJr Chiu, I.M. Nociceptor Sensory Neuron-Immune Interactions in Pain and Inflammation. Trends Immunol. 2017, 38, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raoof, R.; Willemen, H.L.D.M.; Eijkelkamp, N. Divergent roles of immune cells and their mediators in pain. Rheumatology 2018, 57, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momin, A.; Wood, J.N. Sensory neuron voltage-gated sodium channels as analgesic drug targets. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2008, 18, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajaczkowska, R.; Kwiatkowski, K.; Pawlik, K.; Piotrowska, A.; Rojewska, E.; Makuch, W.; Wordliczek, J.; Mika, J. Metamizole relieves pain by influencing cytokine levels in dorsal root ganglia in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Pharmacol. Rep. 2020, 72, 1310–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, Y.O.; Kim, H.E.; Choi, W.S.; Chun, C.H.; Chun, J.S. RNA-binding protein ZFP36L1 regulates osteoarthritis by modulating members of the heat shock protein 70 family. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, B.; Xu, Q.; Shi, Y.; Zhao, R.; Li, H.; Zheng, J.; Liu, F.; Wan, Y.; Wei, B. Pathology of pain and its implications for therapeutic interventions. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunley, B.; Mulligan, E.P.; Chhabra, A.; Fey, N.P.; Wells, J. Relationships between self-perceived and clinical expression of pain and function differ based on the underlying pathology of the human hip. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2023, 24, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Bang, S.; Chandra, S.; Ji, R.R. Inflammation and Infection in Pain and the Role of GPR37. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, M.; Huh, Y.; Ji, R.R. Roles of inflammation, neurogenic inflammation, and neuroinflammation in pain. J. Anesth. 2019, 33, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowty, M.E.; Jesson, M.I.; Ghosh, S.; Lee, J.; Meyer, D.M.; Krishnaswami, S.; Kishore, N. Preclinical to clinical translation of tofacitinib, a janus kinase inhibitor, in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2014, 348, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesen, A.E.; Andresen, T.; Staahl, C.; Drewes, A.M. Human experimental pain models for assessing the therapeutic efficacy of analgesic drugs. Pharmacol. Rev. 2012, 64, 722–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, N.; Guo, Z.; Ye, R.; Guan, L.; Ren, J.; Liang, Y.; Shao, X.; Fang, J.; Fang, J.; Du, J. A systematic review of the pain-related emotional and cognitive impairments in chronic inflammatory pain induced by CFA injection and its mechanism. IBRO Neurosci. Rep. 2025, 18, 414–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burek, D.J.; Massaly, N.; Yoon, H.J.; Doering, M.; Morón, J.A. Behavioral outcomes of complete Freund adjuvant-induced inflammatory pain in the rodent hind paw: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pain 2022, 163, 809–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hipólito, L.; Wilson-Poe, A.; Campos-Jurado, Y.; Zhong, E.; Gonzalez-Romero, J.; Virag, L.; Whittington, R.; Comer, S.D.; Carlton, S.M.; Walker, B.M.; et al. Inflammatory Pain Promotes Increased Opioid Self-Administration: Role of Dysregulated Ventral Tegmental Area μ Opioid Receptors. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 12217–12231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, M.; Xu, F.; Ni, H.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, R.; Lou, Y.; Zhou, J. Neutrophil activation and NETosis are the predominant drivers of airway inflammation in an OVA/CFA/LPS induced murine model. Respir. Res. 2022, 23, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehrenbacher, J.C.; Vasko, M.R.; Duarte, D.B. Models of inflammation: Carrageenan-or complete Freund's Adjuvant (CFA)-induced edema and hypersensitivity in the rat. Curr. Protoc. Pharmacol. 2012, 56, 5.4.1–5.4.4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, F.; Gao, L. Targeted soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibits M1 macrophage polarization to improve cartilage injury in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis. J. Transl. Med. 2025, 23, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; You, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhou, S.; Ma, M.; Han, B. Large extracellular vesicles derived from LPS-preconditioned cardiomyocytes alleviate myocarditis via mediating macrophage polarization and modulating p38 MAPK pathway. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1629676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.J.; Min, G.H.; Kim, D.E.; Shin, S.B.; Yim, H. TSG6 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and tumor-associated macrophage polarization through Smad2/3 and MAPK signaling by facilitating TSG6-CD44-TGFβR1 or EGFR complex formation. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2025, 21, 4701–4718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Zhao, F.; Cheng, H.; Su, M.; Wang, Y. Macrophage polarization: An important role in inflammatory diseases. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1352946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pemmari, A.; Moilanen, E. Macrophage and chondrocyte phenotypes in inflammation. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2024, 135, 537–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassiliou, E.; Farias-Pereira, R. Impact of Lipid Metabolism on Macrophage Polarization: Implications for Inflammation and Tumor Immunity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wan, R.; Peng, W.; Zhao, X.; Bai, W.; Hu, C. Quercetin alleviates ferroptosis accompanied by reducing M1 macrophage polarization during neutrophilic airway inflammation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 938, 175407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Zhou, M.; Yang, H.; Qu, R.; Qiu, Y.; Hao, J.; Bi, H.; Guo, D. Regulatory Mechanism of M1/M2 Macrophage Polarization in the Development of Autoimmune Diseases. Mediat. Inflamm. 2023, 2023, 8821610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, A.; Bullock, D.; Lim, A.; Argemi, J.; Orning, P.; Lien, E.; Bataller, R.; Mandrekar, P. Inhibition of HSP90 and Activation of HSF1 Diminish Macrophage NLRP3 Inflammasome Activity in Alcohol-Associated Liver Injury. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2020, 44, 1300–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, S.; Kwiatkowski, M.; Govorukhina, N.; Bischoff, R.; Melgert, B.N. Meta-Inflammation and Metabolic Reprogramming of Macrophages in Diabetes and Obesity: The Importance of Metabolites. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 746151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Deng, C.; Wang, S.; Dong, X.; Dai, B.; Guo, W.; Guo, Q.; Feng, Y.; Xu, H.; Song, X.; et al. A novel role for the ROS-ATM-Chk2 axis mediated metabolic and cell cycle reprogramming in the M1 macrophage polarization. Redox Biol. 2024, 70, 103059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.; Li, Z.W.; Xu, W.; Tan, Y.; Kuang, M.; Pei, G.; Wang, Z.Q. Salvianolic Acid B Attenuates Liver Fibrosis via Suppression of Glycolysis-Dependent m1 Macrophage Polarization. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tracey, I.; Mantyh, P.W. The cerebral signature for pain perception and its modulation. Neuron 2007, 55, 377–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, R.R.; Nackley, A.; Huh, Y.; Terrando, N.; Maixner, W. Neuroinflammation and Central Sensitization in Chronic and Widespread Pain. Anesthesiology 2018, 129, 343–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Y.; Wu, J.; Yang, W.; Lyu, R.; You, Q.; Li, J.; He, Q.; Zhuang, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; et al. FTO-associated osteoclastogenesis promotes alveolar bone resorption in apical periodontitis male rat via the HK1/USP14/RANK pathway. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Flaswinkel, H.; Joshi, A.; Napoli, M.; Masgrau-Alsina, S.; Kamper, J.M.; Henne, A.; Heinz, A.; Berouti, M.; Schmacke, N.A.; et al. Phosphorylation of PFKL regulates metabolic reprogramming in macrophages following pattern recognition receptor activation. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCallister, C.; Kdeiss, B.; Nikolaidis, N. Biochemical characterization of the interaction between HspA1A and phospho-lipids. Cell Stress Chaperones 2016, 21, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Bossche, J.; Baardman, J.; Otto, N.A.; van der Velden, S.; Neele, A.E.; van den Berg, S.M.; Luque-Martin, R.; Chen, H.J.; Boshuizen, M.C.; Ahmed, M.; et al. Mitochondrial Dysfunction Prevents Repolarization of Inflammatory Macrophages. Cell Rep. 2016, 17, 684–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).