Abstract
The TIFY gene family participates in crucial processes including plant development, stress adaptation, and hormonal signaling cascades. While the TIFY gene family has been extensively characterized in model plant systems and agricultural crops, its functional role in Eucalyptus grandis, a commercially valuable tree species of significant ecological and economic importance, remains largely unexplored. In the present investigation, systematic identification and characterization of the TIFY gene family were performed in E. grandis using a combination of genome-wide bioinformatics approaches and RNA-seq-based expression profiling. Nineteen EgTIFY genes were identified in total and further grouped into four distinct subfamilies, TIFY, JAZ (subdivided into JAZ I and JAZ II), PPD, and ZML, based on phylogenetic relationships. These genes exhibited considerable variation in gene structure, chromosomal localization, and evolutionary divergence. Promoter analysis identified a multitude of cis-acting motifs involved in mediating hormone responsiveness and regulating abiotic stress responses. Transcriptomic profiling indicated that EgJAZ9 was strongly upregulated under methyl jasmonate (JA) treatment, suggesting its involvement in JA signaling pathways. Taken together, these results offer valuable perspectives on the evolutionary traits and putative functional roles of EgTIFY genes.
1. Introduction
TIFY transcription factors, a plant-specific family first identified in Arabidopsis thaliana, belong to the GATA transcription factor superfamily and are characterized by a highly conserved TIFY domain encompassing the core motif TIF[F/Y]XG [1]. The molecular functions of TIFY proteins are primarily associated with protein–protein interactions and regulation of signal transduction, particularly within the jasmonic acid (JA) signaling pathway [2,3,4]. The presence of conserved domains underpins the division of the TIFY gene family into four main subfamilies: TIFY, JAZ (further divided into JAZ I and JAZ II), ZML, and PPD [5,6]. The TIFY subfamily is distinguished by the presence of solely the core TIFY domain [7]. The JAZ subfamily is distinguished by the co-occurrence of the TIFY domain and a C-terminal Jas domain, which is essential for JA signaling [8]. ZML subfamily members possess the TIFY domain, a GATA-type zinc finger domain, and a CCT (CONSTANS, CO-like, and TOC1) motif [9]. The PPD subfamily is characterized by the presence of a PPD domain, a TIFY domain, and a truncated Jas domain that lacks the conserved PY motif [10]. Such structural heterogeneity across subfamilies mirrors their functional divergence and emphasizes their importance in modulating plant growth and development, physiological activities, abiotic stress responses, and hormone signaling pathways.
TIFY gene families have been identified and characterized in a multitude of plant species, with 18 members documented in A. thaliana [3], 20 in Oryza sativa [11], 15 in Salvia miltiorrhiza [12], 19 in Brachypodium distachyon [13], 30 in maize (Zea mays) [14], 16 in Capsicum annuum [15], 21 in Juglans regia [16], 16 in Camellia sinensis [17], and 25 in Populus trichocarpa [7]. Functional studies in A. thaliana have established the participation of TIFY genes in regulating various developmental processes, such as root hair development, lateral root formation, stamen development, and leaf senescence [18,19]. Of these, the JAZ subfamily has garnered the most intensive scrutiny, attributable to its pivotal role in JA signaling pathways. JAZ proteins act as repressive regulators in jasmonate signaling through interactions with basic helix–loop–helix (bHLH) transcription factors such as MYC2 and MYC3, thereby negatively regulating jasmonate-mediated physiological responses [8,18,20]. Overexpression of AtTIFY1/AtZIM facilitates petiole and hypocotyl elongation via the induction of longitudinal cellular expansion [3]. ZML subfamily members have been implicated in regulating hormone pathways related to photoperiodic responses, while AtTIFY4a and AtTIFY4b of the PPD subfamily have been shown to control leaf size and margin curvature in A. thaliana [21,22].
E. grandis, a globally significant fast-growing tree species, holds high economic, ecological, and industrial value. It is widely cultivated for its desirable wood properties and serves as a key raw material in industries such as paper production, construction, and furniture manufacturing [23]. Given its commercial importance and broad adaptability, E. grandis has emerged as a model species for forest genomics research. However, despite the established significance of TIFY genes in plant physiological processes, their systematic characterization in E. grandis remains unreported.
In the current study, a genome-wide identification and analysis of the TIFY gene family in E. grandis were performed through an integration of genome-wide bioinformatics methodologies and RNA-seq-driven expression profiling. These genes were analyzed for their physicochemical properties, conserved motifs, chromosomal distribution, and expression profiles. The expression levels of JAZ subfamily members, including EgJAZ9, EgJAZ10, and EgJAZ11, were significantly upregulated following JA treatment. Their protein sequences contain highly conserved Jas domains similar to those found in Arabidopsis JAZ proteins, indicating their potential involvement in jasmonate signaling. Among them, EgJAZ9 emerges as a promising candidate for further functional investigation. Our results offer valuable perspectives on the structural features and putative functions of EgTIFY genes, laying a foundation for future functional studies and contributing to a deeper understanding of the TIFY family’s role in Eucalyptus development and stress responses.
2. Results
2.1. Identification and Physicochemical Characteristics of EgTIFY Proteins
TIFY protein sequences derived from A. thaliana were employed as query sequences in a BLASTp (TBtools-II) analysis to conduct comparative sequence alignments with E. grandis protein sequences. Based on sequence homology and conserved domain analyses, a total of 19 TIFY family members were identified in E. grandis and categorized into four distinct subfamilies: JAZ (subdivided into JAZ I and JAZ II), PPD, TIFY, and ZML (Table 1). Physicochemical analyses revealed notable differences among the EgTIFY proteins in terms of sequence length, instability index, theoretical isoelectric point (pI), and molecular weight. The proteins varied in length from 104 to 443 amino acids, with EgTIFY1 representing the largest (443 aa) and EgJAZ9 the smallest (104 aa).

Table 1.
Biophysical characteristics of TIFY family proteins in E. grandis.
Isoelectric point analysis indicated that 13 EgTIFY proteins have pI values above 7, while 6 have values below 7, suggesting that the majority of these proteins are basic in nature. The aliphatic index, which reflects thermostability, ranged from 31.19 (EgZML1) to 83.27 (EgJAZ5), indicating relatively minor variation in thermal stability among the family members. All EgTIFY proteins displayed negative GRAVY (Grand Average of Hydropathy) scores, confirming their hydrophilic nature. Among them, EgZML3 was the most hydrophilic (GRAVY = −0.57), while EgJAZ12 showed the lowest degree of hydrophilicity (GRAVY = −0.31). Subcellular localization predictions indicated that all 19 EgTIFY proteins are presumably localized within the nucleus (Table 1).
2.2. Phylogenetic Tree of EgTIFYs
To dissect the evolutionary associations of the TIFY gene family across plant lineages, a phylogenetic tree was constructed utilizing full-length TIFY protein sequences originating from E. grandis (19 sequences), A. thaliana (19), Populus trichocarpa (25), and Physcomitrella patens (14). Following sequence alignment, a neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree was generated (Figure 1). The phylogenetic tree delineated four major subfamilies: JAZ (encompassing JAZ I and JAZ II), PPD, TIFY, and ZML. Among these, the JAZ II subfamily contained the largest number of EgTIFY genes (11), whereas the JAZ I, PPD, and TIFY subfamilies each included a single member. The ZML subfamily comprised five EgTIFY genes. Notably, TIFY genes from E. grandis and P. trichocarpa were dispersed across multiple shared branches, signifying a relatively close evolutionary affinity between these two species (Figure 1).
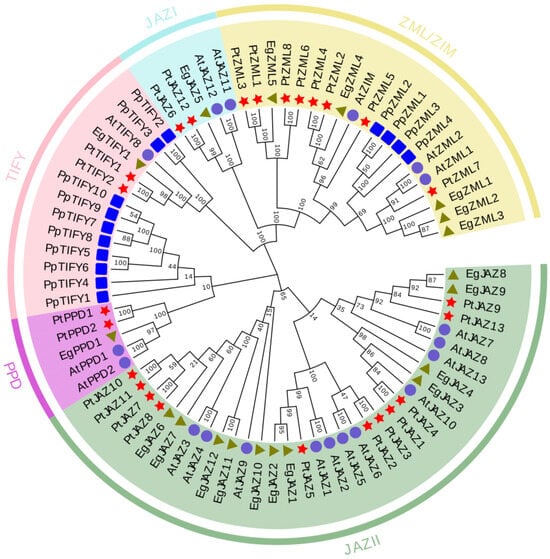
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic tree of TIFY genes in E. grandis, P. trichocarpa, A. thaliana, and Physcomitrium patens. Symbols of different shapes represent TIFY genes from E. grandis (green triangles, Eg), A. thaliana (blue circles, At), P. trichocarpa (red stars, Pt), and P. patens standing bowl moss (blue squares, Pp). The neighbor-joining tree was constructed with 1000 bootstrap replicates.
2.3. Analysis of Gene Structures and Conserved Domains of EgTIFYs
The 19 EgTIFY proteins were classified into four subfamilies according to conserved motifs and phylogenetic relationships (Figure 1). Conserved motifs were detected via the MEME suite, revealing 10 distinct motifs (Figure 2b). Motif 1 was conserved across all EgTIFY proteins, and 17 of the 19 genes contained Motif 2, with the exception of EgZML2 and EgTIFY1. Gene structure analysis revealed that EgTIFYs contained 2–10 exons and 0–4 introns (Figure 2c). Among them, EgZML5 had the most complex structure with 10 exons and 1 intron, while EgJAZ9 and EgZML2 had the simplest structure, each with only 2 exons and no introns.
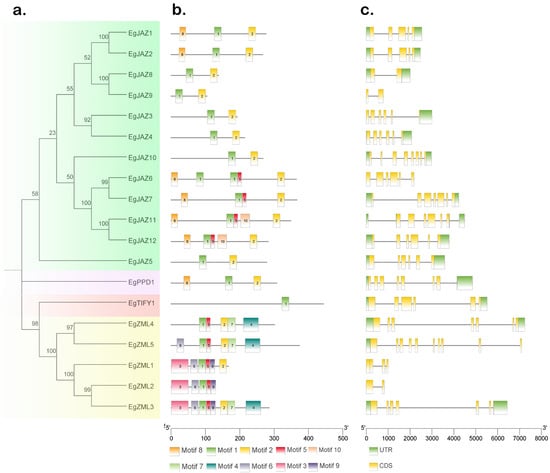
Figure 2.
Analysis of conserved motifs and gene structure of EgTIFYs. (a) Neighbor-joining phylogenetic analysis (Bootstrap: 1000) of EgTIFYs proteins illustrating subfamily classifications, with four different colors representing four subfamilies: light green (JAZ), purple (PPD), red (TIFY), and yellow (ZML). (b) The different colored modules (Motif 1–Motif 10) represent the conserved amino acid sequence patterns in members of the gene family. (c) The intron and exon maps present the structural composition of the gene, with the yellow region representing the coding sequence (CDS) and the green region representing the untranslated region (UTR).
2.4. Chromosomal Localization of EgTIFYs
Chromosomal mapping analysis indicated that the 19 EgTIFY genes are dispersed across nine chromosomes (chromosomes 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 10, and 11; Figure 3). Chromosome 3 harbored the highest number of EgTIFY genes (four: EgJAZ1, EgJAZ2, EgJAZ5, and EgTIFY1), followed by chromosomes 6 and 7, each containing three genes. Chromosome 8 carried two genes, while the remaining chromosomes each contained one. Notably, EgZML1 and EgZML2 were localized to the same scaffold and not anchored to any chromosome. Additionally, the EgTIFY genes were dispersed across chromosomes without forming clusters.
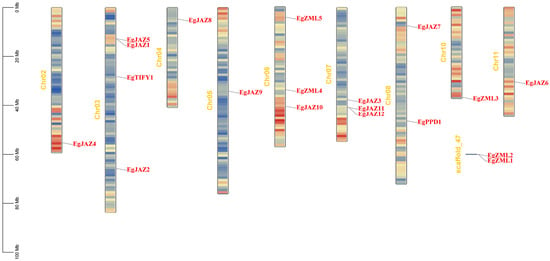
Figure 3.
Chromosome identifiers are centrally positioned. Scale bars (Mb) and color gradients (red: high gene density; blue: low gene density) denote genomic distribution patterns.
2.5. Analysis of Intraspecific and Interspecific Collinearity of EgTIFY Genes
To investigate whole-genome duplication events involving EgTIFY genes, an intra-specific synteny analysis was conducted for the TIFY gene family in E. grandis (Figure 4a). The findings indicated that the TIFY gene family in E. grandis has undergone infrequent intragenomic duplication events, with a mere four pairs of tandem and segmental duplications revealed: EgJAZ6-EgJAZ7, EgJAZ2-EgJAZ1/EgJAZ5, EgJAZ8-EgJAZ9, and EgZML4-EgZML5. In interspecific synteny analyses, 17 collinear gene pairs were identified between E. grandis and A. thaliana, whereas 29 gene pairs were found between E. grandis and P. trichocarpa, indicating a higher degree of evolutionary conservation between E. grandis and P. trichocarpa.
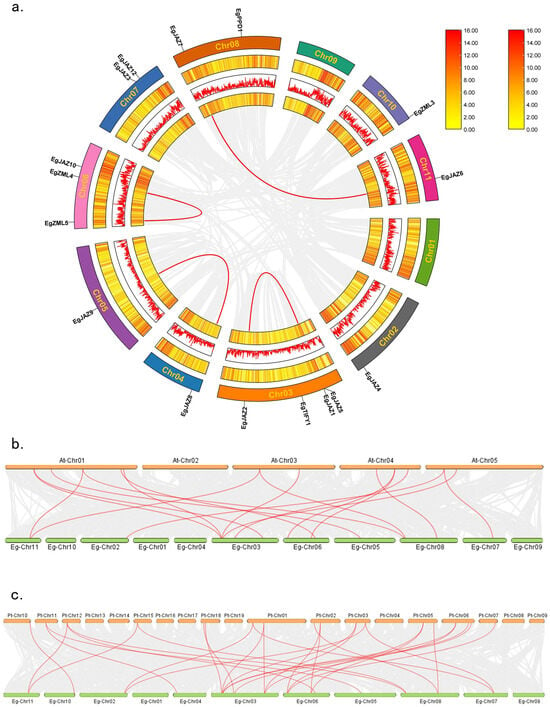
Figure 4.
Collinearity profiles of TIFY family members across E. grandis, P. trichocarpa, and A. thaliana. Intraspecific collinear associations of TIFY family members in E. grandis (a). The three rings from inside to outside represent gene densities, presented as a heatmap and lines, respectively, and the rectangle in the upper right corner represents the gene density scale. The outermost ring represents the chromosome position. Gray lines represent all collinear blocks within the E. grandis genome, whereas red lines indicate segmental duplication events of EgTIFY genes. Additionally, interspecific collinear relationships are depicted between E. grandis and A. thaliana (b), and between E. grandis and P. trichocarpa (c). Red lines mark the duplication events of TIFY gene pairs.
2.6. Analysis of cis-Acting Elements in the Promoters of EgTIFY Genes
To elucidate the regulatory mechanisms governing EgTIFY expression, 2 kb upstream promoter regions of all 19 genes were interrogated for cis-acting elements (Figure 5). Twenty representative elements were uncovered and categorized into four functional classes: development-associated, light-responsive, hormone-responsive, and stress-responsive. Hormone-responsive elements were the most abundant. For instance, EgJAZ11 contained cis-elements responsive to abscisic acid, gibberellin, JA, salicylic acid, auxin, and multiple stress stimuli, suggesting a broad regulatory role in phytohormone signaling.
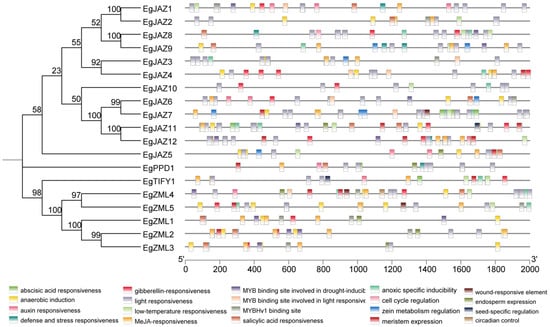
Figure 5.
Prediction of cis-acting elements in the EgTIFYs. The 20 boxs on the lower side show the different cis-acting elements in the TIFY gene family promoters. The NJ tree was constructed 1000 bootstrap replicates.
2.7. Expression Profiles of EgTIFY Genes in Diverse Tissues
To obtain a more profound understanding of the functional roles of TIFY genes in E. grandis, their expression patterns were examined using transcriptome data, and the accuracy of these expression levels was previously validated through quantitative real-time PCR experiments [24]. Expression levels of EgTIFY genes were evaluated across diverse tissues, including leaves, xylem, and phloem, of both 6-month-old and 3-year-old plants (Figure 6). The results revealed that EgTIFY gene expression is highly tissue- and stage-specific. Based on their expression patterns, the genes were categorized into three groups: constitutively expressed, lowly expressed, and stably expressed. Constitutively expressed genes, such as EgJAZ1, EgJAZ5, and EgJAZ11, exhibited consistently high expression across all tissues and developmental stages (Figure 6). In contrast, genes including EgZML1, EgJAZ9, and EgJAZ4 exhibited low expression in all sampled tissues, suggesting limited or specialized roles under normal physiological conditions. Meanwhile, stably expressed genes like EgZML3 and EgZML4 maintained relatively constant expression levels between the two developmental stages, indicating a role in maintaining basic cellular functions (Figure 6a,c). Among all genes, EgJAZ11 and EgJAZ5 showed particularly high expression in xylem and phloem tissues, suggesting a possible role in regulating secondary cell wall formation and vascular development in E. grandis (Figure 6b). Conversely, the consistently low expression levels of EgJAZ4, EgJAZ9, and EgZML1 across tissues may indicate a reduced functional demand or tightly regulated activity under standard growth conditions. Overall, these expression profiles provide meaningful elucidations regarding the tissue-specific and developmental roles of EgTIFY genes in E. grandis physiology.
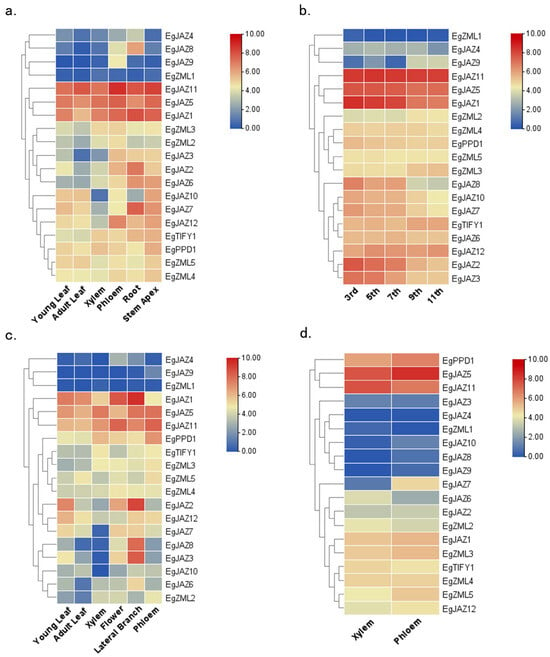
Figure 6.
Tissue-specific expression heatmaps of EgTIFY genes. (a) Transcriptional profiling across juvenile tissues: 6-month-old leaves (young/adult), xylem, phloem, stem apex and roots (b). Differential expression analysis in mature stem internodes (3rd, 5th, 7th, 9th, and 11th) of adult trees. (c) Expression heatmaps in 3-year-old young leaves, adult leaves, xylem, flowers, lateral branches and phloem. (d) Expression heatmap of 6-month-old xylem and phloem tissues in E. grandis. RNA-seq-derived expression values are visualized using a color gradient from blue to red, reflecting low to high expression magnitudes, respectively.
2.8. Expression of EgTIFY Genes Under Abiotic Stress and Phytohormone Treatments
To examine the expression dynamics of the EgTIFY gene family under various abiotic stress and phytohormone treatments, two-month-old E. grandis seedlings were exposed to a set of experimental treatments, following the protocol described by Fan et al. (2024) [24]. These treatments included boron and phosphorus deficiency (applied to both roots and stems), foliar application of SA and JA, and exposure to salt stress. Gene expression profiles were monitored to delineate regulatory patterns in response to these stimuli. Circular visualization of raw expression data indicated that EgJAZ9 was consistently upregulated across all treatments, highlighting its broad responsiveness to diverse environmental cues (Figure 7). Further analysis using row-normalized rectangular graphs revealed distinct temporal variations in gene expression patterns. For example, under boron deficiency, EgJAZ1, EgJAZ2, and EgJAZ3 exhibited a long-term response, with expression peaking in both stems and roots after 21 days of treatment (Figure 7a,c). In contrast, ZML genes (ZML1–5) displayed a rapid response to phosphorus deficiency in stems, reaching maximal expression within 1 h. All genes in the JAZ cluster exhibited induced expression under JA, SA, and salt stress treatments, although their peak expression levels occurred at distinct time points (Figure 7e–g). Notably, EgJAZ9, which displays low basal expression under normal conditions, showed marked upregulation under these stress treatments, indicating strong induction by JA, SA, and salt stress (Figure 7e–g). Under JA and salt stress, several genes, including EgJAZ7, EgJAZ12, and EgPPD1, exhibited biphasic expression patterns, characterized by an initial induction phase followed by downregulation, indicative of a complex regulatory mechanism in response to these stimuli (Figure 7e,f). Under SA treatment, most EgTIFY genes showed progressive upregulation throughout the experimental period (Figure 7g).
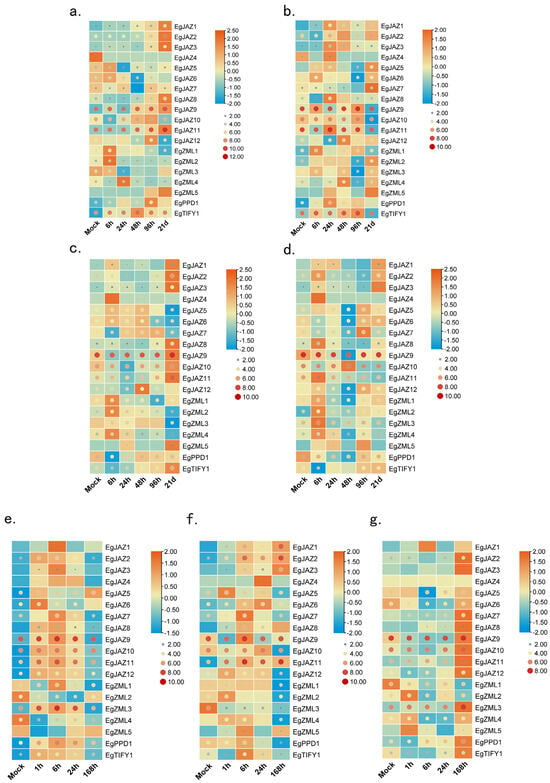
Figure 7.
Gene expression of EgTIFY genes under abiotic stress and hormone treatments. (a–d) Expression pattern of EgTIFY genes under boron deficiency (a,c) and phosphorus deficiency treatment (b,d) after 0 h, 6 h, 24 h, 48 h, 96 h, and 21 d. The root (a,b) and stems (c,d) were used as samples. (e–g) Expression levels of EgTIFY genes at 0 h, 1 h, 6 h, 24 h, and 168 h under JA treatment (e), salt stress (f), and SA treatment (g). Transcript abundance is represented using a blue-to-red gradient, corresponding to log2-normalized RNA-Seq expression values (low to high). The color and size of the circles correlate with raw EgTIFY expression values: larger, redder circles reflect higher expression magnitudes, whereas smaller, bluer circles indicate lower magnitudes. Rectangular plots are row-normalized, with blue representing lower expression at each processing length and deeper orange indicating higher expression at the same length.
2.9. Three-Dimensional Structure Analysis of E. grandis TIFY Gene Family Members
In order to gain a deeper understanding of the structural features and functional diversity of the EgTIFY genes. The 3D architectures of proteins within identical subfamilies display striking structural conservation were performed (Figure 8). These structures were verified using Ramachandran plots (Supplementary Figure S1). In contrast, inter-subfamily comparisons reveal substantially enhanced structural divergence. This variation predominantly stems from disparities in the number and length of α-helical segments, β-turn configurations, and non-regular loop conformations unique to each protein. Such differential arrangements directly manifest as alterations in tertiary folding geometries, potentially accounting for the specialized functional capacities exhibited across these molecular entities [24].
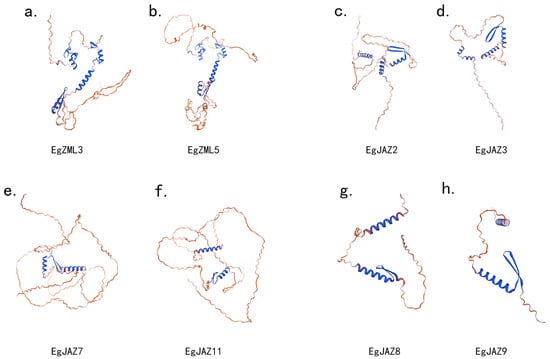
Figure 8.
Three-dimensional structural analysis of EgTIFY gene family members. (a,b) Three-dimensional structure of EgZML3 and EgZML5, belonging to the ZML protein subfamily. (c,d) Three-dimensional structure of EgJAZ2 and EgJAZ3 from the JAZ protein subfamily. (e,f) Three-dimensional structure of EgJAZ7 and EgJAZ11 from the JAZ protein subfamily. (g,h) Three-dimensional structure of EgJAZ8 and EgJAZ9, member sof the JAZ protein subfamily.
3. Discussion
GATA transcription factors, characterized by their unique zinc finger structure, are widely distributed in eukaryotes and represent one of the most extensively studied families of transcription factors [25]. These molecules have been experimentally validated to govern a range of biological processes in plants, exemplified by seed germination, organ development, carbon and nitrogen metabolism, and stress responses [26]. The TIFY gene family is a plant-specific subfamily of GATA transcription factors, named for the conserved TIFY domain, which contains the amino acid sequence TIF[F/Y]XG (where X represents any amino acid). In this study, 19 TIFY gene family members were identified in E. grandis, and comprehensive analyses were conducted to investigate the evolutionary dynamics of this gene family. The number of TIFY members identified in E. grandis is comparable to those found in Actinidia chinensis [27] and the overall family structure is consistent with that of other dicotyledonous plants.
Predictions of subcellular localization demonstrated that all EgTIFY proteins are situated in the nucleus (Table 1). This finding carries notable biological implications, particularly in the context of the TIFY family’s functional conservation and species-specific adaptations. This also suggests that EgTIFYs likely exert their biological functions through direct involvement in nuclear transcriptional networks, potentially governing pathways critical to its growth as a woody species, such as xylem development, stress tolerance, or hormone-mediated responses. Nuclear localization aligns with the canonical role of TIFY proteins as transcriptional regulators, a function well-documented in various plant species [1]. TIFY family members, such as JAZ proteins, are known to modulate gene expression by interacting with transcription factors, hormone receptors, or other regulatory proteins within the nucleus, which is the key processes in stress signaling, growth, and development [28]. The exclusive nuclear localization of EgTIFYs exhibits both conservation and divergence compared to other plants. This result is consistent with findings in cucumber (Cucumis sativus), where all TIFYs were also reported to be nuclear-localized [11], pointing to a conserved functional paradigm in certain species. In contrast, TIFY proteins in other species, such as P. trichocarpa [29] and walnut [16], have been localized to additional subcellular compartments, including chloroplasts, mitochondria, and the endoplasmic reticulum. These differences may reflect species-specific adaptations: while some TIFYs in woody plants like poplar and walnut may have evolved to perform non-nuclear roles (e.g., organelle-specific stress responses or metabolic regulation), the strict nuclear confinement of EgTIFYs suggests a focused specialization in nuclear-mediated transcriptional regulation in E. grandis.
Physicochemical property analysis revealed significant variation among the 19 EgTIFY members (Table 1), which may reflect functional diversification during development or long-term environmental adaptation. Consistent with observations in maize, Ricinus communis, and tobacco, most GATA proteins were found to be structurally stable and hydrophilic [29,30]. Examination of conserved motifs and gene construction revealed that Motif 1 is shared among all EgTIFY transcription factors, suggesting it is a highly conserved feature within the E. grandis genome (Figure 2). Members within the same subfamily displayed analogous motif compositions, reflecting a high level of conservation and suggesting potential functional commonality. For example, Motif 3 was uniquely present in EgZML1, EgZML2, and EgZML3 of the ZML subfamily, suggesting these genes may perform distinct functions in E. grandis.
Phylogenetic analysis divided the 19 EgTIFYs into four subfamilies: TIFY, ZML, JAZ and PPD. The JAZ subfamily was further partitioned into JAZ I and JAZ II subgroups (Figure 1) [31]. The phylogenetic topology of E. grandis TIFY genes closely resembled that of A. thaliana and P. trichocarpa, while Physcomitrium patens lacked members of the JAZ and PPD subfamilies [7,32,33]. This suggests gene loss events in the bryophyte lineage during evolution, whereas angiosperms such as A. thaliana and P. trichocarpa retained these genes, contributing to their more complex gene regulatory networks and enhanced adaptability. Gene family expansion in plants is generally driven by whole-genome duplication, tandem duplication and segmental duplication [34,35]. Comparative genomic investigations demonstrated that TIFY genes in E. grandis exhibit greater collinearity with those in P. trichocarpa than with A. thaliana (Figure 4b,c). This likely reflects that compared to the herbaceous A. thaliana, the two woody species share a more recent common ancestor, which probably accounts for this pattern.
Previous studies have established that cis-acting elements function as critical molecular switches in the transcriptional regulation of genes under abiotic or biotic stress [29]. Analysis of EgTIFY promoter regions identified four classes of hormone-responsive cis-elements, specifically those responsive to auxin, JA, gibberellin, and SA. Within the JAZ subclade (consisting of 12 genes), all members displayed rapid induction following JA treatment, with significant upregulation detectable as early as 1 h post-application. Additionally, these genes exhibited a delayed yet sustained response to SA, with marked upregulation observed after 7 days of treatment (Figure 7). Promoter analysis further revealed that most JAZ genes contain JA-responsive cis-elements, except for JAZ8 and JAZ10; SA-responsive cis-elements were absent in JAZ3, JAZ10, JAZ12, and JAZ7 (Figure 5). These findings suggest that the majority of this JAZ subclade may directly respond to JA and SA signals to coordinate the expression of downstream genes involved in plant growth, development, and defense responses. Previous research has highlighted the pivotal role of MYB transcription factors in regulating plant responses to boron deficiency. For instance, MYB transcription factors in A. thaliana have been implicated to play functional roles under low-boron conditions, mediating adaptation to boron stress via transcriptional reprogramming [36]. In our study, EgZML1 to EgZML4 exhibited a relatively strong and early transcriptional response, with induction detected 1 h after the initiation of boron deficiency treatment (Figure 7a,c). Promoter analysis indicated that these four ZML genes each harbor three MYB-binding cis-elements, suggesting potential transcriptional regulation by MYB factors under boron-deficient conditions. In contrast, ZML5, which lacks MYB-binding sites in its promoter, did not exhibit a similar expression pattern under the same treatment (Figure 5). These observations suggest that the differential responsiveness of ZML genes to boron deficiency may be mediated, at least in part, by the presence or absence of MYB regulatory elements. The number of these cis-elements varied among EgTIFY genes, indicating differential hormone responsiveness and potential functional divergence. Additionally, abiotic stress-related cis-elements, including those responsive to light and low temperature, were detected, suggesting that EgTIFY genes are involved in defense and stress response pathways (Figure 5).
The high economic value of Eucalyptus wood has spurred extensive research aimed at elucidating the genetic mechanisms underlying wood formation, with the objective of improving both wood yield and quality through genetic interventions [37]. Wood formation constitutes a intricate, protracted biological process encompassing orchestrated events including cell division, cellular differentiation, secondary cell wall (SCW) biosynthesis, and programmed cell death (PCD) [38]. Secondary growth is primarily regulated by the vascular cambium and includes the formation of vascular tissues, SCW biosynthesis, lignification, heartwood formation, and PCD. The biosynthesis of SCWs relies on the organized production and assembly of four key components: cellulose and hemicellulose as structural polysaccharides, lignin, structural proteins, and specific secondary metabolites, including flavonoids, tannins, and pectins. Among these, the highly ordered deposition of cellulose microfibrils and lignin is critical for conferring strength and rigidity to the developing xylem tissue [4,5]. JAZ proteins, serving as core constituents of the jasmonic acid signaling pathway, have been demonstrated to participate in a wide array of plant developmental processes. Previous research has established that JAZ genes display tissue-specific expression profiles and fulfill crucial roles in plant development and stress responses. For instance, real-time quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR) analysis revealed that seven CsJAZ genes were preferentially expressed in the roots of tea plants [39]. They act by interacting with a wide variety of proteins, including transcription factors, signaling regulators, and pathogen effectors, to modulate biological outcomes such as anthocyanin accumulation, trichome initiation [24,25], fiber elongation in cotton [40], stamen differentiation [41], flowering time regulation [42,43], pathogen defense [21,44,45], insect resistance [46], and responses to abiotic stresses [47,48]. To better understand the functional roles of TIFY genes in E. grandis, their expression profiles across various tissues and under hormone treatments using transcriptomic data were analyzed (Figure 6 and Figure 7). The reliability of these expression patterns was previously validated through qRT-PCR [24]. EgJAZ1, EgJAZ5, and EgJAZ11 were found to be constitutively expressed at high levels across all tissues, particularly in stem nodes. These genes also maintained strong expression in both 6-month-old and 3-year-old E. grandis individuals (Figure 6). Phylogenetic and sequence similarity analyses indicated that EgJAZ5 is orthologous to PtJAZ6, sharing conserved motifs and a close evolutionary relationship (Figure 1). Significantly, PtJAZ6 exhibits preferential expression in roots and vessels and has been functionally linked to pest response, suggesting that EgJAZ5 may possess analogous biological roles [49]. In contrast, EgZML1 exhibited consistently low expression across tissues, while EgJAZ2 and EgJAZ7 were predominantly expressed in roots, indicating tissue-specific expression and potential involvement in root development or stress responses compared with other species. Based on these observations, it is plausible that EgJAZ5 may play a similar role in E. grandis, contributing to vascular development and cell wall biosynthesis through JA-dependent regulatory mechanisms.
JA, a key regulatory phytohormone involved in secondary metabolism, is widely recognized for its ability to induce the biosynthesis of flavonoids and other specialized metabolites [50]. Within the TIFY gene family, the JAZ subfamily is the most extensively characterized, acting as central repressors in the JA signaling pathway. JAZ proteins act as mediators of plant responses to diverse abiotic stressors, including drought, osmotic stress, salinity, and heavy metal toxicity [51]. In the absence of active JA signaling, JAZ proteins inhibit transcription factors such as MYC and MYB by forming complexes via their conserved ZIM and Jas domains, thereby repressing the transcription of downstream stress-responsive genes [52]. Moreover, members of the TIFY family are also implicated in the regulation of terpenoid biosynthesis, often through interactions with various transcription factors in a hormone-dependent manner [53,54]. Several studies have demonstrated that JA can significantly induce JAZ gene expression. For example, in Prunus persica, PpJAZ1, PpJAZ4, PpJAZ5, and PpJAZ7 were markedly upregulated following treatment with 200 μmol·L−1 JA [39]. In Solanum melongena, JA-induced expression of SmMYB5 was shown to activate a suite of flavonoid biosynthesis genes, including SmCHS, SmF3H, SmDFR, and SmANS, resulting in enhanced flavonoid accumulation [55]. In our study, the promoter region of EgJAZ9 harbors multiple cis-acting elements linked to light responsiveness, JA and ABA sensitivity, alongside a MYB-binding site implicated in drought induction (Figure 5). Phylogenetic analysis identified two close homologs of EgJAZ9, one in P. trichocarpa and another in A. thaliana (Figure 1). Previous studies have shown that PtJAZ9 participates in complex regulatory networks related to pest-induced and cold stress, which is also highly responsive to JA signaling [49]. Additionally, in Arabidopsis, mutation of JAZ7 under dark conditions leads to the release of MYC2/3/4 transcription factors, which bind to G-box motifs in target promoters and activate genes involved in indole-glucosinolate biosynthesis, sulfur metabolism, callose deposition, and JA signaling, thereby promoting dark-induced leaf senescence [56]. Based on these findings and conserved regulatory features, it is plausible that EgJAZ9 may play a central role in JA-mediated signaling and associated physiological processes in E. grandis.
The three-dimensional structure of the EgTIFY protein (Figure 8) highlights a notable abundance of loop regions, primarily attributed to the intrinsic structural disorder within its key functional domains, particularly the Jas domain. This feature is characteristic of the TIFY/JAZ protein family and is essential for their regulatory flexibility [57]. In A. thaliana, the functional jasmonate receptor is formed by a complex between COI1 and JAZ proteins [58]. COI1 contains an open binding pocket that specifically recognizes the bioactive jasmonate hormone, (3R,7S)-jasmonoyl-L-isoleucine (JA-Ile). High-affinity binding of JA-Ile requires a bipartite degron motif within the JAZ protein, composed of a conserved α-helix that docks onto COI1 and an adjacent flexible loop region. This loop plays a critical role in stabilizing the hormone within the COI1 pocket, effectively facilitating hormone perception and subsequent signaling [59]. The prevalence of such disordered regions in EgTIFY proteins may similarly contribute to their structural adaptability and functional interaction with hormonal signaling components in E. grandis [60].
In conclusion, TIFY family members in E. grandis exhibit tissue-specific expression patterns at various developmental stages, suggesting functional divergence likely driven by gene mutations and evolutionary pressures. These findings lay the foundation for future functional validation and the elucidation of TIFY gene regulatory networks. However, the function of these TIFY genes should be further examined by experiments.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Identification of EgTIFYs Members and Analysis of Physicochemical Properties
Nucleotide sequences encoding TIFY family members from E. grandis and A. thaliana were obtained from the Phytozome database (https://phytozome-next.jgi.doe.gov/, accessed on 19 February 2025) and TAIR database (http://www.arabidopsis.org, accessed on 19 February 2025), respectively. These genomic sequences were translated into protein sequences using TBtools-II software (version 1.120) [61]. A total of 19 TIFY family members were identified through comparative sequence alignment of TIFY proteins from A. thaliana and E. grandis, utilizing the “Blast Compare Two Seqs” function in TBtools-II (accessed on 19 February 2025) with an E-value cutoff set at 10−5. Physicochemical properties of E. grandis TIFY proteins, such as molecular mass, isoelectric point, and amino acid count, were analyzed via the ProtParam tool available on the Expasy database (https://www.expasy.org/, accessed on 19 February 2025). Subcellular localization of EgTIFY proteins was predicted using the WoLFPSORT program (https://www.genscript.com/wolf-psort.html, accessed on 19 February 2025).
4.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of the EgTIFYs
TIFYs from A. thaliana, P. patens and P. trichocarpa were used to perform comparative sequence analysis and similarity assessment. A. thaliana genome annotation was obtained from the TAIR (https://www.arabidopsis.org/, accessed on 20 February 2025). Genome annotation information of P. patens and P. trichocarpa was derived from Ensembl Plants (https://plants.ensembl.org/index.html, accessed on 20 February 2025). Evolutionary analyses of the three species were performed using MEGA11, constructed by the neighbor-joining (NJ) method (Bootstrap: 1000) [62]. The evolutionary tree was then categorized and annotated using the evolview (http://www.evolgenius.info/evolview, accessed on 20 February 2025) website.
4.3. Analysis Gene Structures, Conserved Motifs and Conserved Domains of EgTIFYs
The MEME (https://meme-suite.org/meme/, accessed on 20 February 2025) was used to predict the conserved motifs of EgTIFYs, and their conserved structural domains were analyzed by NCBI-CDD (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/cdd/, accessed on 20 February 2025), and finally visualized and analyzed using TBtools-II software.
4.4. Gene Family Chromosomal Distribution and Synteny Analysis
To determine the chromosomal distribution of the 19 E. grandis TIFY genes, the “Gene Location Visualize from GTF/GFF” function in TBtools-II software was used. This tool allowed mapping of each gene to its corresponding physical position on the chromosomes. To further assess the genomic distribution, a gene density heatmap was generated using the “Gene Density Profile” module with a bin size set at 100,000 bp, while maintaining all other parameters at default settings. For collinearity and synteny analysis, gene annotation and sequence files from E. grandis, P. alba and A. thaliana were imported into the “One Step MCScanX” module within TBtools-II software. Syntenic relationships between E. grandis and the two reference species were illustrated using the “Dual Synteny Plot” function. To explore internal collinearity within the E. grandis genome, a genome-wide synteny analysis was also performed using “One Step MCScanX,” and the results were visualized through the “Advanced Circos” module. In the MCScanX analysis, parameters were configured with a BLASTP CPU thread count of 2, an E-value threshold of 10−10, and the top 5 BLAST hits retained for downstream synteny detection.
4.5. Analysis of Promoter cis-Regulatory Element of the EgTIFYs
The promoter sequence of the first 2000 bp upstream of the initiator of TIFY family members was extracted, and its cis-acting elements were predicted using the online website PlantCARE (https://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/plantcare/html/, accessed on 25 February 2025), and finally visualized using TBtools-II software.
4.6. Expression Patterns of EgTIFYs
To examine the tissue-specific expression patterns of E. grandis TIFY genes, as well as the expression profiles under abiotic stress (boron deficiency, phosphorus deficiency, salt stress) and hormone treatments (JA, SA), transcriptome data from our previous study were reanalyzed [24]. Each biological replicate comprised tissues sampled from no fewer than three individual plants, with three technical replicates processed per measurement to ensure data reliability. Tissue dissection was performed manually. For stem-derived samples, longitudinal sections were first made to expose the epidermis. The outer phloem was gently removed using fine-tipped forceps, followed by precise scraping of the underlying xylem layer for collection. Expression quantification data were normalized and transformed using log2 scale prior to visualization. Hierarchical clustering based on Euclidean distance and complete linkage was performed in TBtools-II software to produce heatmaps, enabling the comparative assessment of transcriptional variation across stress conditions and tissue types. This approach facilitated the identification of distinct expression trends among the TIFY genes [24].
4.7. Protein Structure Prediction of EgTIFYs
Three-dimensional structures of EgTIFY proteins were predicted via the SWISS-MODEL platform (https://swissmodel.expasy.org/, accessed on 28 February 2025). Amino acid sequences were uploaded to the website, and models with the highest matching levels were selected—all chosen models showed over 50% similarity. The corresponding files were then exported for further analysis, with similarity verified using Ramachandran plots.
5. Conclusions
In this study, 19 members of the TIFY gene family were identified for the first time at the genome-wide level in E. grandis, and their potential involvement in hormone signaling pathways was predicted based on bioinformatics and expression analyses. Through promoter cis-acting element analysis, the promoter regions of several EgTIFY genes were found to contain gibberellin (GARE-motif), growth hormone (AuxRR-core), JA (CGTCA-motif), and salicylic acid (TCA-element) response elements, indicating that the genes of this family may participate in the growth, development, and stress response of E. grandis through hormone-mediated signaling pathways. The expression of JAZ subfamily member EgJAZ9 was significantly up-regulated after JA treatment, and the Jas structural domains of the protein sequences were highly conserved with the Arabidopsis JAZ proteins, which suggests that these genes are important for jasmonate signaling, of which EgJAZ9 could be a candidate gene for further study.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ijms26167914/s1.
Author Contributions
C.L., Y.H., and R.A.: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Writing—original draft, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing—review and editing. S.Z., A.W. and Y.J.: Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Funding acquisition, Writing—review and editing. C.F.: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was funded by Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (2025A1515012324).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary Materials.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
GlcA: glucuronic acid; Nucl: nucleus; NJ: Neighbor-Joining Algorithm; JA: Methyl Jasmonate; JA-Ile: jasmonoyl-L-isoleucine; SA: salicylic acid; TIFY: highly conserved structural domain (TIF[F/Y]XG); bHLH: helix–loop–helix; E. grandis: Eucalyptus grandis; A. thaliana: Arabidopsis thaliana; P. trichocarpa: Populus trichocarpa; P. patens: Physcomitrella patens.
References
- Singh, P.; Mukhopadhyay, K. Comprehensive Molecular Dissection of TIFY Transcription Factors Reveal Their Dynamic Responses to Biotic and Abiotic Stress in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Meng, G.; Zamin, I.; Wei, T.; Ma, D.; An, L.; Yue, X. Genome-Wide Identification and Functional Analysis of the TIFY Family Genes in Response to Abiotic Stresses and Hormone Treatments in Tartary Buckwheat (Fagopyrum tataricum). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishii, A.; Takemura, M.; Fujita, H.; Shikata, M.; Yokota, A.; Kohchi, T. Characterization of a Novel Gene Encoding a Putative Single Zinc-Finger Protein, ZIM, Expressed during the Reproductive Phase in Arabidopsis Thaliana. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2000, 64, 1402–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikata, M. Characterization of Arabidopsis ZIM, a Member of a Novel Plant-Specific GATA Factor Gene Family. J. Exp. Bot. 2004, 55, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Meng, Y.; Huang, D.; Qi, Y.; Chen, M. Origin and Evolutionary Analysis of the Plant-Specific TIFY Transcription Factor Family. Genomics 2011, 98, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanholme, B.; Grunewald, W.; Bateman, A.; Kohchi, T.; Gheysen, G. The Tify Family Previously Known as ZIM. Trends Plant Sci. 2007, 12, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Pan, F.; Chen, D.; Chu, W.; Liu, H.; Xiang, Y. Genome-Wide Identification and Analysis of the Populus Trichocarpa TIFY Gene Family. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 115, 360–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chini, A.; Fonseca, S.; Fernández, G.; Adie, B.; Chico, J.M.; Lorenzo, O.; García-Casado, G.; López-Vidriero, I.; Lozano, F.M.; Ponce, M.R.; et al. The JAZ Family of Repressors Is the Missing Link in Jasmonate Signalling. Nature 2007, 448, 666–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Bhardwaj, M.; Tran, L.-S.P. JASMONATE ZIM-DOMAIN Family Proteins: Important Nodes in JasmonicAcid-Abscisic Acid Crosstalk for Regulating Plant Response toDrought. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2021, 22, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.S.; Niu, Y.; Browse, J.; Howe, G.A. Top Hits in Contemporary JAZ: An Update on Jasmonate Signaling. Phytochemistry 2009, 70, 1547–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Du, H.; Tang, N.; Li, X.; Xiong, L. Identification and Expression Profiling Analysis of TIFY Family Genes Involved in Stress and Phytohormone Responses in Rice. Plant Mol. Biol. 2009, 71, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Li, B.; Ma, W.; Wang, D.; Cao, X.; Wang, Z. Genome-Wide Identification of the TIFY Family in Salvia Miltiorrhiza Reveals That SmJAZ3 Interacts With SmWD40-170, a Relevant Protein That Modulates Secondary Metabolism and Development. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 630424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; You, J.; Chan, Z. Identification and Characterization of TIFY Family Genes in Brachypodium Distachyon. J. Plant Res. 2015, 128, 995–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Yu, R.; Han, M.; Wu, Z. Isolation, Structural Analysis, and Expression Characteristics of the Maize TIFY Gene Family. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2015, 290, 1849–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, N.; Zan, T.; Xu, K.; Gao, S.; Yin, Y.; Yao, M.; Wang, F. Genome-Wide Analysis of the TIFY Family and Function of CaTIFY7 and CaTIFY10b under Cold Stress in Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1308721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yu, F.; Yang, G.; Liu, X.; Peng, S. Identification of TIFY Gene Family in Walnut and Analysis of Its Expression under Abiotic Stresses. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Ran, W.; Zhang, J.; Ye, M.; Lin, S.; Li, X.; Sultana, R.; Sun, X. Genome-Wide Identification of the Tify Gene Family and Their Expression Profiles in Response to Biotic and Abiotic Stresses in Tea Plants (Camellia sinensis). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade Galan, A.G.; Doll, J.; Saile, S.C.; Wünsch, M.; Roepenack-Lahaye, E.V.; Pauwels, L.; Goossens, A.; Bresson, J.; Zentgraf, U. The Non-JAZ TIFY Protein TIFY8 of Arabidopsis Thaliana Interacts with the HD-ZIP III Transcription Factor REVOLUTA and Regulates Leaf Senescence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, N.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y. Transcriptional Repression of GIF1 by the KIX-PPD-MYC Repressor Complex Controls Seed Size in Arabidopsis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Sun, L.; Qi, T.; Zhang, B.; Peng, W.; Liu, Y.; Xie, D. The bHLH Transcription Factor MYC3 Interacts with the Jasmonate ZIM-Domain Proteins to Mediate Jasmonate Response in Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant 2011, 4, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baekelandt, A.; Pauwels, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, N.; De Milde, L.; Natran, A.; Vermeersch, M.; Li, Y.; Goossens, A.; Inzé, D.; et al. Arabidopsis Leaf Flatness Is Regulated by PPD2 and NINJA through Repression of CYCLIN D3 Genes. Plant Physiol. 2018, 178, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, D.W.R. PEAPOD Regulates Lamina Size and Curvature in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 13238–13243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myburg, A.A.; Grattapaglia, D.; Tuskan, G.A.; Hellsten, U.; Hayes, R.D.; Grimwood, J.; Jenkins, J.; Lindquist, E.; Tice, H.; Bauer, D.; et al. The Genome of Eucalyptus Grandis. Nature 2014, 510, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Lyu, M.; Zeng, B.; He, Q.; Wang, X.; Lu, M.; Liu, B.; Liu, J.; Esteban, E.; Pasha, A.; et al. Profiling of the Gene Expression and Alternative Splicing Landscapes of Eucalyptus grandis. Plant Cell Environ. 2024, 47, 1363–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwechheimer, C.; Schröder, P.M.; Blaby-Haas, C.E. Plant GATA Factors: Their Biology, Phylogeny, and Phylogenomics. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2022, 73, 123–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, P.; Nutan, K.K.; Singla-Pareek, S.L.; Pareek, A. Abiotic Stresses Cause Differential Regulation of Alternative Splice Forms of GATA Transcription Factor in Rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, J.; Jia, H.; Wu, M.; Zhong, W.; Jia, D.; Wang, Z.; Huang, C. Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of the TIFY Gene Family in Kiwifruit. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; He, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, J. JAZ Proteins: Key Regulators of Plant Growth and Stress Response. Crop J. 2024, 12, 1505–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Leng, X.; Xu, X.; Li, C. Comprehensive Analysis of the TIFY Gene Family and Its Expression Profiles under Phytohormone Treatment and Abiotic Stresses in Roots of Populus Trichocarpa. Forests 2020, 11, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ahammed, G.J.; Wan, C.; Liu, H.; Chen, R.; Zhou, Y. Comprehensive Analysis of TIFY Transcription Factors and Their Expression Profiles under Jasmonic Acid and Abiotic Stresses in Watermelon. Int. J. Genom. 2019, 2019, 6813086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Song, J.; Zhang, J.; Guo, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, X. Genome-Wide Identification of the TIFY Gene Family in Helianthus Annuus and Expression Analysis in Response to Drought and Salt Stresses. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 15138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Li, R.; Liu, X.; Sun, M.; Wu, J.; Zhang, N.; Zhu, Y. The Positive Regulatory Roles of the TIFY10 Proteins in Plant Responses to Alkaline Stress. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beike, A.K.; Lang, D.; Zimmer, A.D.; Wüst, F.; Trautmann, D.; Wiedemann, G.; Beyer, P.; Decker, E.L.; Reski, R. Insights from the Cold Transcriptome of P Hyscomitrella Patens: Global Specialization Pattern of Conserved Transcriptional Regulators and Identification of Orphan Genes Involved in Cold Acclimation. New Phytol. 2015, 205, 869–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, K.; Meng, D.; Mu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Yao, G.; Guo, L. Genomic and Epigenomic Insight into Giga-Chromosome Architecture and Adaptive Evolution of Royal Lily (Lilium regale). Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 5617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, R.; Pokhriyal, E.; Das, S. Complex Interplay of Tandem, Segmental, Whole Genome Duplication, and Re-Organization Drives Expansion of SAUR Gene Family in Brassicaceae. Biochem. Genet. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Fontes, A.; Rexach, J.; Quiles-Pando, C.; Herrera-Rodríguez, M.B.; Camacho-Cristóbal, J.J.; Navarro-Gochicoa, M.T. Transcription Factors as Potential Participants in the Signal Transduction Pathway of Boron Deficiency. Plant Signal. Behav. 2013, 8, e26114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Li, X.; Shang, X. Regeneration and Genetic Transformation in Eucalyptus Species, Current Research and Future Perspectives. Plants 2024, 13, 2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Li, L. Molecular Understanding of Wood Formation in Trees. For. Res. 2022, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Zou, Z.; Xing, H.; Duan, Y.; Zhu, X.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fang, W. Genome-Wide Analysis Reveals Stress and Hormone Responsive Patterns of JAZ Family Genes in Camellia Sinensis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; He, X.; Tu, L.; Zhu, L.; Zhu, S.; Ge, Z.; Zhang, X. Gh JAZ 2 Negatively Regulates Cotton Fiber Initiation by Interacting with the R2R3-MYB Transcription Factor Gh MYB 25-like. Plant J. 2016, 88, 921–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Qi, T.; Huang, H.; Ren, Q.; Wu, D.; Chang, C.; Peng, W.; Liu, Y.; Peng, J.; Xie, D. The Jasmonate-ZIM Domain Proteins Interact with the R2R3-MYB Transcription Factors MYB21 and MYB24 to Affect Jasmonate-Regulated Stamen Development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 1000–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boter, M.; Golz, J.F.; Giménez-Ibañez, S.; Fernandez-Barbero, G.; Franco-Zorrilla, J.M.; Solano, R. FILAMENTOUS FLOWER Is a Direct Target of JAZ3 and Modulates Responses to Jasmonate. Plant Cell 2015, 27, 3160–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.-L.; Yao, J.; Mei, C.-S.; Tong, X.-H.; Zeng, L.-J.; Li, Q.; Xiao, L.-T.; Sun, T.; Li, J.; Deng, X.-W.; et al. Plant Hormone Jasmonate Prioritizes Defense over Growth by Interfering with Gibberellin Signaling Cascade. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E1192–E1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plett, J.M.; Daguerre, Y.; Wittulsky, S.; Vayssières, A.; Deveau, A.; Melton, S.J.; Kohler, A.; Morrell-Falvey, J.L.; Brun, A.; Veneault-Fourrey, C.; et al. Effector MiSSP7 of the Mutualistic Fungus Laccaria Bicolor Stabilizes the Populus JAZ6 Protein and Represses Jasmonic Acid (JA) Responsive Genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 8299–8304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimenez-Ibanez, S.; Boter, M.; Fernández-Barbero, G.; Chini, A.; Rathjen, J.P.; Solano, R. The Bacterial Effector HopX1 Targets JAZ Transcriptional Repressors to Activate Jasmonate Signaling and Promote Infection in Arabidopsis. PLoS Biol. 2014, 12, e1001792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Qi, T.; Fan, M.; Zhang, X.; Gao, H.; Huang, H.; Wu, D.; Guo, H.; Xie, D. The bHLH Subgroup IIId Factors Negatively Regulate Jasmonate-Mediated Plant Defense and Development. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, J.; Joo, J.; Kim, M.; Kim, Y.; Nahm, B.H.; Song, S.I.; Cheong, J.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, J.; Choi, Y.D. OsbHLH148, a Basic Helix-loop-helix Protein, Interacts with OsJAZ Proteins in a Jasmonate Signaling Pathway Leading to Drought Tolerance in Rice. Plant J. 2011, 65, 907–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Wang, F.; Yu, D. Jasmonate Regulates the INDUCER OF CBF EXPRESSION–C-REPEAT BINDING FACTOR/DRE BINDING FACTOR1 Cascade and Freezing Tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 2907–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Wang, S.; Long, L.; Yu, X.; Cai, H.; Chen, P.; Gu, L.; Yang, M. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of PtJAZ Gene Family in Poplar (Populus trichocarpa). BMC Genom. Data 2023, 24, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Fu, X.; Shao, J.; Tang, Y.; Yu, M.; Li, L.; Huang, L.; Tang, K. Transcriptional Regulatory Network of High-Value Active Ingredients in Medicinal Plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2023, 28, 429–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devoto, A. Regulation of Jasmonate-Mediated Plant Responses in Arabidopsis. Ann. Bot. 2003, 92, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.; Yuan, Z.; Chen, M.; Yin, C.; Luo, Z.; Zhao, X.; Liang, W.; Hu, J.; Zhang, D. Jasmonic Acid Regulates Spikelet Development in Rice. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Pei, T.; Lv, B.; Wang, M.; Dong, J.; Liang, Z. Functional Pleiotropism, Diversity, and Redundancy of Salvia Miltiorrhiza Bunge JAZ Family Proteins in Jasmonate-Induced Tanshinone and Phenolic Acid Biosynthesis. Hortic. Res. 2022, 9, uhac166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, T.; Ma, P.; Ding, K.; Liu, S.; Jia, Y.; Ru, M.; Dong, J.; Liang, Z. SmJAZ8 Acts as a Core Repressor Regulating JA-Induced Biosynthesis of Salvianolic Acids and Tanshinones in Salvia Miltiorrhiza Hairy Roots. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 1663–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Dong, Y.; Li, D.; Shi, S.; Zhao, N.; Liao, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H. Eggplant Transcription Factor SmMYB5 Integrates Jasmonate and Light Signaling during Anthocyanin Biosynthesis. Plant Physiol. 2024, 194, 1139–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Di, C.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, K.; Wang, C.; You, Q.; Yan, H.; Dai, S.Y.; Yuan, J.S.; et al. JAZ7 Negatively Regulates Dark-Induced Leaf Senescence in Arabidopsis. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 751–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chini, A.; Ben-Romdhane, W.; Hassairi, A.; Aboul-Soud, M.A.M. Identification of TIFY/JAZ Family Genes in Solanum Lycopersicum and Their Regulation in Response to Abiotic Stresses. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Yao, R.; Chen, L.; Li, S.; Gu, M.; Nan, F.; Xie, D. Dynamic Perception of Jasmonates by the F-Box Protein COI1. Mol. Plant 2018, 11, 1237–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheard, L.B.; Tan, X.; Mao, H.; Withers, J.; Ben-Nissan, G.; Hinds, T.R.; Kobayashi, Y.; Hsu, F.-F.; Sharon, M.; Browse, J.; et al. Jasmonate Perception by Inositol-Phosphate-Potentiated COI1–JAZ Co-Receptor. Nature 2010, 468, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wingert, B.; Krieger, J.; Li, H.; Bahar, I. Adaptability and Specificity: How Do Proteins Balance Opposing Needs to Achieve Function? Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2021, 67, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Tang, J.; Wu, A.; Fan, C.; Li, H. Genome-Wide Identification and Functional Analysis of the GUX Gene Family in Eucalyptus Grandis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).