Early Dysregulation of RNA Splicing and Translation Processes Are Key Markers from Mild Cognitive Impairment to Alzheimer’s Disease: An In Silico Transcriptomic Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
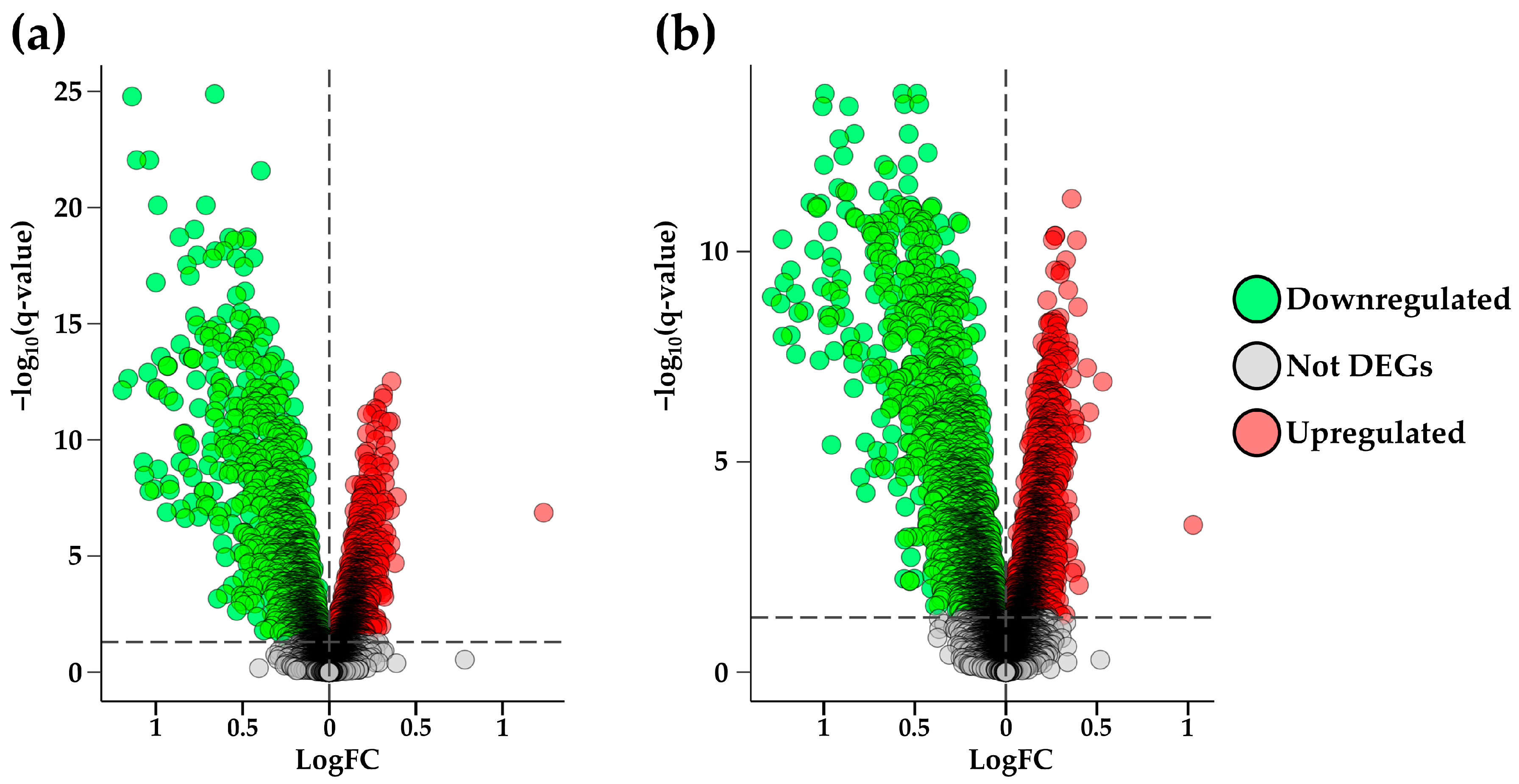
2.1. Differential Expression Analysis
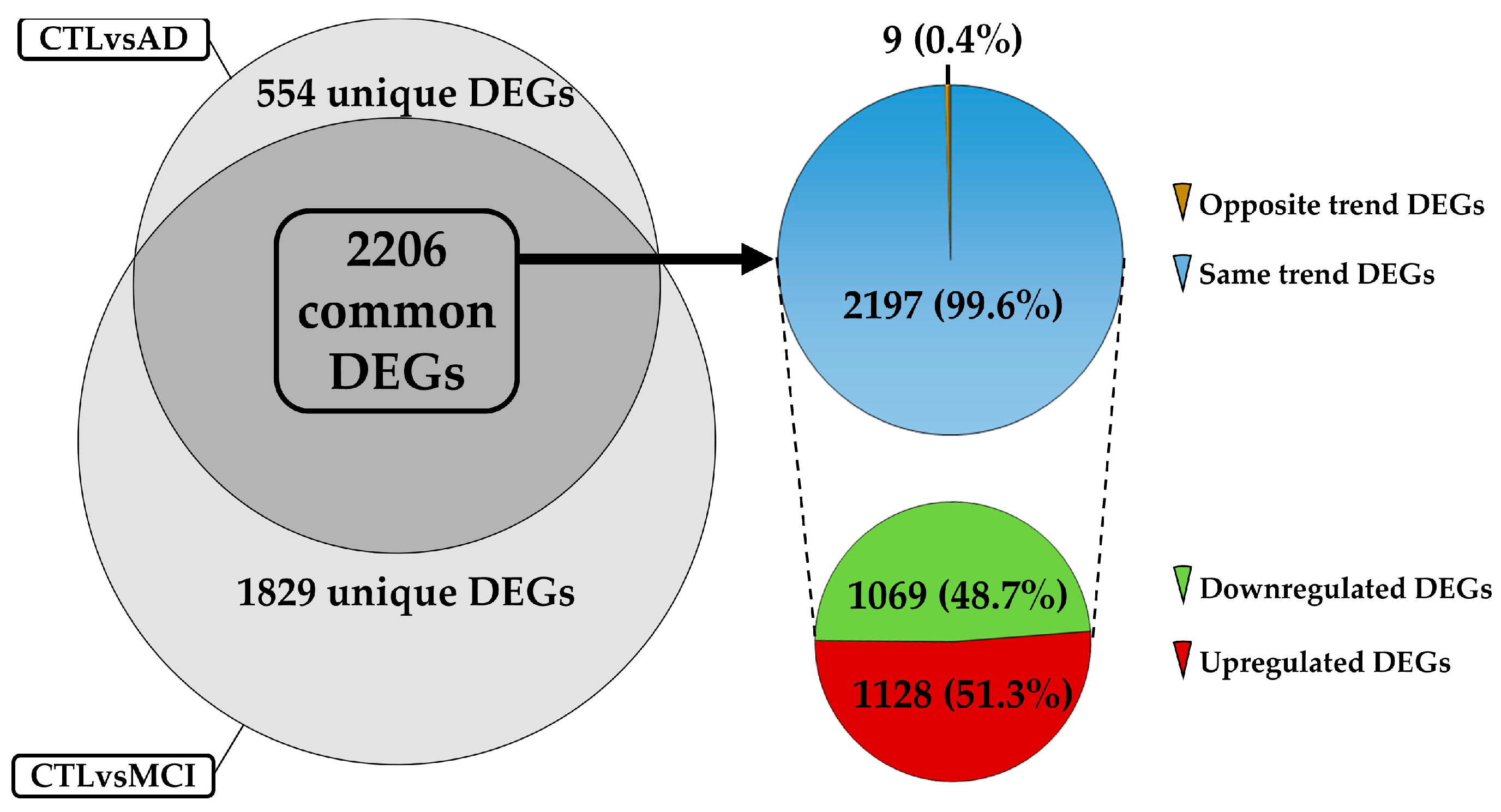
2.2. DEGs Selection and Filtering
2.3. Over-Representation Analysis (ORA)
2.4. Network Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
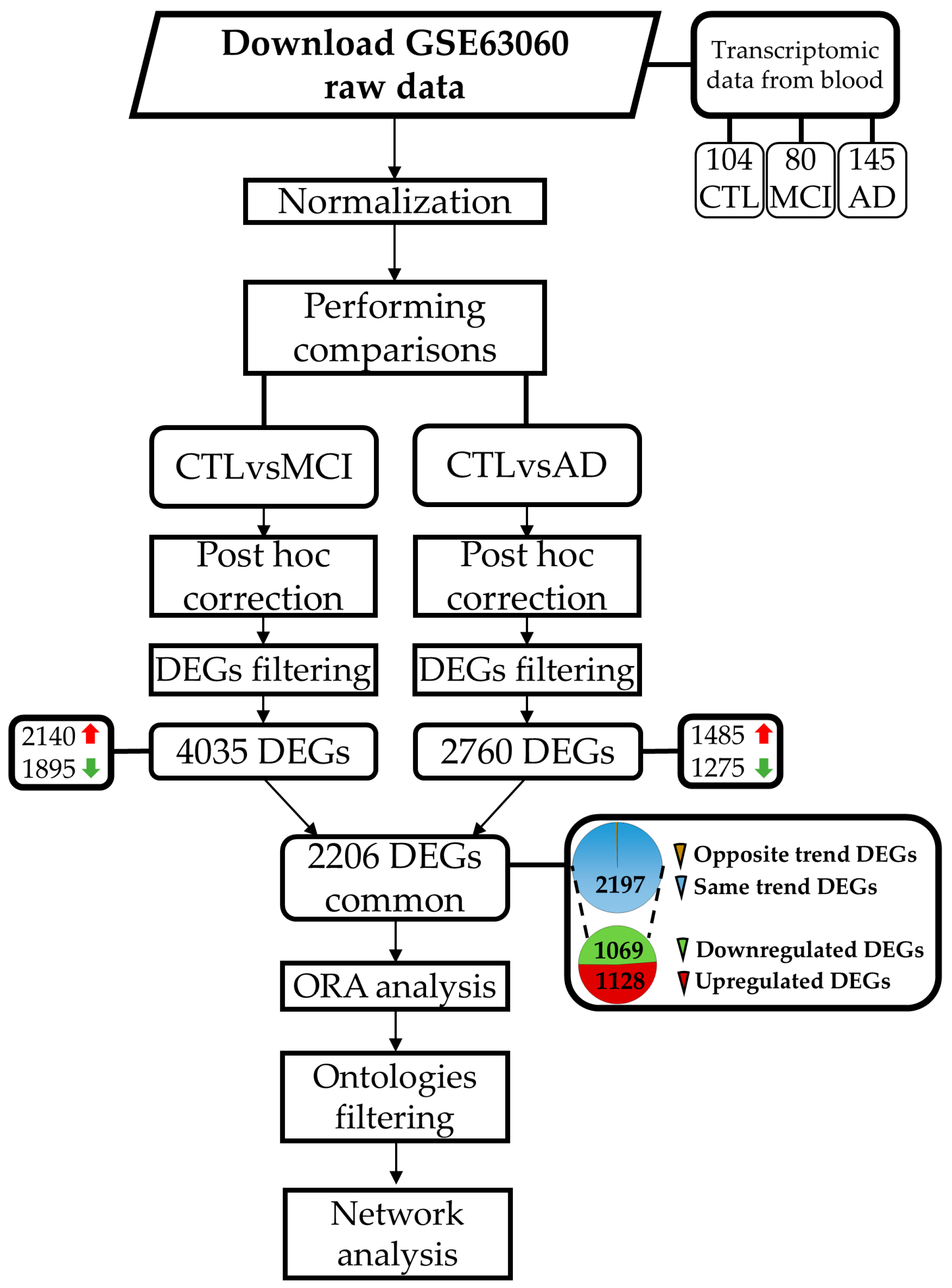
4.1. Dataset Selection
4.2. Dataset Information
4.3. Bioinformatics Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| Aβ | Amyloid beta |
| FAD | AD familial form |
| SAD | AD sporadic form |
| MCI | Mild cognitive impairment |
| CTL | Healthy controls |
| CTLvsAD | Comparison among CTL and AD groups |
| CTLvsMCI | Comparison among CTL and MCI groups |
| DEGs | Differentially expressed genes |
| FDR | False discovery rate |
| FC | Fold change |
| GO | Gene ontology |
| ORA | Over-representation analysis |
| BP | Biological process |
| MF | Molecular function |
| CC | Cellular component |
| SSU | Small subunit |
| GEO | Gene expression omnibus |
References
- Brookmeyer, R.; Johnson, E.; Ziegler-Graham, K.; Arrighi, H.M. Forecasting the global burden of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. J. Alzheimer’s Assoc. 2007, 3, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, S.; Lacayo, P. Biological and disease hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease defined by Alzheimer’s disease genes. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 996030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coon, K.D.; Myers, A.J.; Craig, D.W.; Webster, J.A.; Pearson, J.V.; Lince, D.H.; Zismann, V.L.; Beach, T.G.; Leung, D.; Bryden, L.; et al. A high-density whole-genome association study reveals that APOE is the major susceptibility gene for sporadic late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2007, 68, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Li, Y.; Liang, W.; Wei, Z.Z.; Li, X.; Tian, Y.; Qiao, S.; Yang, Y.; Yang, L.; Wu, D.; et al. The identification of PSEN1 p.Tyr159Ser mutation in a non-canonic early-onset Alzheimer’s disease family. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2022, 120, 103715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, Y.A.; Zhao, N.; Liu, C.C.; Kanekiyo, T.; Yang, A.J.; Goate, A.M.; Holtzman, D.M.; Bu, G. ApoE Cascade Hypothesis in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias. Neuron 2022, 110, 1304–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattsson, N.; Groot, C.; Jansen, W.J.; Landau, S.M.; Villemagne, V.L.; Engelborghs, S.; Mintun, M.M.; Lleo, A.; Molinuevo, J.L.; Jagust, W.J.; et al. Prevalence of the apolipoprotein E epsilon4 allele in amyloid beta positive subjects across the spectrum of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. J. Alzheimer’s Assoc. 2018, 14, 913–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutler, R.G.; Kelly, J.; Storie, K.; Pedersen, W.A.; Tammara, A.; Hatanpaa, K.; Troncoso, J.C.; Mattson, M.P. Involvement of oxidative stress-induced abnormalities in ceramide and cholesterol metabolism in brain aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 2070–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.S.; Beiser, A.S.; Vasan, R.S.; Roubenoff, R.; Dinarello, C.A.; Harris, T.B.; Benjamin, E.J.; Au, R.; Kiel, D.P.; Wolf, P.A.; et al. Inflammatory markers and the risk of Alzheimer disease: The Framingham Study. Neurology 2007, 68, 1902–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, R.J.; Skelton-Robinson, M.; Rossor, M.N. The prevalence and causes of dementia in people under the age of 65 years. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2003, 74, 1206–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacace, R.; Sleegers, K.; Van Broeckhoven, C. Molecular genetics of early-onset Alzheimer’s disease revisited. Alzheimer’s Dement. J. Alzheimer’s Assoc. 2016, 12, 733–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperling, R.A.; Aisen, P.S.; Beckett, L.A.; Bennett, D.A.; Craft, S.; Fagan, A.M.; Iwatsubo, T.; Jack, C.R., Jr.; Kaye, J.; Montine, T.J.; et al. Toward defining the preclinical stages of Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. J. Alzheimer’s Assoc. 2011, 7, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKhann, G.M.; Knopman, D.S.; Chertkow, H.; Hyman, B.T.; Jack, C.R., Jr.; Kawas, C.H.; Klunk, W.E.; Koroshetz, W.J.; Manly, J.J.; Mayeux, R.; et al. The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. J. Alzheimer’s Assoc. 2011, 7, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, J.C.; Storandt, M.; Miller, J.P.; McKeel, D.W.; Price, J.L.; Rubin, E.H.; Berg, L. Mild cognitive impairment represents early-stage Alzheimer disease. Arch. Neurol. 2001, 58, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeCarli, C. Mild cognitive impairment: Prevalence, prognosis, aetiology, and treatment. Lancet Neurol. 2003, 2, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansson, O.; Zetterberg, H.; Buchhave, P.; Londos, E.; Blennow, K.; Minthon, L. Association between CSF biomarkers and incipient Alzheimer’s disease in patients with mild cognitive impairment: A follow-up study. Lancet Neurol. 2006, 5, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klunk, W.E.; Engler, H.; Nordberg, A.; Wang, Y.; Blomqvist, G.; Holt, D.P.; Bergstrom, M.; Savitcheva, I.; Huang, G.F.; Estrada, S.; et al. Imaging brain amyloid in Alzheimer’s disease with Pittsburgh Compound-B. Ann. Neurol. 2004, 55, 306–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielke, M.M.; Fowler, N.R. Alzheimer disease blood biomarkers: Considerations for population-level use. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2024, 20, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlavka, J.P.; Mattke, S.; Liu, J.L. Assessing the Preparedness of the Health Care System Infrastructure in Six European Countries for an Alzheimer’s Treatment. Rand Health Q. 2019, 8, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Mattke, S.; Hanson, M. Expected wait times for access to a disease-modifying Alzheimer’s treatment in the United States. Alzheimer’s Dement. J. Alzheimer’s Assoc. 2022, 18, 1071–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Mering, C.; Jensen, L.J.; Snel, B.; Hooper, S.D.; Krupp, M.; Foglierini, M.; Jouffre, N.; Huynen, M.A.; Bork, P. STRING: Known and predicted protein-protein associations, integrated and transferred across organisms. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, D433–D437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelucci, F.; Spalletta, G.; di Iulio, F.; Ciaramella, A.; Salani, F.; Colantoni, L.; Varsi, A.E.; Gianni, W.; Sancesario, G.; Caltagirone, C.; et al. Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) patients are characterized by increased BDNF serum levels. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2010, 7, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, Y.S.; Chin, M.K. Echocardiographic left ventricular hypertrophy in Chinese endurance athletes. Br. J. Sports Med. 1990, 24, 274–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaillou, T.; Kirby, T.J.; McCarthy, J.J. Ribosome biogenesis: Emerging evidence for a central role in the regulation of skeletal muscle mass. J. Cell. Physiol. 2014, 229, 1584–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laferte, A.; Favry, E.; Sentenac, A.; Riva, M.; Carles, C.; Chedin, S. The transcriptional activity of RNA polymerase I is a key determinant for the level of all ribosome components. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 2030–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freed, E.F.; Prieto, J.L.; McCann, K.L.; McStay, B.; Baserga, S.J. NOL11, implicated in the pathogenesis of North American Indian childhood cirrhosis, is required for pre-rRNA transcription and processing. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.; Whittall, J.B. WDR75: An essential protein for ribosome assembly undergoing purifying selection. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0318395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phipps, K.R.; Charette, J.; Baserga, S.J. The small subunit processome in ribosome biogenesis-progress and prospects. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2011, 2, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Zhu, X.; Zheng, S.; Tan, D.; Dong, M.Q.; Ye, K. Cryo-EM structure of an early precursor of large ribosomal subunit reveals a half-assembled intermediate. Protein Cell 2019, 10, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafita-Navarro, M.C.; Hao, Y.H.; Jiang, C.; Jang, S.; Chang, T.C.; Brown, I.N.; Venkateswaran, N.; Maurais, E.; Stachera, W.; Zhang, Y.; et al. ZNF692 organizes a hub specialized in 40S ribosomal subunit maturation enhancing translation in rapidly proliferating cells. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 113280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wehner, K.A.; Baserga, S.J. The sigma(70)-like motif: A eukaryotic RNA binding domain unique to a superfamily of proteins required for ribosome biogenesis. Mol. Cell 2002, 9, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Chen, Y.; Chen, F.; Huang, D.; Shi, H.; Lo, L.J.; Chen, J.; Peng, J. Sas10 controls ribosome biogenesis by stabilizing Mpp10 and delivering the Mpp10-Imp3-Imp4 complex to nucleolus. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 2996–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorbas, C.; Nicolas, E.; Wacheul, L.; Huvelle, E.; Heurgue-Hamard, V.; Lafontaine, D.L. The human 18S rRNA base methyltransferases DIMT1L and WBSCR22-TRMT112 but not rRNA modification are required for ribosome biogenesis. Mol. Biol. Cell 2015, 26, 2080–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.L.; Bonnard, A.A.; Wang, F.; Ruaud, L.; Guimiot, F.; Li, Y.; Defer, I.; Wang, Y.; Marchand, V.; Motorin, Y.; et al. New ZNHIT3 Variants Disrupting snoRNP Assembly Cause Prenatal PEHO Syndrome with Isolated Hydrops. medRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzel, M.; Rohrmoser, M.; Schlee, M.; Grimm, T.; Harasim, T.; Malamoussi, A.; Gruber-Eber, A.; Kremmer, E.; Hiddemann, W.; Bornkamm, G.W.; et al. Mammalian WDR12 is a novel member of the Pes1-Bop1 complex and is required for ribosome biogenesis and cell proliferation. J. Cell Biol. 2005, 170, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, N.J.; Burnside, C.; Klinge, S. Principles of mitoribosomal small subunit assembly in eukaryotes. Nature 2023, 614, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; Mou, X.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Z.; Vanderburg, C.R.; Rogers, J.T.; Huang, X. Independent component analysis of Alzheimer’s DNA microarray gene expression data. Mol. Neurodegener. 2009, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Sun, L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, D. Oxidative stress, mitochondrial damage and neurodegenerative diseases. Neural Regen. Res. 2013, 8, 2003–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falkenberg, M.; Gaspari, M.; Rantanen, A.; Trifunovic, A.; Larsson, N.G.; Gustafsson, C.M. Mitochondrial transcription factors B1 and B2 activate transcription of human mtDNA. Nat. Genet. 2002, 31, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Lim, J.; Liu, B.; Li, Y.; Vartak, R.; Stankiewicz, T.; Montgomery, S.; Lu, B. Ubiquitination of ABCE1 by NOT4 in Response to Mitochondrial Damage Links Co-translational Quality Control to PINK1-Directed Mitophagy. Cell Metab. 2018, 28, 130–144.E7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, C.; Li, Y.; Mascarenhas, C.; Lin, Q.; Li, K.; Vyrides, I.; Grant, C.M.; Panaretou, B. The function of ORAOV1/LTO1, a gene that is overexpressed frequently in cancer: Essential roles in the function and biogenesis of the ribosome. Oncogene 2014, 33, 484–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kispal, G.; Sipos, K.; Lange, H.; Fekete, Z.; Bedekovics, T.; Janaky, T.; Bassler, J.; Aguilar Netz, D.J.; Balk, J.; Rotte, C.; et al. Biogenesis of cytosolic ribosomes requires the essential iron-sulphur protein Rli1p and mitochondria. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, V.D.; Muhlenhoff, U.; Stumpfig, M.; Seebacher, J.; Kugler, K.G.; Renicke, C.; Taxis, C.; Gavin, A.C.; Pierik, A.J.; Lill, R. The deca-GX3 proteins Yae1-Lto1 function as adaptors recruiting the ABC protein Rli1 for iron-sulfur cluster insertion. eLife 2015, 4, e08231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, Y.; Granneman, S.; Thoms, M.; Manikas, R.G.; Tollervey, D.; Hurt, E. Coupled GTPase and remodelling ATPase activities form a checkpoint for ribosome export. Nature 2014, 505, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassio, C.A.; Schofield, B.J.; Seiser, R.M.; Johnson, A.W.; Lycan, D.E. Dominant mutations in the late 40S biogenesis factor Ltv1 affect cytoplasmic maturation of the small ribosomal subunit in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 2010, 185, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosil, M. Ribosome synthesis-unrelated functions of the preribosomal factor Rrp12 in cell cycle progression and the DNA damage response. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2011, 31, 2422–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.J.; Lee, H.W.; Lee, Y.S.; Shim, D.M.; Seo, S.W. RRP12 is a crucial nucleolar protein that regulates p53 activity in osteosarcoma cells. Tumour Biol. J. Int. Soc. Oncodev. Biol. Med. 2016, 37, 4351–4358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, R.J.; Hellen, C.U.; Pestova, T.V. The mechanism of eukaryotic translation initiation and principles of its regulation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleich, S.; Strassburger, K.; Janiesch, P.C.; Koledachkina, T.; Miller, K.K.; Haneke, K.; Cheng, Y.S.; Kuechler, K.; Stoecklin, G.; Duncan, K.E.; et al. DENR-MCT-1 promotes translation re-initiation downstream of uORFs to control tissue growth. Nature 2014, 512, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Ortega, K.; Garcia-Esparcia, P.; Gil, L.; Lucas, J.J.; Ferrer, I. Altered Machinery of Protein Synthesis in Alzheimer’s: From the Nucleolus to the Ribosome. Brain Pathol. 2016, 26, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Will, C.L.; Luhrmann, R. Spliceosome structure and function. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a003707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, K.; Reed, R. Human step II splicing factor hSlu7 functions in restructuring the spliceosome between the catalytic steps of splicing. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 841–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Will, C.L.; Urlaub, H.; Achsel, T.; Gentzel, M.; Wilm, M.; Luhrmann, R. Characterization of novel SF3b and 17S U2 snRNP proteins, including a human Prp5p homologue and an SF3b DEAD-box protein. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 4978–4988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chari, A.; Golas, M.M.; Klingenhager, M.; Neuenkirchen, N.; Sander, B.; Englbrecht, C.; Sickmann, A.; Stark, H.; Fischer, U. An assembly chaperone collaborates with the SMN complex to generate spliceosomal SnRNPs. Cell 2008, 135, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palo, A.; Patel, S.A.; Sahoo, B.; Chowdary, T.K.; Dixit, M. FRG1 is a direct transcriptional regulator of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay genes. Genomics 2023, 115, 110539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, R.; Hartmuth, K.; Mohlmann, S.; Urlaub, H.; Ficner, R.; Luhrmann, R. Phosphorylation of human PRP28 by SRPK2 is required for integration of the U4/U6-U5 tri-snRNP into the spliceosome. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2008, 15, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, N.J.; Hershberger, C.E.; Gu, X.; Schueger, C.; DiPasquale, W.M.; Brick, J.; Saunthararajah, Y.; Maciejewski, J.P.; Padgett, R.A. Functional analyses of human LUC7-like proteins involved in splicing regulation and myeloid neoplasms. Cell Rep. 2021, 35, 108989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebhardt, A.; Habjan, M.; Benda, C.; Meiler, A.; Haas, D.A.; Hein, M.Y.; Mann, A.; Mann, M.; Habermann, B.; Pichlmair, A. mRNA export through an additional cap-binding complex consisting of NCBP1 and NCBP3. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pabis, M.; Neufeld, N.; Steiner, M.C.; Bojic, T.; Shav-Tal, Y.; Neugebauer, K.M. The nuclear cap-binding complex interacts with the U4/U6.U5 tri-snRNP and promotes spliceosome assembly in mammalian cells. Rna 2013, 19, 1054–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilchert, C.; Wittmann, S.; Vasiljeva, L. The regulation and functions of the nuclear RNA exosome complex. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meola, N.; Domanski, M.; Karadoulama, E.; Chen, Y.; Gentil, C.; Pultz, D.; Vitting-Seerup, K.; Lykke-Andersen, S.; Andersen, J.S.; Sandelin, A.; et al. Identification of a Nuclear Exosome Decay Pathway for Processed Transcripts. Mol. Cell 2016, 64, 520–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apicco, D.J.; Zhang, C.; Maziuk, B.; Jiang, L.; Ballance, H.I.; Boudeau, S.; Ung, C.; Li, H.; Wolozin, B. Dysregulation of RNA Splicing in Tauopathies. Cell Rep. 2019, 29, 4377–4388.E4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heese, K.; Nakayama, T.; Hata, R.; Masumura, M.; Akatsu, H.; Li, F.; Nagai, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Kosaka, K.; Suemoto, T.; et al. Characterizing CGI-94 (comparative gene identification-94) which is down-regulated in the hippocampus of early stage Alzheimer’s disease brain. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2002, 15, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Harnpicharnchai, P.; Jakovljevic, J.; Tang, L.; Guo, Y.; Oeffinger, M.; Rout, M.P.; Hiley, S.L.; Hughes, T.; Woolford, J.L., Jr. Assembly factors Rpf2 and Rrs1 recruit 5S rRNA and ribosomal proteins rpL5 and rpL11 into nascent ribosomes. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 2580–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibanez-Cabellos, J.S.; Seco-Cervera, M.; Picher-Latorre, C.; Perez-Machado, G.; Garcia-Gimenez, J.L.; Pallardo, F.V. Acute depletion of telomerase components DKC1 and NOP10 induces oxidative stress and disrupts ribosomal biogenesis via NPM1 and activation of the P53 pathway. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2020, 1867, 118845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.C.; Han, X.; Shaw, T.I.; Fu, Y.; Sun, H.; Niu, M.; Wang, Z.; Jiao, Y.; Teubner, B.J.W.; Eddins, D.; et al. Alzheimer’s disease-associated U1 snRNP splicing dysfunction causes neuronal hyperexcitability and cognitive impairment. Nat. Aging 2022, 2, 923–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaiswal, A.S.; Williamson, E.A.; Srinivasan, G.; Kong, K.; Lomelino, C.L.; McKenna, R.; Walter, C.; Sung, P.; Narayan, S.; Hromas, R. The splicing component ISY1 regulates APE1 in base excision repair. DNA Repair 2020, 86, 102769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Q.; Kayikci, M.; Odermatt, P.; Meyer, K.; Michels, O.; Saxena, S.; Ule, J.; Schumperli, D. Splicing changes in SMA mouse motoneurons and SMN-depleted neuroblastoma cells: Evidence for involvement of splicing regulatory proteins. RNA Biol. 2014, 11, 1430–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, S.; Bell, M.; Lyons, D.N.; Rodriguez-Rivera, J.; Ingram, A.; Fontaine, S.N.; Mechas, E.; Chen, J.; Wolozin, B.; LeVine, H., 3rd; et al. Pathological Tau Promotes Neuronal Damage by Impairing Ribosomal Function and Decreasing Protein Synthesis. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 1001–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athar, A.; Fullgrabe, A.; George, N.; Iqbal, H.; Huerta, L.; Ali, A.; Snow, C.; Fonseca, N.A.; Petryszak, R.; Papatheodorou, I.; et al. ArrayExpress update—From bulk to single-cell expression data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D711–D715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.; Domrachev, M.; Lash, A.E. Gene Expression Omnibus: NCBI gene expression and hybridization array data repository. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sood, S.; Gallagher, I.J.; Lunnon, K.; Rullman, E.; Keohane, A.; Crossland, H.; Phillips, B.E.; Cederholm, T.; Jensen, T.; van Loon, L.J.; et al. A novel multi-tissue RNA diagnostic of healthy ageing relates to cognitive health status. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritchie, M.E.; Phipson, B.; Wu, D.; Hu, Y.; Law, C.W.; Shi, W.; Smyth, G.K. Limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentleman, R.C.; Carey, V.J.; Bates, D.M.; Bolstad, B.; Dettling, M.; Dudoit, S.; Ellis, B.; Gautier, L.; Ge, Y.; Gentry, J.; et al. Bioconductor: Open software development for computational biology and bioinformatics. Genome Biol. 2004, 5, R80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Hu, E.; Cai, Y.; Xie, Z.; Luo, X.; Zhan, L.; Tang, W.; Wang, Q.; Liu, B.; Wang, R.; et al. Using clusterProfiler to characterize multiomics data. Nat. Protoc. 2024, 19, 3292–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safdari, H.A.; Kasvandik, S.; Polte, C.; Ignatova, Z.; Tenson, T.; Wilson, D.N. Structure of Escherichia coli heat shock protein Hsp15 in complex with the ribosomal 50S subunit bearing peptidyl-tRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, 12515–12526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Genes Family | Genes Included |
|---|---|
| EXOSC | EXOSC1, EXOSC3, EXOSC7, EXOSC8, EXOSC9 |
| MRPL | MRPL1, MRPL3, MRPL13, MRPL15, MRPL17, MRPL18, MRPL21, MRPL22, MRPL24, MRPL27, MRPL32, MRPL33, MRPL35, MRPL36, MRPL39, MRPL40, MRPL42, MRPL45, MRPL46, MRPL47, MRPL48, MRPL50, MRPL51, MRPL58 |
| MRPS | MRPS7, MRPS17, MRPS18C, MRPS21, MRPS22, MRPS23, MRPS28, MRPS31, MRPS33 |
| RPL | RPL3, RPL4, RPL5, RPL6, RPL7, RPL11, RPL12, RPL17, RPL21, RPL23, RPL24, RPL26, RPL26L1, RPL27, RPL30, RPL31, RPL34, RPL35, RPL35A, RPL36AL, RPL39, RPL41 |
| RPS | RPS3A, RPS4X, RPS6, RPS7, RPS10, RPS12, RPS13, RPS14, RPS17, RPS18, RPS20, RPS21, RPS24, RPS25, RPS27, RPS27A, RPS27L, RPS29 |
| DEGs | Regulation | Function | Possible Role in Neurodegeneration | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UTP6, UTP11, UTP14A | Downregulated | Required for SSU biogenesis and involved in nucleolar processing of pre-18 S ribosomal RNA. | Downregulation of UTP11 is observed in early stages of AD and is implicated in nucleolar stress and altered ribosomal biogenesis. | [62] |
| RPF1, RPF2 | Downregulated | Involved in ribosomal large subunit assembly. | Depletion of RPF2 blocks the 27 pre-RNA-processing process, inducing nucleolar stress. | [63] |
| NOP58, NOP10, DKC1 | Downregulated | Required for 60 S ribosomal subunit biogenesis. Core component of snoRNP particles. | Depletion of DKC1 and NOP10 causes increased oxidative stress and impaired ribosomal biogenesis. Both of these processes are closely implicated in the pathophysiology of neurodegenerative diseases. | [64] |
| RPL30, RPL34, RPL4 | Downregulated | Component of the large ribosomal subunit. | Downregulation of these ribosomal proteins are observed in hippocampal samples from AD. | [36] |
| EIF3E, EIF3M | Downregulated | Component of the eIF-3 complex, which is required for several steps in the initiation of protein synthesis. | The low expression of the factor eIF3 was observed in hippocampus samples from patients with AD. | [49] |
| SNRPG, SNRPD2, SNRPF, SNRPA, SNRPB2 | Downregulated | Structural components of the protein core of the U1 snRNP complex, involved in the recognition of the 5′ splicing site. | There is no direct evidence of their downregulation in the neurodegeneration process. However, alteration of the U1 snRNP complex is associated with splicing defects in the brains of AD patients. | [65] |
| PRPF18, ISY1, SLU7 | Downregulated | Factors involved in pre-RNA splicing | Involved in DNA splicing and repair (via APE1); although there is no direct evidence in neurodegeneration, its downregulation may reduce the response to genotoxic damage. | [66] |
| GEMIN6, GEMIN2 | Downregulated | The SMN complex catalyzes the assembly of snRNPs, the components of spliceosome. | The SMN complex deficit may contribute to SMA and neuronal splicing dysfunctions and neurodegeneration. | [67] |
| LTO1 | Upregulated | Required for biogenesis of the large ribosomal subunit and initiation of translation. | The upregulation, although not directly associated with neurodegeneration, could reflect a compensatory mechanism against oxidative stress, one of the mechanisms relevant in neurodegenerative diseases. | [40] |
| Sample Groups | Age Mean | Sex Distribution |
|---|---|---|
| CTL | 72.4 ± 6.3 | 42 M 62 F |
| MCI | 74.5 ± 6.0 | 41 M 39 F |
| AD | 75.4 ± 6.6 | 46 M 99 F |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
D’Angiolini, S.; Gugliandolo, A.; Calì, G.; Chiricosta, L. Early Dysregulation of RNA Splicing and Translation Processes Are Key Markers from Mild Cognitive Impairment to Alzheimer’s Disease: An In Silico Transcriptomic Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7303. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157303
D’Angiolini S, Gugliandolo A, Calì G, Chiricosta L. Early Dysregulation of RNA Splicing and Translation Processes Are Key Markers from Mild Cognitive Impairment to Alzheimer’s Disease: An In Silico Transcriptomic Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(15):7303. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157303
Chicago/Turabian StyleD’Angiolini, Simone, Agnese Gugliandolo, Gabriella Calì, and Luigi Chiricosta. 2025. "Early Dysregulation of RNA Splicing and Translation Processes Are Key Markers from Mild Cognitive Impairment to Alzheimer’s Disease: An In Silico Transcriptomic Analysis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 15: 7303. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157303
APA StyleD’Angiolini, S., Gugliandolo, A., Calì, G., & Chiricosta, L. (2025). Early Dysregulation of RNA Splicing and Translation Processes Are Key Markers from Mild Cognitive Impairment to Alzheimer’s Disease: An In Silico Transcriptomic Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(15), 7303. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157303






