Abstract
Helicobacter pylori infection is the strongest known risk factor for the development of gastric cancer. The bacterium leverages several unique virulence factors to its advantage in order to colonize the human host. Among these, T4SS-delivered cytotoxin-associated gene A (CagA) has the most well-established links to severe forms of disease. To explore the effect of lactobacilli in disrupting CagA functions within host cells, we expressed HA-tagged humanized cagA in the human gastric epithelial AGS cell line and studied both the phosphorylation levels of CagA and its downstream binding partners. We found that gastric-specific Lactobacillus gasseri Kx110 A1 suppressed the phosphorylation of CagA and inhibited phosphorylation-dependent downstream signaling, resulting in the suppression of CagA-induced cell elongation of AGS cells, commonly known as the hummingbird phenotype. Surprisingly, phosphorylation-independent signaling was unaffected by L. gasseri. Furthermore, our confocal microscopy analysis revealed that CagA was mislocalized to the cytoplasm, suggesting that L. gasseri interferes with its membrane localization and thereby hinders its phosphorylation. Live L. gasseri that had direct contact with host cells was found to be necessary to suppress the hummingbird phenotype. In summary, the data suggest that a L. gasseri strain can inhibit CagA phosphorylation and suppress cell elongation.
1. Introduction
Helicobacter pylori is a highly successful gastric pathogen that inhabits about half the population of the world []. The bacterium is the causative agent of gastric diseases, including chronic inflammation, ulcers, gastritis, and mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma and adenocarcinoma []. Cytotoxicity-associated gene A (CagA), produced by H. pylori, is one of more than 30 genes expressed from the 40 kb DNA segment known as the cag pathogenicity island (cagPAI), and the role of CagA in virulence has been well-documented [,]. Several studies have demonstrated a strong link between CagA and disease severity; hence, the ability of H. pylori to produce CagA is considered a direct measure of its virulence.
CagA is translocated by H. pylori into host cells by the bacterial Type-4-secretion system (T4SS) secretion apparatus. Once inside the cells, CagA localizes itself to the inner surface of the plasma membrane by interactions with phosphatidylserine [], where it subsequently undergoes tyrosine phosphorylation by host tyrosine kinases specifically at the Glu-Pro-Ile-Tye-Ala (EPIYA) motifs at the C-terminal [,]. Phosphorylated CagA then goes on to interact with several proteins, one of them being SHP-2 (Src homology-2 protein tyrosine phosphatase), which is a critical step for signaling to the actin cytoskeleton []. Normally, SHP-2 plays an important role in cell growth and motility [,]. Deregulation causes abnormal morphological changes in cells, characterized by dramatic cell elongation, which is aptly termed the hummingbird phenotype due to retraction defects []. Both membrane tethering of CagA and activation of SHP-2 are necessary to trigger the hummingbird phenotype, as can be seen in studies involving gastric cells transfected with CagA and SHP-2 mutant constructs, as well as by the addition of SHP-2-specific phosphatase inhibitor calpeptin to cells, both of which show failure to result in the hummingbird phenotype [,].
In addition to its phosphorylation-dependent effects, CagA can also regulate host signaling independently of its phosphorylation status. CagA binds to tight junction (ZO-1, JAM-A) and adherens junction proteins (E-cadherin, β-catenin), and its interaction with the polarity-regulating kinase PAR1b/MARK is especially important, as it interferes with microtubule organization and cell polarity []. These phosphorylation-independent interactions are crucial for disrupting epithelial cell polarity and compromising barrier integrity, contributing to disease progression. Extensive studies on CagA have revealed links to the activation of Rho GTPases, host cell actin cytoskeleton reorganization, the activation of protooncogenes or changes in their expression, the recruitment of transcription factor NF-kb, and the cytokine storm in response to infection [,,].
Furthermore, in light of the urgent need for novel therapeutic approaches to H. pylori in response to antibiotic resistance, there is no specific treatment to date that is directed toward CagA. The use of lactobacilli as novel therapeutic agents, either on their own or in conjunction with antibiotics, is gaining traction. These bacteria form part of the normal gut microflora and combat a broad range of pathogens through competition for space, the release of anti-bacterial molecules such as bacteriocins, organic acids, and hydrogen peroxide, as well as by downregulation of pathogenic virulence factors or modulation of the host immune system []. They can counteract H. pylori infections by downregulation of the adhesion protein SabA, which results in reduced colonization []. On the host side, they are also capable of modulating cytokine responses, such as TNF, IL-6, and IL-8 production [,]. In this study, we investigated the effect of lactobacilli on CagA functions and identified the ability of L. gasseri Kx110 A1 to suppress the CagA-phosphorylation-mediated hummingbird phenotype, thereby paving the way for the development of a novel therapeutic agent against H. pylori infection.
2. Results
2.1. Suppression of the H. pylori-Mediated Hummingbird Phenotype by L. gasseri
Changes in gastric cell morphology by H. pylori are well-studied and involve the CagA effector molecule, which is injected into host cells and confers dramatic cell elongation. To study whether lactobacilli can suppress the elongation of gastric cells into the so-called hummingbird phenotype, we infected gastric AGS cells with H. pylori for 24 h, followed by 16 h incubation with different Lactobacillus strains. We found that the strain L. gasseri Kx110 A1 (L. gas) was able to suppress cell elongation induced by H. pylori (Figure 1A–C). The ability to suppress the hummingbird phenotype was dependent on bacterial load, since L. gasseri at a lower MOI did not affect elongation (Figure 1F). Two other Lactobacillus strains, L. brevis (L. bre) and L. crispatus (L. cris), did not suppress cell elongation, demonstrating strain specificity (Figure 1D,E).
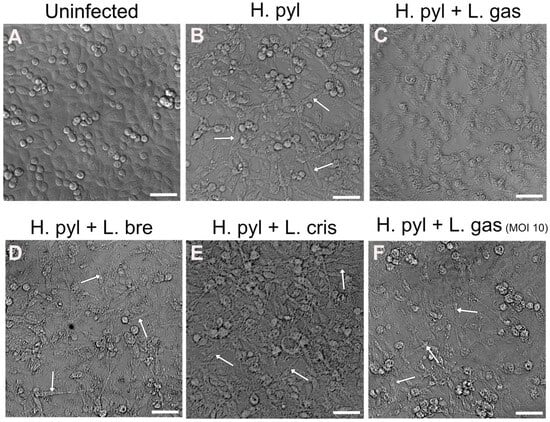
Figure 1.
L. gasseri suppresses H. pylori- induced hummingbird phenotype in gastric epithelial AGS cells. Uninfected cells (A) and infected cells with H. pylori (B) at a MOI of 100 for 24 h, followed by 16 h treatment with L. gasseri (L. gas) (C), L. brevis (L. bre) (D), L. crispatus (L. crisp) (E) at a MOI of 50, and L. gasseri (L. gas) at a MOI of 10 (F). Differential interference contrast images of PFA-fixed AGS cells were captured with a Leica DMi8 microscope (Leica Microsystems, Wetzlar, Germany) using a 10× objective. White arrows mark the presence of elongated cells. Scale bar: 50 µm.
2.2. Lactobacillus Gasseri Suppress Elongation in CagA-Transfected Gastric Cells
We have previously shown that some lactobacilli can inhibit the attachment of H. pylori to gastric cells by downregulating its virulence []. To rule out the possibility that the suppression of the hummingbird phenotype was a result of less CagA being translocated due to reduced H. pylori attachment, we used CagA-transfected cells instead of whole H. pylori. The incubation of CagA-transfected cells with L. gasseri efficiently suppressed the hummingbird phenotype, with a statistically confirmed reduced number of elongated cells (Figure 2A), which eliminated variation in bacterial adhesion as a possible mechanism. Incubation with L. brevis, L. crispatus, or L. salivarius (Figure 2B) did not suppress the elongation of the gastric cells. Further, a vaginally isolated L. gasseri-vag strain was incapable of bringing about an effect on altered cell shape (Figure 2B). These data demonstrate that the addition of a gastrically isolated L. gasseri strain to gastric cells with CagA-induced hummingbird phenotype significantly suppresses cell elongation.
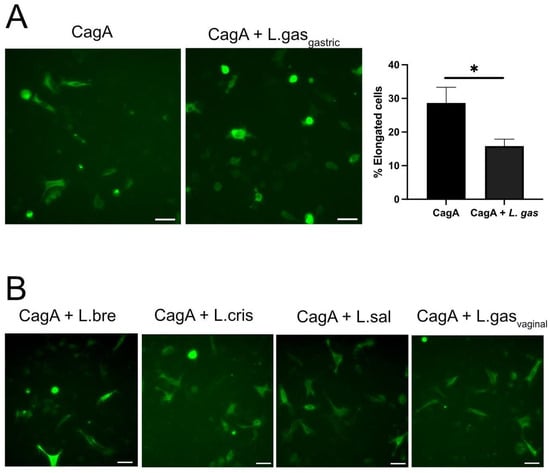
Figure 2.
L. gasseri suppresses CagA-induced hummingbird phenotype in gastric epithelial AGS cells. Gastric AGS cells transfected for 48 h with a CagA construct (pcDNA3.1-CagA) were incubated with different Lactobacillus strains for 5 h. PFA-fixed cells were stained with rabbit-anti-HA antibodies to detect CagA, followed by anti-rabbit IgG Alexa Fluor 488, and imaged by a Leica DMi8 microscope using a 10× objective. (A) CagA-transfected cells were incubated with L. gasseri (CagA+L. gas) or with RPMI medium alone (CagA). The graph displays the percentage of elongated cells after counting at least one hundred cells, on three independent occasions. * p < 0.05, using a student t-test. (B) Treatment of CagA-transfected cells with L. brevis (L. bre), L. crisptatus (L. cris), L salaviarus (L. sal), or a vaginal L. gasseri strain (L. gas vaginal) for 5 h. Scale bars: 50 µm.
2.3. Inhibition of Phosphorylation of CagA by L. gasseri Reduces CagA Interaction with the SHP-2 Phosphatase
Elongation of cells requires phosphorylation of CagA []. To elucidate the mechanism behind the suppression of cell elongation by L. gasseri, CagA-transfected AGS cells were incubated with or without L. gasseri with empty vectors as a control. Phosphorylation of CagA in immunoprecipitated samples was then analyzed using anti-phosphotyrosine antibodies. We could observe suppression of phosphorylation of CagA in the L. gasseri samples compared to the untreated controls (Figure 3A). Phosphorylated CagA is known to interact with and activate the SHP2 phosphatase [,]. As expected, we found lower levels of SHP-2 in co-immunoprecipitated samples that were treated with L. gasseri compared to the untreated controls (Figure 3A). These data show that L. gasseri can suppress CagA-induced cell elongation by inhibiting the phosphorylation of CagA, leading to inhibition of CagA interaction with SHP-2 and blockage of SHP-2 activation, which is essential for cell elongation.
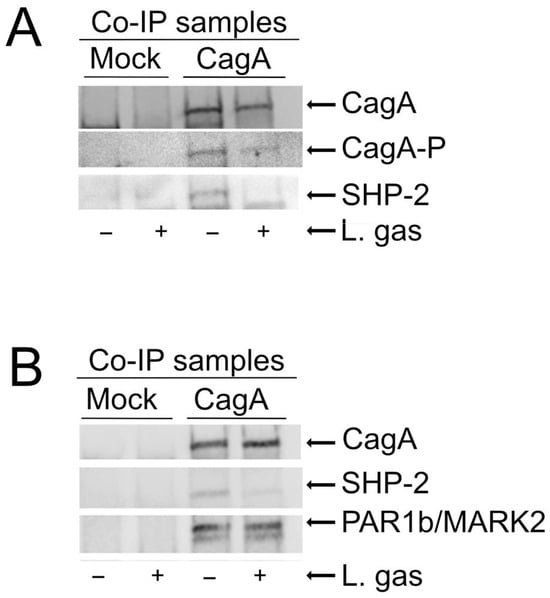
Figure 3.
L. gasseri inhibits phosphorylation of CagA and reduces interaction with SHP2. AGS cells transfected with either the CagA construct or an empty vector (pcDNA3.1) were incubated for 5 h in RPMI medium, either with or without Lactobacillus gasseri (+). Cells were then lysed, and immunoprecipitation was performed using anti-HA antibodies to pull down CagA. Co-immunoprecipitated samples (Co-IP sample) were resolved on 4-20% precast polyacrylamide gels and transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. (A) CagA (anti-HA), CagA-P (anti-phospho-tyrosine), SHP-2 (anti-SHP2) (B) CagA, SHP-2, and Par1b/MARK2.
2.4. L. gasseri Does Not Interfere with Phosphorylation-Independent Functions of CagA
Since CagA is also known to mediate cytoskeletal changes independent of its phosphorylation status by interaction with PAR1/MARK kinases [,], we investigated whether L. gasseri could also affect this pathway. PAR1b/MARK2 expression in CagA-immunoprecipitated samples incubated with or without L. gasseri was analyzed, with an empty vector as control in both cases. Interestingly, we could not detect any differences in PAR1b/MARK2 levels in immunoprecipitated samples incubated with L. gasseri, as compared to those incubated with medium alone. Taken together, these results suggest that L. gasseri specifically suppresses the phosphorylation-dependent signaling of CagA (Figure 3B).
2.5. L. gasseri Disrupts the Membrane Localization of CagA
Once translocated into host cells, CagA needs to be tethered to the inner plasma membrane in order to be phosphorylated by host kinases. Therefore, we carefully investigated whether L. gasseri disturbs the CagA membrane localization and hence hinders its ability to carry out its phosphorylation-dependent functions. CagA-expressing cells grown in chamber slides were analyzed by confocal microscopy after treatment with L. gasseri. In the control, i.e., untreated CagA-expressing elongated cells, CagA was strongly localized to the membranes. Interestingly, compared to untreated cells, CagA staining in L. gasseri-treated cells was diffused in the cytoplasm, suggesting that L. gasseri interfered with the localization of CagA to the membrane (Figure 4).
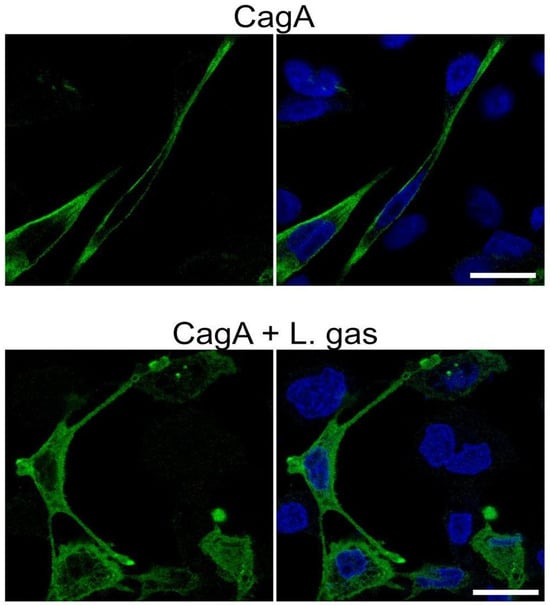
Figure 4.
L. gasseri interferes with the membrane localization of CagA. Gastric AGS cells transfected with the CagA construct pcDNA3.1-CagA were incubated with L. gasseri (L. gas) at an MOI of 100 or RPMI medium alone for 5 h. Cells were then PFA-fixed, stained with anti-HA antibodies to detect CagA (green). DAPI (blue) was included in panels to the right to detect the nuclei. Stained cells were then analyzed by a Zeiss LSM 780 confocal microscope (Carl Zeiss AB, Oberkochen, Germany). Images represent a single z-section at the center of the cells. Scale bar: 20 µm.
2.6. Live and Contact-Dependent Mechanism Underlies L. gasseri-Mediated Suppression of the Hummingbird Phenotype
In order to determine whether the active component(s) of lactobacilli were secreted/released into the supernatant or if live lactobacilli were needed for suppression of the hummingbird phenotype, we incubated CagA expressing cells with live or formaldehyde-fixed L. gasseri, or with L. gasseri conditioned medium, i.e., bacteria-free supernatants from L. gasseri. Interestingly, we observed that while cell elongation was reduced after incubation with live L. gasseri, neither formaldehyde-fixed L. gasseri nor the conditioned medium from the bacteria could mediate suppression of the hummingbird phenotype (Figure 5). These data suggest that the whole live L. gasseri triggers suppression of the hummingbird phenotype in gastric cells infected by H. pylori.
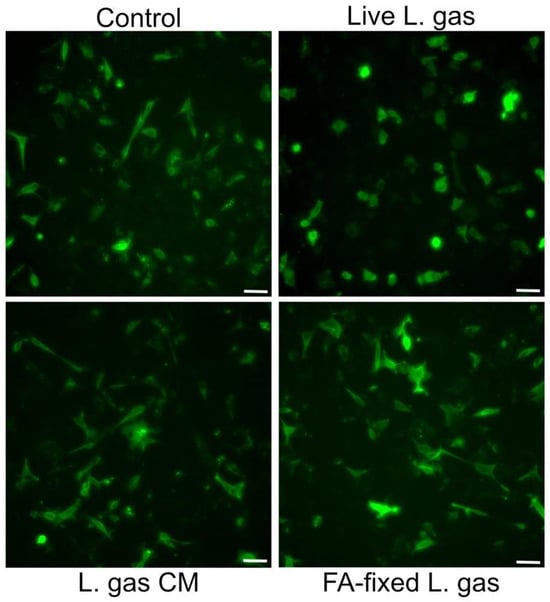
Figure 5.
A live and contact-dependent mechanism underlies L. gasseri-mediated suppression of the hummingbird phenotype. Gastric AGS cells transfected with CagA construct pcDNA3.1-CagA were incubated with live L. gasseri (L. gas) at an MOI of 100, or with 4% PFA-fixed L. gasseri (FA-fixed L. gas), or with conditioned medium prepared from L. gasseri (L. gas CM) for 5 h. Images of PFA-fixed cells were then captured with a Leica DMi8 microscope (Leica Microsystems, Wetzlar, Germany) using a 20× objective. Scale bar: 50 µm.
3. Discussion
The AGS cell line has been widely used as a model system to study CagA-induced effects, owing to its unique ability to undergo rapid and pronounced morphological changes upon ectopic expression of CagA. These morphological alterations, known as the “hummingbird” phenotype, are characterized by marked cell elongation and spindle-like protrusions. The distinct and easily observable nature of this phenotype makes AGS cells a valuable tool for monitoring CagA activity in both qualitative and quantitative assays. In addition, the hummingbird phenotype is a direct segue into oncogenic cell progression, since cells exhibiting this phenotype have increased cell motility and scattering, resembling epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) [].
Taking advantage of these characteristics, we established an assay using AGS cells to efficiently screen for Lactobacillus strains that can counteract CagA-induced morphological changes. Through a pilot-scale experiment, we identified the gastric-specific Lactobacillus gasseri Kx110 A1 strain as an effective suppressor of the CagA-induced hummingbird phenotype, establishing a foundation for large-scale screening of probiotics or potential therapeutic candidates. We assessed the ability of Lactobacillus gasseri to suppress the CagA-induced hummingbird phenotype in AGS cells by employing two complementary approaches: infection with CagA-positive Helicobacter pylori and direct ectopic expression of CagA via HA-tagged CagA plasmid transfection. The infection model mimics a more physiological context in which CagA is delivered to host cells by the H. pylori type IV secretion system at biologically relevant concentrations, while the transfection approach allows us to evaluate the direct effect of CagA in the absence of other bacterial components. In both approaches, L. gasseri significantly reduced the hummingbird phenotype, indicating it can interfere with CagA’s effects regardless of how it is introduced into the cells.
Since we observed a suppression of cell elongation by CagA in the presence of L. gasseri, we were interested in identifying the mechanism behind it. Unlike polarized epithelial cell lines such as MDCK, which require extensive remodeling of adherens junctions and cytoskeletal architecture, AGS cells lack well-defined cell polarity and tight junctions and do not express detectable levels of membrane-associated E-cadherin. These characteristics make AGS cells more permissive to rapid and pronounced morphological transformation into the highly elongated hummingbird phenotype upon CagA expression [,].
As a result, they are inherently more responsive to CagA-induced changes. However, the same properties reduce their reliance on CagA’s phosphorylation-independent mechanisms because AGS cells already exhibit a depolarized, junction-deficient phenotype. Consequently, the transformation in AGS cells is predominantly driven by phosphorylation-dependent pathways, particularly SHP2 activation and cytoskeletal reorganization. This implies that phenotypic screening assays using AGS cells are more likely to identify inhibitors that target CagA’s phosphorylation-dependent functions, while phosphorylation-independent activities may be underrepresented or overlooked. Consistent with this hypothesis, we found that the L. gasseri strain inhibited phosphorylation of CagA. The phosphorylated CagA-SHP-2 interaction could be considered the most crucial to fulfill H. pylori-induced changes in abnormal cell morphology and motility. SHP-2 consists of a pair of SH-2 domains at its N-terminal and a protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) at its C-terminal []. Phosphorylated CagA is capable of binding to the SH2 domain of SHP-2 and aberrantly activating it by maintaining it in a relaxed state; this exposes the PTPase domain, which dephosphorylates and inactivates key regulators of focal adhesion formation, affecting the control of normal cell morphology [,,,].
By co-immunoprecipitation experiments, we were able to observe that L. gasseri reduced the amount of phosphorylated CagA in cells, and consequently, the CagA interaction with SHP-2 was also lowered in cells treated with L. gasseri (Figure 3). SHP-2 is an oncoprotein owing to its strong ties with CagA-based carcinogenetic activity [], and lowering its activity through L. gasseri could be a key point in preventing the conversion of a normal cell to an ultimately cancerous phenotype. The reduced level of phosphorylated CagA limits its interaction with the SHP-2 phosphatase, which is oncogenic in nature and promotes tumor growth.
CagA can also interact with PAR1b/MARK2 kinases independent of its phosphorylation status. Normally, PAR1b is involved in the maintenance and establishment of epithelial cell polarity by phosphorylating MAPs and destabilizing microtubules [,]. CagA is capable of directly binding and inhibiting PAR1b, thereby disrupting tight junctions and causing loss of apico-basal cell polarity. Notably, PAR1b also promotes CagA multimerization, which leads to stronger and more stable interactions with SHP2 []. Thus, the CagA-PAR1b interaction, although phosphorylation-independent, could also indirectly promote the hummingbird phenotype in infected cells [,]. To test whether L. gasseri was able to influence CagA activity independent of its phosphorylation, we looked at Par1b/MARK2 levels in CagA-transfected cells treated with L. gasseri, in comparison to cells treated with RPMI media as controls. SHP-2 expression was also checked in these experiments. Interestingly, we found that L. gasseri did not affect the interaction between CagA and PAR1b/MARK2, while SHP-2 showed lower levels of interaction in the L. gasseri-treated samples (Figure 4).
Since we saw that L. gasseri exclusively influenced CagA, we hypothesized that lactobacilli could perhaps interfere with the localization of CagA to the cell membrane. In order to interact with its downstream binding partner SHP-2, it is necessary for CagA to be first tethered to the membrane, where it undergoes phosphorylation by host kinases; only then can the phosphorylated CagA-SHP-2 complex form []. On the other hand, cytosolic, unphosphorylated CagA is sufficient to interact with PAR1b []. We used confocal microscopy to analyze the localization of HA-tagged CagA within the cells and observed that the staining was dispersed in the cytoplasm, in contrast to the membrane-associated localization of CagA seen in RPMI-treated controls (Figure 4), showing that L. gasseri mislocalized CagA within the cells and prevented it from anchoring to the cell membrane. Further, the incubation of CagA-expressing gastric cells with the L. gasseri strain interfered with CagA tethering to the membrane, as evidenced by its increased cytoplasmic staining and less membrane staining. By using CagA-transfected cells, our experimental model did not involve the H. pylori T4SS and its potential co-factors. These findings provide further support for studying the effect of Lactobacillus strains in the prevention and suppression of H. pylori-induced cell damage and highlight the importance of identifying effective Lactobacillus strains that might be used as treatments or preventive agents in the future.
In this study, we found that live lactobacilli in direct contact with the host cells were necessary to suppress CagA-induced cell elongation (Figure 5). These findings suggest that lactobacilli may bind to the host cell surface and activate a signaling pathway that disrupts the localization of CagA beneath the inner plasma membrane, possibly by blocking its interaction with phosphatidylserine or other membrane components. In the future, it would be interesting to identify and characterize the active component of the lactobacilli that confer this protective effect on the host. It would be motivating to validate these findings using animal or organoid models that more closely mimic physiological conditions, including the presence of mucus, microflora, and an acidic environment. It would also be valuable to investigate non-specific stress and immune responses of host cells, as well as to further characterize the L. gassseri Kx110 strain and compare it to other Lactobacillus species. At this stage, we do not know whether other L. gasseri isolates from the stomach may have similar properties. Future studies should focus on a more detailed characterization and whole-genome sequencing of the L. gasseri Kx110 A1 strain to identify potential genetic determinants responsible for its protective effects.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains
The Helicobacter pylori strain 67:21 [] was grown on Columbia blood agar plates (Thermo Fisher, Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) supplemented with 8% defibrinated horse blood and 8% inactivated horse serum (Håtunalab, Uppsala, Sweden) for 3 days at 37 °C under microaerophilic conditions. The Lactobacillus strains used are described and listed in Table 1. Lactobacilli were grown on Rogosa agar plates and then cultured overnight in MRS broth (Oxoid Inc., Hampshire, UK) at 37 °C and 5% CO2 in a humidified environment. Prior to each experiment, overnight cultures of lactobacilli were washed and resuspended in RPMI 1640 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS, Sigma-Aldrich, Burlington, MA, USA).

Table 1.
Lactobacillus strains used in this study.
4.2. Cell Culture
The gastric epithelial cell line AGS (ATCC, CRL-1739) was cultured in RPMI 1640 (Thermo Fisher, Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS, Sigma Aldrich, Burlington, MA, USA) and maintained at 37 °C and 5% CO2 in a humidified environment.
4.3. Plasmids and Transfection
For the transfection of AGS cells, the humanized cagA gene, along with a hemagglutinin (HA) tag, as previously described in Ohnishi et al., 2008 [], was modified by the addition of HindIII and EcoRV restriction sites at the 5′ and 3′ ends, respectively. The customized constructs, cloned into pcDNA3.1(+) plasmid vectors (pcDNA3.1-CagA), were purchased from GenScript (Piscataway, NJ, USA). Empty pcDNA3.1(+) plasmid vectors (Genscript) were used as a mock transfection control. All constructs were transfected into AGS cells using Opti-mem (Thermo Fisher) and Lipofectamine 2000 (Thermo Fisher), as per the manufacturer’s instructions.
4.4. Infection of Gastric Cells with Whole H. pylori and Lactobacilli
Gastric AGS cells grown in 12-well plates were infected with H. pylori at an MOI of 100 for 24 h, followed by an overnight infection with lactobacilli at an MOI of 50 or 10, at 37 °C and 5% CO2 in a humidified environment. After overnight incubation, the cells were washed with PBS and fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 10 min. Differential interference contrast images of the fixed cells were collected using a Leica DMi8 microscope (Leica Microsystems, Wetzlar, Germany) with a 10× objective.
4.5. Infection of CagA-Expressing Gastric Cells with Lactobacilli
Gastric cells grown in 12-well plates were transfected with 1 µg of pcDNA3.1-CagA or empty pcDNA3.1 vectors and left for a further 48 h prior to infection with either lactobacilli at an MOI of 100 or RPMI media as a control, at 37 °C and 5% CO2 in a humidified environment. After 5 h of incubation, the cells were washed with PBS and fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 10 min and then analyzed by immunohistochemistry, as described below.
4.6. Immunocytochemistry and Confocal Microscopy
CagA-expressing AGS cells, treated with either lactobacilli or RPMI medium as a control, were paraformaldehyde-fixed, blocked with 5% BSA for 1 h at room temperature, and then treated with rabbit anti-HA (#3724, Cell Signaling Technology #3724, 1:1000) for 1 h at RT to detect CagA-HA. Cells were washed three times with PBST (PBS + 0.02% Tween20) containing 0.5% BSA and incubated with anti-rabbit IgG Alexa Flour 488 (A21206; Thermo Fisher) for 1 h at RT, washed three times with PBST again, and then finally incubated with DAPI solution (1 mM, Thermo Fisher) for 30 min at RT. Following the final three washes, 400 µL PBS was added to each well, and the cells were analyzed using a Leica DMi8 microscope for images. For confocal analysis, AGS cells were cultured on chamber slides, mounted using ProLong Gold Antifade Mountant with DAPI (Thermo Fisher), and imaged using a Zeiss LSM 780 confocal microscope (Carl Zeiss AB, Oberkochen, Germany).
4.7. Co-Immunoprecipitation
AGS cells in 6 cm dishes were transfected with 8 µg of pcDNA3.1-CagA or empty pcDNA3.1 vectors and left for a further 48 h prior to infection with either lactobacilli at an MOI of 100 or RPMI media as a control, at 37 °C and 5% CO2 in a humidified environment. After 5 h of incubation, cells were washed once with PBS, and the cell lysates of each sample were collected in 500 µL of IP lysis buffer (Thermo Fisher), supplemented with a 1× EDTA-free protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche, Basel, Switzerland), 2 mM Na3VO4, and 2 mM NaF (Sigma-Aldrich). Rabbit anti-HA (#3724; Cell Signaling Technology, 5 µL, 1:1000) was added to each sample and incubated overnight at 4 °C with gentle shaking. The next day, 25 µL of Protein A/G Magnetic Beads (Thermo Fisher) was added to each sample and incubated at 4 °C for 1 h, with gentle shaking. Sample-bound magnetic beads were then washed with IP lysis buffer three times and finally resuspended in 25 µL of 2× sample buffer (Bio-Rad) containing 5% B-mercaptoethanol (Sigma-Aldrich). The samples were stored at −20 °C until Western Blotting.
4.8. Western Blotting
Thawed samples were heated to 95 °C for 10 min, centrifuged for 1 min at 10,000× g, and then loaded onto 4–20% precast polyacrylamide gels (Bio-Rad). After separation, the proteins were transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane (Bio-Rad) using a semi-dry transfer system (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). The blots were incubated for 1 h at room temperature in blocking buffer (Intercept Blocking Buffer, LI-COR, or 5% BSA), followed by overnight incubation at 4 °C with primary antibodies: HA-CagA (#3724T; Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA, USA), anti-phosphotyrosine (ab10321; Abcam, Cambridge, UK), SHP-2 (sc-7384; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA, USA), and PAR1b/MARK2 (PA5-84966; Thermo Fisher). After three washes, the blots were incubated with secondary antibodies and detected using either the LI-COR Odyssey system or chemiluminescence (Bio-Rad, #1705062), depending on the type of secondary antibody used.
4.9. Fixation and Preparation of Conditioned Medium from L. gasseri
L. gasseri grown on Rogosa plates was inoculated in MRS broth and grown overnight at 37 °C. The following day, cultures were centrifuged at 4500× g for 10 min, resuspended in fresh MRS broth, and allowed to grow further for 2 h at 37 °C. The cultures were then re-centrifuged, and the resulting bacterial pellets were resuspended in RPMI 1640 to an optical density (OD) of 1.0 (5 × 107 cfu/mL). For the preparation of fixed lactobacilli, the bacteria were spun down, and the pellets were treated with 4% formaldehyde for 10 min. They were washed three times with PBS and then resuspended in RPMI medium to a concentration of 5 × 107 bacteria/mL. For the preparation of conditioned medium, the bacteria were further incubated in RPMI for 2 h and then filter-sterilized to collect the conditioned medium.
Author Contributions
R.K.G., T.S. and A.-B.J. designed research; R.K.G., T.S. and A.C.S. performed research; R.K.G., T.S. and A.-B.J. analyzed data; R.K.G., T.S. and A.-B.J. wrote the paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the Swedish Research Council Dnr (2019-01355) and the Swedish Cancer Society (grants to A-BJ), and Stockholm University.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Chris Molenaar and the Imaging facility at Stockholm University for support with microscopy, Johan Ankarklev for letting us use the Leica microscope, and the Pathology Core Facility at Karolinska University Hospital for tissue sectioning.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
References
- Hooi, J.K.Y.; Lai, W.Y.; Ng, W.K.; Suen, M.M.Y.; Underwood, F.E.; Tanyingoh, D.; Malfertheiner, P.; Graham, D.Y.; Wong, V.W.S.; Wu, J.C.Y.; et al. Global Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori Infection: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, A.; Crowe, S.E. Helicobacter pylori in gastric malignancies. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2012, 14, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boonyanugomol, W.; Chomvarin, C.; Hahnvajanawong, C.; Sripa, B.; Kaparakis-Liaskos, M.; Ferrero, R.L. Helicobacter pylori cag pathogenicity island (cagPAI) involved in bacterial internalization and IL-8 induced responses via NOD1- and MyD88-dependent mechanisms in human biliary epithelial cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Censini, S.; Lange, C.; Xiang, Z.; Crabtree, J.E.; Ghiara, P.; Borodovsky, M.; Rappuoli, R.; Covacci, A. Cag, a pathogenicity island of Helicobacter pylori, encodes type I-specific and disease-associated virulence factors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 14648–14653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, C.Y.; Sheu, B.S.; Wu, J.J. Helicobacter pylori infection: An overview of bacterial virulence factors and pathogenesis. Biomed. J. 2016, 39, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatakeyama, M. Structure and function of Helicobacter pylori CagA, the first-identified bacterial protein involved in human cancer. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B 2017, 93, 196–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, K.R.; Joo, Y.M.; Jang, S.; Yoo, Y.J.; Lee, H.S.; Chung, I.S.; Olsen, C.H.; Whitmire, J.M.; Merrell, D.S.; Cha, J.H. Polymorphism in the CagA EPIYA motif impacts development of gastric cancer. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 959–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutsumi, R.; Higashi, H.; Higuchi, M.; Okada, M.; Hatakeyama, M. Attenuation of Helicobacter pylori CagA SHP-2 signaling by interaction between CagA and C-terminal Src kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 3664–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.H.; Qu, C.K.; Henegariu, O.; Lu, X.; Feng, G.S. Protein-tyrosine phosphatase Shp-2 regulates cell spreading, migration, and focal adhesion. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 21125–21131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Qu, C.K. Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase SHP-2 (PTPN11) in Hematopoiesis and Leukemogenesis. J. Signal Transduct. 2011, 2011, 195239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segal, E.D.; Cha, J.; Lo, J.; Falkow, S.; Tompkins, L.S. Altered states: Involvement of phosphorylated CagA in the induction of host cellular growth changes by Helicobacter pylori. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 14559–14564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashi, H.; Tsutsumi, R.; Muto, S.; Sugiyama, T.; Azuma, T.; Asaka, M.; Hatakeyama, M. SHP-2 tyrosine phosphatase as an intracellular target of Helicobacter pylori CagA protein. Science 2002, 295, 683–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutsumi, R.; Takahashi, A.; Azuma, T.; Higashi, H.; Hatakeyama, M. Focal adhesion kinase is a substrate and downstream effector of SHP-2 complexed with Helicobacter pylori CagA. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 26, 261–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadat, I.; Higashi, H.; Obuse, C.; Umeda, M.; Murata-Kamiya, N.; Saito, Y.; Lu, H.; Ohnishi, N.; Azuma, T.; Suzuki, A.; et al. Helicobacter pylori CagA targets PAR1/MARK kinase to disrupt epithelial cell polarity. Nature 2007, 447, 330–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wessler, S.; Gimona, M.; Rieder, G. Regulation of the actin cytoskeleton in Helicobacter pylori-induced migration and invasive growth of gastric epithelial cells. Cell Commun. Signal. 2011, 9, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.A.; Tummuru, M.K.; Blaser, M.J.; Kerr, L.D. Activation of IL-8 gene expression by Helicobacter pylori is regulated by transcription factor nuclear factor-kappa B in gastric epithelial cells. J. Immunol. 1998, 160, 2401–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer-ter-Vehn, T.; Covacci, A.; Kist, M.; Pahl, H.L. Helicobacter pylori activates mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades and induces expression of the proto-oncogenes c-fos and c-jun. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 16064–16072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colautti, A.; Orecchia, E.; Comi, G.; Iacumin, L. Lactobacilli, a Weapon to Counteract Pathogens through the Inhibition of Their Virulence Factors. J. Bacteriol. 2022, 204, e0027222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Klerk, N.; Maudsdotter, L.; Gebreegziabher, H.; Saroj, S.D.; Eriksson, B.; Eriksson, O.S.; Roos, S.; Linden, S.; Sjolinder, H.; Jonsson, A.B. Lactobacilli Reduce Helicobacter pylori Attachment to Host Gastric Epithelial Cells by Inhibiting Adhesion Gene Expression. Infect. Immun. 2016, 84, 1526–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebremariam, H.G.; Qazi, K.R.; Somiah, T.; Pathak, S.K.; Sjolinder, H.; Ekström, E.S.; Jonsson, A.B. Lactobacillus gasseri Suppresses the Production of Proinflammatory Cytokines in Helicobacter pylori-Infected Macrophages by Inhibiting the Expression of ADAM17. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Ma, F.Z.; Deng, X.J.; Yuan, H.; Ma, H.S. Lactobacilli inhibit interleukin-8 production induced by Helicobacter pylori lipopolysaccharide-activated Toll-like receptor 4. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 5090–5095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backert, S.; Moese, S.; Selbach, M.; Brinkmann, V.; Meyer, T.F. Phosphorylation of tyrosine 972 of the Helicobacter pylori CagA protein is essential for induction of a scattering phenotype in gastric epithelial cells. Mol. Microbiol. 2001, 42, 631–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagnoli, F.; Buti, L.; Tompkins, L.; Covacci, A.; Amieva, M.R. Helicobacter pylori CagA induces a transition from polarized to invasive phenotypes in MDCK cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 16339–16344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amieva, M.R.; Vogelmann, R.; Covacci, A.; Tompkins, L.S.; Nelson, W.J.; Falkow, S. Disruption of the epithelial apical-junctional complex by Helicobacter pylori CagA. Science 2003, 300, 1430–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weydig, C.; Starzinski-Powitz, A.; Carra, G.; Lower, J.; Wessler, S. CagA-independent disruption of adherence junction complexes involves E-cadherin shedding and implies multiple steps in Helicobacter pylori pathogenicity. Exp. Cell Res. 2007, 313, 3459–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hof, P.; Pluskey, S.; Dhe-Paganon, S.; Eck, M.J.; Shoelson, S.E. Crystal structure of the tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2. Cell 1998, 92, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi-Kanemitsu, A.; Knight, C.T.; Hatakeyama, M. Molecular anatomy and pathogenic actions of Helicobacter pylori CagA that underpin gastric carcinogenesis. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 17, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easton, J.B.; Royer, A.R.; Middlemas, D.S. The protein tyrosine phosphatase, Shp2, is required for the complete activation of the RAS/MAPK pathway by brain-derived neurotrophic factor. J. Neurochem. 2006, 97, 834–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroun, C.R.; Naujokas, M.A.; Holgado-Madruga, M.; Wong, A.J.; Park, M. The tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2 is required for sustained activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase and epithelial morphogenesis downstream from the met receptor tyrosine kinase. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 8513–8525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagase, L.; Hayashi, T.; Senda, T.; Hatakeyama, M. Dramatic increase in SHP2 binding activity of Helicobacter pylori Western CagA by EPIYA-C duplication: Its implications in gastric carcinogenesis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drewes, G.; Ebneth, A.; Preuss, U.; Mandelkow, E.M.; Mandelkow, E. MARK, a novel family of protein kinases that phosphorylate microtubule-associated proteins and trigger microtubule disruption. Cell 1997, 89, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, D.; Brennwald, P.J.; Rodriguez-Boulan, E.; Musch, A. Mammalian PAR-1 determines epithelial lumen polarity by organizing the microtubule cytoskeleton. J. Cell Biol. 2004, 164, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, S.; Higashi, H.; Lu, H.; Azuma, T.; Hatakeyama, M. Structural basis and functional consequence of Helicobacter pylori CagA multimerization in cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 32344–32352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, M.; Shi, F.; Zheng, S.; Xiong, L.; Zheng, L. A review of signal pathway induced by virulent protein CagA of Helicobacter pylori. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1062803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higashi, H.; Tsutsumi, R.; Fujita, A.; Yamazaki, S.; Asaka, M.; Azuma, T.; Hatakeyama, M. Biological activity of the Helicobacter pylori virulence factor CagA is determined by variation in the tyrosine phosphorylation sites. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 14428–14433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backert, S.; Tegtmeyer, N.; Selbach, M. The versatility of Helicobacter pylori CagA effector protein functions: The master key hypothesis. Helicobacter 2010, 15, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).