Th2-High Severe Asthma with Hypereosinophilia in the Spectrum of Type 2 Inflammatory Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. T2-High Asthma
2.1. Hypereosinophilia and T2-High Asthma
2.2. Other T2 Conditions
2.3. EGPA and Asthma
2.4. HES and Asthma
3. Treatment of Hypereosinophilic Asthma
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Summary
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABL1 | v-abl Abelson murine leukemia viral oncogene homolog 1 |
| ABPA | allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis |
| ACEI | Angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitor |
| ACQ | Asthma Control Questionnaire |
| ACR/EULAR | American College of Rheumatology and European League Against Rheumatism |
| AED | Anticonvulsant drug |
| AD | atopic dermatitis |
| ARV | antiretroviral drug |
| AR | allergic rhinitis |
| Ath | artery thrombosis |
| ATS | American Thoracic Society |
| BTP | bronchothermoplasty |
| CEL | chronic eosinophilic leukemia |
| CCL | C-C motif chemokine ligand |
| CEP | chronic eosinophilic pneumonia |
| CNPG | chronic prurigo nodularis |
| COX-1 | cyclooxygenase-1 |
| CRSwNP | chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps |
| CTX | cyclophosphamide |
| CU | chronic urticaria |
| CSU | chronic spontaneous urticaria |
| CXCL | C-X-C motif ligand |
| CystLTR | cysteinyl leukotriene receptor |
| DRESS | drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms |
| DVT | deep vein thrombosis |
| EGID | eosinophilic gastrointestinal disease |
| EGPA | eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis |
| EN | erythema nodosum |
| EOS | eosinophil |
| EoE | eosinophilic esophagitis |
| EP | eosinophilic pneumonia |
| EPO | (human) erythropoietin |
| ERS | European Respiratory Society |
| ES | eosinophilic sinusitis |
| ET | essential thrombocytopenia |
| FA | food allergy |
| FeNO | fractional exhaled nitric oxide |
| FGFR | fibroblast growth factor receptor |
| FLT3 | FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 |
| GE | eosinophilic gastroenteritis |
| GERD | gastroesophageal reflux disease |
| GINA | Global Initiative for Asthma |
| GM-CSF | granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor |
| HE | hypereosinophilia |
| HES | hypereosinophilic syndrome |
| HESN | HES neoplasia |
| HESR | HES reactive |
| HESI | HES idiopathic |
| HESFA | HES familial |
| HU | hydroxyurea |
| ICI | immune checkpoints inhibitor |
| ICS | inhaled corticosteroid |
| IL | interleukin |
| IL-5R | interleukin-5 receptor |
| ILC | innate lymphoid cell |
| IM | immunomodulator |
| JAK | Janus kinase |
| JAKi | Janus Kinase inhibitor |
| KI | kinase inhibitor |
| KIT | KIT proto-oncogene, encoding tyrosine kinase receptor |
| LABA | long-acting beta2-agonist |
| LHEA | late-onset hypereosinophilic asthma |
| LTRA | leukotriene receptor agonist |
| MAb | monoclonal antibody |
| MART/SMART | maintenance and reliever therapy/single-inhaler MART |
| MIRACLE trial | Multicenter InSync Randomized Clinical Evaluation trial |
| MPN | myeloproliferative neoplasm |
| N-ERD | NSAID-exacerbated respiratory disease |
| NEST | The Nucala Effectiveness Study |
| NP | nasal polyposis |
| NSAID | Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug |
| OCS | oral corticosteroid |
| OM | otitis media |
| OSM | oncostatin M |
| PCM1 | pericentriolar material 1 |
| PDE5 | phosphodiesterase 5 |
| PDGFR | platelet-derived growth factor receptor |
| PE | pulmonary embolism |
| PN | prurigo nodularis |
| PPI | proton-pump inhibitor |
| PV | polycythemia vera |
| REALTI-A | The REAL-world effectiveness of mepolizumab In paTIent care—Asthma |
| ReQualBi study | Re-Qualification of the asthma patient on Biologic therapy study |
| RTX | rituximab |
| SABA | short-acting β2-agonist |
| SA | severe asthma |
| SEM | systemic eosinophilic manifestation |
| STAT | signal transducer and activator of transcription pathway |
| TKI | tyrosine kinase inhibitor |
| TSLP | Thymic stromal lymphopoietin |
| T2 | Type 2 |
| VCAM-1 | vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 |
| VKC | vernal keratoconjunctivitis |
| WARF | warfarin |
| WBC | white blood cell |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| XOI | xanthine oxidase inhibitor |
References
- Global Initiative for Asthma. Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention. 2024. Available online: https://ginasthma.org/2024-report/ (accessed on 23 March 2025).
- World Health Organization: WHO. Chronic Respiratory Diseases. 15 July 2019. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/chronic-respiratory-diseases#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- Yuan, L.; Tao, J.; Wang, J.; She, W.; Zou, Y.; Li, R.; Ma, Y.; Sun, C.; Bi, S.; Wei, S.; et al. Global, regional, national burden of asthma from 1990 to 2021, with projections of incidence to 2050: A systematic analysis of the global burden of disease study 2021. EClinicalMedicine 2025, 80, 103051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Global Initiative for Asthma. Difficult-to-Treat and Severe Asthma in Adolescent and Adult Patients. 2023. Available online: https://www.ginasthma.org/severe-asthma (accessed on 23 March 2025).
- Sim, S.; Choi, Y.; Park, H.S. Update on Inflammatory Biomarkers for Defining Asthma Phenotype. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2024, 16, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lommatzsch, M.; Blumchen, K.; Beck, L.A.; Bousquet, J.; Brusselle, G.G.; Fokkens, W.J.; Hamelmann, E.; Lau, S.; Ott, H.; Pfaar, O.; et al. Roads to remission: Evolving treatment concepts in type 2 inflammatory diseases. EClinicalMedicine 2025, 80, 103050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabèze, L.; Marchand-Adam, S.; Borie, R.; Justet, A.; Dupin, C.; Dombret, M.C.; Crestani, B.; Taillé, C. Severe asthma with blood hypereosinophilia associated with JAK2 V617F mutation: A case series. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1802248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valent, P.; Klion, A.D.; Roufosse, F.; Simon, D.; Metzgeroth, G.; Leiferman, K.M.; Schwaab, J.; Butterfield, J.H.; Sperr, W.R.; Sotlar, K.; et al. Proposed refined diagnostic criteria and classification of eosinophil disorders and related syndromes. Allergy 2023, 78, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikhail, E.S.; Ghatol, A. Hypereosinophilic Syndrome. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK599558/ (accessed on 2 April 2025).
- Emmi, G.; Bettiol, A.; Gelain, E.; Bajema, I.M.; Berti, A.; Burns, S.; Cid, M.C.; Cohen Tervaert, J.W.; Cottin, V.; Durante, E.; et al. Evidence-Based Guideline for the diagnosis and management of eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2023, 19, 378–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlBloushi, S.; Al-Ahmad, M. Exploring the immunopathology of type 2 inflammatory airway diseases. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1285598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogulur, I.; Mitamura, Y.; Yazici, D.; Pat, Y.; Ardicli, S.; Li, M.; D’Avino, P.; Beha, C.; Babayev, H.; Zhao, B.; et al. Type 2 immunity in allergic diseases. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2025, 22, 211–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Liu, G. Eosinophilic Asthma: Pathophysiology and Therapeutic Horizons. Cells 2024, 13, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelaia, C.; Vatrella, A.; Gallelli, L.; Lombardo, N.; Sciacqua, A.; Savino, R.; Pelaia, G. Role of p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase in Asthma and COPD: Pathogenic Aspects and Potential Targeted Therapies. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2021, 15, 1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saggini, R.; Pellegrino, R. MAPK is implicated in sepsis, immunity, and inflammation. Int. J. Infection. 2024, 8, 100–104. Available online: https://www.biolife-publisher.it/iji/mapk-is-implicated-in-sepsis-immunity-and-inflammation/ (accessed on 25 May 2025).
- Suwala, Z.; Marchewka, U.; Bieńkowski, B.; Feja, K.; Łuczak, E.; Jachowicz, K.; Petryla, P.; Ostafin, K.; Rektor, N.; Minkner, M. Allergic march: A comprehensive approach to diagnosing, treating and preventing atopic diseases. J. Educ. Health Sport 2023, 45, 388–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaillant, A.A.J.; Modi, P.; Syed, H.A.; Jan, A. Atopy. In Irritant Dermatitis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, A.; Lunding, L.P.; Zissler, U.M.; Vock, C.; Webering, S.; Ehlers, J.C.; Orinska, Z.; Chaker, A.; Schmidt-Weber, C.B.; Lang, N.J.; et al. IL-37 regulates allergic inflammation by counterbalancing pro-inflammatory IL-1 and IL-33. Allergy Eur. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 77, 856–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toniato, E. IL-37 is an inhibitory cytokine that could be useful for treating infections. Int. J. Infect. 2024, 8, 1–2. Available online: https://www.biolife-publisher.it/iji/il-37-is-an-inhibitory-cytokine-that-could-be-useful-for-treating-infections/ (accessed on 25 May 2025).
- Pavord, I.D.; Bel, E.H.; Bourdin, A.; Chan, R.; Han, J.K.; Keene, O.N.; Liu, M.C.; Martin, N.; Papi, A.; Roufosse, F.; et al. From DREAM to REALITI-A and beyond: Mepolizumab for the treatment of eosinophil-driven diseases. Allergy 2021, 77, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardi, C.; Berti, A.; Cottini, M. The emerging roles of eosinophils: Implications for the targeted treatment of eosinophilic-associated inflammatory conditions. Curr. Res. Immunol. 2022, 3, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, S.L.; Mules, T.C.; Le Gros, G.; Inns, S. The immunoregulatory potential of eosinophil subsets. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2024, 102, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanuru, S.; Sapra, A. Eosinophilia. In Travel Medicine; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shomali, W.; Gotlib, J. World Health Organization and International Consensus Classification of eosinophilic disorders: 2024 update on diagnosis, risk stratification, and management. Am. J. Hematol. 2024, 99, 946–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, F.L. Approach to the patient with eosinophilia. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 104, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiappini, E. Unraveling the diagnostic puzzle of eosinophilia in children. Glob. Pediatr. 2024, 7, 100104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, G.N.; Christoffersen, M.N.; Lindegaard, H.M.; Davidsen, J.R.; Hartmeyer, G.N.; Assing, K.; Mortz, C.G.; Martin-Iguacel, R.; Møller, M.B.; Kjeldsen, A.D.; et al. The multidisciplinary approach to eosinophilia. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1193730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, C.E.; Khoury, P. Approach to Eosinophilia Presenting With Pulmonary Symptoms. Chest 2020, 159, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, J.; Thomas, L. Chronic Eosinophilic Leukemia Presenting as Asthma. Am. Thorac. Soc. Int. Conf. Meet. Abstr. 2021, 203, A1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Tanaka, J.; Kobayashi, K.; Kamide, Y. Treatments of refractory eosinophilic lung diseases with biologics. Allergol. Int. 2023, 72, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyoshima, M.; Tsuchiya, K.; Suda, T. Late-onset hypereosinophilic asthma accompanied by systemic eosinophilic manifestations. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 48 (Suppl. S60), PA4199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.H.; Rabkin, C.S.; Engels, E.A.; Song, M. Associations between eosinophils and cancer risk in the UK Biobank. Int. J. Cancer 2024, 155, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wechsler, M.E.; Munitz, A.; Ackerman, S.J.; Drake, M.G.; Jackson, D.J.; Wardlaw, A.J.; Dougan, S.K.; Berdnikovs, S.; Schleich, F.; Matucci, A.; et al. Eosinophils in Health and Disease: A State-of-the-Art Review. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2021, 96, 2694–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffari, S.; Rezaei, N. Eosinophils in the tumor microenvironment: Implications for cancer immunotherapy. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omero, F.; Speranza, D.; Murdaca, G.; Cavaleri, M.; Marafioti, M.; Cianci, V.; Berretta, M.; Casciaro, M.; Gangemi, S.; Santarpia, M. The Role of Eosinophils, Eosinophil-Related Cytokines and AI in Predicting Immunotherapy Efficacy in NSCLC. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Jain, N.; Raju, S. MARKED HYPEREOSINOPHILIA IN A PATIENT WITH ASTHMA AND NASAL POLYPS CONFOUNDING HYPEREOSINOPHILIC SYNDROME. CHEST 2023, 164, A89–A90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsurumaki, H.; Matsuyama, T.; Ezawa, K.; Koga, Y.; Yatomi, M.; Aoki-Saito, H.; Chikamatsu, K.; Hisada, T. Rapid Effect of Benralizumab for Hypereosinophilia in a Case of Severe Asthma with Eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Medicina 2019, 55, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gael, M.; Schoeffler, A.; Bursztejn, A.C. Efficacy of dupilumab in chronic prurigo: A multicentre retrospective study. Ann. Dermatol. Vénéréologie 2025, 152, 103336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esnault, S.; Bernau, K.; Floerke, H.L.; Dendooven, A.; Delaunay, E.; Dill-McFarland, K.A.; Altman, M.C.; Busse, W.W.; Rosenkranz, M.A.; Tattersall, M.C.; et al. Oncostatin-M Is Produced by Human Eosinophils and Expression Is Increased in Uncontrolled Severe Asthma. Allergy 2025, 80, 1154–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarnieri, K.M.; Saba, N.K.; Schwartz, J.T.; Devonshire, A.L.; Bufford, J.; Casale, T.B.; Rothenberg, M.E.; Andorf, S. Food allergy characteristics associated with co-existing eosinophilic esophagitis in FARE Registry participants. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2023, 11, 1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carucci, L.; Votto, M.; Licari, A.; Marseglia, G.L.; Berni Canani, R. Food allergy: Cause or consequence of pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis? Potential implications of ultraprocessed foods in prevention and management. Front. Allergy 2023, 4, 1138400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakabe, M.; Tobino, K.; Obata, Y.; Sogabe, S.; Uchida, K.; Murakami, Y. Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis developed during treatment with benralizumab for severe asthma: A case report and literature review. Respirol. Case Rep. 2024, 12, e01431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuna, P.; Jassem, E.; Wiatr, E.; Bazan-Socha, S.; Kupryś-Lipińska, I. Hyper eosinophilic diseases—Diagnosis and therapeutic approach—Practical position of the Polish working group. Otolaryngol. Pol. Pol. Otolaryngol. 2024, 78, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puan, Y.; Ong, K.Y.; Tiew, P.Y.; Wen Chen, G.X.; Teo, N.W.Y.; Low, A.H.L.; Wechsler, M.E.; Koh, M.S. Characteristics of Severe Asthma Clinic Patients With Eosinophilic Granulomatosis With Polyangiitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2025, 13, 361–368.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, L.; Jesenak, M.; Bjermer, L.; Hanania, N.A.; Seys, S.F.; Diamant, Z. Biologics in severe asthma: A pragmatic approach for choosing the right treatment for the right patient. Respir. Med. 2023, 218, 107414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.A.; Langford, C.A.; Maz, M.; Abril, A.; Gorelik, M.; Guyatt, G.; Archer, A.M.; Conn, D.L.; Full, K.A.; Grayson, P.C.; et al. 2021 American College of Rheumatology/Vasculitis Foundation Guideline for the Management of Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody—Associated Vasculitis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021, 73, 1366–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, M.; Ohshima, N.; Kawashima, M.; Shiina, M.; Kitani, M.; Suzukawa, M. Severe Asthma Where Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis Became Apparent after the Discontinuation of Dupilumab. Intern. Med. 2022, 61, 755–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poisson, C.; Chenivesse, C.; Cuvillon, E.; Barnig, C.; Clarot, C.; Dupin, C.; Mangiapan, G.; Rolland-Debord, C.; Bonniaud, P.; Taillé, C. Asthma loss of control after switch from anti-IL5/5R drugs to dupilumab in severe eosinophilic asthma: A case series. Eur. Respir. J. 2024, 64 (Suppl. S68), PA5369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serin, I.; Serin, I.; Ulusoy, A.; Ulusoy, A.; Onar, M.I.; Ulusoy, A.; Dogu, M.H.; Onar, M.I.; Onar, M.I.; Dogu, M.H.; et al. COVID-19 Pneumonia or Hypereosinophilic Syndrome? J. Med. Cases 2020, 11, 400–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuek, S.L.; Pettman, C.; Neeland, M.R.; Harrison, J.; Mehr, S.; Shanthikumar, S.; Beggs, S. Eosinophilia and wheeze: Thinking beyond asthma. Breathe 2024, 20, 230126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwee, J.; Huynh, L.; Du, S.; Kwon, N.; Jakes, R.W.; Alfonso-Cristancho, R.; Baylis, L.; Requena, G.; Khanal, A.; Rothenberg, M.E.; et al. Hypereosinophilic syndrome in Europe: Retrospective study of treatment patterns, clinical manifestations, and healthcare resource utilization. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2023, 130, 768–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riego, M.A.; Poon, J.; Naik, R. Misdiagnosis of Asthma in a Patient with Hypereosinophilic Syndrome with Cardiac Involvement. Am. Thorac. Soc. Int. Conf. Meet. Abstr. 2021, 203, A2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Li, X.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, H.; Deng, J.; Xing, S.; Zhang, J. Clinical analysis of hypereosinophilic syndrome first presenting with asthma-like symptoms. Ann. Med. 2022, 54, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teringová, E.; Penz, P.; Mištinová, J.P.; Orban, M. Hypereosinophilic syndrome presenting with progressive cardiac cachexia: A case report. Eur. Heart J. Case Rep. 2023, 7, ytad280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonakowski, M.; Kuprys-Lipinska, I.; Lacwik, P.; Stasiolek, M.; Matysiak, M. Hypereosinophilic syndrome with central nervous system involvement treated with anti-IL-5 therapy. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2021, 51, 102871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finley, A.; Wild, L. M121 HYPEREOSINOPHILIA IN A PATIENT WITH UNCONTROLLED ASTHMA. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2021, 127, S86–S87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, N.; Latha, S.; Kumar, A. Safety and efficacy of monoclonal antibodies targeting IL-5 in severe eosinophilic asthma: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Health Sci. Rev. 2023, 8, 100103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strong, A.; Lin, T.; Sverrild, A.; Mackay, A.; Lee, J.; Zubrinich, C.; Pham, J.; Bosco, J.; Denton, E.; Dols, M.; et al. Dupilumab-associated hypereosinophilia in severe asthma. ERJ Open Res. 2024, 10, 00048–02024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawlewicz-Mroczka, A.; Przybyszowski, M.; Bochenek, G.; Mroczka, M.; Sładek, K. Erythema nodosum followed by eosinophilic pneumonia as an adverse effect of dupilumab treatment in a patient with severe asthma. Respir. Med. Case Rep. 2024, 52, 102136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masumoto, N.; Oshikata, C.; Nakadegawa, R.; Motobayashi, Y.; Osada, R.; Manabe, S.; Kaneko, T.; Tsurikisawa, N. Dupilumab suppresses relapsing chronic eosinophilic pneumonia with severe asthma. Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 2023, 85, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dighriri, I.M.; Alnughaythir, A.I.; Albesisi, A.A.; Alhuwaimel, D.I.; Alotaibi, A.S.; Alghowaidi, L.A.; Almalki, F.H.; Al-Bukhari, J.N.; Alshammari, T.R.; Alwathnani, F.H.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Mepolizumab in the Management of Severe Eosinophilic Asthma: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2023, 15, e49781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, B.A. Center for Drug Evaluation and Research Application Number: 125526Orig1s000 Summary Review Summary Review of Regulatory Action. 2015. Available online: https://www.ginasthma.org/ (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- Roufosse, F.; Kahn, J.E.; Rothenberg, M.E.; Wardlaw, A.J.; Klion, A.D.; Kirby, S.Y.; Gilson, M.J.; Bentley, J.H.; Bradford, E.S.; Yancey, S.W.; et al. Efficacy and safety of mepolizumab in hypereosinophilic syndrome: A phase III, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 146, 1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Lehebi, R.O.; Al Ahmad, M.; Maturu, V.N.; Mesa, A.G.; Mahboub, B.; Garcia, E.; Fernandez, P.; Soares, C.; Abreu, G.; dos Santos, D.; et al. Real-World Effectiveness of Mepolizumab in Severe Asthma: Results from the Multi-country, Self-controlled Nucala Effectiveness Study (NEST). Adv. Ther. 2024, 41, 4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munari, S.; Ciotti, G.; Cestaro, W.; Corsi, L.; Tonin, S.; Ballarin, A.; Floriani, A.; Dartora, C.; Bosi, A.; Tacconi, M.; et al. Severe hypereosinophilia in a patient treated with dupilumab and shift to mepolizumab: The importance of multidisciplinary management. A case report and literature review. Drugs Context 2024, 13, 2024–3-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashiro, H.; Nanri, M.; Kuwahara, Y.; Kurihara, Y.; Kimura, S.; Takahashi, K. Possible Biological Heterogeneity of Airway Mucus Plugs in a Patient with Asthma. J. Asthma Allergy 2024, 17, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Yang, J.; Chen, Y. Efficacy and safety of treatment with benralizumab for eosinophilic asthma. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 111, 109131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, K.; Sun, D.; Dai, R.; Samoro, R.; Park, H.S.; Åstrand, A.; Cohen, D.; Jison, M.; Shih, V.H.; Werkström, V.; et al. Benralizumab efficacy and safety in severe asthma: A randomized trial in Asia. Respir. Med. 2024, 229, 107611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pini, L.; Bagnasco, D.; Beghè, B.; Braido, F.; Cameli, P.; Caminati, M.; Caruso, C.; Crimi, C.; Guarnieri, G.; Latorre, M.; et al. Unlocking the Long-Term Effectiveness of Benralizumab in Severe Eosinophilic Asthma: A Three-Year Real-Life Study. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuno, O.; Minamoto, S. Rapid effect of benralizumab for severe asthma with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 64, 101965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Just, J.; Bourgoin, M.; Amat, F.; Cottel, N.; Lambert, N.; Wanin, S. Childhood-onset severe hypereosinophilic asthma: Efficacy of benralizumab. ERJ Open Res. 2020, 6, 00339–02020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Llano, L.A.P.; Cosío, B.G.; Astiárraga, I.L.; Campos, G.S.; Alonso, M.Á.T.; Malanda, N.M.; Galo, A.P.; Landa, I.U.; de la Rosa, F.J.M.; García-Moguel, I. Asthma Control in Patients with Severe Eosinophilic Asthma Treated with Reslizumab: Spanish Real-Life Data. J. Asthma Allergy 2022, 15, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, S.; Kroes, J.A.; Eger, K.A.; Mau Asam, P.F.; Hofstee, H.B.; Bendien, S.A.; Braunstahl, G.J.; Broeders, M.E.A.C.; Imming, L.M.; Langeveld, B.; et al. Real-World Effectiveness of Reslizumab in Patients With Severe Eosinophilic Asthma—First Initiators and Switchers. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2022, 10, 2099–2108.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Choi, G.S.; Lee, E.M. Successful Treatment of Imatinib-Induced DRESS Syndrome Using Reslizumab without Cessation of Imatinib: A Case Report. Case Rep. Oncol. 2022, 14, 1548–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.; Youn, D.Y.; Park, H.S.; Ye, Y.M.; Park, Y.B.; Ban, G.Y. Non-episodic Angioedema With Eosinophilia Successfully Treated With Reslizumab. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2020, 12, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, J.D.; Solary, E.; Abla, O.; Akkari, Y.; Alaggio, R.; Apperley, J.F.; Bejar, R.; Berti, E.; Busque, L.; Chan, J.K.C.; et al. The 5th edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours: Myeloid and Histiocytic/Dendritic Neoplasms. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, P.; Akuthota, P.; Kwon, N.; Steinfeld, J.; Roufosse, F. HES and EGPA: Two Sides of the Same Coin. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2023, 98, 1054–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabe, A.P.J.; Loke, W.J.; Gurjar, K.; Brackley, A.; Lucero-Prisno, D.E. Global Burden of Asthma, and Its Impact on Specific Subgroups: Nasal Polyps, Allergic Rhinitis, Severe Asthma, Eosinophilic Asthma. J. Asthma Allergy 2023, 16, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.E.; Sim, D.W.; Koh, Y.-I. Etiologies and differential markers of eosinophilia-associated diseases in the Allergy Department of a single university hospital. Allergy Asthma Respir. Dis. 2019, 7, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Tuyub, Y.H.; González-Iñiguez, K.D.; Lizarazo-Guiza, P.C.; García-García, S.R. Benralizumab: Effectiveness in Patients with Uncontrolled Severe Eosinophilic Asthma at 6 and 12 Months at a Third-Level Care Hospital. Capacity for ICS-LABA Therapy Reduction. J. Asthma Allergy 2024, 17, 1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jue, J.H.; Shim, Y.J.; Park, S.; Kim, D.H.; Jung, H.R. Korean Adolescent Patient with Manifestations of Lymphocyte Variant Hypereosinophilic Syndrome and Episodic Angioedema with Eosinophilia, Treated with Reslizumab. Iran. J. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2022, 21, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Chen, S.N. Case Report: Off-label treatment of idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome with Omalizumab. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1095737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihssane, M.; Asmae, M.; Nisrine, A.; Habiba, B.A.; Elouafi, N.; Ismaili, N. Myocarditis with neurological and dermatological involvement in idiopathic Hypereosinophilic syndrome: Case report. Radiol. Case Rep. 2025, 20, 1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panek, M.; Majos, A.; Kupczyk, M. Rekwalifikacja pacjenta w trakcie terapii biologicznej astmy ciężkiej [Conference presentation]. In Proceedings of the 17. Konferencja Szkoleniowa Polskiego Towarzystwa Alergologicznego (PTA), Toruń, Poland, 9–12 April 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Criado, P.R.; Ianhez, M.; Miot, H.A.; Criado, R.F.J.; Talhari, C.; Müller Ramos, P. DRESS syndrome: An interaction between drugs, latent viruses, and the immune system. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2024, 100, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.B.; Hung, W.K.; Wang, C.W.; Lee, C.C.; Hung, S.I.; Chung, W.H. Advances in understanding of the pathogenesis and therapeutic implications of drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms: An updated review. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1187937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
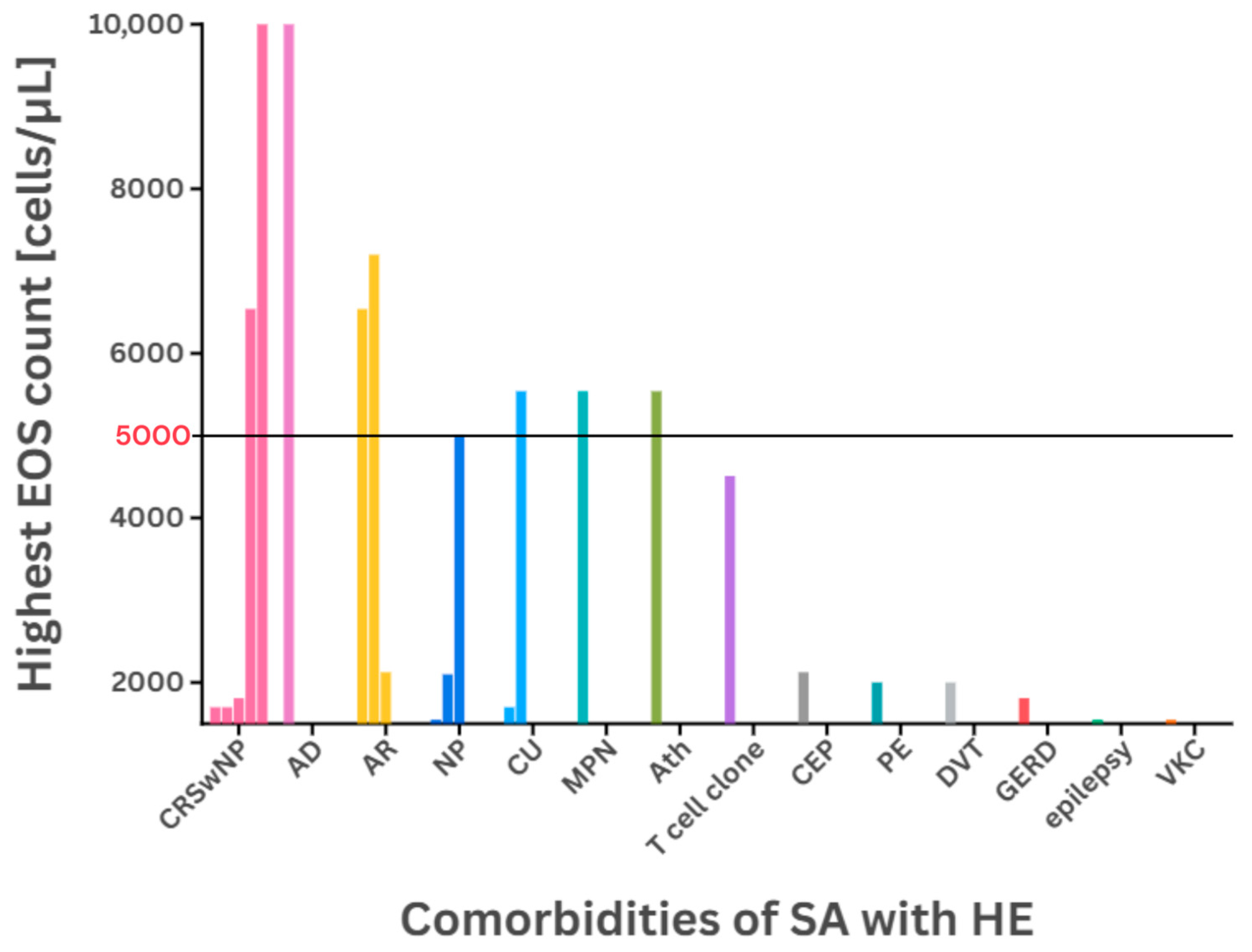

| Patient Details [(M) Male/(F) Female (Age)] | Highest EOS Count [cells/µL] | Comorbidities | Previous Treatment | Administered Medication | [Source] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M (51) | >1700 | CRSwNP | OCS, omalizumab, BTP | benralizumab | [37] |
| M (55) | 7200 | AR | SABA, OCS | ICS/LABA, LTRA, SABA | [56] |
| F (36) | 5540 | CU, MPN | HU, WARF, ICS | OCS | [7] |
| F (54) | 4510 | T cell clone | ICS | OCS | |
| M (62) | 2000 | PE, DVT | ICS, WARF | OCS | |
| 4 M 11 F (mean 43.7) | - 1,2 | EP, ES, GE, OM | - 1 | OCS | [31] |
| F (32) | 6540 | CRSwNP, AR | - 1 | polypectomy | [36] |
| F (22) | 2125 | CEP, AR | ICS/LABA, OCS | OCS, dupilumab | [60] |
| F | 1810 | CRSwNP, GERD | OCS, omalizumab, mepolizumab | OCS, omalizumab, benralizumab | [71] 3,4 |
| M | 1550 | NP, VKC, epilepsy | OCS, omalizumab, mepolizumab | OCS, omalizumab, mepolizumab, benralizumab | |
| M | 5000 | NP | OCS, omalizumab, mepolizumab | OCS, omalizumab, mepolizumab, benralizumab | |
| M | 1700 | CRSwNP, CU | OCS, omalizumab, mepolizumab | OCS, omalizumab, mepolizumab, benralizumab | |
| M | 40,400 | CRSwNP, AD | OCS, omalizumab, mepolizumab | OCS, IM, omalizumab, mepolizumab, benralizumab | |
| F | 2100 | NP | OCS, omalizumab, mepolizumab | OCS, omalizumab, mepolizumab, benralizumab |
| Condition | Mild (%) | Moderate (%) | Severe (%) | Asthma Cases with HE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Allergic diseases | 59.8 | 10.8 | - 1 | +++ |
| Parasitic infestation | 22.7 | 29.7 | 14.3 | - |
| Drug allergy | 13.4 | 37.8 | 14.3 | - |
| HES | 1.0 | 8.1 | 21.4 | - |
| EGPA | 1.0 | 2.7 | 28.6 | - |
| ABPA | 1.0 | 2.7 | 7.1 | - |
| CEP | - 1 | 8.1 | 7.1 | + |
| EGID | 1.0 | - 1 | 7.1 | + |
| Drug | Used in | Efficacy | [Source] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| medication resolving HE | mepolizumab | SA, CRSwNP, EGPA, HES | SA | 83% reduction at 12 months 1 | [63] |
| HES | 92% reduction at 32 weeks | ||||
| benralizumab | SA, HES, EoE, CRSwNP 3 | HES | down to 0 cells/μL by week 4 2 | [25] | |
| 612.78 cells reduction at 12 months | [80] | ||||
| reslizumab | HES 4 | 5438 to <500 cells/μL at 21 months | [81] | ||
| omalizumab | HESI | 4310 to 1000 cells/μL at 17 months | [82] | ||
| 7010 to 2230 cells/μL at 3 months | |||||
| OCS | HESI | 2100 to <500 cells/μL at 6 months 5 | [83] | ||
| asthma medication resulting in HE | dupilumab | SA, CSU | 280 to 310 cells/μL in 4 weeks 6 | [47] | |
| 400 to 4900 cells/μL in 4 weeks | [58] | ||||
| 500 to 2000 cells/μL in 16 weeks | |||||
| 600 to 9000 cells/μL in 16 weeks | |||||
| 800 to 2500 cells/μL in 16 weeks | |||||
| 50 to 5000 cells/μL in 16 weeks | |||||
| 300 to 2000 cells/μL in 6 months 6 | |||||
| 750 to 4880 cells/μL in >2 months 7 | [55] | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Malaya, E.; Marszałek, K.; Kuna, P.; Kupczyk, M.; Panek, M. Th2-High Severe Asthma with Hypereosinophilia in the Spectrum of Type 2 Inflammatory Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5342. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115342
Malaya E, Marszałek K, Kuna P, Kupczyk M, Panek M. Th2-High Severe Asthma with Hypereosinophilia in the Spectrum of Type 2 Inflammatory Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(11):5342. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115342
Chicago/Turabian StyleMalaya, Elizabeth, Kamil Marszałek, Piotr Kuna, Maciej Kupczyk, and Michał Panek. 2025. "Th2-High Severe Asthma with Hypereosinophilia in the Spectrum of Type 2 Inflammatory Diseases" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 11: 5342. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115342
APA StyleMalaya, E., Marszałek, K., Kuna, P., Kupczyk, M., & Panek, M. (2025). Th2-High Severe Asthma with Hypereosinophilia in the Spectrum of Type 2 Inflammatory Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(11), 5342. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115342





