Abstract
The majority of early-onset colorectal cancers (EOCRCs) are not substantiated by germline variants in the main CRC predisposition genes (the “DIGE” panel). To identify potentially novel EOCRC-specific predisposition genes, we analyzed 585 cancer pathway genes in an EOCRC patient cohort (n = 87, diagnosis ≤ 40 years, DIGE-), and compared their variant spectrum to the GnomAD cancer-free database. We identified high-impact variants (HVs) in 15 genes significantly over-represented in EOCRC. Among the 32 unrelated patients with a CRC family history (i.e., with a potentially dominant transmission pattern), 9 presented HVs in ten genes, four of which had a DNA repair function. We subsequently sequenced these 15 genes in a cohort of 82 late-onset CRCs (diagnosis ≥ 50 years, DIGE-) and found variants in 11 of these genes to be specific to EOCRC. We then screened these 11 genes in our patient database (n = 6482), which only contained 2% of EOCRCs (DIGE-), and identified two other EOCRC cases diagnosed after our cohort constitution, with HVs in RECQL4 and NUTM1. Altogether, we found that 37.5% and 18.75% of patients carrying heterozygous NUTM1 and RECQL4 HVs, respectively, in our database were diagnosed with EOCRC. Our work has identified a pattern of germline variants not previously associated with EOCRC.
1. Introduction
Early-onset colorectal cancer (EOCRC) is a rare disease, characterized by late diagnosis/late-stage disease and left-sided primary tumors [,,,]. EOCRC is more prevalent in men and associated with a family history of colorectal cancer (CRC), inflammatory bowel disease, alcohol and tobacco use, a sedentary lifestyle, and obesity (body mass index ≥ 30) [,]. It is generally accepted that 5–10% of familial CRCs are caused by a genetic predisposition transmitted by a Mendelian pattern of inheritance, as Lynch syndrome and familial polyposis syndromes []. A French consensus colorectal gene panel (DIGE panel) [] is therefore routinely used identifying germline pathogenic (PV) or likely pathogenic (LPV) variants or copy number variants (CNV, deletions or duplications) in 20% of EOCRC cases. Multi-gene testing [,,,], or whole exome sequencing (WES) [,,,,,,], have been used to identify candidate genes for EOCRC risk. However, these studies have either tested small gene panels in large patient cohorts based on relatively non-selective inclusion criteria [,,] or performed large molecular analyses (WES) on smaller cohorts (between 16 and 51 patients) [,,,].
The aim of the current study was therefore to identify additional EOCRC predisposition genes by sequencing 585 genes in a highly selective EOCRC cohort (age of diagnosis ≤ 40 years age) DIGE- (n = 87), with and without a CRC family history. We then compared this EOCRC gene variant’s profile to a late-onset CRC patient cohort DIGE- (LOCRC, diagnosed after 50 years of age, n = 82), and we screened the candidate genes in our local NGS patient database to search for variants in these new genes in additional EOCRC cases.
2. Results
2.1. EOCRC Cohort Characteristics
The DIGE-, EOCRC (n = 87) and LOCRC (n = 82) cohorts had a median age at diagnosis of 34 and 62.5 years, respectively (Table 1), a sex ratio (F/M) of 1.35 (p = 0.197 compared to LOCRC cohort, see Table 1). The EOCRC cohort characteristics were consistent with the literature in terms of distal disease (43.5% sigmoid or rectum involvement) or metastasis (23.5% metastatic disease) [,,,,,,], and differed significantly from the LOCRC cohort (p < 0.002). As described in the literature in other EOCRC cohorts, our EOCRC cases were mainly microsatellite stable (MSS) or had low microsatellite instability (MSI-L) (76.2%) and were therefore mismatch repair proficient (pMMR), whereas LOCRCs had high microsatellite instability (MSI-H) and were mismatch repair deficient (dMMR).

Table 1.
EOCRC (n = 87) and LOCRC (n = 82) patient characteristics.
Most patients had no additional medical history of cancer excluding EOCRC (87.4%) (Table 1).
Only 38.1% of all EOCRCs had a CRC family history, 34.4% of these with an affected first-degree and 75.0% a second-degree relative. This distribution differed significantly in the LOCRC cohort, with 75.8% (p < 0.001) and 39.4% (p = 0.004) having an affected first- and second-degree relative, respectively. This was consistent with previous studies reporting a first-degree family history in 15.0% (3/20) and 13.6% (3/22) of EOCRC cases [,].
2.2. Shortlisting of Germline High-Impact Variants in EOCRC Patients
By sequencing germline DNA for 87 EOCRC patients and filtering variants on a 585-gene panel (Figure 1 and Supporting Information Table S1), we identified 10 truncating variants (TVs i.e., frameshift and non-sense variant), 4 missense variants identified as LPVs or PVs in the ClinVar database, and 3 splice variants (SVs) in 15 different genes over-represented in our EOCRC population (adjusted p-value < 0.05) (Figure 2 and Table 2), while 329 variants were classified as of unknown significance (VUS). Among the 15 EOCRC patients with high-impact variants (HVs: TVs, SVs, and variants known to be PVs/LPVs), none carried VUS in DIGE panel genes, with the exception of EOCRC#16 with a VUS in the exonuclease domain of POLD1 (Supporting Information Table S2).
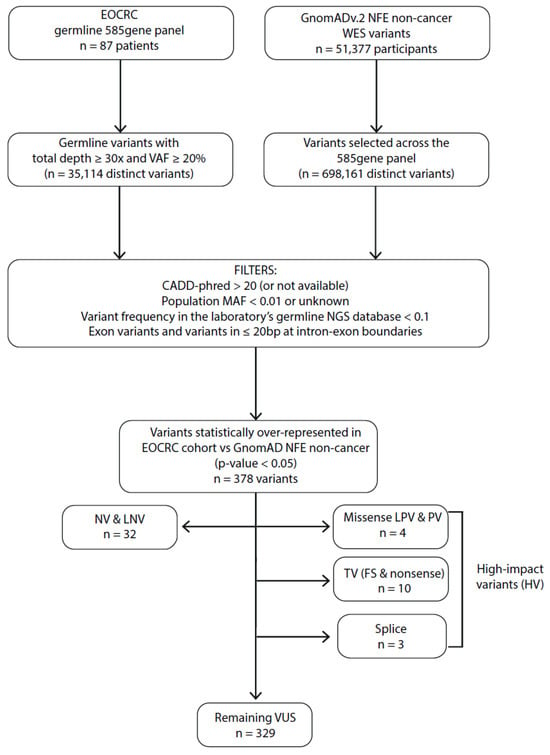
Figure 1.
Filtering process to identify EOCRC susceptibility variants for the monogenic dominant hypothesis. MAF: minor allele frequency; VAF: variant allele frequency; bp: base pair; NFE: Non-Finnish European; WES: whole exome sequencing; EOCRC: early-onset colorectal cancer; PV: pathogenic variant; LPV: likely pathogenic variant; VUS: variant of unknown significance; LNV: likely neutral variant; NV: neutral variant; TV: truncating variants (frameshift (FS) and non-sense variants); CADD-phred: Combined Annotation Dependent Depletion score.
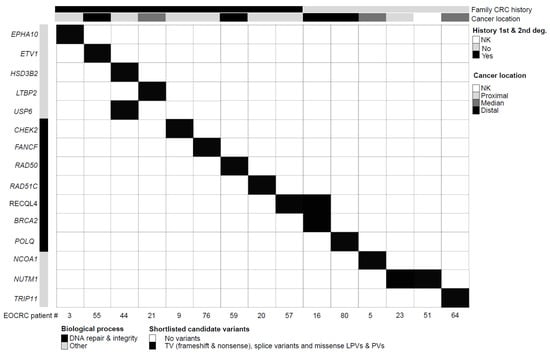
Figure 2.
Clinical and molecular features of EOCRC patients with germline HVs. Each column corresponds to a patient (patient number specified). The upper section provides patient clinical features. Genes are grouped by biological processes (gene ontology). The upper section details patient clinical characteristics (1st- or 2nd-degree family history of colorectal cancer, anatomical digestive tract location of the disease). EOCRC: early-onset colorectal cancer; deg.: degree of kinship; NK: not known/not available; TV: truncating variants; PV: pathogenic variant; LPV: likely pathogenic variant.

Table 2.
Molecular characteristics of germline HVs in EOCRC patients. p-values are specified for each variant.
Even though the relatively young age of the EOCRC cohort makes clonal hematopoiesis (CH) an unlikely rationale, we checked that the 15 EOCRC HVs were not included in the list of frequently mutated genes in CH [], and that the variant allele frequencies (VAFs) were >35% (Figure 2 and Table 2). Patient EOCRC#09 carried a CHEK2 gene variant included in the CH list, with a VAF of 47%, which seemed too high to be consistent with CH.
We pursued our analysis by successively investigating a dominant hypothesis for EOCRC, as well as recessive and oligogenic hypotheses.
2.3. Investigating a Dominant Transmission Pattern of EOCRC Predisposition
In the EOCRC cohort (n = 87), we identified 15 EOCRC patients carrying statistically over-represented HVs (p < 0.05). Nine of them, presenting a family history of CRC, carried HVs in 10 distinct genes (Figure 2 and Table 2), including genes involved in DNA repair pathways (CHEK2, FANCF, RAD50, and RAD51C) and DNA integrity (RECQL4). Among these patients, EOCRC#09 (CHEK2 variant) had a maternal family history of breast and pancreatic cancer (2nd- and 3rd-degree relatives). His maternal grandmother was diagnosed with both CRC and breast cancer at 65 years of age. CHEK2 germline PVs/LPVs are considered as moderate-risk factors for breast cancer. Patient EOCRC#57 (RECQL4 variant) presented with a mucinous adenocarcinoma of the ascending colon at the age of 32 and her father was diagnosed with CRC at the age of 64. EOCRC#57 was heterozygous for the RECQL4 PV (no evidence of compound heterozygosity) and did not exhibit any syndrome features of RECQL4-associated recessive syndromes as Rothmund–Thomson (RTS, MIM #268400), RAPADILINO (MIM #266280) and Baller–Gerold (BGS, MIM #218600)) []. The remaining HVs in the EOCRCs with a family CRC history mapped to genes involved in steroid biosynthesis (HSD3B2), transcription regulation (ETV1), and other cellular pathways (EPHA10, LTBP2, and USP6). Patient EOCRC#44 who carries HVs in both HSB3B2 and USP6 genes presented with adenocarcinoma of the ascending colon at the age of 36 and his father was reported with CRC (unknown age at diagnosis).
The remaining six EOCRC patients with HVs had no family history of CRC. They carried seven variants in six distinct genes (Figure 2 and Table 2), including DNA repair (BRCA2 and POLQ) and DNA integrity genes (RECLQL4). Patient EOCRC#16 with both BRCA2 (a PV inherited from her father) and RECQL4 variants presented with a rectal adenocarcinoma at 39 years of age. The remaining variants mapped to genes involved in transcription regulation (NCOA1), Golgi apparatus trafficking (TRIP11), and possibly cell proliferation by modulation of TERT expression (NUTM1). In addition to the EOCRC initially reported at the age of 37, patient EOCRC#64 (TRIP11 variant) was diagnosed with pineal dysgerminoma at the age of 21 and relapsed with a malignant germinoma. Patients EOCRC#23 (adenocarcinoma of the appendix at 36 years of age) and EOCRC#51 (colon cancer diagnosed at 38), from unrelated families, carried the same TV in NUTM1.
To investigate whether variants in these genes are associated with early onset, we screened these 15 genes in the LOCRC cohort (Table 3 and Supporting Information Table S3). Four HVs (in the CHEK2, FANCF, POLQ, and TRIP11 genes), and 28 VUSs were identified in these 15 genes in LOCRC. Eleven genes were completely devoid of HVs in the LOCRC cohort. Six LOCRC patients (7.3%) carried HVs in these genes, compared to 15 EOCRC patients (17.2%). Patients LOCRC#69 and LOCRC#74 carried the same TV in CHEK2, but only LOCRC#69 had a CRC family history. Whilst two EOCRC patients carried the same HV in the RECQL4 gene (one with and the other without a CRC family history) and two other EOCRC patients (both with a CRC family history) presented with the same HV in the NUTM1 genes, none of the LOCRC patients had HVs in either of these genes. These analyses highlight HV profile differences between EOCRC and LOCRC patients.

Table 3.
Screening for HVs in 15 genes of interest in the LOCRC cohort revealed HVs in CHEK2, FANCF, POLQ, and TRIP11 genes (no HV in BRCA2, EPHA10, ETV1, HSD3B2, LTBP2, NCOA1, NUTM1, RAD50, RAD51C, RECQL4, and USP6). p-values are specified for each variant.
To further explore whether variants of these 11 genes might be associated with EOCRC, we screened our germline NGS database for HVs in 10 of these genes (BRCA2 was excluded) (Table 4). Approximately 80% of the patients included in our local NGS database (n = 6482) were tested for breast/ovarian cancer, 10–15% for polyposis or CRC (of which 2% are DIGE- EOCRC patients (n = 130)), and 5–10% for other cancers or rare cancer-free members of high-risk families. Of the 130 EOCRC DIGE- patients in this database, 87 were included in our current EOCRC cohort and 43 had been integrated in this database between the interval between the end of cohort inclusion and the screening of the NGS database. Indeed, BRCA2 PVs are not associated with CRC [], and the frequency of BRCA2 HVs in the EOCRC cohort does not appear to be higher than in the general population. HVs in NUTM1, RECQL4, RAD50, RAD51C, EPHA10, ETV1, LTBP2, NCOA1, and USP6 genes were identified in 103 “new” database patients (Table 4) but not to HSD3B2. No additional EOCRC case was identified among the screened database individuals with HVs in RAD50, RAD51C, EPHA10, ETV1, LTBP2, NCOA1, and USP6). In contrast, additional EOCRC cases were identified by screening the NUTM1 and RECQL4 genes. A more recent EOCRC patient (DIGE-) was identified with RECQL4 c.2547_2548del, p.(Phe850Profs*33) TV, and is subsequently referred to as “EOCRC#88new”. She had a rectal cancer at the age of 39 but had no family history of CRC. The NUTM1 TV c.3406C>T, p.(Arg1136*) was also identified in an additional EOCRC (DIGE-) patient (“EOCRC#89new”). This patient presented with adenocarcinoma of the descending colon at the age of 31. Her mother and her only maternal aunt, respectively, developed CRC at 51 and 52 years of age. Finally, 37.5% (3/8) of heterozygous NUTM1 TV carriers and 18.75% (3/16) of heterozygous RECQL4 TV or SV carriers in our database have been diagnosed with EOCRC, suggesting the involvement of these genes in EOCRC risk.

Table 4.
Screening of our local NGS database for HVs in 10 candidate genes (n = 6482 patients, of which 130 are DIGE- EOCRCs patients).
2.4. Investigating a Monogenic Recessive Transmission and an Oligogenic Pattern of EOCRC Predisposition
In the subgroup of EOCRC patients without a CRC family history (n = 52) (Figure 3), no significant homozygous variants (VAF ≥ 80%) were identified compared to the GnomAD of the subgroup non-cancer of non-Finnish European origin (NFE). To investigate the recessive compound heterozygous hypothesis, we reported five EOCRC patients carrying at least two variants of the same gene (CNTRL (patient EOCRC#5 and EOCRC#72), POLD1 (patient EOCRC#18), RECQL4 (patient EOCRC#16), and TCF12 (patient EOCRC#12) (Figure 3, Supporting Information Table S2). These four genes were then screened in the LOCRC cohort and the whole NGS database without identified patients carrying a recurrent pattern of multiple or homozygous variants in these genes (Supporting Information Table S4). Finally, we wanted to investigate a possible recurrent pattern of gene association among sporadic patients (oligogenic hypothesis). However, the limited size of our population and the major limitations of large but targeted sequencing did not allow us to conclude for an oligogenic transmission pattern of EOCRC predisposition (Supporting Information Table S5).
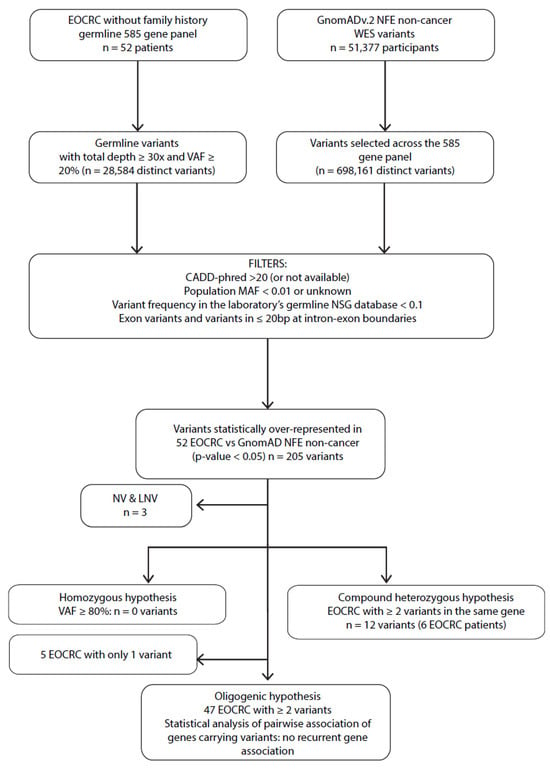
Figure 3.
Filtering process to identify EOCRC susceptibility variants for monogenic recessives (homozygous and compound heterozygous) and oligogenic approaches. MAF: minor allele frequency; VAF: variant allele frequency; bp: base pair; NFE: non-Finnish European; WES: whole exome sequencing; EOCRC: early-onset colorectal cancer; LNV: likely neutral variant; NV: neutral variant; CADD-phred: Combined Annotation Dependent Depletion score.
3. Discussion
To identify potentially novel gene variants that predispose to EOCRC, we successively examined dominant, recessive, and oligogenic hypotheses as appropriate in the part of our cohort with (n = 32) and without (n = 52) a family history of CRC, analyzed on a 585-gene panel.
We identified HVs that were significantly over-represented in our EOCRC cohort compared to the GnomAD non-cancer NFE population, in the following 15 genes: BRCA2, POLQ, RAD50, RAD51C, RECQL4, CHEK2, FANCF, EPHA10, ETV1, HSD3B2, LTBP2, NCOA1, NUTM1, TRIP11, and USP6. This approach of statistical comparison between our cohort germline data and that of GnomAD NFE non-cancer substantially reduces the possibility of incidental findings. Previous studies investigating EOCRC populations at age cut-offs ranging from 40 to 55 years, either with small gene panels on larger populations [,,], or by exome analysis on smaller populations [,,,,,], identified variants predominantly in DNA repair genes [,,,,] and in putative novel cancer genes such as EIF2AK4, PTPN12, and LRP6 [,]. Our findings are consistent with these studies since 50% of our candidate (HV) genes are involved in DNA repair pathways. Although BRCA1 and BRCA2 PVs/LPVs have previously been reported in 0.3 to 5% of EOCRC patients [,,,,], the frequency of BRCA variants in EOCRC cohorts may simply reflect the frequency of these PVs/LPVs in the general population. A recent meta-analysis confirmed this conclusion by showing that carriers of BRCA1/2 mutations are not at increased risk of CRC [].
It is worth noting that most of the variants (five out of seven) identified in DNA repair genes occurred in EOCRC patients with a 1st- or 2nd-degree family history of CRC. DNA repair is the main pathway involved in various germline family cancer predispositions (as family breast cancer and colorectal cancer). However, among the subgroup of 32 EOCRC patients with a CRC family history, 4 additional patients carried variants in genes regulating TGF-β signaling (LTBP2), transcription (ETV1), cell–cell communication (EPHA10), steroid biosynthesis (HSD3B2), and vesicle-mediated transport (USP6), suggesting that cellular pathways other than DNA repair may also be involved in EOCRC risk.
It should be noted that no family analysis has been carried out for the HVs detected in this work, so the inherited or de novo status of these variants is unknown.
In the 52 EOCRC patients without a CRC family history, the recessive hypothesis was explored without identifying a homozygous variant of interest. Similarly, the search for compound heterozygosity was inconclusive and the oligogenic hypothesis could not be confirmed. In this EOCRC population without a family history of CRC, we also examined a dominant hypothesis by identifying six patients presented with HVs in six distinct genes, three patients with HVs in DNA repair genes (BRCA2, POLQ, and RECQL4), and four patients with variants in genes regulating other cellular functions such as transcription (NCOA1), Golgi trafficking (TRIP11), and TERT regulation (NUTM1). POLQ variants, a DNA polymerase with helicase activity involved in DNA repair, have been reported in early-onset breast cancer women [], and seem to be associated (but not confirmed) to CRC risk []. To our knowledge, TRIP11, which maintains Golgi apparatus structure and interacts with thyroid hormone receptor beta, has not been involved in CRC oncogenesis. In contrast, NCOA1 (or SRC-1/RIP160) is one of the main transcription co-activators of nuclear receptors [] and binds to β-catenin, a major actor of the Wnt pathway, extensively described in CRC oncogenesis [].
We then attempted to determine whether this variant pattern is specific to the early onset of disease by analyzing the variant profile of these 15 genes of interest in a cohort composed of 82 LOCRC patients. Eleven out of the fifteen genes (BRCA2, RAD50, RAD51C, RECQL4, EPHA10, ETV1, HSD3B2, LTBP2, NCOA1, NUTM1, and USP6) carried HVs exclusively in the EOCRC cohort, suggesting a distinct germline background between EOCRC and LOCRC.
We next assessed whether the analysis of these 10 genes of interest (BRCA2 excluded) could lead to the identification of other EOCRC patients in our local NGS database. No other EOCRC patient was detected among individuals with HVs in RAD50, RAD51C, and USP6 genes. However, two other EOCRC cases diagnosed after the recruiting period of our cohort carried truncated variants in NUTM1 and RECQL4. Both variants (three patients) of NUTM1 identified in EOCRC patients in the current study are located in exon 8, and both variants (three patients) of RECQL4 identified are located in the sequence encoding the helicase domain of the protein (exons 9 and 15). RECQL4 (RecQ-Like Helicase 4) encodes a DNA helicase that controls recombination, replication, and DNA repair []. Bi-allelic RECQL4 defects are implicated in autosomal recessive inheritance syndromes (RTS, RAPALIDINO, and BGS), but none of our RECQL4 TVs heterozygous carriers showed clinical features of these conditions. Both RECQL4 variants are located in the helicase domain of the protein [,,,,]. A retrospective study of heterozygous RECQL4 carriers from RTS families found no significant difference in cancer risk compared to the general population, but the locations of the RECQL4 variants were not well defined in this study []. The NUTM1 gene encodes the NUT protein (nuclear protein in testis, or C15orf55), which may up-regulate telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) expression by binding to the TERT promoter SP1 binding site []. Patients EOCRC#51 and EOCRC#23 carry the same heterozygous NUTM1 variant predicted to truncating the NUT protein C-terminus involving the nuclear localization sequence []. An additional EOCRC#89 new patient carried a heterozygous variant of NUTM1 also truncating the protein. Further studies are required to investigate the potential role of this C-terminal truncated NUTM1 protein in EOCRC oncogenesis. Interestingly, a previous genome-wide association study in a Korean population identified three loci associated with CRC; one of these included NUTM1, specifically the 20 amino acids before the C-terminus of NUTM1 (rs2279685, chr5:34649631) [].
Heterozygous TVs in NUTM1 and RECQL4 appear to be significantly over-represented, in our NGS database, among individuals with a history of EOCRC, with 38.5% (3/8) of NUTM1 and 18.75% (3/16) of RECQL4 TV carriers diagnosed with EOCRC while the proportion of EOCRC patients (germline DIGE-) in our NGS database was 2% (130/6482). The EOCRC phenotype appears to be highly over-represented among the heterozygous NUTM1 and RECQL4 TV carriers.
To conclude, our study identifies distinct germline patterns of variants in 10 genes depending on the EOCRC patient family history with (RAD50, RAD51C, RECQL4, EPHA10, ETV1, LTPB2, USP6 genes) or without (NCOA1, NUTM1, TRIP11 genes) family history of CRC, absent in a population with a later CRC diagnosis (LOCRC). In addition, two genes of this pattern, NUTM1 and RECQL4, led to identify other cases of EOCRC from our whole NGS database. This work paves the way for further studies (for example, functional testing) to determine the role of at least NUTM1 and RECQL4 genes in EOCRC risk and oncogenesis. These data, once confirmed by larger studies, would have potential application for EOCRC risk assessment and follow-up and for further treatments or preventions (as the use of low dose of aspirin to reduce CRC incidence).
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cohorts
All CRC (or small bowel cancer) patients referred to our institute between 2016 and 2021, DIGE-, were included in the analysis. We identified a DIGE- EOCRC cohort consisting of unrelated, adult patients (n = 87) initially diagnosed with either early-onset colorectal or small bowel cancer (≤40 years of age at diagnosis), and a DIGE- cohort of late-onset CRC (or small bowel cancer) patients diagnosed after 50 years of age (LOCRC, n = 82). All patients gave their written informed consent for the germline genetic analysis of cancer genes for both diagnostic and research purposes.
Small bowel and appendix cancer were accounted as proximal disease location due to their histology of digestive track adenocarcinoma: we have endeavored to remain exhaustive. These cases of small bowel and appendicular adenocarcinoma represent only a limited fraction of the studied cohorts (4.7% and 3.5% in EOCRC and 2.6% and 0% in LOCRC, respectively).
Tumor MMR and microsatellite status were determined from formalin-fixed colorectal or small bowel tumor tissue as previously described [].
The clinicopathological characteristics of patients and their families were collected through the medical files from the genetic consultation.
4.2. Germline 585-Gene Panel Sequencing
Blood DNA was sequenced with the customized Comprehensive Cancer Panel (Roche, Bâle, Switzerland) of 585 cancer predisposition/cancer pathway genes (Supporting Information Table S6), and analyzed as described previously ([] and Supporting Information Table S7). Variants with a total sequencing depth of ≥30x and a variant allele frequency (VAF) ≥20% were selected for further analyses.
4.3. Variant Analysis and Classification
All coding (SNVs, small insertions and deletions) and intron variants (located in ≤20 bp intron DNA at intron/exon boundaries) were further evaluated. Rare variants were filtered by their predicted pathogenicity score (Combined Annotation Dependent Depletion—CADD-Phred score [] > 20 or not available), by their minor allele frequency (MAF) in GnomAD (whole base < 1%) and were identified in fewer than 10% of NGS database samples (Figure 1 and Figure 2). Copy number variants (CNVs), not available in GnomADv2, were not evaluated.
Variants significantly over-represented in the DIGE-EOCRC group were classified according to the ACMG (American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics) recommendations []. Neutral and likely neutral (NV/LNV) variants were excluded from the analysis. Statistically significant variants were confirmed by reviewing the BAM files with the Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV). Potential splice variants (SVs) were considered if located in the exon or in the 2 base pairs immediately adjacent to the intron/exon boundary (i.e., −2, −1 or +1, +2 relative to the splice junction) and if splice effect impact was predicted by both SpliceAI and SPIP pipelines [,].
4.4. Control Population for Statistical Analysis of NGS Data
The NGS data from the EOCRC cohort were compared to the germline data from the GnomADv2 “non-cancer” subpopulation of NFE origin (51,377 patients) [], restricted to the 585-gene target regions (F/M ratio close to 0.5; 85% of this control population being over 40 years of age).
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Categorical variables are expressed as frequencies and percentages and continuous variables as medians with ranges. Comparisons of the frequency of each variant between the DIGE- EOCRC and the GnomAD non-cancer NFE population were performed using the Fisher’s exact test with a Benjamini–Hochberg procedure for multiple testing. Comparisons between the DIGE- EOCRC and LOCRC groups were assessed using the Chi-squared or Fisher’s exact test for categorical variables and the Kruskal–Wallis test for continuous variables. All statistical tests were two-tailed and p-values < 0.05 were considered statistically significant. Statistical analyses were performed using R (v4.1.2) and the STATA software (v18) (Stata Corporation, College Station, TX, USA). Gene ontology term scoring and pathway enrichment analysis were performed with the g: Profiler [].
4.6. Screening the Local NGS Database for Candidate Gene Variants
Our NGS database (n = 6482 patients) was screened for the presence of candidate HVs identified in the EOCRC cohort.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ijms26104672/s1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.T., P.V.P., A.A.S., J.P. and J.G.; methodology, J.P., L.M., J.G., N.M., B.C. and T.F.; formal analysis, J.P., L.M., J.G., N.M., B.C. and T.F.; investigation, P.V.P., A.A.S., C.V., L.G., N.L. and C.T.; resources, P.V.P., E.C., G.C., D.B., M.M., J.S., N.L. and R.G.; data curation, P.V.P. and N.L.; writing—original draft preparation, C.T. and P.V.P.; writing—review and editing, C.T., P.V.P. and B.C.; visualization, P.V.P.; supervision, C.T. and P.V.P.; project administration, C.T.; funding acquisition, C.T. and P.V.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study has been registered on the Health Data Hub (number: F20231031170826, MR004).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in this study.
Data Availability Statement
Patient germline genetic data generated in the context of healthcare are stored in the Oncogenetics Laboratory of the IUCT-Oncopole in Toulouse, and are not openly accessible, in accordance with French law (Civil Code and Bioethics Act). However, we can provide information on reasonable request. Data relevant to the present work are presented in the main text, and additional information (in particular on VUSs in the EOCRC and LOCRC cohorts) is provided as Supporting Information.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Lydia Loncle, Pauline Dejean, Aurelia Da Cruz, Isabelle Gitlaw, Dominique Telly, and Emilie Lestrade from the Toulouse Oncogenetics Laboratory, without whom this work would not have been possible. We would also like to thank the French association Comminges Sans Frontières for funding a part of the ancillary expenses associated with this work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| ADK | Adenocarcinoma |
| ALL | Acute lymphocytic leukemia |
| BGS | Baller–Gerold syndrome |
| CADD | Combined Annotation Dependent Depletion score |
| CH | Clonal hematopoiesis |
| CLL | Chronic lymphocytic leukemia |
| CNV | Copy number variant |
| CRC | Colorectal cancer |
| dMMR | Mismatch repair deficient |
| EOCRC | Early-onset colorectal cancer |
| HVs | High-impact variants: TVs, SVs or variants known to be PVs/LPVs |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| LPV | Likely pathogenic variant |
| LOCRC | Late-onset colorectal cancer |
| LNV | Likely neutral variant |
| MAF | Minor allele frequency |
| MSI-H | High microsatellite instability |
| MSI-L | Low microsatellite instability |
| MSS | Microsatellite stable |
| NET | Neuroendocrine tumor |
| NFE | Non-Finnish European |
| NGS | Next Generation Sequencing |
| NV | Neutral variant |
| pMMR | Mismatch repair proficient |
| PV | Pathogenic variant |
| RTS | Rothmund–Thomson syndrome |
| SV | Splice variant |
| TVs | Truncating variants, i.e., frameshift and non-sense variant |
| VAF | Variant allele frequency |
| VUS | Variant of unknown significance |
| WES | Whole exome sequencing |
References
- Mauri, G.; Sartore-Bianchi, A.; Russo, A.G.; Marsoni, S.; Bardelli, A.; Siena, S. Early-onset colorectal cancer in young individuals. Mol. Oncol. 2019, 13, 109–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coccia, P.F.; Pappo, A.S.; Beaupin, L.; Borges, V.F.; Borinstein, S.C.; Chugh, R.; Dinner, S.; Folbrecht, J.; Frazier, A.L.; Goldsby, R.; et al. Adolescent and Young Adult Oncology, Version 2.2018, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Canc Netw. 2018, 16, 66–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willauer, A.N.; Liu, Y.; Pereira, A.A.L.; Lam, M.; Morris, J.S.; Raghav, K.P.S.; Morris, V.K.; Menter, D.; Broaddus, R.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; et al. Clinical and molecular characterization of early-onset colorectal cancer. Cancer 2019, 125, 2002–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daca Alvarez, M.; Quintana, I.; Terradas, M.; Mur, P.; Balaguer, F.; Valle, L. The Inherited and Familial Component of Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer. Cells 2021, 10, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.H.; Liu, P.H.; Zheng, X.; Keum, N.; Zong, X.; Li, X.; Wu, K.; Fuchs, C.S.; Ogino, S.; Ng, K.; et al. Sedentary Behaviors, TV Viewing Time, and Risk of Young-Onset Colorectal Cancer. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2018, 2, pky073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.H.; Wu, K.; Ng, K.; Zauber, A.G.; Nguyen, L.H.; Song, M.; He, X.; Fuchs, C.S.; Ogino, S.; Willett, W.C.; et al. Association of Obesity With Risk of Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer Among Women. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoffel, E.M.; Murphy, C.C. Epidemiology and Mechanisms of the Increasing Incidence of Colon and Rectal Cancers in Young Adults. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhooge, M.; Baert-Desurmont, S.; Corsini, C.; Caron, O.; Andrieu, N.; Berthet, P.; Bonadona, V.; Cohen-Haguenauer, O.; De Pauw, A.; Delnatte, C.; et al. National recommendations of the French Genetics and Cancer Group—Unicancer on the modalities of multi-genes panel analyses in hereditary predispositions to tumors of the digestive tract. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2020, 63, 104080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearlman, R.; Frankel, W.L.; Swanson, B.; Zhao, W.; Yilmaz, A.; Miller, K.; Bacher, J.; Bigley, C.; Nelsen, L.; Goodfellow, P.J.; et al. Prevalence and Spectrum of Germline Cancer Susceptibility Gene Mutations Among Patients With Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoffel, E.M.; Koeppe, E.; Everett, J.; Ulintz, P.; Kiel, M.; Osborne, J.; Williams, L.; Hanson, K.; Gruber, S.B.; Rozek, L.S. Germline Genetic Features of Young Individuals With Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 897–905.E1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhunussova, G.; Afonin, G.; Abdikerim, S.; Jumanov, A.; Perfilyeva, A.; Kaidarova, D.; Djansugurova, L. Mutation Spectrum of Cancer-Associated Genes in Patients With Early Onset of Colorectal Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beltrami, C.M.; do Canto, L.M.; Villacis, R.A.R.; Petersen, A.H.; Aagaard, M.M.; Cury, S.S.; Formiga, M.; Junior, S.A.; Rogatto, S.R. The repertoire of germline variants in patients with early-onset rectal cancer. Cancer Commun. 2022, 42, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanskanen, T.; Gylfe, A.E.; Katainen, R.; Taipale, M.; Renkonen-Sinisalo, L.; Jarvinen, H.; Mecklin, J.P.; Bohm, J.; Kilpivaara, O.; Pitkanen, E.; et al. Systematic search for rare variants in Finnish early-onset colorectal cancer patients. Cancer Genet. 2015, 208, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.X.; Fu, L.; de Voer, R.M.; Hahn, M.M.; Jin, P.; Lv, C.X.; Verwiel, E.T.; Ligtenberg, M.J.; Hoogerbrugge, N.; Kuiper, R.P.; et al. Candidate colorectal cancer predisposing gene variants in Chinese early-onset and familial cases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 4136–4149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Voer, R.M.; Hahn, M.M.; Weren, R.D.; Mensenkamp, A.R.; Gilissen, C.; van Zelst-Stams, W.A.; Spruijt, L.; Kets, C.M.; Zhang, J.; Venselaar, H.; et al. Identification of Novel Candidate Genes for Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer Susceptibility. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1005880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toh, M.R.; Chiang, J.B.; Chong, S.T.; Chan, S.H.; Ishak, N.D.B.; Courtney, E.; Lee, W.H.; Syed Abdillah Al, S.; Carson Allen, J., Jr.; Lim, K.H.; et al. Germline Pathogenic Variants in Homologous Recombination and DNA Repair Genes in an Asian Cohort of Young-Onset Colorectal Cancer. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2018, 2, pky054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thutkawkorapin, J.; Lindblom, A.; Tham, E. Exome sequencing in 51 early onset non-familial CRC cases. Mol. Genet. Genomic Med. 2019, 7, e605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikaeel, R.R.; Symonds, E.L.; Kimber, J.; Smith, E.; Horsnell, M.; Uylaki, W.; Tapia Rico, G.; Hewett, P.J.; Yong, J.; Tonkin, D.; et al. Young-onset colorectal cancer is associated with a personal history of type 2 diabetes. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 17, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Rozadilla, C.; Alvarez-Barona, M.; Quintana, I.; Lopez-Novo, A.; Amigo, J.; Cameselle-Teijeiro, J.M.; Roman, E.; Gonzalez, D.; Llor, X.; Bujanda, L.; et al. Exome sequencing of early-onset patients supports genetic heterogeneity in colorectal cancer. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunet, T.; Berutti, R.; Dill, V.; Hecker, J.S.; Choukair, D.; Andres, S.; Deschauer, M.; Diehl-Schmid, J.; Krenn, M.; Eckstein, G.; et al. Clonal hematopoiesis as a pitfall in germline variant interpretation in the context of Mendelian disorders. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2022, 31, 2386–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siitonen, H.A.; Sotkasiira, J.; Biervliet, M.; Benmansour, A.; Capri, Y.; Cormier-Daire, V.; Crandall, B.; Hannula-Jouppi, K.; Hennekam, R.; Herzog, D.; et al. The mutation spectrum in RECQL4 diseases. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 17, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullinane, C.M.; Creavin, B.; O’Connell, E.P.; Kelly, L.; O’Sullivan, M.J.; Corrigan, M.A.; Redmond, H.P. Risk of colorectal cancer associated with BRCA1 and/or BRCA2 mutation carriers: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Surg. 2020, 107, 951–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felicio, P.S.; Grasel, R.S.; Campacci, N.; de Paula, A.E.; Galvao, H.C.R.; Torrezan, G.T.; Sabato, C.S.; Fernandes, G.C.; Souza, C.P.; Michelli, R.D.; et al. Whole-exome sequencing of non-BRCA1/BRCA2 mutation carrier cases at high-risk for hereditary breast/ovarian cancer. Hum. Mutat. 2021, 42, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raskin, L.; Guo, Y.; Du, L.; Clendenning, M.; Rosty, C.; Colon Cancer Family, R.; Lindor, N.M.; Gruber, S.B.; Buchanan, D.D. Targeted sequencing of established and candidate colorectal cancer genes in the Colon Cancer Family Registry Cohort. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 93450–93463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, C.A.; Qin, L.; Tien, J.C.; Young, L.S.; Xu, J. The function of steroid receptor coactivator-1 in normal tissues and cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 8, 470–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triki, M.; Lapierre, M.; Cavailles, V.; Mokdad-Gargouri, R. Expression and role of nuclear receptor coregulators in colorectal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 4480–4490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luong, T.T.; Bernstein, K.A. Role and Regulation of the RECQL4 Family during Genomic Integrity Maintenance. Genes 2021, 12, 1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grelet, M.; Blanck, V.; Sigaudy, S.; Philip, N.; Giuliano, F.; Khachnaoui, K.; Morel, G.; Grotto, S.; Sophie, J.; Poirsier, C.; et al. Outcomes of 4 years of molecular genetic diagnosis on a panel of genes involved in premature aging syndromes, including laminopathies and related disorders. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2019, 14, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, A.; Inoue, S.; Onwuzurike, N. Rothmund-Thomson syndrome (RTS) with osteosarcoma due to RECQL4 mutation. BMJ Case Rep. 2018, 2018, bcr-2017-222384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindor, N.M.; Furuichi, Y.; Kitao, S.; Shimamoto, A.; Arndt, C.; Jalal, S. Rothmund-Thomson syndrome due to RECQ4 helicase mutations: Report and clinical and molecular comparisons with Bloom syndrome and Werner syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2000, 90, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Maldergem, L.; Siitonen, H.A.; Jalkh, N.; Chouery, E.; De Roy, M.; Delague, V.; Muenke, M.; Jabs, E.W.; Cai, J.; Wang, L.L.; et al. Revisiting the craniosynostosis-radial ray hypoplasia association: Baller-Gerold syndrome caused by mutations in the RECQL4 gene. J. Med. Genet. 2006, 43, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Giacalone, B.A.; Rideau, T.T.; Scheurer, M.E.; Lupo, P.J.; Wang, L.L. Cancer risk among RECQL4 heterozygotes. Cancer Genet. 2022, 262–263, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amisaki, M.; Tsuchiya, H.; Sakabe, T.; Fujiwara, Y.; Shiota, G. Identification of genes involved in the regulation of TERT in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, C.A.; Miyoshi, I.; Kubonishi, I.; Grier, H.E.; Perez-Atayde, A.R.; Fletcher, J.A. BRD4-NUT fusion oncogene: A novel mechanism in aggressive carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 304–307. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lim, E.B.; Oh, H.S.; Kim, K.C.; Kim, M.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, B.J.; Nho, C.W.; Cho, Y.S. Identification and functional validation of HLA-C as a potential gene involved in colorectal cancer in the Korean population. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labrousse, G.; Vande Perre, P.; Parra, G.; Jaffrelot, M.; Leroy, L.; Chibon, F.; Escudie, F.; Selves, J.; Hoffmann, J.-S.; Guimbaud, R.; et al. The hereditary N363K POLE exonuclease mutant extends PPAP tumor spectrum to glioblastomas by causing DNA damage and aneuploidy in addition to increased mismatch mutagenicity. NAR Cancer 2023, 5, zcad011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Saati, A.; Vande Perre, P.; Plenecassagnes, J.; Gilhodes, J.; Monselet, N.; Cabarrou, B.; Lignon, N.; Filleron, T.; Telly, D.; Perello-Lestrade, E.; et al. Multigene Panel Sequencing Identifies a Novel Germline Mutation Profile in Male Breast Cancer Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rentzsch, P.; Witten, D.; Cooper, G.M.; Shendure, J.; Kircher, M. CADD: Predicting the deleteriousness of variants throughout the human genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D886–D894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaganathan, K.; Kyriazopoulou Panagiotopoulou, S.; McRae, J.F.; Darbandi, S.F.; Knowles, D.; Li, Y.I.; Kosmicki, J.A.; Arbelaez, J.; Cui, W.; Schwartz, G.B.; et al. Predicting Splicing from Primary Sequence with Deep Learning. Cell 2019, 176, 535–548.E24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leman, R.; Parfait, B.; Vidaud, D.; Girodon, E.; Pacot, L.; Le Gac, G.; Ka, C.; Ferec, C.; Fichou, Y.; Quesnelle, C.; et al. SPiP: Splicing Prediction Pipeline, a machine learning tool for massive detection of exonic and intronic variant effects on mRNA splicing. Hum. Mutat. 2022, 43, 2308–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karczewski, K.J.; Francioli, L.C.; Tiao, G.; Cummings, B.B.; Alfoldi, J.; Wang, Q.; Collins, R.L.; Laricchia, K.M.; Ganna, A.; Birnbaum, D.P.; et al. The mutational constraint spectrum quantified from variation in 141,456 humans. Nature 2020, 581, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raudvere, U.; Kolberg, L.; Kuzmin, I.; Arak, T.; Adler, P.; Peterson, H.; Vilo, J. g:Profiler: A web server for functional enrichment analysis and conversions of gene lists (2019 update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W191–W198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).