Abstract
Cysteine-rich angiogenic factor 61 (CCN1/Cyr61) is a matricellular protein that is induced and secreted in response to growth factors. Our previous work showed that 18:1-lysophosphatidic acid (LPA), which activates the G protein-coupled receptor LPAR1, induces CCN1 between 2–4 h in PC-3 human prostate cancer cells in a manner than enhances cell-substrate adhesion. While the time course of induction suggests that CCN1 contributes to intermediate events in LPA action, the roles of CCN1 in LPA-mediated signal transduction have not been fully elucidated. This study utilized a comprehensive global proteomics approach to identify proteins up- or down-regulated in response to treatment of PC-3 cells with LPA for three hours, during the time of peak CCN1 levels. In addition, the effects of siRNA-mediated CCN1 knockdown on LPA responses were analyzed. The results show that, in addition to CCN1, LPA increased the levels of multiple proteins. Proteins up-regulated by LPA included metastasis-associated in colon cancer protein 1 (MACC1) and thrombospondin-1 (TSP1/THBS1); both MACC1 and TSP1 regulated cancer cell adhesion and motility. LPA down-regulated thioredoxin interacting protein (TXNIP). CCN1 knockdown suppressed the LPA-induced up-regulation of 30 proteins; these included MACC1 and TSP1, as confirmed by immunoblotting. Gene ontology and STRING analyses revealed multiple pathways impacted by LPA and CCN1. These results indicate that CCN1 contributes to LPA signaling cascades that occur during the intermediate phase after the initial stimulus. The study provides a rationale for the development of interventions to disrupt the LPA-CCN1 axis.
1. Introduction
Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) refers to a family of simple lipids that are derived from membrane phospholipids. LPA acts as an agonist for G protein-coupled receptors; seven LPA receptors (LPARs) have been identified, and several are expressed in human prostate cancer (CaP) cell lines []. Our previous studies have shown that LPA is produced by human prostate cancer cells, where LPA can act as an autocrine mediator []. Oleoyl (18:1)-LPA can induce cell proliferation, migration, and adhesion in CaP cells, responses that are predominantly mediated by LPAR1 [,,,,]. In terms of early events in signal transduction, LPA activates Erk MAPK, Akt, and FAK in CaP cells within a few minutes [,]. Other rapid responses characteristic of LPAR activation include increases in intracellular calcium and activation of Rho []. However, for LPA to initiate longer-term responses such as adhesion and proliferation, it is important to consider intermediate events that occur subsequent to the initial acute changes in signal transduction, linking early events in signaling to later changes in cellular function.
Among its many cellular actions, LPA has been shown to regulate proteins in extracellular matrix (ECM) [,,]. LPA has been shown to induce expression of certain ECM proteins. One of these proteins is the matricellular protein CCN1, also known as Cyr61, which is induced in a Rho-dependent manner []. CCNs are secreted proteins that possess domains that allow them to interact with other proteins on the cell membrane (e.g., integrins) as well as with proteins in the ECM (e.g., fibronectin). In this way, CCNs can exert agonist-like activity and facilitate interactions between integrins and ECM proteins. The CCN family consists of six members; CCN1 and CCN2 are unique in that they are inducible. CCN1 can be rapidly induced, at the transcriptional level, by growth factors and by the phospholipid mediators LPA and sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) []. The induced protein is detected within a few hours after the stimulus, making CCN1 a potential mediator of subsequent signaling events. For example, Lau and colleagues demonstrated roles for CCN1 role in cell attachment, spreading, and chemotaxis in fibroblasts [,].
Not surprisingly, CCN1 is involved in cancer progression. Previous studies showed that LPA induces CCN1 in stromal and epithelial prostatic cells and that CCN1 is a viable marker for benign prostatic hyperplasia []. It has also been shown that LPA can activate Rho and induce CCN1 in astrocytoma cell lines []. CCN1 is induced through the activation of the transcriptional co-activator YAP in cancer cells []. Induced CCN1 is rapidly secreted from cells, appearing in the extracellular matrix []. Since CCN1 is a ligand for integrins, it is likely that further downstream signaling is mediated, at least in part, through integrins [,].
Our studies have shown that CCN1 is detected in human prostate cancer cells 2–6 h after the addition of LPA [,]. This led us to hypothesize that CCN1 plays a role in the intermediate phase of LPA response in these cells. Our previous results show that, in PC-3 cells, CCN1 plays an important role in LPA-induced cell adhesion that is observed after two hours []. Others have shown that CCN1 is required for PC-3 cell proliferation []. However, the full spectrum of LPA responses during an “intermediate” phase after LPAR1 activation has not been previously characterized. Also, a comprehensive analysis of the effects of CCN1 knockdown has not previously been reported. Global proteomics is an unbiased approach that can be used to quantify differences in protein expression between biological samples. The current study utilized global proteomics to address two goals. The first goal was to characterize changes in protein expression occurring three hours after LPAR1 activation in PC-3 cells. The second goal was to determine whether CCN1 is involved in any of these intermediate LPA responses. To address these goals, we performed global proteomics analyses comparing cells incubated with and without LPA, in the absence and presence of CCN1 knockdown.
2. Results
2.1. Identification of Proteins Differentially Expressed after LPA Treatment
The first analysis examined differences in expression between untreated cells and LPA-treated cells. For both conditions, cells were incubated with a scrambled siRNA as a negative control for concomitant CCN1 siRNA treatments of other cell groups (see Section 2.2). Comparing cells incubated with and without LPA, untargeted global proteomics revealed 4299 proteins that were expressed in both treatment groups. There were 199 proteins uniquely expressed in LPA-treated PC-3 cells, compared to 321 proteins that were unique to the control group (Figure 1A).
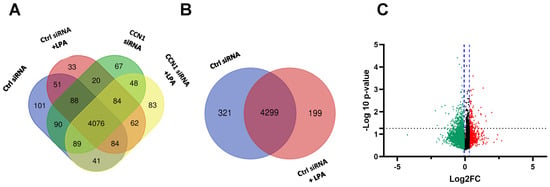
Figure 1.
Proteins differentially expressed in PC-3 cells treated with LPA. (A) Venn diagram, prepared using Draw Venn Diagram (ugent.be), showing number of proteins detected in all four treatment groups used in this study (± LPA (3 h), ± control siRNA or CCN1 siRNA). (B) Venn diagram showing number of proteins detected in the two treatment groups treated with control siRNA, with and without LPA. (C) Volcano plot showing proteins (individual dots) differentially expressed between cells treated with and without LPA. FC = fold change (treated vs. untreated). The x-axis displays the fold-change; the y-axis shows statistical significance. The black dotted line indicates the threshold for statistical significance (p < 0.05). The blue dotted lines indicate the region without statistically significant fold-change. Red and green colors indicate proteins up-regulated and down-regulated, respectively, in response to LPA.
Corroborating previous findings that LPA induces proteins that directly or indirectly modulate downstream signaling pathways, our analysis revealed that 256 proteins were up-regulated in PC-3 cells treated with LPA (Figure 1C). Notably, CCN1 was one of the most highly up-regulated proteins in the LPA treatment group. This is in agreement with our previous results demonstrating prominent induction of CCN1 by LPA in PC-3 cells []. The 3 h time point used for the LPA incubation was within the peak time of CCN1 induction and was approximately 1 h after maximal induction as previously detected by immunoblotting []. Among the top 20 proteins significantly up-regulated by LPA were metastasis associated in colon cancer protein 1 (MACC1), thrombospondin-1 (TSP1), transcription factor Jun-B, and Dickkopf-related protein 1 (DKK1). The most highly up-regulated proteins are listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Proteins significantly up-regulated in response to LPA. The top twenty proteins with respect to fold change (with LPA ÷ without LPA) are listed.
Quantified proteomic results for proteins of particular interest are shown in Figure 2. Several of the proteins that were up-regulated by LPA, including CCN1, play cellular roles that are potentially relevant to the effects of LPA on prostate cancer cell adhesion and migration. MACC1 is an oncogene product that serves as a prognostic biomarker for multiple cancers []. MACC1 prominently enhances tumor cell migration and also inhibits immune surveillance. While the precise mechanisms are still being elucidated, MACC1 exerts multiple signaling effects in tumor cells including Erk and Akt activation. MACC1 effects on cell–ECM interactions are complex and may vary between cell types. MACC1 protein levels are regulated both transcriptionally and post-transcriptionally; the latter involving epigenetic regulation as well as protein stabilization []. Thrombospondin-1 (TSP1), like CCN1, is a matricellular protein that interacts with cell surface receptors as well as extracellular matrix components []. TSP1 has many physiological roles, including in wound healing, but is not generally overexpressed in tumor cells. Nonetheless, TSP1 contributes to cell adhesion and migration, and suppresses immune responses []. JUNB is a transcription factor that is one component of AP-1 complexes []. It is up-regulated during the S-phase of the cell cycle, and is important for cell division, but also can play roles in epithelial–mesenchymal transition and tumor cell invasion. Previous work has identified a role for JUNB in CCN1-mediated responses []. DKK1 is a secreted protein that is a prognostic biomarker for multiple cancers, including prostate cancer []. DKK1 modulates immune cell function in a way that contributes to an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment and affects cell adhesion and motility to enhance metastasis. Together, the up-regulation of CCN1, MACC1, TSP1, JUNB, and DKK1 point to multiple steps by which LPA can potentially regulate cell–ECM interactions.
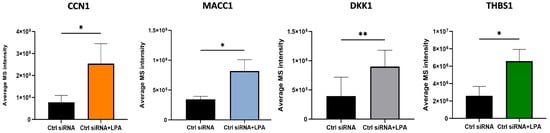
Figure 2.
Quantified changes in expression levels of selected proteins up-regulated by LPA. Cells were treated for 3 h with and without 10 µM LPA for the proteomics analysis. Each bar represents mean ± SD from triplicate cell incubations; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01.
Interestingly, our analysis of down-regulated proteins (Table 2) also showed lowered levels of the LPA receptor, LPAR1, which mediates most of the effects of LPA in PC-3 cells []. A decrease in LPAR1 could be anticipated, as GPCRs are frequently down-regulated following prolonged stimulation by agonists. Another protein down-regulated in response to LPA was thioredoxin interacting protein (TXNIP), which will be discussed in more detail below.

Table 2.
Proteins significantly down-regulated in response to LPA. The top ten proteins with respect to fold change (with LPA ÷ without LPA) are listed.
Gene enrichment analysis [] was carried out to reveal major pathways impacted by LPA after 3 h. This analysis revealed that the up-regulated pathways included integrin signaling, mitosis, and wounding response, as well as negative regulation of cell junctions (Figure 3). All these pathways are consistent with known actions of LPA [].
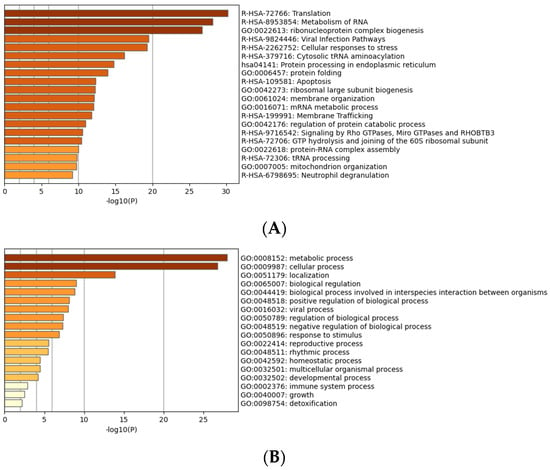
Figure 3.
Gene ontology (GO) analysis of proteins differentially expressed in response to LPA. (A) Proteins grouped by molecular functions. (B) Proteins grouped by biological processes.
A STRING analysis (known and predicted protein–protein interaction analysis) was conducted to examine the interrelationships between proteins up-regulated by LPA that are related to cell adhesion (Figure 4). In this analysis, TSP-1 was identified as essential for linking CCN1 functionally to other LPA-responsive proteins.
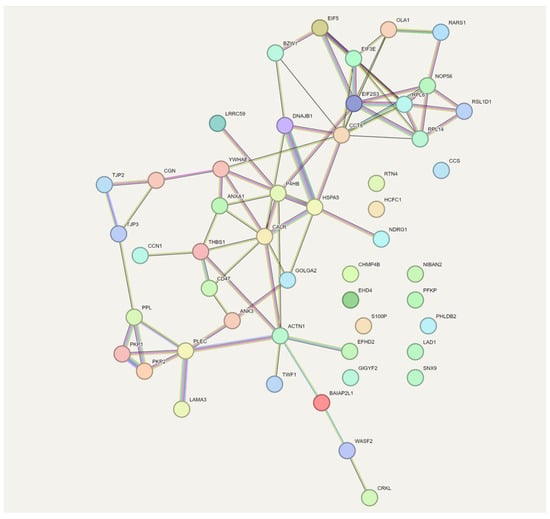
Figure 4.
STRING analysis of proteins up-regulated by LPA that are related to cell adhesion. STRING analysis depicts protein-protein interaction networks. Different colored lines between proteins indicate various types of evidence (co-expression, experimental, database, etc.). The colors for each protein reflect their assignment to various protein families.
2.2. Identification of Proteins Differentially Expressed after CCN1 Knockdown
The goal of this series of analyses was to determine whether knockdown of CCN1 would affect the proteomic responses observed in response to LPA. The cell incubations in which cells incubated with CCN1 siRNA were incubated with and without LPA were performed concomitantly with those discussed above in Section 2.1. Prior to proceeding with the proteomics analyses, successful knockdown of CCN1 was confirmed by immunoblotting of whole-cell extracts for CCN1. The conditions used for the CCN1 siRNA incubation had been optimized previously for a maximal decrease in CCN1 after LPA induction []; the extent of the knockdown was approximately 50%. Proteomics quantification and an immunoblot demonstrating the knockdown will be presented in Section 2.3. It should be noted that immunoblotting is inherently less quantitative than proteomics analysis.
As shown in Figure 5, 4297 proteins were detected in the CCN1 knockdown groups (± LPA), of which 276 proteins were uniquely expressed in cells treated with CCN1 siRNA and then incubated with LPA. From the overall analysis, many of the proteins that were most responsive to LPA before CCN1 knockdown were still up-regulated by LPA following CCN1 knockdown. However, our analysis revealed 30 LPA-responsive proteins for which the extent of the LPA induction was decreased after CCN1 expression was suppressed (Figure 1A). The differences in LPA response before and after CCN1 knockdown can be seen by comparing Table 1 and Table 3. In these two tables, CCN1, MACC1, DKK1, and TBS1 were all included as LPA-responsive proteins, but for each protein the fold increase in response to LPA was lower after incubation with CCN1 siRNA.
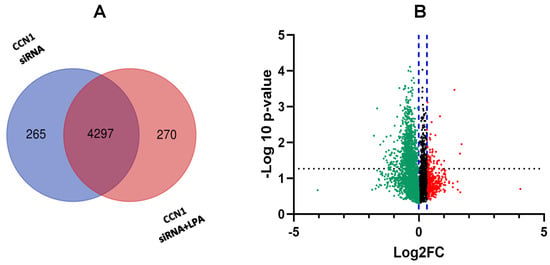
Figure 5.
Proteomic differences observed in response to LPA after CCN1 knockdown. (A) Venn diagram showing number of proteins detected in the two treatment groups (cells incubated with and without LPA for three hours, after treatment with CCN1 siRNA). (B) Volcano plot showing proteins differentially expressed proteins between cells treated with and without LPA. FC = fold change (treated vs. untreated). The x-axis displays the fold-change; the y-axis shows statistical significance. The black dotted line indicates the threshold for statistical significance. The blue dotted lines indicate the region without statistically significant fold-change. Red and green colors indicate proteins up-regulated and down-regulated, respectively, in response to LPA.

Table 3.
Proteins significantly up-regulated by LPA in cells incubated with CCN1 siRNA. The top twenty proteins with respect to fold change (with LPA ÷ without LPA) are listed.
The proteins down-regulated by LPA (Table 4) were, in some respects, similar before and after CCN1 knockdown (compare Table 2 and Table 4). For example, LPAR1 was down-regulated before and after CCN1 expression was suppressed. Another protein that appears on both lists of down-regulated proteins (Table 2 and Table 4) is the thioredoxin interacting protein (TXNIP). TXNIP is a member of the arrestin family that plays complex biological roles, and can be either pro- or antitumorigenic in different types of cancers []. TXNIP has been reported to be decreased in prostate cancer and to act as a tumor suppressor; in one study, overexpression of TXNIP in PC-3 cells inhibited proliferation, migration, and invasion []. The role of TXNIP in LPA response in these cells had not been previously investigated, and deserves further attention since its LPA-induced down-regulation can potentially contribute to LPA-induced proliferation. There are also proteins in Table 4 that did not appear in Table 2, indicating that CCN1 knockdown enhanced the down-regulation of these proteins in response to LPA. These include FAM92B/ciBAR1, a protein that plays essential roles in ciliogenesis [] and autophagy []. It should be noted that the serum starvation performed prior to our cell incubations, as a necessity to remove the LPA that is contained in serum, can induce a multitude of cellular responses [] that include ciliogenesis and autophagy []. Thus, some of the proteomic responses to LPA likely reflect reversal of the effects of serum starvation. Another interesting protein that appeared on the list of proteins down-regulated by LPA only after CCN1 knockdown is syndecan-1 (SDC-1). CCN1 exerts many of its effects by binding to syndecan-4 []; however, both SDC-1 and -4 are involved in cell adhesion []. SDC-1 is overexpressed in cancers and is shed into the extracellular environment []. Our proteomic analysis of cell-associated proteins does not discern whether the LPA-induced decrease in SDC-1 might be due to enhanced shedding. Up-regulation of SDC-1 is associated with more aggressive prostate tumors [].

Table 4.
Proteins significantly down-regulated by LPA in cells incubated with CCN1 siRNA. The top ten proteins with respect to fold change (with LPA ÷ without LPA) are listed.
The proteomic effects of CCN1 knockdown alone (without LPA) are also pertinent. A list of the top 20 proteins up- and down-regulated after CCN1 knockdown, without LPA treatment, is provided in the Supplementary Materials (Figures S1 and S2, Table S1). One interesting protein that is altered following CCN1 knockdown is prostate-associated microseminoprotein (MSMP/PSMP). The name “PSMP” refers to the fact that the protein was identified as being secreted by PC-3 cells []. Our results show that CCN1 knockdown increased levels of MSMP. The functions of MSMP have not been fully elucidated although it can act as a chemoattractant for macrophages []; the latter study indicated that MSMP is a chemokine ligand for the receptor CCR2. MSMP is up-regulated in prostate cancer cells in hypoxic conditions, resulting in increased drug resistance [].
Gene ontology analysis of proteins differentially expressed in response to LPA after CCN1 knockdown is shown in Figure 6. The profile of the GO results is distinct from that observed before the reduction in CCN1 levels (compare Figure 3 and Figure 6). For example, involvement of the Rho pathway was on the list before CCN1 knockdown, but not after CCN1 knockdown. Positive regulation of protein kinase activity was prominent after CCN1 knockdown, but not before.
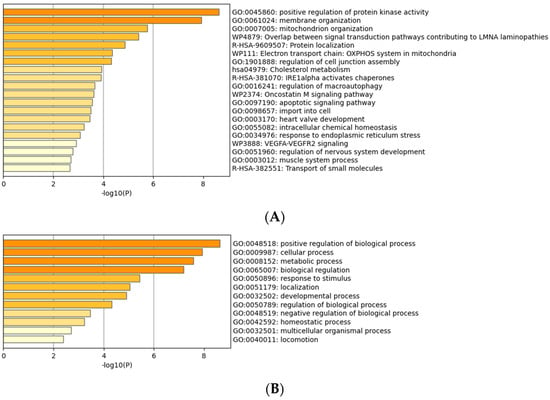
Figure 6.
Gene ontology (GO) analysis of proteins differentially expressed in response to LPA after CCN1 knockdown. (A) Proteins grouped by molecular functions. (B) Proteins grouped by biological processes.
The expression levels of LPA-responsive proteins in all four experimental conditions are presented in Figure 7. Notably, several of the proteins that were most responsive to LPA in the control situation were less responsive to LPA following CCN1 knockdown. These included proteins discussed earlier: CCN1, TSP1, MACC1, JUNB, and DKK1. Note that the net LPA response (not shown in Figure 7) is calculated by subtracting baseline expression, and that CCN1 knockdown alone affected basal expression in some cases.
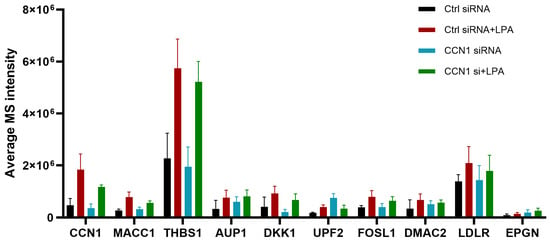
Figure 7.
Proteins up-regulated in response to LPA and inhibited after CCN1 knockdown. The bar graph depicts average data independent acquisition values for selected top ten proteins where the LPA response (at 3 h) was inhibited after CCN1 knockdown.
2.3. Effects of CCN1 Knockdown on LPA-Induced Up-Regulation of MACC1 and TSP1
Based on the proteomics analyses, we selected MACC1 as an LPA-responsive protein worthy of further consideration. Our study showed that LPA induces MACC1 in PC-3 cells after three hours, and that CCN1 knockdown reduced the MACC1 protein levels (Table 1 and Table 3). These proteomic analysis results, presented as bar graphs in Figure 2 and Figure 7, confirm that the effect of LPA on MACC1 protein levels was decreased after CCN1 knockdown. The suppression of MACC1 induction was statistically significant but was partial, consistent with the partial knockdown of CCN1 that was achieved. To gain further insight into the changes in protein levels, we conducted immunoblotting experiments to examine the time course of the effects of LPA on MACC1, as well as the effects of CCN1 knockdown on this induction. Although immunoblotting results are less accurately quantifiable than a proteomics analysis, immunoblotting lends itself to rapid comparison of protein expression under multiple experimental conditions.
The quantified effects of LPA on MACC1 and CCN1, before and after CCN1 knockdown, are shown in Figure 8A,B. Figure 8C presents the time course of the effects of LPA on MACC1 protein levels. The first observation is that the LPA-induced up-regulation of MACC1 is not as dramatic as that of CCN1. MACC1 is detected in PC-3 cells prior to LPA addition. In response to LPA, MACC1 protein levels increase to achieve maximal levels at 3–4 h, during the peak of CCN1 induction.
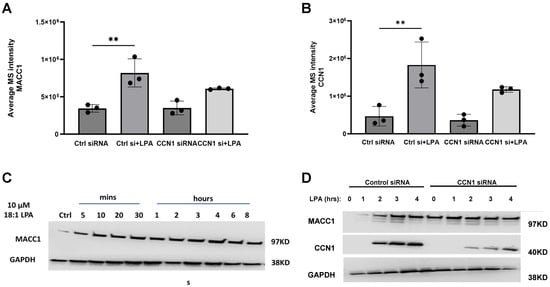
Figure 8.
Effects of CCN1 knockdown on MACC1 and CCN1 1 protein Levels. (A,B) Expression levels of MACC1 (A) and CCN1 (B) were quantified from the proteomics data for cells incubated ± 10 µM LPA for 3 h, with and without CCN1 knockdown. These data are also presented in Figure 7. Data points represent mean ± SD of values from triplicate incubations; ** = p < 0.01. (C,D) Serum-starved PC-3 cells, incubated with control siRNA or CCN1 siRNA, were incubated with 10 µM LPA the indicated times. Whole-cell extracts were immunoblotted for MACC1, CCN1, and GAPDH (loading control) as indicated, on separate gels. Each blot is representative of results from three separate experiments.
In Figure 8D, the time course of MACC1 up-regulation by LPA is compared between control cells and cells subjected to CCN1 knockdown. At the 3 h time point, MACC1 was visibly up-regulated by LPA in cells incubated with control siRNA, but not in cells incubated with CCN1 siRNA. As in Figure 8C, it is apparent that MACC1 is expressed in the absence of LPA, and that the extent of up-regulation is moderate. Interestingly, in both Figure 8C,D, LPA appears to increase the level of immunoreactive MACC1 at early times (5–60 min), prior to a transcriptional response. These results, which were not further explored here, suggest that LPA may alter the cellular distribution of MACC1, the retention of MACC1 in cells, and/or the accessibility of MACC1 to the immunoblotting antibody.
In an additional series of immunoblotting experiments (Figure 9), the expression levels of CCN1, MACC1, and TSP1 were analyzed in cells incubated for three hours with and without LPA treatment, with and without CCN1 knockdown. TSP1 was re-examined because while it is clearly up-regulated by LPA (Figure 2), the effects of CCN1 knockdown on this response were more equivocal (Figure 7). The results of the immunoblots visually confirm the quantified results of the proteomics analysis, showing that LPA increases the levels of CCN1, MACC1, and TSP1, and that CCN1 knockdown partially inhibits the responses to LPA.
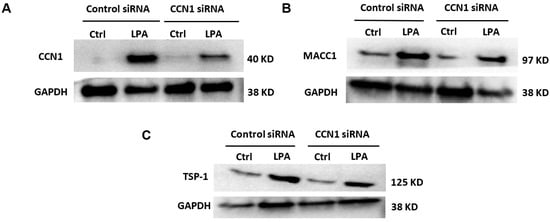
Figure 9.
Effects of LPA on CCN1, MACC1, and TSP1 levels with and without CCN1 knockdown. (A–C): Serum-starved PC-3 cells that had been incubated with control siRNA or CCN1 siRNA were incubated for 3 h with 10 µM 18:1-LPA, with separate sets of cells for each panel. Whole-cell lysates were immunoblotted for CCN1 (A), MACC1 (B), TSP-1 (C), and GAPDH (loading control); the GAPDH blots were performed using the same samples but on separate gels.
3. Discussion
This work examined events occurring in a human prostate cancer cell line three hours after the addition of LPA, a lipid growth factor that activates LPAR1 in these cells. Our study is the first to report the proteomic changes occurring in human prostate cancer cells after LPA treatment, and the first to examine the role of CCN1. Our observations corroborate our previous studies showing that LPA induces CCN1 in human prostate cancer cell lines [,]. The global proteomics analysis showed that CCN1 was one of the most highly up-regulated proteins in response to LPA.
Of particular importance, the results from this study show that a number of proteins related to cell adhesion, cell signaling, and the microenvironment are altered due to LPA treatment in PC-3 cells. The up-regulated proteins included TSP1, DKK1, JUNB, and MACC1. TXNIP was one of the proteins down-regulated by LPA. To our knowledge, the LPA-mediated modulations of these proteins (except for TSP1) are novel findings. The fact that expression levels were changed within three hours suggests that the identified proteins may play roles in bridging acute LPA-initiated signals with longer-term modulation of cellular function. While the analysis provided insight into a variety of proteins, it should be kept in mind that one of the limitations of this study is that all the proteomic differences were captured only at a 3 h time point, which may not represent the optimal time for all of the proteins. This unique time point was chosen to allow examination of the role of CCN1, which is induced by LPA after 2–4 h.
With respect to the role of CCN1, our results showed that CCN1 knockdown suppressed the LPA-induced up-regulation of multiple proteins in PC-3 cells, including ECM-related proteins. Consistent with these results, the STRING analysis identified adhesion-related pathways that were linked to CCN1 via TSP1. One of the pathways identified in the GO analysis is the Rho pathway. Rho GTPases are primary downstream components that transduce signals in response to LPA []. The GO profile for LPA response was quite different before and after CCN1 knockdown, particularly with respect to the Rho pathway which was prominent only in the presence of CCN1. This is interesting since Rho is acutely activated by LPA; alterations in Rho-related proteins seen three hours after LPA addition could reflect compensatory changes following Rho activation, but the results of the CCN1 knockdown suggest that the Rho pathway is also modulated by CCN1. More specifically, our results showed that RAC2, a member of RAC family of Rho GTPases involved in cell adhesion molecular function, was up-regulated by LPA in a manner that was suppressed by CCN1 knockdown. RACs function through regulating and organizing cytoskeleton, enhancing cell migration and cell spreading. This mechanism is usually regulated by the PAK4/LIMK1/Cofilin pathway, as demonstrated in CaP cells []. Our data also showed that Cofilin-2 was one of the LPA-responsive proteins decreased in response to CCN1 knockdown.
We chose to investigate MACC1 in more detail. LPA up-regulation of MACC1 was inhibited after CCN1 knockdown. Previous studies have shown a positive correlation between CCN1 and MACC1 in colorectal cancer []. MACC1 and CCN1 are both implicated in cancer metastasis, adhesion, and survival [,,,]. MACC1 was initially discovered in colorectal cancer []. It has been implicated in tumor progression and migration in various solid tumors, and is a potential prognostic marker in breast, colorectal, pancreatic, prostate, gastric and lung cancers [,,,]. A recent publication reports similar findings for prostate cancer []. While previous studies mention that overexpression of MACC1 is associated with poor prognosis in PC patients, the full spectrum of the cellular roles of MACC1 is still being determined. MACC1 regulates transcription of c-MET in the nucleus but is also found in cytoplasm and mitochondria []. MACC1 can participate in clathrin-mediated endocytosis and receptor recycling []. Thus, the roles and regulation of MACC1 in prostate cancer require further investigation.
MACC1 potentially participates in LPA-mediated signaling. In terms of cellular responses relevant to cancer, MACC1 has primarily been implicated in cell migration [], an important event during tumor dissemination [], but is also involved in other events including cell adhesion [,]. The complex process of cell migration results in cancer metastasis and is dependent on several events such as reorganization of cytoskeleton, and cell–matrix adhesion to facilitate anchorage points in the extracellular matrix space []. MACC1 is directly phosphorylated by MEK1, a component of the Erk mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway, resulting in enhanced Erk activation as well as migration and metastasis in colon cancer cells []. MACC1-enhanced transcriptional events contribute to epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) in pancreatic cancer cells []. Previous work showed that CCN1 and MACC1 cooperate to promote human colorectal cancer cell metastasis, adhesion, migration, differentiation, angiogenesis, and survival []. In summary, emerging evidence suggests a potential interplay between MACC1 and CCN1.
While our results suggest that CCN1 plays a role in maintaining MACC1 levels in PC-3 cells, we have not tested the extent to which MACC1 is pre- and/or post-transcriptionally regulated by LPA in these cells. Although previous studies have reported the transcriptional induction of MACC1 by various receptor agonists [,], a detailed time course has usually not been examined. In addition, LPA has not been previously reported to increase MACC1 levels. These are novel aspects of the current study. The immunoblotting time course (Figure 8) shows that MACC1 is expressed in serum-starved cells prior to LPA addition. Although MACC1 levels are reproducibly increased 3 h after LPA addition, the extent of the increase ~2-fold) is relatively modest. Thus, LPA could potentially increase cellular MACC1 levels by stabilizing the protein (for example), rather than by increasing its transcription. Also, it is important to note that our whole-cell extracts included detergent-soluble cellular proteins, and not ECM proteins. Events altering protein secretion or solubility could potentially affect the proteomic results. With respect to possible early (<60 min) effects of LPA on MACC1 levels (Figure 8), MACC1 can be phosphorylated by MEK1 (the protein kinase that phosphorylates Erk) [], and Erk is activated within 5 min of LPA addition to PC-3 cells [,]. Thus, both early and intermediate signaling events may impact MACC1 activity and protein levels through mechanisms that remain to be addressed.
CCN1 knockdown suppressed the ability of LPA to increase MACC1 levels. Again, several mechanisms could be in play. Although CCN1 is a secreted protein, it has been suggested to play roles in the nucleus [,]. Thus, CCN1 could conceivably alter protein expression at the transcriptional level, either directly or indirectly through integrin-mediated signaling events. On the other hand, CCN1 has also been shown to alter the levels of other proteins via protein–protein interactions []. In this way, CCN1 could either stabilize or destabilize its binding partners. Further exploration of the interactions between CCN1 and MACC1 are warranted.
Turning to other proteins up-regulated by LPA, thrombospondin-1 is a secreted protein that regulates cell adhesion by binding to integrins []. Its role in the ECM is complex and context-dependent, but, in general, TSP1 levels are lower in the tumor microenvironment, and overexpression of TSP1 inhibits tumor growth while enhancing invasion. However, tumor-promoting effects of TSP1 have also been reported. TSP-1 is an inducible protein, and its levels have been reported to increase in response to LPA in several model systems. For example, LPA induces TSP1 at the transcriptional level in rat cortical astrocytes through the LPA receptor LPAR1 []. LPA has been previously shown to induce TSP1 in PC-3 cells after an 8 h treatment []. Since both CCN1 and TSP1 bind to integrins, the net effect of simultaneously increasing both CCN1 and TSP1 is difficult to predict. It is intriguing that STRING analysis (Figure 4) identified a central role for TSP1. It is likely that, since TSP1 plays a negative role in cell–substrate adhesion, TSP1 up-regulation contributes to the transient nature of the effect of LPA on adhesion observed in our previous studies [].
Other proteins of interest, identified in the proteomics analysis, are TXNIP and MSMP/PSMP. The roles of these proteins in prostate cancer cells in the context of LPA response remain to be fully explored.
Our results have paved the way towards exploring newer directions to understand the cellular roles of CCN1. This study has opened possibilities that deserve further exploration. Matricellular proteins such as CCN1 represent new targets for potential therapeutic interventions for prostate cancer, and in other diseases where CCN1 and/or the LPA-CCN axis play a crucial role.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), trypsin protease, iodoacetamide (IAA), and the bicinchoninic acid (BCA) protein assay kit were obtained from Thermo Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA). Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) and bovine serum albumin (BSA) were purchased from Sigma Life Science (Burlington, MA, USA). Acetone and LC-MS-grade acetonitrile were purchased from Sigma Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA) and VWR BDH Chemical (Radnor, PA, USA), respectively. LC-MS-grade formic acid and methanol were procured from Fisher Chemical (Fair Lawn, NJ, USA). Dithiothreitol (DTT) was obtained from Fisher Bioreagents (Pittsburgh, PA, USA).
4.2. Cell Culture
PC-3 cells were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (Manassas, VA, USA). The cells were grown in RPMI 1640 medium supplemented with 10% (v/v) fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Hyclone/Cytiva; Marlborough, MA, USA) and 50 U/mL penicillin/50 µg/mL streptomycin. The cells were maintained on standard tissue culture plastic in an incubator at 37 °C with 5% CO2.
4.3. Cell Incubations and Sample Preparation
PC-3 cells were seeded at 200,000 cells/well in a 6-well plate in RPMI-1640 media supplemented with 10% FBS. CCN1 siRNA complex, scrambled siRNA complex, and transfection medium were then incubated with the cells according to the manufacturer’s recommendations (Santa Cruz Biotechnologies; Santa Cruz, CA, USA) in a volume of 1 mL per well. The cells were incubated at 37 °C in a cell culture incubator for 5–7 h, then an additional 1 mL of RPMI medium supplemented with 20% FBS was added. After 18–24 h, the medium was changed to RPMI-1640 supplemented with 10% FBS. Cells were incubated for 48 h in a cell culture incubator, serum-starved for 24 h, then incubated with and without 10 µM LPA for 3 h. After removal of the media, the cells were washed thrice with ice cold PBS, and cell lysates were collected at 4 °C in an 8 M urea buffer (pH 8.0) containing 0.1 M ammonium bicarbonate and protease inhibitors. The lysates were subjected to BCA analysis to determine protein concentration. Following the above step, the lysate samples were incubated with 25 mM dithiothreitol (DTT) in deionized water at 37 °C for one hour. The sample was then alkylated with 60 mM IAA in dark and RT for 30 min. After adding sufficient 0.1 M ammonium bicarbonate to dilute the sample mixture to 1.6 M urea, the mixture was digested with trypsin overnight with a 1:40 (enzyme: protein) ratio at room temperature. The digested sample was desalted by passage through a C18 SPE cartridge (Waters Corporation, Pleasanton, CA, USA) and then dried down for LC/MS.
4.4. LC-MS Analysis
The proteomics data were acquired by analyzing the digested samples using Easy-nLC 200 coupled with a Q Exactive HF Hybrid Quadrupole-Orbitrap Mass Spectrometer (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Peptides were separated using a Pepmap RSLC C18 (25 cm × 75 µm) column (2 µm, 100 A) with an 80 min gradient program (buffer A: 0.1% formic acid; buffer B: 80% acetonitrile with 0.1% formic acid) as follows: 0–5 min (2–6% buffer B), 5–60 min (6–30% buffer B), 60–65 min (30–100% buffer B), and 65–80 min (100% buffer B). The flow rate was 300 nL/min. MS analysis was performed with spray voltage of 1.7 kV in data-independent acquisition (DIA) mode. Global proteomics data were acquired using the following conditions: mass range (m/z), 350–1025 with variable isolation windows; MS1 resolution, 120,000; MS2 resolution: 30,000.
4.5. Immunoblotting
Whole-cell extracts containing equal amounts of protein (30 µg), prepared as described previously [], were separated by SDS-PAGE on 12% or 15% Laemmli gels, transferred to PVDF membranes, and incubated with primary antibody (overnight at 4 °C) and then secondary antibody (1–2 h at room temperature) in Tris-buffered saline (pH 7.8) containing 4 μg/mL BSA and 0.1% Tween-20. Antibodies recognizing CCN1 and CCN2 were from Cell Signaling Technology (Danvers, MA, USA) (#14479S; #86641S). Antibodies recognizing MACC1 (#86290) and GAPDH were from Cell Signaling Technologies and Santa Cruz Biotechnologies, respectively. Secondary antibodies, anti-rabbit, and anti-mouse (IgG HRP-linked; #7076; #7076S, respectively) were obtained from Cell Signaling Technologies. Primary and secondary antibodies were used at 1:1000 and 1:2000 dilutions, respectively. Blots were developed using enhanced chemiluminescence reagents (Pierce Biotechnology, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and imaged using a GelDoc system (Bio-Rad; Hercules, CA, USA). Protein expression was quantified by densitometry using ImageJ software (https://imagej.net/ij/ access date 12 December 2023). Results were normalized to the GAPDH loading control after background subtraction.
4.6. Data Analysis
LC-MS data were searched using DIA-NN (version 18.1.1) (https://github.com/vdemichev/DiaNN; access date 1 December 2023), with library-free analysis. Deep learning-based in silico spectral library generation was enabled with human FASTA database. The maximum number of missed cleavages was 1 as default. Fixed medication includes carbamidomethylation, N-term M excision, and variable modification only sets oxidation (M). Unrelated run and MBR (match between run) was selected, and all other parameters used the default setting.
Proteins were identified with 1% false discovery rate (FDR). Further processing of data was performed using Microsoft Excel (Microsoft 365 MSO version 2401) and Graph Pad PRISM (Prism 10 for Windows 64-bit).
Proteins that were found in 2 out of 3 replicates were considered detectable. Proteins found in 1 out of 3 replicates were considered not detected. All detected proteins were assessed for the total protein count, which was visualized by Venn diagram (http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/Venn/; access date 9 December 2023). Proteins detected in 2 out of 3 replicates were compared for their abundance using volcano plots where the minimum log fold change was 1.25 and the significance value was <0.05. Pathways were determined by utilizing the STRING database (www.string-db.org; access date 14 December 2023) and Metascape (www.metascape.org; access date 10 December 2023).
Supplementary Materials
The supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ijms25042067/s1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.B. and K.E.M.; methodology, K.E.M., P.B., G.Y. and B.P.; software, B.P.; validation, P.B., G.Y., B.P. and K.E.M.; formal analysis, P.B.; investigation, P.B., K.E.M. and B.P.; resources, B.P. and K.E.M.; data curation, P.B. and K.E.M.; writing—original draft preparation, P.B. and K.E.M.; writing—review and editing, P.B., G.Y., B.P. and K.E.M.; visualization, P.B. and K.E.M.; supervision, K.E.M.; project administration, K.E.M.; funding acquisition, K.E.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the College of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Washington State University.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The proteomics data are in the process of being archived in the PRIDE Proteomics Identifications database.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge support from the proteomics core facility located at Washington State University Health Sciences. We particularly thank Dilip Kumar Singh for assistance with data visualization and analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Gibbs, T.C.; Rubio, M.V.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, Y.; Kipp, K.R.; Meier, K.E. Signal transduction responses to lysophosphatidic acid and sphingosine 1-phosphate in human prostate cancer cells. Prostate 2009, 69, 1493–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Gibbs, T.C.; Mukhin, Y.V.; Meier, K.E. Role for 18:1 lysophosphatidic acid as an autocrine mediator in prostate cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 32516–32526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, M.M.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Meier, K.E. Eicosopentaneoic Acid and Other Free Fatty Acid Receptor Agonists Inhibit Lysophosphatidic Acid- and Epidermal Growth Factor-Induced Proliferation of Human Breast Cancer Cells. J. Clin. Med. 2016, 5, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, M.M.; Liu, Z.; Meier, K.E. Positive and Negative Cross-Talk between Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor 1, Free Fatty Acid Receptor 4, and Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in Human Prostate Cancer Cells. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2016, 359, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Hopkins, M.M.; Zhang, Z.; Quisenberry, C.B.; Fix, L.C.; Galvan, B.M.; Meier, K.E. Omega-3 fatty acids and other FFA4 agonists inhibit growth factor signaling in human prostate cancer cells. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2015, 352, 380–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.W.; Herr, D.R.; Noguchi, K.; Yung, Y.C.; Lee, C.W.; Mutoh, T.; Lin, M.-E.; Teo, S.T.; Park, K.E.; Mosley, A.N.; et al. LPA receptors: Subtypes and biological actions. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2010, 50, 157–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P.V.; Pattabiraman, P.P.; Kopczynski, C. Role of the Rho GTPase/Rho kinase signaling pathway in pathogenesis and treatment of glaucoma: Bench to bedside research. Exp. Eye Res. 2017, 158, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattabiraman, P.P.; Maddala, R.; Rao, P.V. Regulation of plasticity and fibrogenic activity of trabecular meshwork cells by Rho GTPase signaling. J. Cell. Physiol. 2014, 229, 927–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattabiraman, P.P.; Rao, P.V. Mechanistic basis of Rho GTPase-induced extracellular matrix synthesis in trabecular meshwork cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2010, 298, C749–C763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, C.T.; Stupack, D.; Brown, J.H. G protein-coupled receptors go extracellular: RhoA integrates the integrins. Mol. Interv. 2008, 8, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, J.I.; Lau, L.F. Taking aim at the extracellular matrix: CCN proteins as emerging therapeutic targets. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2011, 10, 945–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kireeva, M.L.; Mo, F.E.; Yang, G.P.; Lau, L.F. Cyr61, a product of a growth factor-inducible immediate-early gene, promotes cell proliferation, migration, and adhesion. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1996, 16, 1326–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, L.F.; Lam, S.C. The CCN family of angiogenic regulators: The integrin connection. Exp. Cell Res. 1999, 248, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, S.; Yokoyama, M.; Zhang, X.; Prakash, K.; Nagao, K.; Hatanaka, T.; Getzenberg, R.H.; Kakahi, Y. Increased expression of CYR61, an extracellular matrix signaling protein, in human benign prostatic hyperplasia and its regulation by lysophosphatidic acid. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 2929–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, C.T.; Radeff-Huang, J.; Matteo, R.; Hsiao, A.; Subramaniam, S.; Stupack, D.; Brown, J.H. Thrombin receptor and RhoA mediate cell proliferation through integrins and cysteine-rich protein 61. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 4011–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, T.; Zu, Y.; Qin, Z.; Robichaud, P.; Betcher, S.; Calderone, K.; He, T.; Johnson, T.M.; Voorhees, J.J.; Fisher, G.J. Elevated YAP and its downstream targets CCN1 and CCN2 in basal cell carcinoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2014, 184, 937–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balijepalli, P.; Knode, B.K.; Nahulu, S.A.; Abrahamson, E.L.; Nivison, M.P.; Meier, K.E. Role for CCN1 in lysophosphatidic acid response in PC-3 human prostate cancer cells. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 2022, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Chen, C.C.; Lau, L.F. Adhesion of human skin fibroblasts to Cyr61 is mediated through integrin alpha 6 beta 1 and cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 24953–24961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.D.; Zhang, F.; Hao, F.; Chun, J.; Xu, X.; Cui, M.Z. Matricellular protein Cyr61 bridges lysophosphatidic acid and integrin pathways leading to cell migration. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 5774–5783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzen, C.A.; Chen, C.-C.; Todorovic, V.; Juric, V.; Monzon, R.I.; Lau, L.F. Matrix protein CCN1 is critical for prostate carcinoma cell proliferation and TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Mol. Cancer Res. 2009, 7, 1045–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, H.; Walther, W.; Zincke, F.; Kobelt, D.; Imbastari, F.; Erdem, M.; Kortum, B.; Dahlmann, M.; Stein, U. MACC1—The first decade of a key metastasis molecule from gene discovery to clinical translation. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2018, 37, 805–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy-Ullrich, J.E. Thrombospondin 1 and Its Diverse Roles as a Regulator of Extracellular Matrix in Fibrotic Disease. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2019, 67, 683–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Bronson, S.M.; Pal-Nath, D.; Miller, T.W.; Soto-Pantoja, D.R.; Roberts, D.D. Functions of Thrombospondin-1 in the Tumor Microenvironment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, R.; Su, Z.Z.; Lee, S.G.; Azab, B.; Boukerche, H.; Sarkar, D.; Fisher, P.B. Inhibition of AP-1 by SARI negatively regulates transformation progression mediated by CCN1. Oncogene 2010, 29, 4412–4423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Benavente, B.; Fathinajafabadi, A.; de la Fuente, L.; Gandia, C.; Martinez-Ferriz, A.; Pardo-Sanchez, J.M.; Millian, L.; Conesa, A.; Romero, O.A.; Carretero, J.; et al. New roles for AP-1/JUNB in cell cycle control and tumorigenic cell invasion via regulation of cyclin E1 and TGF-beta2. Genome Biol. 2022, 23, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rackner, R.D.; Thiele, S.; Gobel, A.; Browne, A.; Fuessel, S.; Erdmann, K.; Wirth, M.P.; Frohner, M.; Todenhofer, T.; Muders, M.H.; et al. High serum levels of Dickkof-1 are associated with a poor prognosis in prostate cancer patients. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 649. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhou, B.; Pache, L.; Chang, M.; Khodabakhshi, A.H.; Tanaseichuk, O.; Benner, C.; Chanda, S.K. Metascape provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of systems-level datasets. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Pan, T.; Liu, Z.; McCarthy, C.; Vicencio, J.M.; Cao, L.; Alfano, G.; Swaidan, A.A.; Yin, M.; Beatson, R.; et al. The role of TXNIP in cancer: A fine balance between redox, metabolic, and immunological tumor control. Br. J. Cancer 2023, 129, 1877–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Xie, R.; Xie, S.; Wu, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Xu, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, T.; et al. Thioredoxin interacting proteins (TXNIP) acts as a tumor suppressor in human prostate cancer. Cell Biol. Int. 2020, 44, 2094–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.-Q.; Chen, X.; Fisher, C.; Siller, S.S.; Zelikman, K.; Kuriyama, R.; Takemaru, K.-I. BAR domain-containing FAM92 proteins interact with Chibby1 to facilitate ciliogenesis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2016, 36, 2668–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pampliega, O.; Orhon, I.; Patel, B.; Sridhar, S.; Diaz-Carretero, A.; Beau ICodogno, P.; Satir, B.; Satir, P.; Cuervo, A. Functional interaction between autophagy and ciliogenesis. Nature 2013, 502, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirkmajer, S.; Chibalin, A.V. Serum starvations: Caveat emptor. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2011, 301, C272–C279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Khan, Z.; Westlake, C.J. Ciliogenesis membrane dynamics and organization. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 133, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afratis, N.A.; Nikitovic, D.; Multhaupt, H.A.B.; Theocharis, A.D.; Couchman, J.R.; Karamanos, N.K. Syndecans—Key regulators of cell signaling and biological functions. FEBS J. 2017, 284, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Wu, X.; Le, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Q.; Huang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Wu, L. The role and therapeutic value of syndecan-1 in cancer metastasis and drug resistance. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 9, 784983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazniewska, J.; Li, K.L.; Johnson, I.R.D.; Sorvina, A.; Logan, J.; Artini, C.; Moore, C.; Ung, B.S.-Y.; Karageorgos, L.; Hickey, S.M.; et al. Dynamic interplay between sortilin and syndecan-1 contributes to prostate cancer progression. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 13489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valtonen-Andre, C.; Bjartell, A.; Hellsten, R.; Lilja, H.; Harkonen, P.; Lundwall, A. A highly conserved protein secreted by the prostate cancer cell line PC-3 is expressed in benign and malignant prostate tissue. Biol. Chem. 2007, 388, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, P.; Li, H.; Han, M.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Tu, J.; Shi, X.; Fu, Y. PSMP Is Discriminative for Chronic Active Antibody-Mediated Rejection and Associate with Intimal Arteritis in Kidney Transplantation. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 661911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitamura, T.; Pradeep, S.; McGuire, M.; Wu, S.Y.; Ma, S.; Hatakeyama, H.; Lyons, Y.A.; Hisamatsu, T.; Noh, K.; Villar-Prados, A.; et al. Induction of anti-VEGF therapy resistance by upregulated expression of microseminoprotein (MSMP). Oncogene 2018, 37, 722–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Fang, J.; Chen, S.; Wang, W.; Meng, S.; Liu, B. Nonconserved miR-608 suppresses prostate cancer progression through RAC2/PAK4/LIMK1 and BCL2L1/caspase-3 pathways by targeting the 3′-UTRs of RAC2/BCL2L1 and the coding region of PAK4. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 5716–5734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Gu, J.; Gao, Y. MicroRNA target for MACC1 and CYR61 to inhibit tumor growth in mice with colorectal cancer. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 13983–13993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Bui, N.T.; Ho, M.T.; Kim, Y.M.; Cho, M.; Shin, D.B. Dexamethasone Inhibits TGF-beta1-Induced Cell Migration by Regulating the ERK and AKT Pathways in Human Colon Cancer Cells Via CYR61. Cancer Res. Treat. 2016, 48, 1141–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Deng, Y.; Mao, Z.; Ma, X.; Fan, X.; Cui, L.; Qu, L.; Xie, D.; Zhang, J. CCN1 promotes tumorigenicity through Rac1/Akt/NF-κB signaling pathway in pancreatic cancer. Tumour Biol. 2012, 33, 1745–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.T.; Ding, X.; Ni, Q.F.; Jin, S.J. Targeting MACC1 by RNA interference inhibits proliferation and invasion of bladder urothelial carcinoma in T24 cells. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 7937–7944. [Google Scholar]
- Stein, U.; Walther, W.; Arlt, F.; Schwabe, H.; Smith, J.; Fichtner, I.; Birchmeier, W.; Schlag, P.M. MACC1, a newly identified key regulator of HGF-MET signaling, predicts colon cancer metastasis. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burock, S.; Herrmann, P.; Wendler, I.; Niederstrasser, M.; Wenecke, K.-D.; Stein, U. Circulating metastasis associated in colon cancer 1 transcripts in gastric cancer patient plasma as diagnostic and prognostic biomarker. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Kang, M.X.; Lu, W.J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wu, Y.L. MACC1: A potential molecule associated with pancreatic cancer metastasis and chemoresistance. Oncol. Lett. 2012, 4, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cai, M.; Weng, Y.; Zhang, F.; Meng, D.; Song, J.; Zhou, H.; Xie, Z. Circulating MACC1 as a novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for non-small cell lung cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 141, 1353–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashktorab, H.; Hermann, P.; Nourale, M.; Shokrani, B.; Lee, E.; Haidary, T.; Brim, H.; Stein, U. Increased MACC1 levels in tissues and blook identify colon adenoma patients at high risk. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wen, L.; Cao, J.; Yang, J.; Yuan, Y. Diagnostic value of PSA, TAP and MACC1 expression in blood of patients with prostate cancer. J. Shanghai Jiao Tong Univ. (Med. Sci.) 2022, 42, 496–501. [Google Scholar]
- Imbastari, F.; Dahlman, M.; Sorbert, A.; Mattioli, C.C.; Mari, T.; Scholz, F.; Timm, L.; Twamley, S.; Migotti, R.; Walther, W.; et al. MACC1 regulates clathrin-mediated endocytosis and receptor recycling of transferrin receptor and EGFR in colorectal cancer. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 3525–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohmann, T.; Hohmann, U.; Dehghani, F. MACC1-induced migration in tumors: Current state and perspectives. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1165676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo-Cordero, J.J.; Hodgson, K.M.; Condeelis, J.S. Directed cell invasion during metastasis. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2012, 24, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohmann, T.; Hohmann, U.; Kolbe, M.R.; Dahlmann, M.; Kobelt, D.; Stein, U.; Dehghani, F. MACC1 driven alterations in cellular biomechanics facilitate cell motility in glioblastoma. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 18, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eble, J.A.; Niland, S. The extracellular matrix in tumor progression and metastasis. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2019, 36, 171–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobelt, D.; Perez-Hernandez, D.; Fleuter, C.; Dahlmann, M.; Zincke, F.; Smith, J.; Migotti, R.; Popp, O.; Burock, S.; Walther, W.; et al. The newly identified MEK1 tyrosine phosphorylation target MACC1 is druggable by approved MEK1 inhibitors to restrict colorectal cancer metastasis. Oncogene 2021, 40, 5286–5301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Luo, Y.; Cen, Y.; Qiu, X.; Li, J.; Jie, M.; Yang, S.; Qin, S. MACC1 promotes pancreatic cancer metastasis by interacting with the EMT regulator SNAI1. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobelt, D.; Zhang, C.; Clayton-Lucey, I.A.; Glauben, R.; Voss, C.; Siegmund, B.; Stein, U. Pro-inflammatory TNF-α and IFN-γ promote tumor growth and metastasis via induction of MACC1. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osaki, M.; Inaba, A.; Nishikawa, K.; Sugimoto, Y.; Shomori, K.; Inoue, T.; Oshimura, M.; Ito, H. Cysteine-rich protein 61 suppresses cell invasion via down-regulation of matrix metalloproteinase-7 expression in the human gastric carcinoma cell line MKN-45. Mol. Med. Rep. 2010, 3, 711–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perbal, B. The concept of the CCN protein family revisited: A centralized coordination network. J. Cell Commun. Signal 2018, 12, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, S.E.; Kay, E.J.; Neilson, L.J.; Henze, A.T.; Serneels, J.; McGhee, E.J.; Dhayade, S.; Nixon, C.; Mackey, J.B.; Santi, A.; et al. Tumor matrix stiffness promotes metastatic cancer cell interaction with the endothelium. EMBO J. 2017, 36, 2373–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisaoka-Nakashima, K.; Yokoe, T.; Watanabe, S.; Nakamura, Y.; Kajitani, N.; Okada-Tsuchioka, M.; Takebayashi, M.; Nakata, Y.; Morioka, N. Lysophosphatidic acid induces thrombospondin-1 production in primary cultured rat cortical astrocytes. J. Neurochem. 2021, 158, 849–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, Y.S.; Lindholm, P.F. Constitutive and inducible expression of invasion-related factors in PC-3 prostate cancer cells. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 20, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).