Sodium Channel β Subunits—An Additional Element in Animal Tetrodotoxin Resistance?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sequence Alignment and Curation
4.2. Testing for Signatures of Positive Selection
4.3. Testing for Signatures of Convergent Evolution
D Protein Reconstruction and Labelling
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miyazawa, K.; Noguchi, T. Distribution and Origin of Tetrodotoxin. J. Toxicol. Toxin Rev. 2001, 20, 11–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katikou, P.; Gokbulut, C.; Kosker, A.R.; Campàs, M.; Ozogul, F. An Updated Review of Tetrodotoxin and Its Peculiarities. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnikova, D.I.; Magarlamov, T.Y. An Overview of the Anatomical Distribution of Tetrodotoxin in Animals. Toxins 2022, 14, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitelaw, B.L.; Cooke, I.R.; Finn, J.; Zenger, K.; Strugnell, J.M. The Evolution and Origin of Tetrodotoxin Acquisition in the Blue-Ringed Octopus (Genus Hapalochlaena). Aquat. Toxicol. 2019, 206, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarova, M.; Rycek, L.; Hajicek, J.; Baidilov, D.; Hudlicky, T. Tetrodotoxin: History, Biology, and Synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 18338–18387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catterall, W.A.; Cestèle, S.; Yarov-Yarovoy, V.; Yu, F.H.; Konoki, K.; Scheuer, T. Voltage-Gated Ion Channels and Gating Modifier Toxins. Toxicon 2007, 49, 124–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catterall, W.A. Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels at 60: Structure, Function and Pathophysiology. J. Physiol. 2012, 590, 2577–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catterall, W.A. Forty Years of Sodium Channels: Structure, Function, Pharmacology, and Epilepsy. Neurochem. Res. 2017, 42, 2495–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruben, P.C. (Ed.) Voltage Gated Sodium Channels; Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology Series; Volume 221.
- William, A. Catterall From Ionic Currents to Molecular Review Mechanisms: The Structure and Function of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels. Neuron 2000, 26, 13–25. [Google Scholar]
- Noda, M.; Suzuki, H.; Numa, S.; Stühmer, W. A Single Point Mutation Confers Tetrodotoxin and Saxitoxin Insensitivity on the Sodium Channel II. FEBS Lett. 1989, 259, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terlau, H.; Heinemann, S.H.; Stühmer, W.; Pusch, M.; Conti, F.; Imoto, K.; Numa, S. Mapping the Site of Block by Tetrodotoxin and Saxitoxin of Sodium Channel II. FEBS Lett. 1991, 293, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catterall, W.A.; Goldin, A.L.; Waxman, S.G. International Union of Pharmacology. XLVII. Nomenclature and Structure-Function Relationships of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels. Pharmacol. Rev. 2005, 57, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.; Liu, D.; Wu, K.; Lei, J.; Yan, N. Structures of Human Nav1.7 Channel in Complex with Auxiliary Subunits and Animal Toxins. Science 2019, 1308, 1303–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Shen, H.; Wu, K.; Huang, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, X.; Lei, J.; et al. Structure of the Human Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel Nav1.4 in Complex with Β1. Science 2018, 362, eaau2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvage, S.C.; Jeevaratnam, K.; Huang, C.L.H.; Jackson, A.P. Cardiac Sodium Channel Complexes and Arrhythmia: Structural and Functional Roles of the Β1 and Β3 Subunits. J. Physiol. 2023, 601, 923–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Li, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Pan, X.; Wu, J.; Cristofori-Armstrong, B.; Smith, J.J.; Chin, Y.K.Y.; Lei, J.; Zhou, Q.; et al. Structural Basis for the Modulation of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels by Animal Toxins. Science 2018, 362, eaau2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, A.H.; Muttenthaler, M.; Dutertre, S.; Himaya, S.W.A.; Kaas, Q.; Craik, D.J.; Lewis, R.J.; Alewood, P.F. Conotoxins: Chemistry and Biology; ACS Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2019; Volume 119, ISBN 1323883894. [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesh, B.; Lu, S.Q.; Dandona, N.; See, S.L.; Brenner, S.; Soong, T.W. Genetic Basis of Tetrodotoxin Resistance in Pufferfishes. Curr. Biol. 2005, 15, 2069–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jost, M.C.; Hillis, D.M.; Lu, Y.; Kyle, J.W.; Fozzard, H.A.; Zakon, H.H. Toxin-Resistant Sodium Channels: Parallel Adaptive Evolution across a Complete Gene Family. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2008, 25, 1016–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanifin, C.T.; Gilly, W.F. Evolutionary History of a Complex Adaptation: Tetrodotoxin Resistance in Salamanders. Evolution 2015, 69, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodie, E.D.; Feldman, C.R.; Hanifin, C.T.; Motychak, J.E.; Mulcahy, D.G.; Williams, B.L.; Brodie, E.D. Parallel Arms Races between Garter Snakes and Newts Involving Tetrodotoxin as the Phenotypic Interface of Coevolution. J. Chem. Ecol. 2005, 31, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucciarelli, G.M.; Alsalek, F.; Kats, L.B.; Green, D.B.; Shaffer, H.B. Toxic Relationships and Arms-Race Coevolution Revisited. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2022, 10, 63–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, C.R.; Brodie, E.D.; Brodie, E.D.; Pfrender, M.E. Constraint Shapes Convergence in Tetrodotoxinresistant Sodium Channels of Snakes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 4556–4561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isom, L.L. Sodium Channel β Subunits: Anything but Auxiliary. Neuroscientist 2001, 7, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Malley, H.A.; Isom, L.L. Sodium Channel β Subunits: Emerging Targets in Channelopathies. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2015, 77, 481–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namadurai, S.; Yereddi, N.R.; Cusdin, F.S.; Huang, C.L.H.; Chirgadze, D.Y.; Jackson, A.P. A New Look at Sodium Channel β Subunits. Open Biol. 2015, 5, 140192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angsutararux, P.; Zhu, W.; Voelker, T.L.; Silva, J.R. Molecular Pathology of Sodium Channel Beta-Subunit Variants. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 761275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.C.; Ragsdale, D.S.; Malhotra, J.D.; Mattei, L.N.; Braun, P.E.; Schachner, M.; Isom, L.L. Tenascin-R Is a Functional Modulator of Sodium Channel β Subunits. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 26511–26517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yereddi, N.R.; Cusdin, F.S.; Namadurai, S.; Packman, L.C.; Monie, T.P.; Slavny, P.; Clare, J.J.; Powell, A.J.; Jackson, A.P. The Immunoglobulin Domain of the Sodium Channel Β3 Subunit Contains a Surface-Localized Disulfide Bond That Is Required for Homophilic Binding. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 568–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.M.; Wilson, M.J.; Azam, L.; Gajewiak, J.; Rivier, J.E.; Bulaj, G.; Olivera, B.M.; Yoshikami, D. Co-Expression of NaVβ Subunits Alters the Kinetics of Inhibition of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels by Pore-Blocking μ-Conotoxins. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 168, 1597–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.J.; Zhang, M.M.; Gajewiak, J.; Azam, L.; Rivier, J.E.; Olivera, B.M.; Yoshikami, D. α- And β-Subunit Composition of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels Investigated with µ-Conotoxins and the Recently Discovered ΜO§-Conotoxin GVIIJ. J. Neurophysiol. 2015, 113, 2289–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilchrist, J.; Das, S.; van Petegem, F.; Bosmans, F. Crystallographic Insights into Sodium-Channel Modulation by the Β4 Subunit. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E5016–E5024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvage, S.C.; Rahman, T.; Eagles, D.A.; Rees, J.S.; King, G.F.; Huang, C.L.H.; Jackson, A.P. The Β3-Subunit Modulates the Effect of Venom Peptides ProTx-II and OD1 on NaV1.7 Gating. J. Cell. Physiol. 2023, 238, 1354–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Gilchrist, J.; Bosmans, F.; van Petegem, F. Binary Architecture of the Nav 1.2-Β2 Signaling Complex. eLife 2016, 5, e10960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priest, B.T.; Blumenthal, K.M.; Smith, J.J.; Warren, V.A.; Smith, M.M. ProTx-I and ProTx-II: Gating Modifiers of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels. Toxicon 2007, 49, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akondi, K.B.; Muttenthaler, M.; Dutertre, S.; Kaas, Q.; Craik, D.J.; Lewis, R.J.; Alewood, P.F. Discovery, Synthesis, and Structure-Activity Relationships of Conotoxins. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 5815–5847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, K.; Pollock, D.D. Detecting Macroevolutionary Genotype–Phenotype Associations Using Error-Corrected Rates of Protein Convergence. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 7, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruta, S.; Yamaoka, K.; Yotsu-Yamashita, M. Two Critical Residues in P-Loop Regions of Puffer Fish Na+ Channels on TTX Sensitivity. Toxicon 2008, 51, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Thiel, J.; Khan, M.A.; Wouters, R.M.; Harris, R.J.; Casewell, N.R.; Fry, B.G.; Kini, R.M.; Mackessy, S.P.; Vonk, F.J.; Wüster, W.; et al. Convergent Evolution of Toxin Resistance in Animals. Biol. Rev. 2022, 97, 1823–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brackenbury, W.J.; Isom, L.L. Na+ Channel β Subunits: Overachievers of the Ion Channel Family. Front. Pharmacol. 2011, 2, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrera, L.; Moran, O. Β1-Subunit Modulates the Nav1.4 Sodium Channel by Changing the Surface Charge. Exp. Brain Res. 2006, 172, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, L.; Wu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, G.; Peng, W.; Shen, H.; Lei, J.; Yan, N. Structure of the Nav1.4-Β1 Complex from Electric Eel. Cell 2017, 170, 470–482.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reimche, J.S.; del Carlo, R.E.; Brodie, E.D.; McGlothlin, J.W.; Schlauch, K.; Pfrender, M.E.; Brodie, E.D.; Leblanc, N.; Feldman, C.R. The Road Not Taken: Evolution of Tetrodotoxin Resistance in the Sierra Garter Snake (Thamnophis couchii) by a Path Less Travelled. Mol. Ecol. 2022, 31, 3827–3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geffeney, S.L.; Cordingley, J.A.; Mitchell, K.; Hanifin, C.T. In Silico Analysis of Tetrodotoxin Binding in Voltage-Gated Sodium Ion Channels from Toxin-Resistant Animal Lineages. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, H.K.; Basu, G. Conformational Landscape of Substituted Prolines. Biophys. Rev. 2020, 12, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Li, Z.; Huang, X.; Huang, G.; Gao, S.; Shen, H.; Liu, L.; Lei, J.; Yan, N. Molecular Basis for Pore Blockade of Human Na + Channel Na v 1.2 by the m-Conotoxin KIIIA. Science 2019, 363, 1309–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Santiago, L.F.; Pertin, M.; Morisod, X.; Chen, C.; Hong, S.; Wiley, J.; Decosterd, I.; Isom, L.L. Sodium Channel Β2 Subunits Regulate Tetrodotoxin-Sensitive Sodium Channels in Small Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons and Modulate the Response to Pain. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 7984–7994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namadurai, S.; Balasuriya, D.; Rajappa, R.; Wiemhöfer, M.; Stott, K.; Klingauf, J.; Edwardson, J.M.; Chirgadze, D.Y.; Jackson, A.P. Crystal Structure and Molecular Imaging of the Nav Channelβ3 Subunit Indicates a Trimeric Assembly. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 10797–10811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartshornes, R.P.; Messnerg, D.J. Sodium Channel from Rat Brain. J. Biol. Chem. 1982, 257, 13888–13891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abderemane-Ali, F.; Rossen, N.D.; Kobiela, M.E.; Craig, R.A.; Garrison, C.E.; Chen, Z.; Colleran, C.M.; O’connell, L.A.; Du Bois, J.; Dumbacher, J.P.; et al. Evidence That Toxin Resistance in Poison Birds and Frogs Is Not Rooted in Sodium Channel Mutations and May Rely on “Toxin Sponge” Proteins. J. Gen. Physiol. 2021, 153, e202112872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portugal, S.J.; Murn, C.P.; Sparkes, E.L.; Daley, M.A. The Fast and Forceful Kicking Strike of the Secretary Bird. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, R58–R59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrott, M.L.; Doody, J.S.; McHenry, C.; Clulow, S.; Parrott, M.L.; Doody, J.S.; McHenry, C.; Clulow, S. Eat Your Heart out: Choice and Handling of Novel Toxic Prey by Predatory Water Rats. Aust. Mammal. 2019, 42, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z. PAML 4: Phylogenetic Analysis by Maximum Likelihood. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 1586–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly Accurate Protein Structure Prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varadi, M.; Anyango, S.; Deshpande, M.; Nair, S.; Natassia, C.; Yordanova, G.; Yuan, D.; Stroe, O.; Wood, G.; Laydon, A.; et al. AlphaFold Protein Structure Database: Massively Expanding the Structural Coverage of Protein-Sequence Space with High-Accuracy Models. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D439–D444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera—A Visualization System for Exploratory Research and Analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
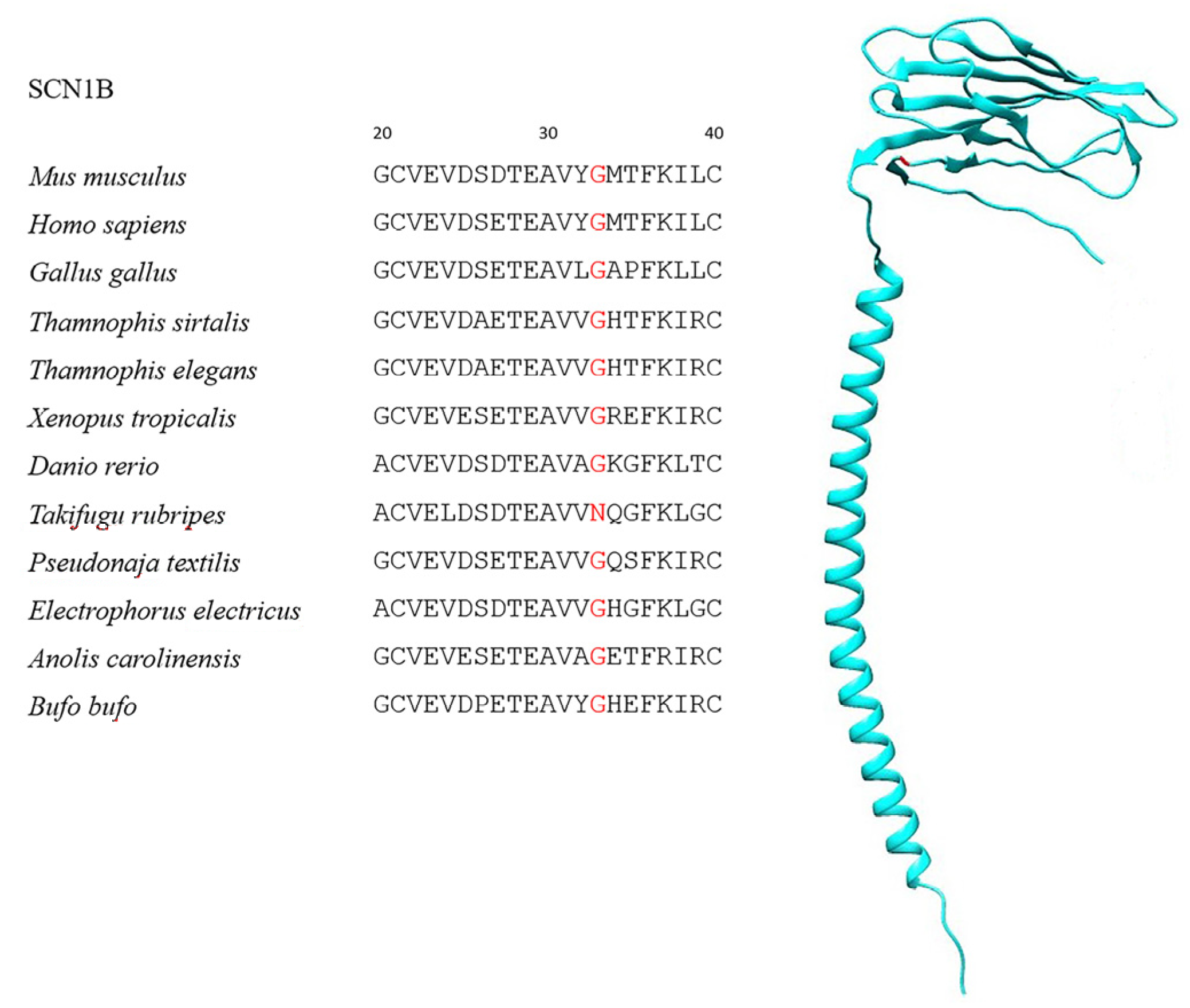
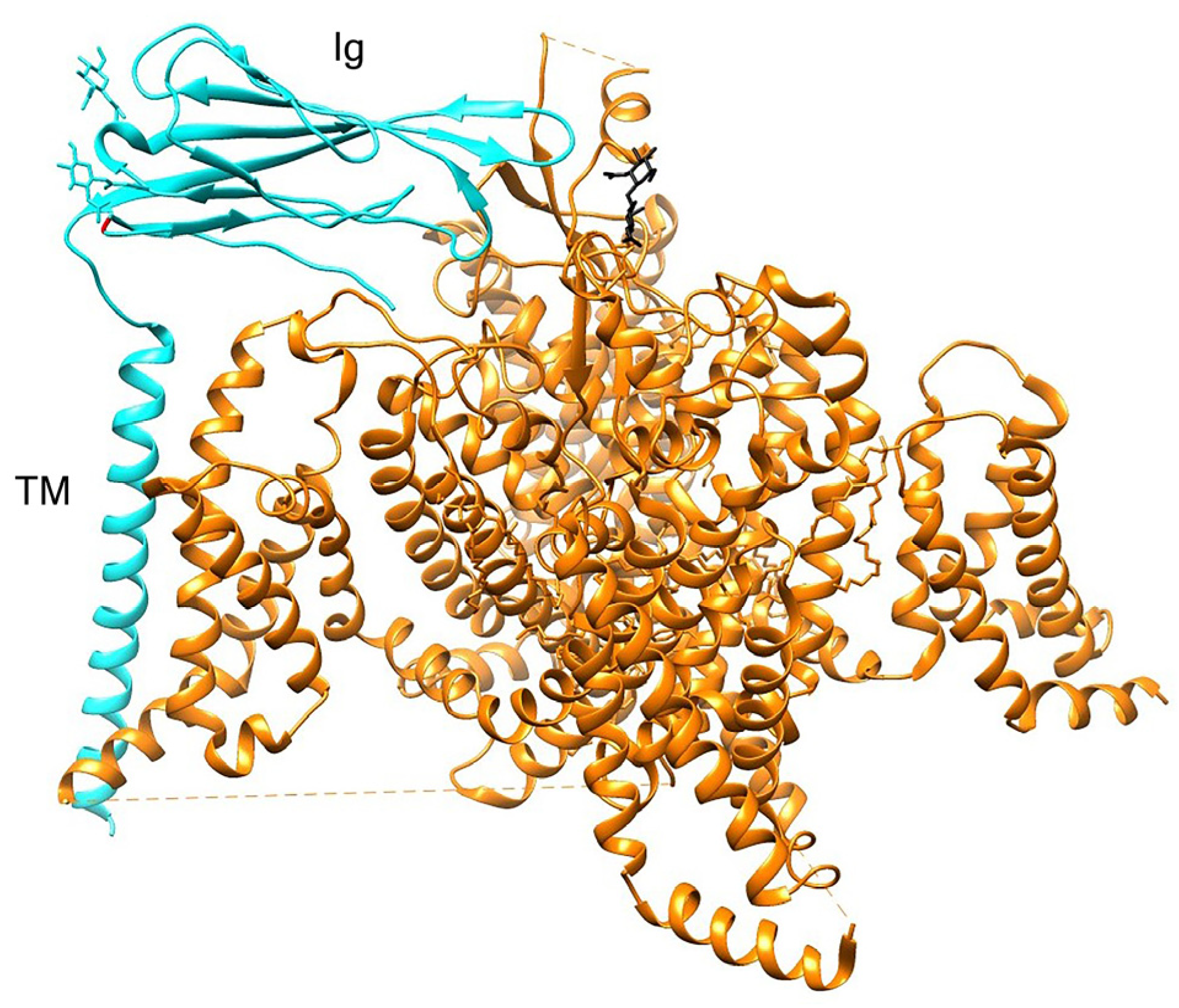
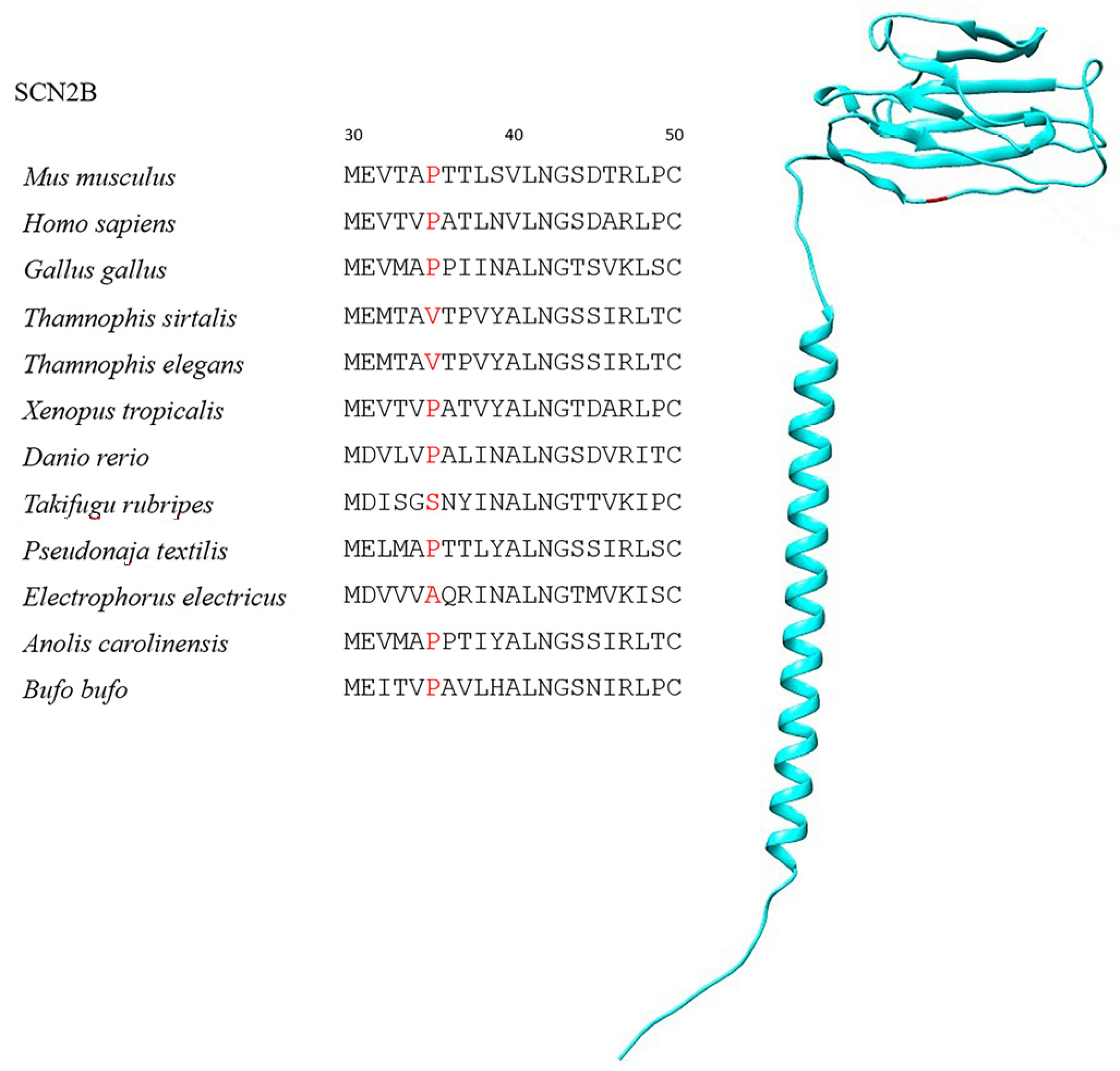
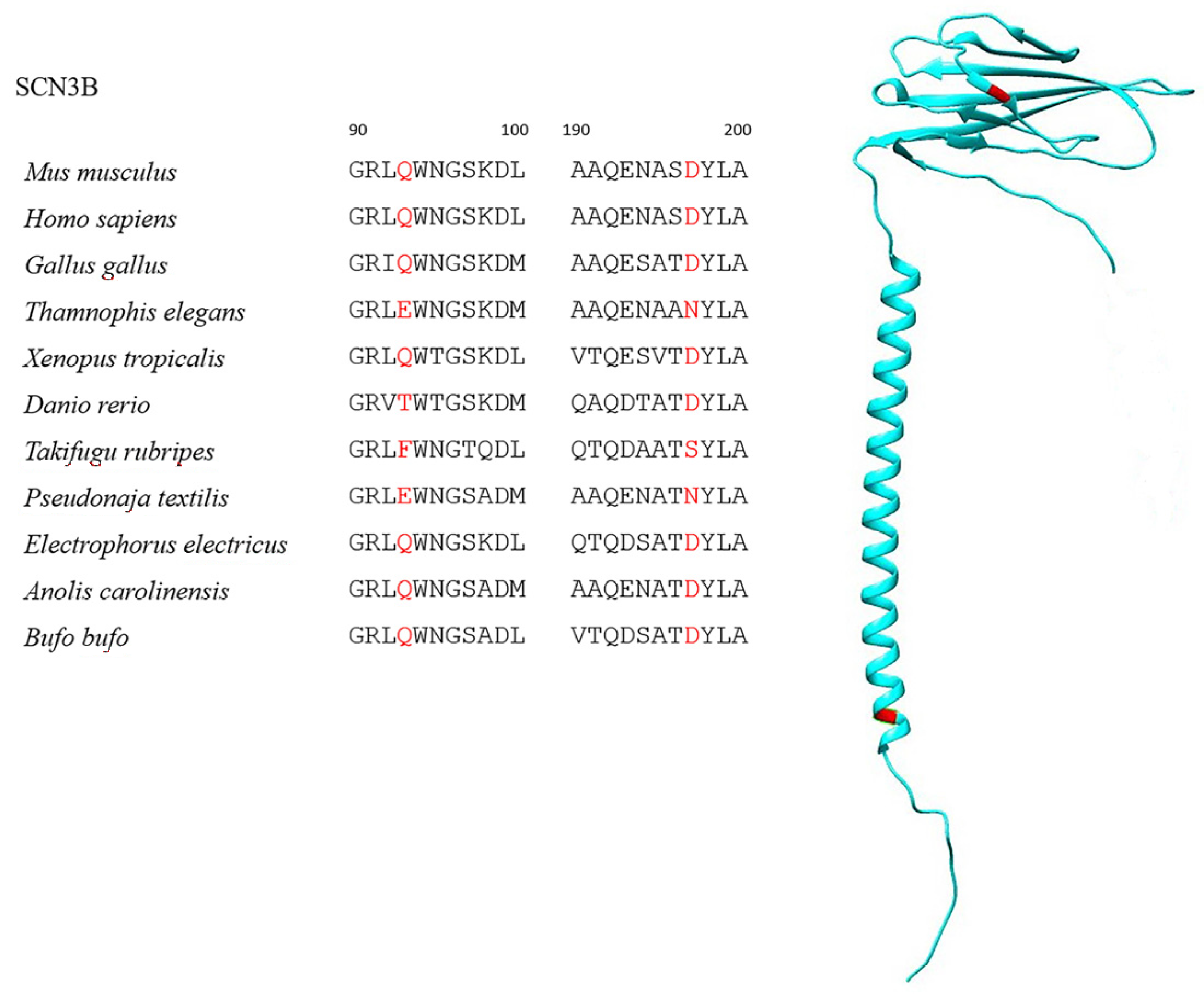
| Species | Class | TTX-Resistant |
|---|---|---|
| Homo sapiens | Mammal | No |
| Mus musculus | Mammal | No |
| Gallus gallus | Bird | No |
| Anolis carolinensis | Reptile | No |
| Thamnophis sirtalis | Reptile | Yes |
| Thamnophis elegans | Reptile | Yes |
| Pseudonaja textilis | Reptile | No |
| Bufo bufo | Amphibian | No |
| Xenopus tropicalis | Amphibian | No |
| Takifugu rubripes | Fish | Yes |
| Danio rerio | Fish | No |
| Electrophorus electricus | Fish | No |
| Maximum Sequence Length (without Signal Peptide) | Positions under Positive Selection | Substitutions | Prob (ω > 1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCN1B | 201 | 15 | G33N | 95.6% |
| SCN2B | 197 | 6 | P35V, P35S | 99.5% |
| SCN3B * | 199 | 70 | Q93E, Q93F, Q93T | 98.6% |
| 174 | D197N, D197S | 99.2% | ||
| SCN4B | 208 | - | - | - |
| Combinatorial Substitution Categories | SCN1B | SCN2B | SCN3B * | SCN4B |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Convergence | 0.019 | 0.004 | 0.108 | 0.088 |
| Discordant Convergence | 0.023 | 0.001 | 0.095 | 0.752 |
| Congruent Convergence | 0.020 | 0.008 | 0.134 | 0.088 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seneci, L.; Mikheyev, A.S. Sodium Channel β Subunits—An Additional Element in Animal Tetrodotoxin Resistance? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031478
Seneci L, Mikheyev AS. Sodium Channel β Subunits—An Additional Element in Animal Tetrodotoxin Resistance? International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(3):1478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031478
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeneci, Lorenzo, and Alexander S. Mikheyev. 2024. "Sodium Channel β Subunits—An Additional Element in Animal Tetrodotoxin Resistance?" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 3: 1478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031478
APA StyleSeneci, L., & Mikheyev, A. S. (2024). Sodium Channel β Subunits—An Additional Element in Animal Tetrodotoxin Resistance? International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(3), 1478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031478






