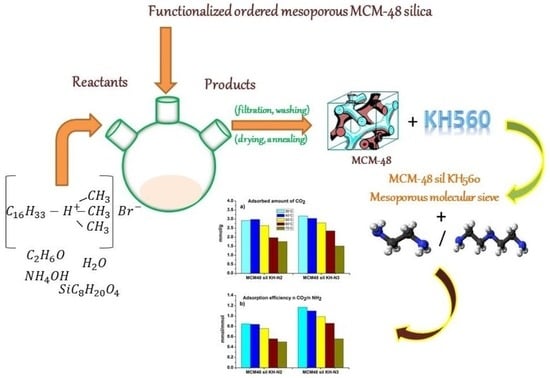
Functionalized Ordered Mesoporous MCM-48 Silica: Synthesis, Characterization and Adsorbent for CO2 Capture
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
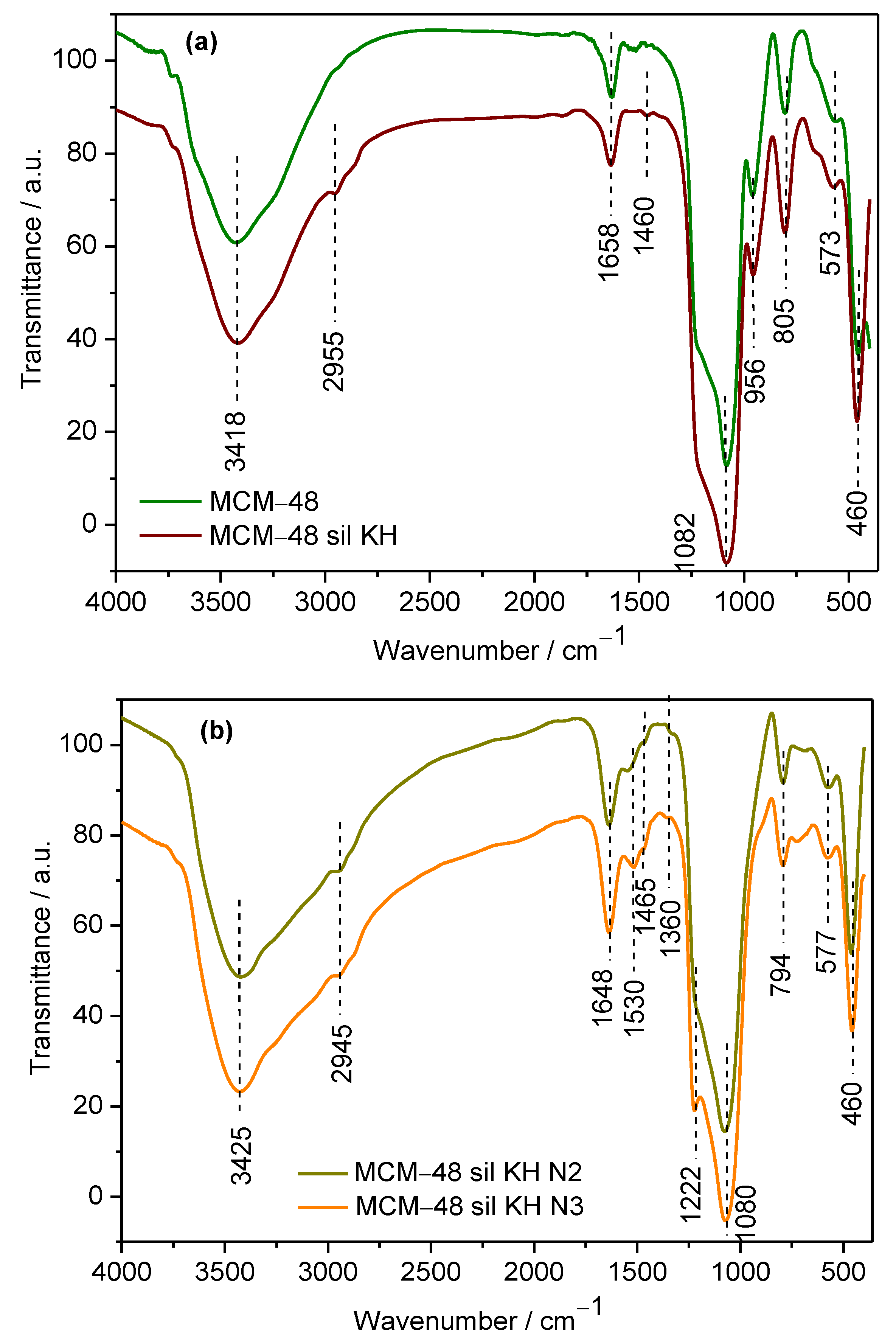
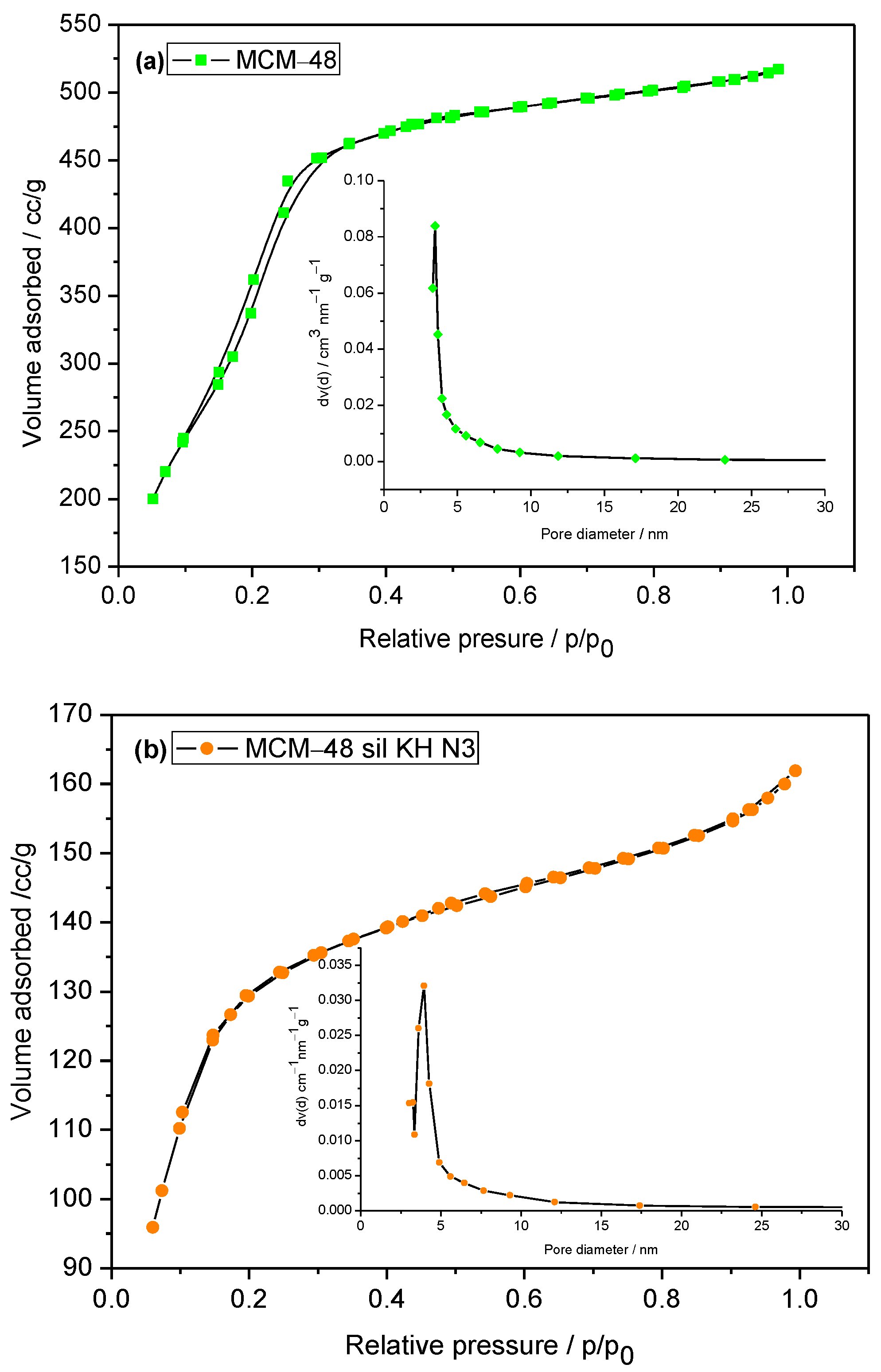
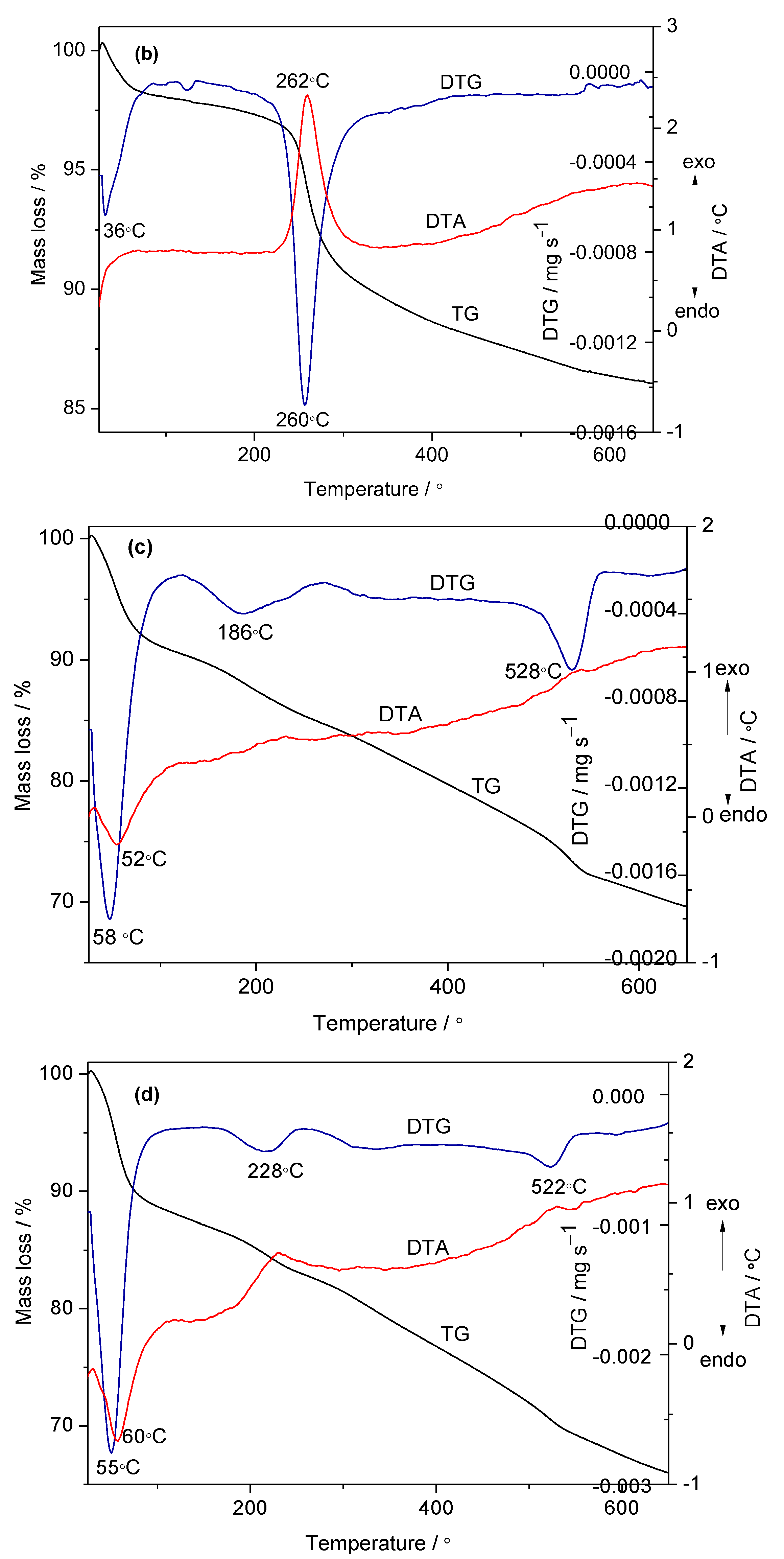
2.1. Physical—Chemical Characterization
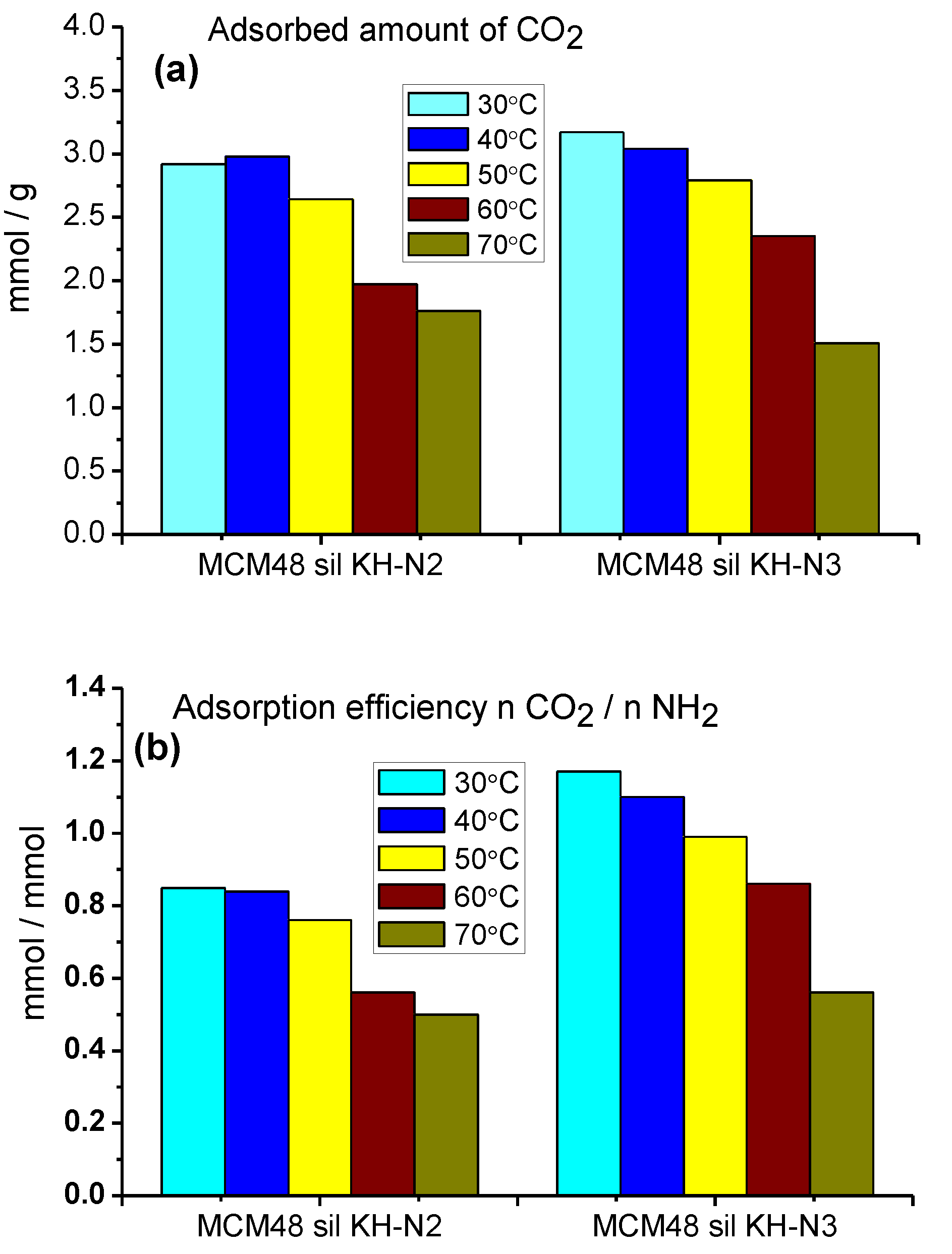
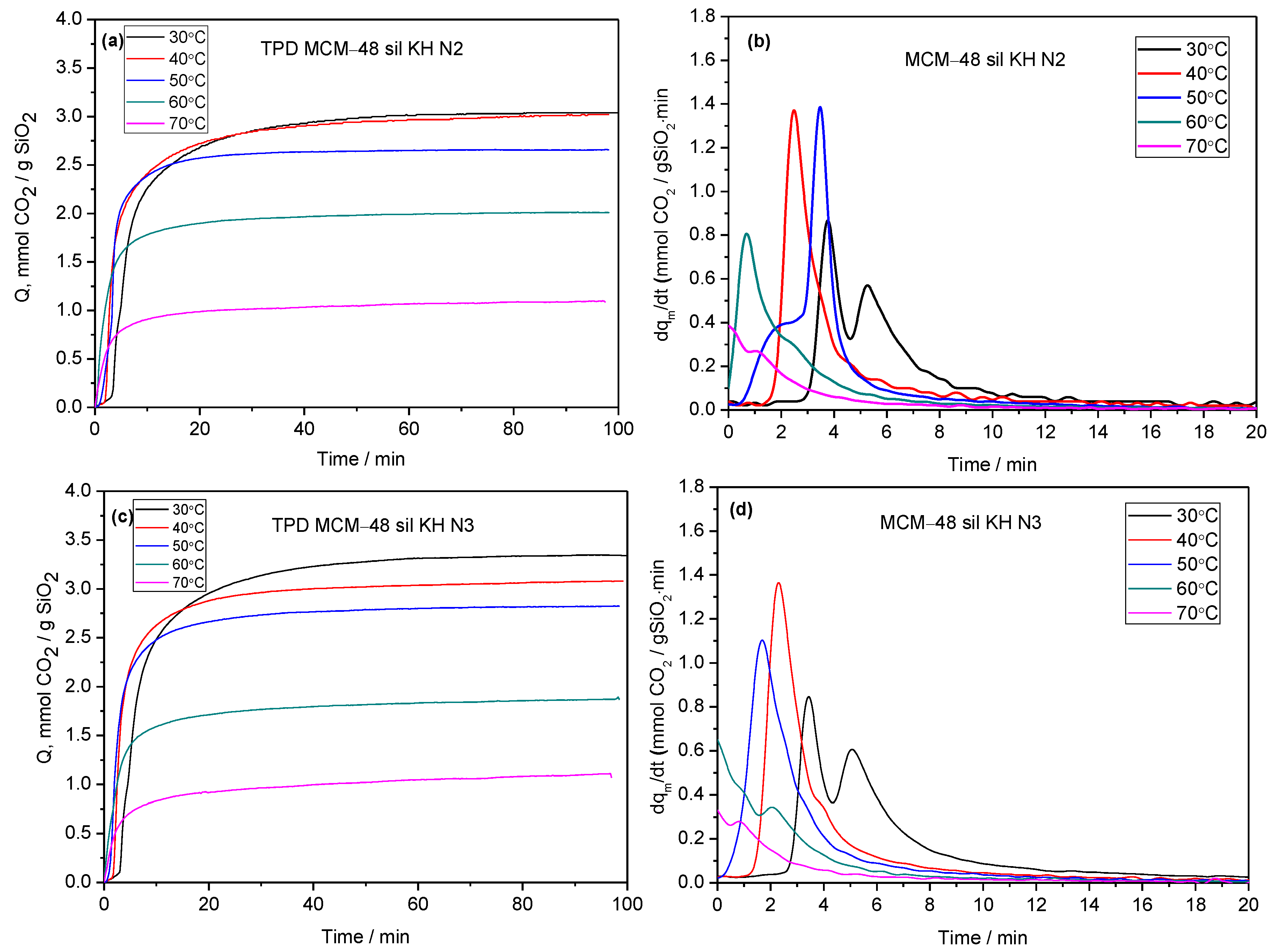
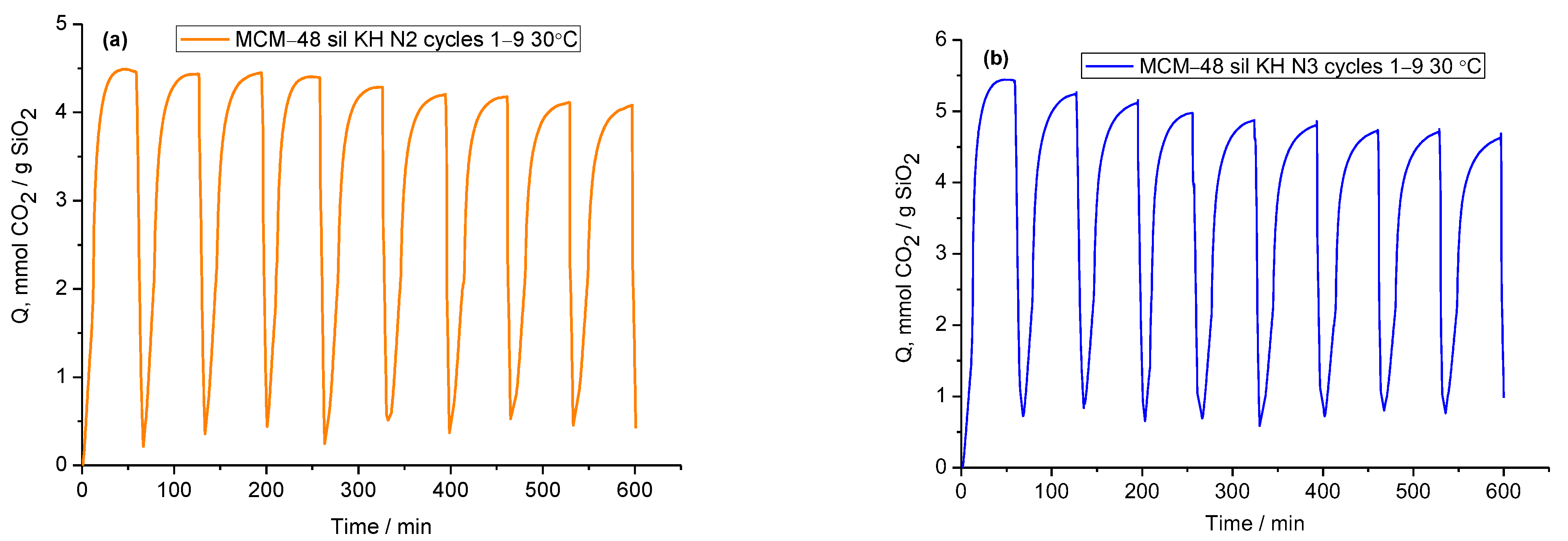
2.2. CO2 Adsorption–Desorption Measurements
3. Methods and Materials
3.1. Preparation of the Samples
3.2. Characterization of the Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yaacob, N.F.F.; Yazid, M.R.M.; Maulud, K.N.A.; Basri, N.E.A. A review of the measurement method, analysis and implementation policy of carbon dioxide emission from transportation. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fracaroli, A.M.; Furukawa, H.; Suzuki, M.; Dodd, M.; Okajima, S.; Gándara, F.; Reimer, J.A.; Yaghi, O.A. Metal–organic frameworks with precisely designed interior for carbon dioxide capture in the presence of water. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2014, 136, 8863–8866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Shi, X.C.; Tan, P.; Qi, S.C.; Gu, C.; Yang, T.; Peng, S.S.; Liu, S.Q.; Sun, L.B. Controllable CO2 capture in metal–organic frameworks: Making targeted active sites respond to light. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 21894–21900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, T.H.; Hudson, M.R.; Mason, J.A.; Queen, W.L.; Dutton, J.D.; Sumida, K.; Micklash, K.J.; Kaye, S.S.; Brown, C.M.; Long, J.R. Evaluation of cation-exchanged zeolite adsorbents for post-combustion carbon dioxide capture. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, B.; Elmegreen, B.; Kuroda, M.A.; Gu, Z.; Lin, G.; Zeng, S. Crown nanopores in graphene for CO2 capture and filtration. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 6274–6281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, X.Y.; Viriya, V.; Chew, T.L.; Oh, P.C.; Ong, Y.T.; Ho, C.D.; Jawad, Z.A. Synthesis, Characterization and gas adsorption of unfunctionalized and TEPA-functionalized MSU-2. Processes 2022, 10, 1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, C.; Ahn, W.-S. Recent progress on CO2 capture using amine-functionalized silica. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2019, 16, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vartuli, J.C.; Schmitt, S.D.; Krege, C.T.; Roth, W.J.; Leonowicz, M.E.; McCullen, S.B.; Hellring, S.D.; Beck, J.S.; Schlenker, J.L.; Olson, D.H.; et al. Effect of surfactant silica molar ratios on the formation of mesoporous molecular-sieves-inorganic mimicry of surfcatant liquid cristal phases and mechanistic implications. Chem. Mater. 1994, 6, 2317–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoen, A.H. Infinite Periodic Minimal Surfaces without Intersections; NASA Technnical Note TD-5541; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 1970.
- Schumacher, K.; Grun, M.; Unger, K.K. Novel synthesis of spherical MCM-48. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 1999, 27, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burleigh, M.C.; Markowitz, M.A.; Spector, M.S.; Gaber, B.P. Amine-functionalized periodic mesoporous organosilicas. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 4760–4766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loy, D.A.; Beach, J.V.; Baugher, B.M.; Assink, R.A.; Shea, K.J.; Tran, J.; Small, J. Dialkylene carbonate-bridged. Chem. Mater. 1999, 12, 3333–3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, M.; Tsunoji, N.; Sano, T. Mesoporous MCM-48 immobilized with aminopropyltriethoxysilane: A potential catalyst for transesterification of triacetin. Catal. Lett. 2014, 147, 1040–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Chen, Y.C.; Lu, X.; Ling, Y.; Lin, B. Facile preparation of mesoporous MCM-48 containing silver nanoparticles with fly ash as raw materials for co catalytic oxidation. Micromachines 2021, 12, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mureseanu, M.; Filip, M.; Somacescu, S.; Baran, A.; Carja, G.; Parvulescu, V. Ce, Ti modified MCM-48 mesoporous photocatalysts: Effect of the synthesis route on support and metal ion properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 444, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Yin, M.; Su, C.; Guo, N.; Huang, X.; Han, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, G.; Yun, Z. Recent developments in the field of dehydration of bio-renewable glycerol to acrolein over molecular sieve catalysts. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2023, 117, 85–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Ding, J.; Shao, R.; Xu, W.; Zhi Yun, Z. Dehydration of glycerol to acrolein over Wells–Dawson and Keggin type phosphotungstic acids supported on MCM-41 catalysts. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 316, 797–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.Y.; Yang, R.T.; Chinn, D.; Munson, C.L. Amine-grafted MCM-48 and silica xerogel as superior sorbents for acidic gas removal from natural gas. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2003, 42, 2427–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.T.; Park, Y.K.; Ko, Y.S.; Lee, Y.J.; Margandan, B. Highly siliceous MCM-48 from rice husk ash for CO2 adsorption. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control. 2009, 3, 545–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yismaw, S.; Ebbinghaus, S.G.; Wenzel, M.; Poppitz, D.; Gläser, R.; Matysik, J.; Bauer, F.; Enke, D. Selective functionalization of the outer surface of MCM-48-type mesoporous silica nanoparticles at room temperature. J. Nanopart. Res. 2020, 22, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, M.; Tiscornia, I.; Iglesia, Ó.; Mallada, R.; Santamaría, J. Monoamine-grafted MCM-48: An efficient material for CO2 removal at low partial pressures. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 175, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, D.; Dong, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Li, X.; Chu, Y.; Xu, J. Lead-free Cs2AgBiBr6 nanocrystals confined in MCM-48 mesoporous molecular sieve for efficient photocatalytic CO2 reduction. RRL Solar. 2023, 7, 2300038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.W.; Lee, W.J.; Nam, S.; Ryoo, H.; Kim, J.N.; Ko, C.H. Mesoporous structure control of silica in room-temperature synthesis under basic conditions. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 149654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, M.J.B.; Silva, A.O.S.; Aquino, J.M.F.B.; Fernandes, V.J., Jr.; Araujo, A.S. Thermal analysis applied to template removal from siliceous MCM-48 nanoporous material. J. Ther. Anal. Calorim. 2005, 79, 493–497. [Google Scholar]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.; Olivier, J.; Rodriquez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K. Physisorption of gases, with special references to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Tehnical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghomari, K.; Benhamou, A.; Hamacha, R.; Bengueddach, B.; Nousir, S.; Shiao, T.C.; Roy, R.; Azzouz, A. TPD and DSC insights in the basicity of MCM-48 like silica and modified counterparts. Thermochim. Acta 2015, 600, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suba, M.; Popa, A.; Verdeș, O.; Borcănescu, S.; Barvinschi, P. Ni and Ce grafted ordered mesoporous silica KIT-6 for CO2 adsorption. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borcanescu, S.; Popa, A.; Bajuk-Bogdanović, D.; Holclajtner-Antunović, I.; Uskoković-Marković, S. Amino-functionalized mesoporous materials used for CO2 adsorption. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2021, 20, 1893–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, R.; Calleja, G.; Arencibia, A.; Sanz-Perez, E.S. CO2 adsorption on branched polyethyleneimine-impregnated mesoporous silica SBA-15. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 5323–5328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caplow, M. Kinetics and carbamate formation and breakdown. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1968, 90, 6795–6803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreenivasulu, B.; Gayatri, D.V.; Sreedhar, I.; Raghavan, K.V. A journey into the process and engineering aspects of carbon capture technologies. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2015, 41, 1324–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, K.; Ravikovitch, P.I.; Chesne, A.D.; Neimark, A.V.; Unger, K.K. Characterization of MCM-48 materials. Langmuir 2000, 16, 4648–4654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagiyalakshmi, M.; Yun, L.J.; Anuradha, R.; Jang, H.T. Synthesis of chloropropylamine grafted mesoporous MCM-41, MCM-48 and SBA-15 from rice husk ash: Their application to CO2 chemisorption. J. Porous Mater. 2010, 17, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Yang, J.; Fei, Z.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X.; Tang, J.; Cui, M.; Qiao, X. A simple strategy to improve PEI dispersion on MCM-48 with long-alkyl chains template for efficient CO2 adsorption. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 10975–10983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, M.R.; Phanon, D.; Silveira, G.Q.; Llewellyn, P.L.; Ronconi, C.M. Amine-modified MCM-41 mesoporous silica for carbon dioxide capture. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2011, 143, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Mihra, A.; Samanta, A.N. Amine-impregnated MCM-41 in post-combustion CO2 capture: Synthesis, characterization, isotherm modelling. Adv. Powder Technol. 2019, 30, 3231–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melendez-Ortiz, H.I.; Perera-Mercado, Y.; Mercado-Silva, J.A.; Olivares-Maldonado, Y.; Castruita, G.; Garcia-Cerda, L.A. Functionalization with amine-containing organosilane of mesoporous silica MCM-41 and MCM-48 obtained at room temperature. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 9701–9707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| No. | Sample | Specific Surface Area (m2/g) | Pore Volume BJHDes (cc/g) | Average Pore Diameter BJHDes (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | MCM-48 | 1466.5 | 0.802 | 3.48 |
| 2. | MCM-48 sil KH | 652 | 0.295 | 3.91 |
| 3. | MCM-48 sil KH N2 | 419 | 0.211 | 3.93 |
| 4. | MCM-48 sil KH N3 | 505.3 | 0.251 | 3.23 |
| Support | Amine Type | Adsorption Conditions | CO2 Adsorption Capacity (mmol CO2/g ads) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCM-48 | APTES | 25 °C, up to 1 bar CO2 | 2.05 | Huang et al. [18] |
| SBA-15 | CPA | 25 °C, up to 1 bar CO2 | 1.50 | Bhagiyalakshmi et al. [32] |
| MCM-48 | 1.10 | |||
| MCM-41 | 1.70 | |||
| Si-MCM-41 | MEA DEA TEA | 25 °C, up to 1 bar pure CO2 | 0.46–0.65 | Mello et al. [35] |
| MCM-41 | APTES | 20 °C, up to 1 bar CO2 | 0.78 | Mukherjee et al. [36] |
| MEA | 25–60 °C, up to 1 bar CO2 | 1.71 | ||
| BZA | 0.66 | |||
| AEEA | 1.07 | |||
| MCM-48 | PEI | 25 °C, up to 1 bar pure CO2 | 2.59 | Qian et al. (2019) [34] |
| MCM-48 sil KH N2 | EDA | 30 °C, up to 1 bar CO2 | 2.92 | This work |
| MCM-48 sil KH N3 | DETA | 30 °C, up to 1 bar CO2 | 3.17 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Borcănescu, S.; Popa, A.; Verdeș, O.; Suba, M. Functionalized Ordered Mesoporous MCM-48 Silica: Synthesis, Characterization and Adsorbent for CO2 Capture. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10345. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241210345
Borcănescu S, Popa A, Verdeș O, Suba M. Functionalized Ordered Mesoporous MCM-48 Silica: Synthesis, Characterization and Adsorbent for CO2 Capture. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(12):10345. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241210345
Chicago/Turabian StyleBorcănescu, Silvana, Alexandru Popa, Orsina Verdeș, and Mariana Suba. 2023. "Functionalized Ordered Mesoporous MCM-48 Silica: Synthesis, Characterization and Adsorbent for CO2 Capture" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 12: 10345. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241210345
APA StyleBorcănescu, S., Popa, A., Verdeș, O., & Suba, M. (2023). Functionalized Ordered Mesoporous MCM-48 Silica: Synthesis, Characterization and Adsorbent for CO2 Capture. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(12), 10345. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241210345