A New Structural Model of Apolipoprotein B100 Based on Computational Modeling and Cross Linking
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
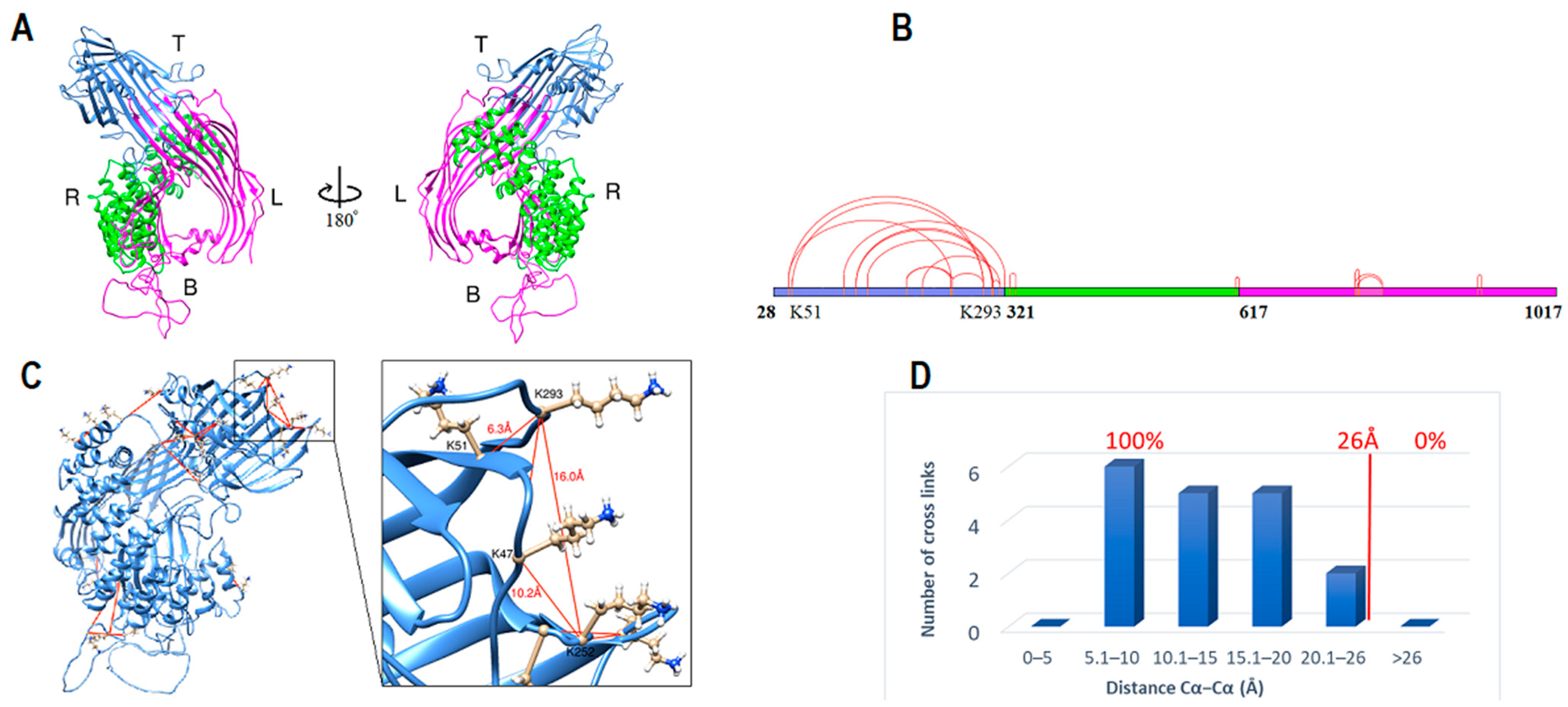
2.1. ApoB-100 Subunit I Homology Modeling
2.2. Subunit II Modeling
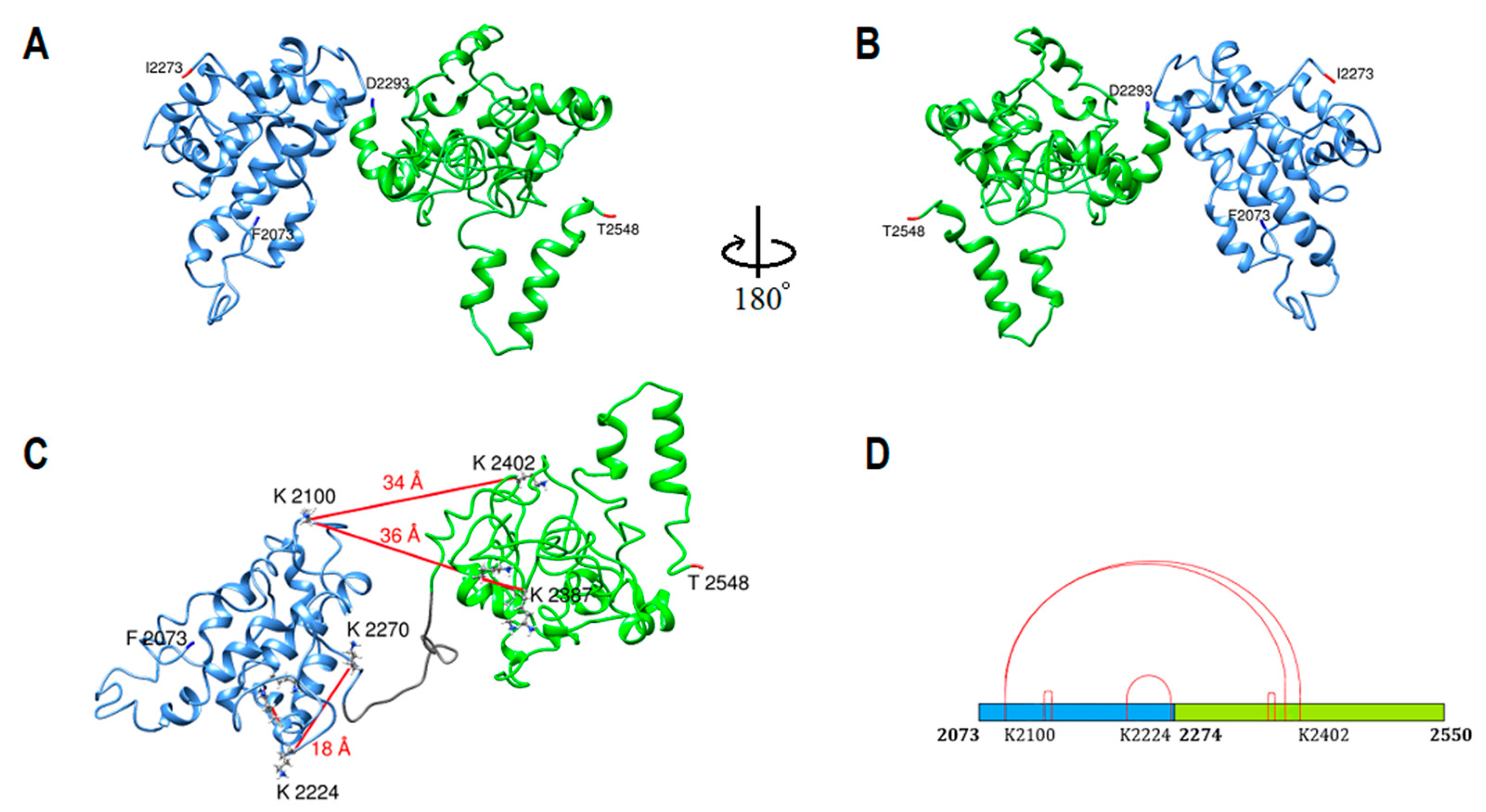
2.3. Subunit III Homology Modeling
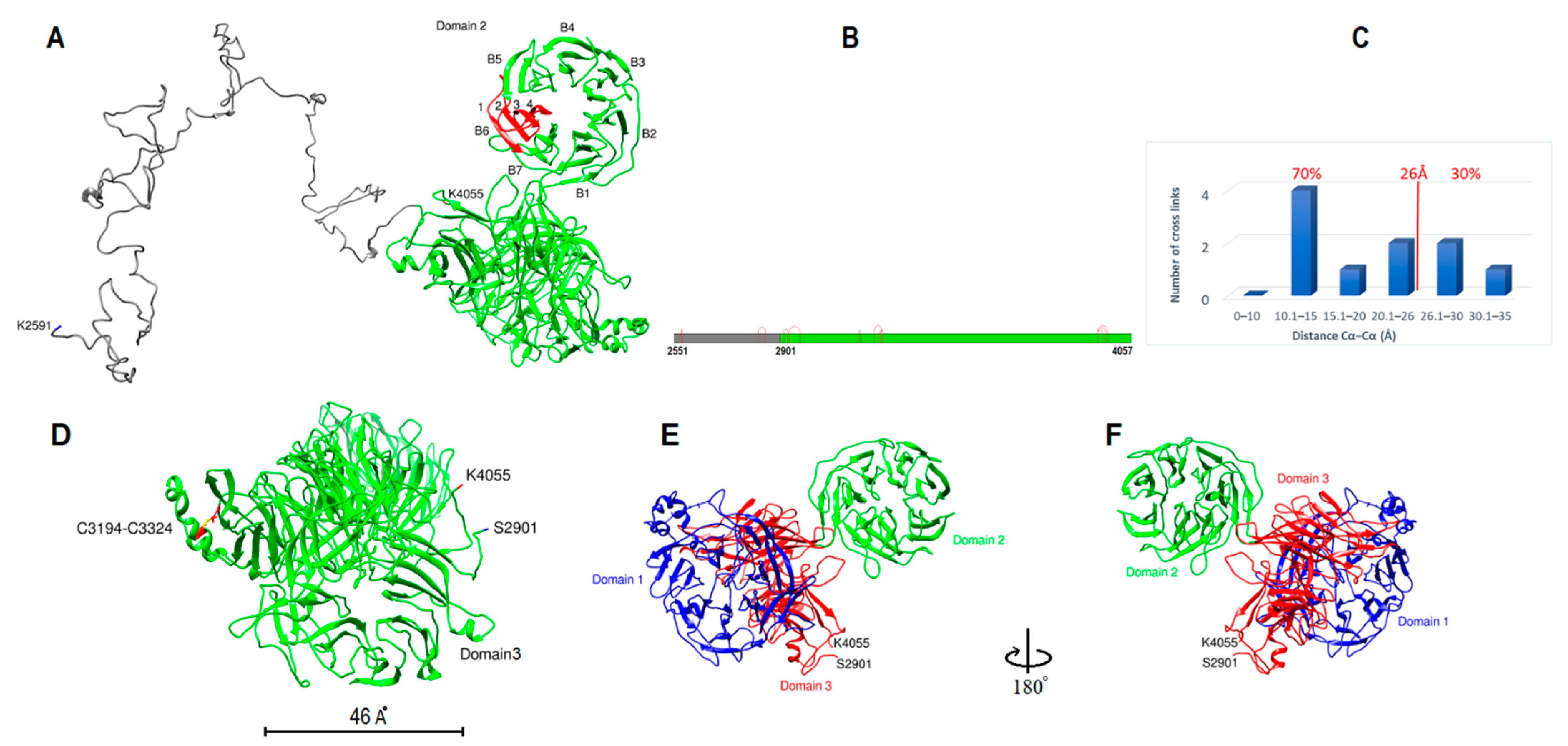
2.4. Subunit IV Modeling
2.5. Subunit V Homology Modeling
2.6. Domain Boundaries Prediction and Secondary Structure Determination
2.7. Sequence and Structural Comparison to Lipovitellin
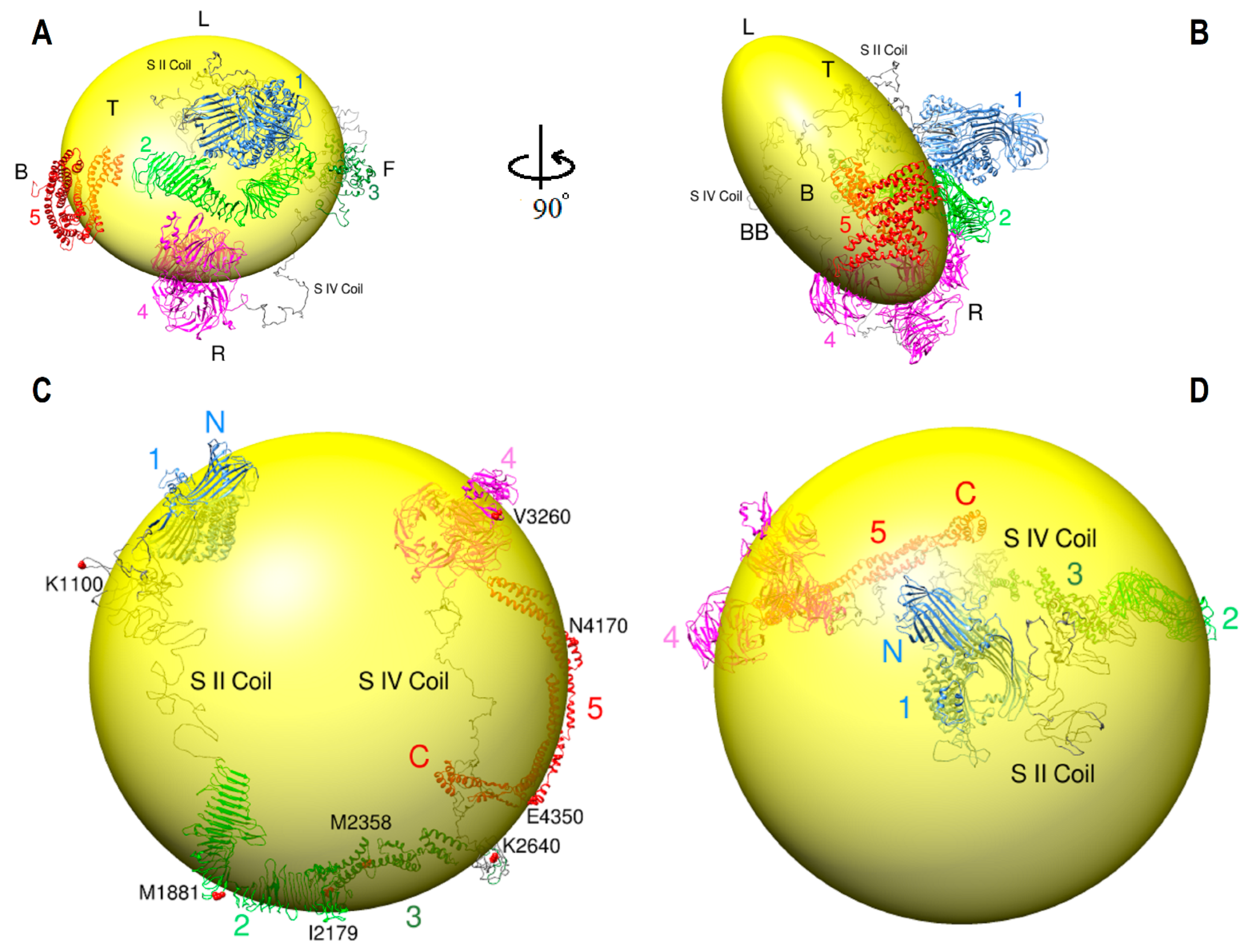
2.8. ApoB-100 Architecture and Dynamics
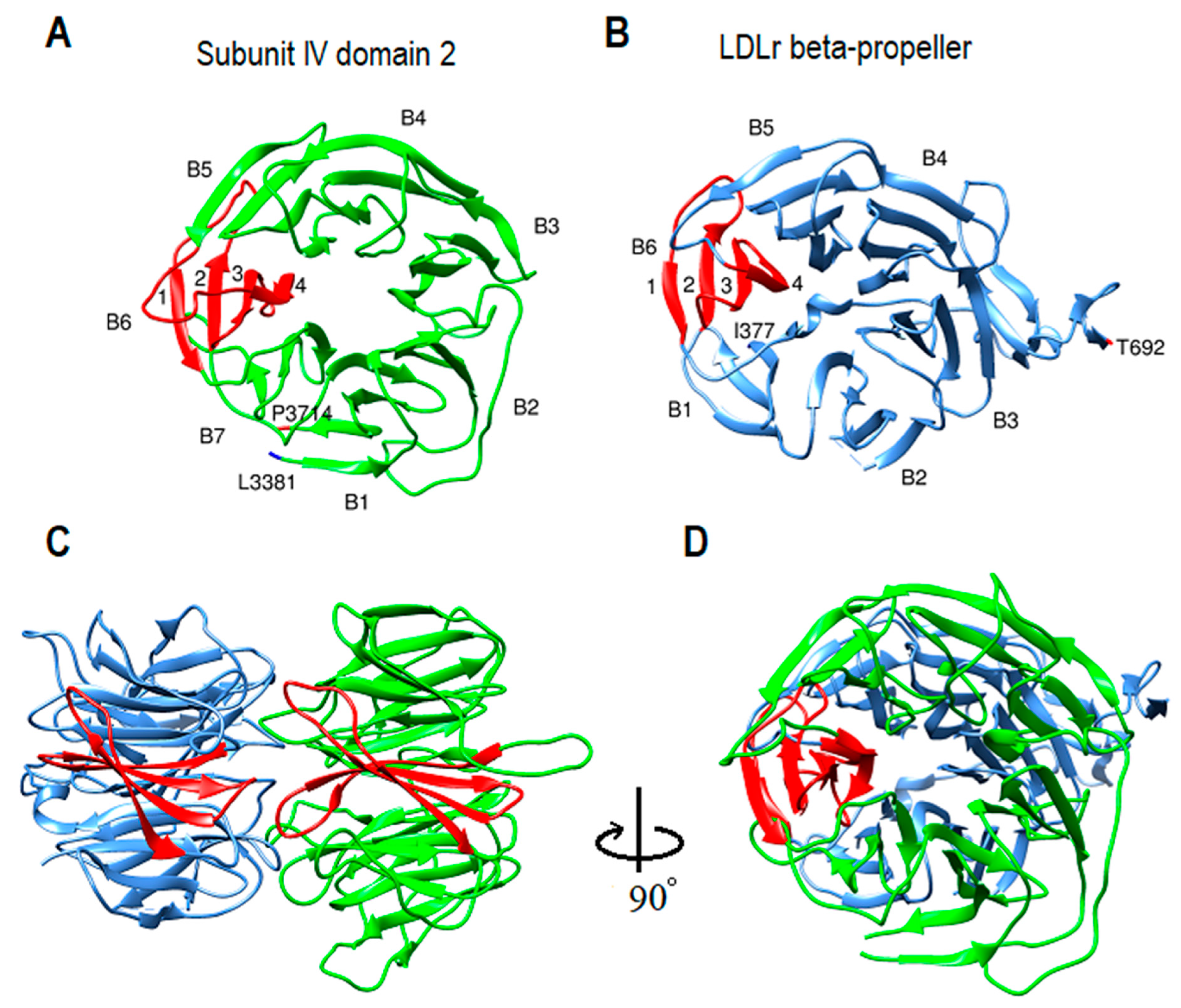
2.9. β-propeller Folds and Apob-100 Docking Region
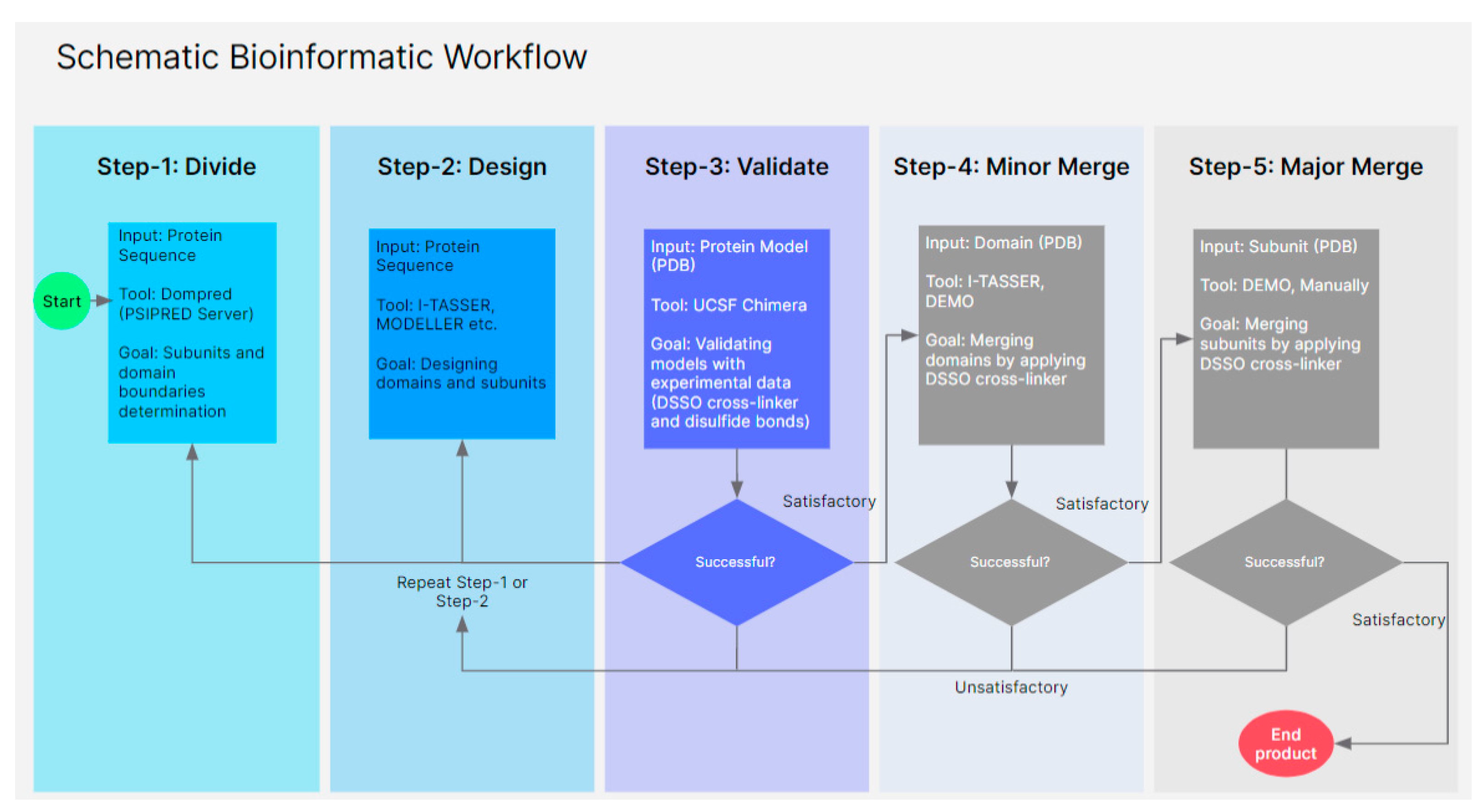
3. Methods and Materials
3.1. Sequences and Domain Prediction
3.2. Database Search and Modeling
3.3. Plasma Lipoprotein Separation by Sequential Ultracentrifugation
3.4. Cross-Linking Assay
3.5. Sample Preparation for Mass Spectrometry with Double Trypsin Digestion
3.6. Mass Spectrometry
3.7. Mass Spectrometry Data Analysis
3.8. Protein Painting
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olofsson, S.-O.; Boren, J. Apolipoprotein B: A clinically important apolipoprotein which assembles atherogenic lipoproteins and promotes the development of atherosclerosis. J. Intern. Med. 2005, 258, 395–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, J.L.; Brown, M.S. A Century of Cholesterol and Coronaries: From Plaques to Genes to Statins. Cell 2015, 161, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bochkov, V.N.; Tkachuk, V.; Kuzmenko, Y.S.; Borisova, Y.L.; Bühler, F.R.; Resink, T.J. Characteristics of low and high density lipoprotein binding and lipoprotein-induced signaling in quiescent human vascular smooth muscle cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 1994, 45, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sidorkiewicz, M. Hepatitis C Virus Uses Host Lipids to Its Own Advantage. Metabolites 2021, 11, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pian, M.S.; Dobbs, L.G. Lipoprotein-stimulated surfactant secretion in alveolar type II cells: Mediation by heterotrimeric G proteins. Am. J. Physiol. Content 1997, 273, L634–L639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voyno-Yasenetskaya, T.A.; Dobbs, L.G.; Erickson, S.K.; Hamilton, R.L. Low density lipoprotein- and high density lipoprotein-mediated signal transduction and exocytosis in alveolar type II cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 4256–4260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cladaras, C.; Hadzopoulou-Cladaras, M.; Nolte, R.T.; Atkinson, D.; Zannis, V.I. The complete sequence and structural analysis of human apolipoprotein B-100: Relationship between apoB-100 and apoB-48 forms. EMBO J. 1986, 5, 3495–3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knott, T.J.; Pease, R.J.; Powell, L.M.; Wallis, S.C.; Rall, S.C., Jr.; Innerarity, T.L.; Blackhart, B.; Taylor, W.H.; Marcel, Y.; Milne, R.; et al. Complete protein sequence and identification of structural domains of human apolipoprotein B. Nature 1986, 323, 734–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-H.; Habib, G.; Yang, C.-Y.; Gu, Z.-W.; Lee, B.R.; Weng, S.-A.; Silberman, S.R.; Cai, S.-J.; Deslypere, J.P.; Rosseneu, M.; et al. Apolipoprotein B-48 Is the Product of a Messenger RNA with an Organ-Specific In-Frame Stop Codon. Science 1987, 238, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolenaars, M.M.; Madsen, O.; Rodenburg, K.W.; Van der Horst, D.J. Molecular diversity and evolution of the large lipid transfer protein superfamilys. J. Lipid Res. 2007, 48, 489–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelness, G.S.; Ledford, A.S. Evolution and mechanism of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoprotein assembly. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2005, 16, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biterova, E.I.; Isupov, M.N.; Keegan, R.M.; Lebedev, A.A.; Sohail, A.A.; Liaqat, I.; Alanen, H.I.; Ruddock, L.W. The crystal structure of human microsomal triglyceride transfer protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 17251–17260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, M.E. Is vitellogenin an ancestor of apolipoprotein B-100 of human low-density lipoprotein and human lipoprotein lipase? Biochem. J. 1988, 255, 1057–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raag, R.; Appelt, K.; Xuong, N.-H.; Banaszak, L. Structure of the lamprey yolk lipid-protein complex lipovitellin-phosvitin at 2.8 Å resolution. J. Mol. Biol. 1988, 200, 553–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmins, P.A.; Poliks, B.; Banaszak, L. The Location of Bound Lipid in the Lipovitellin Complex. Science 1992, 257, 652–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, C.J.; Anderson, T.A.; Read, J.; Chester, S.; Harrison, G.B.; Köchl, S.; Ritchie, P.J.; Bradbury, P.; Hussain, F.S.; Amey, J.; et al. The structure of vitellogenin provides a molecular model for the assembly and secretion of atherogenic lipoproteins. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 285, 391–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segrest, J.P.; Jones, M.K.; Dashti, N. N-terminal domain of apolipoprotein B has structural homology to lipovitellin and microsomal triglyceride transfer protein: A “lipid pocket” model for self-assembly of apob-containing lipoprotein particles. J. Lipid Res. 1999, 40, 1401–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, P.E.; Manchekar, M.; Dashti, N.; Jones, M.K.; Beigneux, A.; Young, S.; Harvey, S.C.; Segrest, J.P. Assembly of Lipoprotein Particles Containing Apolipoprotein-B: Structural Model for the Nascent Lipoprotein Particle. Biophys. J. 2005, 88, 2789–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriško, A.; Etchebest, C. Theoretical model of human apolipoprotein B100 tertiary structure. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2006, 66, 342–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Atkinson, D. Enhancing the Contrast of ApoB to Locate the Surface Components in the 3D Density Map of Human LDL. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 405, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Rudenko, G.; Ludtke, S.J.; Deisenhofer, J.; Chiu, W.; Pownall, H.J. Model of human low-density lipoprotein and bound receptor based on CryoEM. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 107, 1059–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, D.; Yu, Y.; Kuang, Y.L.; Liu, J.; Krauss, R.M.; Ren, G. Single-molecule 3D imaging of human plasma intermediate-density lipoproteins reveals a polyhedral structure. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2019, 1864, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Antwerpen, R.; La Belle, M.; Navratilova, E.; Krauss, R.M. Structural heterogeneity of apoB-containing serum lipoproteins visualized using cryo-electron microscopy. J. Lipid Res. 1999, 40, 1827–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryson, K.; Cozzetto, D.; Jones, D.T. Computer-assisted protein domain boundary prediction using the Dom-Pred server. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2007, 8, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchan, D.W.; Jones, D.T. The PSIPRED protein analysis workbench: 20 years on. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W402–W407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, L.; Stephens, A.; Nam, S.-Z.; Rau, D.; Kübler, J.; Lozajic, M.; Gabler, F.; Söding, J.; Lupas, A.N.; Alva, V. A Completely Reimplemented MPI Bioinformatics Toolkit with a New HHpred Server at its Core. J. Mol. Biol. 2018, 430, 2237–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabler, F.; Nam, S.; Till, S.; Mirdita, M.; Steinegger, M.; Söding, J.; Lupas, A.N.; Alva, V. Protein Sequence Analysis Using the MPI Bioinformatics Toolkit. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2020, 72, e108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrand, A.; Remmert, M.; Biegert, A.; Söding, J. Fast and accurate automatic structure prediction with HHpred. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2009, 77, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, B.; Sali, A. Comparative Protein Structure Modeling Using MODELLER. Curr. Protoc. Protein Sci. 2016, 86, 2.9.1–2.9.37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Y. I-TASSER server: New development for protein structure and function predictions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W174–W181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Freddolino, P.L.; Zhang, Y. COFACTOR: Improved protein function prediction by combining structure, sequence and protein–protein interaction information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W291–W299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, C.B.; Yu, C.; Novitsky, E.J.; Huszagh, A.S.; Rychnovsky, S.D.; Huang, L. Developing an Acidic Residue Reactive and Sulfoxide-Containing MS-Cleavable Homobifunctional Cross-Linker for Probing Protein–Protein Interactions. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 8315–8322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, A.; Chiu, C.-L.; Vellucci, D.; Yang, Y.; Patel, V.R.; Guan, S.; Randall, A.; Baldi, P.; Rychnovsky, S.D.; Huang, L. Development of a Novel Cross-linking Strategy for Fast and Accurate Identification of Cross-linked Peptides of Protein Complexes. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2011, 10, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapovalov, M.V.; Dunbrack, R.L., Jr. A smoothed backbone-dependent rotamer library for proteins derived from adaptive kernel density estimates and regressions. Structure 2011, 19, 844–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera? A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.Y.; Kim, T.W.; Weng, S.A.; Lee, B.R.; Yang, M.L.; Gotto, A.M., Jr. Isolation and characterization of sulfhydryl and disulfide peptides of human apolipoprotein B-100. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 5523–5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biegert, A.; Söding, J. De novo identification of highly diverged protein repeats by probabilistic consistency. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Hu, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y. Assembling multidomain protein structures through analogous global structural alignments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 15930–15938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Zhang, Y. Improving the Physical Realism and Structural Accuracy of Protein Models by a Two-Step Atomic-Level Energy Minimization. Biophys. J. 2011, 101, 2525–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bañuelos, S.; Arrondo, J.L.R.; Goi, F.M.; Pifat, G. Surface-Core Relationships in Human Low Density Lipoprotein as Studied by Infrared Spectroscopy. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 9192–9196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.C.; Chapman, M.J.; Klane, J.P. Secondary structure and thermal behavior of trypsin-treated low-density lipoproteins from human serum, studied by circular dichroism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Lipids Lipid Metab. 1983, 754, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goormaghtigh, E.; De Meutter, J.; Vanloo, B.; Brassuer, R.; Rosseneu, M.; Ruysschaert, J.-M. Evaluation of the secondary structure of apo B-100 in low-density lipoprotein (LDL) by infrared spectroscopy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Lipids Lipid Metab. 1989, 1006, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.R.; Banaszak, L.J. Lipid−protein interactions in lipovitellin. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 9398–9409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, T.A.; Levitt, D.G.; Banaszak, L.J. The structural basis of lipid interactions in lipovitellin, a soluble lipoprotein. Structure 1998, 6, 895–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banaszak, L.; Sharrock, W.; Timmins, P. Structure and Function of a Lipoprotein: Lipovitellin. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biophys. Chem. 1991, 20, 221–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, B.M.; Gruber, M.A.B.G.; Ab, G. The evolution of egg yolk proteins. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 1989, 53, 33–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharrock, W.J.; Rosenwasser, T.A.; Gould, J.; Knott, J.; Hussey, D.; Gordon, J.I.; Banaszak, L. Sequence of lamprey vitellogenin: Implications for the lipovitellin crystal structure. J. Mol. Biol. 1992, 226, 903–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, M.; DiMaio, F.; Anishchenko, I.; Dauparas, J.; Ovchinnikov, S.; Lee, G.R.; Wang, J.; Cong, Q.; Kinch, L.N.; Schaeffer, R.D.; et al. Accurate prediction of protein structures and interactions using a three-track neural network. Science 2021, 373, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterton, J.E.; Phillips, M.L.; Curtiss, L.K.; Milne, R.; Fruchart, J.C.; Schumaker, V.N. Immunoelectron microscopy of low density lipoproteins yields a ribbon and bow model for the conformation of apolipoprotein B on the lipoprotein surface. J. Lipid Res. 1995, 36, 2027–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Walsh, M.T.; Small, D.M. Apolipoprotein B is conformationally flexible but anchored at a triolein/water interface: A possible model for lipoprotein surfaces. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 6871–6876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fath, S.; Mancias, J.D.; Bi, X.; Goldberg, J. Structure and Organization of Coat Proteins in the COPII Cage. Cell 2007, 129, 1325–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chufán, E.E.; De, M.; Eipper, B.A.; Mains, R.E.; Amzel, L.M. Amidation of Bioactive Peptides: The Structure of the Lyase Domain of the Amidating Enzyme. Structure 2009, 17, 965–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujihashi, M.; Peapus, D.H.; Kamiya, N.; Nagata, Y.; Miki, K. Crystal Structure of Fucose-Specific Lectin from Aleuria aurantia Binding Ligands at Three of Its Five Sugar Recognition Sites. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 11093–11099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abergel, C.; Bouveret, E.; Claverie, J.-M.; Brown, K.; Rigal, A.; Lazdunski, C.; Bénédetti, H. Structure of the Escherichia coli TolB protein determined by MAD methods at 1.95 Å resolution. Structure 1999, 7, 1291–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-N.; Chin, K.-H.; Wang, A.H.-J.; Chou, S.-H. The First Crystal Structure of Gluconolactonase Important in the Glucose Secondary Metabolic Pathways. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 384, 604–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosanac, I.; Maun, H.R.; Scales, S.; Wen, X.; Lingel, A.; Bazan, J.F.; De Sauvage, F.J.; Hymowitz, S.G.A.; Lazarus, R. The structure of SHH in complex with HHIP reveals a recognition role for the Shh pseudo active site in signaling. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2009, 16, 691–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.K.-M.; Chan, N.-L.; Wang, A.H.-J. The many blades of the β-propeller proteins: Conserved but versatile. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2011, 36, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guevara, J.; Prashad, N.; Ermolinsky, B.; Gaubatz, J.W.; Kang, D.; Schwarzbach, A.E.; Loose, D.S.; Guevara, N.V. Apo B100 similarities to viral proteins suggest basis for LDL-DNA binding and transfection capacity. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 1704–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banfi, C.; Brioschi, M.; Barcella, S.; Wait, R.; Begum, S.; Galli, S.; Rizzi, A.; Tremoli, E. Proteomic analysis of human low-density lipoprotein reveals the presence of prenylcysteine lyase, a hydrogen peroxide-generating enzyme. Proteomics 2009, 9, 1344–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, H.; Meng, W.; Takagi, J.; Eck, M.J.; Springer, T.A.; Blacklow, S.C. Implications for familial hypercholesterolemia from the structure of the LDL receptor YWTD-EGF domain pair. Nat. Genet. 2001, 8, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milne, R.; Theolis, R., Jr.; Maurice, R.; Pease, R.J.; Weech, P.K.; Rassart, E.; Fruchart, J.C.; Scott, J.; Marcel, Y.L. The use of monoclonal antibodies to localize the low density lipoprotein receptor-binding domain of apolipoprotein B. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 19754–19760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Henry, L.; Ho, Y.K.; Pownall, H.J.; Rudenko, G. Mechanism of LDL binding and release probed by structure-based mutagenesis of the LDL receptor. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Consortium, T.; Bateman, A.; Martin, M.-J.; Orchard, S.; Magrane, M.; Agivetova, R.; Ahmad, S.; Alpi, E.; Bow-ler-Barnett, E.H.; The UniProt Consortium. UniProt: The universal protein knowledgebase in 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D480–D489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Kucukural, A.; Zhang, Y. I-TASSER: A unified platform for automated protein structure and function prediction. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 725–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y. I-TASSER server for protein 3D structure prediction. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, S.L.; Mezulis, C.; Yates, W.-M. The Phyre2 web portal for protein modeling, prediction and analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 845–858. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schumaker, V.N.; Puppione, D.L. Sequential flotation ultracentrifugation[M]//Methods in enzymology. Methods Enzym. 1986, 128, 155–170. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Lössl, P.; Scheltema, R.; Viner, R.; Heck, A.J.R. Optimized fragmentation schemes and data analysis strategies for proteome-wide cross-link identification. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haymond, A.; Dey, D.; Carter, R.; Dailing, A.; Nara, V.; Nara, P.; Luchini, A. Protein painting, an optimized MS-based technique, reveals functionally relevant interfaces of the PD-1/PD-L1 complex and the YAP2/ZO-1 complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 11180–11198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segrest, J.P.; Jones, M.K.; De Loof, H.; Dashti, N. Structure of apolipoprotein B-100 in low density lipoproteins. J. Lipid Res. 2001, 42, 1346–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| PDB ID/Chain | Molecule | Classification | Probability | E-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1LSH_A | Lipovitellin | Lipid binding protein | 100.0 | 4 × 10−107 | 5 × 10−112 |
| 6I7S_G | Microsomal triglyceride transfer protein | Lipid transport | 100.0 | 1 × 10−73 | 1.3 × 10−78 |
| 4D50_A | Deoxyhypusine hydroxylase | Oxidoreductase | 98.0 | 0.0062 | 8.1 × 10−8 |
| 5N3U_A | Phycocyanobilin lyase | Lyase | 97.2 | 0.11 | 1.4 × 10−6 |
| 4XL5_C | bGFP-A | Protein binding | 97.0 | 0.56 | 7.3 × 10−6 |
| 6QH5_A | AP-2 complex subunit alpha | Protein transport | 97.0 | 0.33 | 4.2 × 10−6 |
| 4L7M_B | Putative uncharacterized protein | Unknown function | 96.9 | 0.38 | 5 × 10−6 |
| 5NZR_K | Coatomer subunit gamma-1 | Transport protein | 96.9 | 0.54 | 7 × 10−6 |
| 5FUR_I | Transcription initiation factor TFIID | Transcription | 96.8 | 0.057 | 7.4 × 10−7 |
| 6QH5_B | AP-2 complex subunit beta | Protein transport | 96.8 | 0.92 | 1.2 × 10−5 |
| 2DB0_B | 253aa long hypothetical protein | Protein binding | 96.7 | 0.62 | 8 × 10−6 |
| 6YAF_B | AP-2 complex subunit beta | Endocytosis | 96.7 | 0.41 | 5.3 × 10−6 |
| 6GWC_C | IE5 ALPHAREP | Cell cycle | 96.7 | 0.81 | 1 × 10−5 |
| 1JDH_A | Beta-catenin | Transcription | 96.4 | 0.87 | 1.1 × 10−5 |
| 5XJG_A | Vacuolar protein 8 | Signaling protein | 96.3 | 0.48 | 6.3 × 10−6 |
| 5N3U_B | Phycocyanobilin lyase subunit beta | Lyase | 96.3 | 0.27 | 3.6 × 10−6 |
| 1OYZ_A | Hypothetical protein yibA | Structural genomics | 95.4 | 0.69 | 9 × 10−6 |
| 1TE4_A | Conserved protein MTH187 | Structural genomics | 95.3 | 0.72 | 9.3 × 10−6 |
| PDB ID/Chain | Molecule | Classification | Probability | E-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2L7B_A | Apolipoprotein E | Lipid transport | 96.2 | 1.1 | 2 × 10−5 |
| 1LS4_A | Apolipophorin III | Lipid transport | 96.0 | 0.98 | 1.7 × 10−5 |
| 3R2P_A | Apolipoprotein A-I | Lipid transport | 95.9 | 0.91 | 1.6 × 10−5 |
| 3R2P_A | Apolipoprotein A-I | Lipid transport | 96.8 | 0.37 | 6.4 × 10−6 |
| 2L7B_A | Apolipoprotein E | Lipid transport | 96.4 | 1.00 | 1.8 × 10−5 |
| 5VJ4_A | Uncharacterized protein | Lipid binding protein | 96.4 | 0.58 | 1 × 10−5 |
| 2LEM_A | Apolipoprotein A-I | Lipid transport | 96.2 | 0.99 | 1.7 × 10−5 |
| PDB ID/Chain | Molecule | Classification | Probability | E-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1EQ1_A | Apolipophorin III | Lipid binding protein | 93.44 | 4 | 7 × 10−5 |
| 1KMI_Z | Chemotaxis protein | Signaling protein | 91.98 | 6.7 | 1.2 × 10−4 |
| 2L7B_A | Apolipoprotein E | Lipid transport | 97.6 | 0.14 | 2.5 × 10−6 |
| 3S84_A | Apolipoprotein A-IV | Transport protein | 97.3 | 0.27 | 4.7 × 10−6 |
| 2LEM_A | Apolipoprotein A-I | Lipid transport | 97.1 | 0.24 | 4.1 × 10−6 |
| 3K2S_B | Apolipoprotein A-I | Lipid binding protein | 96.9 | 0.64 | 1.1 × 10−5 |
| 3R2P_A | Apolipoprotein A-I | Lipid transport | 96.6 | 0.72 | 1.3 × 10−5 |
| Subunit/Domain | Residue Number | α-Helix (Percentage of Total Content) | β-Strand (Percentage of Total Content) | Coil (Percentage of Total Content) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subunit I | 28–1017 | 7% | 6.5% | ~8% |
| Subunit II | 1018–2072 | <0.5% | 12.5% | 10.5% |
| Subunit III | 2073–2550 | ~5.0% | 0% | ~5.0% |
| Subunit IV | 2551–4057 | ~1% | 22% | 10.5% |
| Subunit V | 4058–4563 | ~10.5% | 0% | ~1% |
| Total | 28–4563 | ~24% | 41% | 35% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeiran, K.; Gordon, S.M.; Sviridov, D.O.; Aponte, A.M.; Haymond, A.; Piszczek, G.; Lucero, D.; Neufeld, E.B.; Vaisman, I.I.; Liotta, L.; et al. A New Structural Model of Apolipoprotein B100 Based on Computational Modeling and Cross Linking. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11480. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911480
Jeiran K, Gordon SM, Sviridov DO, Aponte AM, Haymond A, Piszczek G, Lucero D, Neufeld EB, Vaisman II, Liotta L, et al. A New Structural Model of Apolipoprotein B100 Based on Computational Modeling and Cross Linking. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(19):11480. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911480
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeiran, Kianoush, Scott M. Gordon, Denis O. Sviridov, Angel M. Aponte, Amanda Haymond, Grzegorz Piszczek, Diego Lucero, Edward B. Neufeld, Iosif I. Vaisman, Lance Liotta, and et al. 2022. "A New Structural Model of Apolipoprotein B100 Based on Computational Modeling and Cross Linking" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 19: 11480. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911480
APA StyleJeiran, K., Gordon, S. M., Sviridov, D. O., Aponte, A. M., Haymond, A., Piszczek, G., Lucero, D., Neufeld, E. B., Vaisman, I. I., Liotta, L., Baranova, A., & Remaley, A. T. (2022). A New Structural Model of Apolipoprotein B100 Based on Computational Modeling and Cross Linking. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(19), 11480. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911480










