Abstract
Mitochondria are the largest source of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and are intracellular organelles that produce large amounts of the most potent hydroxyl radical (·OH). Molecular hydrogen (H2) can selectively eliminate ·OH generated inside of the mitochondria. Inflammation is induced by the release of proinflammatory cytokines produced by macrophages and neutrophils. However, an uncontrolled or exaggerated response often occurs, resulting in severe inflammation that can lead to acute or chronic inflammatory diseases. Recent studies have reported that ROS activate NLRP3 inflammasomes, and that this stimulation triggers the production of proinflammatory cytokines. It has been shown in literature that H2 can be based on the mechanisms that inhibit mitochondrial ROS. However, the ability for H2 to inhibit NLRP3 inflammasome activation via mitochondrial oxidation is poorly understood. In this review, we hypothesize a possible mechanism by which H2 inhibits mitochondrial oxidation. Medical applications of H2 may solve the problem of many chronic inflammation-based diseases, including coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
1. Introduction
Inflammation is induced by the release of proinflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-18, produced by macrophages and neutrophils in direct response to a triggering stimulus. Normally, the production of these cytokines is transient; however, if the cytokines are continuously produced by some disturbance, the inflammation can be delayed and chronic inflammation may develop. Minor but prolonged inflammation can damage the living body and induce chronic inflammation. Recent studies have shown that mitochondria play a key role in producing IL-1β and IL-18 [1]. It has also been reported that mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) activate the nucleotide-binding and oligomerization domain-like receptor family pyrin, which contains a complex of intracellular proteins known as 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome, and that its stimulation triggers the production of inflammatory cytokines [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11].
The mitochondrial selective hydroxyl radical (·OH) scavenger may block the cascade leading to the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome in the human body, because a large amount of ·OH can be produced in the mitochondria [12]. Modern medical treatment can control acute inflammatory diseases, but it cannot control chronic inflammatory diseases. Attempts have been made to develop effective therapeutics to control chronic inflammatory diseases, but their development strategies have been unsatisfactory, because they are not based on the underlying mechanisms of chronic inflammatory diseases.
Molecular hydrogen (H2) is an antioxidant that can selectively scavenge ·OH, which is the most potent oxidant among ROS [12]. Among the homonuclear diatomic molecules (N2, O2, etc.) that can permeate the cell membrane, only H2 is able to scavenge ·OH, which is always generated inside of mitochondria [13,14]. It has been shown by literature that H2 in various animal models of inflammation may be based on mechanisms to inhibit mitochondrial oxidation and NLRP3 inflammasome activation [15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23]. However, the ability for H2 to inhibit mitochondrial oxidation and NLRP3 inflammasome activation is poorly understood. In this review, we will propose a possible mechanism by which H2 inhibits NLRP3 activation via the inhibition of mitochondrial oxidation and then present a perspective on the potential effects of H2 on chronic inflammatory diseases including coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Furthermore, since senescence is a part of chronic inflammation, we will mention the potential of H2 to control senescence.
2. Mitochondrial Roles in the Regulation of Inflammation
Inflammation is considered to be one of the immediate responses of the innate immune system. Inflammation is triggered by the invasion of pathogens or by mechanical damage to cells and tissues. These responses are recognized by pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), which include toll-like receptors (TLRs) attached to the cell membrane or nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptors (NLRs) presented in the cytoplasm [24]. Pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) are recognized by PRRs in infections. In the presence of mechanical damage, damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) are also recognized by PRRs. After PAMPs or DAMPs are recognized by PRRs, innate immune responses are initiated [25]. These responses utilize innate immune cells such as macrophages, neutrophils, and proinflammatory cytokines, and the responses can be considered as a regulated host defense mechanism. However, on rare occasions when uncontrolled or excessive responses occur, the result is severe inflammation, leading to acute or chronic inflammatory diseases.
Inflammasomes are multiprotein complexes that play a role in signal transduction. Inflammasomes play an important role in mediating innate inflammatory responses; they assemble in response to a variety of stimuli, including PAMPs and DAMPs. Among inflammasomes, NLRP3 has been extensively studied and characterized because of its critical role in immunity and inflammation [26,27]. The major components of this signaling platform include the NLRP3 protein, its adaptor protein apoptosis-associated speck-like proteins containing a CARD (ASC), and caspase-1, which is cleaved by this multiprotein complex. The cleavage of procaspase-1 cleaves the proinflammatory cytokines, such as IL-1β and IL-18, into their active forms, producing active caspase-1, a proteolytic enzyme that induces an inflammatory response.
The activity of NLRP3 is strongly inhibited by ubiquitination under normal conditions. However, when the cells are stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or ATP, deubiquitination of NLRP3 is induced. The NLRP3 induces the activation of proinflammatory cytokines by releasing this suppression [28]. LPS and ATP induce the production of proinflammatory cytokines via transmembrane TLR4 and P2X purinoceptor 7 (P2 × 7) receptors, respectively. The process of this induction is dependent on the production of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (mtROS). Furthermore, oxidized mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA), an oxidation product of ROS released from mitochondria, has been reported to bind and activate NLRP3 [6]. Mitochondria-targeted antioxidants may inhibit NLRP3-induced activation of inflammatory cells by inhibiting the production of oxidized mtDNA. In addition, recent studies have identified cytidine/uridine monophosphate kinase 2 (CMPK2) as a molecule required to induce gene expression for the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome, through stimulations with molecules such as LPS [29].
3. H2 as a Mitochondria-Targeted ·OH Scavenger
H2 is a flammable, colorless, odorless, and non-toxic gas. The first report on the therapeutic effect of H2 was published by Dole et al. in 1975 [30]. They demonstrated that hyperbaric treatment of 2.5% oxygen gas and 97.5% H2 gas could markedly induce tumor regression in mice. However, research on medical applications of H2 was not extensively conducted except for some pioneering studies. In 2007, Ohsawa et al. reported that H2 ameliorated ischemia-reperfusion injuries in a rat model with cerebral infarction [12]. They demonstrated that H2 selectively scavenges two types of potent ROS, namely ·OH and peroxynitrite (ONOO-). However, we cannot overlook the pioneering study by Yanagihara et al. in 2005, two years before Ohsawa’s study. They reported that the intake of neutral H2-rich water produced by electrolysis can effectively reduce oxidative stress caused by chemical oxidants in rats [31]. H2 has been characterized as a potent antioxidant capable of attenuating oxidative stress-related diseases [32,33]. H2 has remarkable therapeutic effects on various diseases, including cancer [34], sepsis [35], cardiovascular disease [36], neuronal disease [37], diabetes [38], metabolic syndrome [39], etc. Up until now, more than 800 original papers regarding the medical use of H2, including approximately 70 clinical trials, have been reported. As observed from the production of H2 in the intestines, adverse effects caused by H2 has not been observed in many clinical studies [40,41,42,43,44,45,46]. In recent papers, we reviewed that H2 is promising for medical applications due to its marked efficacy and for having no adverse effects [47].
Vitamins, known as antioxidants, are unable to scavenge ·OH generated inside of mitochondria because they have difficulty penetrating cell membranes and reaching intracellular organelles such as mitochondria. Homonuclear diatomic molecules that can exist in living bodies are nitrogen molecule (N2), oxygen molecule (O2), H2, and halogens (Cl2, I2, etc.). Among these, O2 is converted to energy in living bodies and is used for oxidation and hydroxylation of biological materials by oxygenating enzymes. Halogens in general are extremely active and act as poisons to the living body. On the other hand, N2 is an inactive molecule because it does not react with substances constituting of cells and there is no metabolic system that metabolizes the N2.
H2 is also an inactive molecule that has no metabolic system in mammalian cells and does not interact with biological substances, but it is a molecule that can react with ·OH, which are generated inside mitochondria [12]. In addition, because H2 itself is an inert substance and the reaction product of H2 and ·OH is a water molecule, it does not have any adverse effects on the living body, unlike drugs. In a recent paper, we proposed that H2 is the only molecule that can enter mitochondria and undergo a hydrogen withdrawal reaction with ·OH [13,14]. Thus, H2 is the only diatomic molecule that can enter mitochondria to protect cells from cytotoxicity caused by ·OH. Since H2 is a diatomic molecule essential for the survival of life, we proposed in the paper that H2 is a “philosophical molecule” [14].
4. Effects of H2 on Inflammation and Its Mechanisms
4.1. Possible Mechanisms for Targeting mtROS Production and NLRP3 Activation by H2
It has been shown that the NLRP3 inflammasome has been linked to disease such as atherosclerosis, acute and chronic respiratory diseases, Alzheimer’s disease, traumatic brain injury, acute kidney injury (AKI), chronic kidney disease (CKD), and cancer [4]. NLRP3 inflammasome-dependent inflammatory responses are known to be triggered by a variety of signals that endanger the host, including infection, tissue damage, and metabolic abnormalities [1]. Recent paper suggest that mitochondria integrate these different signals and relay this information to NLRP3 inflammasomes [1]. Dysfunctional mitochondria generate ROS, which in turn activate the inflammasomes.
In contrast, NLRP3 inflammasomes are negatively regulated by autophagy, which is a catabolic process that removes damaged or dysfunctional organelles including mitochondria. Activation of the inflammasome and IL-18 signaling pathway is largely protected in colitis-associated colorectal cancer. However, excessive inflammation driven by the inflammasome and IL-1β signaling pathways promotes breast cancer, fibrosarcoma, gastric cancer, and lung metastasis in a context-dependent manner [48]. Some literature has shown that H2 can be involved in various models of inflammation based on mechanisms of mitochondrial oxidation inhibition and NLRP3 inflammasome activation (Table 1) [15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23].

Table 1.
Mechanisms of H2 targeting the inhibitions of mtROS production and NLRP3 inflammasome activation.
Recently, it has been reported that the production of mtROS in LPS-stimulated macrophages trigger the activation of NLRP3, but this production can be suppressed by mitochondria-targeted antioxidants. Ren et al. examined the effects of H2 on the activation of NLRP3 inflammasomes in in vitro experiments using mouse RAW264.7 cells [15]. They reported that the stimulation of these cells with LPS increased the expression of NLRP3, caspase-1, and IL-1β with the production of mtROS in the absence of H2, but the treatment of H2 suppressed the production of mtROS and the expression of NLRP3, caspase-1, and IL-1β. In addition, they reported that the elimination of mtROS by H2 in response to LPS stimulation consequently inhibited the mtROS-mediated NLRP3 deubiquitination, a non-transcriptional signal [15]. These results report a possible mechanism by which H2 inhibits the mtROS-mediated activation of NLRP3 production.
It has been shown that ROS induce oxidative stress and that this stress is one of the important etiological factors of acute pancreatitis. Ren et al. also examined the effects of intraperitoneal injection of H2-rich saline on the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in a mouse model with acute pancreatitis [16]. The results showed that in the control group, NLRP3 inflammasome activation, increased nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) activity, and increased production of inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-1β were observed, but these changes were significantly suppressed by H2 -rich saline administration. In addition, an increase in malondialdehyde (MDA) levels and a decrease in superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity were also observed in the control group, whereas the administration of H2-rich saline caused a decrease in MDA levels and an increase in SOD activity. Histopathological examination of the pancreas also confirmed the efficacy of H2 -rich saline administration. They reported that the administration of H2-rich saline in acute pancreatitis contributed to the inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation [16].
Ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) disorders of the intestine often lead to inflammatory reactions and coagulopathy. H2 exhibits anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-apoptotic effects, but its efficacy on intestinal I/R has been unclear. Yang et al. investigated the effects of intravenous administration of H2-rich saline on intestinal I/R in an experiment on rats [17]. They reported that the administration of H2-rich saline improved the survival rate of the rats and ameliorated intestinal damage, edema, and apoptosis. In addition, in this paper, they reported that the administration of H2-rich saline improved inflammatory response and also markedly ameliorated I/R-mediated coagulopathy in the intestine. They also reported that H2-rich saline inhibited the activation of NF-κB and NLRP3 inflammasomes in peripheral blood mononuclear cells [17]. They suggested that the improvement of coagulopathy and inflammation by administration of H2-rich saline was partly due to the NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway.
Limb I/R is a clinical condition that is associated with high morbidity and mortality. Zou et al. investigated the efficacy and mechanism of H2-rich saline on acute lung injury in rats induced by Limb I/R [18]. H2-rich saline was administered intraperitoneally when the clips of limbs were released. The results showed that H2-rich saline improved survival and the edema, injury, and apoptosis in lung tissues. H2-rich saline also decreased levels of TNF-α, IL-6, myeloperoxidase, and MDA in blood and lung tissue, and increased the activity of SOD. In addition, the H2-rich saline solution dawn-regulated the protein expression of chemerin and NLRP3 in lung tissue [18]. These results indicate that the activated chemerin/NLRP3 signaling pathway is partly involved in the mechanism by which H2 ameliorates acute lung injury.
Neuropathic pain is a complication after spinal nerve injury, and inflammasomes are thought to be a trigger for neuropathic pain. In a previous study, Chen et al. confirmed the protective effects of H2 on a rat model with neuropathic pain, but the mechanism of its efficacy was unclear. Therefore, they investigated the effect of intraperitoneal administration of H2-rich saline on this pain model [19]. The results showed that neuropathic pain stimulated NLRP3 inflammasome activation and an autophagy pathway in spinal microglial cells. H2 induced autophagy-related protein expression and inhibited NLRP3 pathway activation. Furthermore, H2 alleviated the hyperpathia induced by neuropathic pain. They reported that H2 ameliorated hyperpathia through its mechanism to inactivate autophagy-mediated NLRP3 inflammasomes [19].
Early brain injury (EBI) after subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) occurs within 72 h and is associated with inflammation and apoptosis. Recent reports have shown that H2-rich saline improves EBI after SAH, but the mechanism remained unclear. Shao et al. investigated the mechanism of H2-rich saline on a rat model with SAH [20]. The results showed that in the control group, SAH increased the protein levels of NLRP3, ASC, caspase-1, IL-1β, and cleaved caspase-3, and the mRNA levels of IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α in brain tissue, but these changes were ameliorated in the H2 group. In addition, there was an increase in ROS and MDA and a decrease in SOD in brain tissue in the control group, but these changes were improved in the H2 group [20]. They reported that inactivation of the NF-κB pathway and NLRP3 inflammasome was partly involved in the mechanism by which H2-rich saline improved inflammation in EBI [20].
SAH is a cerebrovascular disease with poor prognosis. NLRP3 plays an important role in the inflammatory response, which may lead to vascular endothelial cell damage and disruption of the blood-brain barrier (BBB). Zhuang et al. examined the effects of H2 gas inhalation in a rat model of SAH [21]. SAH upregulated the expression of NLRP3 and ASC, accompanied by an increase in inflammatory and apoptotic markers. However, inhalation of H2 gas decreased these markers and also suppressed the expression of NLRP3 and ASC. Moreover, H2 gas inhalation also improved cerebral edema and vasospasm. They reported that the mechanism by which H2 suppresses oxidative stress-related endothelial cell injuries may partly involve the suppression of the activation of the ROS/NLRP3 axis [21].
Sepsis-associated encephalopathy (SAE) is a major cause of death, and oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis have been implicated in its pathogenesis. Xie et al. investigated the mechanism of H2-rich saline on SAE [22]. The results showed that SAE increased the expression of NLRP3 and Nrf2 in microglia, while MCC950, an inhibitor of NLRP3, suppressed the expression of NLRP3, the release of IL-1β and IL-18, apoptosis, and mitochondrial dysfunction. H2-rich saline increased Nrf2 expression and inhibited SAE-induced NLRP3 expression, caspase-1, IL-1β and IL-18 release, apoptosis, and mitochondrial dysfunction in wild-type (WT) mice, while these effects of H2 were not observed in Nrf2 knockout (KO) mice [22]. They reported that the Nrf2-mediated NLRP3 pathway is involved in the mechanism by which H2 suppresses the SAE.
Sepsis is also a condition in which an organism loses control over an infection and develops lethal organ failure. Chen et al. examined the effects of H2-rich saline in a mouse model of sepsis induced by cecal ligation (CLP). Similarly, they also examined the effects of H2 treatment on macrophages induced by LPS [23]. The results showed that H2 treatment attenuated vital organ damage, inflammatory response, mitochondrial dysfunction, and NLRP3 pathway activation. Furthermore, H2 treatment induced autophagy in macrophages induced by LPS and CLP. They reported that H2 ameliorated mitochondrial dysfunction via autophagy-mediated NLRP3 inactivation [23].
Recently, Chen et al. demonstrated that H2 has neuroprotective effects on many diseases, such as neurodegenerative disease, traumatic brain injury, depression, sabarachnoid hemorrhage, and cognitive dysfunction [49]. In this review, they indicated that excessive ROS stimulate the expression of NF-κB, and promote the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines by activating the NLRP3 inflammasome, and that H2 may attenuate the inflammatory response in various CNS diseases through the inhibitory effects of NLRP3 inflammasomes. Moreover, Li et al. also reported in the review that the activation of NLRP3 inflammasomes is one of the inflammatory mechanisms in pancreatitis [50], because in the experiment by Ren et al. using acute pancreatic mice, H2 markedly suppressed ROS production at the source and NLRP3 inflammasome expression [16].
4.2. Possible Mechanisms by H2 Excluding Inhibitions of mtROS Production and NLRP3 Activation
In the previous chapter, we discussed a possible mechanism targeting mtROS production and NLRP3 activation by H2, but cellular pathways related to the downstream of PRRs and TLRs activation should also be considered. Many papers have reported the anti-inflammatory effects of H2, but very few have reported its mechanisms in detail. Some papers have discussed the possibility of NF-κB, mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK), and heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) pathways as possible mechanisms for the anti-inflammatory effects of H2.
NF-κB is a transcription factor that regulates the expression of target genes such as cytokines, chemokines, adhesion molecules, and oxidative stress-related enzymes. Wang et al. investigated the effects and mechanisms of H2-rich saline on amyloid-β (Aβ)-induced inflammation and oxidative stress models in rats [51]. H2-rich saline was administered intraperitoneally after intraventricular administration of Aβ1-42 in rats. As a result, the levels of IL-1β, 8-hydroxy-2’-deoxyguanosine (8-OH-dG), c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK), and NF-κB in brain tissues were increased after Aβ1-42 administration, while administration of H2-rich saline decreased levels of IL-1β and 8-OH-dG and activation of JNK and NF-κB [51]. They reported that the inhibitory effects of H2 on Aβ-induced neuroinflammation and oxidative stress were involved in the suppression of JNK and NF-κB activations.
MAPK pathway includes the extracellular-signal-regulated protein kinase (ERK), JNK, and p38 MAPK subfamilies, which function as key molecules transmitting extracellular signals to the nucleus. Liu et al. investigated the effect of intraperitoneal administration of H2-rich saline on hepatic injury rats with obstructive jaundice. The hepatic injury was induced by bile duct ligation [52]. The results showed that the levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) in serum, MDA, myeloperoxidase activity, TNFα, IL-1β, IL-6, and high-mobility group 1 (HMGB1) in tissues were significantly increased, while H2-rich saline decreased these levels and improved histopathological liver damage [52]. In addition, H2-rich saline increased the activities of the antioxidant enzymes SOD and catalase, and it downregulated the activation of ERK1/2 [52]. These results suggest that the ameliorating effects of H2 on inflammation and oxidative stress in a rat model with liver injuries are partly due to the inhibition of the ERK1/2 pathway.
Itoh et al. stimulated mouse RAW264 cells with LPS and interferon-γ (IFN-γ) to investigate the effect of H2 treatment on nitric oxide (NO) production [53]. The results showed that H2 treatment inhibited the phosphorylation of ASK1, as well as its downstream signaling molecules, p38 MAPK and JNK. In addition, NO production was significantly suppressed by H2 treatment [53]. Furthermore, H2-rich water ameliorated type II collagen-induced arthritis in a mouse that was used as a model of human rheumatoid arthritis. They considered that H2 regulates macrophage signaling, and furthermore, the mechanism by which H2 suppresses the inflammation in mice was involved in the modification of signaling in the MAPK pathway such as with ASK, p38, and JNK [53].
Aquaporins (AQP1) and AQP5 play an important role in scavenging extravascular lung water in patients with sepsis-induced lung injury. It has been reported that H2-rich saline has a protective effect on sepsis-induced lung injury. Tao et al. investigated whether AQP1 and AQP5 are involved in the inhibitory effect of H2-rich saline on lung injuries [54]. Rats were administered with LPS intratracheally, followed by intraperitoneal administration of H2-rich saline. LPS significantly impaired lung function and downregulated the expression of AQP1 and AQP5, but these changes were attenuated by the administration of H2-rich saline. Furthermore, H2-rich saline suppressed LPS-induced p38 MPPK and JNK. They reported that the downregulation of AQP1 and AQP5 was associated with suppressions of p38 MAPK and JNK expressions [54].
Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is a disease that can progress to liver fibrosis without effective control. Li et al. investigated the efficacy and mechanism of H2-rich water in a mouse model with NASH [55]. The results showed that compared to the control group, the H2 group showed lower levels of ALT and AST and milder histological damage. In addition, H2-rich water inhibited liver inflammation and fibrosis, as well as apoptosis. Furthermore, in experiments using cultured hepatocytes, H2 treatment suppressed LPS-induced production of inflammatory cytokines through the HO-1/IL-10-independent pathway [55]. They reported that the protective effect of H2-rich water on hepatic injury in NASH is mediated by the HO-1/AMPK pathway [55].
4.3. Our Hypothesis of H2 on Inflammatory Disease
Our suggested mechanism of H2 on chronic inflammatory diseases is that H2 may inhibit the cascade leading to the activation of NLRP3 by scavenging excess mtROS, and this inhibition may lead to the suppression of IL-1β and IL-18 production. However, previous papers supporting this mechanism have not shown that the ROS is ·OH itself. The most oxidatively produced ROS in mitochondria is ·OH [13,14]. Therefore, in this review, we hypothesized that the ·OH scavenging effects of H2 may lead to the suppression of NLRP3 activation through the inhibition of mtDNA oxidation (Figure 1). In the future, it will be necessary to identify the exact ROS responsible for mitochondrial oxidation and to analyze in detail the mechanism by which H2 inhibits mitochondrial oxidation.
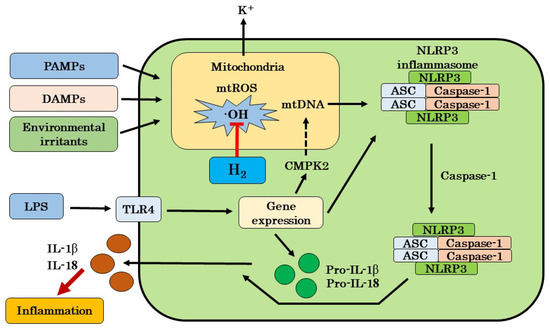
Figure 1.
A possible mechanism of H2 on inflammatory diseases targeting the mtROS production and NLRP3 inflammasome activation. H2 can selectively eliminate ·OH generated inside of mitochondria, and inhibit the cascade leading to NLRP3 activation by scavenging excess mtROS, and this inhibition leads to the suppression of IL-1β and IL-18 production. ROS: reactive oxygen species; ·OH: hydroxyl radicals; H2: molecular hydrogen; IL-1β: interleukin-1β; IL-18: interleukin-18; NLRP3: nucleotide-binding and oligomerization domain-like receptor family pyrin domain-containing 3; TLR4: toll-like receptor 4; PAMPs: pathogen-associated molecular patters; DAMPs: damage-associated molecular patters; ASC: apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD; LPS: lipopolysaccharide; mtROS: mitochondrial reactive oxygen species; mtDNA: mitochondrial DNA; CMPK2: cytidine/uridine monophosphate kinase 2.
In addition, we cannot deny the possibility that as another mechanism, H2 regulates cellular pathways related to the downstream of PRRs and TLRs activation. We believe that further research is needed to analyze the mechanisms of the anti-inflammatory effects of H2.
5. Possibility of H2 Gas Therapy for COVID-19
The epidemic caused by SARS-CoV-2, which began in Wuhan, China, in December 2019, has exploded into a worldwide pandemic, with more than 96.2 million cases of infection and 2.06 million deaths worldwide as of 22 January 2021. In the infectious disease named COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2 uses angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptors as its receptor. The infection with the virus begins when a spike on the surface of the virus binds to the receptor on the surface of host cells. When the viral spike binds to its receptor (ACE2), the virus enters the intracellular vesicle. In these intracellular vesicles, the virus undergoes degradation and genetic information is released into the cytoplasm, where the virus replicates and multiplies.
The mechanism by which the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in the cytoplasm induces inflammation is not well understood, but the extrapolated theory by influenza viruses can be used [56]. The cytoplasmic components of the virus recognize TLR7 and other sensor molecules, and the mitochondria produce large amounts of ROS, including ·OH. These ROS oxidize mtDNA, which presumably drives the cascade from NLRP3 to the release of proinflammatory cytokines. Recently, Ratajczak et al. demonstrated that the overactivation of NLRP3 induced by SARS-CoV-2 infection may be a trigger of “cytokine storm” [57]. Indeed, Rodrigues et al. indicated that the NLRP3 inflammasome is activated in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection [58]. They found active NLRP3 inflammasome in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and tissues of postmortem patients upon autopsy in patients with COVID-19. They also indicated that the inflammasome-derived products including active caspase-1 and IL-18 in the sera correlated with the markers of severity, such as IL-6 and LDH [58]. Thus, from these recent papers, H2 may inhibit the cascade from NLRP3 to the release of proinflammatory cytokines and thereby reduce the SARS-CoV-2-induced inflammation.
A short-term, open-label, multicenter clinical trial was conducted in China using H2 gas in 90 patients with COVID-19 [59]. The patients in the treatment group (44 patients) inhaled a H2-O2 gas mixture (67% H2, 33% O2), while patients in the control group (46 patients) received only standard treatment (daily O2 gas therapy) until discharge. The results showed that improvements in the disease severity, dyspnoea, cough, chest distress, chest pain, and oxygen saturation were greater in the treatment group than in the control group, suggesting that inhalation of H2 gas with oxygen gas is useful. Although the mechanisms of the ameliorating effects of H2 gas inhalation on COVID-19 needs further investigation, these results indicate that H2 gas inhalation may improve symptoms including acute and chronic inflammations caused by COVID-19.
6. Current Perspective for Chronic Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is at the root of many diseases. It is no exaggeration to say that “chronic inflammation is the source of all diseases”, since chronic inflammation is involved in many diseases, such as atherosclerosis, diabetes, dyslipidemia, liver cirrhosis, atopic dermatitis, asthma, rheumatoid arthritis, ulcerative colitis, Alzheimer’s disease, depression, cancer, etc. [4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11]. On the other hand, the relationship between chronic inflammation and senescence has also been studied by Arai et al. in a cohort study of more than 1,500 people with longevity [60]. They showed that inflammation markers are associated with life expectancy, and that the people with low inflammation markers tending to have a longer life expectancy than those with high inflammation markers. Thus, chronic inflammation is not only associated with diseases but also with senescence.
Modern medicine does not contribute to the fundamental treatment of diseases, because medicine is a targeted therapy that focuses on improving symptoms. In addition, with recent developments in medical technology, modern medicine can cure acute inflammatory diseases, but it is far from being able to treat chronic inflammatory diseases. Despite the fact that H2 is a safe medical gas, medical researchers have not looked at the medical applications of H2 in the past. Although many clinical and animal study papers have been published showing the efficacy of H2 in treating chronic inflammatory diseases, to the best of our knowledge, no review article has been published that focus on the mechanism by which H2 inhibits the cascade from the inhibition of mitochondrial oxidation to the activation of NLRP3 inflammasomes. The medical applications of H2 can solve the problem of many chronic inflammation-based diseases, including COVID-19. In addition, H2 may have the potential to control not only inflammatory diseases but also senescence.
7. Conclusions
Inflammation is induced by the release of inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β and IL-18 produced by macrophages and neutrophils in direct response to a triggering stimulus. However, when an uncontrolled or exaggerated response occurs, the resulting severe inflammation can lead to acute or chronic inflammatory diseases. It has been reported that mitochondria-related ROS activate the NLRP3 inflammasome, and its stimulation triggers the production of these inflammatory cytokines [1]. Modern medical treatment can control acute inflammatory diseases, but it cannot control chronic inflammatory diseases.
H2 was found to be a potent scavenger, with no adverse effects on the human body, that selectively scavenges ·OH, the most oxidizing ROS [12]. Mitochondrial selective ·OH scavengers may block the cascade leading to the activation of NLRP3 inflammasomes in humans. It has been shown by literature that H2 can be in the various animal models with inflammation based on the mechanisms of mitochondrial oxidation inhibition and NLRP3 inflammasome activation [15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23]. We do not know how H2 can inhibit mitochondrial oxidation, as NLRP3 inflammasome activation is poorly understood. In this paper, we hypothesized a possible mechanism by which H2 can inhibit NLRP3 activation via the inhibition of mitochondrial oxidation, and then presented a perspective on the potential effects of H2 in chronic inflammatory diseases. The medical applications of H2 can solve the problems of many chronic inflammation-based diseases including COVID-19. Additionally, H2 may even have the potential to control not only inflammatory diseases but also senescence.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.-i.H. and Y.T.; methodology, S.-i.H., B.S. and F.S.; investigation, S.-i.H. and Y.I.; writing—original draft preparation, S.-i.H.; writing—review and editing, S.-i.H., Y.I., B.S., H.Y., Y.T. and F.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Yoko Satoh and Yoshihiro Mitekura (MiZ Company Limited) for their excellent advice on writing this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
- Tschopp, J. Mitochondria: Sovereign of inflammation? Eur. J. Immunol. 2011, 41, 1196–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismael, S.; Ahmed, H.A.; Adris, T.; Parveen, K.; Thakor, P.; Ishrat, T. The NLRP3 inflammasome: A potent therapeutic target for traumatic brain injury. Neural Regen. Res. 2020, 16, 49–57. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseinian, N.; Cho, Y.; Lockey, R.F.; Kolliputi, N. The role of the NLRP3 inflammasome in pulmonary diseases. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2015, 9, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozaki, E.; Campbell, M.; Doyle, S.L. Targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome in chronic inflammatory diseases: Current perspectives. J. Inflamm. Res. 2015, 8, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baldrighi, M.; Mallat, Z.; Li, X. NLRP3 inflammasome pathways in atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 2017, 267, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, K.; Crother, T.R.; Karlin, J.; Dagvadorj, J.; Chiba, N.; Chen, S.; Ramanujan, V.K.; Wolf, A.J.; Vergnes, L.; Ojcius, D.M.; et al. Oxidized mitochondrial DNA activates the NLRP3 inflammasome during apoptosis. Immunity 2012, 36, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinon, F.; Burns, K.; Tshopp, J. The inflammasome: A molecular platform triggering activation of inflammatory caspases and processing of proIL-beta. Mol. Cell. 2002, 10, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olhava, E.J.; Roush, W.R.; Seidel, H.M.; Glick, G.D.; Latz, E. Targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome in inflammatory diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 588–606. [Google Scholar]
- Swanson, K.V.; Deng, M.; Ting, J.P.Y. The NLRP3 inflammasome: Molecular activation and regulation to therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Callaway, J.B.; Ting, J.P.Y. Inflammasomes: Mechanism of action, role in disease, and therapeutics. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strowig, T.; Henao-Mejia, J.; Elinav, E.; Flavel, R. Inflammasomes in health and disease. Nature 2012, 481, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohsawa, I.; Ishikawa, M.; Takahashi, K.; Watanabe, M.; Nishimaki, K.; Yamagata, K.; Katsura, K.I.; Katayama, Y.; Asoh, S.; Ohta, S. Hydrogen acts as a therapeutic antioxidant by selectively reducing cytotoxic oxygen radicals. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, S.I.; Ichikawa, Y.; Kurokawa, R.; Takefuji, Y.; Satoh, F. A “philosophical molecule,” hydrogen may overcome senescence and intractable diseases. Med. Gas Res. 2020, 10, 47–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichikawa, Y.; Satoh, B.; Hirano, S.I.; Kurokawa, R.; Takefuji, Y.; Satoh, F. Proposal of next-generation medical care “Mega-hydrogen Therapy”. Med. Gas Res. 2020, 10, 140–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.D.; Wu, X.B.; Jiang, R.; Hao, D.P.; Liu, Y. Molecular hydrogen inhibits lipopolysaccharide-triggered NLRP3 inflammasome activation in macrophages by targeting the mitochondrial reactive oxygen species. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1863, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.D.; Ma, J.; Hou, J.; Xiao, W.J.; Jin, W.H.; Wu, J.; Fan, K.H. Hydrogen-rich saline inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation and attenuates experimental acute pancreatitis in mice. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 930894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Guo, Y.; Fan, X.; Chen, Y.; Yang, B.; Liu, K.X.; Zhou, J. Amelioration of coagulation disorders and inflammation by hydrogen-rich solution reduces intestinal ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats through NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway. Mediat. Inflamm. 2020, 2020, 4359305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, R.; Wang, M.H.; Chen, Y.; Fan, X.; Yang, B.; Du, J.; Wang, X.B.; Liu, K.X.; Zhou, J. Hydrogen-rich saline attenuates acute lung injury induced by limb ischemia/reperfusion via down-regulating chemerin and NLRP3 in rats. Shock 2018, 52, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhou, C.; Xie, K.; Meng, X.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Y. Hydrogen-rich saline alleviated the hyperpathia and microglia activation via autophagy mediated inflammasome inactivation in neuropathic pain rats. Neuroscience 2019, 421, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, A.; Wu, H.; Hong, Y.; Tu, S.; Sun, X.; Wu, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, J.; Sheng, J. Hydrogen-rich saline attenuated subarachnoid hemorrhage-induced early brain injury in rats by suppressing inflammatory response: Possible involvement of NF-κB pathway and NLRP3 inflammasome. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 3462–3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, K.; Zuo, Y.C.; Scherchan, P.; Wang, J.K.; Yan, X.X.; Liu, F. Hydrogen inhalation attenuates oxidative stress related endothelial cells injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 13, 1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Meng, X.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Chen, H. Hydrogen attenuates sepsis-associated encephalopathy by NRF2 mediated NLRP3 pathway inactivation. Inflamm. Res. 2015, 69, 697–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Mao, X.; Meng, X.; Li, Y.; Feng, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Xie, K. Hydrogen alleviates mitochondrial dysfunction and organ damage via autophagy-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome inactivation in sepsis. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 44, 1309–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, D.R.; Beck, P.L.; Muruve, D.A. Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptors and inflammasomes in the pathogenesis of non-microbial inflammation and disease. J. Innate. Immun. 2012, 4, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallet, S.M.; Puri, V.; Gibson, F.C. Linkage of infection to adverse systemic complication: Periodontal disease, toll-like receptors, and other pattern recognition systems. Vaccines 2018, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Man, S.M.; Kanneganti, T.D. Regulation of inflammasome activation. Immunol. Rev. 2015, 265, 6–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, E.I.; Sutterwala, F.S. Initiation and perpetuation of NLRP3 inflammasome activation and assembly. Immunol. Rev. 2015, 265, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juliana, C.; Fernandes-Alnemri, T.; Kang, S.; Farias, A.; Qin, F.; Alnemri, E.S. Non -transcriptional priming and deubiquitination regulate NLRP3 inflammasome activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 36617–36622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Liang, S.; Sanchez-Lopez, E.; He, F.; Shalapour, S.; Lin, X.J.; Wong, J.; Ding, S.; Seki, E.; Schnabl, B.; et al. New mitochondrial DNA synthesis enables NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Nature 2018, 560, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dole, M.; Wilson, F.R.; Fife, W.P. Hyperbaric hydrogen therapy: A possible treatment for cancer. Science 1975, 190, 152–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagihara, T.; Arai, K.; Miyamae, K.; Sato, B.; Shudo, T.; Yamada, M.; Aoyama, M. Electrolyzed hydrogen-saturated water for drinking use elicits an antioxidative effect; a feeding test with rats. Biosci. Biotrechnol. Biochem. 2005, 69, 1985–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, S. Molecular hydrogen as a preventive and therapeutic medical gas: Initiation, development and potential of hydrogen medicine. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 144, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohta, S. Molecular hydrogen as a novel antioxidant: Overview of the advantages of hydrogen for medical applications. Methods Enzymol. 2015, 555, 289–317. [Google Scholar]
- Akagi, J.; Baba, H. Hydrogen gas restores exhausted CD8+ T cells in patients with advanced colorectal cancer to improve prognosis. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 41, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, M.; Shimizu, K.; Ogura, H.; Kurakawa, T.; Umemoto, E.; Motooka, D.; Nakamura, S.; Ichimaru, N.; Takeda, K.; Takahara, S.; et al. Hydrogen-rich saline regulates intestinal barrier dysfunction, dysbiosis and bacterial translocation in a murine model of sepsis. Shock 2018, 50, 640–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsumata, Y.; Sano, F.; Abe, T.; Tamura, T.; Fujisawa, T.; Shiraishi, Y.; Kohsaka, S.; Ueda, I.; Homma, K.; Suzuki, M.; et al. The effects of hydrogen gas inhalation on adverse left ventricular remodeling after percutaneous coronary intervention for ST-elevated myocardial infraction. First pilot study in humans. Circ. J. 2017, 81, 940–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, S.; Nagatani, K.; Otani, N.; Nawashiro, H.; Sugawara, T.; Wada, K.; Mori, K. Hydrogen improves neurological function through attenuation of blood-brain barrier disruption in spontaneously hypertensive stroke-prone rats. BMC Neurosci. 2015, 16, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Jin, K.; Xu, H.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Z. Subcutaneous injection of hydrogen gas is a novel effective treatment for type 2 diabetes. J. Diabetes Investig. 2018, 9, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakao, A.; Toyoda, Y.; Sharma, P.; Evans, M.; Guthrie, N. Effectiveness of hydrogen rich water on antioxidant status of subjects with potential metabolic syndrome: An open label pilot study. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2010, 46, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoritaka, A.; Takanashi, M.; Hirayama, M.; Nakahara, T.; Ohta, S.; Hattori, N. Pilot study of H2 therapy in Parkinson’s disease. A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Mov. Disord. 2013, 28, 836–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, H.; Nishijima, Y.; Ohta, S.; Sakamoto, M.; Kinone, K.; Horikoshi, T.; Tamaki, M.; Takeshita, H.; Futatuki, T.; Ohishi, W.; et al. Hydrogen gas inhalation treatment in acute cerebral infarction: A randomized controlled clinical study on safety and neuroprotection. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. 2017, 26, 2587–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, H.; Nishijima, Y.; Adachi, N.; Tachibana, S.; Chitoku, S.; Mukaihara, S.; Sakamoto, M.; Kudo, Y.; Nakazawa, J.; Kaneko, K.; et al. Improved brain MRI indices in the acute brain stem infarct sites treated with hydroxyl radical scavengers, Edaravone and hydrogen, as compared to Edaravone alone. A non-controlled study. Med. Gas Res. 2011, 1, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishibashi, T.; Sato, B.; Rikitake, M.; Seo, T.; Kurokawa, R.; Hara, Y.; Naritomi, Y.; Hara, H.; Nagao, T. Consumption of water containing a high concentration of molecular hydrogen reduces oxidative stress and disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: An open-label pilot study. Med. Gas Res. 2012, 2, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi, T.; Sato, B.; Shibata, S.; Sakai, T.; Hara, Y.; Naritomi, Y. Therapeutic efficacy of infused molecular hydrogen in saline on rheumatoid arthritis: A randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled pilot study. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 21, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimaki, K.; Asada, T.; Ohsawa, I.; Nakajima, E.; Ikejima, C.; Yokota, T.; Kamimura, N.; Ohta, S. Effects of molecular hydrogen assessed by an animal model and a randomized clinical study on mild cognitive impairment. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2017, 15, 482–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Mu, F.; Lu, T.; Ma, Y.; Du, D.; Xu, K. A gallbladder carcinoma patient with pseudo-progressive remission after hydrogen inhalation. Oncol. Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 8645–8651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, S.i.; Ichikawa, Y.; Sato, B.; Satoh, F.; Takefuji, Y. Hydrogen is promising for medical applications. Clean. Technol. 2020, 2, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karki, R.; Man, S.M.; Kanneganti, T.D. Inflammasome and cancer. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2017, 5, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhang, H.T.; Qin, S.C. Neuroprotective effects of molecular hydrogen: A critical review. Neurosci. Bull. 2020. Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, G.; Suo, L.; Zhang, J. Recent advances in studies of molecular hydrogen in the treatment of pancreatitis. Life Sci. 2021, 264, 118641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Li, J.; Yang, R.; Zhang, J.H.; Cao, Y.P.; Sun, X.J. Hydrogen-rich saline reduces oxidative stress and inflammation by inhibit of JNK and NF-kB activation in a rat model of amyloid-beta-induced Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 491, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Shen, W.F.; Sun, H.Y.; Fan, D.F.; Nakao, A.; Cai, J.M.; Yan, G.; Zhou, W.P.; Shen, R.X.; Yang, J.M.; et al. Hydrogen-rich saline protects liver injury in rats with obstructive jaundice. Liver Int. 2010, 30, 958–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, T.; Hamada, N.; Terazawa, R.; Ito, M.; Ohno, K.; Ichihara, M.; Nozawa, Y.; Ito, M. Molecular hydrogen inhibits lipopolysaccharide/interferon γ-induced nitric oxide production of signal transduction in macrophages. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 411, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, B.; Liu, L.; Wang, W.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, J. Effects of hydrogen-rich saline on aquaporin 1,5 in septic rat lungs. J. Surg. Res. 2016, 202, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.W.; Takahara, T.; Que, W.; Fujino, M.; Guo, W.Z.; Hirano, S.I.; Ye, L.P.; Li, X.K. Hydrogen-rich water protects liver injury in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis through HO-1 enhancement via IL-10 and Sirt 1 signaling. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2021. Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichinohe, T.; Yamazaki, T.; Koshiba, T.; Yanagi, Y. Mitochondrial protein mitofusin 2 is required for NLRP3 inflammasome activation after RNA virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 17963–17968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratajczak, M.Z.; Kurcia, M. SARS-CoV-2 infection and overactivation of Nlrp3 inflammasome as a trigger of cytokine “storm” and risk factor for damage of hematopoietic stem cells. Leukemia 2020, 34, 1726–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, T.S.; de Sá, K.S.G.; Ishimoto, A.Y.; Becerra, A.; Oliveira, S.; Almeida, L.; Gonçalves, A.V.; Perucello, D.B.; Andrade, W.A.; Castro, R. Inflammasomes are activated in response to SARS-CoV-2 infection and are associated with COVID-19 severity in patients. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 218, e20201707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, W.J.; Wei, C.H.; Chen, A.L.; Sun, X.C.; Guo, G.Y.; Zou, X.; Shi, J.D.; Lai, P.Z.; Zheng, Z.G.; Zhong, N.S. Hydrogen/oxygen mixed gas inhalation improves disease severity and dyspnea in patients with Coronavirus disease 2019 in a recent multicenter, open-label clinical trial. J. Thorac. Dis. 2020, 12, 3448–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, Y.; Iinuma, T.; Takayama, M.; Abe, Y.; Fukuda, R.; Ando, J. The Tokyo oldest survey on total health (TOOH): A longitudinal cohort study of multidimensional components of health and well-being. BMC Geriatr. 2010, 10, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).