The author wishes to make the following correction to this paper [1]:
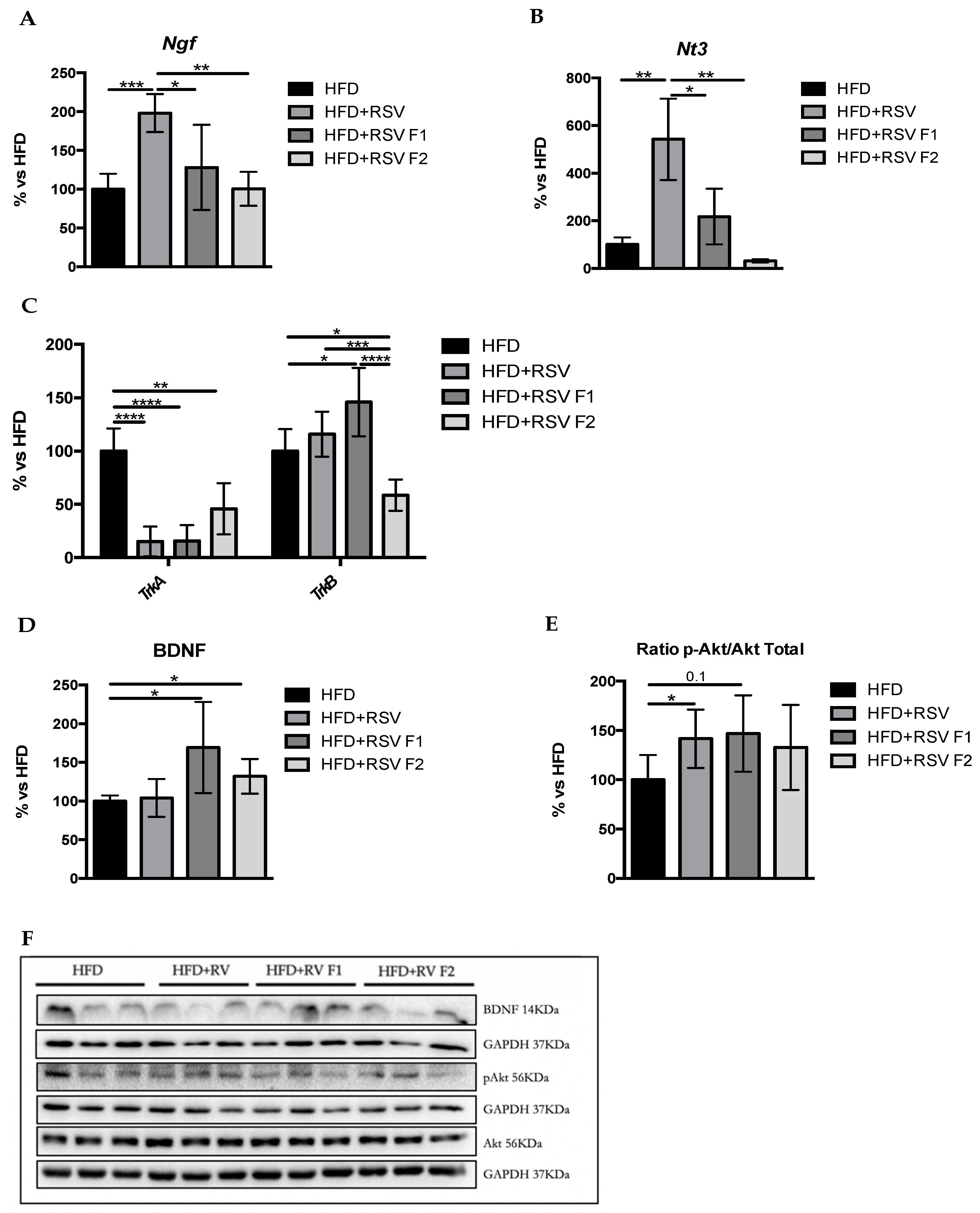
In the original article, there was a mistake in Figure 5F. All WBs experiments were performed with 14 samples in total, where the 2 bands that are not shown correspond to the control group without dietary intervention, so the article shows the 12 bands that correspond to the HFD, HFD + RSV, HFD + RSV F1 and HFD + RSV F2. The corrected Figure 5F appears below.
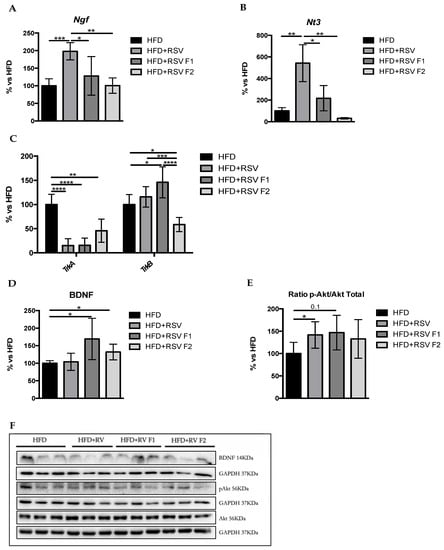
Figure 5.
Synaptic plasticity markers in the hippocampus of SAMP8 mice at 6 months of age. Results of gene expression of Ngf (A), Nt3 (B), and their receptors, TrkA and TrkB (C). Quantifications (D,E) and representative results by WB of BDNF and p-Akt (F). Gene expression levels were measured by real-time PCR from hippocampal tissue. Data from each group were compared with the HFD group (set at 100%). The means and standard error of the mean (SEM) in bar graphs are adjusted to 100% for each gene of the HFD group; n = 16–24 (HFD n = 4–6, HFD + RSV n = 4–6, HFD + RSV F1 n = 4–6, HFD + RSV F2 n = 4–6; for each group, females: n = 3–4, males: n = 3–4). Statistics: * p < 0.05; ** p <0.01; *** p < 0.001; **** p < 0.0001.
The authors apologize for any inconvenience caused and state that the scientific conclusions are unaffected. The original article has been updated.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Reference
- Izquierdo, V.; Palomera-ávalos, V.; Pallàs, M.; Griñán-Ferré, C. Resveratrol supplementation attenuates cognitive and molecular alterations under maternal high-fat diet intake: Epigenetic inheritance over generations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).