Abstract
Lithium silicate (Li4SiO4) material can be applied for CO2 capture in energy production processes, such as hydrogen plants, based on sorption-enhanced reforming and fossil fuel-fired power plants, which has attracted research interests of many researchers. However, CO2 absorption performance of Li4SiO4 material prepared by the traditional solid-state reaction method is unsatisfactory during the absorption/regeneration cycles. Improving CO2 absorption capacity and cyclic stability of Li4SiO4 material is a research highlight during the energy production processes. The state-of-the-art kinetic and quantum mechanical studies on the preparation and CO2 absorption process of Li4SiO4 material are summarized, and the recent studies on the effects of preparation methods, dopants, and operating conditions on CO2 absorption performance of Li4SiO4 material are reviewed. Additionally, potential research thoughts and trends are also suggested.
1. Introduction
The emission of anthropogenic CO2 into the environment has aggravated the trend of global warming [1], which has become one of the most threatening problems in recent decades, and the largest emission sources of CO2 are fossil fuel-fired power plants [2]. Hence, various techniques have been reported to capture CO2 from the flue gas released from fossil fuel-fired power plants [3], and CO2 capture and storage (CCS) has been recognized as one of the most effective techniques to mitigate CO2 emission [4,5]. In the process of CCS, CO2 is captured from flue gas and stored for utilization and sequestration instead of being released to the environment directly. Recent studies have found that various lithium-based materials, such as LiFeO2 [6], Li2CuO2 [7], Li2ZrO3 [7,8,9], Li8SiO6 [10,11], and Li4SiO4 [9], are capable of effective CO2 capture. Among these materials, Li4SiO4, with a variety of applications [12,13], has better application potential, owing to its higher CO2 sorption capacity, cyclic stability than LiFeO2, Li2CuO2, and Li8SiO6, and lower cost than that of Li2ZrO3 [9]. Additionally, the regeneration temperature of Li4SiO4 material is much lower compared with the calcium-based CO2 sorbents, indicating that lower energy consumption is required for the regeneration. Li4SiO4 material is usually obtained by the solid-state reaction method with Li2CO3 and SiO2 at high temperature, which is shown in Equation (1) [14]:
The basic reversible reaction for CO2 sorption by Li4SiO4 material follows Equation (2), and the process is shown in Figure 1. In the absorption reactor, CO2 in flue gas from fossil fuel-fired power plants or syngas from hydrogen plants based on sorption-enhanced reforming is absorbed by Li4SiO4 at 500 to 600 °C, thus the gas, almost free of CO2, is exhausted from the reactor. The generated Li2SiO3 and Li2CO3 are transported to the regeneration reactor, where Li4SiO4 is regenerated at temperatures higher than 700 °C and sent to the absorption reactor for the next CO2 absorption cycle, and CO2-rich gas can be obtained in the regeneration reactor.
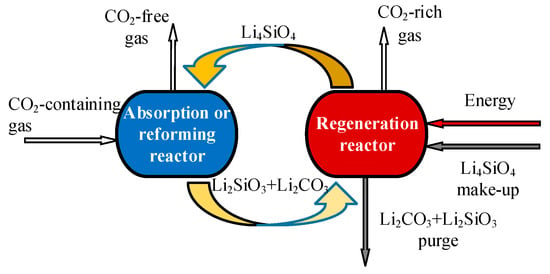
Figure 1.
Application of Li4SiO4 material for CO2 absorption for fossil fuel-fired power plants or hydrogen plants based on sorption-enhanced reforming.
It can be calculated according to Equation (2) that the theoretical CO2 absorption capacity of Li4SiO4 is 367 mg CO2/g Li4SiO4, which is much higher than that of Li2ZrO3 (125 mg/g) [9].
Additionally, CO2 absorption by Li4SiO4 material can also contribute to sorption-enhanced hydrogen production, as shown in Figure 1, where methane and ethanol are usually selected [15]. In the process of methane or ethanol reforming, CO2 is a necessary while undesired product. With in situ CO2 absorption by Li4SiO4 material, the concentration of CO2 in syngas can be reduced, and the reaction equilibrium of reforming can be shifted to hydrogen production simultaneously, thus the CO2 absorption capacity of Li4SiO4 material is the key factor to determine the hydrogen production efficiency [16,17]. This section will be discussed in detail in Section 6.
However, the CO2 absorption capacity and cyclic stability of pristine Li4SiO4 material prepared by the solid-state reaction method is low, which is mainly due to the smooth surface of pristine Li4SiO4 particles generated at high temperature, thus the surface area and pore volume of Li4SiO4 material are low, and the reaction between CO2 and Li4SiO4 is limited [18]. Therefore, a large number of works have been conducted to improve the pore structure of Li4SiO4, such as the application of organic precursors, which is conducive to the formation of pores, and doping with eutectic salts, which is favorable for the decrease of CO2 diffusion resistance [19,20].
Since CO2 absorption by Li4SiO4 material was firstly reported, abundant studies have been revealed the reaction mechanism and improved the cyclic CO2 absorption performance [21]. This work introduces the latest research progress on CO2 absorption performance of Li4SiO4 material. In addition, thermodynamic and kinetic comprehension of the reaction between CO2 and Li4SiO4 are illustrated, and strategies to enhance the cyclic CO2 absorption performance of Li4SiO4 material are summarized. Additionally, applications of Li4SiO4 material in sorption-enhanced hydrogen production are reviewed, and studies on CO2 absorption by Li4SiO4 material at the molecular scale are also reviewed briefly. Finally, the major drawback that hinders the large-scale application of Li4SiO4 material for CO2 absorption is introduced.
2. Thermodynamics and Kinetics of CO2 Absorption by Li4SiO4
2.1. Reaction Model for Synthesis of Li4SiO4
Li4SiO4 material is usually synthesized by the solid-state reaction method, and the preparation process is illustrated by Equation (1) [22,23], and a core-shell model was suggested for the solid-state reaction between Li2CO3 and SiO2, which is shown in Figure 2. In the first step, Li2CO3 reacts with SiO2 at their contact part, and a thin Li2SiO3 layer is formed. Li2SiO3 is the intermediate product, which continues to react with Li2CO3 to form Li4SiO4 eventually. Li4SiO4 and Li2SiO3 layers become thicker with the reaction, and internal SiO2 is covered by the layers in the meantime. Thus, Li+ and O2− must diffuse through the product layer before contacting with internal SiO2, and it is the limited step that limiting the synthesis of Li4SiO4, because the diffusion process is much slower than the reaction. Consequently, alternative synthesis methods and precursors for the synthesis of Li4SiO4 have been reported, which will be discussed in the following section [24].
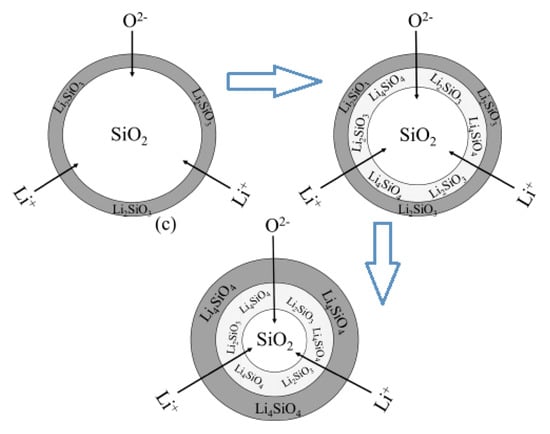
Figure 2.
Core-shell model for synthesis of Li4SiO4 by the solid-state route [24].
2.2. Kinetic Study for CO2 Absorption by Li4SiO4
Figure 3 shows the CO2 absorption performance of Li4SiO4 materials prepared by the solid-state reaction method and the sol-gel method in a thermogravimetric analyzer (TGA) [25], and the CO2 absorption amount (mg CO2/g sorbent) was used to evaluate the CO2 absorption capacity of Li4SiO4 materials, which is calculated according to Equation (3):
where CN is the amount of CO2 absorbed by the Li4SiO4 material, mg/g; N represents the number of cycles; m1 represents the initial mass of Li4SiO4 material, g; and m2 represents the mass of the sample during CO2 absorption, mg. The CO2 absorption stage of Li4SiO4 occurs at temperatures lower than 400 °C, and the CO2 absorption rate increases suddenly when the temperature reaches around 500–600 °C. Weight losses of two Li4SiO4 materials are observed when the temperature exceeds 720 °C, indicating the reaction converts to the regeneration of Li4SiO4 materials, and the regeneration reaction is much faster than the absorption process. As shown in Figure 3, the CO2 absorption capacity of Li4SiO4 material prepared by the sol-gel method is higher than that prepared by the solid-state reaction method, which will be discussed in Section 3.3.3.
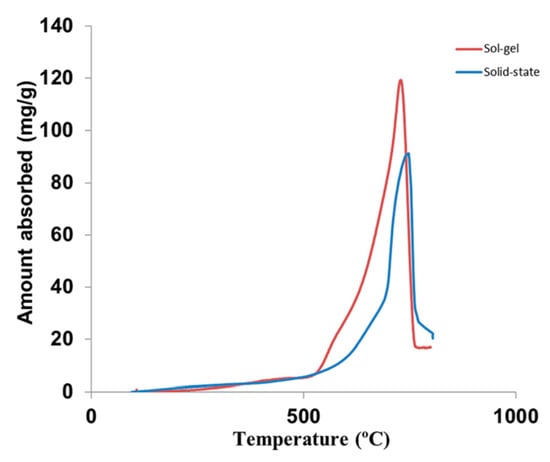
Figure 3.
CO2 absorption by Li4SiO4 material in pure CO2 with respect to temperature [25].
2.3. Thermodynamic Study for CO2 Capture by Li4SiO4
Figure 4 shows the equilibrium partial pressure of CO2 over Li4SiO4 material as a function of temperature [26], and the maximum temperature of CO2 absorption by Li4SiO4 material is determined by the corresponding CO2 partial pressure. When CO2 partial pressure is 100% at 1 atm, it can be inferred from Figure 4 that the equilibrium temperature is around 715 °C, which agrees well with the results that discussed above. The corresponding temperature of CO2 absorption by Li4SiO4 material can be determined by the CO2 partial pressure, and CO2 absorption by Li4SiO4 material occurs when the temperature is lower than the equilibrium temperature, otherwise Li4SiO4 material is regenerated. As a result, CO2 absorption and regeneration regions of Li4SiO4 material are divided by the equilibrium line.
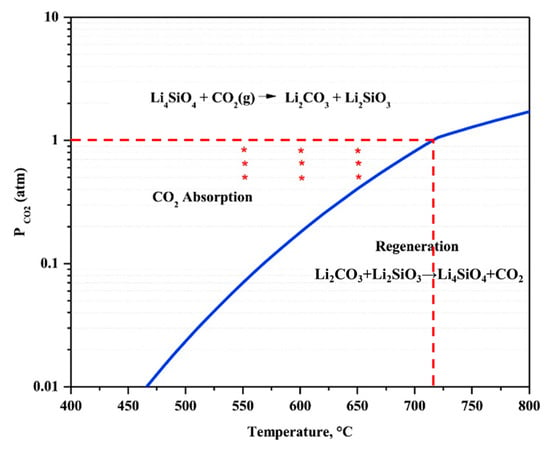
Figure 4.
Equilibrium CO2 partial pressure as a function of temperature for the absorption of CO2 of Li4SiO4 [26].
2.4. Reaction Mechanism and Reaction Model of CO2 Capture by Li4SiO4
The double-shell mechanism is regarded as the most appropriate model for the reaction between CO2 and Li4SiO4 [27], which is schematically illustrated in Figure 5. At the beginning of the reaction, CO2 molecules react with Li4SiO4 particles to generate a double shell composed of Li2CO3 and Li2SiO3, which covers the internal Li4SiO4. Then the reactants diffuse through the double shell to continue the reaction, and the thickness of the double shell increases as the reaction proceeds. Thus, the second stage is much slower than the first stage, owing to the high diffusion resistance of the reactants. Therefore, decreasing the diffusion resistance is conducive to the reaction between CO2 and Li4SiO4. The presence of steam and doping of molten salts are believed to reduce the diffusion resistance in the double shell, which will be discussed in the following section. Additionally, the shrinking core model and the unreacted core model were well-reported in many studies, which are also involved with the external product shell and internal unreacted core, and the models are similar to that of the double-shell model.
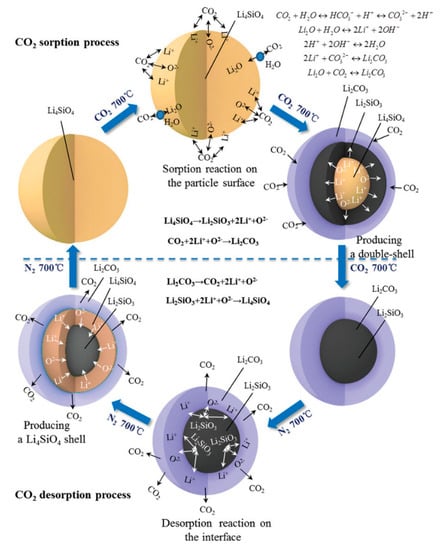
Figure 5.
Double-shell mechanism of Li4SiO4 material for CO2 absorption and regeneration [27].
TGA curves of CO2 absorption by Li4SiO4 at various temperatures are present in Figure 6, and weight gain of Li4SiO4 was used to evaluate its CO2 absorption performance, which can be calculated according to Equation (4):
where WN is the weight gain of Li4SiO4 material during the Nth cycles, wt.%; and CN is the amount of CO2 absorbed by Li4SiO4 material during the Nth cycles, mg/g. CO2 absorption capacity of Li4SiO4 increases with the temperature rising from 460 to 560 °C. Li4SiO4 shows a fast CO2 absorption stage in a short time and a slow CO2 absorption stage in the following long time, which are controlled by the chemical reaction and diffusion, respectively [28]. Most of the TGA curves are fitted to the double exponential model, which is shown in Equation (5):
where y represents the weight gain of Li4SiO4 material after CO2 absorption; k1 and k2 denote two exponential constants for the chemical reaction-controlled stage and the diffusion-controlled stage, respectively; and two pre-exponential factors A and B are the intervals that control the corresponding stages [28].
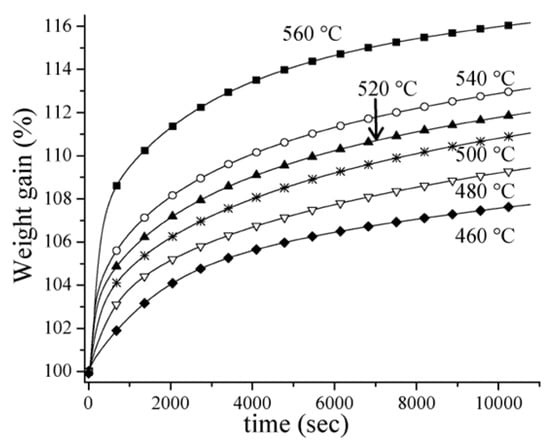
Figure 6.
Isotherms obtained in a CO2 atmosphere at various temperatures [28].
Table 1 presents the kinetic parameters of the double exponential model fitted to the reaction between CO2 and Li4SiO4 [28]. As presented in Table 1, the values of k1 are usually one order of magnitude higher than those of k2, and B are always larger than A, indicating that CO2 absorption over the surface of Li4SiO4 controlled by chemical reaction is a rapid process, and CO2 absorption controlled by diffusion occurs in a large interval of time. Thus, CO2 absorption controlled by diffusion is the limiting step hindering the absorption of CO2 by Li4SiO4 [29,30].

Table 1.
Kinetic parameters of reaction between Li4SiO4 and CO2 for double exponential model [28].
Although the double exponential model is widely used due to its simplicity, Ortiz et al. [26] thought that this model was short of the theoretical mechanism to support its fitting with the experimental data. Zhang et al. [27] reported that the Avrami–Erofeev model was relevant to the reaction mechanism of the formation and growth of product crystals, which are shown as Equations (6) and (7):
where α refers to the degree of conversion; K denotes the kinetic constant; k equals to Kn; and n is the kinetic parameter; t represents the time. Equation (7) is an equation of a straight line with slope n in the coordinates ln (−ln (1 − α)) vs. ln t. If the value of n is higher than 1, the absorption reaction is controlled by the formation and growth of product crystals. When n equals to 0.5 approximately, the absorption reaction is controlled by the diffusion of ions [31].
As illustrated in Figure 7, the curves of Avrami–Erofeev model look similar to TGA curves obtained from 550 to 700 °C, and the rapid chemical reaction-controlled stage and the slow diffusion-controlled stage can be easily distinguished at every temperature. Additionally, Zhang et al. [27] reported that the Avrami–Erofeev model suited the regeneration process of Li4SiO4 material, and the entire regeneration process was controlled by the rate of the formation and growth of product crystals, which was also confirmed by Xiang et al. [32]. Thus, the Avrami–Erofeev model is more suitable for CO2 absorption by Li4SiO4.
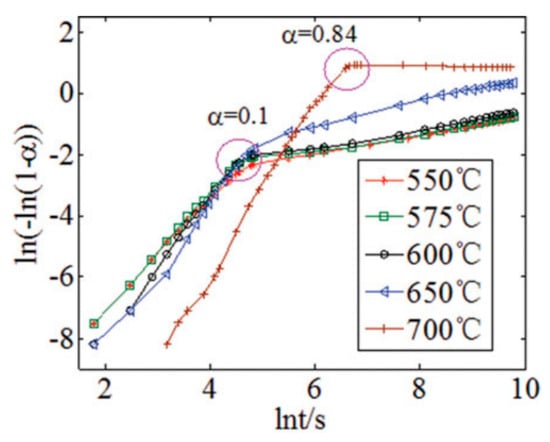
Figure 7.
Fit of kinetic experimental data by the Avrami–Erofeev model [27].
3. Synthesis of Li4SiO4 Materials with Superior Cyclic Absorption/Regeneration Performance
It is clear that Li4SiO4 material synthesized by the solid-state reaction method from SiO2 and Li2CO3 achieves low CO2 absorption capacity, due to the low porosity of Li4SiO4 generated at high temperatures during the preparation. Thus, the CO2 absorption capacity of Li4SiO4 decreases rapidly with the number of cycles, which is the main disadvantage of Li4SiO4 material in industrial applications. The various methods have been reported to enhance the cyclic performance of Li4SiO4 material prepared by solid-state reaction method, such as hydration [33] and ball milling [34,35]. The strategies to enhance the cyclic performance of Li4SiO4 can be categorized as follows: (i) reducing the diffusion resistance by adding solid solutions or molten salts; (ii) using alternative precursors; and (iii) using a more appropriate synthesis method.
3.1. Modification for Li4SiO4 Prepared by Solid-State Reaction
As discussed above, high temperature during the preparation by the solid-state reaction method of Li4SiO4 leads to sintering, and the core of Li4SiO4 usually cannot react with CO2. Thus, Yin et al. [33] proposed a hydration process to improve the pore structure of Li4SiO4 material. First, Li4SiO4 material was prepared by the solid-state reaction method, and then distilled water was added to the samples and stirred at 80 °C for 4 h. They reported that dense particles formed during the solid-state reaction preparation could be split into fine particles, so the porous structure and high cyclic CO2 absorption capacity of Li4SiO4 was obtained by hydration process.
Romero-Ibarra et al. [34] used the ball milling process to modify the surface properties of Li4SiO4 material, and they found that the ball milling process decreased the particle size and improved the surface area of Li4SiO4 material. Kanki et al. [35] reported that the ball milling process could promote CO2 absorption of Li4SiO4 material at lower temperatures, and longer ball milling duration led to higher CO2 absorption capacity. Additionally, the doping of K2CO3 in Li4SiO4 material improved its CO2 absorption capacity under short ball milling duration.
3.2. Doping of Solid Solutions or Molten Salts
3.2.1. Solid Solutions
The CO2 absorption rate of Li4SiO4 material is mainly controlled by the diffusion of ions and CO2. Zhao et al. [36] reported that solid solution usually formed with the doping of Al2O3 during solid-state preparation, thus increased oxygen vacancies could promote the diffusion in the product layer. Ortiz-Landeros et al. [37] reported that Al2O3 addition and ball milling could extend the range of CO2 absorption temperature. In addition, Ortiz-Landeros et al. [38] compared Li4+x(Si1−xAlx)O4 with Li4−x(Si1−xVx)O4 as the solid solutions, and the results showed that diffusion resistance of CO2 and ions in Li4+x(Si1−xAlx)O4 was diminished, while the presence of V was adverse to the diffusion through the product layer.
3.2.2. Molten Salts
The doping of alkali metals, such as Na and K, could produce a layer of molten salts with low eutectic temperature, which reduced diffusion resistance effectively, thus the limiting step of Li4SiO4 material for CO2 absorption could be resolved. The CO2 absorption performance of various alkali metal-doped Li4SiO4 materials is summarized in Table 2 [39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46].

Table 2.
Summary of CO2 absorption performance of Na and K doped Li4SiO4 materials.
As presented in Table 2, Na and K were the most commonly reported alkali metals to enhance the CO2 absorption performance of Li4SiO4 material. In order to determine the most appropriate doping method for K2CO3, Seggiani et al. [39] compared eutectic doping and simple mechanical addition of K2CO3, and they found that Li4SiO4 particles obtained from mechanical addition were smaller, as shown in Figure 8, so the mechanical doping method may be more appropriate for the doping of K2CO3. Olivares-Marín [47] et al. synthesized K2CO3-doped Li4SiO4 material with fly ash as the silicon precursor, and they reported that the CO2 absorption capacity of the prepared Li4SiO4 material increased with the increase of the dopant amount. It is also worth noting that Zhang et al. [42] reported that the K2CO3 doped Li4SiO4 material cooperated well with the Ni/γ-Al2O3 catalyst in the sorption-enhanced steam methane reforming (SE-SMR) system, and high-purity hydrogen (>95%) could be obtained at lower temperatures ranging from 500 to 550 °C, and the presence of steam in the regeneration atmosphere could improve the reaction rate obviously. Mejía-Trejo et al. [48] prepared Na-doped Li4SiO4 material by doping Na2CO3 into the starting materials of TEOS and Li2CO3 through the co-precipitation route, and they noted that the addition of Na2CO3 increased the activity and reduced the equilibrium temperature of Li4SiO4 material for CO2 absorption, and Li3.85Na0.15SiO4 had the highest CO2 absorption capacity among various Na-doped Li4SiO4 materials. Seggiani et al. [40] noted that dopants like K2CO3 and Na2CO3 could form eutectic mixtures with Li2CO3, which melted at high temperatures (>500 °C), so the diffusion of ions and CO2 was enhanced in the diffusion-controlled stage. Yang et al. [43] reported that orderly crystalline arrangement of Li4SiO4 was broken by doped K2CO3 and Na2CO3 for their different crystal sizes, thus more pores and larger specific surface area were generated.

Figure 8.
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images of Li4SiO4 samples obtained from different doping methods: eutectic doping (qE); simple mechanical addition (qK) [39].
3.2.3. Other Dopants
Wang et al. [49] prepared K-, Mg-, Cr-, and Ce-doped Li4SiO4 and found that Ce was the most difficultly doped into the Li4SiO4 crystal lattice among the four elements. However, Ce was the most effective to inhibit the aggregation of Li4SiO4 grains, so Ce-doped Li4SiO4 achieved the highest CO2 absorption performance. Subha et al. [50] studied the CO2 absorption by Li4SiO4 material doped with Y2O3, Gd2O3 or LaPO4, and found that both Y2O3 and Gd2O3 improved the CO2 absorption capacity of Li4SiO4, and Y2O3-doped Li4SiO4 retained the highest CO2 absorption capacity due to the segregation of second phase created by the doped unreacted Y2O3. Chen et al. [51] reported that Ca-doped Li4SiO4 material achieved high CO2 absorption capacity and they proposed a modified double-shell mechanism to describe the CO2 absorption and regeneration mechanism of Ca-doped Li4SiO4 as shown in Figure 9. The transformation of Ca2SiO4 to Li2CaSiO4 during CO2 absorption process was beneficial of transferring CO2 from Li4SiO4 surface to the core, which reduced the diffusion resistance and improved CO2 absorption, and regeneration was also correspondingly enhanced.
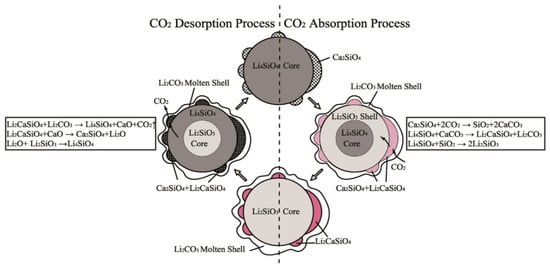
Figure 9.
CO2 absorption and regeneration mechanism of Ca-doped Li4SiO4 [51].
Additionally, doping of organic matter can also enhance the CO2 absorption property of Li4SiO4 material due to the formation of the porous structure. Wang et al. [30,52] prepared carbon-coated Li4SiO4 material by the sol-gel method, and gluconic acid and citric acid were used as the complexing agents, respectively. During the carbonization stage, gluconic acid and citric acid decomposed, and a mesoporous carbon coating covered the surface of Li4SiO4 material, which suppressed the growth of Li4SiO4 grains. As a result, the cyclic CO2 absorption capacities and rates of carbon-coated Li4SiO4 materials were higher than that of uncoated Li4SiO4 during multiple absorption/regeneration cycles. Furthermore, CMK-3, as a kind of porous carbon material [53], was also introduced into the Li4SiO4 material. Jeoung et al. [54] prepared CMK-modified Li4SiO4, while the cyclic absorption capacity of CMK-modified Li4SiO4 decreased obviously with the number of cycles.
It has been reviewed in this part that doping of metal elements, such as K, Na, Ca, Ce, Y, Al, or organic matters, can enhance the CO2 absorption capacities of Li4SiO4 material. The limitation in the diffusion-controlled stage for Li4SiO4 is reduced greatly with the doping of solid solution or molten salts, and the porous structure of Li4SiO4 by doping of organic matters is obtained. The additive amounts are minor, but the CO2 absorption performance of Li4SiO4 can be greatly enhanced.
3.3. Selection of Alternative Precursors for Preparation of Li4SiO4
Li4SiO4 material is usually prepared from Li2CO3 and SiO2, which are not able to create a favorable surface characteristic for CO2 absorption. Recent studies have shown that Li4SiO4 materials prepared from alternative precursors, especially organic precursors, rather than Li2CO3 and SiO2 achieve high CO2 absorption capacities and cyclic stability. In this section, the effects of precursors on CO2 absorption capacity of Li4SiO4 material are summarized.
3.3.1. Lithium Precursors
Kim et al. [29] synthesized Li4SiO4 material from LiOH and fumed silicate by the solid-state reaction method. They reported that the synthesis temperature could be reduced to 600 °C due to the use of LiOH, and the obtained Li4SiO4 showed higher CO2 absorption capacity compared with those synthesized at 700 °C and 800 °C, which achieved 298 mg/g after 10 cycles. Wang et al. [55] synthesized Li4SiO4 with LiOH by the sol-gel technique and they found that LiOH-synthesized Li4SiO4 particles were primarily composed of porous grains, and the average grain size of Li4SiO4 prepared by the sol-gel method was much smaller than that synthesized by the solid-state reaction method.
Weng et al. [56] synthesized Li4SiO4 from LiNO3 as lithium precursor and tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) as a silicon precursor by the sol-gel method. The CO2 absorption capacity of the obtained Li4SiO4 material increased with increasing temperature from 400 to 500 °C in 2% CO2. Bretado et al. [14] reported that the solid-state reaction method was more appropriate than the sol-gel method for the preparation of Li4SiO4 material when LiNO3 was used as the lithium precursor. However, Subha et al. [25] reported that the sol-gel method was superior to the solid-state reaction method for Li4SiO4 material prepared from LiNO3 and colloidal silica. This indicates that the most appropriate synthesis method depends on the lithium and silicon precursors simultaneously.
Compared with inorganic lithium precursors, organic lithium-containing materials seems more appropriate as the lithium precursor for the preparation of Li4SiO4 material. Yang et al. [19] used lithium acetate and lithium lactate to prepare novel Li4SiO4 materials by the impregnated suspension method. As shown in Figure 10, the two novel Li4SiO4 materials showed a bulgier morphology and more porous structure, compared with Li4SiO4 synthesized by the solid-state reaction method. Absorption capacities of Li4SiO4 material prepared from lithium acetate or lithium lactate as the lithium precursors were almost six times higher than that of a conventional Li4SiO4 material. Additionally, the CO2 absorption capacities and conversions of Li4SiO4 material prepared from lithium acetate or lithium lactate showed an incremental tendency over 40 cycles, and the conversion of Li4SiO4 prepared from lithium acetate was approximately 70% even in the last cycle, which was calculated according to Equation (8):
where XN is the conversion of Li4SiO4 during the Nth cycle, %; and m0 is the theoretical CO2 absorption capacity of Li4SiO4 material, which is 367 mg/g. Lee et al. [57] used Li and a Si-containing metal-organic framework (MOF) as the silicon precursor, and the prepared Li4SiO4 material was able to convert into Li4SiO4 thermally. The as-prepared material had a coral-like morphology, so the contact area between CO2 and Li4SiO4 material was enhanced, and the Li4SiO4 material showed higher CO2 absorption capacity than that prepared by the conventional solid-state reaction method.
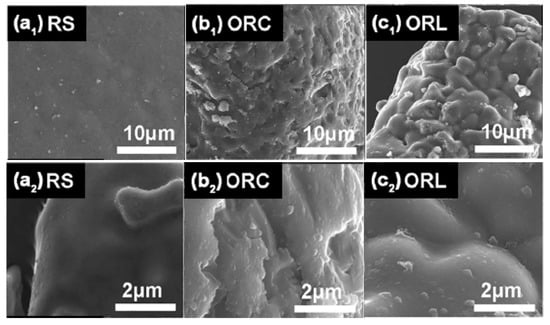
Figure 10.
SEM images of three kinds of Li4SiO4 materials prepared with Li2CO3 (RS), lithium acetate (ORC) and lithium lactate (ORL) [19].
In this section, CO2 absorption performance of Li4SiO4 material synthesized from various lithium sources was reviewed. It is known to all that the price of Li-containing materials is quite high now, including Li2CO3, LiOH, LiNO3 or organic lithium precursors mentioned above, so it is necessary to find other alternative Li-containing materials, especially wastes, with lower prices as the lithium precursor for the preparation of Li4SiO4 material.
3.3.2. Silicon Precursors
SiO2 is an essential raw material for the synthesis of Li4SiO4. In addition to pure SiO2, there are many SiO2-rich industrial wastes which have attracted researchers’ interests, such as rice husk ash (RHA) and fly ash (FA). In this section, the effects of alternative silicon precursors on CO2 absorption performance of Li4SiO4 material are critically reviewed.
Wang et al. [20] selected two kinds of RHA samples as the silicon precursors for the preparation of Li4SiO4 material, which contained the SiO2 contents of 94.71 and 98.84 wt.%, respectively. HCl aqueous solution was used to pretreat the two RHA samples, then Li4SiO4 materials were synthesized by the solid-state reaction method with Li2CO3. The employment of RHA produced a smaller particle size, larger pore volume, and surface area compared with pure Li4SiO4 material. They reported a weight gain of nearly 135 % over 15 cycles, which was much higher than that of pure Li4SiO4 material. Furthermore, Wang et al. [58] pretreated rice husk samples at 600 and 1000 °C, respectively, and cyclic performances of the two RHA-synthesized Li4SiO4 materials pretreated at 1000 °C achieved better CO2 absorption performance, which was similar to that of the RHA-derived Li4SiO4 material mentioned above. To study the effects of RHA as the silicon precursor on the CO2 absorption properties of Li4SiO4 material, Wang et al. [59] selected RHA and two kinds of nanosilica (Aerosil and quartz) to prepare Li4SiO4 materials by solid-state reaction method, and SEM images and BET analysis indicated that RHA-synthesized Li4SiO4 material possessed higher surface area and larger pore volume. Furthermore, the weight gain of RHA-synthesized Li4SiO4 material was higher and faster than that of the two nanosilica-synthesized Li4SiO4 materials, and its cyclic CO2 absorption capacity reached nearly 30 wt.% over 15 cycles. The authors ascribed this phenomenon to the almost unchanged surface morphology of Li4SiO4 material prepared from RHA over multiple absorption/regeneration cycles. Qiao et al. [60] also noted that RHA-derived Li4SiO4 material could enhance the yield of H2 and reduce the energy consumption in the process of sorption-enhanced steam ethanol reforming.
Fly ash (FA) is a kind of hazardous mineral residue released from coal-fired power plants, and it accounts for approximately 88% in the total coal ash content, which contains a high silicon content, thus it has been used to fabricate useful materials [61,62]. Therefore, Li4SiO4 materials can also be prepared from FA as a silicon precursor. Olivares-Marín et al. [47] fabricated Li4SiO4 material from Li2CO3 and three kinds of FA, and the samples were doped with several amounts ranging from 5 to 40 mol% of K2CO3. The cyclic CO2 absorption capacity of one of the doped FA-Li4SiO4 was approximately 100 mg/g over 10 cycles, which was far below the theoretical absorption capacity of Li4SiO4 material synthesized from pure SiO2, but it was relatively stable over multiple cycles. Sanna et al. [63] synthesized Na/Li-FA Li4SiO4 material with different molar ratios of Li2CO3, FA, and Na2CO3, and the material was doped with K2CO3. They reported that the CO2 absorption capacity of the obtained Li4SiO4 material was approximately 50 mg/g in low CO2 concentration in the presence of water vapor, and water vapor had no effect on the cyclic CO2 absorption capacity.
Shan et al. [64] selected diatomite as silicon precursor, containing the SiO2 content of approximately 75% [65], and zeolite was also chosen as precursor for comparison. Li4SiO4 was synthesized by the solid-state reaction method. Li4SiO4 synthesized from diatomite showed higher CO2 absorption capacity. Li4SiO4 material synthesized from diatomite achieved better CO2 absorption performance than that synthesized from pure SiO2 because of the higher specific surface area of the former [66]. In order to determine the optimum molar ratio of Li2CO3 to SiO2, Shan et al. [65] prepared a series of Li4SiO4 containing the molar ratios of Li2CO3 to SiO2 ranging from 2.0 to 2.8 and their CO2 absorption capacities carbonated under 50 vol.% CO2 at 620 °C for 30 min were shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
CO2 absorption performances of Li4SiO4 materials with different molar ratios of Li2CO3 to SiO2 [65].
As presented in Table 3, when molar ratio of Li2CO3 to SiO2 was 2.6:1, CO2 absorption capacity reached 30.32 wt.% (82.62% of the theoretical value). The CO2 absorption capacity of Li4SiO4 material with this molar ratio decreased from 34.14 to 27.70 wt.% over 16 cycles. However, Shan et al. [67] pointed out that high temperature (900 °C) during the solid-state reaction preparation process resulted in the sintering of Li4SiO4 easily, so they selected the impregnation precipitation method to prepare Li4SiO4 materials, which was operated at lower temperature. Diatomite, LiNO3, and NH3·H2O were selected as the starting materials with the Li:Si molar ratio of 5.2:1, and the reactions involved are shown in Equations (9) and (10). When carbonated in 50 vol.% CO2 and regenerated in pure N2 at 700 °C, both for 30 min, cyclic CO2 absorption capacity of Li4SiO4 synthesized by the impregnation precipitation method was quite stable, which decreased from 34.14 to 33.09 wt.% as the cycle number increases from 1 to 15.
Halloysite is also a SiO2-containing material with a SiO2 content of about 50 wt.% [68]. Niu et al. [69] synthesized Li4SiO4 from treated halloysite nanotubes (HNTs) with HCl aqueous solution and Li2CO3 by the solid-state reaction method at 800 °C. The content of Al2O3 of HNTs is 43.859%, and the presence of Al3+ was beneficial to the enlargement of Li4SiO4 crystalline structure, which is beneficial for its CO2 absorption performance [37]. The CO2 absorption capacity of halloysite-synthesized Li4SiO4 material was approximately 30 wt.% over 10 cycles, which was higher than that of SiO2-synthesized Li4SiO4 material.
In this section, CO2 absorption performances of Li4SiO4 materials synthesized from various silicon precursors were reviewed. Li4SiO4 synthesized from RHA, diatomite and halloysite exhibited high CO2 absorption capacity, while fly ash was not a good lithium precursor. Some elements in these silicon precursors other than pure SiO2 are possibly beneficial for the CO2 absorption properties of Li4SiO4 materials, which will be discussed in the following sections. There are a large number of Si-containing materials, especially industrial wastes like steel slag, so the following research will focus on these materials. The studies on alternative silicon precursors for the preparation of Li4SiO4 materials have obtained great progress, while the major problem that limits the practical application of Li4SiO4 is the high price of Li-containing materials, and the cost of Li4SiO4 will not be reduced by much even if SiO2 is free of charge, so the future research should focus on alternative lithium precursors.
3.3.3. Synthesis Methods
Most of the Li4SiO4 materials were synthesized by the traditional solid-state reaction method at a relatively high temperature (900 °C). The solid-state reaction method has been widely used because of its simplicity, while Bretado et al. [14] reported that high temperature during the solid-state reaction process resulted in contamination and volatilization. In addition, the microstructure and composition of Li4SiO4 materials were difficult to control and agglomeration and sintering of the materials also occurred in the preparation process [24,29]. Thus, Bretado et al. [14] selected the impregnated suspension method to prepare Li4SiO4 material and they found that the conversion of the obtained Li4SiO4 material (98.4%) was higher than that prepared by the solid-state reaction method (94.9%).
Subha et al. [25] reported that the platelet-shaped Li4SiO4 material synthesized from LiNO3 and colloidal silica by a sol-gel method achieved an absorption capacity of 350 mg/g. Additionally, the platelet-shaped Li4SiO4 material was coated with a porous carbon mesh, and the cyclic absorption/regeneration performance of the platelet-shaped Li4SiO4 material retained approximately 120 mg/g over eight cycles. The CO2 absorption rates of the coated Li4SiO4 materials were faster than those of the uncoated ones. Additionally, the sol-gel method was superior to the solid-state reaction method when LiOH was selected as the lithium precursor [29,55]. However, the impregnation precipitation method was superior to the solid-state reaction method when diatomite was selected as the silicon precursor [67]. Venagas et al. [70] reported that Li4SiO4 materials synthesized by the sol-gel method was not completely pure, probably because the use of a microwave oven resulted in the sublimation of Li4SiO4.
4. Effects of Particle Properties on CO2 Absorption Performance of Li4SiO4 Material
The newly synthesized Li4SiO4 powder is too fine, and elutriation might occur in the reactor, especially in fluidized bed reactors, in industrial applications. In addition, powdery Li4SiO4 materials cannot create effective fluidization, while most of the studies on CO2 absorption by Li4SiO4 material were conducted on fixed bed reactors or TGA. Thus, pelletization may be an effective method for the practical application of Li4SiO4 materials. The effects of the particle properties on CO2 absorption performance of Li4SiO4 material were critically reviewed in this section.
Pacciani et al. [71] studied the CO2 absorption by the pelletized Li4SiO4 materials, which were doped with less than 10 vol.% K2CO3 and Li2TiO3 as a binder. The CO2 absorption capacity of the pelletized Li4SiO4 material was 23 wt.% carbonated in 10 vol.% CO2. However, Kato et al. [72] reported that the pelletized Li4SiO4 materials were more prone to lose their cyclic stability due to the sintering which was caused by the short length of material particles. Essaki et al. [73] prepared cylinder-type K2CO3 doped Li4SiO4 materials with the diameter of 3 mm and length of 6 mm, while the CO2 absorption capacity of a Li4SiO4 pellet was not so high as that of Li4SiO4 powder. Puccini et al. [74] synthesized K2CO3-doped Li4SiO4 by the solid-state reaction method, and they selected cellulose fiber as the binder. The Li4SiO4 material pellets with a diameter of 6 mm and lengths of 1.5, 2.5, and 3.5 mm were prepared, but the prepared Li4SiO4-based pellets did not show superior cyclic performance and the conversion of the Li4SiO4 pellets decreased to below 28% after 10 cycles. Furthermore, Puccini et al. [75] selected layered graphite and carbon nanotubes as the binders, and thermogravimetric analysis showed that layered graphite was a more suitable binder than carbon nanotubes. It is noteworthy that the cyclic performance of Li4SiO4 pellets with a binder of layered graphite was more superior than that of the pellets mentioned in [74], as shown in Figure 11.
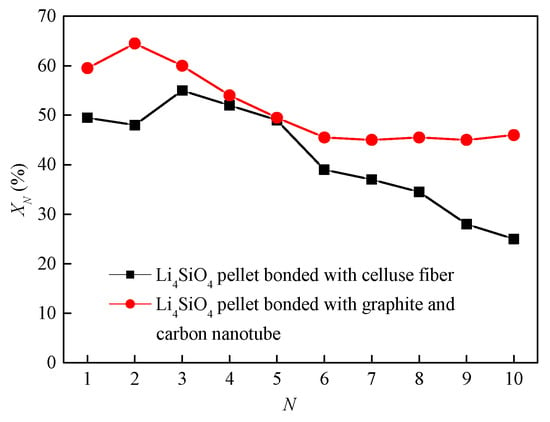
Figure 11.
Cyclic CO2 absorption by Li4SiO4 materials with different binders [74,75].
Pelletization is an essential procedure for the practical application of Li4SiO4, but few researchers studied the CO2 absorption performance of the pelletized Li4SiO4 materials in fluidized bed reactors. Additionally, mechanical intensity and wearing characteristics of pelletized Li4SiO4 materials have seldom been reported.
5. Effects of Reaction Conditions on CO2 Absorption Performance of Li4SiO4 Material
Realistic reaction conditions for CO2 absorption by Li4SiO4 material is very complicated, which involves the absorption atmosphere, absorption temperature, regeneration (desorption) temperature, and operating pressure, etc. Hence, the effects of reaction conditions on the CO2 absorption performance of Li4SiO4 materials are reviewed in this section.
5.1. Reaction Atmosphere
5.1.1. CO2 Concentration
The practical CO2 concentration in the flue gas from fossil fuel-fired power plant is about 15 vol.% [76], but pure CO2 is usually selected as the absorption atmosphere of Li4SiO4, and the CO2 absorption performance under the practical lower CO2 concentration has been overlooked. In fact, CO2 concentration in sorption-enhanced hydrogen production process is also usually low. Therefore, it is necessary to investigate the CO2 absorption performance of Li4SiO4 material in low CO2 concentrations.
Pacciani et al. [71] reported that the CO2 absorption rate of Li4SiO4 material rose apparently when CO2 concentration in absorption atmosphere increased from 2.5 to 24.5 vol.%. Essaki et al. [77] prepared the pelletized Li4SiO4 materials with an average particle size of 5 mm and K2CO3 and Li2ZrO3 were doped into the materials to promote the absorption reaction and prevent reduction of absorption capacity, respectively. The absorption property of Li4SiO4 pellets was investigated in 5 vol.% CO2 at first, and they found that 500 °C was the most appropriate temperature in the range of 400–600 °C for the CO2 absorption by Li4SiO4. However, when the absorption tests were carried out in 10 or 15 vol.% CO2, it was found that the CO2 absorption capacity rose as the temperature increased from 400 to 600 °C. Essaki et al. [77] ascribed this phenomenon to the influence of reaction equilibrium, as shown in Figure 12. The equilibrium temperature of CO2 absorption and regeneration showed an increasing trend with increasing CO2 concentration, and the weight increase was used to evaluate the CO2 absorption performance of Li4SiO4 material, which can be calculated according to Equation (11):
where IN is the weight increase of Li4SiO4 material during the Nth cycle, wt.%; WN is the weight gain, wt.%; N is the number of cycles. It was also noteworthy that the CO2 absorption process of Li4SiO4 was limited in low CO2 concentration (5 vol.%), while it was controlled by the diffusion of Li+ and O2− in high CO2 concentration (15 vol.%).
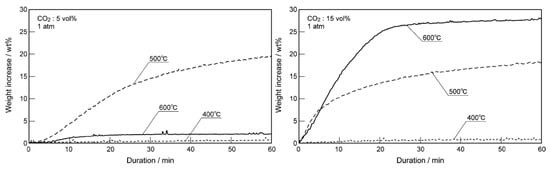
Figure 12.
Weight increase of Li4SiO4 at different temperatures in different CO2 concentrations [77].
Researchers found that the limits of low CO2 concentration could be counteracted by the addition of dopants. Puccini et al. [78] found Li4SiO4 material doped with 30 wt.% K2CO3 maintained a stable CO2 absorption capacity (approximately 160 mg/g) after 25 cycles in 4 vol.% CO2 at 580 °C. It is worth noting that Seggiani et al. [39] reported that CO2 absorption capacity of K2CO3-doped Li4SiO4 material was superior than 20 wt.% over four cycles in 4 vol.% CO2. Furthermore, Seggiani et al. [40] also reported that the CO2 absorption capacity of Na2CO3-doped Li4SiO4 material in 4 vol.% CO2 was 7 wt.%, and it was quite stable over 25 cycles. Adding some dopants can improve the CO2 absorption capacity of Li4SiO4 material, but the improvement in lower CO2 concentration is still relatively lower compared with that in higher CO2 concentration. The CO2 absorption performance of Li4SiO4 material in high CO2 concentration has been well studied by researchers. Thus, Li4SiO4 materials with high absorption capacity, fast absorption rate, and good cyclic stability in low CO2 concentrations should be investigated for industrial application.
5.1.2. Presence of Steam
Apart from CO2, steam also exists in realistic CO2 absorption conditions, and the content of steam during the typical sorption-enhance hydrogen production process is more than 30%. Ochoa-Fernández et al. [79] reported that steam could promote the mobility of alkaline ions, indicating that the limiting resistance of the CO2 absorption reaction could be reduced. Thus, the presence of steam in the absorption atmosphere also has non-negligible effect on the CO2 absorption capacity of Li4SiO4 material.
Ochoa-Fernández et al. [80] reported that the presence of 10 vol.% steam in the absorption atmosphere could raise the CO2 capacity from 9.5 to 29 wt.%. Additionally, they also found that the presence of steam accelerated the regeneration reaction: the regeneration process became faster and more thorough with the presence of steam, and cyclic CO2 absorption performance of Li4SiO4 material degraded slightly after eight cycles with the presence of steam, almost the same as the experimental data obtained in dry atmosphere. Quinn et al. [81] used pelletized Li4SiO4 materials for CO2 absorption in 14.7% CO2, 2.6% steam in N2 at 550 °C, and they found that the CO2 absorption capacity after 10 min was almost three times higher than that in dry atmosphere. Furthermore, Sanna et al. [63] synthesized Li4SiO4 material from FA as SiO2 precursor, and the CO2 absorption capacity was enhanced by steam. Puccini et al. [82] also noted that the CO2 absorption rate was accelerated correspondingly with increasing steam concentration from 10 to 30 vol.%.
As mentioned above, the presence of steam contributes to the CO2 absorption by Li4SiO4 material, because the addition of steam maybe enhances the mobility of Li+ and O2− [27,83], thus the resistance of diffusion is reduced, so the CO2 absorption capacity of Li4SiO4 is enhanced by steam.
5.1.3. Gas Contaminants
NOx and SO2 are common gas contaminants which have done great harm to the environment and people’s health. Thus, the effects of NOx and SO2 in the flue gas on the CO2 absorption by Li4SiO4 material should be considered. The effects of NOx and SO2 on the CO2 absorption performance of Li4SiO4 material could be great despite of their minor contents [82].
Puccini et al. [82] performed CO2 absorption tests in an atmosphere of 4 vol.% CO2 and various concentrations of NO, and the results showed that NO in the absorption atmosphere does not show a harmful effect on the CO2 absorption capacity of Li4SiO4 material. Furthermore, when the concentration of SO2 in the absorption atmosphere increased from 0 to 2000 ppm, the weight change of Li4SiO4 material increased with the increase of SO2 concentration, but the regeneration performance of Li4SiO4 material in the presence of SO2 was worse compared with that in the absence of SO2. Additionally, the cyclic CO2 absorption performance of Li4SiO4 material was negatively influenced in the presence of SO2 under absorption and regeneration atmospheres [71]. The authors ascribed this phenomenon to the nonreversible reaction between SO2 and Li4SiO4, as shown in Equations (12) and (13):
The formation of Li2SO3 and Li2SO4 prevented the regeneration of the materials, indicating that the presence of SO2 in the absorption atmosphere has an adverse effect on the absorption performance of Li4SiO4 material [82]. In general, NO had no negative impact on the CO2 absorption property of Li4SiO4 materials, while SO2 had an adverse effect due to the formation of the irreversible Li2SO3 and Li2SO4, so SO2 must be scrubbed prior to the trapping of CO2. However, the exact joint role and acting mechanism of NO and SO2 in the process of CO2 capture are still unknown, and the effects of other contaminants, like HCl or H2S, on the CO2 absorption by Li4SiO4 material are not clear, thus further research is necessary.
5.2. Reaction Temperature
As shown in Figure 4, the equilibrium temperatures of absorption and regeneration increase as the CO2 partial pressure rises monotonously. In other words, each equilibrium temperature corresponds with a partial pressure of CO2 in the absorption atmosphere. Essaki et al. [77] reported that when the absorption temperature of Li4SiO4 pellets provided by Toshiba varied from 400 to 600 °C in 5 vol.% CO2, and results showed that weight increase at 500 °C was 20 wt.%, which was much higher than those at 400 °C and 600 °C. Additionally, Quinn et al. [81] reported that 625 °C was the most appropriate temperature for the absorption of Toshiba-provided Li4SiO4 pellets in a pure CO2 atmosphere. This confirmed the conclusion that the equilibrium temperature of the reaction between Li4SiO4 and CO2 rises with increasing CO2 partial pressure.
Different kinds of Li4SiO4 materials accommodate diverse appropriate absorption temperatures. Qiao et al. [60] synthesized Li4SiO4 material from RHA and Li2CO3, and they found that the most suitable temperature for absorption was 650 °C in a pure CO2, while Puccini et al. [78] reported that 580 °C was the optimum temperature for K-doped Li4SiO4 materials, and Wang et al. [30] pointed out that 575 °C was the most appropriate for the CO2 absorption by Li4SiO4.
Temperature during the regeneration process also had a deep effect on CO2 absorption performance on Li4SiO4 material. Ochoa-Fernández et al. [80] reported that the ratio and degree of regeneration increased when the regeneration temperature rose from 525 to 575 °C. This indicates that a higher regeneration temperature is possibly advantageous for the regeneration of Li4SiO4 material, while too high a regeneration temperature intensifies the sintering of the material, which is extremely harmful.
6. Application of Li4SiO4 Material in Sorption-Enhanced Hydrogen Production
Sorption-enhanced hydrogen production is one of the most important applications of Li4SiO4 material as a CO2 acceptor, which mainly consists of sorption-enhanced steam methane reforming (SE-SMR) and sorption-enhance steam ethanol reforming (SE-SER). Overall reactions of SE-SMR and SE-SER are shown in Equations (14) and (15), respectively:
In the SE-SMR and SE-SER processes, in situ CO2 removal of Li4SiO4 material as the CO2 acceptor shifts the reaction equilibrium to hydrogen production, and exothermal absorption of CO2 by the Li4SiO4 material provides heat for reforming, thus high hydrogen yield can be achieved.
Rusten et al. [84] conducted SE-SMR with CO2 absorption by Li4SiO4 material in a fixed bed reactor at 848 K and 2 MPa, and syngas with the hydrogen concentration of 87% was obtained, which was higher than that obtained when Li2ZrO3 was used as a CO2 acceptor. Essaki et al. [85] introduced commercial Li4SiO4 pellets into SE-SMR process, and the experiments were carried out on a vertical furnace. It was reported that methane conversion at 550 °C was 80%, and hydrogen concentration reached 93.6 vol.% in syngas. The performance of Li4SiO4 pellets in the SE-SER process was also tested, and the results showed that the concentrations of hydrogen and CO in syngas were higher than 99 vol.% and less than 0.12 vol.%, respectively, indicating that Li4SiO4 pellets were promising as the CO2 acceptor for the SE-SER process [86]. Zhang et al. [42] reported K2CO3-doped Li4SiO4 material coupled well with the Ni/γ-Al2O3 catalyst, and hydrogen concentration in the syngas was higher than 95 vol.%. In addition, they found that homogeneous distribution of Li4SiO4 material and catalyst led to higher hydrogen concentration in the syngas.
It can be concluded from the studies above that hydrogen yield and concentration were mainly dependent on the performance of Li4SiO4 materials, thus Li4SiO4 materials with superior CO2 absorption performance should be investigated. Additionally, Li4SiO4 materials may be applicable to various sorption-enhanced hydrogen production, and raw materials for gasification could be biomass, sludge, coal, etc.
7. Density Functional Theory Studies on Li4SiO4 Material
Duan et al. [87] studied CO2 absorption performance on monoclinic and triclinic phases of Li4SiO4 using density functional theory, and they found that the thermodynamic properties of the two phases were similar to each other. The calculation results showed that reaction heat of the reaction between Li4SiO4 and CO2 was consistent with the experimental data. Kong et al. [88] reported that the (0 1 0) plane was the most stable low-Miller index plane of Li4SiO4, and the adsorption and dissociation behaviors of molecular H2O on the Li4SiO4 (0 1 0) plane were investigated. They found that molecular H2O was more inclined to be absorbed on O atoms on the surface.
8. Conclusions
Research progress of Li4SiO4 materials for CO2 capture in energy production processes, including hydrogen plants based on sorption-enhanced reforming and fossil fuel-fired power plants, were reviewed in this paper. Thermodynamic and kinetic studies on the preparation and CO2 absorption of Li4SiO4 material were demonstrated, and the diffusion of CO2 and ions through the product layer seemed to be the limiting step for CO2 absorption by Li4SiO4 material. Since Li4SiO4 material prepared by the traditional solid-state reaction method only achieved low CO2 absorption capacity, methods to enhance the CO2 absorption performance of Li4SiO4 material were illustrated. Introducing a solid solution and molten salts could reduce the diffusion resistance in the product layer, and using hydration, ball milling, or organic precursors could increase the contact area of CO2 and Li4SiO4, which is beneficial for CO2 absorption by Li4SiO4 material. The sol-gel method seemed to be most appropriate for preparation of Li4SiO4 material, which is beneficial for the formation of porous structure. The effects of gas contaminants and reaction conditions on CO2 absorption performance of Li4SiO4 material and the applications of Li4SiO4 material in the sorption-enhanced hydrogen production process were summarized. In view of the current studies reviewed in this work, potential research thoughts and trends are suggested as follows:
(i) Most of the laboratory experiments were carried out on TGA or fixed-bed reactors, while fluidized bed was the common equipment in practical application for the absorption of CO2 under most energy production conditions. Additionally, powdery Li4SiO4 materials could not create effective fluidization, while studies on the performance of pelletized Li4SiO4 materials were insufficient. As a result, more focus should be attached to the CO2 absorption performance of pelletized Li4SiO4 material in fluidized bed reactors.
(ii) Application of Li4SiO4 materials on sorption-enhanced hydrogen production is an important aspect, and hydrogen yield and concentration were considerable, while fewer studies involved this area. Additionally, CO2 absorption performance of Li4SiO4 materials in realistic sorption-enhanced hydrogen production conditions (i.e., low CO2 concentration in the presence of steam) deserves to be studied.
(iii) Preparation cost of Li4SiO4 materials is the main problem that limits its industrial application, thus many studies investigated the feasibility of silicon-containing solid wastes as a silicon precursor. However, the main factor that controls the cost of Li4SiO4 materials is the expensive lithium precursor. As a result, it is suggested that lithium-containing wastes can be tested for the possibility as a lithium precursor, and Li4SiO4 materials prepared from inexpensive lithium-containing wastes may be promising for large-scale CO2 absorption.
Funding
This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (51876105) and the Fundamental Research Funds of Shandong University (2018JC039). The APC was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (51876105).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Fiore, A.D.; Alterio, V.; Monti, S.M.; Simone, G.D.; Ambrosio, K.D. Thermostable carbonic anhydrases in biotechnological applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 15456–15480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.H. Advances in Catalysts for CO2 Reforming of Methane. ACS Symp. Ser. 2010, 1056, 155–174. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Li, Y.; Shi, L.; He, Z.; Wang, Z. Fabrication and CO2 capture performance of magnesia-stabilized carbide slag by by-product of biodiesel during calcium looping process. Appl. Energy 2016, 168, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kezhen, Y.; James, G.D.; Zimmerman, W.B. Periodic CO2 Dosing Strategy for Dunaliella salina Batch Culture. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 11509–11521. [Google Scholar]
- Kierzkowska, A.M.; Pacciani, R.; Müller, C.R. CaO-Based CO2 Sorbents: From Fundamentals to the Development of New, Highly Effective Materials. Chemsuschem 2013, 6, 1130–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, M.; Essaki, K.; Nakagawa, K.; Suyama, Y.; Terasaka, K. CO2 absorption properties of lithium ferrite for application as a high-temperature CO2 absorbent. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 2005, 113, 684–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara-Garcia, H.A.; Ramírez-Moreno, M.J.; Ortiz-Landeros, J.; Pfeiffer, H. CO2 chemisorption in Li2CuO2 microstructurally modified by ball milling process: Study performed with different physicochemical CO2 capture conditions. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 57880–57888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, K.; Murayama, N.; Shibata, J. Absorption and release of carbon dioxide with various metal oxides and hydroxides. Mater. Trans. 2007, 48, 2739–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, M.; Yoshikawa, S.; Nakagawa, K. Carbon dioxide absorption by lithium orthosilicate in a wide range of temperature and carbon dioxide concentrations. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 2002, 21, 485–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Ibarra, I.C.; Durán-Muñoz, F.; Pfeiffer, H. Influence of the K-, Na- and K-Na-carbonate additions during the CO2 chemisorption on lithium oxosilicate (Li8SiO6). Greenh. Gases Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán-Muñoz, F.; Romero-Ibarra, I.C.; Pfeiffer, H. Analysis of the CO2 chemisorption reaction mechanism in lithium oxosilicate (Li8SiO6): A new option for high-temperature CO2 capture. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 3919–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spataru, C.I.; Ianchis, R.; Petcu, C.; Nistor, C.L.; Purcar, V.; Trica, B.; Nitu, S.G.; Somoghi, R.; Alexandrescu, E.; Oancea, F. Synthesis of non-toxic silica particles stabilized by molecular complex oleic-acid/sodium oleate. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, R.; Chao, Z.; Zhao, L.; Wei, Y.; Song, E. Emodin-loaded magnesium silicate hollow nanocarriers for anti-angiogenesis treatment through inhibiting VEGF. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 16936–16948. [Google Scholar]
- Bretado, M.E.; Guzmán Velderrain, V.; Lardizábal Gutiérrez, D.; Collins-Martínez, V.; Ortiz, A.L. A new synthesis route to Li4SiO4 as CO2 catalytic/sorbent. Catal. Today 2005, 107–108, 863–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arstad, B.; Prostak, J.; Blom, R. Continuous hydrogen production by sorption enhanced steam methane reforming (SE-SMR) in a circulating fluidized bed reactor: Sorbent to catalyst ratio dependencies. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 189–190, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rout, K.R.; Jakobsen, H.A. A numerical study of pellets having both catalytic- and capture properties for SE-SMR process: Kinetic- and product layer diffusion controlled regimes. Fuel Process. Technol. 2013, 106, 231–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Jakobsen, H.A. The modeling of circulating fluidized bed reactors for SE-SMR process and sorbent regeneration. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2014, 108, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, J. The influencing factor for CO2 absorption of Li4SiO4 at high temperature. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Measuring Technology and Mechatronics Automation, Shangshai, China, 6–7 January 2011; pp. 839–841. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Liu, W.; Sun, J.; Hu, Y.; Wang, W.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, M. Preparation of novel Li4SiO4 sorbents with superior performance at low CO2 concentration. ChemSusChem 2016, 9, 1607–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Guo, X.; Zhao, P.; Wang, F.; Zheng, C. High temperature capture of CO2 on lithium-based sorbents from rice husk ash. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 189, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Hong, M.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Gu, C. CO2 absorption properties of Ti- and Na-doped porous Li4SiO4 prepared by a sol–gel process. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 4698–4706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Meng, J.B.; Luo, D.L. Synthesis and characterization of lithium silicate powders. Fusion Eng. Des. 2009, 84, 2124–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carella, E.; Hernandez, M. High lithium content silicates: A comparative study between four routes of synthesis. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 9499–9508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Cheng, W.; Jin, X.; Wang, G.; Lu, H.; Wang, H.; Chen, D.; Fan, B.; Hou, T.; Zhang, R. Effect of the particle size of quartz powder on the synthesis and CO2 Absorption properties of Li4SiO4 at high temperature. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 1886–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subha, P.V.; Nair, B.N.; Hareesh, P.; Mohamed, A.P.; Yamaguchi, T.; Warrier, K.G.K.; Hareesh, U.S. Enhanced CO2 absorption kinetics in lithium silicate platelets synthesized by a sol-gel approach. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 12792–12798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López Ortiz, A.; Escobedo Bretado, M.A.; Guzmán Velderrain, V.; Meléndez Zaragoza, M.; Salinas Gutiérrez, J.; Lardizábal Gutiérrez, D.; Collins-Martínez, V. Experimental and modeling kinetic study of the CO2 absorption by Li4SiO4. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 16656–16666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Han, D.; Liu, Y.; Qian, Y.; Zhu, Z. Analysis of CO2 sorption/desorption kinetic behaviors and reaction mechanisms on Li4SiO4. AIChE J. 2013, 59, 901–911. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Mosqueda, R.; Pfeiffer, H. Thermokinetic analysis of the CO2 chemisorption on Li4SiO4 by using different gas flow rates and particle sizes. J. Phys. Chem. A 2010, 114, 4535–4541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Jang, H.D.; Choi, M. Facile synthesis of macroporous Li4SiO4 with remarkably enhanced CO2 adsorption kinetics. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 280, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, P.; Yin, Z.; Su, Z.; Sun, J. Synthesis of a highly efficient Li4SiO4 ceramic modified with a gluconic acid-based carbon coating for high-temperature CO2 capture. Appl. Energy 2016, 183, 1418–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagorowsky, G.; Prikhod’ko, G.; Ogenko, V.; Koval’chuk, G. Investigation of kinetics of solid-phase synthesis of lithium orthosilicate. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 1999, 55, 699–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, C.; Yu, Y. Reaction kinetics for the synthesis of li4sio4 by solid state reaction from Li2SiO3 and Li2CO3 for tritium breeder. J. Fusion Energy 2016, 35, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Wang, K.; Zhao, P.; Tang, X. Enhanced CO2 Chemisorption properties of Li4SO4, Using a water hydration-calcination technique. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 1142–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Ibarra, I.C.; Ortiz-Landeros, J.; Pfeiffer, H. Microstructural and CO2 chemisorption analyses of Li4SiO4: Effect of surface modification by the ball milling process. Thermochim. Acta 2013, 567, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanki, K.; Maki, H.; Mizuhata, M. Carbon dioxide absorption behavior of surface-modified lithium orthosilicate/potassium carbonate prepared by ballmilling. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 18893–18899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Long, X.; Chen, X.; Xiao, C.; Gong, Y.; Guan, Q.; Li, J.; Xie, L.; Chen, X.; Peng, S. Design, synthesis and characterization of the advanced tritium breeder: Li4+xSi1−xAlxO4 ceramics. J. Nucl. Mater. 2015, 467, 911–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Landeros, J.; Romero-Ibarra, I.C.; Gómez-Yáñez, C.; Lima, E.; Pfeiffer, H. Li4+x(Si1−xAlx)O4 solid solution mechanosynthesis and kinetic analysis of the CO2 chemisorption process. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 6303–6311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Landeros, J.; Gómez-Yáñez, C.; Palacios-Romero, L.M.; Lima, E.; Pfeiffer, H. Structural and thermochemical chemisorption of CO2 on Li4+x(Si1−xAlx)O4 and Li4−x(Si1−xVx)O4 solid solutions. J. Phys. Chem. A 2012, 116, 3163–3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seggiani, M.; Puccini, M.; Vitolo, S. High-temperature and low concentration CO2 sorption on Li4SiO4 based sorbents: Study of the used silica and doping method effects. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2011, 5, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seggiani, M.; Puccini, M.; Vitolo, S. Alkali promoted lithium orthosilicate for CO2 capture at high temperature and low concentration. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2013, 17, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.; Ni, Y.; Zhu, Z. Absorption behaviors study on doped Li4SiO4 under a humidified atmosphere with low CO2 concentration. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 17913–17920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Shen, C.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Y. Steam methane reforming reaction enhanced by a novel K2CO3-doped Li4SiO4 sorbent: Investigations on the sorbent and catalyst coupling behaviors and sorbent regeneration strategy. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 4831–4842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liu, W.; Sun, J.; Hu, Y.; Wang, W.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, M. Alkali-doped lithium orthosilicate sorbents for carbon dioxide capture. Chemsuschem 2016, 9, 2480–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Qi, L.; Dai, K. Effect of Na-doping on CO2 absorption of Li4SiO4. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 2006, 22, 860–863. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, P.; Yin, Z.; Su, Z.; Sun, J. Molten sodium-fluoride-promoted high-performance Li4SiO4-based CO2 sorbents at low CO2 concentrations. Appl. Energy 2017, 204, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, W.; Yin, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, P. High-capacity Li4SiO4-based CO2 sorbents via a facile hydration-nacl doping technique. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 6257–6265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares-Marín, M.; Drage, T.C.; Maroto-Valer, M.M. Novel lithium-based sorbents from fly ashes for CO2 capture at high temperatures. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2010, 4, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejía-Trejo, V.L.; Fregoso-Israel, E.; Pfeiffer, H. Textural, Structural, and CO2 chemisorption effects produced on the lithium orthosilicate by its doping with sodium (Li4−xNaxSiO4). Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 7171–7176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Yin, Z.; Zhao, P.; Zhou, Z.; Su, Z.; Sun, J. Development of metallic element-stabilized Li4SiO4 sorbents for cyclic CO2 capture. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 42, 4224–4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subha, P.V.; Nair, B.N.; Hareesh, P.; Mohamed, A.P.; Yamaguchi, T.; Warrier, K.G.K.; Hareesh, U.S. CO2 absorption studies on mixed alkali orthosilicates containing rare-earth second-phase additives. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 5319–5326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xiong, Z.; Qin, Y.; Gong, B.; Tian, C.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, C. High-temperature CO2 sorption by Ca-doped Li4SiO4 sorbents. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 13077–13085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Yin, Z.; Zhao, P. Synthesis of macroporous Li4SiO4 via a citric acid-based sol–gel route coupled with carbon coating and its CO2 chemisorption properties. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 2990–2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, S.; Joo, S.; Ryoo, R.; Kruk, M.; Jaroniec, M.; Liu, Z.; Ohsuna, T.; Terasaki, O. Synthesis of new, nanoporous carbon with hexagonally ordered mesostructure. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 10712–10713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeoung, S.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Moon, H.R. Effects of porous carbon additives on the CO2 absorption performance of lithium orthosilicate. Thermochim. Acta 2016, 637, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, X.; Zhao, P.; Guo, X. High temperature capture of CO2 on lithium-based sorbents prepared by a water-based sol-gel technique. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2014, 37, 1552–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, D.; Wan, J. Synthesis and adsorption process of lithium taking used as high-temperature CO2 sorbents. Sci. Technol. Rev. 2011, 29, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H.; Moon, B.; Kim, T.K.; Jeoung, S.; Moon, H.R. Thermal conversion of a tailored metal-organic framework into lithium silicate with an unusual morphology for efficient CO2 capture. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 15130–15134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, P.; Wang, J. Effects of calcination temperature on the structure and CO2 sorption properties of Li4SiO4 sorbents from Rice Husk Ash. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Mechatronics, Electronic, Industrial and Control Engineering, Shenyang, China, 15–17 November 2014; pp. 760–763. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Zhao, P.; Guo, X.; Li, Y.; Han, D.; Chao, Y. Enhancement of reactivity in Li4SiO4-based sorbents from the nano-sized rice husk ash for high-temperature CO2 capture. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 81, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.; Lisbona, P.; Guo, X.; Lara, Y.; Romeo, L.M. Energy assessment of ethanol-enhanced steam reforming by means of Li4SiO4 carbon capture. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 1879–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, M.; Jamaludin, L.; Hussin, K.; Bnhussain, M.; Ghazali, C.; Ahmad, M. Fly Ash Porous Material using Geopolymerization Process for High Temperature Exposure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 4388–4395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah, M.; Hussin, K.; Bnhussain, M.; Ismail, K.; Yahya, Z.; Razak, R. Fly Ash-based Geopolymer Lightweight Concrete Using Foaming Agent. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 7186–7198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanna, A.; Ramli, I.; Mercedes Maroto-Valer, M. Development of sodium/lithium/fly ash sorbents for high temperature post-combustion CO2 capture. Appl. Energy 2015, 156, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, S.; Jia, Q.; Jiang, L.; Wang, Y. Effect of different silicon sources on CO2 absorption properties of Li4SiO4 at high temperature. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 213, 515–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, S.; Jia, Q.; Jiang, L.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Peng, J. Novel Li4SiO4-based sorbents from diatomite for high temperature CO2 capture. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 5437–5441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, S.; Jia, Q.; Jiang, L.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Peng, J. Preparation and kinetic analysis of Li4SiO4 sorbents with different silicon sources for high temperature CO2 capture. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2012, 57, 2475–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, S.; Li, S.; Jia, Q.; Jiang, L.; Wang, Y.; Peng, J. Impregnation Precipitation Preparation and Kinetic Analysis of Li4SiO4-Based Sorbents with Fast CO2 Adsorption Rate. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 6941–6945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joussein, E.; Petit, S.; Churchman, J.; Theng, B.; Righi, D.; Delvaux, B. Halloysite clay minerals—A review. Clay Miner. 2005, 40, 383–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, M.; Li, X.; Ouyang, J.; Yang, H. Lithium orthosilicate with halloysite as silicon source for high temperature CO2 capture. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 44106–44112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venegas, M.J.; Fregoso-Israel, E.; Escamilla, R.; Pfeiffer, H. Kinetic and reaction mechanism of CO2 sorption on Li4SiO4: Study of the particle size effect. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2007, 46, 2407–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacciani, R.; Torres, J.; Solsona, P.; Coe, C.; Quinn, R.; Hufton, J.; Golden, T.; Vega, L.F. Influence of the concentration of CO2 and SO2 on the absorption of CO2 by a lithium orthosilicate-based absorbent. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 7083–7088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, M.; Nakagawa, K.; Essaki, K.; Maezawa, Y.; Takeda, S.; Kogo, R.; Hagiwara, Y. Novel CO2 absorbents using lithium-containing oxide. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2005, 2, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essaki, K.; Kato, M.; Nakagawa, K. CO2 removal at high temperature using packed bed of lithium silicate pellets. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 2006, 114, 739–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puccini, M.; Seggiani, M.; Vitolo, S. Lithium silicate pellets for CO2 capture at high temperature. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2003, 35, 373–378. [Google Scholar]
- Puccini, M.; Stefanelli, E.; Seggiani, M.; Vitolo, S. Removal of CO2 from flue gas at high temperature using novel porous solids. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2016, 47, 139–144. [Google Scholar]
- Aaron, D.; Tsouris, C. Separation of CO2 from Flue Gas: A Review. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2005, 40, 321–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essaki, K.; Kato, M.; Uemoto, H. Influence of temperature and CO2 concentration on the CO2 absorption properties of lithium silicate pellets. J. Mater. Sci. 2005, 40, 5017–5019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puccini, M.; Seggiani, M.; Vitolo, S. CO2 capture at high temperature and low concentration on Li4SiO4 based sorbents. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2013, 32, 1279–1284. [Google Scholar]
- Ochoa-Fernandez, E.; Rønning, M.; Yu, X.; Grande, T.; Chen, D. Compositional effects of nanocrystalline lithium zirconate on its CO2 capture properties. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa-Fernández, E.; Zhao, T.; Rønning, M.; Chen, D. Effects of steam addition on the properties of high temperature ceramic CO2 acceptors. J. Environ. Eng. 2009, 135, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, R.; Kitzhoffer, R.J.; Hufton, J.R.; Golden, T.C. A high temperature lithium orthosilicate-based solid absorbent for post combustion CO2 capture. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 9320–9327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puccini, M.; Stefanelli, E.; Seggiani, M.; Vitolo, S. The effect of flue gas contaminants on CO2 capture at high temperature by Li4SiO4- based sorbents. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2015, 43, 1093–1098. [Google Scholar]
- Essaki, K.; Nakagawa, K.; Kato, M.; Uemoto, H. CO2 absorption by lithium silicate at room temperature. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 2004, 37, 772–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusten, H.K.; Ochoa-Fernández, E.; Lindborg, H.; Chen, D.; Jakobsen, H.A. Hydrogen production by sorption-enhanced steam methane reforming using lithium oxides as CO2-acceptor. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 46, 8729–8737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essaki, K.; Muramatsu, T.; Kato, M. Effect of equilibrium shift by using lithium silicate pellets in methane steam reforming. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2008, 33, 4555–4559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essaki, K.; Muramatsu, T.; Kato, M. Effect of equilibrium-shift in the case of using lithium silicate pellets in ethanol steam reforming. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2008, 33, 6612–6618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Parlinski, K. Density functional theory study of the structural, electronic, lattice dynamical, and thermodynamic properties of Li4SiO4 and its capability for CO2 capture. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 84, 3382–3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Yu, Y.; Ma, S.; Gao, T.; Xiao, C.; Chen, X. Adsorption mechanism of H2O molecule on the Li4SiO4 (0 1 0) surface from first principles. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2018, 691, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).