Abstract
A new series of 4-aryl and 4-alkyl-4-N-arylamine-1-butenes (homoallylamines) were synthesized and some of them transformed to 4-aryl or alkylquinolines. All of them showed strong antifungal activities against human pathogenic fungi in vitro, being Epider-mophyton floccosum the most susceptible species.
Introduction
As part of our project devoted to the search for antifungal agents [1,2,3], we synthesized a series of new 4-aryl- or 4-alkyl-N-arylamine-1-butenes and transformed some of them into biologically impor-tant 2-substituted 4-methyl-tetrahydroquinolines and quinolines [4]. We evaluated them for antifungal properties with agar dilution assays and studied their structure-activities relationships (SAR).
Experimental
Chemistry. Homoallylamines 12-22 were prepared via the addition of Grignard reagent to aldimines 1-11. Electrophilic cyclization of two of them, compounds 12 and 13 under acidic conditions, led to tetrahydroquinolines 23 and 24, which were oxidised to quinolines 25 and 26 with DDQ (Scheme 1)
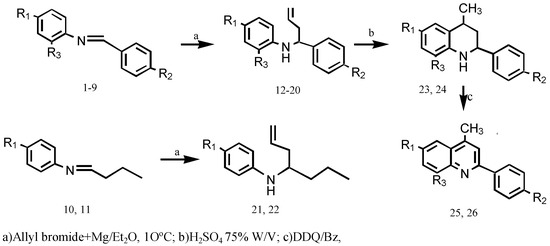
Scheme 1
Microorganisms. We used standardized human pathogenic fungi from CEREMIC or ATCC. at con-centrations up to 50 μg/mL [1,2].
Antifungal evaluation. The dilution agar method was used according with reported procedures [1,2].
Results and Discussion
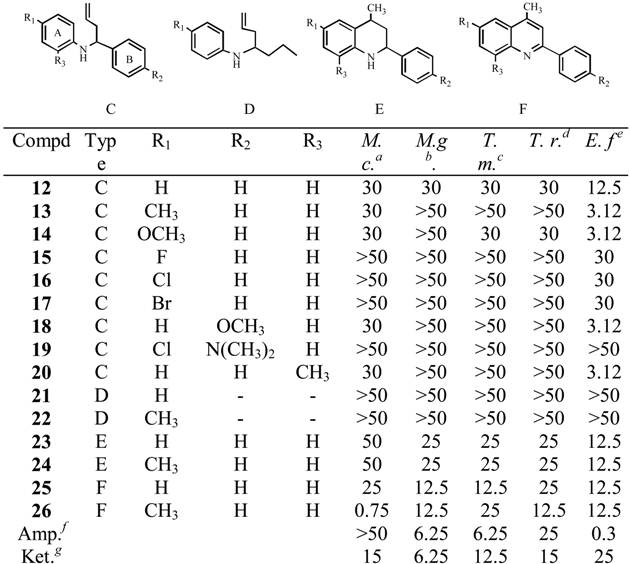
All compounds tested showed antifungal properties against dermatophytes (3.12<MIC<50 μg/mL), in particular against Epidermophyton floccosum, similar to those obtained with Amphotericin or Keto-conazole (Table 1). Substituents on benzene rings A or B increased four times the activity respective the non-substituted analogs. The change of an OMe from position 4 to 2 in rings A or B increased the activity twice.

Table 1.
MIC values (μg/mL) of homoallylamines, tetrahydroquinolines and quinolines acting against dermatophytes.
References and Notes
- Zacchino, S.; Rodríguez, G.; Pezzenati, G.; Orellana, G.; Enriz, D.; González Sierra, M. J. Nat. Prod. 1997, 60, 659–662. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zacchino, S.; Santecchia, C.; López, S.; Gattuso, S.; Muñoz, J.; Cruañes, A.; Vivot, E.; Salinas, A.; Ruiz, R.; Ruiz, S. Phytomedicine 1998, 5, 389–395. [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, A.; Giannini, F.; Baldoni, H.; Suvire, F.; Zacchino, S.; Sosa, C.; Enriz, R.; Csazar, P.; Czismadia, I. J. of Molecular Structure (TEOCHEM) 1999, 463, 283–303.
- Kuznetsov, V.; Andreeva, E.; Prostakov, N. Khim. Farm. Zh. 1995, 29, 61–62, (1996) Chem. Abst. 124, 48.290. This work is part of: Urbina et al., Inhibitors of the fungal wall. Synthesis of 4-aryl- 4-N-arylamine-1-butenes and related compounds with inhibitory activities on β(1-3) glucan and chitin synthases, Bioorganic & Med. Chem., in press.