Abstract
Tropomyosin receptor kinases (Trks) are transmembrane receptor tyrosine kinases named TrkA, TrkB, and TrkC and encoded by the NTRK1, NTRK2, and NTRK3 genes, respectively. These kinases have attracted significant attention and represent a promising therapeutic target for solid tumor treatment due to their vital role in cellular signaling pathways. First-generation TRK inhibitors, i.e., Larotrectinib sulfate and Entrectinib, received clinical approval in 2018 and 2019, respectively. However, the use of these inhibitors was significantly limited because of the development of resistance due to mutations. Fortunately, the second-generation Trk inhibitor Repotrectinib (TPX-0005) was approved by the FDA in November 2023, while Selitrectinib (Loxo-195) has provided an effective solution to this issue. Another macrocycle-based analog, along with many other TRK inhibitors, is currently in clinical trials. Two of the three marketed drugs for NTRK fusion cancers feature a pyrazolo[1,5-a] pyrimidine nucleus, prompting medicinal chemists to develop numerous novel pyrazolopyrimidine-based molecules to enhance clinical applications. This article focuses on a comprehensive review of chronological synthetic developments and the structure–activity relationships (SAR) of pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine derivatives as Trk inhibitors. This article will also provide comprehensive knowledge and future directions to the researchers working in the field of medicinal chemistry by facilitating the structural modification of pyrazolo [1,5-a]pyrimidine derivatives to synthesize more effective novel chemotherapeutics as TRK inhibitors.
1. Introduction
The tropomyosin receptor kinases (Trks) are part of the cell surface receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) family. Tropomyosin receptor kinases A, B, and C (TrkA, TrkB, and TrkC) are encoded by the genes encoding neurotrophic receptor tyrosine kinase 1, 2, and 3 (NTRK1, NTRK2, and NTRK3). NTRK1, NTRK2, and NTRK3 are homologous genes that encode receptor tyrosine kinases involved in neural development and function. In the mammalian nervous system, these Trks are crucial for synaptic plasticity and neuronal growth [1]. Transmembrane receptor proteins, or TRKs, are composed of three domains: an intracellular domain with activity, a transmembrane domain, and an extracellular ligand-binding domain [2]. The overall sequence homology of the kinase domains of TrkA, TrkB, and TrkC ranges from 71.9% to 78.3%, with TrkB and TrkC exhibiting the highest degree of similarity [3,4]. Many ligands that activate the receptors distinguish the three subtypes of TRKs (Figure 1) from one another. Mainly, nerve growth factor (NGF), neurotrophin-7, and neurotrophin-6 bind to TrkA, and activation of TrkA triggers various signaling pathways involved in cell survival, differentiation, and growth, particularly in neurons and neuroblastomas [5]. On the other hand, brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and neurotrophin-4/5 bind to TrkB and atypical activation of TrkB due to mutations or fusions involving NTRK2 can contribute to oncogenic transformation in certain cancers. [6]. Neurotrophin-3 (NT3) is the only nerve growth factor that particularly binds to TrkC and alterations such as mutations or fusions involving NTRK3 can lead to constitutive activation of TrkC, contributing to oncogenesis in specific cancer contexts. [7,8]. When neurotrophins are recognized extracellularly by their cognate Trk receptor, the cytosolic catalytic domain of the receptor’s tyrosine residues becomes dimerized and transphosphorylated. This leads to the activation of multiple downstream signal transduction pathways, such as PI3K-AKT and RAS-MAPK, and regulates the nervous system and neuronal cell cycle, proliferation, apoptosis, survival, and differentiation [9,10,11,12,13]. However, in the pathophysiology of malignant cancer in humans, Trks can be seen to be active through NTRK gene fusions [13,14]. Over 100 distinct NTRK fusion partners have been found in various malignancies to date, with the first NTRK fusion gene, TPM3-NTRK1, found in human colorectal carcinoma in 1982 [15,16]. It has been suggested that TRK proteins have been considered efficient “pan-cancer” targets for the treatment of various cancers harboring NTRK fusions [17,18]. A broad spectrum of cancer types, i.e., NTRK fusions, are found across a wide variety of cancer types [19,20]. NTRK fusions are often driver mutations in the cancers in which they occur. A driver mutation is a genetic alteration that provides a selective growth advantage to cancer cells, contributing to their proliferation and survival [21,22]. Preclinical and clinical studies have demonstrated that cancers with NTRK fusions are highly sensitive to Trk inhibitors. Trk inhibitors specifically target the abnormal TRK fusion proteins, inhibiting their function and thereby inhibiting growth [23]. Trk inhibitors have shown remarkable clinical efficacy in patients with cancers harboring NTRK fusions. Responses have been durable and often lead to significant clinical benefits, including tumor shrinkage and prolonged progression-free survival. This makes Trk inhibitors promising options for patients with advanced or metastatic cancers that harbor these specific genetic alterations [24,25]. Acute myeloid leukemia (AML), lung cancer, cylindrical tumors, breast cancer, human neuroblastoma, colon cancer, melanoma, thyroid cancer, ovarian cancer, prostate cancer, large cell neuroendocrine tumors, pediatrics gliomas and astrocytomas, intrahepatic cholangiocarcinomas, gastrointestinal stromal tumors, gallbladder adenocarcinomas, pancreatic carcinomas, and many other cancers have been associated with oncogenic forms of NTRK [26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44]. Therefore, using TRK small molecule inhibitors is the primary strategy for targeting NTRK fusion genes. Over the past decade, TRKs have been an area of interest for many researchers/scientists and pharmaceutical industries worldwide. Thus, TRKs have become an important anticancer target for extensive investigation. Eventually, many efforts have been made in the development of anticancer agents, leading to an increase in the large number of TRK inhibitors. NTRK fusion is not only involved in cancer metastasis but also in various other diseases such as asthma [45], interstitial cystitis [46], inflammatory diseases such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease [47], atopic dermatitis [48], eczema and psoriasis [49], pain [50], Alzheimer’s disease [51], and inflammation [52].
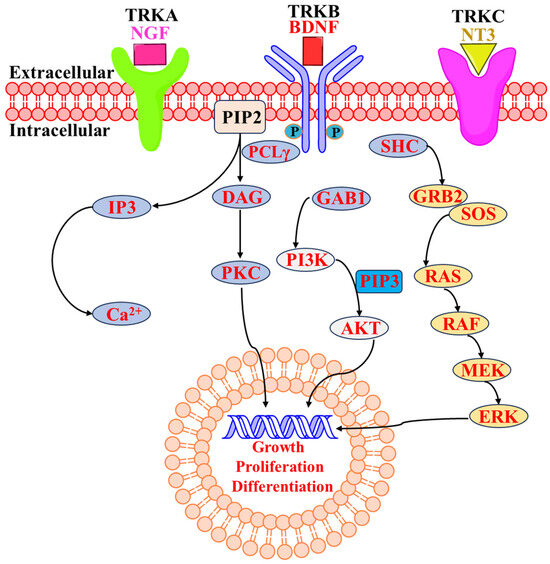
Figure 1.
Schematic presentation of Trk receptors and their major signal transduction pathway [53,54].
Larotrectinib (brand name Vitrakvi®, 2018, Bayer AG; Leverkusen, Germany) and Entrectinib (brand name Rozlytrek®, 2019, Genentech Inc. Group of Roche pharma, Basel, Switzerland) are first-generation Trk inhibitors on the market (Figure 2) [55,56,57]. Both drugs were found to have massive clinical findings against Trk; however, the emergence of drug resistance in clinics restricted their extensive use. In continuation, the emergence of drug resistance further led to the identification of a new generation of drugs to combat these resistances, i.e., second-generation Trk inhibitors were discovered. Repotrectinib (TPX-0005) was approved by the FDA in November 2023 while Selitrectinib (Loxo-195), the macrocycle-based representative, along with many other inhibitors, is currently being used in clinical trials [58,59,60]. Amongst the three marketed drugs for NTRK fusion cancer, two of them consist of a pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine nucleus (PP), which leads to the development of many more small molecules consisting of a PP moiety. Thus, in this review, we have discussed the importance of the PP moiety in the development of novel NTRK fusion inhibitors by incorporating various synthetic strategies and structure–activity relationship (SAR) analysis.
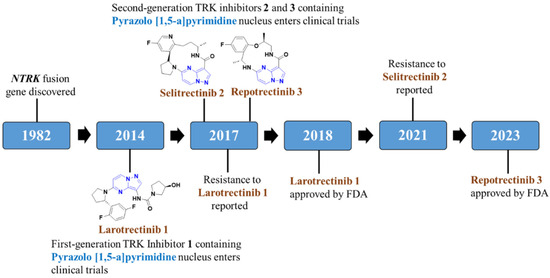
Figure 2.
Development of NTRK fusion inhibitors consisting of a pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine moiety.
2. Synthetic Strategies
Pyrazolopyrimidine is a fused heterocycle consisting of two N-heterocycles, i.e., pyrazole and pyrimidine. It is a prominent scaffold in medicinal chemistry along with pesticide and therapeutics. It has been engineered to exhibit specific modes of action, including activities as central nervous system (CNS) agents, anti-bacterial agents, anti-inflammatory agents, anti-cancer agents, anti-fungal agents, antiviral agents, and ligands for estrogen receptors [61,62]. It has also been found in multiple kinase inhibitors such as protein kinase, CDK, Trk, EGFR, and FGFR [63]. The basic structures of pyrazolopyrimidine are primarily divided into four categories: pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine, pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine, pyrazolo[4,3-d]pyrimidine, and pyrazolo[1,5-c]pyrimidine [64] (Figure 3).
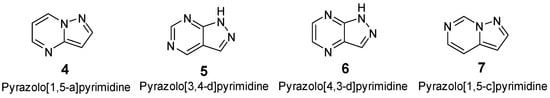
Figure 3.
Different fundamental isoforms of pyrazolopyrimidines.
Numerous methodologies have been reported in the literature for the synthesis of the PP scaffold; the majority of which entail an electrophilic reaction with 1H-pyrazole-5-amine and its derivatives. Due to its prevalence in NTRK fusion inhibitors, we have also covered the synthesis and biological action of PP among the four isoforms. PP can be readily synthesized by using enamines, β-diketones, and α,β-unsaturated ketones reacted with 1H-pyrazole-5-amine [65]. Herein, we have discussed various synthetic strategies for the synthesis of PP, which have been represented schematically in Figure 4.
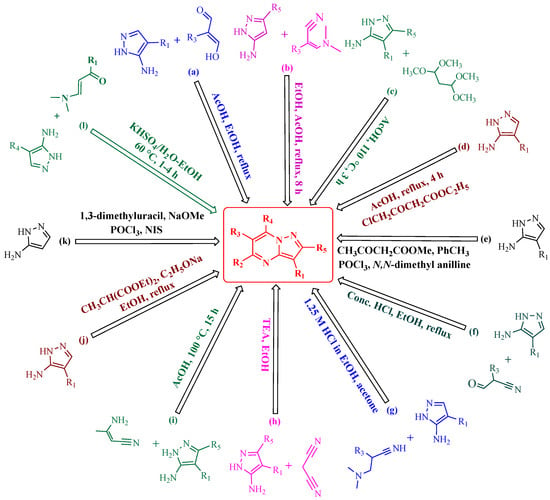
Figure 4.
Schematic representation of various synthetic strategies to obtain the PP skeleton.
Fraley et al. have synthesized the desired novel PP by treating a 4-phenylpyrazolamine derivative with phenyl acrylaldehyde in the presence of acetic acid and ethanol as a solvent (route a) [66]. Elmaati and El-Taweel have used the substituted enaminones and reacted them with 5-aminopyrazole to furnish the PP derivatives (route b) [67].
Campton et al. invented the reaction of 5-aminopyrazole derivatives with 1,1,3,3- tetramethoxypropane in acidic conditions to obtain the product PP (route c) [68]. Li and colleagues synthesized PP by performing the reaction between 5-aminopyrazole and ethyl 4-chloroacetoacetate in the presence of acetone as a solvent under refluxed conditions (route d) [69]. Paruch et al. invented the one-pot synthesis of new PP analogs by reacting 1H-pyrazol-5-amine derivatives with methyl-3-oxobutanoate, phosphorus oxychloride, and N,N dimethylaniline under inert conditions (route e) [70]. Frey and co-workers have successfully synthesized novel 7-aminopyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidines through a cyclocondensation reaction between 5-aminopyrazole derivatives with 3-oxo-2-phenyl propanenitrile (route f) [71]. Gommermann et al. performed the cyclization reaction of 1H-pyrazol-5-amine derivatives with 3-(dimethylamino)-2-(4-nitrophenyl) acrylonitrile to obtain the substituted PP under acidic conditions (1.25 M HCl in ethanol) in acetone (route g) [72]. Enany and co-workers acquired the final compound PP by reacting 5-aminopyrazole and malononitrile in the presence of an organic base such as triethylamine and ethanol as a solvent (route h) [73]. Ivachtchenko et al. carried out the reaction of amino-substituted 1H-pyrazol-5-amine and 3-aminobut-2-enenitrile in acetic acid to furnish the PP compound (route i) [74]. Kosugi et al. acquired a novel PP derivative by reacting amino pyrazole with a 2-substituted malonic acid diester in the presence of sodium ethoxide in ethanol under reflux conditions (route j) [75]. Dwyer and colleagues carried out a condensation reaction of 5-aminopyrazole with 1,3-dimethyluracil in the presence of phosphorus oxychloride, sodium methoxide, and N-iodosuccinimide to yield the PP derivatives (route k) [76]. Vishwakarma et al. carried out the reaction of 5-aminopyrazole with α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds in the presence of KHSO4 in an aqueous medium at 60 °C to obtain the desired product PP (route l) [77].
3. Pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine as TRK Inhibitors
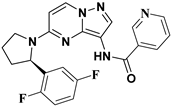
Julia Hass and her colleagues introduced a new series of picolinamide-substituted PP derivatives in 2010 and evaluated them for Trk inhibition (see Figure 5). Among the 105 compounds studied, compounds 8 and 9 demonstrated excellent enzymatic inhibition of TrkA, each with an IC50 value of 1.7 nM. The presence of the amide bond of picolinamide at the third position of the pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine ring significantly enhanced activity. Furthermore, substitution with a 2,5-difluorophenyl-substituted pyrrolidine at the fifth position further increased Trk inhibition activity. Picolinamide can be replaced with various heterocyclic moieties to potentially enhance activity in the nanomolar range. The strategic positioning of the picolinamide moiety and further substitution with a 2,5-difluorophenyl-substituted pyrrolidine highlight promising directions for enhancing Trk inhibition. Future research focusing on optimizing these molecular structures with other heterocycles could possibly lead to even more potent Trk inhibitors with potential therapeutic applications [78].
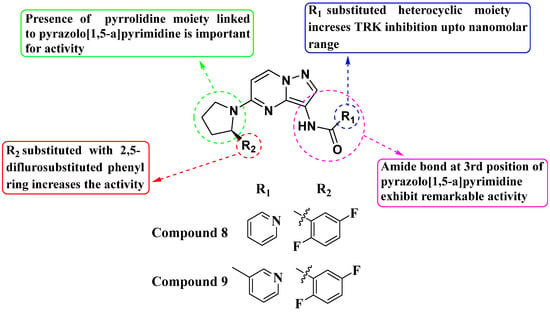
Figure 5.
SAR study of pyrrolidine-linked PP derivatives as TrkA inhibitors.
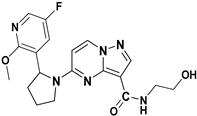
In 2011, Allen and his team designed and synthesized a new library of novel 3-carboxamide-linked PP derivatives (Figure 6) and evaluated them for their TrkA inhibitory activity. Compounds 10 and 11 emerged as potent TrkA inhibitors, displaying IC50 values of 0.2 nM and 0.4 nM, respectively. These compounds also demonstrated inhibitory effects against JAK and TYK in enzymatic assays. The structure–activity relationship (SAR) analysis indicated that the carboxamide moiety at the third position significantly enhances TrkA inhibition. Additionally, substituting alcohol or N-heterocyclic moieties at the NH of the carboxamide further boosts activity. Furthermore, the presence of a 2,5-difluorophenyl or substituted pyridine linked to pyrrolidine at the fifth position of the molecule contributes to increased activity. The study underscores the critical role of the carboxamide moiety and specific substitutions of heterocycles at the -NH group and fifth position in maximizing inhibitory activity against TrkA, while also suggesting potential inhibitory effects against JAK and TYK. Further exploration and substitution of bioactive groups at the -NH of the carboxamide hold promise for developing even more potent Trk inhibitors [79].
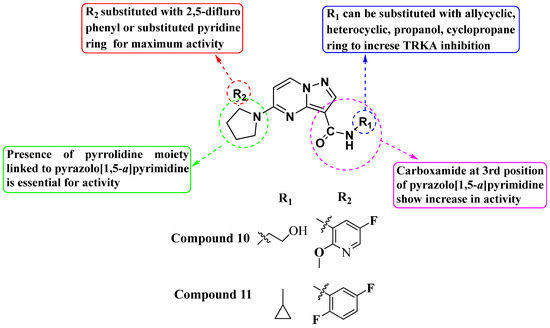
Figure 6.
SAR study of carboxamide-linked PP derivatives as TrkA inhibitors.
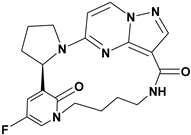
Andrews and colleagues (2011) synthesized a new series of macrocyclic pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine derivatives and evaluated their activity using the TrkA Elisa enzyme assay. Within this series, most molecules exhibited potent activity, with IC50 values ranging between 1 and 100 nM. Compounds 12 and 13, which feature a pyridine or pyridinone ring attached to a pyrrolidine moiety, showed particularly strong inhibition. The presence of a carboxamide group significantly enhanced activity, while its absence resulted in reduced activity (IC50 values above 100 nM). Substituting the pyrrolidine with other heterocycles such as oxazolidin-2-one decreased activity. The R3 group could be substituted with ethenone, sulphonyl, or left unsubstituted to improve activity. In the macrocyclic structure, replacing R2 with a hydroxy group maximized activity (see Figure 7). The SAR study concluded that exploring modifications around the carboxamide group could possibly enhance potency and selectivity. Variations in the pyrrolidine moiety and other heterocyclic replacements were suggested to optimize the biological activity [80].
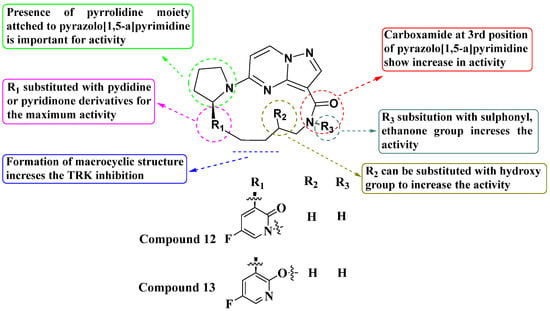
Figure 7.
SAR study of macrocyclic PP derivatives as Trk inhibitors.
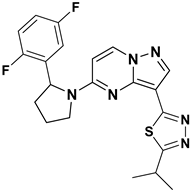
Kim Moonsoo (2016) reported a new series of heteroaryl-substituted PP derivatives as Trk inhibitors (Figure 8). Compounds 14 and 15 emerged as the most potent in both enzymatic and cell-based assays, with IC50 values of less than 10 nM. Kim also evaluated these compounds for cell proliferation in KM12 cell lines, where they demonstrated an IC50 value of less than 10 nM. The SAR study revealed that heteroaryl substitution, particularly with thiadiazole, oxadiazole, and triazole at the third position of the PP scaffold, enhances inhibitory activity against Trk receptors. Furthermore, substitution with pyrrolidine at the fifth position further improves inhibition efficacy. The SAR study interprets that the substitution of the pyrrolidine moiety with halogens such as fluorine enhances activity, suggesting specific modifications that could optimize Trk inhibition. It has been anticipated that future efforts may be explored with other halogens or functional groups on the pyrrolidine moiety to further optimize Trk inhibition [81].
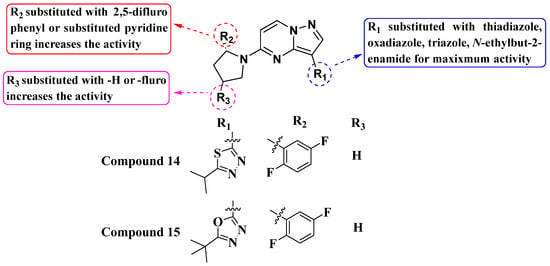
Figure 8.
SAR study of heteroaryl-substituted PP derivatives as Trk inhibitors.
Pal et al. (2019) developed and synthesized a novel library of pyrazole- and triazole-substituted PP derivatives intended as inhibitors of TrkA WT kinase for cancer treatment (Figure 9). They utilized a foundational scaffold similar to the approved drug Larotrectinib, which features a 2,5-difluorophenyl-substituted pyrrolidine linked to the fifth position of pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine. Various groups were substituted at the third position to optimize activity. Compound 16, incorporating pyrazole-3-carbonitrile, and compound 17, incorporating a triazole, exhibited IC50 values of >10 nM. The choice of substituents (pyrazole-3-carbonitrile and triazole) at the third position of the scaffold was crucial for achieving high activity against TrkA kinase. This suggests that modifications at this position can significantly influence inhibitory potency. Further exploration and optimization of substituents at the third position and potentially other positions of the scaffold could be pursued to improve potency and selectivity. This iterative process could lead to the discovery of even more effective TrkA inhibitors [82].
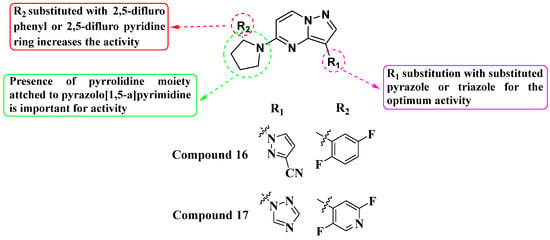
Figure 9.
SAR study of pyrazole- and triazole-substituted PP derivatives as TrkA WT inhibitors.
In 2019, Wenglowsky and colleagues reported on the synthesis of a new library of nitrile-substituted PP compounds designed as NTRK1 inhibitors (Figure 10). Among these, Compounds 18 and 19 emerged as particularly potent, each exhibiting an IC50 value of >10 nM against NTRK1 and demonstrating inhibition of KM12 cell proliferation with IC50 values of less than 10 nM. Both compounds feature a core pyrrolidine-linked PP scaffold. The introduction of a nitrile substitution at the third position significantly enhanced their activity, while the addition of fluorine to the pyrrolidine ring further improved NTRK1 inhibition. Additionally, substituting fluorine at the sixth position contributed to maximizing their activity. Furthermore, incorporating 2,5-difluorophenyl or pyridine moieties onto the pyrrolidine ring enhanced their efficacy. The SAR findings underscore the importance of structural modifications in optimizing the potency of NTRK1 inhibitors. The combination of nitrile, fluorine, and specific aromatic substitutions demonstrates a synergistic effect in enhancing biological activity. Continued exploration of structural modifications is recommended to fine-tune the potency, selectivity, and pharmacokinetic properties of these compounds. This could involve systematic variation in substituents and scaffold alterations guided by computational modeling and further experimental validation [83].
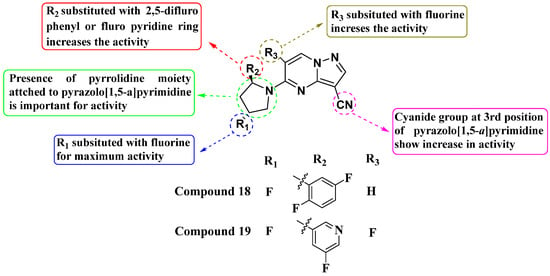
Figure 10.
SAR study of nitrile-substituted PP derivatives as NTRK inhibitors.
Lin et al. (2019) synthesized a novel series of substituted macrocyclic PPs based on the molecule Repotrectinib as NTRK inhibitors (see Figure 11). Compounds 20 and 21 were identified as potent inhibitors of NTRK1, NTRK2, and NTRK3 with IC50 values of <0.02 nM each. The macrocyclic structure, incorporating an amide linkage, was crucial for achieving maximum activity. This suggests that the specific spatial arrangement provided by the macrocyclic framework is crucial for binding affinity and biological activity against the NTRK kinases. Substitution of the carbonyl of the amide with sulfur further enhanced NTRK inhibition. This modification likely alters the electronic properties or hydrogen bonding capabilities of the amide linkage, improving the interaction with the target enzymes. Additionally, the introduction of a methyl group on the macrocyclic structures significantly improved their activity, possibly through enhancing hydrophobic interactions [84].
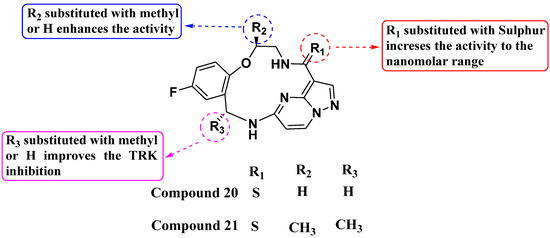
Figure 11.
SAR study of macrocyclic PP derivatives as NTRK inhibitors.
Hongbin Liu et al. (2019) developed novel derivatives of 5-azabicyclohexane-substituted PP and evaluated their inhibitory activity against Trk fusion mutations. Compound 22 exhibited the highest activity against TrkA, TrkB, and TrkC with IC50 values of 3 nM, 14 nM, and 1 nM, respectively (see Figure 12). Furthermore, compound 22 demonstrated potent inhibition of KM12 cell proliferation with an IC50 of 1 nM. Importantly, the presence of a 2,5-difluorophenyl substitution at the fifth position of the azabicyclohexane scaffold was identified as crucial for optimal inhibitory activity against Trk receptors. Additionally, the presence of a hydroxypyrrolidine moiety further enhanced the activity. This SAR information is crucial for guiding future compound optimization efforts. Continued optimization of the compounds based on the SAR findings could lead to the development of even more potent inhibitors with improved pharmacokinetic properties and reduced off-target effects [85].
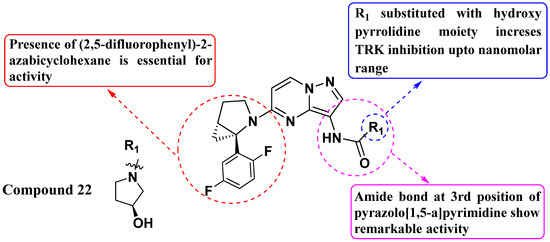
Figure 12.
SAR study of 5-azabicyclohexane-substituted PP derivatives as Trk inhibitors.
Cui et al. (2020) introduced a novel series of substituted macrocyclic kinase inhibitors based on the PP scaffold (Figure 13). Compounds 23 and 24, inspired by Repotrectinib, feature a macrocyclic structure with amide substitutions and demonstrate inhibition of cell proliferation in TRKA KM12 cells with IC50 values of 0.1 and 0.2 nM, respectively. These compounds also exhibit activity against the JAK2 SET2 cell line [23 = 1479 nM; 24 = 3.9 nM] and the BTK cell line [23 = 179 nM; 24 = 14.25 nM]. The introduction of a macrocyclic structure based on the PP scaffold was crucial for enhancing kinase inhibition. Amide substitutions significantly enhance activity against TRKA, indicating the importance of specific interactions conferred by the amide bonds. The attachment of a methyl group to the macrocycle further enhances inhibition potency, suggesting that structural modifications can fine-tune and improve biological activity [86].
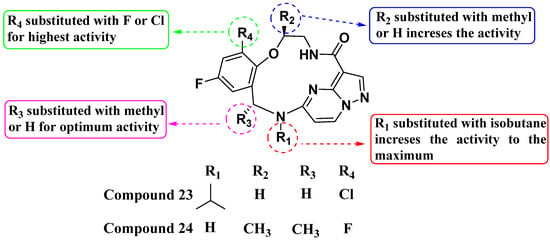
Figure 13.
SAR study of macrocyclic kinase inhibitors based on the PP scaffold.
Li Zhu et al. (2020) synthesized and evaluated a novel series of substituted amino PP compounds as inhibitors of the neurotrophic factor Trk. They tested a total of 52 molecules for their ability to inhibit Trk activity, identifying compounds 25, 26, and 27 as the most potent with IC50 values of less than 1 nM (see Figure 14). These compounds effectively inhibit TrkA, TrkB, and TrkC with an IC50 of 1 nM. The structure–activity relationship (SAR) analysis indicates that substituting the pyrrolidine moiety with 2,5-difluorophenyl and fluorine enhances activity significantly. Additionally, the presence of an amino group at the second position and a carboxamide at the third position further enhance Trk inhibition. Subsequent observations suggest that substituting the -NH group of the carboxamide with a methyl or hydroxy cyclohexyl moiety contributes to maximizing activity. While the compounds showed potent inhibitory activity, future studies should focus on the exploration of modification on the other substituents in the place of methyl or hydroxy cyclohexyl for better inhibition [87].
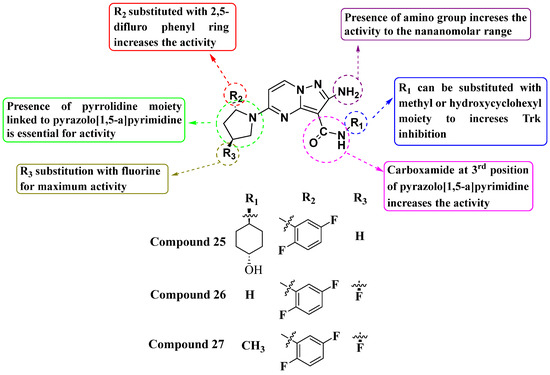
Figure 14.
SAR study of amino PP derivatives as Trk inhibitors.
Yihan Wang et al. synthesized and evaluated a series of novel substituted PP macrocyclic compounds against all three Trks in 2020 (Figure 15). Among these, compound 28 demonstrated the highest activity with IC50 values of 0.17 nM, 0.07 nM, and 0.07 nM against TrkA, TrkB, and TrkC, respectively. The macrocyclic structure offers advantages over the first drug Larotrectinib. Macrocycles often have improved binding affinity and selectivity due to their conformational rigidity and ability to form specific interactions with the target receptor. The presence of a carboxamide at the third position enhances Trk inhibitory activity. This suggests that specific modifications at this position could be further explored to optimize potency and selectivity. Additionally, replacing the hydrogen atom of the pyrrolidine with a deuterium moiety helps achieve activity in the nanomolar range. This isotopic substitution technique can potentially improve the pharmacokinetic properties of the compound, such as enhancing metabolic stability or altering pharmacokinetic profiles [88].
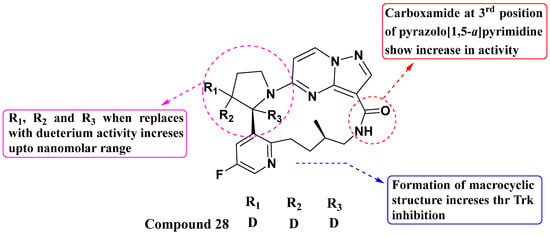
Figure 15.
SAR study of substituted PP macrocyclic derivatives as Trk inhibitors.
Wang and his colleagues, in 2021 and 2022, discovered a novel series of macrocyclic PP derivatives as selective Trk inhibitors. Among them, compounds 29 and 30 exhibited the highest inhibitory activity against TrkA, TrkC, ALK, and ROS (Figure 16). Compound 29 (TRK A = 0.6 nM, TRK C = 0.1 nM, ALK = 901 nM, Ros1 = 2.2 nM) and compound 30 (TRK A = 1.61 nM, TRK C = 0.05 nM, ALK = 10.40 nM, Ros1 = 0.16 nM) showed promising potency as TrkA, TrkC, ALK, and ROS inhibitors. Wang also conducted cell proliferation assays using the Ba/F3 LMNA-NTRK1-WT stably transfected cell line. The SAR (Structure–Activity Relationship) study revealed that the presence of a carboxamide group at the third position enhances Trk inhibition. Additionally, Wang and his team synthesized and evaluated substituted pyridine-linked isoxazolidine or morpholine derivatives in place of pyrrolidine within the macrocyclic PP derivatives. This modification led to achieving inhibition in the nanomolar range. Furthermore, continued exploration of structural modifications, including cyclic groups such as cyclopropane and tetrahydrofuran, could lead to compounds with improved pharmacokinetic properties and selectivity profiles [89,90].
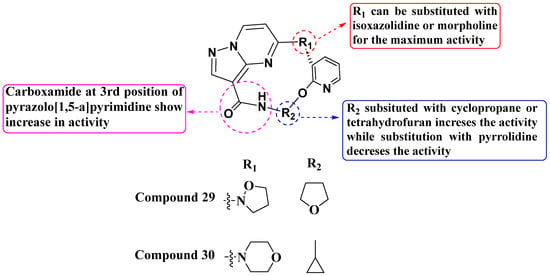
Figure 16.
SAR study of macrocyclic PP derivatives as selective Trk inhibitors.
Zhang, Zhou, and their colleagues (2021) reported a novel macrocyclic analog as a potent TRK inhibitor (Figure 17). Compound 31 displayed superior TRKG595R kinase inhibition with an IC50 value of 13.1 nM and moderate antiproliferative activity against the Ba/F3-LMNA-NTRK1 cell line with an IC50 value of 0.080 µM. Furthermore, it exhibited better kinase inhibition (IC50 value of 0.646 µM) compared to the standard LOXO-101 in the Ba/F3-LMNA-NTRK1-G595R cell line. SAR studies revealed that substitution with a sulfonamide group at the R1 position is crucial for TRKG595R inhibition. Conversely, a sulfonamide with an amide linker at R1 was not tolerated and led to decreased activity. At the R2 position, the chiral methyl group did not confer activity, and substitution with urea also did not exhibit TRKG595R inhibition. Increasing the carbon chain length tended to sustain strong inhibition of TRKA; however, inhibition against the TRKG595R variant was comparatively less effective than with other compounds. Compounds with a two-carbon side chain showed significantly higher activity compared to those with a three-carbon side chain. At the R3 position, chloromethyl substituents were preferred, followed by methyl and ethyl groups. Further exploration of R1 substitutions, particularly variations of the sulfonamide group, could enhance potency and selectivity against TRKG595R while maintaining overall kinase inhibition [91].
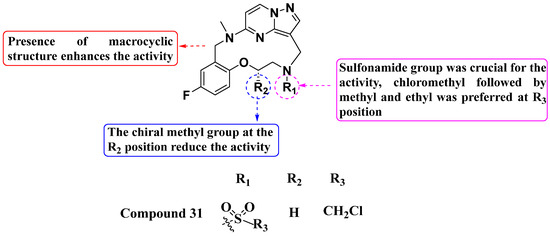
Figure 17.
SAR study of sulfonamide-substituted macrocyclic PP derivatives as Trk inhibitors.
Tang and Fan et al. (2021) developed a novel series of PP-based TRK inhibitors (Figure 18). Among these, compound 32 exhibited IC50 values of 1.9 nM, 3.1 nM, and 2.3 nM against TrkA, TrkB, and TrkC, respectively. Compound 33 showed IC50 values of 3.2 nM, 5.5 nM, and 3.3 nM, compound 34 showed IC50 values of 1.8 nM, 4.1 nM, and 2.3 nM, compound 35 showed IC50 values of 2.5 nM, 3.1 nM, and 2.6 nM, and compound 36 showed IC50 values of 1.4 nM, 2.4 nM, and 1.9 nM. These values indicate significant inhibition against TrkA, TrkB, and TrkC compared to the standard drug Larotrectinib, which showed IC50 values of 1.2 nM, 2.1 nM, and 2.1 nM, respectively. Extensively, The SAR studies highlighted the importance of a 3-pyrrolidinol scaffold with a hydroxy group at the R1 position for effective interaction with the solvent-accessible domain of Trk receptors. Substitution at R1 and modifications at the 5-position (introduction of (R)-1-(2,5-difluorophenyl)-N-methylethane-1-amine) significantly enhanced inhibitory potency. Additionally, methyl substitution at the benzylic amine notably increased inhibitory activity by 20 times compared to compound 33, demonstrating the sensitivity of the compounds to small structural modifications [92].
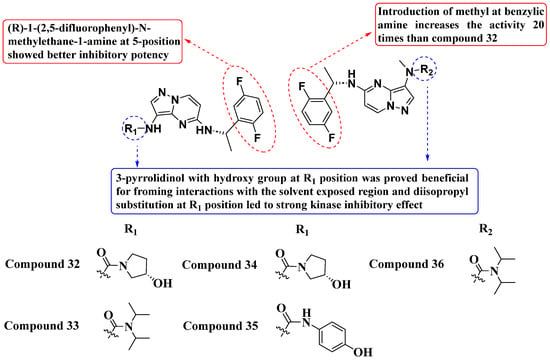
Figure 18.
SAR study of novel PP-based TrkA, TrkB, and TrkC inhibitors.
Wang, Tian, et al. (2021) discovered a second generation of macrocyclic compounds as potent Pan-Trk kinase inhibitors through structural modification and optimization, resulting in enhanced physicochemical and oral pharmacokinetic parameters (see Figure 19). Compound 37, known as LPM4870108, exhibited significant activity against both wild-type and mutant forms of TrkA and TrkC. In vitro evaluation of compound 37 demonstrated inhibition in enzymatic assays against TrkA, TrkAG595R, TrkAG667C, TrkC, ALK, and Ros1 with IC50 values of 2.4 ± 0.3 nM, 3.5 ± 0.5 nM, 2.3 ± 0.3 nM, 0.2 ± 0.1 nM, 182.0 ± 14.2 nM, and 1.0 ± 0.3 nM, respectively. Cellular assays against Ba/F3 TTRK, Ba/F3 TrkAG595R, Ba/F3 TrkAF589L, Ba/F3 TrkAG667A, Ba/F3 TrkCG623R, and Ba/F3 SLC34A2-Ros1 showed IC50 values of 0.6 ± 0.1 nM, 7.7 ± 0.5 nM, 4.9 ± 0.2 nM, 0.8 ± 0.1 nM, 2.7 ± 0.2 nM, and 2.3 ± 0.3 nM, respectively. LOXO-195 and TPX-0005 were used as standards. The SAR study identified key structural features crucial for potency and selectivity. The pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine moiety was essential for forming a hinge interaction with the Met592 residue, influencing binding affinity. The addition of a morpholine group at a specific position improved selectivity by reducing off-target effects. Fluorine incorporation enhanced interactions with Asn655, while a pyridine ring supported hydrophobic interactions, contributing to overall potency. The lipophilicity of compound 37 was increased, leading to enhanced metabolic stability and a favorable in vivo profile with reduced toxicity [93].
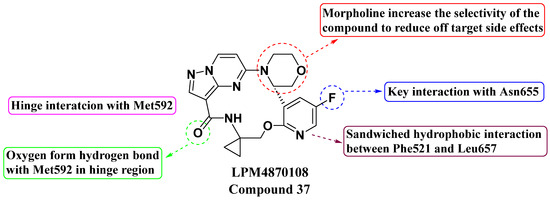
Figure 19.
SAR study of second-generation macrocyclic PP derivatives as Pan-Trk inhibitors.
In addressing acquired resistance in second-generation inhibitors, Huang et al. (2022) employed ring-opening scaffold-hopping strategies to design and synthesize a series of PP analogs substituted with 3-Pyrazolyl, replacing the 3-pyrrolidinol moiety (Figure 20). Pyrazole was utilized to optimize molecular orientation and minimize steric conflicts. Among these compounds, compound 38 exhibited potent kinase inhibitory activity against TrkAF589L and TrkAG595R mutations. However, it did not enhance enzymatic inhibition against TrkAG667C. Structural refinement of compound 38 resulted in the development of compound 39, which emerged as the most potent within the series. Compound 39 demonstrated IC50 values of 2.3 nM, 0.4 nM, and 0.5 nM against the TrkAF589L, TrkAG667C, and TrkAG595R cell lines, respectively, surpassing Selitrectinib as the standard drug. Structure–activity relationship (SAR) studies revealed that the presence of oxygen in the oxanyl group contributed to potency, occupying the mutation site of x-DFG. Additionally, both the difluoro phenyl group and the ring-opening of the pyrrolidine ring optimized molecular orientation to minimize steric hindrance. The N1 atom of pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine formed a hydrogen bond with the amino acid Met592 in the hinge region. This insight into SAR underscores the importance of molecular interactions in designing potent kinase inhibitors. Compound 39 exhibited improved pharmacokinetic properties and demonstrated significant antitumor activity, achieving tumor growth inhibition rates of 97% at 30 mg/kg/dose and 73% at 100 mg/kg/dose in xenograft mouse models for both TrkAWT and TrkAG667C mutations [94].
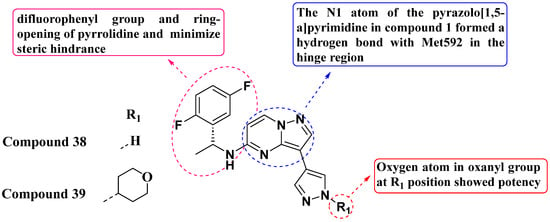
Figure 20.
SAR study of 3-Pyrazolyl-substituted PP derivatives as Trk inhibitors.
Second-generation inhibitors such as TPX-0005 (Repotrectinib, Augtyro, Bristol Myers Squibb Company, Princeton, New Jersey, US) have proven more effective than first-generation inhibitors. First-generation Trk inhibitors encountered issues with drug resistance mutations. In 2022, Fan et al. designed and synthesized a new series of second-generation PP analogs, which were demonstrated to be effective as Trk inhibitors (Figure 21). Compounds 40 (with IC50 values of 1.40 nM and 1.80 nM) and 41 (with IC50 values of 0.86 nM and 6.92 nM) showed enhanced inhibition of TrkA and Trk-AG595R, respectively. TPX-0005 was used as a positive control. Compound 41 also displayed inhibitory activity against ALK with an IC50 value of 350 nM, yet selectively inhibited Trk, potentially reducing toxic effects. Structure–activity relationship (SAR) studies revealed that a fluorine atom at position X is crucial for activity. Shifting the fluorine position on the benzene ring and cyclization adjacent to the pyrimidine moiety did not significantly affect TPX-0005’s activity but enhanced its selectivity. The configuration and position of the methyl group at R2 notably influenced its activity. A (R)-methyl group at the R1 position exhibited activity comparable to the standard LOXO-101. Overall, these findings underscore the promising potential of these second-generation Trk inhibitors, offering improved efficacy and selectivity over their predecessors [95].
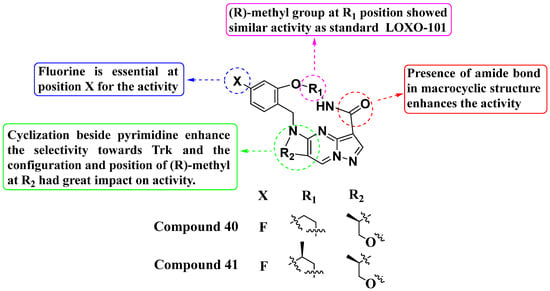
Figure 21.
SAR study of second-generation PP derivatives as Trk inhibitors.
In 2023, Al-Qadhi and his colleagues designed and synthesized a novel series of 7-aryl-3-substituted PP analogs, evaluating their inhibition against RTK and STK (Figure 22). Compound 42 demonstrated potent enzymatic inhibition against TrkA and ALK2, with IC50 values of 0.087 μM and 0.105 μM, respectively. This compound also exhibited robust antiproliferative activity against two cell lines, KM12 (IC50 = 0.82 μM) and EKVX (IC50 = 4.13 μM). Compound 43 also showed significant potency against TrkA in the sub-micromolar range. Additionally, it demonstrated antiproliferative activity against various cell lines: MCF7 (IC50 = 3.36 μM), HCT116 (IC50 = 1.40 μM), and EKVX (IC50 = 3.49 μM), with notable safety profiles. Larotrectinib was used as a standard reference. The electron-withdrawing group at the seventh position of the aryl ring was found to be more favorable than the electron-donating group. The cyano (CN) group at the third position played a crucial role in enhancing the activity of the compounds. Moreover, the oxadiazole substitution at the R-position showed remarkable cytotoxicity against various tumor cells [96].
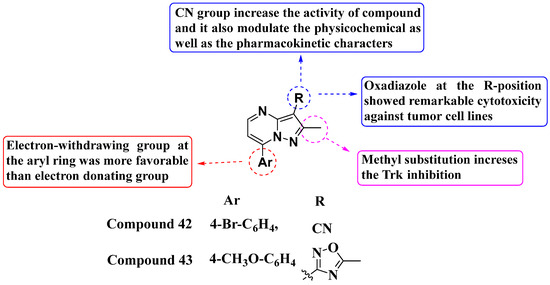
Figure 22.
SAR study of 7-aryl-3-substituted PP derivatives as RTK and STK inhibitors.
Recently, Metwally et al. (2024) developed a new series of molecules and evaluated their efficacy against MCF7, HepG2, and HCT116 cell lines (see Figure 23). Compounds 44 and 47 exhibited the most promising inhibitory activity against TrkA, with IC50 values of 0.064 ± 0.0037 μg/mL and 0.047 ± 0.0027 μg/mL, respectively, while Larotrectinib served as the positive control. Notably, all potent compounds (44, 45, 46, and 47) induced cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase. Compound 46 demonstrated the highest apoptosis rate (36.72%) among them, surpassing compounds 44 (34.70%), 45 (21.14%), and 47 (26.54%). Structure–activity relationship (SAR) studies revealed that the introduction of a donor group, such as a methoxy group in the aryl moiety, enhanced the anticancer activity across the MCF-7, HepG-2, and HCT-116 cell lines. Furthermore, the incorporation of an Arylhydrazo group with the methoxy group notably increased anticancer efficacy, specifically against MCF-7 and HepG-2 cells. Interestingly, compounds where R = C6H5 demonstrated significant anticancer activity against the HCT116 cell line. Based on SAR findings, further optimizing the chemical structure could improve potency, selectivity, and pharmacokinetic properties. Exploration of additional substituents or modifications could enhance efficacy against specific cancer types [97].
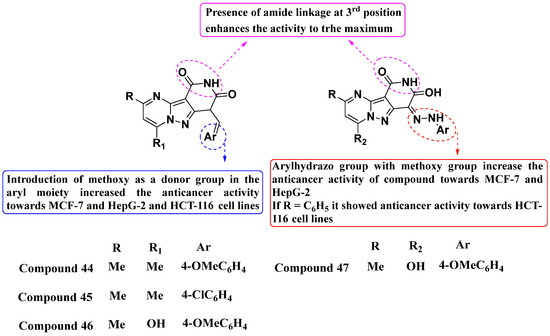
Figure 23.
SAR study of fused PP derivatives as TrkA inhibitors.
4. Summary
In this review, the development of pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine derivatives as Trk inhibitors was discussed in detail. Following the identification of NTRK1 as an oncogene in 1982 by Mariano Barbacid and colleagues, the actual development of NTRK inhibitors began in 2015. Currently, only three drugs are marketed as Trk inhibitors, two of which contain a pp nucleus. The potency of the pp nucleus in Trk inhibition has drawn the attention of researchers, leading to the development of many small molecules based on the pp core nucleus as Trk inhibitors. Several macrocyclic molecules containing the pp core nucleus are undergoing clinical trials as Trk inhibitors. This review provides insights into the SAR studies of several PP derivatives, highlighting that substitution at the third and fifth positions of PP was essential for Trk inhibition. Compounds with an amide or carboxamide bond at the third position tend to exhibit Trk inhibition in the nanomolar range. Substituting a pyrrolidine ring at the fifth position offers advantages over other rings. The pyrrolidine ring, especially when electronegatively substituted, enhances Trk inhibition. Some compounds with substitutions at positions other than the third and fifth also demonstrate excellent inhibitory effects. The important structural features alongside potency values are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
The chemical structure features and IC50 value of potent compounds.
5. Conclusions
This article discusses the significance of pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine derivatives as Trk inhibitors, which are crucial for treating solid tumors. Extensive research into the pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine nucleus indicates significant potential for diverse opportunities in anticancer drug discovery. Trk inhibitors with this core structure, such as Larotrectinib sulfate, Entrectinib, Repotrectinib, and Selitrectinib, are already on the market. However, the effectiveness of some of these is limited due to resistance mutations. A macrocycle-based analog and several other TRK inhibitors are currently undergoing clinical trials. This study concludes that structural modifications of the pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine nucleus have led to compounds 20 and 21, which exhibit NTRK IC50 values >0.02 nM. Compounds 23 and 24 show TRKA (KM12 cell) inhibition with IC50 values of 0.1 nM and 0.2 nM, respectively. These compounds could be further optimized to develop potent leads. This article provides comprehensive synthetic and SAR-based information on the pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine core to aid in the development of potent and novel derivatives as TRK inhibitors in medicinal chemistry. Therefore, further exploration of the pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine scaffold is essential to identify additional TRK inhibitors with enhanced clinical applications in the future.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.C.; methodology, A.T.M., S. and A.K.D.; software, S.C. and A.K.D.; validation, A.T.M. and S.; investigation, S.C., A.T.M., S., A.K.D., C.C. and P.C.; resources, S.C., P.C. and C.C.; and data curation, A.T.M. and S.; writing—original draft preparation, S.C.; writing—review and editing, S.C., A.T.M., S., A.K.D., P.C. and C.C.; supervision, S.C., P.C. and C.C.; project administration, S.C.; funding acquisition, S.C., P.C. and C.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
S.C. acknowledges NIPER-Raebareli for providing necessary laboratory infrastructure and facilities. S.C. acknowledges Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB) [Grant no. CRG/2019/005102], New Delhi for providing research grant. This research was funded by the Ministry of Science and Technology in Taiwan, grant numbers MOST 110-2113-M-039-001 and MOST 111-2221-E-039-009. This research was funded by FDCT grants from Macao Science and Technology University to PC (Project Code: 0005-2023-RIA1).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable
Acknowledgments
Amol T Mahajan and Shivani are grateful to the Department of Pharmaceuticals (DoP), Ministry of Chemical and Fertilizer’s, Government of India for providing Junior Research Fellowships. The NIPER-Raebareli manuscript communication number is NIPER-R/Communication/609.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
| PP | Pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine |
| TRK | Tropomyosin Receptor Kinases |
| SAR | Structure-Activity Relationship |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| NGF | Nerve Growth Factor |
| BDNF | Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor |
| NT3 | Neurotrophin-3 |
| AML | Acute Myeloid Leukemia |
| CNS | Central Nervous System |
| CDK | Cyclin-Dependent Kinases |
| RTK | receptor tyrosine kinases |
| EGFRs | Epidermal Growth Factor Receptors |
| FGFRs | Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptors |
| ALK | Anaplastic lymphoma kinase |
| ROS1 | ROS proto-oncogene 1, receptor tyrosine kinase |
References
- Huang, E.J.; Reichardt, L.F. Neurotrophins: Roles in Neuronal Development and Function. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 24, 677–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozaki, R.; Yoshizawa, T.; Tsukamoto, K.; Kato, H.; Kawabata, K. Abstract 2954A: A Potent and Selective TRK Inhibitor ONO-5390556, Shows Potent Antitumor Activity against Both TRK-Rearranged Cancers and the Resistant Mutants. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 2954A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan Huse, J.K. Review the Conformational Plasticity of Protein Kinases. Cell 2002, 109, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, T.; Wang, G.; Liu, Y.; Feng, L.; Wang, M.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Ouyang, L. Development of Small-Molecule Tropomyosin Receptor Kinase (TRK) Inhibitors for NTRK Fusion Cancers. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 355–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalpan, D.R.; Martin-Zanca, D.; Parada, L.F. Tyrosine Phosphorylation and Tyrosine Kinase Activity of the Trk Proto-Oncogene Product Induced by NGF. Nature 1991, 350, 158–160. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, R.; Nanduri, V.; Jing, S.; Lamballe, F.; Tapley, P.; Bryant, S.; Cordon-Cardo, C.; Jones, K.R.; Reichardt, L.F.; Barbacid, M. The MB Tyrosine Protein Kinase Is a Receptor for Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Neurotrophin-3. Cell 1991, 65, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakizawa, S. Neurotrophin-3. In Handbook of Hormones (Second Edition); Ando, H., Ukena, K., Nagata, S., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2021; pp. 483–485. ISBN 978-0-12-820649-2. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Song, L.; Li, Y.; Guo, J.; Huang, S.; Du, S.; Li, W.; Cao, R.; Cui, S. Neurotrophin-3 Promotes Peripheral Nerve Regeneration by Maintaining a Repair State of Schwann Cells after Chronic Denervation via the TrkC/ERK/c-Jun Pathway. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozano-Ureña, A.; Frade, J.M. Differential Contribution of TrkB and P75NTR to BDNF-Dependent Self-Renewal, Proliferation, and Differentiation of Adult Neural Stem Cells. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2023, 16, 1271820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.L.; Khan, M.I.; Wang, J.; Ali, R.; Ali, S.W.; Zahra, Q.-A.; Kazmi, A.; Lolai, A.; Huang, Y.L.; Hussain, A.; et al. Role of Receptor Tyrosine Kinases Mediated Signal Transduction Pathways in Tumor Growth and Angiogenesis—New Insight and Futuristic Vision. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 180, 739–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batool, Z.; Azfal, A.; Liaquat, L.; Sadir, S.; Nisar, R.; Inamullah, A.; Faiz Ghalib, A.U.; Haider, S. Receptor Tyrosine Kinases (RTKs): From Biology to Pathophysiology. In Receptor Tyrosine Kinases in Neurodegenerative and Psychiatric Disorders; Mansour, H.M., Khattab, M.M., El-khatib, A.S., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 117–185. ISBN 978-0-443-18677-6. [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham, M.E.; Greene, L.A. A Function-Structure Model for NGF-Activated TRK. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 7282–7293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaishnavi, A.; Le, A.T.; Doebele, R.C. TRKing down an Old Oncogene in a New Era of Targeted Therapy. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amatu, A.; Sartore-Bianchi, A.; Siena, S. NTRK Gene Fusions as Novel Targets of Cancer Therapy across Multiple Tumour Types. Open 2016, 1, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulciani, S.; Santos, E.; Lauver, A.V.; Long, L.K.; Aaronson, S.A. Oncogene in Solid Human Tumours. Nature 1982, 300, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Zanca, D.; Hughes, S.H.; Barbacid, M. A Human Oncogene Formed by the Fusion of Truncated Tropomyosin and Protein Tyrosine Kinase Sequences. Nature 1986, 319, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amatu, A.; Sartore-Bianchi, A.; Bencardino, K.; Pizzutilo, E.G.; Tosi, F.; Siena, S. Tropomyosin Receptor Kinase (TRK) Biology and the Role of NTRK Gene Fusions in Cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, VIII5–VIII15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pestana, R.C.; Sen, S.; Hobbs, B.P.; Hong, D.S. Histology-Agnostic Drug Development—Considering Issues beyond the Tissue. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 555–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maristella Bungaro, E.G. NTRK1/2/3: Biology, Detection and Therapy. Precis Cancer Med. 2024, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Forsythe, A.; Zhang, W.; Phillip Strauss, U.; Fellous, M.; Korei, M.; Keating, K. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Neurotrophic Tyrosine Receptor Kinase Gene Fusion Frequencies in Solid Tumors. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2020, 12, 1758835920975613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somwar, R.; Hofmann, N.E.; Smith, B.; Odintsov, I.; Vojnic, M.; Linkov, I.; Tam, A.; Khodos, I.; Mattar, M.S.; de Stanchina, E.; et al. NTRK Kinase Domain Mutations in Cancer Variably Impact Sensitivity to Type I and Type II Inhibitors. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theik, N.W.Y.; Muminovic, M.; Alvarez-Pinzon, A.M.; Shoreibah, A.; Hussein, A.M.; Raez, L.E. NTRK Therapy among Different Types of Cancers, Review and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannantuono, G.M.; Riondino, S.; Sganga, S.; Rosenfeld, R.; Guerriero, S.; Carlucci, M.; Capotondi, B.; Torino, F.; Roselli, M. NTRK Gene Fusions in Solid Tumors and TRK Inhibitors: A Systematic Review of Case Reports and Case Series. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Lu, X. Selective Type II TRK Inhibitors Overcome XDFG Mutation Mediated Acquired Resistance to the Second-Generation Inhibitors Selitrectinib and Repotrectinib. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2024, 14, 517–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.S.J.; Tan, D.S.P. TRK Inhibitors: Managing on-Target Toxicities. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1109–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocco, E.; Scaltriti, M.; Drilon, A. NTRK Fusion-Positive Cancers and TRK Inhibitor Therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 731–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Schneider, B.; Nagel, S.; Geffers, R.; Kaufmann, M.; Quentmeier, H.; Drexler, H.G.; MacLeod, R.A.F. Spliceosomal Targeting in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells with ETV6-NTRK3 Fusion. Blood 2009, 114, 5042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enkavi, G.; Girych, M.; Moliner, R.; Vattulainen, I.; Castrén, E. TrkB Transmembrane Domain: Bridging Structural Understanding with Therapeutic Strategy. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2024, 49, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regua, A.T.; Aguayo, N.R.; Jalboush, S.A.; Doheny, D.L.; Manore, S.G.; Zhu, D.; Wong, G.L.; Arrigo, A.; Wagner, C.J.; Yu, Y.; et al. Trka Interacts with and Phosphorylates Stat3 to Enhance Gene Transcription and Promote Breast Cancer Stem Cells in Triple-Negative and Her2-Enriched Breast Cancers. Cancers 2021, 13, 2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, A.M.; Lo, H.W. Inhibiting TRK Proteins in Clinical Cancer Therapy. Cancers 2018, 10, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuther, G.W.; Lambert, Q.T.; Caligiuri, M.A.; Channing, A.; Der, J. Identification and Characterization of an Activating TrkA Deletion Mutation in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 8655–8666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roccato, E.; Miranda, C.; Ranzi, V.; Gishizki, M.; Pierotti, M.A.; Greco, A. Biological Activity of the Thyroid TRK-T3 Oncogene Requires Signalling through Shc. Br. J. Cancer 2002, 87, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranzi, V.; Meakin, S.O.; Miranda, C.; Mondellini, P.; Pierotti, M.A.; Greco, A. The Signaling Adapters Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor Substrate 2 and 3 Are Activated by the Thyroid TRK Oncoproteins. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 922–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lee, Y.C.; Chen, J.Y.; Huang, C.J.; Chen, H.S.; Yang, A.H.; Hang, J.F. Detection of NTRK1/3 Rearrangements in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Using Immunohistochemistry, Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization, and Next-Generation Sequencing. Endocr. Pathol. 2020, 31, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Liu, Y.; Shi, X.; Zhou, W.; Zeng, X. Elaboration of NTRK-Rearranged Colorectal Cancer: Integration of Immunoreactivity Pattern, Cytogenetic Identity, and Rearrangement Variant. Dig. Liver Dis. 2023, 55, 1757–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Chong, K.Y.; Hartwich, T.M.P.; Bi, F.; Witham, A.K.; Patrick, D.; Morrisson, M.J.; Cady, S.L.; Cerchia, A.P.; Kelk, D.; et al. Ovarian BDNF Promotes Survival, Migration, and Attachment of Tumor Precursors Originated from P53 Mutant Fallopian Tube Epithelial Cells. Oncogenesis 2020, 9, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dionne, C.A.; Camoratto, A.M.; Jam, J.P.; Emerson, E.; Neff, N.; Vaught, J.L.; Murakata, C.; Djakiew, D.; Lamb, J.; Bova, S.; et al. Cell Cycle-Independent Death of Prostate Adenocarcinoma Is Induced by the Trk Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor CEP-751 (KT6587)’. Clin. Cancer Res. 1998, 4, 1887–1898. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Q.; Shimahara, Y. Expression of Nerve Growth Factor Receptors Is Correlated with Progression and Prognosis of Human Pancreatic Cancer. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 21, 850–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchetti, A.; Felicioni, L.; Pelosi, G.; Del Grammastro, M.; Fumagalli, C.; Sciarrotta, M.; Malatesta, S.; Chella, A.; Barassi, F.; Mucilli, F.; et al. Frequent Mutations in the Neurotrophic Tyrosine Receptor Kinase Gene Family in Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Lung. Hum. Mutat. 2008, 29, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Huang, K.; Shi, M.; Huo, Y.; Han, L.; Liu, B.; Li, Y. Research Advances in the Role of the Tropomyosin Family in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, J.S.; Wang, K.; Gay, L.; Al-Rohil, R.; Rand, J.V.; Jones, D.M.; Lee, H.J.; Sheehan, C.E.; Otto, G.A.; Palmer, G.; et al. New Routes to Targeted Therapy of Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinomas Revealed by Next-Generation Sequencing. Oncologist 2014, 19, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, E.; Chmielecki, J.; Tang, C.M.; Wang, K.; Heinrich, M.C.; Kang, G.; Corless, C.L.; Hong, D.; Fero, K.E.; Murphy, J.D.; et al. FGFR1 and NTRK3 Actionable Alterations in “Wild-Type” Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hechtman, J.F.; Benayed, R.; Hyman, D.M.; Drilon, A.; Zehir, A.; Frosina, D.; Arcila, M.E.; Dogan, S.; Klimstra, D.S.; Ladanyi, M.; et al. Pan-Trk Immunohistochemistry Is an Efficient and Reliable Screen for the Detection of NTRK Fusions. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2017, 41, 1547–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pishvaian, M.J.; Garrido-Laguna, I.; Liu, S.V.; Multani, P.S.; Chow-Maneval, E.; Rolfo, C. Entrectinib in TRK and ROS1 Fusion-Positive Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer. Precis. Oncol. 2018, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freund-Michel, V.; Frossard, N. The Nerve Growth Factor and Its Receptors in Airway Inflammatory Diseases. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 117, 52–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, V.Y.; Zvara, P.; Dattilio, A.; Redman, T.L.; Allen, S.J.; Dawbarn, D.; Stroemer, R.P.; Vizzard, M.A. Decrease in Bladder Overactivity with REN1820 in Rats with Cyclophosphamide Induced Cystitis. J. Urol. 2005; 173, pp. 1016–1021. [Google Scholar]
- Di Mola, F.F.; Friess, H.; Zhu, Z.W.; Koliopanos, A.; Bley, T.; Sebastiano, D.; Innocenti, P.; Zimmermann, A.; Büchler, M.W. Nerve Growth Factor and Trk High Affinity Receptor (TrkA) Gene Expression in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gut 2000, 46, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, Y.C.; Hagströmer, L.; Emtestam, L.; Johansson, O. Increased Nerve Growth Factor and Its Receptors in Atopic Dermatitis: An Immunohistochemical Study. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2006, 298, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raychaudhuri, S.P.; Sanyal, M.; Weltman, H.; Kundu, S.; Ãw, R. K252a, a High-Affinity Nerve Growth Factor Receptor Blocker, Improves Psoriasis: An In Vivo Study Using the Severe Combined Immunodeficient Mouse-Human Skin Model. J. Invest Dermatol. 2004, 122, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, M.; Kuroda, Y.; Murata, E. NGF/TrkA Signaling as a Therapeutic Target for Pain. Pain Pract. 2016, 16, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savaskan, E.; Müller-Spahn, F.; Olivieri, G.; Bruttel, S.; Otten, U.; Rosenberg, C.; Hulette, C.; Hock, C.; Savaskan, E. Alterations in Trk A, Trk B and Trk C Receptor Immunoreactivities in Parietal Cortex and Cerebellum in Alzheimer’s Disease. Eur. Neurol. 2000, 44, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prencipe, G.; Minnone, G.; Strippoli, R.; De Pasquale, L.; Petrini, S.; Caiello, I.; Manni, L.; De Benedetti, F.; Bracci-Laudiero, L. Nerve Growth Factor Downregulates Inflammatory Response in Human Monocytes through TrkA. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 3345–3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numakawa, T.; Odaka, H. Chapter 3—Roles of Trk Receptors, Tyrosine Kinase Receptors for Neurotrophins, in the Developing CNS. In Receptor Tyrosine Kinases in Neurodegenerative and Psychiatric Disorders; Mansour, H.M., Khattab, M.M., El-khatib, A.S., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 79–115. ISBN 978-0-443-18677-6. [Google Scholar]
- Stoleru, B.; Madalina Popescu, A.; Elise Tache, T.; Maria Neamtu, O.; Emami, G.; Tataranu, L.G.; Buteica, A.S.; Dricu, A.; Purcaru, S.O. Tropomyosin-Receptor-Kinases Signalling in the Nervous System. Maedica-A J. Clin. Med. 2013, 8, 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Laetsch, T.W.; Hong, D.S. Tropomyosin Receptor Kinase Inhibitors for the Treatment of TRK Fusion Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 4974–4982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, W.; Lakkaniga, N.R.; Carlomagno, F.; Santoro, M.; McDonald, N.Q.; Lv, F.; Gunaganti, N.; Frett, B.; Li, H.Y. Insights into Current Tropomyosin Receptor Kinase (TRK) Inhibitors: Development and Clinical Application. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 1731–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roviello, G.; D’Angelo, A.; Sciortino, M.; Mini, E.; Nobili, S.; De Logu, F.; Massi, D. TRK Fusion Positive Cancers: From First Clinical Data of a TRK Inhibitor to Future Directions. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2020, 152, 103011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, J.J.; Schirrmacher, R.; Farrell, K.; Bernard-Gauthier, V. Tropomyosin Receptor Kinase Inhibitors: An Updated Patent Review for 2010-2016–Part I. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2017, 27, 733–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drilon, A.; Nagasubramanian, R.; Blake, J.F.; Ku, N.; Tuch, B.B.; Ebata, K.; Smith, S.; Lauriault, V.; Kolakowski, G.R.; Brandhuber, B.J.; et al. A Next-Generation TRK Kinase Inhibitor Overcomes Acquired Resistance to Prior Trk Kinase Inhibition in Patients with TRK Fusion-Positive Solid Tumors. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 963–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drilon, A.; Ou, S.H.I.; Cho, B.C.; Kim, D.W.; Lee, J.; Lin, J.J.; Zhu, V.W.; Ahn, M.J.; Camidge, D.R.; Nguyen, J.; et al. Repotrectinib (Tpx-0005) Is a next-Generation Ros1/Trk/Alk Inhibitor That Potently Inhibits Ros1/Trk/Alk Solvent-Front Mutations. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 1227–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherukupalli, S.; Karpoormath, R.; Chandrasekaran, B.; Hampannavar, G.A.; Thapliyal, N.; Palakollu, V.N. An Insight on Synthetic and Medicinal Aspects of Pyrazolo[1,5-a]Pyrimidine Scaffold. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 126, 298–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, M.; Kumar, R. Medicinal Attributes of Pyrazolo[3,4-d]Pyrimidines: A Review. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 5657–5668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, N.S.M.; Ali, G.M.E.; Ibrahim, D.A.; Elmetwali, A.M. Medicinal Attributes of Pyrazolo[1,5-a]Pyrimidine Based Scaffold Derivatives Targeting Kinases as Anticancer Agents. Futur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 2, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashad, A.E.; Abdelmegid, M.; Shamroukh, A.H.; Abdelmegeid, F.M. The Chemistry of Pyrazolopyrimidines and Their Applications. Org. Chem. Ind. J. 2014, 10, 224–250. [Google Scholar]
- Salem, M.A.; Helal, M.H.; Gouda, M.A.; Abd EL-Gawad, H.H.; Shehab, M.A.M.; El-Khalafawy, A. Recent Synthetic Methodologies for Pyrazolo[1,5-a]Pyrimidine. Synth. Commun. 2019, 49, 1750–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraley, M.E.; Hoffman, W.F.; Rubino, R.S.; Hungate, R.W.; Tebben, A.J.; Rutledge, R.Z.; Mcfall, R.C.; Huckle, W.R.; Kendall, R.L.; Coll, K.E.; et al. Synthesis and Initial SAR Studies of 3,6-Disubstituted Pyrazolo[1,5-a]Pyrimidines: A New Class of KDR Kinase Inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2002, 12, 2767–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu Elmaati, T.M.; El-Taweel, F.M.A. Routes to Pyrazolo[3,4-e][1,4]Thiazepine, Pyrazolo[1,5-a]Pyrimidine and Pyrazole Derivatives. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2003, 50, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compton, D.R.; Carlson, K.E.; Katzenellenbogen, J.A. Pyrazolo[1,5-a]Pyrimidines as Estrogen Receptor Ligands: Defining the Orientation of a Novel Heterocyclic Core. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 14, 5681–5684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhao, Y.F.; Zhao, X.L.; Yuan, X.Y.; Gong, P. Synthesis and Anti-Tumor Activities of Novel Pyrazolo[1,5-a]Pyrimidines. Arch. Pharm. 2006, 339, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paruch, K.; Dwyer, M.P.; Alvarez, C.; Brown, C.; Chan, T.Y.; Doll, R.J.; Keertikar, K.; Knutson, C.; McKittrick, B.; Rivera, J.; et al. Pyrazolo[1,5-a]Pyrimidines as Orally Available Inhibitors of Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 2. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 6220–6223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, R.R.; Curtin, M.L.; Albert, D.H.; Glaser, K.B.; Pease, L.J.; Soni, N.B.; Bouska, J.J.; Reuter, D.; Stewart, K.D.; Marcotte, P.; et al. 7-Aminopyrazolo[1,5-a]Pyrimidines as Potent Multitargeted Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 3777–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gommermann, N.; Buehlmayer, P.; Von Matt, A.; Breitenstein, W.; Masuya, K.; Pirard, B.; Furet, P.; Cowan-Jacob, S.W.; Weckbecker, G. New Pyrazolo[1,5a]Pyrimidines as Orally Active Inhibitors of Lck. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 3628–3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Enany, M.M.; Kamel, M.M.; Khalil, O.M.; El-Nassan, H.B. Synthesis and Antitumor Activity of Novel Pyrazolo[1,5-a]Pyrimidine Derivatives. Eur. J. Chem. 2011, 2, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ivachtchenko, A.V.; Golovina, E.S.; Kadieva, M.G.; Kysil, V.M.; Mitkin, O.D.; Tkachenko, S.E.; Okun, I.M. Synthesis and Structure-Activity Relationship (SAR) of (5,7-Disubstituted 3-Phenylsulfonyl-Pyrazolo[1,5-a]Pyrimidin-2-Yl)-Methylamines as Potent Serotonin 5-HT 6 Receptor (5-HT 6R) Antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 8161–8173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosugi, T.; Mitchell, D.R.; Fujino, A.; Imai, M.; Kambe, M.; Kobayashi, S.; Makino, H.; Matsueda, Y.; Oue, Y.; Komatsu, K.; et al. Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase-Activated Protein Kinase 2 (MAPKAP-K2) as an Anti-inflammatory Target: Discovery and in Vivo Activity of Selective Pyrazolo[1,5-a]Pyrimidine Inhibitors Using a Focused Library and Structure-Based Optimization Approach. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 6700–6715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, M.P.; Keertikar, K.; Paruch, K.; Alvarez, C.; Labroli, M.; Poker, C.; Fischmann, T.O.; Mayer-Ezell, R.; Bond, R.; Wang, Y.; et al. Discovery of Pyrazolo[1,5-a]Pyrimidine-Based Pim Inhibitors: A Template-Based Approach. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 6178–6182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, A.S.; Kaping, S.; Vishwakarma, J.N. A Facile Environment-Friendly One-Pot Two-Step Regioselective Synthetic Strategy for 3,7-Diarylpyrazolo[1,5-a]Pyrimidines Related to Zaleplon and 3,6-Diarylpyrazolo[1,5-a]Pyrimidine-7-Amines Assisted by KHSO4 in Aqueous Media. Mol. Divers. 2015, 19, 759–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, J.; Andrews, S.W.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, G. Substituted Pyrazolo[1,5-a]Pyrimidine Compounds as TRK Kinase Inhibitors. WO 2010048314, 29 April 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, S.; Andrews, S.S.; Condroski, K.R.; Haas, J.; Huang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Kercher, T.; Seo, J. Substituted Pyrazolo [1,5-a]Pyrimidine Compounds as TRK Kinase Inhibitors. WO 2011006074, 13 January 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, S.W.; Condroski, K.R.; Haas, J.; Jiang, Y.; Kolakowski, G.R.; Seo, J.; Yang, H.-W.; Zhao, Q. Macrocyclic Compounds as TRK Kinase Inhibitors. WO 2011146336, 24 November 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.; Lee, C.; Lee, G.; Yoon, C.; Seo, J.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, M.; Jeong, H.; Choi, H.; Jung, M.E.; et al. Fused Ring Heteroaryl Compounds and Their Use as Trk Inhibitors. WO 2016097869, 4 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, K.; Ciblat, S.; Albert, V.; Bruneau-Latour, N.; Boudreault, J. 5-(2-(2,5-Difluorophenyl)Pyrrolidin-1-Yl)-3-(1H-Pyrazol-1-Yl)Pyrazolo[1,5-a]Pyrimidine Derivatives and Related Compounds as Trk Kinase Inhibitors for Treating Cancer. WO 2019118584, 20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wenglowsky, S.M.; Miduturu, C.V.; Neil Bifulco, J.R.; Kim, J.L. Compounds and Compositions for Treating Disorders to NTRK. US 10370379B2, 6 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Ying, Y.; Liao, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Yuan, J.; Jia, W.; Wang, W. Compound Having Macrocyclic Molecular Structure and Use Thereof. WO 2019149131, 8 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Tan, H.; He, C.; Wang, X.; Liu, Q.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Gao, Y.; Jiang, L.; Linghu, L.; et al. Substituted (2-Azabicyclo [3.1.0] Hexan-2-Yl) Pyrazolo [1, 5-a] Pyrimidine and Imidazo[1, 2-b] Pyridazine Compounds as Trk Kinases Inhibitors. WO 2019174598, 19 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, J.J.; LI, Y.; Rogers, E.W.; Zhai, D.; Ung, J. Macrocycle Kinase Inhibitors. US 10689400B2, 23 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Hu, Y.; Wu, W.; Dai, L.; Duan, X.; Yang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Han, Y.; Peng, Y.; Kong, F.; et al. Amino Pyrazolopyrimidine Used as Neurotrophic Tyrosine Kinase Receptor Inhibitors. US 10829492B2, 10 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, J. Substituted Pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine Macrocyclic Compound. EP 3744723A1, 2 December 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, J.; Chen, S. Pyrazolopyrimidine Derivative as Selective Trk Inhibitor. US 20210403485 A1, 30 December 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Sun, J.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.L.; Chen, S. Pyrazolopyrimidine Derivatives and Use Thereof. US 11,464,780 B2, 11 October 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Cai, S.; Zhao, T.; Xu, L.; Guan, D.; Li, J.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, H. Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Macrocyclic Derivatives as TRK Inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2021, 53, 128409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Han, T.; Tang, C.; Fan, W. Pyrazolo[1,5-a]Pyrimidine Based Trk Inhibitors: Design, Synthesis, Biological Activity Evaluation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2021, 31, 127712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yu, P.; Dong, L.; Wang, W.; Duan, S.; Wang, B.; Gong, X.; Ye, L.; Wang, H.; Tian, J. Discovery of the Next-Generation Pan-TRK Kinase Inhibitors for the Treatment of Cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 10286–10296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Wu, F.X.; Wang, M.S.; Xu, H.C.; Zhuo, L.S.; Yang, G.F.; Huang, W. Discovery of 3-Pyrazolyl-Substituted Pyrazolo[1,5-a]Pyrimidine Derivatives as Potent TRK Inhibitors to Overcome Clinically Acquired Resistance. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 241, 114654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, C.; Fan, W. Pyrazolo[1,5-a]Pyrimidine Derivatives of the Second-Generation TRK Inhibitor: Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2022, 63, 128646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Qadhi, M.A.; Allam, H.A.; Fahim, S.H.; Yahya, T.A.A.; Ragab, F.A.F. Design and Synthesis of Certain 7-Aryl-2-Methyl-3-Substituted Pyrazolo{1,5-a}Pyrimidines as Multikinase Inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 262, 115918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metwally, N.H.; Deeb, E.A.; Hasani, I.W. Synthesis, Anticancer Evaluation, Molecular Docking and ADME Study of Novel Pyrido[4ʹ,3ʹ:3,4]Pyrazolo[1,5-a]Pyrimidines as Potential Tropomyosin Receptor Kinase A (TrKA) Inhibitors. BMC Chem. 2024, 18, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).