QCL Infrared Spectroscopy Combined with Machine Learning as a Useful Tool for Classifying Acetaminophen Tablets by Brand
Abstract
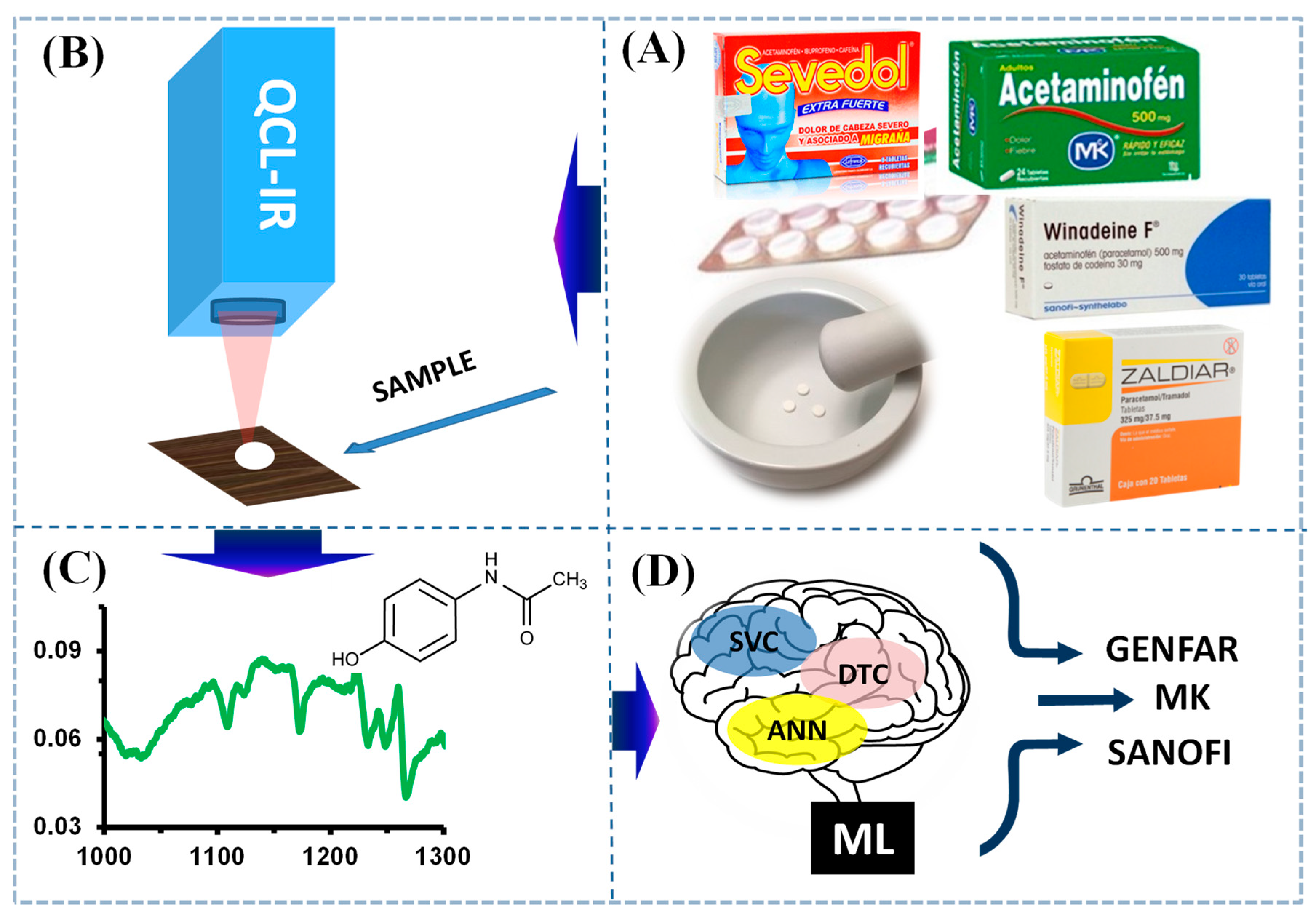
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Infrared Spectra Analysis of AAP
2.2. Spectral Identification
2.3. Machine Learning Analysis
2.3.1. Principal Component Analysis
2.3.2. Analysis of Machine Learning Using SVC, DTC, and ANN
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sample and Standard Acquisition
3.2. Sample Preparation
3.3. Acquisition of Spectra
3.4. Machine Learning Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FDA. Counterfeit Medicine. Available online: http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/ResourcesForYou/Consumers/BuyingUsingMedicineSafely/CounterfeitMedicine/ (accessed on 2 February 2024).
- Pathak, R.; Gaur, V.; Sankrityayan, H.; Gogtay, J. Tackling Counterfeit Drugs: The Challenges and Possibilities. Pharm. Med. 2023, 37, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Health and Well-Being. Available online: https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/major-themes/health-and-well-being (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- El-Dahiyat, F.; Fahelelbom, K.M.S.; Jairoun, A.A.; Al-Hemyari, S.S. Combatting Substandard and Falsified Medicines: Public Awareness and Identification of Counterfeit Medications. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 754279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. 1 in 10 Medical Products in Developing Countries is Substandard or Falsified. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/28-11-2017-1-in-10-medical-products-in-developing-countries-is-substandard-or-falsified (accessed on 28 November 2017).
- Ziavrou, K.S.; Noguera, S.; Boumba, V.A. Trends in counterfeit drugs and pharmaceuticals before and during COVID-19 pandemic. Forensic Sci. Int. 2022, 338, 111382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, K. Fake covid vaccines boost the black market for counterfeit medicines. BMJ 2021, 375, 2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caragea, G.; Avram, O.; Pauna, A.; Costea, A.; Tudosie, M. Acetaminophen, a therapeutic or an extremely toxic remedy—A review. J. Mind Med. Sci. 2022, 9, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, J.B. Colorimetric Determination of Acetaminophen. J. Pharm. Sci. 1969, 58, 469–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arıkan, C.C.; Kulabaş, N.; Küçükgüzel, İ. Synthesis and standardization of an impurity of acetaminophen, development and validation of liquid chromatographic method. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2023, 223, 115123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.; Gamal, M.; Nasr, M. Optimization of Analytical Method for Simultaneous Determination of Acetaminophen, Caffeine, and Aspirin in Tablet Dosage Form. Pharm. Chem. J. 2023, 56, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.N.; Pickersgill, R.; Stefanec, M. Colorimetric determination of acetaminophen. Clin. Biochem. 1983, 16, 220–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, A.M. Spectrophotometric Determination of Paracetamol in Some Manufactured Tablets in Iraqi markets. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. 2017, 42, 53–57. [Google Scholar]
- Magerusan, L.; Pogacean, F.; Pruneanu, S. Enhanced Acetaminophen Electrochemical Sensing Based on Nitrogen-Doped Graphene. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazan, M.; Tashkhourian, J.; Haghighi, B. A novel electrochemical sensor based on MoO3 nanobelt-graphene oxide composite for the simultaneous determination of paracetamol and 4-aminophenol. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2023, 140, 110549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wartewig, S.; Neubert, R.H.H. Pharmaceutical applications of Mid-IR and Raman spectroscopy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 1144–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roggo, Y.; Chalus, P.; Maurer, L.; Lema-Martinez, C.; Edmond, A.; Jent, N. A review of near infrared spectroscopy and chemometrics in pharmaceutical technologies. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2007, 44, 683–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scappaticci, C.; Spera, S.; Biancolillo, A.; Marini, F. Detection and Quantification of Alprazolam Added to Long Drinks by Near Infrared Spectroscopy and Chemometrics. Molecules 2022, 27, 6420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Lin, L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, G.; Luo, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, H. Pharmaceutical application of multivariate modelling techniques: A review on the manufacturing of tablets. RSC Advances 2021, 11, 8323–8345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziémons, E.; Mantanus, J.; Lebrun, P.; Rozet, E.; Evrard, B.; Hubert, P. Acetaminophen determination in low-dose pharmaceutical syrup by NIR spectroscopy. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2010, 53, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szostak, R.; Mazurek, S. Quantitative determination of acetylsalicylic acid and acetaminophen in tablets by FT-Raman spectroscopy. Analyst 2001, 127, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanmohammadi, M.; Garmarudi, A.B.; Moazzen, N.; Ghasemi, K. Qualitative Discrimination Between Paracetamol Tablets Made by Near Infrared Spectroscopy and Chemometrics With Regard to Polymorphism. J. Struct. Chem. 2010, 51, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallah, M.A.; Sherazi, S.T.H.; Bhanger, M.I.; Mahesar, S.A.; Bajeer, M.A. A rapid Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopic method for direct quantification of paracetamol content in solid pharmaceutical formulations. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 141, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oloyede, O.O.; Alabi, Z.O.; Akinyemi, A.O.; Oyelere, S.F.; Oluseye, A.B.; Owoyemi, B.C.D. Comparative evaluation of acetaminophen form (I) in commercialized paracetamol brands. Sci. Afr. 2023, 19, e01537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokari, A.; Guo, S.; Bocklitz, T. Exploring the Steps of Infrared (IR) Spectral Analysis: Pre-Processing, (Classical) Data Modelling, and Deep Learning. Molecules 2023, 28, 6886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, C.A.M.; Greenop, M.; Ashton, L.; Rehman, I.U. Applications of machine learning in spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2020, 56, 733–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Chen, H.; Lin, Z. Brand classification of detergent powder using near-infrared spectroscopy and extreme learning machines. Microchem. J. 2021, 160, 105691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yang, Q.; Lu, J. Classification of washing powder brands using near-infrared spectroscopy combined with chemometric calibrations. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 120, 625–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrión-Roca, W.; Colón-Mercado, A.M.; Castro-Suarez, J.R.; Caballero-Agosto, E.R.; Colón-González, F.M.; Centeno-Ortiz, J.A.; Ríos-Velázquez, C.; Hernández-Rivera, S.P. Chemical sensing of common microorganisms found in biopharmaceutical industries using MIR laser spectroscopy and multivariate analysis. J. Biophotonics 2024, 17, e202300391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zorin, I.; Gattinger, P.; Ebner, A.; Brandstetter, M. Advances in mid-infrared spectroscopy enabled by supercontinuum laser sources. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 5222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayerhöfer, T.G.; Popp, J. Beer’s Law—Why Absorbance Depends (Almost) Linearly on Concentration. ChemPhysChem 2019, 20, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faist, J.; Capasso, F.; Sivco, D.L.; Sirtori, C.; Hutchinson, A.L.; Cho, A.Y. Quantum Cascade Laser. Science 1994, 264, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plata-Enríquez, J.L.; Puche-Mercado, J.F.; Palmer-Velázquez, S.; Carrión-Roca, W.; Colón-González, F.M.; Hernández-Rivera, S.P. Analytical Method Development Using Quantum Laser Cascade Spectroscopy with Diffuse and Attenuated Total Reflectance for Determining Low Concentrations of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients. Austin J. Anal. Pharm. Chem. 2023, 10, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childs, D.T.D.; Hogg, R.A.; Revin, D.G.; Rehman, I.U.; Cockburn, J.W.; Matcher, S.J. Sensitivity Advantage of QCL Tunable-Laser Mid-Infrared Spectroscopy Over FTIR Spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2015, 50, 822–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moynihan, H.A.; O’Hare, I.P. Spectroscopic characterisation of the monoclinic and orthorhombic forms of paracetamol. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 247, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amado, A.M.; Azevedo, C.; Ribeiro-Claro, P.J.A. Conformational and vibrational reassessment of solid paracetamol. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2017, 183, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zapata, F.; López-Fernández, A.; Ortega-Ojeda, F.; Quintanilla, G.; García-Ruiz, C.; Montalvo, G. Introducing ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy through Analysis of Acetaminophen Drugs: Practical Lessons for Interdisciplinary and Progressive Learning for Undergraduate Students. J. Chem. Educ. 2021, 98, 2675–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matkovic, S.R.; Valle, G.M.; Galle, M.; Briand, L.E. Desarrollo y validación del análisis cuantitativo de Ibuprofeno en comprimidos por espectroscopía infrarroja. Acta Farm. Bonaer. 2004, 23, 527–532. [Google Scholar]
- Galán-Freyle, N.J.; Pacheco-Londoño, L.C.; Román-Ospino, A.D.; Hernández-Rivera, S.P. Applications of Quantum Cascade Laser Spectroscopy in the Analysis of Pharmaceutical Formulations. Appl. Spectrosc. 2016, 70, 1511–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdalla, M.A. Determination of Caffeine, the Active Ingredient in Different Coffee Drinks and its Characterization by FTIR/ATR and TGA/DTA. Int. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2015, 2, 257765. [Google Scholar]
- Bakalska, R.; Ivanova, B.; Kolev, T. Solid-state IR-LD spectroscopy of codeine and N-norcodeine derivatives. Open Chem. 2006, 4, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjunan, V.; Santhanam, R.; Marchewka, M.K.; Mohan, S. Comprehensive quantum chemical and spectroscopic (FTIR, FT-Raman, 1H, 13C NMR) investigations of O-desmethyltramadol hydrochloride an active metabolite in tramadol—An analgesic drug. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 122, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepak, S.N.; Hari, B.N.V. Optimization, Development and evaluation of Microemulsion for the release of combination of Guaifenesin and Phenylephrine. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 3, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, H.; Chung, H. New discrimination method combining hit quality index based spectral matching and voting. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 758, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E2310-04; Standard Guide for Use of Spectral Searching by Curve Matching Algorithms with Data Recorded Using Mid-Infrared Spectroscopy. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2009. [CrossRef]
- Beattie, J.R.; Esmonde-White, F.W.L. Exploration of Principal Component Analysis: Deriving Principal Component Analysis Visually Using Spectra. Appl. Spectrosc. 2021, 75, 000370282098784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mijwil, M.M.; Aljanabi, M. A Comparative Analysis of Machine Learning Algorithms for Classification of Diabetes Utilizing Confusion Matrix Analysis. Baghdad Sci. J. 2023, 21, 1712–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananey-Obiri, D.; Sarku, E. Predicting the Presence of Heart Diseases using Comparative Data Mining and Machine Learning Algorithms. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2020, 176, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitorus, A.; Lapcharoensuk, R. A rapid method to predict type and adulteration of coconut milk by near-infrared spectroscopy combined with machine learning and chemometric tools. Microchem. J. 2023, 195, 109461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachie, C.Y.E.; Obiri-Ananey, D.; Alfaro-Cordoba, M.; Tawiah, N.A.; Aryee, A.N.A. Classification of oils and margarines by FTIR spectroscopy in tandem with machine learning. Food Chem. 2024, 431, 137077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedregosa, F.; Buitinck, L.; Louppe, G.; Grisel, O.; Varoquaux, G.; Mueller, A. Scikit-learn. GetMobile Mob. Comput. Commun. 2015, 19, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trespalacios, J.A.M.; Suarez, J.R.C.; Fernández, J.H. Application of Fourier Transform Spectroscopy and Machine Learning to Determine Green Ethylene Content in Samples of Ethylene-Propylene Impact Copolymers. J. Southwest Jiaotong Univ. 2023, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera, B.; Piñol, V.L.; Mata, J.B.; Kim, K. A machine learning based classification models for plastic recycling using different wavelength range spectrums. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 374, 133883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Country | APIs Present | Brand |
|---|---|---|
| Colombia | Acetaminophen 500 mg | AG |
| Colombia | Acetaminophen 500 mg | Best |
| Colombia | Acetaminophen 500 mg | Genfar |
| Puerto Rico | Acetaminophen 500 mg | GSK |
| Colombia | Acetaminophen 500 mg | La Sante |
| Mexico | Acetaminophen 650 mg | Perrigo |
| Colombia | Acetaminophen 500 mg | MK |
| Colombia | Acetaminophen 325 mg | Grunenthal |
| Tramadol 37.5 mg | ||
| Colombia | Acetaminophen 250 mg | La Francol |
| Ibuprofen 400 mg | ||
| Caffeine 65 mg | ||
| Colombia | Acetaminophen 500 mg | Sanofis |
| Codeine phosphate 30 mg | ||
| Puerto Rico | Acetaminofén 325 mg | Tylenol |
| Guaifenesin 200 mg | ||
| Phenylephrine HCl 5 mg |
| Tylenol | Sanofi | Lafrancol | Grunenthal | MK | Perrigo | Lasante | GSK | Genfar | Best | AG | Spectral Library |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.89 | 0.91 | 0.50 | 0.66 | 0.89 | 0.96 | 0.98 | 0.93 | 0.96 | 0.97 | 0.93 | Lasante |
| 0.90 | 0.93 | 0.59 | 0.79 | 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.97 | 0.93 | 0.92 | 0.97 | 0.98 | Best |
| 0.87 | 0.90 | 0.47 | 0.57 | 0.85 | 0.95 | 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.94 | 0.92 | 0.89 | Genfar |
| 0.82 | 0.91 | 0.67 | 0.84 | 0.99 | 0.89 | 0.93 | 0.91 | 0.89 | 0.98 | 0.99 | AG |
| 0.89 | 0.91 | 0.56 | 0.73 | 0.90 | 0.94 | 0.91 | 0.93 | 0.90 | 0.93 | 0.91 | Sanofi |
| 0.45 | 0.56 | 0.99 | 0.71 | 0.70 | 0.46 | 0.50 | 0.53 | 0.47 | 0.59 | 0.67 | Lafrancol |
| 0.81 | 0.90 | 0.70 | 0.89 | 0.99 | 0.87 | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.85 | 0.96 | 0.99 | MK |
| 0.63 | 0.73 | 0.71 | 0.99 | 0.89 | 0.66 | 0.66 | 0.71 | 0.57 | 0.79 | 0.84 | Grunenthal |
| 0.93 | 0.94 | 0.46 | 0.66 | 0.87 | 0.99 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.89 | Perrigo |
| 0.87 | 0.93 | 0.53 | 0.71 | 0.89 | 0.96 | 0.93 | 0.99 | 0.95 | 0.93 | 0.91 | GSK |
| 0.98 | 0.89 | 0.45 | 0.63 | 0.81 | 0.93 | 0.89 | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.90 | 0.82 | Tylenol |
| Values | Hyperparameters | Method |
|---|---|---|
| 1.023292 | C | SVC |
| 0 | Γ | |
| Lineal | Kernel | |
| 7 | Max_depth | DTC |
| 5 | Min_samples_split | |
| log_loss | Criterion | |
| 20 | Neurons | ANN |
| 1 | Hidden layers | |
| lbfgs | Solver |
| Hyperparameters | Method | |
|---|---|---|
| , [0.01; …; 2] [0; 0.07; …; 1] × 102 | C | SVC |
| Γ | ||
| [‘linear’; ‘Rbf’; ‘Sigmoid’] | Kernel | |
| [3; 5; 7; 10][2; 5; 10] | Max_depth | DTC |
| Min_samples_split | ||
| [‘Gini’; ‘Entropy’; ‘Log_loss’] | Criterion | |
| [5; 10; 20] | Neurons | ANN |
| [1; 2; 3] | Hidden layers | |
| [‘Lbfgs’; ‘Sgd’; ‘Adam’] | Solver |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martínez-Trespalacios, J.A.; Polo-Herrera, D.E.; Félix-Massa, T.Y.; Hernandez-Rivera, S.P.; Hernandez-Fernandez, J.; Colpas-Castillo, F.; Castro-Suarez, J.R. QCL Infrared Spectroscopy Combined with Machine Learning as a Useful Tool for Classifying Acetaminophen Tablets by Brand. Molecules 2024, 29, 3562. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29153562
Martínez-Trespalacios JA, Polo-Herrera DE, Félix-Massa TY, Hernandez-Rivera SP, Hernandez-Fernandez J, Colpas-Castillo F, Castro-Suarez JR. QCL Infrared Spectroscopy Combined with Machine Learning as a Useful Tool for Classifying Acetaminophen Tablets by Brand. Molecules. 2024; 29(15):3562. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29153562
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartínez-Trespalacios, José A., Daniel E. Polo-Herrera, Tamara Y. Félix-Massa, Samuel P. Hernandez-Rivera, Joaquín Hernandez-Fernandez, Fredy Colpas-Castillo, and John R. Castro-Suarez. 2024. "QCL Infrared Spectroscopy Combined with Machine Learning as a Useful Tool for Classifying Acetaminophen Tablets by Brand" Molecules 29, no. 15: 3562. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29153562
APA StyleMartínez-Trespalacios, J. A., Polo-Herrera, D. E., Félix-Massa, T. Y., Hernandez-Rivera, S. P., Hernandez-Fernandez, J., Colpas-Castillo, F., & Castro-Suarez, J. R. (2024). QCL Infrared Spectroscopy Combined with Machine Learning as a Useful Tool for Classifying Acetaminophen Tablets by Brand. Molecules, 29(15), 3562. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29153562








