Abstract
With heimionones A–E (1–5), five new terpenoids were isolated from submerged cultures of Heimiomyces sp. in addition to the previously described compounds hispidin, hypholomin B, and heimiomycins A and B. Planar structures of the metabolites were elucidated by 1D and 2D NMR in addition to HRESIMS data. While ROESY data assigned relative configurations, absolute configurations were determined by the synthesis of MTPA esters of 1, 3, and 5. The [6.3.0] undecane core structure of compounds 3–5 is of the asteriscane-type, however, the scaffold of 1 and 2 with their bicyclo [5.3.0] decane core and germinal methyl substitution is, to our knowledge, unprecedented. Together with several new compounds that were previously isolated from solid cultures of this strain, Heimiomyces sp. showed an exceptionally high chemical diversity of its secondary metabolite profile.
1. Introduction
In the ever-growing effort to isolate, identify, and characterize novel natural products, the kingdom of Fungi serves as a well-known, reliable, and nearly inexhaustible source. Ongoing developments in numerous modern techniques significantly support the identification of hitherto unknown secondary metabolites, leading to a continuously rising number of newly discovered molecules. With regard to the ca. 35.000 species comprising [] and therefore the second-largest phylum of the kingdom Fungi, the Basidiomycota have proven to produce chemically very diverse secondary-metabolite profiles next to their biological diversity []. While there are Basidiomycota that mainly produce several congeners of the same compound family, such as members of the genus Armillaria, which are known for their large amount of structurally closely related sesquiterpenoids aryl esters [], there are also genera that show a high chemical diversity within their secondary metabolite profile concerning the presence of different core structures. Heimiomyces sp. (MUCL 56078) is an example of the latter since our previous studies already led to the isolation and identification of heimiocalamenes C–E (8–10) and heimiomycins A–C (11–13) [], as well as bis-heimiomycins A–D (14–17), heimiomycins D–E (18–19) and heimiocalamenes A–B (20–21) [], showing the enormous potential of this specimen to produce chemically very diverse secondary metabolites. Intriguingly, the secondary metabolite pattern of Heimiomyces sp. even changed drastically after switching the cultivation conditions from solid rice cultures to submerged cultures.
We herein present the isolation, structural elucidation, and biological evaluation of the new terpenoids heimionones A–E (1–5) with uncommon bicyclo [5.3.0] decane and [6.3.0] undecane core structures, respectively, that were isolated from submerged cultures of Heimiomyces sp. alongside the previously described heimiomycins A–B (11–12) [], as well as hispidin and hypholomin B (6–7) [,].
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Isolation and Structure Elucidation of Metabolites from Heimiomyces sp. (Figure 1, Figure 2 and Figure 3)
Heimionone A (1) was isolated as a yellow oil from the mycelial extracts of liquid cultures. Based on an HRESIMS analysis, its molecular formula was assigned as C22H28O5 according to the molecular ion cluster at m/z 373.2012 [M + H]+ (calcd. for C22H29O5 373.2023) indicating nine degrees of unsaturation. 1H NMR and HSQC data (Table S6) led to the identification of six methyls at δH 1.02 (s, H3-12), 1.13 (s, H3-11), 1.40 (d, J = 6.3 Hz, H3-15), 1.77 (s, H3-7′), 1.82 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, H3-6′), and 2.31 (s, H3-13), three oxymethines at δH 4.70 (q, H-14), 5.14 (s, H-9), and 6.12 (s, H-1), and five olefinic methines at δH 5.81 (d, J = 15.7 Hz, H-2′), 6.07 (q, H-5′), 7.35 (d, J = 15.7 Hz, H-3′), 7.56 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, H-4), and 7.69 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, H-5). The 13C and HMBC NMR data (Table S6) revealed the presence of 22 carbon resonances, including two carbonyl carbons (δC 187.5, C-7; 168.6, C-1′); ten sp2-hybridized carbons, comprising five nonprotonated carbons (δC 153.0, C-2; 152.4, C-3; 151.7, C-6; 146.1, C-8; 135.3, C-4′) and five methines (δC 152.6, C-3′; 139.2, C-5′; 138.6, C-5; 131.8, C-4; 115.1, C-1′); one quaternary carbon (δC 45.5, C-10); three methines (δC 84.2, C-9; 83.5, C-1; 67.8, C-14); and six methyl carbons (δC 26.1, C-15; 22.3, C-13; 20.7, C-12; 20.5, C-11; 14.8, C-6′; 11.9 C-7′). The carbonyl and sp2-hybridized carbons accounted for seven degrees of unsaturation, suggesting two rings in the scaffold of heimionone A (1). By analyzing the 1H-1H COSY data, the first spin system was given due to correlations between H3-13, H-5, H-4, H-14, and H3-15. Correlations between H3-11/H3-12, H2-9, and H-1 led to the identification of the second spin system. HMBC correlations from H3-13 to C-4/C-5/C-6/C-7/C-8 and H-4 to C-2/C-3/C-5/C-6/C-7/C-8 revealed a cyclohepta-3,5,8-triene-7-one ring. The 14-hydroxyethyl moiety was deduced from the HMBC correlations of H3-15 to C-3/C-14. Further HMBC correlations from H3-11 and H3-12 to C-1/C-9/C-10, from H-9 to C-2/C-8/C-10/C-11, and from H-1 to C-2/C-8/C-9/C-10/C-11 led to the identification of a dimethylcyclopentane substructure that was fused to the cyclohepta-3,5,8-triene-7-one ring across C-2 and C-8. HMBC correlations from H3-6′ to C-3′/C-4′/C-5′/C-7′ and from H-3′ to C-1′/C-2′/C-4′/C-5′/C-7′ revealed the presence of a 4′-methylhexa-2′,4′-dienoic acid partial structure that was fused to C-1 according to an HMBC correlation from H-1 to C-1′. The E ∆2′,3′ configuration was assigned according to the large coupling constants (J = 15.7 Hz) between the olefinic methines H-2′ and H-3′, while the ∆4′,5′ configuration was assigned as E due to the ROESY correlation between H-3′ and H-5′. Furthermore, this structural elucidation was supported by the comparison of the 1H and 13C data to the ones of daldinin F (Figure S17 and Table S11), which was reported to carry the same side chain as heiminone A []. The relative configuration of the bicyclic core was obtained by the evaluation of ROE data. Due to the key correlation between H-1 and H3-12, these protons were arbitrarily assigned to the α face of the molecule. A correlation between H-9β/H-11 indicated an β orientation of these protons. Finally, the absolute configuration was determined by Mosher’s method. The derivatization of heimionone A (1) to its corresponding R- and S-MTPA esters at position C-9 and C-14 was done with S- and R-MTPA chloride. The pattern of ∆δS,R chemical shifts (see Figure 3) with positive values of H-4, H-5, H3-11, and H3-12, and negative ones of H3-13 and H3-15 determined the 1S,9R,14S absolute configuration.
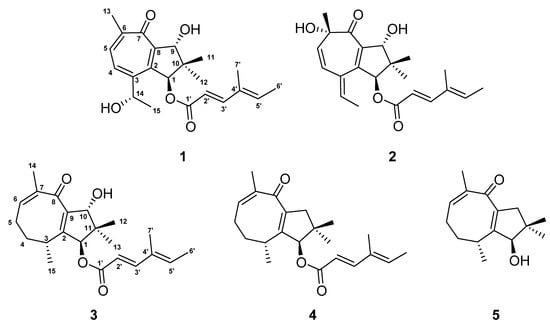
Figure 1.
Chemical structures of heimionone A–E (1–5) isolated from liquid cultures of Heimiomyces sp.
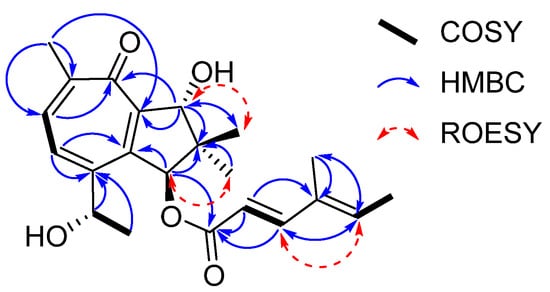
Figure 2.
Key COSY, HMBC, and ROESY correlations of heimionone A (1).
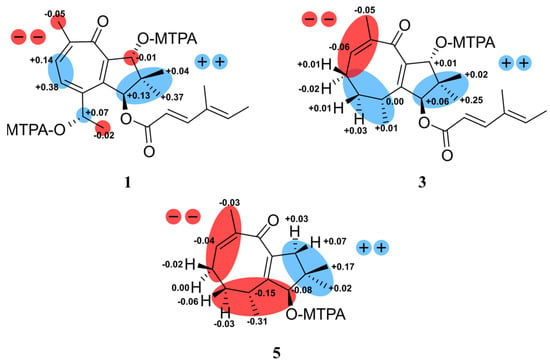
Figure 3.
The ΔδSR values of (S)/(R) MTPA esters obtained from heimionone A (1) diagnostic for 1S,9R,14S; heimionone C (3) diagnostic for 1S,3R,10R and heimionone E (5) diagnostic for 1R,3R.
Heimionone B (2), which is closely related to 1, was obtained as a yellow oil from the supernatant extracts of liquid cultures. Its HRESIMS data indicated the same molecular formula (C22H28O5) as obtained for 1. 1H and 13C data showed high similarities to 1. They differ by the relocation of the hydroxy function from C-14 for 1 to C-6 (δC 78.7) for 2, whereas the oxymethine at C-14 was replaced by an olefinic methine (δH 6.16, δC 141.6). The cyclohepta-4,8-diene-7-one scaffold was confirmed by HMBC correlations of H3-13 to C-5/C-6/C-7 and H-4 to C-2/C-3/C-6. Relative configuration was assigned according to the ROE correlations. In particular, interactions between H-9β and H3-11 and between H-1α and H3-12 implied the same configuration as 1. Additionally, correlations among H-9α/H3-11/H3-13 defined the 6R configuration. The absolute configuration of 2 was confirmed by comparison to heimionone A (1) as 1S,9R,6R.
The yellow oil heimionone C (3) was isolated from the mycelial extracts of liquid cultures with a molecular formula of C22H30O4, implying eight degrees of unsaturation. Analysis of the 1H and 13C spectra showed similarities to those of 1 and 2. HMBC and COSY interactions confirmed the presence of the previously described dimethylcyclopentane substructure carrying a 4′-methylhexa-2′,4′-dienoc acid partial structure that was fused to C-1. A spin system was given based on 1H-1H COSY correlations among H3-14, H-6, H2-5, H2-4, H-3, and H3-15. Furthermore, HMBC correlations from H3-14 to C-6/C-7/C-8, H2-4 to C-3/C-5, and H3-15 to C-2/C-3/C-4 led to the identification of the 3,7-dimethylcycloocta-6,9-dien-8-one ring that was fused to the dimethylcyclopentane ring across C-2 and C-9 according to correlations from H-1/H-3/H3-15 to C-2 and from H-1/H-10/H3-12 to C-9. The relative configuration was deduced by an analysis of ROE data. Due to the key correlations among H-1α/H-4α/H-5α/H3-13/H3-15, these protons were arbitrarily assigned to the α face of the molecule. Correlations between H-3β/H-4β/H-5β and between H-10β/H3-12 indicated a β orientation of these protons. Finally, the absolute configuration was determined after heimionone C (3) was derivatized to its corresponding S- and R-MTPA esters at position C-10 in the course of Mosher’s method. The ∆δSR chemical shift pattern (see Figure 3) indicated R-configuration of C-10 and thus a 1S,3R,10R absolute configuration.
Heimionone D (4) was obtained as a yellow oil from the mycelial extracts of liquid cultures with a molecular formula of C22H30O3. The 1D and 2D NMR data of 4 suggested a high similarity to 3. They only differ in the absence of a hydroxy function, which was replaced by a methylene (δH 2.30 H-10α; 2.77, H-10β). This was confirmed by the HMBC correlations from H-1, H3-12, and H3-13 to C-10 (δC 47.8). The ROESY correlations among H-1α/H-4α/H-5α/H-10α/H3-13/H3-15 implied 4 has the same configuration as heimionone C (3).
Heimionone E (5) was isolated as a yellow oil from the mycelial extracts of liquid cultures. Its NMR spectroscopic data were highly similar to the ones of heimionone D (4). They only differ in the absence of the 4′-methylhexa-2′,4′-dienoc acid moiety that was replaced by the hydroxy function at position C-1. Finally, the absolute configuration was determined as 1R,3SR after heimionone E (5) was derivatized to its corresponding S- and R-MTPA esters at position C-1 using Mosher’s method with both R- and S-MTPA chloride.
Compounds 3–5 can be assigned to the asteriscanes according to their characteristic four methyl groups on the five-eight-membered ring system [].
Although the bicyclo [5.3.0] decane scaffold of 1 and 2 is part of daucane-, isodaucane, aromadendrane, lactarane-, africane, gualane-, nor-guaiane and pseudoguaiane-type sesquiterpenoids, the methyl pattern of 1 and 2 with its germinal demethylation of C-10 is different from those []. Thus, the carbon backbone of 1 and 2 can be regarded as a new scaffold. Nevertheless, nardoguaianone E-I with similar structures were previously described after isolation from Nardostachys chinensis []. Interestingly, asteriscane-type sesquiterpenoids have been isolated from the soft coral Sinularia capillosa [].
Furthermore, hispidin (6) [] and hypholomin B (7) [], both of which have been described to show antioxidant effects [,], were isolated from the submerged cultures of Heimiomyces sp., together with heimiomycins A (11) and B (12), which were previously published from fermentations of the same fungal strain under different conditions [].
Interestingly, the secondary metabolite profile of Heimiomyces sp. mainly changed after the cultivation conditions were switched from solid to liquid media. While our previous experiments led to the isolation and identification of bis-heimiomycins A–D (14–17) and heimiomycins D–E (18–19) [] from cultures on a solid rice medium, other compounds such as heimiocalamenes C–E (8–10), heimiomycins A–C (11–13) and heimiocalamenes A–B (20–21) [,], as well as the herein described heimionones A–E (1–5), were isolated after cultivation of Heimiomyces sp. in liquid YM6.3 and an MOF medium, respectively. Up to this point, this strain has already shown impressive chemical diversity. Since several other, yet unidentified, minor peaks were observed in the UV/Vis- and MS-spectra of its extracts, there is a potential even to find more exciting and new secondary metabolites if their production in more significant amounts can be triggered, for example by another change in the cultivation conditions.
2.2. Biological Assays
To evaluate the antimicrobial activity of compounds 1–5 a serial-dilution assay against several Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria as well as fungal strains was carried out, though no outstanding activities were observed (Table S4). Furthermore, all compounds were tested for their cytotoxicity against the human cervical cancer cell line KB3.1 and the mouse fibroblast cell line L929 where heimionone A (1) and heimionone C (3) showed weak cytotoxic effects (Table S5).
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
Optical rotations were measured using the 241 polarimeter (PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA, USA). Measurements of the UV spectra were carried out using the UV-Vis spectrophotometer UV-2450 (Shimadzu, Kyōto, Japan) and measurements of the ECD spectra were carried out using a J-815 spectropolarimeter (Jasco, Pfungstadt, Germany). NMR spectra were obtained using the Avance III 500 MHz spectrometer equipped with a BBFO (plus) SmartProbe (1H 500 MHz, 13C 125 MHz) and the Avance III 700 MHz spectrometer equipped with a 5 mm TCI cryoprobe (1H 700 MHz, 13C 175 MH) (both Bruker, Billerica, MA, USA). NMR data were referenced to selected chemical shifts of acetonitrile-d3 (1H: 1.94 ppm, 13C: 1.4 ppm), methanol-d4 (1H: 3.31 ppm, 13C: 49.2 ppm), and pyridine-d5 (1H: 7.22 ppm), respectively. HRESIMS mass spectra were recorded with a 1200 series HPLC-UV system (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA) in combination with an ESI-TOF-MS (Maxis, Bruker). Performance of the measurements was conducted with a 2.1 × 50 mm, 1.7 µm, C18 Acquity UPLC BEH (Waters, Milford, MA, USA) column, using MilliQ H2O + 0.1% formic acid as solvent A and MeCN + 0.1% formic acid as solvent B (gradient: 5% B for 0.5 min increasing to 100% B in 19.5 min and maintaining 100% B for 5 min, flow rate: 0.6 mL/min, UV detection: 200–600 nm).
3.2. Fungal Material
Heimiomyces sp. (MUCL 56078) was collected by C. Decock and J. C. Matasyoh from Mount Elgon National Reserve in Kenya (1°7′6″ N, 34°31′30″ E). The genus was identified, and a dried specimen was deposited, as previously described by Cheng et al. [].
3.3. Seed Culture and Fermentation of Heimiomyces sp.
The maintenance of Heimiomyces sp. cultures was carried out on YM6.3 agar plates. A 500 mL Erlenmeyer shape culture flask containing 200 mL of YM6.3 medium (10 g/L malt extract, 4 g/L d-glucose, 4 g/L yeast extract, pH 6.3) was used for inoculation with three 50 mm2 sized pieces of well-grown mycelium from YM6.3 agar plates. The seed culture was incubated at 23 °C and 140 min−1 on a rotary shaker for 23 days. For the following homogenization an Ultra-Turrax® (T25 easy clean digital, IKA, Staufen im Breisgau, Germany), equipped with an S 25 N–25 F dispersing tool was used at 8000 rpm for 10–20 s. The homogenized culture broth was utilized as inoculum by transferring 3 mL per flask into 15 500 mL Erlenmeyer shape culture flasks containing 200 mL of YM6.3 medium and subsequently, the incubation was performed at 23 °C and 140 min−1 on a rotary shaker. Consumption of the glucose was monitored using test strips (Medi-Test Glucose, Macherey-Nagel, Düren, Germany) leading to a termination of the fermentation process two days after the culture broth tested negative for glucose.
3.4. Harvest and Extraction
Separation of the mycelium and supernatant was carried out by centrifugation at 5100 min−1 for 15 min (lab centrifuge 4-16KS, Sigma Laborzentrifugen GmbH, Osterode am Harz, Germany). Extraction of the mycelium was performed with acetone in an ultrasonic bath for 30 min, twice. The liquid phase was evaporated at 40 °C after separation from the solid phase by filtration, leading to a remaining aqueous phase that was subsequently diluted with water and extracted against ethyl acetate. Afterward, the organic phase was evaporated to dryness (40 °C) and led to 607 mg of extract from the mycelium. Extraction of the supernatant was carried out with ethyl acetate (1:1) in a separatory funnel, twice. Evaporation of the organic phase at 40 °C led to 251 mg extract from the supernatant of YM6.3 cultures. Both extracts were filtered using the SPME StrataTM-X 33 µm Polymeric RP cartridge (Phenomenex, Aschaffenburg, Germany).
3.5. Analytical HPLC
The extracts obtained from liquid cultures of Heimiomyces sp. were dissolved in acetone to yield a concentration of 10 mg/mL. Analysis of the samples was performed with an analytical HPLC device (Dionex UltiMate 3000 series, Sunnyvale, CA, USA) coupled to an ion trap mass spectrometer (amazon speed™ by Bruker). As mobile phase HPLC grade water and MeCN, both containing 0.1% of formic acid, were used. After injection of 2 μL of the samples, the separation was carried out over an ACQUITY-UPLC® BEH C18 column (50 × 2.1 mm; particle size: 1.7 μm) (Waters) with a flow rate of 600 μL/min. The gradient started at 5% of MeCN, then increased to 100% MeCN in 20 min and remained for 5 min at 100%. To evaluate the obtained chromatograms, the appropriate analysis software (Data Analysis, version 4.4 by Bruker) was used.
3.6. Isolation of Compounds 1–5 via Reversed-Phase Liquid Chromatography
After evaluation of the analytical data, the extracts were separated via RP HPLC using a Gilson PLC 2250 Purification System (Limburg, Germany). The extract obtained from the supernatant of the culture broth was purified using the SynergiTM Polar RP 250 × 50 mm, 80 Å, 10 µm (Phenomenex); solvent A: MilliQ water + 0.1% formic acid, solvent B: acetonitrile + 0.1% formic acid, flow rate: 50 mL/min, gradient: 5 min B at 20%, increasing to 100% B in 80 min, maintaining 100% B for 10 min. This yielded compound 5 (3.83 mg, tR = 44.0–44.75 min), compound 2 (2.46 mg, tR = 47.5–48.5 min), compound 1 (3.5 mg, tR = 49.5–50.5 min) and compound 3 (1.26 mg, tR = 65.0–66.0 min). The extract obtained from the mycelium of the culture broth was purified using the same equipment and conditions. This yielded compound 1 (1.77 mg, tR = 49.5–50.5 min), compound 3 (1.87 mg, tR = 58.5–59.5 min), and compound 4 (2.31 mg, tR = 68.0–68.5 min).
3.7. Spectral Data of Compounds 1–5
Heimionone A (1): yellow oil; [α]25D +250 (c 0.50, MeOH); UV/vis (0.01 mg/mL, MeOH) λmax(logε): 325 (3.99), 268 (4.48), 247 (4.48), 202 (3.82) nm; ECD (0.2 mg/mL, MeOH) λ(Δε): 265 (+19.8), 243 (−18.0), 220 (−1.2), 202 (−7.6) nm, Figure S1; 1H and 13C NMR data (MeOH-d4), Table 1 and Table S6; ESIMS m/z 373.19 [M + H]+, 371.24 [M − H]−; HRESIMS m/z 373.2012 [M + H]+ (calcd. for C22H29O5, 373.2023); tR = 9.2 min (analytical HPLC).

Table 1.
1H and 13C spectroscopic data of compounds 1, 2, and 5 in methanol-d4 and 3–4 in acetonitrile-d3 (δ in ppm).
Heimionone B (2): yellow oil; [α]25D +230 (c 0.10, MeOH); UV/vis (0.01 mg/mL, MeOH) λmax(logε): 329 (3.70), 267 (4.23), 248 (4.22), 198 (4.73) nm; ECD (0.2 mg/mL, MeOH) λ(Δε): 266 (+10.2), 241 (−7.7), 222 (+0.1) nm, Figure S1; 1H and 13C NMR data (MeOH-d4), Table 1 and Table S7); ESIMS m/z 373.21 [M + H]+, 371.04 [M − H]−; HRESIMS m/z 373.2011 [M + H]+ (calcd. for C22H29O5, 373.2010); tR = 9.3 min (analytical HPLC).
Heimionone C (3): yellow oil; [α]25D +156 (c 0.50, MeOH); UV/vis (0.01 mg/mL, MeOH) λmax(logε): 376 (3.18), 269 (4.35), 198 (4.41) nm; ECD (0.2 mg/mL, MeOH) λ(Δε): 270 (+8.9), 241 (−0.6), 219 (+0.2), 205 (−10.8) nm, Figure S2; 1H and 13C NMR data (acetonitrile-d3), Table 1 and Table S8; ESIMS m/z 341.25 [M − H2O + H]+, 375.28 [M – H + H2O]−; HRESIMS m/z 381.2034 [M + Na]+ (calcd. for C22H30NaO4, 381.2036); tR = 11.9 min (analytical HPLC).
Heimionone D (4): yellow oil; [α]25D +72 (c 1.00, MeOH); UV/vis (0.01 mg/mL, MeOH) λmax(logε): 268 (3.68), 198 (4.50) nm; ECD (0.4 mg/mL, MeOH) λ(Δε): 270 (+1.9), 247 (−0.7), 218 (+0.6), 200 (−3.7) nm, Figure S2; 1H and 13C NMR data (acetonitrile-d3) Table 1 and Table S9; ESIMS m/z 365.20 [M + Na]+; HRESIMS m/z 365.2086 [M + Na]+ (calcd. for C22H30NaO3, 365.2087); tR = 14.1 min (analytical HPLC).
Heimionone E (5): yellow oil; [α]25D +20 (c 0.25, MeOH); UV/vis (0.05 mg/mL, MeOH) λmax(logε): 266 (3.83), 202 (3.82) nm; ECD (1.0 mg/mL, MeOH) λ(Δε): 404 (+0.2), 361 (−1.0), 319 (+0.2), 255 (−2.0), 225 (+1.0), 204 (−6.8) nm, Figure S2; 1H and 13C NMR data (methanol-d4, Table 1 and Table S10; ESIMS m/z 235.07 [M + H]+, 251.06 [M – H + H2O]−; HRESIMS m/z 235.1694 [M + H]+ (calcd. for C15H23O2, 235.1693); tR = 8.1 min (analytical HPLC).
3.8. Preparation of the (R)- and (S)-MTPA Ester Derivatives of 1, 3, and 5
The 0.5 mg of each compound were dissolved in 300 µL deuterated pyridine. Afterward, 2 µL of (R)-(−)-α-methoxy-α-(trifluoromethyl)phenylacetyl chloride were added into the solution and left for 15 min at room temperature. The reaction was monitored by analytical HPLC/MS. Another 2 µL of R-MTPA were added if the compounds were not completely converted into the corresponding Mosher-ester. Immediately after Mosher esterification, the samples were transferred into 3.0 mm NMR tubes. This was followed by measurements of 1H NMR (Tables S1–S3), 1H,1H-COSY NMR, 1H,13C-HSQC NMR, and 1H,13C-HMBC NMR spectra. The same procedure was repeated with another 0.5 mg of each compound using (S)-(+)- α-methoxy- α-(trifluoromethyl)phenylacetyl chloride. Evaluation of the obtained ΔδSR values was conducted as described by Hoye et al. [].
3.9. Antimicrobial Assay
Antimicrobial activities of all isolated compounds were assessed by performing a serial-dilution assay resulting in the determination of their minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) against several yeast, fungal, and bacterial strains (Table S4). The assay was carried out in 96-well microtiter plates, as previously described by Harms et al. [].
3.10. Cytotoxicity Assay
The in vitro cytotoxicity of compounds 1–5 against the mouse fibroblast cell line L929 and the cervix carcinoma cell line KB3.1 (Table S5) was assessed in 96-well plates, as previously published by Harms et al. [].
4. Conclusions
Five new terpenoids, namely heimionones A-E (1–5), with uncommon bicyclo [5.3.0] decane and [6.3.0] undecane core structures, respectively, were isolated from submerged cultures of Heimiomyces sp. (MUCL 56078). In association with the previously described hispidin (6), hypholomin B (7), heimiocalamenes C–E (8–10), and heimiomycins A–C (11–13), as well as bis-heimiomycins A–D (14–17), heimiomycins D–E (18–19), and heimiocalamenes A–B (20–21), it becomes clear that Heimiomyces sp. is capable of producing a chemically very diverse spectrum of secondary metabolites. On top of that, a high number of as yet unidentified minor peaks were observed in the UV/Vis- and MS-spectra of the extracts obtained from Heimiomyces sp., therefore especially this strain should be considered for further analysis of its secondary metabolism, particularly for cultivation in more different media. Since all isolated compounds did not show outstanding activities in the antimicrobial and cytotoxicity assays, they can be considered for other assays with different targets. However, our findings once again show the importance of examining unexplored species from the tropics for their secondary metabolism during the search for novel natural products.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/molecules28093723/s1, Figure S1. ECD spectra of 1 and 2; Figure S2. ECD spectra of 3–5; Figure S3. 1H NMR spectrum (700 MHz, pyridine-d5) of the S-MTPA ester of heimionone A (1); Figure S4. COSY NMR spectrum (700 MHz, pyridine-d5) of the S-MTPA ester of heimionone A (1); Figure S5. 1H NMR spectrum (700 MHz, pyridine-d5) of the R-MTPA ester of heimionone A (1); Figure S6. COSY NMR spectrum (700 MHz, pyridine-d5) of the R-MTPA ester of heimionone A (1); Figure S7. 1H NMR spectrum (700 MHz, pyridine-d5) of the S-MTPA ester of heimionone C (3); Figure S8. COSY NMR spectrum (700 MHz, pyridine-d5) of the S-MTPA ester of heimionone C (3); Figure S9. 1H NMR spectrum (700 MHz, pyridine-d5) of the R-MTPA ester of heimionone C (3); Figure S10. COSY NMR spectrum (700 MHz, pyridine-d5) of the R-MTPA ester of heimionone C (3); Figure S11. 1H NMR spectrum (700 MHz, pyridine-d5) of the S-MTPA ester of heimionone E (5); Figure S12. 1H NMR spectrum (700 MHz, pyridine-d5) of the R-MTPA ester of heimionone E (5); Figure S13. COSY NMR spectrum (700 MHz, pyridine-d5) of the R-MTPA ester of heimionone E (5); Figure S14. Previously described compounds that were observed in submerged cultures of Heimiomyces sp. 6: hispidin, 7: hypholomin B.; Figure S15. Compounds previously isolated from Heimiomyces sp.: 8–10: heimiocalamenes C–E (including originally proposed and revised structure of 10), 11–13: heimiomycins A–C; Figure S16. Compounds previously isolated from Heimiomyces sp. 14–17: bis-heimiomycins A–D, 18–19: heimiomycins D–E, 20–21: heimiocalamenes A–B; Figure S17. Chemical structures of heimionone A (1) and daldinin F []; Figures S18–S47: NMR spectra. Table S1. 1H NMR data (700 MHz, Pyridine-d5, δ in ppm) of (S)/(R) MTPA esters obtained from heimionone A (1); Table S2. 1H NMR data (700 MHz, Pyridine-d5, δ in ppm) of (S)/(R) MTPA esters obtained from heimionone C (3); Table S3. 1H NMR data (700 MHz, Pyridine-d5, δ in ppm) of (S)/(R) MTPA esters obtained from heimionone E (5); Table S4. Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC in µg/mL) for bacterial and fungal strains; Table S5. Half inhibitory concentration (IC50 in µM); Table S6. NMR spectroscopic data (13C (δC), 175 MHz and 1H (δH), 500 MHz, methanol-d4) for heimionone A (1); Table S7. NMR spectroscopic data (13C (δC), 175 MHz and 1H (δH), 700 MHz, methanol-d4) for heimionone B (2); Table S8. NMR spectroscopic data (13C (δC), 125 MHz and 1H (δH), 500 MHz, acetonitrile-d3) for heimionone C (3); Table S9. NMR spectroscopic data (13C (δC), 175 MHz and 1H (δH), 700 MHz, acetonitrile-d3) for heimionone D (4); Table S10. NMR spectroscopic data (13C (δC), 175 MHz and 1H (δH), 700 MHz, methanol-d4) for heimionone E (5); Table S11. Comparison of the NMR spectroscopic data for the 4-methylhexa-2,4-dienoic acid partial structure of heimionone A (1) (13C (δC), 175 MHz and 1H (δH), 500 MHz, methanol-d4) and daldinin F (13C (δC), 150 MHz and 1H (δH), 600 MHz, chloroform-d1) [].
Author Contributions
Formal analysis, F.S.; investigation, S.P. and A.K.; resources, J.C.M. and C.D.; writing—original draft preparation, S.P.; writing—review and editing, F.S. and M.S.; project administration, M.S.; funding acquisition, M.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
S.P. is grateful for a grant from the Life Science-Stiftung zur Förderung von Wissenschaft und Forschung (LSS). Furthermore, this research benefitted from the financial support of the “ASAFEM” Project (Grant No. IC-070) under the ERAfrica Programme of the European Commission; beneficiaries J.C.M, C.D., and M.S. Finally, the authors want to acknowledge the European Union’s H2020 Research and Innovation Staff Exchange program (H2020-MSCA-RISE), Grant No. 101008129: MYCOBIOMICS.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data are available in the Supporting Information of the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank W. Collisi and C. Kakoschke for performing the bioassays and NMR spectroscopic measurements, respectively. T. Cheng and C. Chepkirui are thanked for providing supporting data and biological material from their previous experiments. At last, S. Pfütze wants to thank E. Charria, J-P. Wennrich, K. Becker, S. Reinecke, E. Surges, and C. Lambert for their expert advisory assistance.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Sample Availability
Samples of the isolated compounds are not available from the authors, due to consumption for structure elucidation and bioassays.
References
- Kirk, P.M.; Cannon, P.F.; David, J.C.; Stalpers, J.A. Ainsworth and Bisby’s Dictionary of the Fungi; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Sandargo, B.; Chepkirui, C.; Cheng, T.; Chaverra-Muñoz, L.; Thongbai, B.; Stadler, M.; Hüttel, S. Biological and chemical diversity go hand in hand: Basidiomycota as source of new pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals. Biotechnol. Adv. 2019, 37, 107344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dörfer, M.; Gressler, M.; Hoffmeister, D. Diversity and bioactivity of Armillaria sesquiterpene aryl ester natural products. Mycol. Prog. 2019, 18, 1027–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.; Chepkirui, C.; Decock, C.; Matasyoh, J.C.; Stadler, M. Heimiomycins A–C and calamenens from the African basidiomycete Heimiomyces sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 2501–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfütze, S.; Khamsim, A.; Surup, F.; Decock, C.; Matasyoh, J.C.; Stadler, M. Calamene-type sesqui-, mero-, and bis-sesquiterpenoids from cultures of Heimiomyces sp., a basidiomycete collected in Africa. J. Nat. Prod. 2023, 86, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, R.L.; Lewis, D.G.; Wilson, D.V. 983. Constituents of the Higher Fungi. Part I. Hispidin, a new 4-hydroxy-6-styryl-2-pyrone from Polyporus hispidus (Bull.) Fr. J. Chem. Soc. 1961, 4995–5002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiasson, J.-L.; Gluchoff-Fiasson, K.; Steglich, W. Über die Farb- und Fluoreszenzstoffe des Grünblättrigen Schwefelkopfes (Hypholoma fasciculare, Agaricales). Chem. Ber. 1977, 110, 1047–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quang, D.N.; Hashimoto, T.; Tanaka, M.; Stadler, M.; Asakawa, Y. Cyclic azaphilones daldinins E and F from the ascomycete fungus Hypoxylon fuscum (Xylariaceae). Phytochemistry 2004, 65, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, G.-F.; Liang, H.-B.; Liu, W.-X.; Zhu, F.; Li, P.-L.; Li, G.-Q.; Yao, J.-C. Bicyclo [6.3.0] undecane sesquiterpenoids: Structures, biological activities, and syntheses. Molecules 2019, 24, 3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foley, D.A.; Maguire, A.R. Synthetic approaches to bicyclo [5.3.0]decane sesquiterpenes. Tetrahedron 2010, 66, 1131–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaya, Y.; Akasaka, M.; Takeuji, Y.; Tanitsu, M.; Niwa, M.; Oshima, Y. Novel guaianoids, nardoguaianone E–I, from Nardostachys chinensis Roots. Tetrahedron 2000, 56, 7679–7683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Chen, W.; Liu, D.; van Ofwegen, L.; Proksch, P.; Lin, W. Asteriscane-type sesquiterpenoids from the soft coral Sinularia capillosa. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 1753–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, I.-H.; Chung, S.-K.; Lee, K.-B.; Yoo, Y.-C.; Kim, S.-K.; Kim, G.-S.; Song, K.-S. An antioxidant hispidin from the mycelial cultures of Phellinus linteus. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2004, 27, 615–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.-Y.; Lee, I.-K.; Seok, S.-J.; Lee, H.-J.; Kim, Y.-H.; Yun, B.-S. Antioxidant polyphenols from the mycelial culture of the medicinal fungi Inonotus xeranticus and Phellinus linteus. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 104, 1824–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoye, T.R.; Jeffrey, C.S.; Shao, F. Mosher Ester analysis for the determination of absolute configuration of stereogenic (chiral) carbinol carbons. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 2451–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harms, K.; Surup, F.; Stadler, M.; Stchigel, A.M.; Marin-Felix, Y. Morinagadepsin, a depsipeptide from the fungus Morinagamyces vermicularis gen. et comb. nov. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).