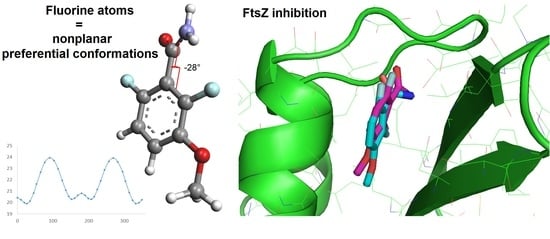
Importance of the 2,6-Difluorobenzamide Motif for FtsZ Allosteric Inhibition: Insights from Conformational Analysis, Molecular Docking and Structural Modifications
Abstract
1. Introduction
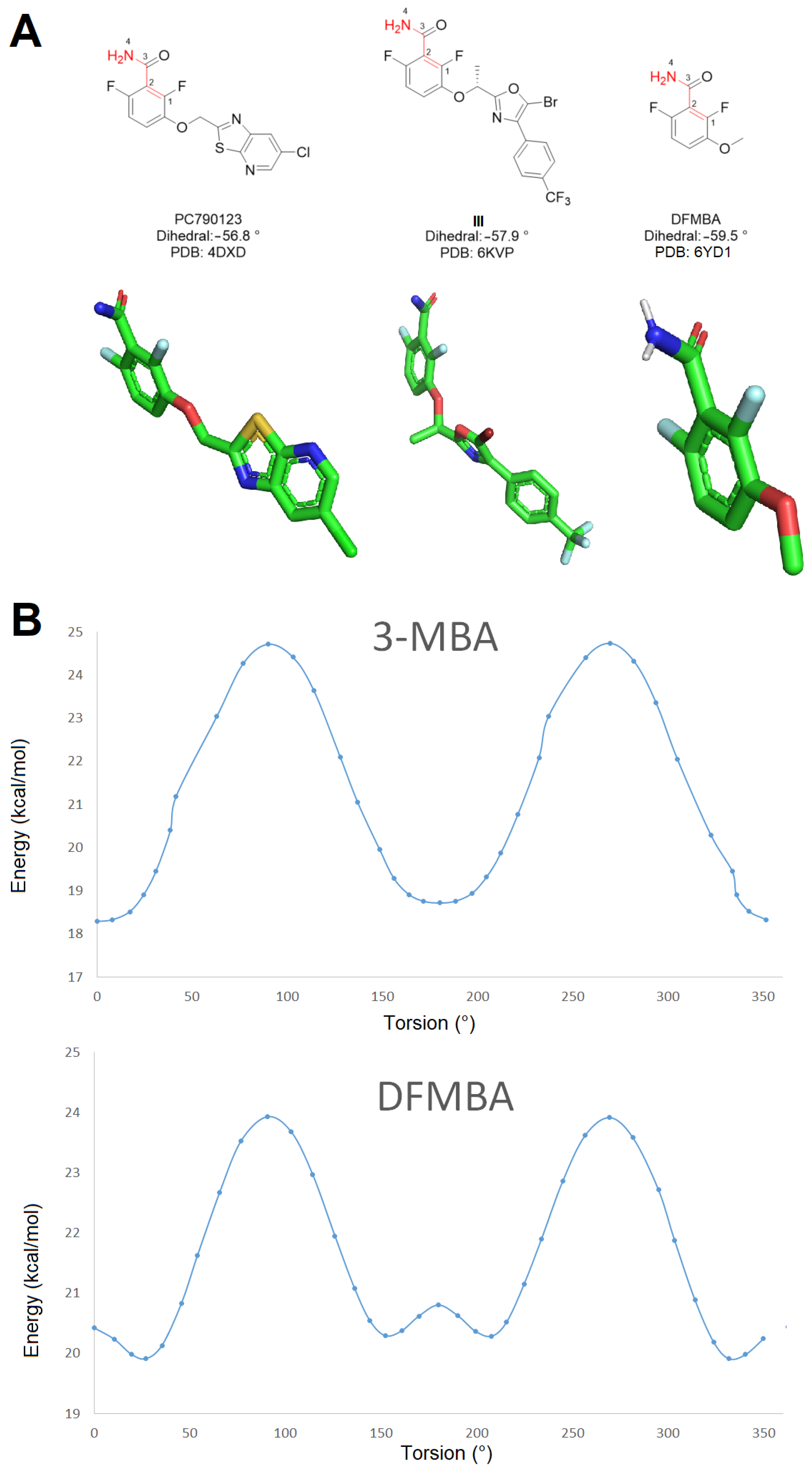
2. Results and Discussion
3. Experimental
3.1. Conformational Analysis
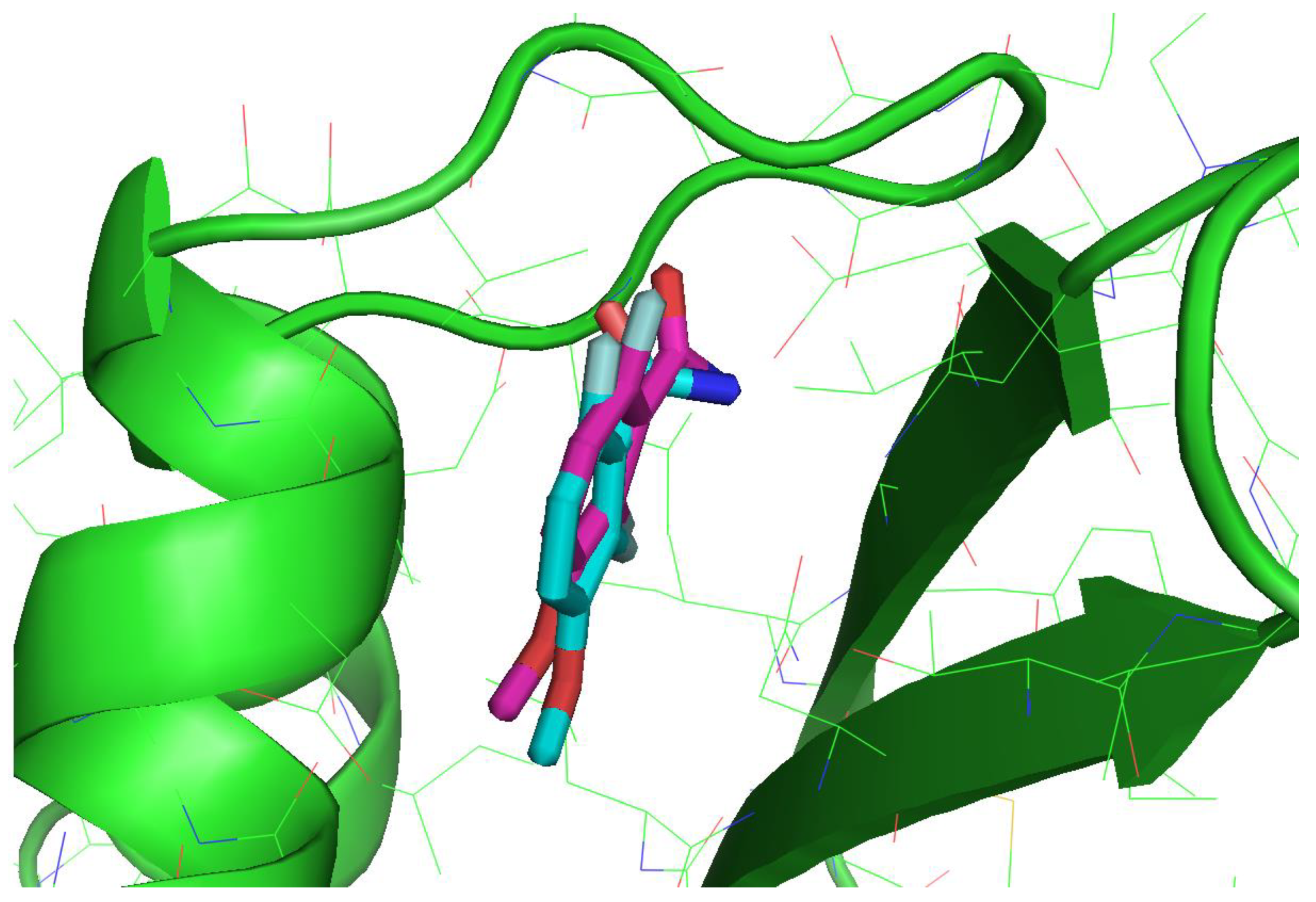
3.2. Molecular Docking
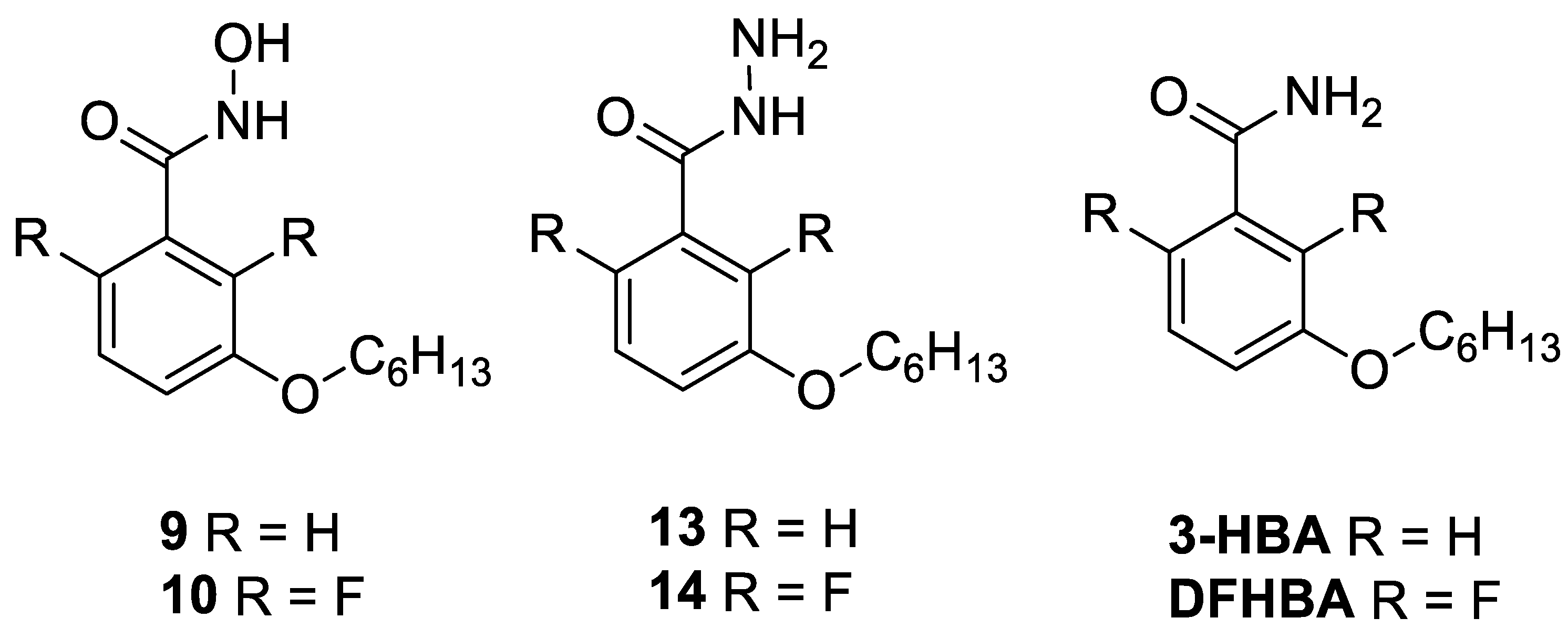
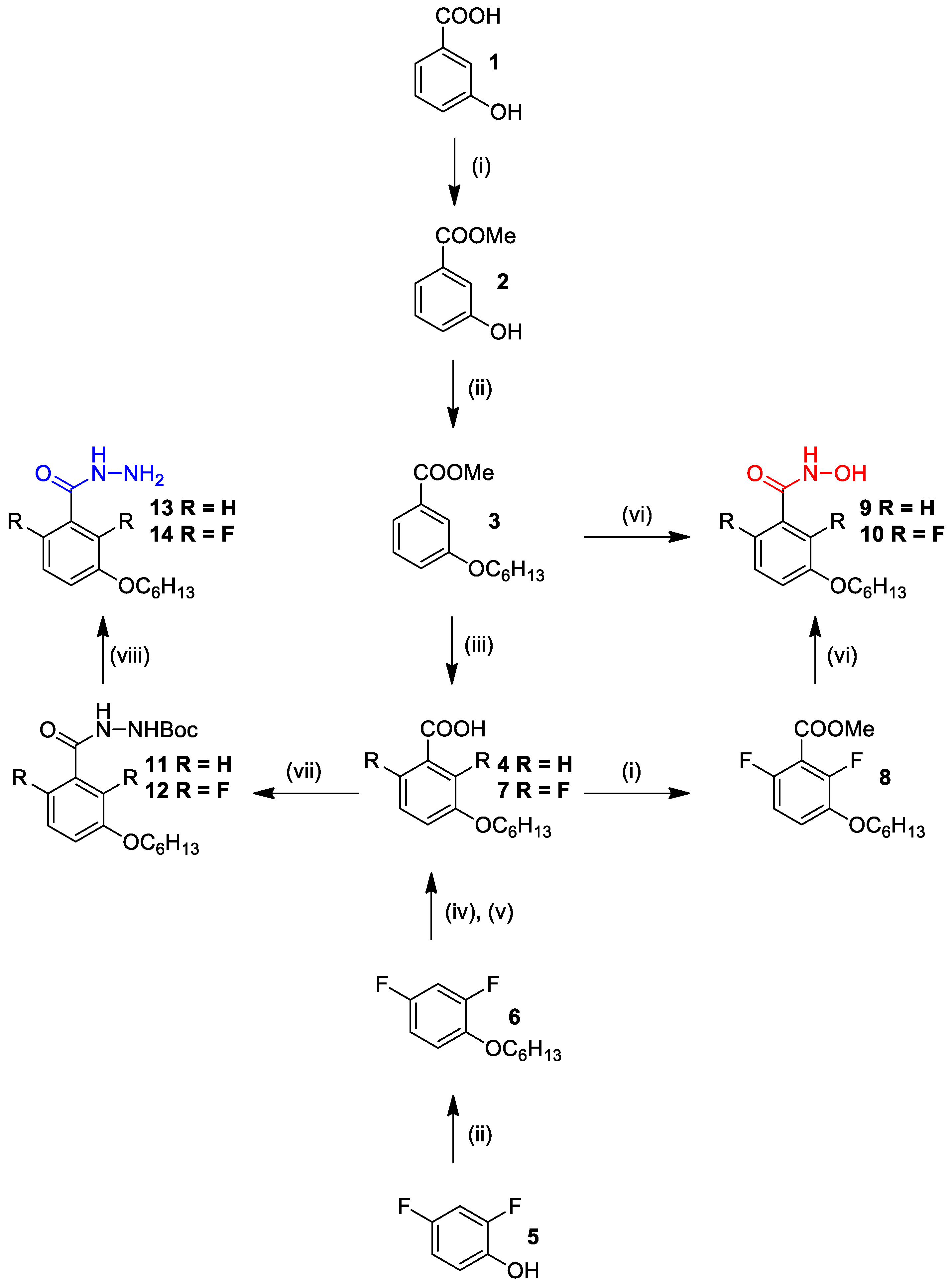
3.3. Chemistry
3.3.1. (i) General Procedure for Methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate
Methyl 3-Hydroxybenzoate (2)
Methyl 2,6-Difluoro-3-(hexyloxy)benzoate (8)
3.3.2. (ii) General Procedure for Methyl 3-(hexyloxy)benzoate
Methyl 3-(hexyloxy)benzoate (3)
2,4-Difluoro-1-(hexyloxy)benzene (6)
3.3.3. (iii) Procedure for 3-(hexyloxy)benzoic Acid
3-(Hexyloxy)benzoic Acid (4)
3.3.4. (iv), (v) Procedure for 2,6-difluoro-3-(hexyloxy)benzoic Acid
2,6-Difluoro-3-(Hexyloxy)Benzoic Acid (7)
3.3.5. (vi) General Procedure for 3-(hexyloxy)-N-hydroxybenzamide
3-(Hexyloxy)-N-hydroxybenzamide (9)
2,6-Difluoro-3-(hexyloxy)-N-hydroxybenzamide (10)
3.3.6. (vii) General Procedure for Tert-Butyl 2-(3-(hexyloxy)benzoyl)hydrazine-1-Carboxylate
Tert-Butyl 2-(3-(hexyloxy)benzoyl)hydrazine-1-Carboxylate (11)
Tert-Butyl 2-(2,6-Difluoro-3-(Hexyloxy)benzoyl)hydrazine-1-Carboxylate (12)
3.3.7. (viii) General Procedure for 3-(hexyloxy)benzohydrazide
3-(Hexyloxy)benzohydrazide (13)
2,6-Difluoro-3-(hexyloxy)benzohydrazide (14)
3.4. Biological Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kirkpatrick, C.L.; Viollier, P.H. New(s) to the (Z-)ring. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2011, 14, 691–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haeusser, D.P.; Margolin, W. Splitsville: Structural and functional insights into the dynamic bacterial Z ring. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 305–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, C.; Natale, P.; Cueto, L.; Vicente, M. The keepers of the ring: Regulators of FtsZ assembly. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2016, 40, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Ma, S. The development of FtsZ inhibitors as potential antibacterial agents. ChemMedChem 2012, 7, 1161–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Panda, D. FtsZ inhibition: A promising approach for antistaphylococcal therapy. Drug News Perspect. 2010, 23, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carro, L. Recent Progress in the Development of Small-Molecule FtsZ Inhibitors as Chemical Tools for the Development of Novel Antibiotics. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haranahalli, K.; Tong, S.; Ojima, I. Recent advances in the discovery and development of antibacterial agents targeting the cell-division protein FtsZ. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 6354–6369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, K.A.; Santos, T.M.; Nepomuceno, G.M.; Huynh, V.; Shaw, J.T.; Weibel, D.B. Targeting the Bacterial Division Protein FtsZ. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 6975–6998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, D.; Bhattacharya, D.; Gao, Q.H.; Oza, P.M.; Lin, H.Y.; Hawkins, B.; Hibbs, D.E.; Groundwater, P.W. Identification of agents targeting FtsZ assembly. Future Med. Chem. 2016, 8, 1111–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straniero, V.; Zanotto, C.; Straniero, L.; Casiraghi, A.; Duga, S.; Radaelli, A.; De Giuli Morghen, C.; Valoti, E. 2,6-Difluorobenzamide Inhibitors of Bacterial Cell Division Protein FtsZ: Design, Synthesis, and Structure-Activity Relationships. ChemMedChem 2017, 12, 1303–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huecas, S.; Araújo-Bazán, L.; Ruiz, F.M.; Ruiz-Ávila, L.B.; Martínez, R.F.; Escobar-Peña, A.; Artola, M.; Vázquez-Villa, H.; Martín-Fontecha, M.; Fernández-Tornero, C.; et al. Targeting the FtsZ Allosteric Binding Site with a Novel Fluorescence Polarization Screen, Cytological and Structural Approaches for Antibacterial Discovery. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 5730–5745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.W.; Wu, L.J.; Czaplewski, L.G.; Errington, J. Multiple effects of benzamide antibiotics on FtsZ function. Mol. Microbiol. 2011, 80, 68–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeloh, D.; Wenzel, M.; Rungrotmongkol, T.; Hamoen, L.W.; Tipmanee, V.; Voravuthikunchai, S.P. Effects of rhodomyrtone on Gram-positive bacterial tubulin homologue FtsZ. PeerJ 2017, 5, e2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czaplewski, L.G.; Collins, I.; Boyd, E.A.; Brown, D.; East, S.P.; Gardiner, M.; Fletcher, R.; Haydon, D.J.; Henstock, V.; Ingram, P.; et al. Antibacterial alkoxybenzamide inhibitors of the essential bacterial cell division protein FtsZ. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 524–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haydon, D.J.; Bennett, J.M.; Brown, D.; Collins, I.; Galbraith, G.; Lancett, P.; Macdonald, R.; Stokes, N.R.; Chauhan, P.K.; Sutariya, J.K.; et al. Creating an Antibacterial with in Vivo Efficacy: Synthesis and Characterization of Potent Inhibitors of the Bacterial Cell Division Protein FtsZ with Improved Pharmaceutical Properties. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 3927–3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.R.; Collins, I.; Czaplewski, L.G.; Haydon, D.J. WO2007107758; Antibacterial Agents; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, P.; Ma, S. Exploration of the inhibitory mechanism of PC190723 on FtsZ protein by molecular dynamics simulation. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2022, 114, 108189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haydon, D.J.; Stokes, N.R.; Ure, R.; Galbraith, G.; Bennett, J.M.; Brown, D.R.; Baker, P.J.; Barynin, V.V.; Rice, D.W.; Sedelnikova, S.E.; et al. An inhibitor of FtsZ with potent and selective anti-staphylococcal activity. Science 2008, 321, 1673–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artola, M.; Ruíz-Avila, L.B.; Ramírez-Aportela, E.; Martínez, R.F.; Araujo-Bazán, L.; Vázquez-Villa, H.; Martín-Fontecha, M.; Oliva, M.A.; Martín-Galiano, A.J.; Chacón, P.; et al. The structural assembly switch of cell division protein FtsZ probed with fluorescent allosteric inhibitors. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 1525–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhm, H.J.; Banner, D.; Bendels, S.; Kansy, M.; Kuhn, B.; Müller, K.; Obst-Sander, U.; Stahl, M. Fluorine in medicinal chemistry. Chembiochem 2004, 5, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isanbor, C.; O’Hagan, D. Fluorine in medicinal chemistry: A review of anti-cancer agents. J. Fluor. Chem. 2006, 127, 303–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillis, E.P.; Eastman, K.J.; Hill, M.D.; Donnelly, D.J.; Meanwell, N.A. Applications of Fluorine in Medicinal Chemistry. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 8315–8359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, T.; Badiou, C.; Davy, F.; Queneau, Y.; Dumitrescu, O.; Lina, G.; Soulère, L. Structural Variations in the Central Heterocyclic Scaffold of Tripartite 2,6-Difluorobenzamides: Influence on Their Antibacterial Activity against MDR Staphylococcus aureus. Molecules 2022, 27, 6619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jubb, H.C.; Higueruelo, A.P.; Ochoa-Montaño, B.; Pitt, W.R.; Ascher, D.B.; Blundell, T.L. Arpeggio: A Web Server for Calculating and Visualising Interatomic Interactions in Protein Structures. J. Mol. Biol. 2017, 429, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalvi, V.H.; Rossky, P.J. Molecular origins of fluorocarbon hydrophobicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 13603–13607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, C.M.; Therien, A.G.; Lu, J.; Lee, S.H.; Caron, A.; Gill, C.J.; Lebeau-Jacob, C.; Benton-Perdomo, L.; Monteiro, J.M.; Pereira, P.M.; et al. Restoring methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus susceptibility to beta-lactam antibiotics. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 126ra135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, T.; Yamane, J.; Mogi, N.; Yamaguchi, H.; Takemoto, H.; Yao, M.; Tanaka, I. Structural reorganization of the bacterial cell-division protein FtsZ from Staphylococcus aureus. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2012, 68, 1175–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrer-González, E.; Fujita, J.; Yoshizawa, T.; Nelson, J.M.; Pilch, A.J.; Hillman, E.; Ozawa, M.; Kuroda, N.; Al-Tameemi, H.M.; Boyd, J.M.; et al. Structure-Guided Design of a Fluorescent Probe for the Visualization of FtsZ in Clinically Important Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacterial Pathogens. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulère, L. Computer-Assisted Conformational Analysis of Small Molecules Using VEGA ZZ, a Freely Available Software Program, as an Introduction to Molecular Modeling. J. Chem. Educ. 2021, 98, 2709–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedretti, A.; Villa, L.; Vistoli, G. VEGA: A versatile program to convert, handle and visualize molecular structure on Windows-based PCs. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2002, 21, 47–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedretti, A.; Mazzolari, A.; Gervasoni, S.; Fumagalli, L.; Vistoli, G. The VEGA suite of programs: An versatile platform for cheminformatics and drug design projects. Bioinformatics 2021, 37, 1174–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.J.; Song, Y.N.; Zhan, P.; Zhang, Q.Z.; Liu, X.Y. Conformational restriction: An effective tactic in ‘follow-on’-based drug discovery. Future Med. Chem. 2014, 6, 885–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patani, G.A.; LaVoie, E.J. Bioisosterism: A rational approach in drug design. Chem. Rev. 1996, 96, 3147–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diep, B.A.; Stone, G.G.; Basuino, L.; Graber, C.J.; Miller, A.; des Etages, S.A.; Jones, A.; Palazzolo-Ballance, A.M.; Perdreau-Remington, F.; Sensabaugh, G.F.; et al. The arginine catabolic mobile element and staphylococcal chromosomal cassette mec linkage: Convergence of virulence and resistance in the USA300 clone of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 197, 1523–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, T.; Barbry, A.; Magand, J.; Badiou, C.; Davy, F.; Baudouin, A.; Queneau, Y.; Dumitrescu, O.; Lina, G.; Soulère, L. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Benzo[b]thiophene Acylhydrazones as Antimicrobial Agents against Multidrug-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, W.; Ma, X.; Xiang, G. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of 3-benzylamide derivatives as FtsZ inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 1854–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, M.A. ArgusLaB 4.0.1; Planetaria Software LLC.: Seattle, WA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Laskowski, R.A.; Swindells, M.B. LigPlot+: Multiple ligand-protein interaction diagrams for drug discovery. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2011, 51, 2778–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, D.M.; AP, R.P.; Zazeri, G.; Shamir, S.A.; Mahmoud, A.M.; Wilkinson, F.L.; Alexander, M.Y.; Cornelio, M.L.; Jones, A.M. The modulatory role of sulfated and non-sulfated small molecule heparan sulfate-glycomimetics in endothelial dysfunction: Absolute structural clarification, molecular docking and simulated dynamics, SAR analyses and ADMET studies. RSC Med. Chem. 2021, 12, 779–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavedon, C.; Madani, A.; Seeberger, P.H.; Pieber, B. Semiheterogeneous Dual Nickel/Photocatalytic (Thio)etherification Using Carbon Nitrides. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 5331–5334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Compound | MIC (µg/mL) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| ATCC29213 a | SF8300 b | ST20171643 c | |
| 9, 10, 13, 14 | ≥64 | ||
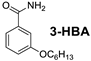 | 256 | 256 | 256 |
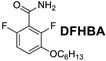 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barbier, T.; Dumitrescu, O.; Lina, G.; Queneau, Y.; Soulère, L. Importance of the 2,6-Difluorobenzamide Motif for FtsZ Allosteric Inhibition: Insights from Conformational Analysis, Molecular Docking and Structural Modifications. Molecules 2023, 28, 2055. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052055
Barbier T, Dumitrescu O, Lina G, Queneau Y, Soulère L. Importance of the 2,6-Difluorobenzamide Motif for FtsZ Allosteric Inhibition: Insights from Conformational Analysis, Molecular Docking and Structural Modifications. Molecules. 2023; 28(5):2055. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052055
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarbier, Thibaut, Oana Dumitrescu, Gérard Lina, Yves Queneau, and Laurent Soulère. 2023. "Importance of the 2,6-Difluorobenzamide Motif for FtsZ Allosteric Inhibition: Insights from Conformational Analysis, Molecular Docking and Structural Modifications" Molecules 28, no. 5: 2055. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052055
APA StyleBarbier, T., Dumitrescu, O., Lina, G., Queneau, Y., & Soulère, L. (2023). Importance of the 2,6-Difluorobenzamide Motif for FtsZ Allosteric Inhibition: Insights from Conformational Analysis, Molecular Docking and Structural Modifications. Molecules, 28(5), 2055. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052055