Abstract
This work describes the design, synthesis, and biological activities of new selenoester derivatives and its homologs thioesters. Thirty-two compounds were developed following an economical synthetic route, achieving small molecules, with structural characteristics similar to those present in antileishmanial drugs such as miltefosine (MIL) and paromomycin (PMN). These compounds were tested in vitro against strains of Leishmania major (L. major) and Leishmania infantum (L. infantum). The L. infantum strain (causative agent of visceral leishmaniasis) exhibited the highest sensitivity. Thus, four selanylacetic acid derivatives (A4, A5, A6 and A8) presented IC50 values below 40 µM in this strain. These derivatives also demonstrated low toxicity and high selectivity in PMA-differentiated THP-1 macrophages. The A4–A6 and A8 derivatives were evaluated in order to determine their pharmacological behavior, using drug combination studies with the reference drugs amphotericin B (AMB), MIL and PMN. Compounds A6 and A8 presented a potent synergistic interaction with MIL, which is the only oral drug available for the treatment of visceral leishmaniasis. Therefore, compounds A6 and A8 present significant potential as therapeutic candidates for the treatment of leishmaniasis based on their remarkable leishmanicidal characteristics and pharmacological synergism.
1. Introduction
Leishmania is a genus of protists comprising more than 17 different species that cause the disease known as leishmaniasis [1]. The disease affects impoverished populations around the World and is mainly associated with malnutrition, population displacement, poor housing conditions, environmental factors, and a general lack of resources [2,3]. The disease has remained as a highly neglected health problem and has become a serious obstacle to the socio-economic development of the affected countries [4]. Leishmania parasites have a complex life cycle as dysmorphic protozoan organisms [5]. The parasite has two forms, each one representing an adaptation to the environmental conditions that the parasite confronts in each of its two hosts: the mammal (amastigote) and its insect vector (promastigote) [6]. The clinical manifestations of leishmaniasis depend on the strain and the immune system status of the host, and include cutaneous leishmaniasis (CL), the most common form of leishmaniasis characterized by ulcerative lesions [7]; mucocutaneous leishmaniasis (MCL), which produces lesions preferentially located in the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract [8]; and visceral leishmaniasis (VL), which is the most severe form of leishmaniasis in which hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, anemia, leucopenia, and thrombocytopenia occur [9]. Currently, the drugs available for the treatment of leishmaniasis have serious limitations such as high toxicity, high cost, limited efficacy, long treatment duration, and development of drug resistance [10].
Selenium (Se) and sulfur (S) are important elements with similar chemical characteristics [11]. They have equivalent oxidation states, covalent radii, electronegativity, and the ability to form multiple bonds. Both elements play important roles in a variety of biological processes. Sulfur compounds have demonstrated cytotoxic and chemopreventive potential, in particular the S derivatives of garlic, which inhibit tumor development in multiple organs [12]. Selenium is essential as a micronutrient and acts as a cofactor for enzymes involved in antioxidant defense and thyroid hormone metabolism [13]. It also exhibits chemopreventive properties and regulates immune function. Selenium compounds are metabolized in more reduced states compared to sulfur derivatives, e.g., selenols, unlike thiols, are more nucleophilic. Comparative studies consistently show that organoselenic compounds have higher antineoplastic and/or chemopreventive activity compared to sulfur analogs [14,15,16]. Our research group has confirmed these findings, observing a significant decrease in antitumor activity when selenium is substituted by sulfur [15,17].
The relationship between Se and parasites, especially in the context of leishmaniasis, has become a captivating area of scientific research, which has been explored over the years by our research group [18,19,20]. The remarkable leishmanicidal activity of Se resides in its influence on several critical factors for the survival and replication of parasites [21]. Through its interaction with the host immune system, Se increases the production of reactive oxygen species and promotes the activation of immune cells, resulting in an enhanced anti-parasitic response [21]. This dual action of Se, targeting both the parasite and the host immune system, positions it as a potent therapeutic agent against leishmaniasis [22].
Bearing this in mind, we report the synthesis and evaluation of 32 novel derivatives containing either Se or S functional groups (Figure 1). For this purpose, different carboxylic acid (linear and cyclic) was used in order to study how structural modifications such as the presence of different bioactive cores, affects the biological activity of these compounds. This strategy can be considered a suitable approach to obtained new compounds, delay the development of resistance, and shorten treatment. The obtained derivatives were evaluated on promastigotes of Leishmania major (L. major) and Leishmania infantum (L. infantum). The most active compounds against Leishmania parasites were tested against PMA-stimulated THP-1-derived macrophages to determine their toxicity and selectivity. Drug combination studies were also carried out to determine their interaction with the reference drugs amphotericin B (AmB), miltefosine (MIL), and paramomincin (PMN).
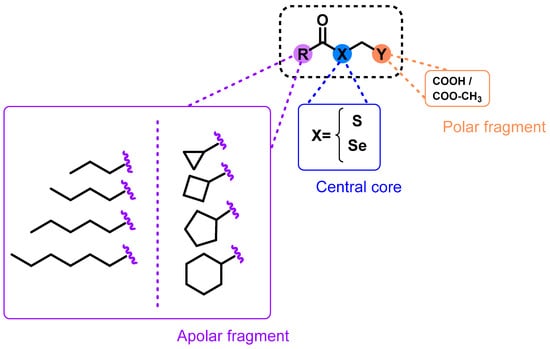
Figure 1.
Design and general structure for the proposed compounds.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Drug Design
Based on our group’s previous experience in the development of selenocompounds, we employed the chemical strategy known as fragment-based design [23] in order to develop 32 novel molecules. The central core of these molecules consisted of selenium (Se) or sulfur (S) atoms linked to a polar head containing carboxylic acid or methyl-carboxylate groups. In addition, an apolar moiety formed by carbo- or heterocyclic structures was incorporated. The introduction of polar and apolar endings in the design (Figure 1) was proposed given that most of the leishmanicidal drugs, such as miltefosine and edelfosine, present this structural feature. This innovative design strategy allowed us to investigate the biological effects resulting from the introduction of Se or S atoms, the incorporation of cyclic or linear chains, and the presence of acid or ester functional groups. In addition, the main objective of this design was to streamline synthetic processes and facilitate the development of new compounds. To the best of our knowledge, the design and biological evaluation of this type of structural modifications had not been studied.
2.2. Chemistry
Herein, we described the synthesis of 32 selenoester and thioether derivatives (Figure 1). These compounds were obtained by a simple, modular, and efficient one-step synthetic procedure. Se and S atoms were used as central cores and decorated with different linear and cyclic aliphatic substituents. The obtained compounds were grouped in four series (A1–8, B1–8, C1–8, and D1–8) (Figure 2) which contained different substituents common to all the series.
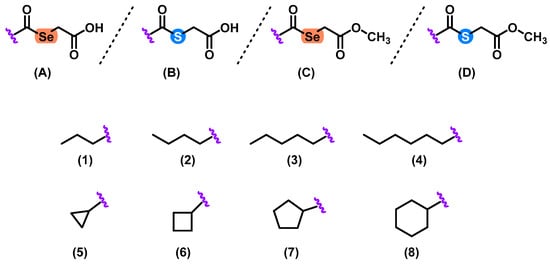
Figure 2.
General structures of the 32 Se and S derivatives. Compounds were arranged in 4 series (A–D) and eight different substituents (1–8) were used.
In order to obtain the target compounds, previously published protocol was followed (Figure 3) [24]. For the synthesis of the Se derivatives (series A and C), EtOH was used as solvent, due to the low water solubility of the acid chlorides used. The exothermic nature of the reaction required the use of an ice bath and a nitrogen (N2) atmosphere in order to avoid the degradation of the sodium hydrogen selenite (NaHSe) formed. This intermediate was not isolated, so it was directly reacted with the different chlorides and bromides (Figure 3). In the case of the S derivatives (series B and D), the synthesis was carried out without form the corresponding S-counterpart, using dichloromethane (DCM) and tetrahydrofuran (THF) as solvents due to the low solubility of the compounds and triethylamine (TEA). This reaction allowed the isolation of the final compounds by evaporation under reduced pressure of the solvent, with no further purification methods. In the case of A1–A8 and C1–C8 derivatives, purification by chromatographic column was necessary. For this reason, the yields of these derivatives are lower than the one obtained for their corresponding S-counterparts. Both Se and S derivatives were stable at room temperature. The structural properties and purity of all compounds were determined by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and spectra are available in the Supplementary Materials (Figures S1–S80).
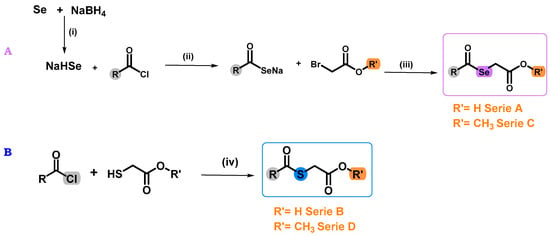
Figure 3.
Synthesis of the target Se (compounds A1–A8 and C1–C8) and S (compounds B1–B8 and D1–D8) derivatives. Reagents and conditions: (A): (i) EtOH, N2, 15 min, 0 °C. (ii) THF, room temperature (r.t.). (iii) r.t. for 2 h. (B): (iv) DCM, TEA, r.t. for 2 h.
2.3. Leishmanicidal Activity against Leishmania Promastigotes
The obtained compounds were screened against cultured promastigotes of L. major and L. infantum based on a previously established protocol [25]. This evaluation was aimed at identifying the lead compounds of this study. Leishmanicidal activity was calculated as the inhibitory concentration 50 (IC50), which represents the concentration required to inhibit 50% of promastigotes. Se derivatives (A1–A8 and C1–C8 series) showed higher leishmanicidal activity than their corresponding S counterparts (B1–B8 and C1–C8 series), except for compounds C4 and D4. The detailed results (Figure 4) indicate that the inclusion of Se correlated with a significant increase in the activity of A1–A8 and C1–C8 series, most of which showed an IC50 below 100 µM in both strains, except for compounds A5 (IC50 = 113.1 µM) in L. major and C4 (IC50 = 116.5 µM) in L. infantum. S derivatives (series B1–B8) showed a different tendency with similar activity (IC50 > 100 µM) in both L. major and L. infantum strains, except for B5 (IC50 = 87.6 µM) against L. infantum. Compounds D1–D8 (S derivatives) showed similar leishmanicidal activity against L. infantum and L. major promastigotes, compounds D4 (IC50 = 87.3 and 79.2 µM), D5 (IC50 = 81.8 and 68.7 µM) and D6 (IC50 = 83.4 and 95.3 µM) being more active towards L. major and L. infantum, respectively.
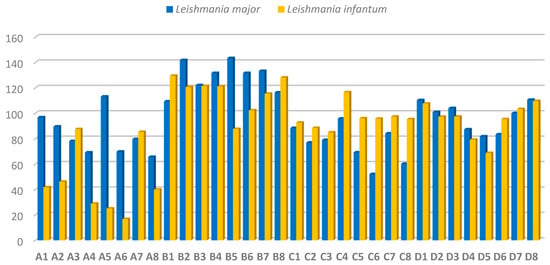
Figure 4.
Antileishmanial activity of the 32 derivatives against promastigotes of L. major and L. infantum expressed as IC50 values (mean ± SD) in µM.
L. infantum promastigotes were the most sensitive, especially against the selanylacetic acid derivatives A4–A6 and A8 (IC50 below 40 µM) and the thiomethylated derivatives D2–D6 (IC50 below 100 µM). These findings suggest that: (i) the nature of the apolar aliphatic fragment (open or cyclic chains) does not significantly influence the potency of the derivatives; (ii) there are no notable differences between the carboxylic acid and methyl ester groups in the polar fragments; (iii) the only clear SAR is that the substitution of the Se atom by S, leads to a decrease in the leishmanicidal effect of the tested derivatives. Compounds A4–A6 and A8, were the lead compounds outperforming their S counterparts being 2- to 5-fold more active towards L. infantum parasites (Figure 4). These results suggest that the presence of the Se atom, cause an enhancement of the anti-leishmanial activity of the derivatives A4–A6 and A8.
2.4. In Vitro Toxicity and Selectivity in THP-1 Macrophages
After a first screening against promastigotes of L. major and L. infantum, those derivatives presenting IC50 values below 40 µM were selected to determine their selectivity index (SI) using macrophages (Table 1). SI values represent the ratio of the CC50 values calculated in macrophages and the IC50 values of parasites. Each compound tested showed superior SI than the reference drugs.

Table 1.
Cytotoxic activity (CC50) of the lead compounds (A4, A5, A6, and A8) and standard drugs (MIL, PMN) against THP-1 cells after 48 h of treatment.
Compounds A4–A6 and A8 were tested on PMA-stimulated THP-1-derived macrophages to assess their toxicity and selectivity. According to Table 2, these lead compounds (A4–A6 and A8) showed low toxicity and high selectivity, outperforming the reference drugs MIL and PMN. These compounds (A4–A6 and A8) were 2 or even 3 times more selective than MIL and PMN against L. major, and up to 5 times more selective against L. infantum. Notably, compound A5 (cyclopropane selanylacetic acid) was the most prominent, with a CC50 = 211.3 µM, while the A6 derivative (cyclobutane selanylacetic acid) (SI = 11) was the most selective compound evaluated, being 15 and 5 times more selective than MIL and PMN in L. major, and 28- and 5-fold more selective than MIL and PMN in L. infantum, respectively.

Table 2.
Fractional inhibitory concentrations of 50% overall mean (ƩFICI50) of the lead compounds (A4–A6 and A8) and the reference drugs (AMB, MIL, and PMN) against L. infantum promastigotes.
2.5. Drug Combination Assay on L. infantum Promastigotes
In view of the current resistance to anti-leishmanial drugs, the current treatment regimen needs to be thoroughly updated and new therapeutic agents are required. Under these circumstances, drug combination is an attractive and effective approach to address this situation. This involves the identification of interactions between two substances, whose combined effects exceed their individual effects. The aim of this approach is to increase treatment efficacy, improve tolerability, reduce treatment duration, reduce treatment costs, and delay the development of resistance. In this regard, we reported the study of pharmacological interaction between aliphatic selanylacetic acid molecules in combination with the standard drugs AMB, MIL, and PMN. Interactions between the lead compounds (A4–A6 and A8) and the reference drugs were determined in terms of their combined and individual effect against L. infantum promastigotes (Table 2).
To determine the nature of the interaction, it is crucial to choose the appropriate doses. Thus, the evaluation of the combination was carried out by a dose–response linear dilution experiment, for which the IC50 value of each substance alone was determined and multiplied by 0.2×, 0.4×, 0.6×, 0.8×, 1×, 1.2×, 1.4×, 1.6×, 1.8×, and 2× times, in order to obtain the different dilutions. Compound A4 (ƩFICI > 0.60) and A5 (ƩFICI > 0.60) showed non-interaction combined with the reference drugs AMB, MIL, and PMN. Compound A6 stood out in this experiment, with synergistic interactions in combination with MIL (ƩFICI = 0.44), borderline synergistic interaction combined with PMN (ƩFICI = 0.54), but without interaction when combined with AMB (ƩFICI = 0.70). Derivative A8 showed the most outstanding behavior due to the borderline synergistic interaction when combined with AMB (ƩFICI = 0.52) and PMN (ƩFICI = 0.52) and presented a synergistic interaction with MIL (ƩFICI = 0.40) (Table 3). Both A6 and A8 were the most outstanding compounds, when combined with fixed ratio solutions of MIL with compounds A6 and A8, exhibited potent synergistic interaction, with a reduction in the IC50 of A6, decreasing from 16.7 to 5.2 μM, in the case of A8, the IC50 decreased from 39.9 to 12.39 µM. A similar effect presented MIL combined with A6 and A8, which showed a decrease in the IC50 from 31.9 to 6.55–9.29 μM against L. infantum promastigotes, respectively.

Table 3.
The absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) properties of the lead compounds and the reference drug MIL and PMN.
2.6. Theorical ADME and Lipinski Properties
The compounds were screened using the pkCSM software (https://biosig.lab.uq.edu.au/pkcsm/, accessed on 18 July 2023). In addition, Lipinski’s rule of five values were analyzed. Compounds A4–A6 and A8, such as MIL, do not violate any of Lipinski’s 5 rules, which is not the case for PMN (3 Lipinski violations). These compounds, during their theorical analysis, showed low skin sensitization and low skin absorbability.
Their predicted high aqueous solubility may be related to the presence of the terminal acid group. Table 3 showed how increase in the number of carbons causes a decrease in solubility, with compound A5 (−0.92) showing the highest solubility, which decreased in the other compounds, without reaching the solubility of the drugs MIL (−6.15) and PMN (−2.38). Intestinal absorption was high for all compounds, which is considered a valid indicator of drug absorption, outperforming the reference compounds. Overall, selanylacetic acid derivatives appear to share comparable or even superior bioavailability, metabolic stability, and transport properties than the drugs available for the treatment of leishmaniasis.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
All reagents were commercially available. The reactions were monitored by thin-layer chromatography (TLC) and the spots were visualized under UV light. The 1H,13C and 77Se-NMR spectra were recorded on a Bruker Avance Neo 400 MHz (Billerica, MA, USA) operating at 400, 100 and 76 MHz, respectively, using deuterated solvent CDCl3. Chemical shifts (δ) are reported in parts per million (ppm) and the coupling constants (J) are expressed in Hertz. Elemental analyses for carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen were performed on a Thermo Fisher FlashSmart™ Elemental Analyzer (Waltham, MA, USA). Melting points (mp) were determined with a Mettler FP82 + FP80 apparatus (Greifensee, Switzerland). The synthesis of the derivatives of series A1–A8 and C1–C8 has sodium hydrogen selenide as a common intermediate, which was synthesized following the previously mentioned protocol.
3.2. General Procedure for the Preparation of Selanylacetic Acid Derivatives (A1–A8)
In a flask under ice and nitrogen atmosphere, 125 mL 0.012 mmol (1 g) elemental selenium was dissolved in 30 mL absolute ethanol. Then, 2 equivalents (eq.) of sodium borohydride (NaBH4) were slowly added. The mixture became exothermic and was stirred continuously in order to obtain a homogeneous, bubble-free mixture (15 min). Then, bromoacetic acid was added (moles) followed by the corresponding acid chloride. THF (5 mL) was added due to the low solubility of these compounds, which caused a change in the color of the reaction from yellow to greyish. This reaction was stirred overnight at room temperature. After this time, reaction was stopped, and a greyish precipitated solid was removed by vacuum filtration and the residue was washed with H2O (3 × 30 mL) and extracted with DCM (3 × 30 mL). A silica gel chromatographic column with hexane/ethyl acetate in a 1:9 ratio was used as a purification method. Oily compounds were obtained, whose purity and structural characteristics were confirmed by elemental analysis and NMR.
2-(butyrylselanyl)acetic acid (A1). From: sodium hydrogen selenide, bromoacetic acid and butyryl chloride. Appearance: Yellow oil. Yield: 15%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 0.98 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 3H, Alif), 1.73 (h, J = 7.4 Hz, 2H, Alif), 2.65 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 2H, Alif), 3.64 (s, 2H, CH2–Se) ppm. 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ = 13.72, 25.23, 49.32, 61.61, 170.34 (–COOH), 199.28 (–COSeR) ppm. 77Se NMR (76 MHz, CDCl3) δ 561.06 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C6H10O3Se (%): C, 34.46; H, 4.82; N, 0.00. Found: C, 34.55; H, 4.72; N, 0.05.
2-(pentanoylselanyl)acetic acid (A2). From: sodium hydrogen selenide, bromoacetic acid, and pentanoyl chloride. Appearance: Colorless oil. Yield: 13%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 0.92 (t, J = 7.3 Hz, 3H, Alif), 1.38 (h, J = 7.4 Hz, 2H, Alif), 1.67 (p, J = 7.5 Hz, 2H, Alif), 2.67 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 2H, Alif), 3.64 (s, 2H, CH2–Se) ppm. 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ = 13.68, 25.26, 27.37, 47.24, 61.63, 170.36 (–COOH), 199.41(–COSeR) ppm. 77Se NMR (76 MHz, CDCl3) δ 559.86 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C7H12O3Se (%): C, 37.68; H, 5.42; N, 0.00. Found: C, 37.49; H, 5.50; N, 0.03.
2-(hexanoylselanyl)acetic acid (A3). From: sodium hydrogen selenide, bromoacetic acid, and hexanoyl chloride. Appearance: Yellow oil. Yield: 12%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 0.83 (m, 3H, Alif), 1.19 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H, Alif), 1.62 (m, 2H, Alif), 2.59 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 2H, Alif), 3.57 (s, 2H, CH2–Se) ppm. 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ = 13.82, 22.27, 25.01, 25.25, 47.48, 61.62, 170.35(–COOH), 199.41 (–COSeR) ppm. 77Se NMR (76 MHz, CDCl3) δ 559.29 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C8H14O3Se (%): C, 40.51; H, 5.95; N, 0.00. Found: C, 40.72; H, 5.65; N, 0.11.
2-(heptanoylselanyl)acetic acid (A4). From: sodium hydrogen selenide, bromoacetic acid, and heptanoyl chloride. Appearance: Green oil. Yield: 18%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 0.88 (t, J = 6.7 Hz, 3H, Alif), 1.28 (m, 6H, Alif), 1.68 (p, J = 7.4 Hz, 2H, Alif), 2.66 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 2H, Alif), 3.64 (s, 2H, CH2–Se) ppm. 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ = 22.41, 28.48, 31.38, 47.53, 170.36(–COOH), 199.43 (–COSeR) ppm. 77Se NMR (76 MHz, CDCl3) δ 559.75 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C9H16O3Se (%): C, 43.03; H, 6.42; N, 0.00. Found: C, 42.899; H, 6.51; N, 0.09.
2-((cyclopropanecarbonyl)selanyl)acetic acid (A5). From: sodium hydrogen selenide, bromoacetic acid, and cyclopropanecarbonyl chloride. Appearance: Colorless oil. Yield: 15%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 1.05 (m, 2H, Alif), 1.27 (d, J = 2.8 Hz, 2H, Alif), 2.14 (m, 1H, Alif), 3.66 (s, 2H, CH2–Se) ppm. 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ = 11.68, 25.33, 61.64, 170.31 (–COOH), 198.89 (–COSeR) ppm. 77Se NMR (76 MHz, CDCl3) δ 555.77 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C6H8O3Se (%): C, 34.80; H, 3.89; N, 0.00. Found: C, 34.91; H, 4.01; N, 0.07.
2-((cyclobutanecarbonyl)selanyl)acetic acid (A6). From: sodium hydrogen selenide, bromoacetic acid, and cyclobutanecarbonyl chloride. Appearance: Colorless oil. Yield: 32%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 1.05 (s, 2H, Alif), 1.25 (m, 4H, Alif), 2.14 (m, 1H, Alif), 3.66 (s, 2H, CH2–Se) ppm. 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ = 11.68, 14.09, 25.33, 25.84, 61.64, 170.31(–COOH), 198.89(–COSeR) ppm. 77Se NMR (76 MHz, CDCl3) δ 555.77 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C7H10O3Se (%): C, 38.02; H, 4.56; N, 0.00. Found: C, 37.89; H, 4.50; N, 0.08.
2-((cyclopentanecarbonyl)selanyl)acetic acid (A7). From: sodium hydrogen selenide, bromoacetic acid, and cyclopentanecarbonyl chloride. Appearance: Colorless oil. Yield: 17%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 1.61 (m, 2H, Alif), 1.71 (m, 2H, Alif), 1.89 (m, 4H, Alif), 3.06 (q, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, Alif), 3.62 (s, 2H, CH2–Se) ppm. 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ = 25.12, 25.70, 30.14, 56.48, 61.51, 170.39 (–COOH), 202.77 (–COSeR) ppm. 77Se NMR (76 MHz, CDCl3) δ 542.62 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C8H12O3Se (%): C, 40.86; H, 5.14; N, 0.00. Found: C, 41.01; H, 5.25; N, 0.10.
2-((cyclohexanecarbonyl)selanyl)acetic acid (A8). From: sodium hydrogen selenide, bromoacetic acid, and cyclohexanecarbonyl chloride. Appearance: Yellow oil. Yield: 22%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 1.26 (m, 4H, Alif), 1.48 (m, 2H, Alif), 1.80 (m, 2H, Alif), 1.98 (m, 2H, Alif), 2.56 (tt, J = 3.6, 11.3 Hz, 2H, Alif), 3.61 (s, 2H, CH2–Se) ppm. 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ = 24.79, 25.31, 25.59, 29.21, 55.69, 61.56, 170.49 (–COOH), 203.27 (–COSeR) ppm. 77Se NMR (76 MHz, CDCl3) δ 542.44 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C9H14O3Se (%): C, 43.38; H, 5.66; N, 0.00. Found: C, 43.49; H, 5.52; N, 0.06.
3.3. General Procedure for the Preparation of Thioglycolic Acid Derivatives (B1–B8)
For the synthesis of the B1–B8 series derivatives, 0.010 mmol thioglycolic acid (1 g) was dissolved in DCM (30 mL) and reacted with the corresponding acid chlorides and 1.01 mmol triethylamine [17] for 2 h. After this time, the reaction was stopped and decanted with H2O (3 × 30 mL) and DCM (3 × 30 mL). The solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure at a rotary evaporator. Oily liquid compounds were obtained, and their purity and structural features were confirmed by elemental analysis and NMR.
2-(butyrylthio)acetic acid (B1). From: thioglycolic acid, triethylamine, and butyryl chloride. Appearance: Light pink oil. Yield: 25%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 0.97 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 3H, Alif), 1.73 (h, J = 7.4 Hz, 2H, Alif), 2.61 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 2H, Alif), 3.74 (s, 2H, CH2–S) ppm. 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ = 13.43, 19.02, 30.95, 45.46, 174.66 (–COOH), 197.56 (–COSR) ppm. Anal. Calcd for C6H10O3S (%): C, 44.43; H, 6.21; N, 0.00. Found: C, 44.56; H, 6.74; N, 0.02.
2-(pentanoylthio)acetic acid (B2). From: thioglycolic acid, triethylamine, and pentanoyl chloride. Appearance: Yellow oil. Yield: 32%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 0.92 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 3H, Alif), 1.37 (h, J = 7.3 Hz, 2H, Alif), 1.66 (m, 2H, Alif), 2.63 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 2H, Alif), 3.73 (s, 2H, CH2–S) ppm. 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ = 13.67, 22.05, 27.49, 30.96, 43.39, 174.33(–COOH), 197.72 (–COSR) ppm. Anal. Calcd for C7H12O3S (%): C, 47.71; H, 6.86; N, 0.00. Found: C, 47.62; H, 6.64; N, 0.04.
2-(hexanoylthio)acetic acid (B3). From: thioglycolic acid, triethylamine, and hexanoyl chloride. Appearance: Yellow oil. Yield: 33%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 0.88 (t, J = 6.7 Hz, 3H, Alif), 1.35 (m, 2H, Alif), 1.68 (m, 2H, Alif), 2.66 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 2H, Alif), 4.17 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 2H, CH2–S) ppm. 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ = 13.98, 22.40, 28.47, 31.37, 47.52, 61.60, 170.33 (–COOH), 199.39 (–COSR) ppm. Anal. Calcd for C8H14O3S (%): C, 50.50; H, 7.42; N, 0.00. Found: C, 50.32; H, 7.07; N, 0.05.
2-(heptanoylthio)acetic acid (B4). From: thioglycolic acid, triethylamine, and heptanoyl chloride. Appearance: Colorless oil. Yield: 12%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 0.88 (t, J = 6.7 Hz, 3H, Alif), 1.35 (m, 2H, Alif), 1.68 (m, 2H, Alif), 2.66 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 2H, Alif), 4.17 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 2H, CH2–S) ppm. 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ = 13.98, 22.40, 28.47, 31.37, 47.52, 61.60, 170.33(–COOH), 199.39 (–COSR) ppm. Anal. Calcd for C9H16O3S (%): C, 52.92; H, 7.89; N, 0.00. Found: C, 53.22; H, 7.67; N, 0.06.
2-((cyclopropanecarbonyl)thio)acetic acid (B5). From: thioglycolic acid, triethylamine, and cyclopropanecarbonyl chloride. Appearance: Colorless oil. Yield: 25%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 1.05 (m, 2H, Alif), 1.23 (m, 2H, Alif), 2.07 (m, 1H, Alif), 3.75 (d, J = 1.9 Hz, 2H, CH2–S) ppm. 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ = 11.68, 25.33, 61.64, 170.29 (–COOH), 198.87 (–COSR) ppm. Anal. Calcd for C6H8O3S (%): C, 44.99; H, 5.03; N, 0.00. Found: C, 45.11; H, 4.87; N, 0.09.
2-((cyclobutanecarbonyl)thio)acetic acid (B6). From: thioglycolic acid, triethylamine, and cyclobutanecarbonyl chloride. Appearance: Colorless oil. Yield: 34%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 1.96 (m, 2H, Alif), 2.26 (m, 2H, Alif), 2.35 (m, 2H, Alif), 3.42 (m, 1H, Alif), 3.73 (s, 2H, CH2–S) ppm. 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ = 18.01, 25.97, 30.77, 37.80, 46.42, 174.54(–COOH), 199.60 (–COSR) ppm. Anal. Calcd for C7H10O3S (%): C, 48.26; H, 5.79; N, 0.00. Found: C, 45.07; H, 6.01; N, 0.12.
2-((cyclopentanecarbonyl)thio)acetic acid (B7). From: thioglycolic acid, triethylamine, and cyclopentanecarbonyl chloride. Appearance: Colorless. Yield: 31%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 0.88 (t, J = 6.7 Hz, 3H, Alif), 1.35 (m, 2H, Alif), 1.68 (m, 2H, Alif), 2.66 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 2H, Alif), 4.17 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 2H, CH2–S) ppm. 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ = 25.12, 25.70, 30.14, 56.48, 61.51, 170.39 (–COOH), 202.77 (–COSR) ppm. Anal. Calcd for C8H12O3S (%): C, 51.05; H, 6.43; N, 0.00. Found: C, 50.88; H, 6.32; N, 0.05.
2-((cyclohexanecarbonyl)thio)acetic acid (B8). From: thioglycolic acid, triethylamine, and cyclohexanecarbonyl chloride. Appearance: Yellow oil. Yield: 34%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 1.27 (m, 3H, Alif), 1.48 (m, 2H, Alif), 1.67 (m, 1H, Alif), 1.79 (m, 2H, Alif), 1.95 (m, 2H, Alif), 2.53 (m, 1H, Alif), 3.70 (s, 2H, CH2–S) ppm. 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ = 25.39, 25.54, 29.36, 30.72, 42.84, 52.26, 174.75 (–COOH), 201.15 (–COSR) ppm. Anal. Calcd for C9H14O3S (%): C, 53.44; H, 6.98; N, 0.00. Found: C, 53.19; H, 7.07; N, -0.02.
3.4. General Procedure for the Preparation of Selanyl Acetate Derivatives (C1–C8)
The reaction was carried out following the procedure used for the A series reaction. Briefly in a flask cooled with ice and nitrogen atmosphere, sodium hydrogen selenide was obtained, which was immediately reacted with methyl bromoacetic acid and the corresponding acid chlorides. THF (5 mL) was added due to the low solubility of these compounds. This reaction was stirred overnight at room temperature. After this time, the reaction was stopped, the organic fraction was filtered off and then the ethanol was evaporated under reduced pressure. Then, decantation was performed with H2O (3 × 30 mL) and DCM (3 × 30 mL). A silica gel chromatographic column with hexane/ethyl acetate (EtOH) in a 8:2 ratio was used as purification method. Oily liquid compounds were obtained, whose purity and structural characteristics were confirmed by elemental analysis and NMR.
Methyl 2-(butyrylselanyl)acetate (C1). From: sodium hydrogen selenide, methyl-2-bromoacetate, and butyryl chloride. Appearance: Yellow oil. Yield: 14%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 0.98 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 3H, Alif), 1.73 (h, J = 7.4 Hz, 2H, Alif), 2.65 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 2H, Alif), 3.65 (s, 2H, CH2–Se), 3.72 (s, 3H, CH3–O) ppm. 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ = 13.36, 18.87, 24.79, 49.29, 52.66, 170.81 (–COOCH3), 199.15 (–COSeR) ppm. 77Se NMR (76 MHz, CDCl3) δ 561.81 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C7H12O3Se (%): C, 37.68; H, 5.42; N, 0.00. Found: C, 38.00; H, 5.31; N, 0.09.
Methyl 2-(pentanoylselanyl)acetate (C2). From: sodium hydrogen selenide, methyl-2-bromoacetate, and pentanoyl chloride. Appearance: Yellow oil. Yield: 12%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 0.98 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 3H), 1.73 (h, J = 7.4 Hz, 2H), 2.65 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 2H), 3.65 (s, 2H, CH2–Se), 3.72 (s, 3H, CH3–O) ppm. 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ = 13.68, 22.06, 27.52, 30.98, 43.41, 52.77, 169.38 (–COOCH3), 197.60 (–COSeR) ppm. 77Se NMR (76 MHz, CDCl3) δ 561.81 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C8H14O3Se (%): C, 40.51; H, 5.95; N, 0.00. Found: C, 40.73; H, 6.12; N, 0.07.
Methyl 2-(hexanoylselanyl)acetate (C3). From: sodium hydrogen selenide, methyl-2-bromoacetate, and hexanoyl chloride. Appearance: Colorless. Yield: 48%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 1.61 (m, 2H, Alif), 1.71 (m, 2H, Alif), 1.89 (m, 4H, Alif), 3.07 (m, 1H, Alif), 3.64 (s, 2H, CH2–Se), 3.72 (s, 3H, CH3–O) ppm. 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ = 22.36, 31.34, 47.46, 52.60, 61.53, 170.74 (–COOCH3), 199.16 (–COSeR) ppm. 77Se NMR (76 MHz, CDCl3) δ 544.50 ppm. Anal. Anal. Calcd for C9H16O3Se (%): C, 43.03; H, 6.42; N, 0.00. Found: C, 42.86; H, 6.32; N, 0.07.
Methyl 2-(heptanoylselanyl)acetate (C4). From: sodium hydrogen selenide, methyl-2-bromoacetate, and cyclohexanecarbonyl chloride. Appearance: Yellow oil. Yield: 7%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 0.88 (m, 3H, Alif), 1.31 (m, 6H, Alif), 1.68 (m, 2H, Alif), 2.66 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 2H), 3.65 (s, 2H, CH2–Se), 3.72 (s, 3H, CH3–O) ppm. 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ = 14.00, 22.42, 25.43, 28.55, 30.97, 31.38, 43.69, 52.76, 169.36 (–COOCH3), 197.59 (–COSeR) ppm. 77Se NMR (76 MHz, CDCl3) δ 560.55 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C10H18O3Se (%): C, 45.29; H, 6.84; N, 0.00. Found: C, 44.94; H, 6.92; N, 0.04.
Methyl 2-((cyclopropanecarbonyl)selanyl)acetate (C5). From: sodium hydrogen selenide, methyl-2-bromoacetate, and cyclohexanecarbonyl chloride. Appearance: Yellow oil. Yield: 15%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 1.05 (m, 2H, Alif), 1.27 (m, 2H, Alif), 2.14 (m, 1H, Alif), 3.67 (s, 2H, CH2–Se), 3.72 (s, 3H, CH3–O) ppm. 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ = 25.88, 29.96, 30.48, 30.99, 43.39, 52.74, 52.88, 169.49 (–COOCH3), 201.02 (–COSeR) ppm. 77Se NMR (76 MHz, CDCl3) δ 557.09 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C7H10O3Se (%): C, 38.02; H, 4.56; N, 0.00. Found: C, 38.14; H, 4.66; N, 0.07.
Methyl 2-((cyclobutanecarbonyl)selanyl)acetate (C6). From: sodium hydrogen selenide, methyl-2-bromoacetate, and cyclohexanecarbonyl chloride. Appearance: Yellow oil. Yield: 19%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 1.05 (m, 2H, Alif), 1.27 (m, 2H, Alif), 2.14 (m, 1H, Alif), 3.67 (s, 2H, CH2–Se), 3.72 (s, 3H, CH3–O) ppm. 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ = 17.85, 24.43, 25.98, 49.80, 52.64, 170.87 (–COOCH3), 201.35 (–COSeR) ppm. 77Se NMR (76 MHz, CDCl3) δ 557.09 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C8H12O3Se (%): C, 40.86; H, 5.14; N, 0.00. Found: C, 41.01; H, 5.31; N, 0.03.
Methyl 2-((cyclopentanecarbonyl)selanyl)acetate (C7). From: sodium hydrogen selenide, methyl-2-bromoacetate, and cyclohexanecarbonyl chloride. Appearance: Yellow oil. Yield: 25%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 1.61 (m, 2H, Alif), 1.71 (m, 2H, Alif), 1.89 (m, 4H, Alif), 3.07 (m, 1H, Alif), 3.64 (s, 2H, CH2–Se), 3.72 (s, 3H, CH3–O) ppm. 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ = 25.88, 29.96, 30.48, 30.99, 43.39, 52.74, 52.88, 169.49 (–COOCH3), 201.02 (–COSeR) ppm. 77Se NMR (76 MHz, CDCl3) δ 544.50 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C9H14O3Se (%): C, 43.38; H, 5.66; N, 0.00. Found: C, 43.10; H, 5.39; N, 0.03.
Methyl 2-((cyclohexanecarbonyl)selanyl)acetate (C8). From: sodium hydrogen selenide, methyl-2-bromoacetate, and cyclohexanecarbonyl chloride. Appearance: Yellow oil. Yield: 20%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 1.27 (m, 4H, Alif), 1.48 (m, 2H, Alif), 1.65 (m, 1H, Alif), 1.80 (m, 2H, Alif), 1.98 (m, 2H, Alif), 2.55 (m, 1H, Alif), 3.62 (s, 2H, CH2–Se), 3.71 (s, 3H, CH3–O) ppm. 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ = 23.40, 24.36, 25.30, 25.58, 29.19, 52.64, 55.66, 61.54, 170.98 (–COOCH3), 203.15 (–COSeR) ppm. 77Se NMR (76 MHz, CDCl3) δ 543.31 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C10H16O3Se (%): C, 45.66; H, 6.13; N, 0.00. Found: C, 45.74; H, 6.26; N, 0.02.
3.5. General Procedure for the Preparation of Methyl Thioglycolate Derivatives (D1–D8)
The derivatives of the D1–D8 series were obtained as a result of the reaction between methyl thioglycolate, TEA and the different acid chlorides using DCM as a solvent with a duration of 2 h. The purities of these compounds were checked by NMR.
Methyl 2-(butyrylthio)acetate (D1). From: methyl thioglycolate, triethylamine, and butyryl chloride. Appearance: Yellow oil. Yield: 45%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 0.97 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 3H, Alif), 1.72 (m, 2H, Alif), 2.60 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 2H, Alif), 3.71 (s, 2H, CH2–S), 3.74 (s, 3H, CH3–O) ppm. 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ = 13.44, 19.04, 30.97, 45.50, 52.77, 169.37 (–COOCH3), 197.48 (–COSR) ppm. Anal. Calcd for C7H12O3S (%): C, 47.71; H, 6.86; N, 0.00. Found: C, 47.57; H, 6.69; N, 0.06.
Methyl 2-(pentanoylthio)acetate (D2). From: methyl thioglycolate, triethylamine, and pentanoyl chloride. Appearance: Yellow oil. Yield: 55%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 0.92 (t, J = 7.7 Hz, 3H, Alif), 1.37 (m, 2H, Alif), 1.66 (m, 2H, Alif), 2.62 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 2H, Alif), 3.71 (s, 2H, CH2–S), 3.74 (s, 3H, CH3–O) ppm. 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ = 13.68, 22.06, 27.52, 30.98, 43.41, 52.77, 169.38 (–COOCH3), 197.60 (–COSR) ppm. Anal. Calcd for C8H14O3S (%): C, 50.50; H, 7.42; N, 0.00. Found: C, 50.62; H, 7.39; N, 0.03.
Methyl 2-(hexanoylthio)acetate (D3). From: methyl thioglycolate, triethylamine, and hexanecarbonyl chloride. Appearance: Colorless oil. Yield: 36%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 0.89 (m, 3H, Alif), 1.32 (m, 4H, Alif), 1.69 (m, 2H, Alif), 2.61 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 2H, Alif), 3.71 (s, 2H, CH2–S), 3.74 (s, 3H, CH3–O) ppm. 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ = 13.85, 22.27, 25.15, 30.98, 31.03, 43.66, 52.77, 169.38(–COOCH3), 197.61 (–COSR) ppm. Anal. Calcd for C9H16O3S (%): C, 52.92; H,7.89; N, 0.00. Found: C, 53.14; H, 8.08; N, 0.04.
Methyl 2-(heptanoylthio)acetate (D4). From: methyl thioglycolate, triethylamine, and heptanecarbonyl chloride. Appearance: Colorless oil. Yield: 22%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 0.88 (m, 3H, Alif), 1.31 (m, 6H, Alif), 1.68 (m, 2H, Alif), 2.61 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 2H, Alif), 3.71 (s, 2H, CH2–S), 3.74 (s, 3H,CH3–O) ppm. 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ = 14.00, 22.42, 25.43, 28.56, 30.98, 31.39, 43.70, 52.76, 169.37 (–COOCH3), 197.61(–COSR) ppm. Anal. Calcd for C10H18O3S (%): C, 55.02; H, 8.31; N, 0.00. Found: C, 54.89; H, 8.19; N, 0.06.
Methyl 2-((cyclopropanecarbonyl)thio)acetate (D5). From: methyl thioglycolate, triethylamine, and cyclopropanecarbonyl chloride. Appearance: Yellow oil. Yield: 25%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 1.01 (m, 2H, Alif), 1.21 (m, 2H, Alif), 2.05 (m, 1H, Alif), 3.73 (s, 2H, CH2–S), 3.74 (s, 3H, CH3–O) ppm. 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ = 11.27, 22.45, 31.00, 52.78, 169.39 (–COOCH3), 197.38 (–COSR) ppm. Anal. Calcd for C7H10O3S (%): C, 48.26; H, 5.79; N, 0.00. Found: C, 48.02; H, 5.95; N, 0.04.
Methyl 2-((cyclobutanecarbonyl)thio)acetate (D6). From: methyl thioglycolate, triethylamine, and cyclobutanecarbonyl chloride. Appearance: Colorless oil. Yield: 65%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 1.95 (m, 2H, Alif), 2.25 (m, 2H, Alif), 2.36 (m, 2H, Alif), 3.41 (m, 1H, Alif), 3.71 (s, 2H, CH2–S), 3.74 (s, 3H. CH3–O) ppm. 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ = 18.01, 25.97, 30.78, 46.46, 52.78, 169.48 (–COOCH3), 199.48 (–COSR) ppm. Anal. Calcd for C8H12O3S (%): C, 51.05; H, 6.43; N, 0.00. Found: C, 49.88; H, 6.26; N, -0.04.
Methyl 2-((cyclopentanecarbonyl)thio)acetate (D7). From: methyl thioglycolate, triethylamine, and cyclopentanecarbonyl chloride. Appearance: Yellow oil. Yield: 31%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 1.60 (m, 2H, Alif), 1.72 (m, 2H, Alif), 1.88 (m, 4H, Alif), 3.03 (m, 1H, Alif), 3.70 (s, 2H, CH2–S), 3.74 (s, 3H, CH3–O) ppm. 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ = 25.88, 30.48, 31.00, 52.75 (m), 52.89, 169.51 (–COOCH3), 201.04 (–COSR) ppm. Anal. Calcd for C9H14O3S (%): C, 53.44; H, 6.98; N, 0.00. Found: C, 53.09; H, 6.69; N, 0.04.
Methyl 2-((cyclohexanecarbonyl)thio)acetate (D8). From: methyl thioglycolate, triethylamine, and cyclohexanecarbonyl chloride. Appearance: Yellow oil. Yield: 45%. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 1.27 (m, 3H, Alif), 1.48 (m, 2H, Alif), 1.66 (m, 1H, Alif), 1.79 (m, 2H, Alif), 1.95 (m, 2H, Alif), 2.53 (m, 1H, Alif), 3.68 (s, 2H, CH2–S), 3.73 (m, 3H, CH3–O) ppm. 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ = 25.42, 25.57, 29.40, 30.71, 52.31, 52.75, 169.51 (–COOCH3), 201.06 (–COSR) ppm. Anal. Calcd for C10H16O3S (%): C, 55.53; H, 7.46; N, 0.00. Found: C, 55.71; H, 7.55; N, 0.05.
3.6. Biology
For all the biological assays, the requested purity for all the tested compounds was ≥95%. Since some of the purified compounds contained some solvent trace, the purity before the biological testing was assessed by elemental analysis. To ensure this purity, the maximal value accepted for the deviation of the carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen percentages was ±0.4. The obtained carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen percentage values for each compound before its evaluation are presented in chemistry part of Section 3.
3.6.1. Parasite Culture
Promastigotes. L. major (clone VI, MHOM/IL/80) and L. infantum (clone, BCN-150) parasites were cultured at 26 °C under continuous shaking in M199 1× medium (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) supplemented with heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS), 25 mM HEPES (pH 7), 0.1 mM adenine, 0.0005% (w/v) haemin, 0.0001% (w/v), 0.0005% (w/v) biotin, 100 IU/mL penicillin and 100 mg/mL penicillin. For each experiment, the culture medium was changed everyday in order to achieve parasite in exponential growth phase.
3.6.2. Cell Culture
Human monocytic leukemia cell line THP-1 cells were cultured in RMPI 1640 medium (Gibco, Leiden, The Netherlands) supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated FBS, 5% penicillin/streptomycin, 1 mM HEPES, 2 mM glutamine at pH 7.2 at 36 °C and 5% CO2.
3.6.3. Leishmanicidal Activity of Glycolic Derivatives against Promastigotes
In order to determine the leishmanicidal activity of the compounds obtained in this study, promastigotes of L. major and L. infantum strains were seeded in 96-well plates (3 ×·106 parasite/mL) in exponential growth phase at increasing concentrations (1–500 μM) of the compounds and maintained at 26 °C. After 48 h of incubation, the IC50 was determined by MTT assay [26]. The absorbance was measured in a MultiskanEX photometric plate reader for microplates at 540 nm. Data were obtained from three independent experiments performed in triplicate.
3.6.4. Cytotoxicity Studies in PMA-Differentiated THP-1 Macrophages
THP-1 cells were seeded at a concentration of 8 × 105 cells/mL in 96-well plates and incubated for 24 h with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) (10 ng/mL) supplemented RPMI 1640 (Gibco, Leiden, The Netherlands). After 24 h, the culture medium was removed, and the cells were treated with the synthesized compounds at different concentrations ranging from 1–500 μM at 37 °C and 5% CO2. After this time, the MTT assay was performed. The cytotoxic concentration values (CC50) were obtained by fitting the data to a sigmoid dose-inhibition curve using GraphPad Prism 7.0 software (GraphPad Software Inc., San Diego, CA, USA). MIL and PMN were used as reference drugs for comparison.
3.6.5. Drug-Sinergy Studies
The fractional inhibitory concentration index (FICI) was used to describe the interaction between the lead compounds A4–A6 and A8 with AmB, PMN and MIL. The compounds were studied in vitro against L. infantum promastigotes after 48 h of treatment. For this purpose, different increasing concentration ratios (0.2×, 0.4×, 0.6×, 0.8×, 1×, 1.2×, 1.4×, 1.6×, 1.8× and 2× times the IC50 of the compounds) were established [27]. Finally, synergy was defined as FICI < 0.5, non-interaction as 0.5 < FICI < 4, and antagonism as FICI > 4. FICI values were obtained from four independent experiments.
3.6.6. Theorical ADME and Lipinski Properties
Absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and toxicity (ADME) parameters were calculated using pkCSM program (https://biosig.lab.uq.edu.au/pkcsm/prediction, accessed on 18 July 2023).
4. Conclusions
In conclusion, the obtained results suggest that the selanylacetic acid derivatives A4–A6 and A8 (IC50 below 40 µM) were the leaders in this study, as they showed the highest activity, being 2- and 5-fold more active than their S counterparts and more potent than MIL (IC50 = 31.9 µM) against L. infantum parasites. These compounds were obtained following a simple, modular, and efficient one-step synthetic procedure, which, when evaluated against PMA-differentiated THP-1 macrophages, showed low toxicity and high selectivity. However, the emergence of drug resistance constitutes a major challenge. In this context, drug combination studies were conducted with the reference drug AMB, MIL and PMN. Results showed that when combining fixed ratio solutions of compounds A6 and A8 with MIL, showed a potent synergistic interaction. Compound A6 exhibited a reduction of the IC50 from 16.7 to 5.2 μM and compound A8 a decrease in the IC50 from 39.9 to 12.39 µM. Miltefosine, the only available oral treatment against visceral leishmaniasis caused by L. infantum, has showed a similar effect presented MIL combined with A6 and A8 which showed, a decrease in the IC50 from 31.9 to 6.55–9.29 μM, against L. infantum promastigotes. These results suggest the possibility that the synergistic interaction observed between the A6 and A8 derivatives may be linked to complementary mechanisms of action that enhance the efficacy of the combination and offer a promising therapeutic approach for the treatment of visceral leishmaniasis. The interesting leishmanicidal activity, the affordability and simplicity of the synthetic process, highlight their innovative design and potential as a leishmanicidal agent. Finally, further studies are required to elucidate the mechanisms of action and evaluate their efficacy during in vivo studies.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/molecules28155845/s1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.H.-F., C.S. and D.P.; Methodology, A.H.-F. and E.M.; Investigation, A.H.-F.; Writing—original draft, A.H.-F.; Writing—review & editing, E.M., C.S. and D.P.; Supervision, C.S. and D.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Institute of Tropical Health of University of Navarra (ISTUN), Caixa Foundation, Roviralta and Ubesol, Spain and to the University of Navarra (ISTUN) for the Ph.D. fellowship.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this manuscript are available to any qualified researcher.
Acknowledgments
A.H.-F. gratefully acknowledges the financial support of the Institute of Tropical Health of University of Navarra (ISTUN), Caixa Foundation, Roviralta and Ubesol, Spain and to the University of Navarra (ISTUN) for the Ph.D. fellowship.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Sample Availability
Samples of the compounds A1–A8, B1–B8, C1–C2 and D1–D8 are available from authors.
References
- Akhoundi, M.; Kuhls, K.; Cannet, A.; Votýpka, J.; Marty, P.; Delaunay, P.; Sereno, D. A Historical Overview of the Classification, Evolution, and Dispersion of Leishmania Parasites and Sandflies. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piscopo, T.V.; Azzopardi, C.M. Leishmaniasis. Postgrad. Med. J. 2007, 83, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utzinger, J.; Becker, S.; Knopp, S.; Blum, J.; Neumayr, A.; Keiser, J.; Hatz, C. Neglected tropical diseases: Diagnosis, clinical management, treatment and control. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2012, 142, w13727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okwor, I.; Uzonna, J. Social and Economic Burden of Human Leishmaniasis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 94, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conceição-Silva, F.; Morgado, F.N. Leishmania Spp-Host Interaction: There Is Always an Onset, but Is There an End? Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serafim, T.D.; Figueiredo, A.B.; Costa, P.A.C.; Marques-Da-Silva, E.A.; Gonçalves, R.; de Moura, S.A.L.; Gontijo, N.F.; da Silva, S.M.; Michalick, M.S.M.; Meyer-Fernandes, J.R.; et al. Leishmania Metacyclogenesis Is Promoted in the Absence of Purines. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurel, M.S.; Tekin, B.; Uzun, S. Cutaneous leishmaniasis: A great imitator. Clin. Dermatol. 2019, 38, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juiz, V.N.; Luciañez, R.R. Leishmaniasis mucocutánea. Acta Otorrinolaringol. Esp. 2016, 67, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, T.J. Viszerale Leishmaniose. Der Chir. 2019, 90, 833–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burza, S.; Croft, S.L.; Boelaert, M. Leishmaniasis. Lancet 2018, 392, 951–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriquez-Figuereo, A.; Morán-Serradilla, C.; Angulo-Elizari, E.; Sanmartín, C.; Plano, D. Small molecules containing chalcogen elements (S, Se, Te) as new warhead to fight neglected tropical diseases. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 246, 115002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parcell, S. Sulfur in human nutrition and applications in medicine. Altern. Med. Rev. 2002, 7, 22–44. [Google Scholar]
- Morán-Serradilla, C.; Angulo-Elizari, E.; Henriquez-Figuereo, A.; Sanmartín, C.; Sharma, A.K.; Plano, D. Seleno-Metabolites and Their Precursors: A New Dawn for Several Illnesses? Metabolites 2022, 12, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvo-Martín, G.; Plano, D.; Encío, I.; Sanmartín, C. Novel N,N′-Disubstituted Selenoureas as Potential Antioxidant and Cytotoxic Agents. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcolea, V.; Plano, D.; Karelia, D.N.; Palop, J.A.; Amin, S.; Sanmartín, C.; Sharma, A.K. Novel seleno- and thio-urea derivatives with potent in vitro activities against several cancer cell lines. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 113, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Pérez, M.; Ali, W.; Marć, M.A.; Handzlik, J.; Domínguez-Álvarez, E. Selenides and Diselenides: A Review of Their Anticancer and Chemopreventive Activity. Molecules 2018, 23, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcolea, V.; Plano, D.; Encío, I.; Palop, J.A.; Sharma, A.K.; Sanmartín, C. Chalcogen containing heterocyclic scaffolds: New hybrids with antitumoral activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 123, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etxebeste-Mitxeltorena, M.; Moreno, E.; Carvalheiro, M.; Calvo, A.; Navarro-Blasco, I.; González-Peñas, E.; Álvarez-Galindo, J.I.; Plano, D.; Irache, J.M.; Almeida, A.J.; et al. Oral Efficacy of a Diselenide Compound Loaded in Nanostructured Lipid Carriers in a Murine Model of Visceral Leishmaniasis. ACS Infect. Dis. 2021, 7, 3197–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnica, P.; Etxebeste-Mitxeltorena, M.; Plano, D.; Moreno, E.; Espuelas, S.; Palop, J.A.; Jiménez-Ruiz, A.; Sanmartín, C. Pre-clinical evidences of the antileishmanial effects of diselenides and selenocyanates. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 30, 127371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, M.; de Lucio, H.; Moreno, E.; Espuelas, S.; Aydillo, C.; Jiménez-Ruiz, A.; Toro, M.Á.; Gutiérrez, K.J.; Martinez_Merino, V.; Cornejo, A.; et al. Synthesis and Leishmanicidal Activity of Novel Urea, Thiourea, and Selenourea Derivatives of Diselenides. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e02200-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.; Silva-Jardim, I.; Thiemann, O. Biological Implications of Selenium and its Role in Trypanosomiasis Treatment. Curr. Med. Chem. 2014, 21, 1772–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobanov, A.V.; Gromer, S.; Salinas, G.; Gladyshev, V.N. Selenium metabolism in Trypanosoma: Characterization of selenoproteomes and identification of a Kinetoplastida-specific selenoprotein. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 4012–4024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.K.; Silakari, O. Counting on Fragment Based Drug Design Approach for Drug Discovery. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 2284–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanmartín, C.; Plano, D.; Domínguez, E.; Font, M.; Calvo, A.; Prior, C.; Encio, I.; Palop, J.A. Synthesis and Pharmacological Screening of Several Aroyl and Heteroaroyl Selenylacetic Acid Derivatives as Cytotoxic and Antiproliferative Agents. Molecules 2009, 14, 3313–3338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, E.; Calvo, A.; Schwartz, J.; Navarro-Blasco, I.; González-Peñas, E.; Sanmartín, C.; Irache, J.M.; Espuelas, S. Evaluation of Skin Permeation and Retention of Topical Dapsone in Murine Cutaneous Leishmaniasis Lesions. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Nagarajan, A.; Uchil, P.D. Analysis of Cell Viability by the MTT Assay. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2018, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fivelman, Q.L.; Adagu, I.S.; Warhurst, D.C. Modified Fixed-Ratio Isobologram Method for Studying In Vitro Interactions between Atovaquone and Proguanil or Dihydroartemisinin against Drug-Resistant Strains of Plasmodium falciparum. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 4097–4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).