Melt Viscoelastic Assessment of Poly(Lactic Acid) Composting: Influence of UV Ageing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials and Methods
2.1.1. Polymers Used and Sample Preparation
2.1.2. Analytical Methods
2.1.3. Melt Rheology
2.1.4. Biodegradation in Compost
2.1.5. Photo-Ageing by UV Irradiation
3. Results and Discussion
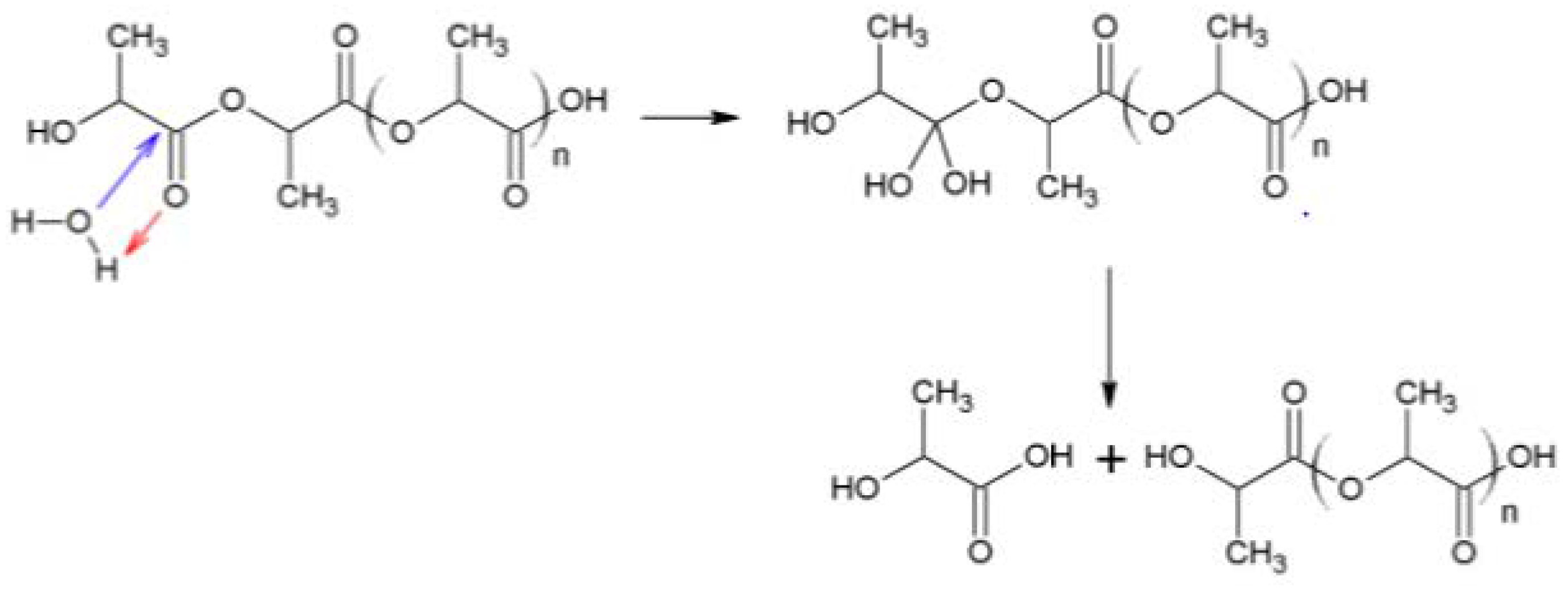
3.1. Biodegradation Pathway
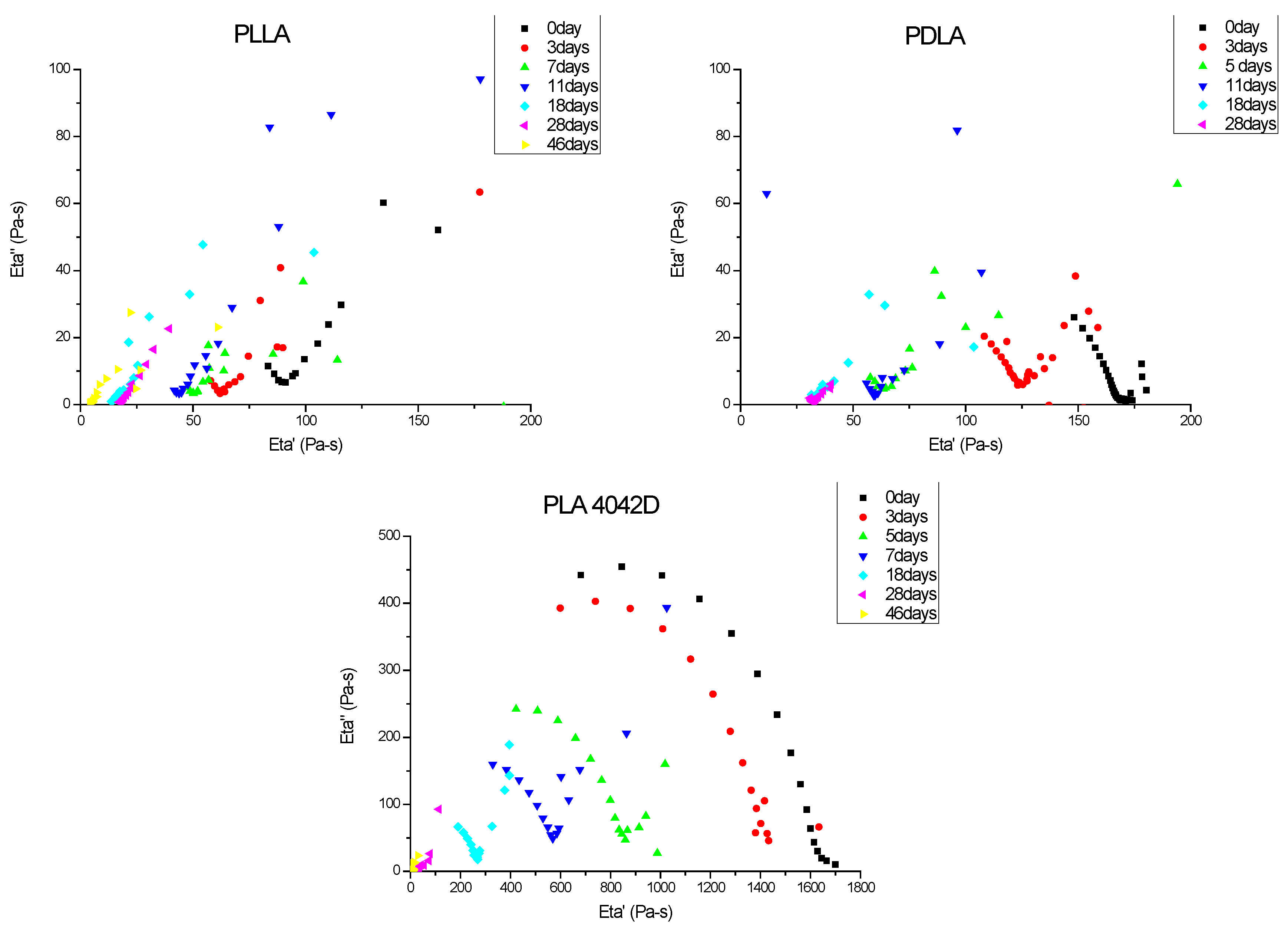
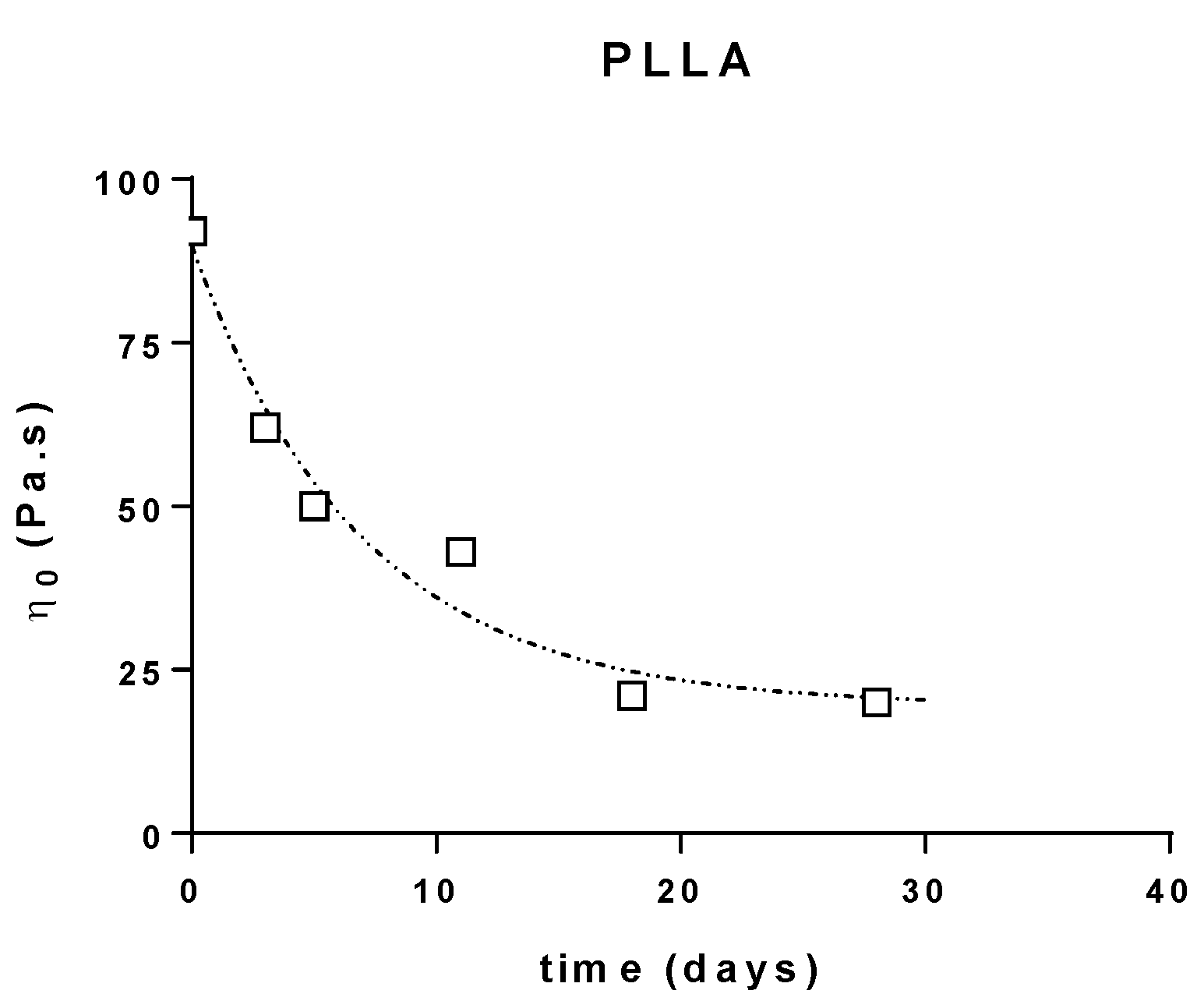
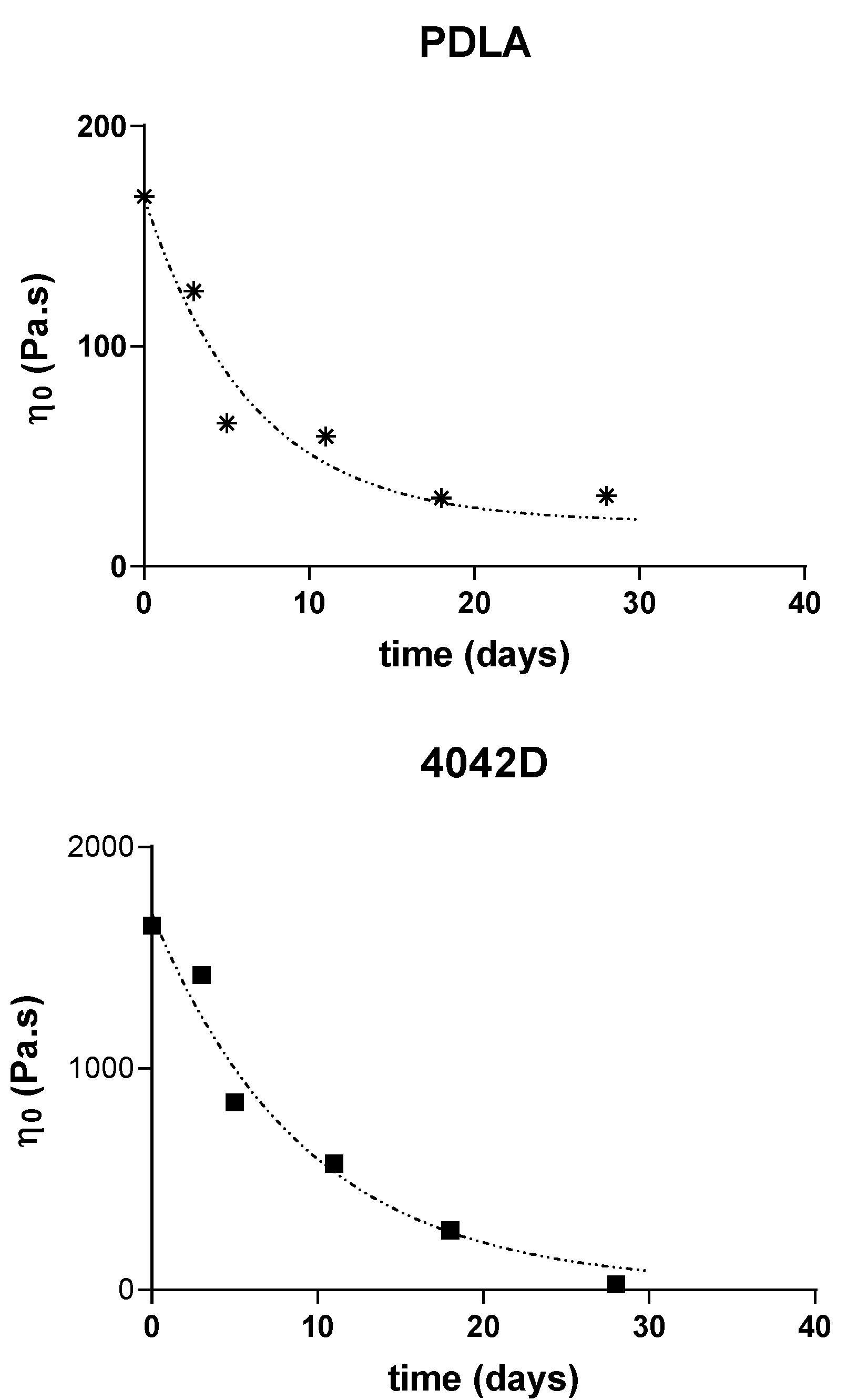
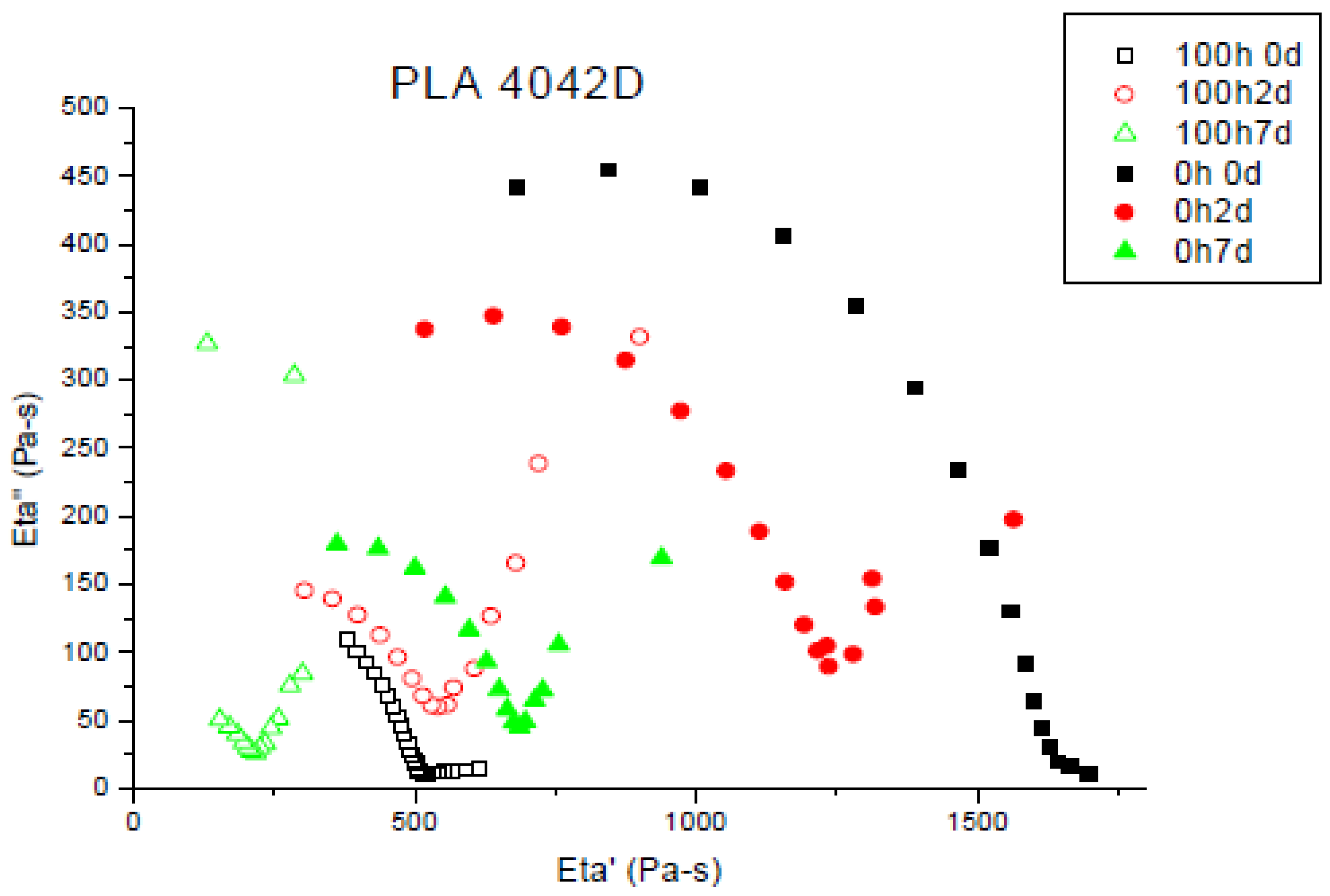
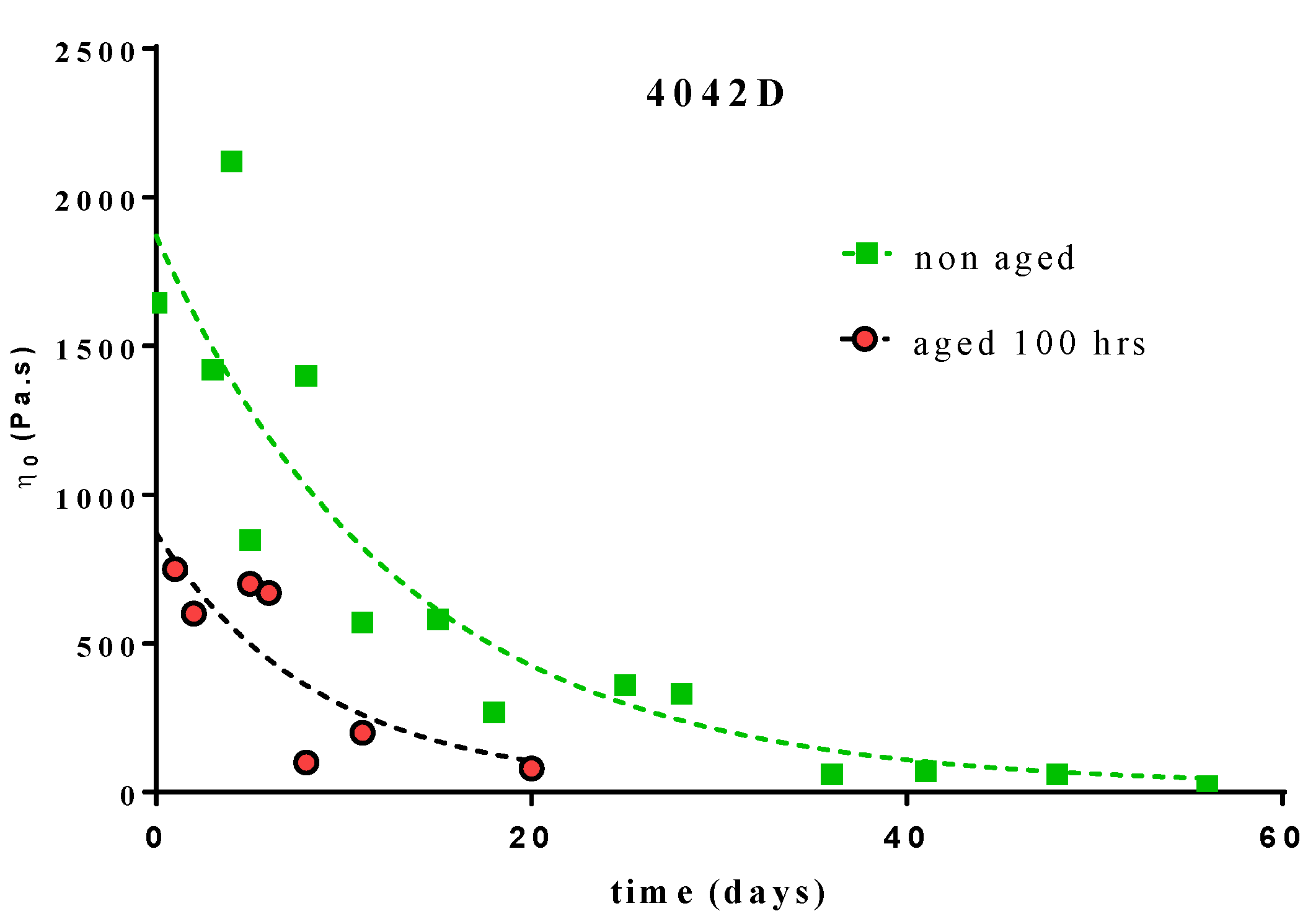
3.2. Melt Viscoelasticity to Evaluate UV-Ageing and Composting
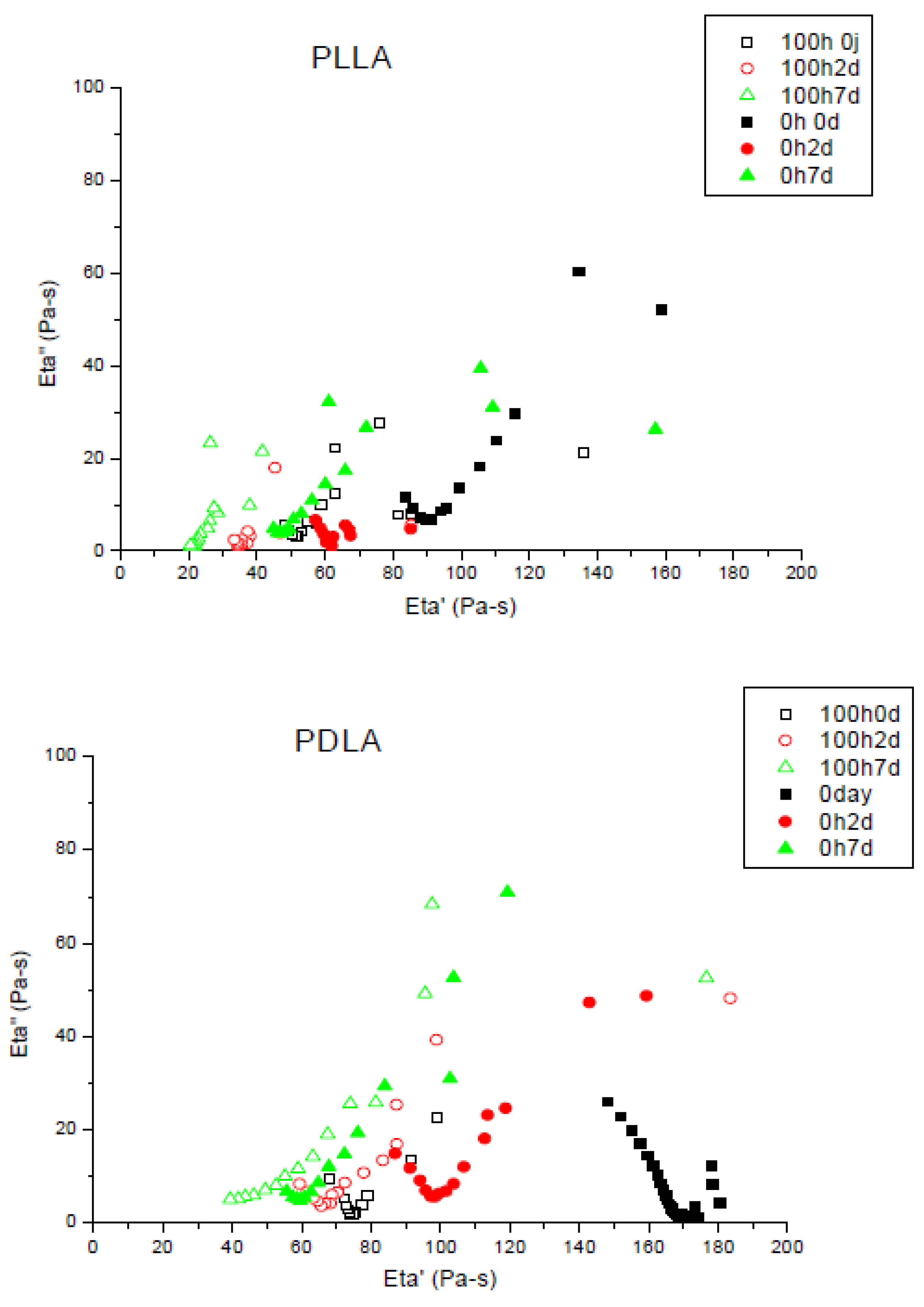
3.2.1. UV Ageing
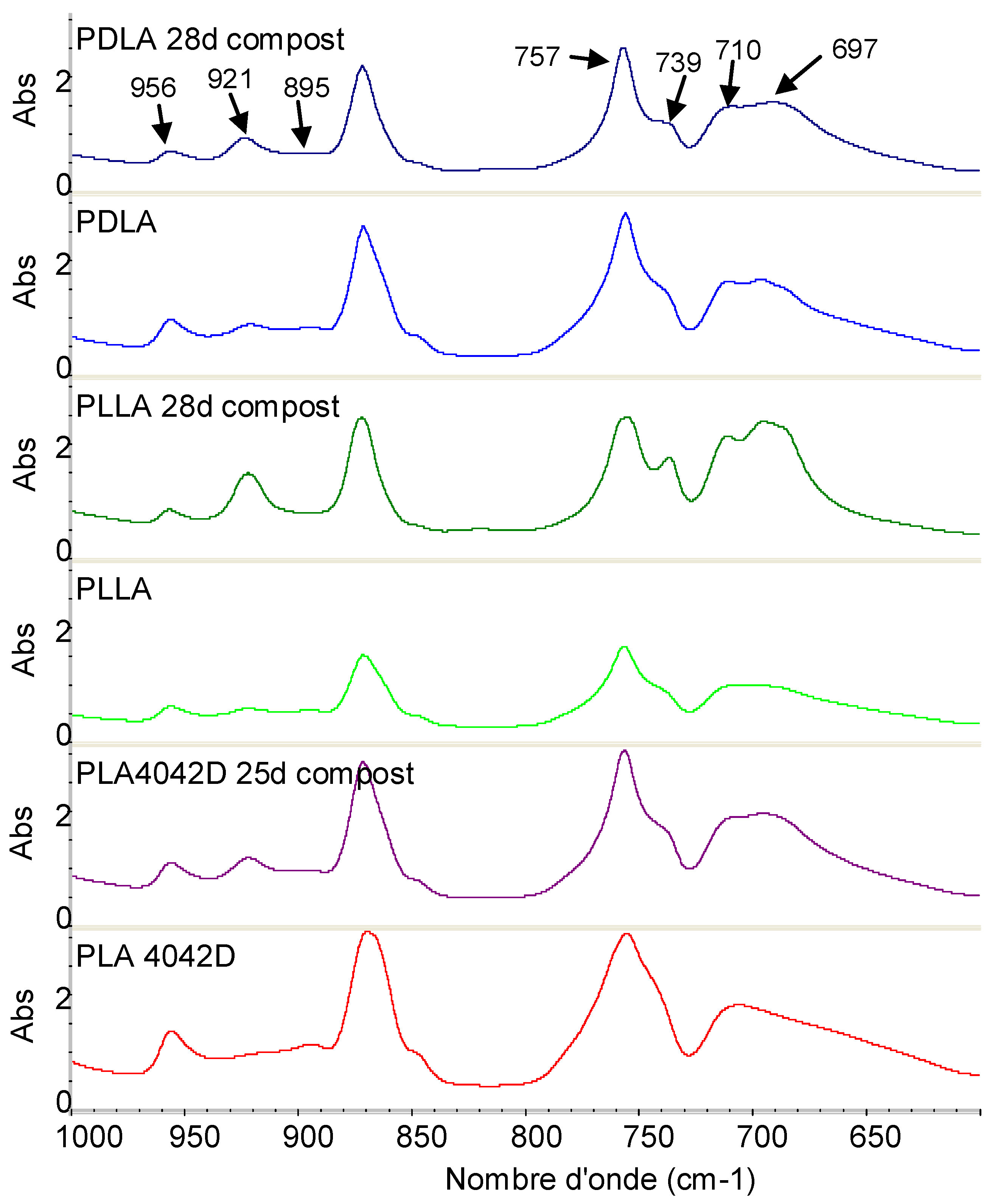
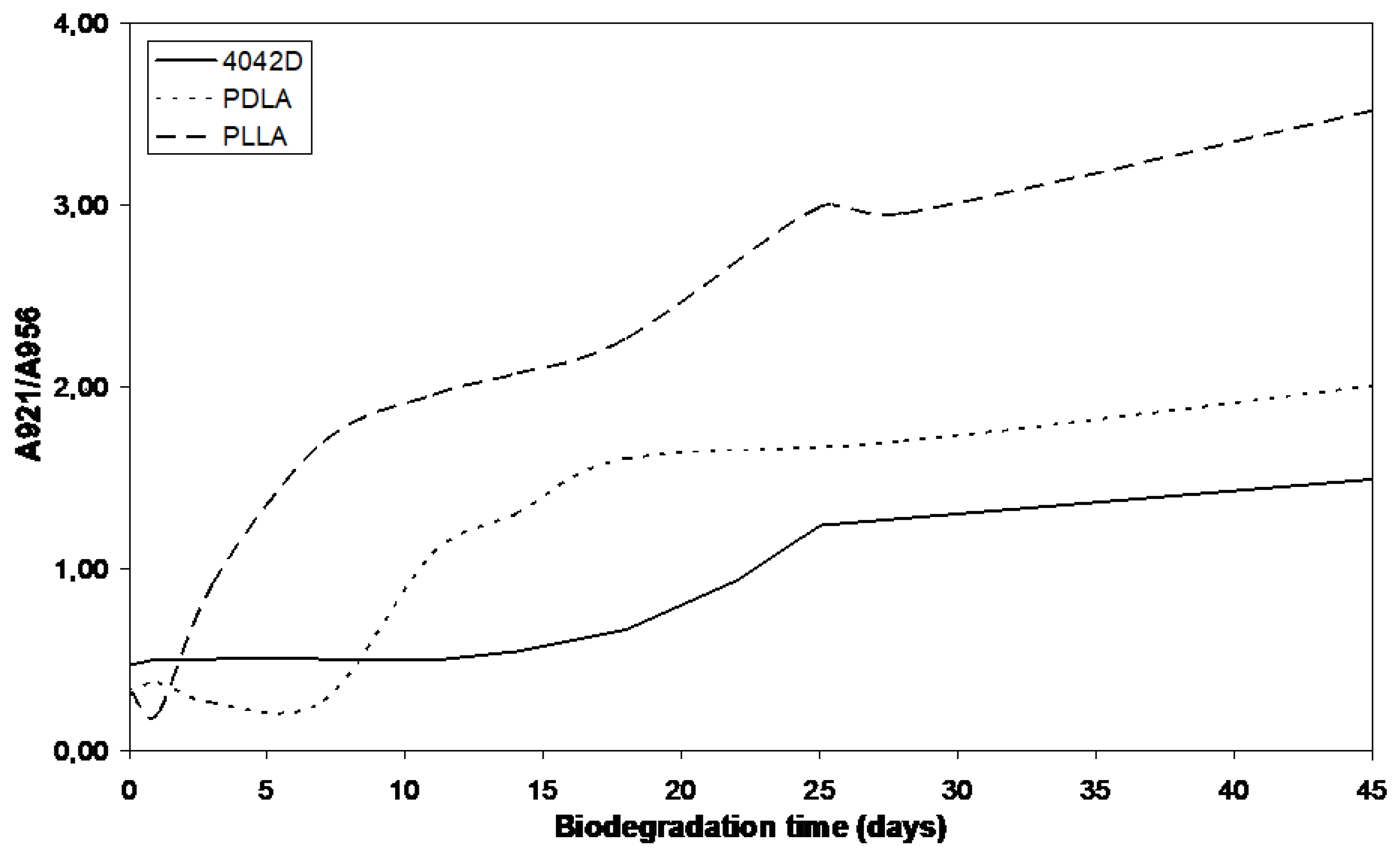
3.2.2. Molecular Weight Evolution during Composting
3.2.3. UV Ageing and Its Impact on Biodegradation
- -
- 100 h UV aged 4042D PLA: k = 0.076 day−1 (R2 = 0.6849)
- -
- non-aged 4042D PLA: k = 0.115 day−1 (R2 = 0.8262)
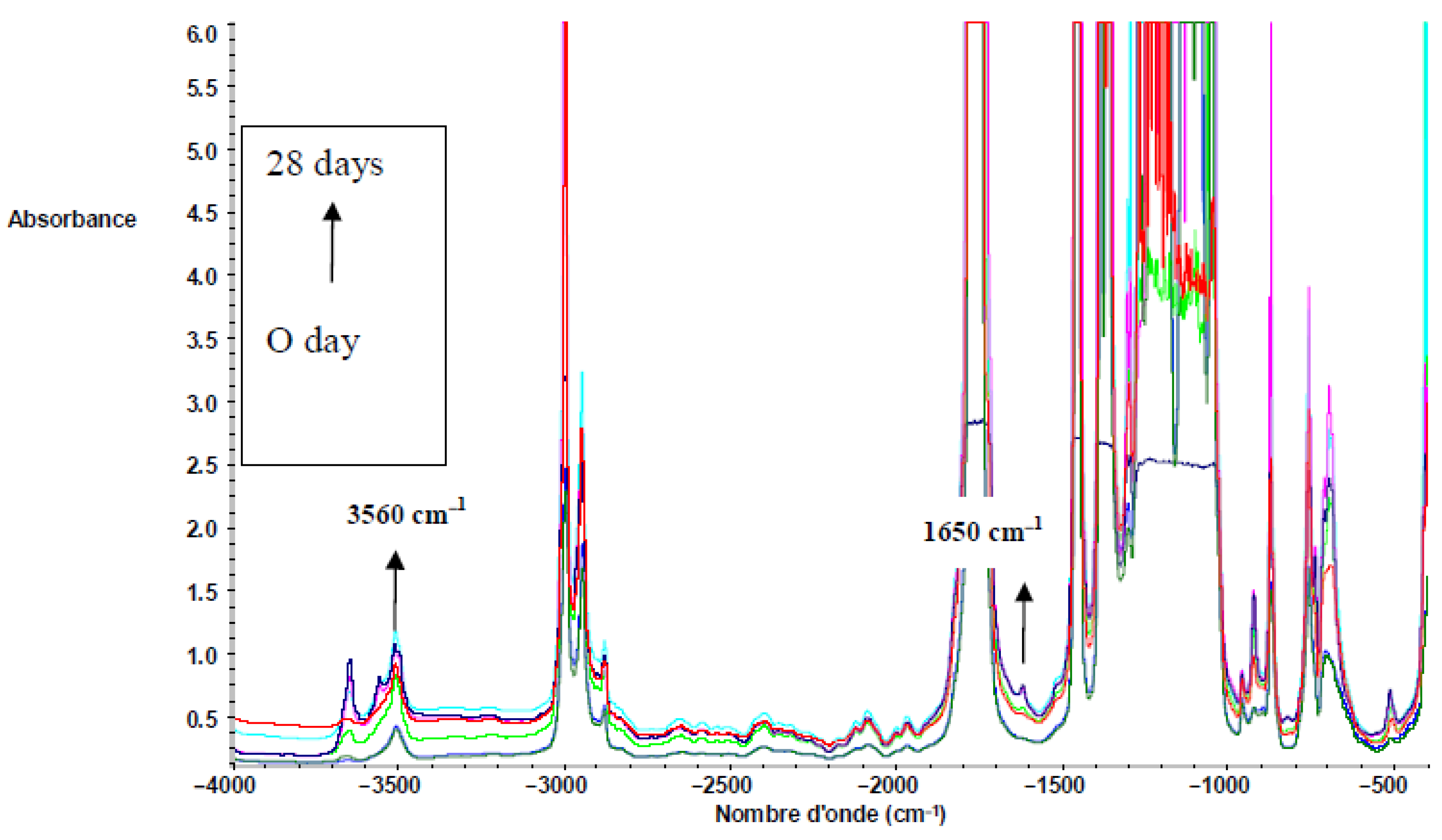
3.2.4. FTIR Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mooney, B.P. The second green revolution? Production of plant-based biodegradable plastics. Biochem. J. 2009, 418, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.-C.; Shetty, A.S.; Wang, M.-S. Biodegradable plastics: A review. Adv. Polym. Technol. 1990, 10, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.H.; Murphy, R.J.; Narayan, R.; Davies, G.B.H. Biodegradable and compostable alternatives to conventional plastics. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2127–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakkarainen, M. Aliphatic polyesters: Abiotic and biotic degradation and degradation products. In Degradable Aliphatic Polyesters; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; pp. 113–138. [Google Scholar]
- Quynh, T.M.; Mitomo, H.; Nagasawa, N.; Wada, Y.; Yoshii, F.; Tamada, M. Properties of crosslinked polylactides (plla & pdla) by radiation and its biodegradability. Eur. Polym. J. 2007, 43, 1779–1785. [Google Scholar]
- Karamanlioglu, M.; Robson, G.D. The influence of biotic and abiotic factors on the rate of degradation of poly(lactic) acid (pla) coupons buried in compost and soil. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 2063–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunt, J. Large-scale production, properties and commercial applications of polylactic acid polymers. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1998, 59, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auras, R.; Harte, B.; Selke, S. An overview of polylactides as packaging materials. Macromol. Biosci. 2004, 4, 835–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natural Fibers, Biopolymers, and Biocomposites, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005.
- Regnell Andersson, S.; Hakkarainen, M.; Inkinen, S.; Södergård, A.; Albertsson, A.-C. Customizing the hydrolytic degradation rate of stereocomplex pla through different pdla architectures. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 1212–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Tenon, M.; Garreau, H.; Braud, C.; Vert, M. Enzymatic degradation of stereocopolymers derived from l-, dl- and meso-lactides. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2000, 67, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, H.; Miyauchi, S. Enzymatic hydrolysis of poly(lactide)s: Effects of molecular weight, l-lactide content, and enantiomeric and diastereoisomeric polymer blending. Biomacromolecules 2001, 2, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, M.; Koelling, K.W.; Chalmers, J.J. Characterization of the degradation of polylactic acid polymer in a solid substrate environment. Biotechnol. Prog. 1998, 14, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pranamuda, H.; Tsuchii, A.; Tokiwa, Y. Poly(l-lactide)-degrading enzyme produced by Amycolatopsis sp. Macromol. Biosci. 2001, 1, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokiwa, Y.; Calabia, B.P. Biodegradability and biodegradation of poly(lactide). Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 72, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagga, U. Testing biodegradability with standardized methods. Chemosphere 1997, 35, 2953–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, D. Polymer weathering: Photo-oxidation. J. Polym. Environ. 2002, 10, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kijchavengkul, T.; Auras, R.; Rubino, M.; Ngouajio, M.; Fernandez, R.T. Assessment of aliphatic–aromatic copolyester biodegradable mulch films. Part ii: Laboratory simulated conditions. Chemosphere 2008, 71, 1607–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stloukal, P.; Verney, V.; Commereuc, S.; Rychly, J.; Matisova-Rychlá, L.; Pis, V.; Koutny, M. Assessment of the interrelation between photooxidation and biodegradation of selected polyesters after artificial weathering. Chemosphere 2012, 88, 1214–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santonja-Blasco, L.; Ribes-Greus, A.; Alamo, R.G. Comparative thermal, biological and photodegradation kinetics of polylactide and effect on crystallization rates. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 771–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, H.; Miyauchi, S. Poly(l-lactide): Vi effects of crystallinity on enzymatic hydrolysis of poly(l-lactide) without free amorphous region. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2001, 71, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantani, R.; Sorrentino, A. Influence of crystallinity on the biodegradation rate of injection-moulded poly(lactic acid) samples in controlled composting conditions. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.A.; Hasan, F.; Hameed, A.; Ahmed, S. Biological degradation of plastics: A comprehensive review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2008, 26, 246–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Commereuc, S.; Askanian, H.; Verney, V.; Celli, A.; Marchese, P.; Berti, C. About the end life of novel aliphatic and aliphatic-aromatic (co)polyesters after uv-weathering: Structure/degradability relationships. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 1321–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.-D.; Sun, B.; Bian, X.-C.; Chen, Z.-M.; Chen, X.-S. Determination of d-lactate content in poly(lactic acid) using polarimetry. Polym. Test. 2010, 29, 771–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarasua, J.-R.; Prud’homme, R.E.; Wisniewski, M.; Le Borgne, A.; Spassky, N. Crystallization and melting behavior of polylactides. Macromolecules 1998, 31, 3895–3905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verney, V.; Michel, A. Representation of the rheological properties of polymer melts in terms of complex fluidity. Rheol. Acta 1989, 28, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palade, L.-I.; Lehermeier, H.J.; Dorgan, J.R. Melt rheology of high l-content poly(lactic acid). Macromolecules 2001, 34, 1384–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorgan, J.R.; Janzen, J.; Clayton, M.P.; Hait, S.B.; Knauss, D.M. Melt rheology of variable l-content poly(lactic acid). J. Rheol. 2005, 49, 607–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verney, V. Rhéologie, oxydation et vieillissement des polymères. Rhéologie 2011, 20, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Husárová, L.; Pekařová, S.; Stloukal, P.; Kucharzcyk, P.; Verney, V.; Commereuc, S.; Ramone, A.; Koutny, M. Identification of important abiotic and biotic factors in the biodegradation of poly(l-lactic acid). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 71, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangari, D.; Vasanthan, N. Study of strain-induced crystallization and enzymatic degradation of drawn poly(l-lactic acid) (plla) films. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 7397–7403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasanthan, N.; Ly, O. Effect of microstructure on hydrolytic degradation studies of poly (l-lactic acid) by ftir spectroscopy and differential scanning calorimetry. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2009, 94, 1364–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, R.T.; McCarthy, S.P.; Gross, R.A. Enzymatic degradability of poly(lactide): Effects of chain stereochemistry and material crystallinity. Macromolecules 1996, 29, 7356–7361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds not available from the authors. |


| References | PLA 4042D | PLLA | PDLA |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mw (g·mol−1) | 209,000 | 138,000 | 149,000 |
| Polydispersity | 1, 8 | 1, 7 | 1, 7 |
| Tg | 59 °C | 59 °C | 59 °C |
| Tm | 150 °C | 180 °C | 178 °C |
| Tc | - | 100 °C | 108 °C |
| Composting Time (Days) | Cellulose | PLLA | PDLA |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 |  |  |  |
| 13 |  |  |  |
| 40 |  |  |  |
| 50 | Absence of cellulose fragments |  |  |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Verney, V.; Ramoné, A.; Delor-Jestin, F.; Commereuc, S.; Koutny, M.; Perchet, G.; Troquet, J. Melt Viscoelastic Assessment of Poly(Lactic Acid) Composting: Influence of UV Ageing. Molecules 2018, 23, 2682. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23102682
Verney V, Ramoné A, Delor-Jestin F, Commereuc S, Koutny M, Perchet G, Troquet J. Melt Viscoelastic Assessment of Poly(Lactic Acid) Composting: Influence of UV Ageing. Molecules. 2018; 23(10):2682. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23102682
Chicago/Turabian StyleVerney, Vincent, Audrey Ramoné, Florence Delor-Jestin, Sophie Commereuc, Marek Koutny, Geoffrey Perchet, and Julien Troquet. 2018. "Melt Viscoelastic Assessment of Poly(Lactic Acid) Composting: Influence of UV Ageing" Molecules 23, no. 10: 2682. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23102682
APA StyleVerney, V., Ramoné, A., Delor-Jestin, F., Commereuc, S., Koutny, M., Perchet, G., & Troquet, J. (2018). Melt Viscoelastic Assessment of Poly(Lactic Acid) Composting: Influence of UV Ageing. Molecules, 23(10), 2682. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23102682







