Abstract
Cellular mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor (c-MET) is closely linked to human malignancies, which makes it an important target for treatment of cancer. In this study, a series of 3-methoxy-N-phenylbenzamide derivatives, N-(3-(tert-butyl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl) benzamide derivatives and N1-(3-fluoro-4-methoxyphenyl)-N3-(4-fluorophenyl) malonamide derivatives were designed and synthesized, some of them were identified as c-MET inhibitors. Among these compounds with new scaffolds having different quinazoline, pyridine and tetrahydro-pyridothienopyrimidine head groups, compound 11c, 11i, 13b, 13h exhibited both potent inhibitory activities against c-MET and high anticancer activity against tested cancer cell lines in vitro. In addition, kinase selectivity assay further demonstrated that both 13b and 13h are potent and selective c-MET inhibitors. Molecular docking supported that they bound well to c-MET and VEGFR2, which demonstrates that they are potential c-MET RTK inhibitors for cancer therapy.
1. Introduction
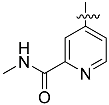
Tyrosine kinase is an enzyme that transfers a phosphate group from ATP to a protein, and it functions as an “on” or “off” switch in many cellular functions. They become potent oncogene that has the potential to cause cancer, when they are often mutated or expressed at high levels [1]. Several receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) inhibitors have been found to have effective anti-tumor activity and some of them have been approved or are in clinical trials. Recent FDA approved drugs Sorafenib (Nexavar) [2] is such example of multi-targeted agents (Figure 1).
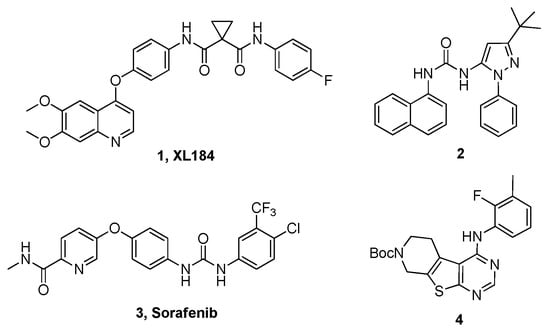
Figure 1.
Representative c-MET inhibitor (1, XL184) and Multi-kinase inhibitor (2–4).
Cellular mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor (c-MET), the hepatocyte growth factor receptor (HGFR), belongs to a subfamily of RTK that are composed of an extracellular a chain and a membrane-spanning b chain connected through a disulfide bond [3,4,5]. Binding of Hepatocyte Growth Factor/Scatter Factor (HGF/SF) to c-MET induces phosphorylation of tyrosine residues on c-MET and activates its downstream signaling pathway [6,7], which is associated with cell proliferation, migration, invasion and survival and is essential for normal embryonic development and wound healing [8,9]. However, it is reported that the c-MET/HGF axis is also involved in the development of various human malignancies. Aberrant or mutated expression of c-MET/HGF axis has been observed in a number of malignancies such as breast, gastric, bladder and lung cancers, which is closely linked to tumorigenesis and metastasis [10,11,12]. Moreover, it is reported that dysregulation of c-MET also correlated with a poor prognosis in clinical studies [13]. Therefore, c-MET shows high potential as a therapeutic target for human cancer.
Well-known agents for targeting the c-MET/HGF axis include anti-HGF antibodies, anti-c-MET antibodies, and c-MET tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs). Among them, c-MET TKIs are the most attractive means to target c-MET pathway, because they are thought to be effective against both ligand-dependent and ligand-independent activation of c-MET [14]. In recent years, a number of c-MET inhibitors have been reported or have entered clinical trials, and many of them are c-MET/VEGFR-2 (vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2) dual inhibitors (see Figure 1) [15,16,17]. For example, Cabozantinib (XL184, BMS-907351) is a potent c-MET inhibitor with IC50 of 1.3 nM and also inhibits VEGFR2, Ret, Kit, Flt-1/3/4, Tie2, and AXL in cell-free assays, respectively. Compounds 2 and 4 represent potential lead compounds with c-MET inhibitory effect in high throughput screening [18,19]. There are two classes of c-MET inhibitors based on their chemical structures or binding modes, but they both have some shortcomings [20,21]. Class I inhibitors bind in a U-shaped conformation to the ATP-binding site at the entrance of a kinase pocket, wrap around Met1211 and bind to a hinge-block, and thus specifically inhibiting MET kinases, such as Crizotinib. Class II inhibitors bind to a region of MET that extends from the ATP binding site to Ile1145 near the C-C-spiral block, such as Cabozantinib. Studies suggested that class II inhibitors maybe more effective than class I inhibitors, but they exhibited off-target effects of other protein kinases, and clinical use of class II inhibitors have shown that these agents cause serious toxic effects in many organs [22,23,24,25]. Therefore, potent c-MET inhibitors with improved selectivity and minimal side effects should be developed.
In this study, we disclose our efforts towards the design and synthesis of new c-MET inhibitors. To further understand the structure–activity relationship (SAR) of this novel series of compounds, different quinazoline, pyridine and tetrahydro-pyridothienopyrimidine fragments were investigated. A series of 3-methoxy-N-phenylbenzamide derivatives, N-(3-(tert-butyl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl) benzamide derivatives and N1-(3-fluoro-4-methoxyphenyl)-N3-(4-fluorophenyl) malonamide derivatives were synthesized, and their inhibitory activities against c-MET and three different cancer cell lines were evaluated. We were interested to see if such modifications were possible within our new classes of molecules compared to the parent compounds.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
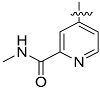
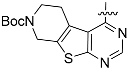
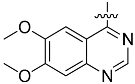
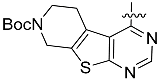
The chemistry described in Scheme 1 shows the synthetic route chosen to obtain quinazolines (Compound 5), pyridines (Compound 6) and tetrahydro-pyridothienopyrimidines (Compound 7) fragments. The reaction of 2-amino-4,5-dimethoxybenzoic acid with formamidine acetate afforded intermediate 6,7-dimethoxyquinazolin-4-ol, which upon reaction with SOCl2 afforded compound 5. The synthetic method of compound 7 is similar to the above process [26,27].
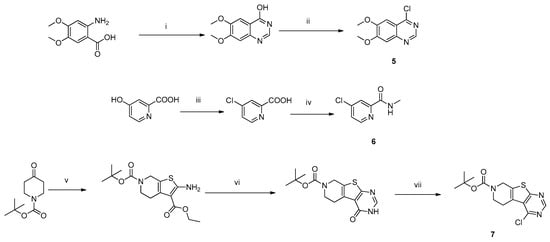
Scheme 1.
The synthesis procedure of the three different headgroups. Reagents and conditions: (i) Formamidine acetate, CH3OCH2CH2OH, 125 °C, 16 h; (ii) THF, SOCl2, reflux, 3 h; (iii) DMF, SOCl2, 120 °C, 6 h; (iv) THF, EDCI, CH3NH2, rt., 3 h; (v) S, NCCH2CO2Et, EtOH, Et3N, rt, 16 h; (vi) Formamidine acetate, DMF, 120 °C, 16 h; (vii) POCl3, DIPEA, toluene, 80 °C, 12 h.
The chemistry described in Scheme 2 shows compound libraries could be made simply by using the reaction protocol with N-(3-(tert-butyl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)-3-hydroxybenzamide (Compound 8) and different head groups. A cyclization reaction with nitrile and hydrazine was carried to afford 3-(tert-butyl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-amine. Compound 8 was synthesized by a conventional peptide synthesis method using ClCOCOCl at 0 °C [28].

Scheme 2.
The synthesis procedure of Compound 9a–c. Reagents and conditions: (i) EtOH, reflux, 16 h; (ii) THF, 3-hydroxybenzoic acid, ClCOCOCl, 0 °C, 3 h; (iii) 5, 6 or 7, DMF, K2CO3, 80 °C, 24 h.
Inspired by the structure of the lead compound 4, we have also designed a series of N-phenylbenzamide derivatives. The synthetic route is shown in Scheme 3. Compounds 10 were synthesized by a conventional peptide synthesis method with aniline and benzoic acid using ClCOCOCl at 0 °C. Then, a typical Williamson ether synthesis was carried on to afford compound 11a–i [29].

Scheme 3.
The synthesis procedure of Compound 11a–i. Reagents and conditions: (i) THF, ClCOCOCl, 0 °C, 3 h; (ii) 5, 6 or 7, DMF, K2CO3, 80 °C, 24 h.
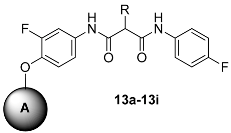
We also combined different head groups to the side chain of lead compound 1, XL184. The synthetic route is shown in Scheme 4. After multi-step protection and de-protection reaction, a series ethyl hydrogen malonate derivative was obtained. Then, Compounds 12 were synthesized by a conventional peptide synthesis method using isobutyl chloroformate and 4-Methylmorpholine. After that, a typical Williamson ether synthesis was carried on to afford compound 13a–i [30].

Scheme 4.
The synthesis procedure of Compound 13a–i. Reagents and conditions: (i) EtONa, CH3I, 0 °C, 5 h, or 1,2-dibromoethane or 1,3-dibromopropane, Bu4NBr, K2CO3, DMF, rt., 12 h; (ii) KOH, EtOH, 0 °C, 5 h; (iii) 4-amino-2-fluorophenol, IBCF, NMM, THF, −15 °C, 5 h; (iv) KOH, EtOH, 0 °C, 5 h; (v) 4-fluoroaniline, IBCF, NMM, THF, −15 °C, 3 h; (vi) 5, 6 or 7, DMF, K2CO3, 80 °C, 24 h.
2.2. Biology
2.2.1. Kinase Inhibitory Assay
All the synthesized compounds were assayed with the enzymatic activity against c-MET. The results were summarized in Table 1, Table 2 and Table 3. Also included was the representative c-MET inhibitor (XL184). Among these compounds, compound 11c, 11i, 13b, 13h showed potent inhibitory activity against c-MET, with IC50 of 0.08 µM (11c), 0.05 µM (11i), 0.02 µM (13b), 0.05 µM (13h), which is compared to XL184 (IC50 = 0.03 µM against c-MET).

Table 1.
Enzymatic and cellular results for compound 9a–c.
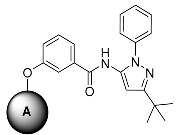


Table 2.
Enzymatic and cellular results for compound 11a–c.
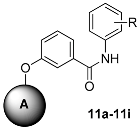


Table 3.
Enzymatic and cellular results for compound 13a–c.

2.2.2. Anti-proliferation against Tumor Cells Assay
All the synthesized compounds were evaluated for their anticancer activity in vitro against HeLa (human cervical carcinoma), Hep-G2 (human liver cancer) and MCF-7 (human breast cancer). The results were also summarized in Table 1, Table 2 and Table 3. It is clear that compound 11c, 11i, 13b, 13h all exhibited good anticancer activity against tested cancer cell lines. Compared to XL184 (IC50 = 6.6 µM against HeLa), these four compounds all showed better anti-proliferation activity against HeLa with compound 11c (IC50 = 0.9 µM against HeLa) exhibiting the highest activity. Similarly, they also showed better anti-proliferation activity against Hep-G2 than XL184 (IC50 = 49.1 µM), and it is obvious that compound 13h (IC50 = 1.7 µM) showed the highest activity, which is far better than XL184. In addition, compound 11i (IC50 = 1.1 µM) and 13b (IC50 = 1.2 µM) had better results against MCF-7 than XL184 (IC50 = 2.6 µM).
2.2.3. Structure Activity Relationship Analysis
Preliminary structure–activity SAR study appeared that different head groups showed great differences in cell and enzymatic activity. Among them, quinazolines (compound 9a, 11a–c, 13a–c), and tetrahydro-pyridothienopyrimidines (compound 9c, 11g–i, 13g–i) head groups provided much better activity than pyridines (compound 9b, 11d–f, 13d–f). For the side chain, N-(3-(tert-butyl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)-3-methoxybenzamide derivatives had lowest activities while malonamide derivatives had lowest activities. For compound 13a–i, different R groups provided different activity, when R group was cyclopropane (compound 13b and 13h), the best activity was observed.
2.2.4. Enzymatic Selectivity Assay
Compound 13b and 13h were further assayed with enzymatic activities against VEGFR-2, c-Kit, PDGFR-b and EGFR to test their kinase selectivity [31]. The results were summarized in Table 4. Compound 13b demonstrated extraordinary selectivity against c-Kit (215 fold), PDGFR-b (>500 fold) and EGFR (>500 fold), but it showed some inhibitory activity against VEGFR-2 (IC50 = 0.1 µM). Compound 13h exhibited extraordinary selectivity against c-Kit (104 fold), PDGFR-b (144 fold) and EGFR (>200 fold), and it also showed some inhibitory activity against VEGFR-2 (IC50 = 0.25 µM).

Table 4.
Kinase selectivity of compounds 13b and 13h.
2.3. Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study
In order to better understand the interaction between compounds and kinases, molecular docking studies on the potent compound 11c and 11i were performed using the Discovery Studio 3.1/CDOCKER protocol [32].
In Figure 2, we showed that compound 11c and 11i could bind to c-MET kinase (PDB: 4MXC) very well. In addition, they can form hydrophobic interaction in the ATP-binding sites of c-MET and VEGFR-2. Compounds formed hydrophobic interaction with residues ILE-1084, ALA-1108, LEU-1157, MET-1160 and ALA-1221 of c-MET.
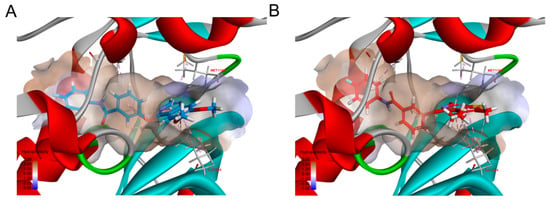
Figure 2.
Binding poses of compound 11c (A) and 11i (B) with c-MET. Compound 11c and 11i were displayed by blue and red, respectively. The important residues and their critical interactions (dash lines) with compounds in the binding site were depicted, hydrogen bond, hydrophobic interactions were colored green and carnation, respectively.
For the better active compounds 13b and 13h, We demonstrated in Figure 3 the compound 13b and 13h docking into the binding site of c-MET kinase (PDB: 4MXC) and VEGFR-2 kinase (PDB: 4ASE). For compound 13b, there are two hydrogen bonds formed by residue MET-1160 and ASP-1222, additional, compound 13b could form hydrophobic interactions with ILE-1084, ALA-1108, MET-1131, LEU-1157, ALA-1221 to c-MET. Compound 13b can form three hydrogen bonds by residue GLU-885, CYS-919, and ASP-1046, there also exist hydrophobic interaction with residue LEU-840, VAL-848, ALA-866, LYS-868, LEU-889, VAL-899, VAL-916, LEU-1035 to VEGFR2. Binding energy of compound 13b is much better than compound 11c and 11i, the dock interaction energy of compound 13b with c-MET, compound 11c and 11i with c-MET is −70.33 kJ/mol, −44.8 kJ/mol and −47.6 kJ/mol, respectively. The nice binding model of compound 13b and 13h with c-MET and VEGFR-2 was consistent with kinase assay data, which indicates that compounds were potent dual c-MET/VEGFR-2 inhibitors.
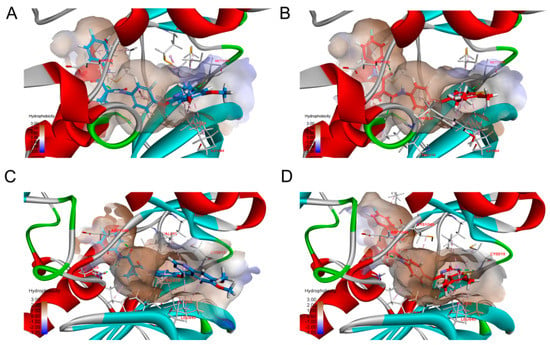
Figure 3.
Binding poses of compound 13b (A,C) and 13h (B,D) with c-MET and VEGFR2. Compound 13b and 13h were displayed by blue and red, respectively. The important residues and their critical interactions (dash lines) with compounds in the binding site were depicted, hydrogen bond, hydrophobic interactions were colored green and carnation, respectively.
To further evaluate the binding affinity between compound 13b and c-MET/VEGFR-2. The molecular dynamics (MD) simulations were performed by using GROMACS package (version 4.5, University of Groningen, Groningen, The Netherlands), the root-mean-square deviation (RMSD) fluctuations is a principal criterion to evaluate the stability of the protein-ligand system.
As shown in Figure 4, although the RMSD values for compound 13b fluctuated in a narrow range around 2700 ps, they remained stable for most of the simulation in c-MET complex. RMSD of compound 13b reach the equilibrium state after about 500 ps and kept stable among the rest of simulation in VEGFR-2 complex, indicating a stabilities of the dynamics equilibriums. In general, the maximum RMSD for each case was lower than 0.2 nm, suggesting that c-MET and VEGFR-2 complexes are reliable and the low RMSD fluctuations of system observed indicated stable binding models of compound 13b with c-MET and VEGFR-2, respectively.
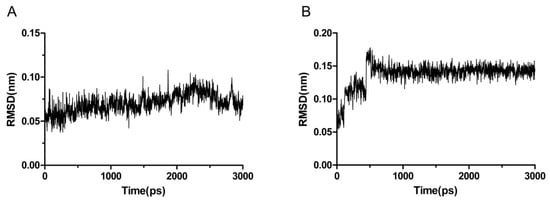
Figure 4.
RMSD of compound 13b with c-MET (A) and VEGFR-2 (B), respectively.
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Chemical Synthesis
All reagents were purchased from commercial sources and used without further purification. Melting points are corrected. 1H-NMR spectra were determined on a Bruker Avance III 400 MHz spectrometer (Bruker, Billerica, MA, USA) in CDCl3 or DMSO-d6 solution. J values were in Hz. Chemical shifts were expressed in ppm downfield from internal standard TMS. HRMS data were obtained using Bruker micro TOF-Q instrument (Bruker) or TOF-MS instrument (Bruker).
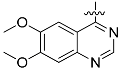
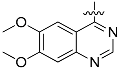
3.1.1. General Procedure for the Preparation of 4-Chloro-6,7-dimethoxyquinazoline (Compound 5)
2-amino-dimethyl aminobenzoic acid 2.02 g (10 mmol) and acetic acid formamidine 2.10 g (20 mmol) were added in 2-methoxy ethanol. The mixture was reflux in 125 °C. After evaporation of solvent, the residue was added in the 10% ammonia solution, stirring, then after filtering, the solid was washed by water to get the brown solid powder (yield 89%). 1.82 g (8.8 mmol) product was dissolved in 25 mL SOCl2, and 30 drops of DMF was added. After heating 7 h to reflux, the solvent was evaporated, then after filtering, the solid was washed by water to get the brown solid powder 4-chloro-6,7-dimethoxyquinazoline (yield 93%).
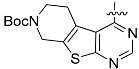
3.1.2. General Procedure for the Preparation of {tert-Butyl,4-chloro-5,6-dihydropyrido(4’,3’:4,5)thieno(2,3-d)pyrimidine-7(8H)-carboxylate} (Compound 7)
The N-(tert-Butoxycarbonyl)-4-piperidone, NCCH2CO2Et and Et3N was mixed at room temperature then stirring for 16 h, and then heated to 120 °C for 16 h in DMF with the formamidine acetate. Then, the intermediate was reacted with POCl3 and DIPEA in toluene to obtain the compound 7 (yield 89%).
3.1.3. General Procedure for the Preparation of {N-(3-(tert-Butyl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)-3-((6,7-dimethoxyquinazolin-4-yl)oxy)benzamide} Derivatives Compound 9a–c
Pivaloylacetonitrile 4.07 g (32 mmol) and Phenylhydrazine 3.51 g (32 mmol) were added to 40 mL ethanol and the mixture was heated to reflux for 15 h. After the solvent was evaporated, [3-(tert-butyl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-amine] was obtained. 138.6 mg (1 mmol) hydroxybenzoic acid in 5 mL THF was added three drops of DMF and reacted with oxalyl chloride 0.5 mL in 0 °C. After 1.5 h reaction, the reaction liquid was dissolved in THF and HCl, which was dissolved in THF solution of 3-(tert-butyl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-amine. After 3 h, the reaction mixture was evaporated; the crude product was purified by column chromatography to obtain compound 8. Compound 8 was further reacted with compounds 5, 6, 7 in the presence of K2CO3 to obtain the final products 9a–c.
Compound 9a: N-(3-(tert-butyl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)-3-((6,7-dimethoxyquinazolin-4-yl)oxy)benzamide. White solid, yield 88%, m.p. 217–219 °C. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO) δ 10.40 (s, 1H), 8.57 (s, 1H), 7.83 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, 1H), 7.79 (s, 1H), 7.64 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.60 (s, 1H), 7.57 (s, 1H), 7.54 (s, 2H), 7.52 (s, 2H), 7.44 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H), 7.40 (s, 1H), 7.31 (t, J = 7.3 Hz, 1H), 6.40 (s, 1H), 4.01(s, 3H), 3.97(s, 3H), 1.31 (s, 9H). HRMS (m/z): calcd. for 524.2292 ([M + H]+), obsd. 524.2294.
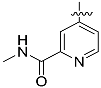
Compound 9b: 4-{3-((3-(tert-butyl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)carbamoylphenoxy}-N-methylpicolinamide: yellow solid, yield 71%. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.78 (d, 5.6 Hz, 1H), 8.35–7.95 (m, 2H), 7.94–7.67 (m, 5H), 7.62–7.42 (m, 2H), 7.39–7.05 (m, 2H), 6.74 (s, 1H), 2.85 (s, 3H), 1.29 (s, 9H). 13C-NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3 ) δ 169.26, 167.39, 166.32, 158.34, 153.42, 151.87, 148.57, 146.98, 139.89, 135.40, 129.43, 128.96, 128.93, 125.18, 123.62, 118.50, 113.11, 112.47, 95.64, 34.41, 28.32, 26.37.HRMS (m/z): calcd. for 470.2192 ([M + H]+), obsd. 470.2181.
Compound 9c: tert-butyl 4-{3-((3-(tert-butyl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)carbamoyl)phenoxy}-5,6-dihydropyrido(4’,3’:4,5)thieno(2,3-d)pyrimidine-7(8H)-carboxylate, yellow solid, yield 71%. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.01–7.67 (m, 5H), 7.67–7.42 (m, 2H), 7.43–7.02 (m, 2H), 4.65–4.55 (m, 2H), 3.70–3.40 (m, 2H), 3.20–3.15 (m, 2H), 1.42 (s, 9H), 1.29 (s, 9H). 13C-NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 170.28, 169.27, 162.31, 157.47, 154.66, 153.42, 151.87, 148.98, 139.89, 138.69, 129.19, 128.96, 128.93, 126.61, 126.27, 125.18, 122.57, 122.30, 119.22, 117.01, 95.64, 81.20, 43.81, 42.71, 34.41, 28.32, 23.62. HRMS (m/z): calcd. for 625.2597 ([M + H]+), obsd. 625.2611.
3.1.4. General Procedure for the Preparation of 3-Methoxy-N-phenylbenzamide Derivatives Compound 11a–i
138.6 mg (1 mmol) hydroxybenzoic acid in 5 mL THF was added three drops of DMF and reacted with oxalyl chloride 0.5 mL in 0 °C. After 1.5 h reaction, the reaction liquid was dissolved in THF and HCl, which was dissolved in THF solution of aniline derivatives. After 3 h, the reaction mixture was evaporated; the crude product was purified by column chromatography to obtain compounds 10. Compounds 10 were further reacted with compounds 5, 6, 7 in the presence of K2CO3 to obtain the final products 11a–i.
Compound 11a: N-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-3-((6,7-dimethoxyquinazolin-4-yl)oxy)benzamide. Yellow solid, yield 86%, m.p. 220–222 °C. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.62 (s, 1H), 7.90 (s, 1H), 7.81 (d, J = 7.4 Hz, 2H), 7.60 (t, J = 8.2 Hz, 1H), 7.53 (s, 1H), 7.47 (t, 2H), 7.33 (s, 1H), 6.99 (dd, J = 8.6, 2.3 Hz, 1H), 6.84 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 1H), 4.07 (d, J = 2.8 Hz, 6H), 3.90 (d, J = 5.2 Hz, 3H), 3.87 (s, 3H). 13C-NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 166.79, 165.05, 154.75, 153.84, 153.57, 149.95, 148.67, 148.21, 138.69, 132.68, 129.19, 126.27, 122.57, 122.29, 118.41, 114.98, 113.43, 111.44, 108.20, 107.06, 56.83.HRMS (m/z): calcd. for 462.1660 ([M + H]+), obsd.462.1665. calcd. for 484.11478 ([M + Na]+), obsd.484.1490.
Compound 11b: N-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-((6,7-dimethoxyquinazolin-4-yl)oxy)benzamide. Faint yellow solid, yield 89%, m.p. 203–205 °C. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO) δ 10.42 (s, 1H), 8.58 (s, 1H), 7.94 (s, 1H), 7.92 (s, 1H), 7.83 (s, 1H), 7.80 (s, 1H), 7.67 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.60 (s, 1H), 7.58 (s, 1H), 7.41 (t, 3H), 4.00 (d, J = 5.4 Hz, 6H). 13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO) δ 165.19, 162.11, 155.85, 154.74, 153.57, 147.81, 137.54, 136.45, 130.37, 129.25, 128.67, 127.37, 122.88, 122.46, 121.79, 114.79, 110.88, 107.91, 57.24.HRMS (m/z): calcd. for 420.1354 ([M + H]+), obsd.436.1059. calcd. for 458. 0878 ([M + Na]+), obsd.458.0883.
Compound 11c: 3-((6,7-dimethoxyquinazolin-4-yl)oxy)-N-(4-fluorophenyl)benzamide. Yellow solid, yield 86%, m.p. 178–180 °C. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO) δ 10.35 (s, 1H), 8.58 (s, 1H), 7.94 (s, 2H), 7.92 (d, J = 2.3 Hz, 2H), 7.79 (q, 1H), 7.67 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.62–7.56 (m, 2H), 7.42 (s, 1H), 7.20 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H), 4.00 (d, J = 5.2 Hz, 6H). 13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO) δ 167.33, 166.05, 162.07, 159.55, 154.65, 153.84, 153.12, 148.21, 138.69, 134.01, 129.03, 125.77, 122.62, 122.03, 115.11, 111.14, 108.30, 55.43.HRMS (m/z): calcd. for 420.1354 ([M + H]+), obsd.420.1356. calcd. for 442.1174 ([M + Na]+), obsd.442.1185.
Compound 11d: 4-{3-((3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)carbamoyl)phenoxy}-N-methylpicolinamide: yellow solid, yield 82%, 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3 ) δ 8.78 (d, J = 5.6 Hz, 1H), 8.22–7.89 (m, 2H), 7.67–7.37 (m, 2H), 7.34 (s, 1H), 7.27–7.04 (m, 3H), 6.91 (d, J = 15.4 Hz, 1H), 6.48 (s, 1H), 3.83 (s, 3H), 3.76 (s, 3H), 2.85 (s, 3H). 13C-NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 168.12, 167.12, 164.25, 157.14, 149.75, 148.47, 147.57, 146.98, 135.32, 132.18, 129.23, 123.62, 118.50, 117.10, 113.43, 113.11, 112.47, 107.06, 56.83, 26.37. HRMS (m/z): calcd. for 407.1481 ([M + H]+), obsd. 407.1499.
Compound 11e: 4-{3-((4-chlorophenyl)carbamoyl)phenoxy}-N-methylpicolinamide: yellow solid, yield 68%. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.62 (d, J = 5.6 Hz, 1H), 8.01–7.78 (m, 2H), 7.81–7.62 (m, 2H), 7.65–7.42 (m, 2H), 7.48–7.29 (m, 3H), 7.16 (m, 1H), 6.52 (s, 1H), 2.85 (s, 3H). 13C-NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 171.77, 169.22, 165.15, 159.14, 149.17, 147.28, 136.46, 135.21, 131.37, 129.44, 127.45, 124.57, 121.78, 118.60, 114.31, 113.17, 24.77. HRMS (m/z): calcd. for 382.0958 ([M + H]+), obsd. 382.0961.
Compound 11f: 4-{3-((4-fluorophenyl)carbamoyl)phenoxy}-N-methylpicolinamide: yellow solid, yield 82%, 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3 ) δ 8.74 (d, J = 5.6 Hz, 1H), 8.02–7.76 (m, 2H), 7.72–7.46 (m, 4H), 7.34 (m, 1H), 7.21–7.01 (m, 3H), 6.50 (s, 1H), 2.85 (s, 3H). 13C-NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 169.39, 168.32, 167.05, 163.07, 159.55, 158.34, 148.57, 146.98, 135.40, 134.03, 132.01, 128.43, 123.62, 122.66, 121.58, 118.51, 115.10, 113.90, 112.17, 110.47, 28.37. HRMS (m/z): calcd. for 407.1481 ([M + H]+), obsd. 407.1499.
Compound 11g: tert-butyl 4-{3-((3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)carbamoyl)phenoxy}-5,6-dihydropyrido(4’,3’:4,5)thieno(2,3-d)pyrimidine-7(8H)-carboxylate: yellow solid, yield 71%, m.p. 103–105 °C. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3 ) δ 8.92 (s, 1H), 8.50 (s, 1H), 7.65–7.40 (m, 2H), 7.34 (m, 1H), 7.29–7.07 (m, 3H), 6.91 (m, 1H), 4.70 (s, 2H), 3.81 (s, 3H), 3.78 (s, 3H), 3.59–3.43 (m, 2H), 3.17 (m, 2H), 1.42 (s, 9H). 13C-NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 170.28, 166.05, 162.31, 157.47, 154.66, 149.95, 148.98, 148.67, 138.69, 132.68, 129.19, 126.61, 126.27, 122.57, 122.30, 119.22, 118.40, 117.01, 113.43, 107.06, 81.20, 56.83, 43.81, 42.71, 28.33, 23.62. HRMS (m/z): calcd. for 563.1964 ([M + H]+), obsd. 563.1921.
Compound 11h: tert-butyl 4-{3-((4-chlorophenyl)carbamoyl)phenoxy}-5,6-dihydropyrido(4’,3’:4,5)thieno(2,3-d)pyrimidine-7(8H)-carboxylate: yellow solid, yield 74%, 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.50 (s, 1H), 7.81–7.67 (m, 2H), 7.61–7.42 (m, 2H), 7.42–7.16 (m, 4H), 4.65 (s, 2H), 3.67–3.40 (m, 2H), 3.17 (m, 2H), 1.42 (s, 9H). 13C-NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3 ) δ 173.11, 168.12, 164.45, 159.26, 155.78, 149.12, 139.57, 136.46, 130.37, 129.26, 128.01, 127.74, 126.77, 123.78, 122.86, 121.41, 118.12, 116.21, 79.31, 44.25, 43.78, 27.32, 24.42. HRMS (m/z): calcd. for 537.1363 ([M + H]+), obsd. 537.1378.
Compound 11i: tert-butyl 4-{3-((4-fluorophenyl)carbamoyl)phenoxy}-5,6-dihydropyrido(4’,3’:4,5)thieno(2,3-d)pyrimidine-7(8H)-carboxylate: yellow solid, yield 77%, 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.50 (s, 1H), 7.73–7.43 (m, 4H), 7.34–7.15 (m, 4H), 4.65 (s, 2H), 3.65–3.42 (m, 2H), 3.18 (m, 2H), 1.42 (s, 9H). 13C-NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3 ) δ 171.01, 167.25, 163.42, 162.01, 159.45, 158.27, 155.84, 147.88, 137.32, 135.05, 134.00, 130.12, 127.42, 125.77, 123.66, 122.57, 121.70, 119.62, 118.71, 116.10, 114.93, 82.18, 44.28, 43.54, 27.43, 24.55. HRMS (m/z): calcd. for 521.1659 ([M + H]+), obsd. 521.1711.
3.1.5. General Procedure for the Preparation of N1-(3-Fluoro-4-hydroxyphenyl)-N3-(4-fluorophenyl)malonamide Derivatives Compounds 12
Diethyl malonate 2.53 mL (17 mmol), iodomethane or 1,2-dibromoethane or 1,3-dibromoethane (22 mmol), K2CO3 5.7 g (42 mmol) and tetrabutylammonium bromide 0.27 g (0.08 mmol) were added in DMF. The mixture is stirred for 16 h at room temperature. After evaporation of solvent, the residue was extracted with ethyl acetate 100 mL three times, and the organic layer was washed with water. After the concentration of the solvent, colorless oil diethyl cyclopropane-1,1-dicarboxylatederivatives were obtained (yield 89%).
Diethyl cyclopropane-1,1-dicarboxylatederivatives (1.0 eq.) were dissolved in EtOH. KOH (1.0 eq.) in ethanol solution was added and stirred for 5 h. After the completion of the reaction, the intermediate was dissolved in THF solution at −15 °C. 4-Methylmorpholine (1.2 eq.), isobutyl chloroformate (1.0 eq.) and 4-amino-2-fluorophenol (1.0 eq.) were added. The crude product was purified by column chromatography, and the above process was repeated. The final product compounds 12 were obtained.
3.1.6. General Procedure for the Preparation of N1-(3-Fluoro-4-methoxyphenyl)-N3-(4-fluorophenyl)malonamide Derivatives Compound 13a–i
Compounds 12 were further reacted with compounds 5, 6, 7 in the presence of K2CO3 to obtain the final products 13a–i as mentioned above.
Compound 13a: N1-{4-((6,7-dimethoxyquinazolin-4-yl)oxy)-3-fluorophenyl}-N3-(4-fluorophenyl)-2,2-dimethylmalonamide. White solid, yield 85%, m.p. 210–212 °C. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.84 (s, 1H), 8.51 (s, 1H), 8.22 (s, 1H), 7.70 (m, 1H), 7.48 (s, 1H), 7.44–7.23 (m, 2H), 7.23–7.15 (m, 1H), 6.97 (t, J = 8.6 Hz, 1H), 3.99 (d, J = 4.3 Hz, 1H), 1.62 (s, 1H). 13C-NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 172.19, 171.92, 165.66, 162.17, 159.64, 156.11, 155.44, 153.27, 152.81, 150.33, 149.47, 136.40, 136.30, 136.20, 136.07, 133.02, 124.10, 122.59, 115.91, 110.17, 109.39, 109.15, 106.81, 100.93, 56.36, 50.76, 24.18. HRMS (m/z): calcd. for 523.1788 ([M + H]+), obsd.535.1791.
Compound 13b: N-{4-[(6,7-dimethoxyquinazolin-4-yl)oxy]-3-fluorophenyl}-N-(4-fluorophenyl)cyclopropane-1,1-dicarboxamide. Yellow solid, yield 86%, m.p. 180–182 °C. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 9.66 (s, 1H), 8.52 (s, 1H), 8.47 (s, 1H), 7.67 (d, J = 11.1 Hz, 1H), 7.48 (s, 1H), 7.38 (dd, J = 9.0, 4.8 Hz, 1H), 7.20 (d, J = 5.5 Hz, 1H), 6.98 (t, J = 8.6 Hz, 1H), 3.99 (d, J = 4.5 Hz, 3H), 1.66 (t, J = 6.1 Hz, 1H), 1.58–1.51 (m, 1H). 13C-NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 169.43, 168.43, 164.68, 156.04, 152.69, 150.36, 149.45, 136.42, 136.03, 124.07, 122.95, 122.87, 116.10, 115.96, 115.73, 110.20, 109.63, 109.40, 106.78, 100.96, 56.37, 31.93, 29.70, 29.29, 22.69, 17.61, 14.12. HRMS (m/z): calcd. for 521.1631 ([M + H]+), obsd.521.1634.
Compound 13c: N-{4-((6,7-dimethoxyquinazolin-4-yl)oxy)-3-fluorophenyl}-N-(4-fluorophenyl)cyclobutane-1,1-dicarboxamide. White solid, yield 80%, m.p. 250–252 °C. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.58 (s, 1H), 8.53 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 8.16 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H), 7.80 (dd, J = 11.9, 2.1 Hz, 1H), 7.57–7.48 (m, 1H), 7.35–7.30 (m, 1H), 7.28 (d, J = 3.4 Hz, 1H), 7.03 (t, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 4.06 (d, J = 4.5 Hz, 1H), 2.06–1.90 (m, 1H), 1.28–1.23 (m, 1H). 13C-NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 170.54, 170.40, 164.67, 160.91, 158.47, 156.02, 155.52, 153.05, 152.69, 150.34, 149.44, 136.64, 136.12, 133.38, 124.14, 122.02, 121.94, 115.88, 115.65, 110.16, 109.09, 108.86, 106.78, 100.93, 56.36, 56.02, 29.76, 15.67. HRMS (m/z): calcd. for 535.1788 ([M + H]+), obsd.535.1793.
Compound 13d: N1-(4-fluorophenyl)-2,2-dimethyl-N3-{4-((2-(methylcarbamoyl)pyridin-4-yl)oxy]phenyl}malonamide. Faint yellow solid, yield 82%, m.p. 113–115 °C. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.72 (s, 1H), 8.54 (s, 1H), 8.37 (d, J = 5.6 Hz, 1H), 8.02 (d, J = 4.0 Hz, 1H), 7.66 (d, J = 1.9 Hz, 1H), 7.60–7.50 (m, 3H), 7.09–6.99 (m, 4H), 6.94 (dd, J = 5.6, 2.5 Hz, 1H), 2.99 (d, J = 5.1 Hz, 3H), 1.70 (s, 6H). 13C-NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 171.71, 166.36, 164.46, 160.93, 158.50, 152.26, 150.23, 149.67, 135.10, 133.32, 122.47, 122.39, 122.32, 121.43, 115.81, 115.59, 114.10, 110.12, 50.69, 29.70, 26.15, 25.36, 24.24. HRMS (m/z): calcd. for 451.1776 ([M + H]+), obsd.451.1779. Calcd. for 473.1596 ([M + Na]+), obsd.473.1602.
Compound 13e: N-(4-fluorophenyl)-N-{4-((2-(methylcarbamoyl)pyridin-4-yl)oxy)phenyl}cyclopropane-1,1-dicarboxamide. White solid, yield 82%, m.p. 138–140 °C. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 9.46 (s, 2H), 8.31 (d, J = 5.6 Hz, 1H), 7.99 (d, J = 4.9 Hz, 1H), 7.54–7.50 (m, 2H), 7.49 (s, 1H), 7.43–7.36 (m, 1H), 6.99 (s, 1H), 6.96 (d, J = 2.6 Hz, 1H), 6.94 (s, 1H), 6.91 (4, 1H), 4.03 (q, 1H), 2.88 (d, J = 5.1 Hz, 3H), 1.19 (t, 2H), 1.13 (d, J = 6.1 Hz, 2H). 13C-NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 169.65, 169.34, 166.39, 164.64, 152.09, 150.24, 149.81, 135.18, 133.43, 123.21, 122.91, 121.42, 115.72, 115.50, 114.39, 109.72, 64.43, 60.43, 28.89, 26.18, 25.35, 21.05, 17.91, 14.19. HRMS (m/z): calcd. for 624.2087 ([M + H]+), obsd.449.1620. calcd. for 471.1439 ([M + Na]+), obsd.471.1464.
Compound 13f: N-(4-fluorophenyl)-N-{4-((2-(methylcarbamoyl)pyridin-4-yl)oxy)phenyl}cyclobutane-1,1-dicarboxamide. White solid, yield 77%, m.p. 192–194 °C. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.29 (s, 1H), 8.27 (d, J = 5.1 Hz, 1H), 8.14 (s, 1H), 7.94 (d, J = 4.5 Hz, 1H), 7.60–7.56 (m, 1H), 7.54 (s, 1H), 7.49–7.38 (m, 1H), 6.96 (dd, J = 8.6, 4.5 Hz, 1H), 6.92 (s, 1H), 6.86 (dd, J = 5.5, 2.5 Hz, 1H), 2.92 (d, J = 5.1 Hz, 1H), 2.68 (t, J = 7.9 Hz, 1H), 2.01–1.88 (m, 1H). 13C-NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 170.49, 170.45, 166.31, 164.53, 152.28, 150.10, 149.71, 135.33, 121.96, 121.88, 121.81, 121.43, 115.80, 115.57, 114.09, 110.09, 64.42, 55.91, 29.78, 26.14, 25.35, 15.68. HRMS (m/z): calcd. for 463.1776 ([M + H]+), obsd.463.1779. calcd. for 485.1596 ([M + Na]+), obsd.485.1602.
Compound 13g: tert-butyl-4-{2-fluoro-4-(3-((4-fluorophenyl)amino)-2,2-dimethyl-3-oxopropanamido)phenoxy}-5,6-dihydropyrido(4’,3’:4,5)thieno(2,3-d)pyrimidine-7(8H)-carboxylate. Faint yellow solid, yield 75%, m.p. 126–128 °C. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.92 (s, 1H), 8.48 (s, 1H), 8.24 (s, 1H), 7.75 (dd, 1H), 7.53–7.45 (m, 2H), 7.25–7.18 (m, 2H), 7.05 (t, J = 8.6 Hz, 2H), 4.74 (s, 2H), 3.80 (t, J = 5.4 Hz, 2H), 3.18 (s, 2H), 1.69 (s, 6H), 1.51 (s, 9H). 13C-NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 171.94, 171.13, 169.06, 162.68, 159.13, 158.67, 154.55, 152.49, 136.38, 135.74, 135.61, 132.99, 124.02, 122.59, 122.51, 118.09, 115.93, 115.81, 115.71, 109.35, 109.11, 80.57, 50.74, 31.93, 29.70, 29.66, 29.37, 28.43, 24.20, 22.70, 19.55, 14.12. HRMS (m/z): calcd. for 624.2087 ([M + H]+), obsd.624.2091. Calcd. for 646.1906 ([M + Na]+), obsd.646.1913.
Compound 13h: tert-butyl-4-{2-fluoro-4-(1-((4-fluorophenyl)carbamoyl)cyclopropanecarboxamido)phenoxy}-5,6-dihydropyrido(4’,3’:4,5)thieno(2,3-d)pyrimidine-7(8H)-carboxylate. White solid, yield 82%, m.p. 171–173 °C. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 9.76 (s, 1H), 8.52 (s, 1H), 8.41 (s, 1H), 7.65–7.34 (m, 3H), 7.22–7.12 (m, 2H), 6.97 (t, J = 8.6 Hz, 2H), 4.66 (s, 2H), 3.72 (t, J = 5.6 Hz, 2H), 3.11 (s, 2H), 1.54 (dd, J = 7.7, 4.9 Hz, 2H), 1.43 (s, 9H), 1.18 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 4H). 13C-NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 169.56, 169.03, 168.49, 162.68, 161.13, 158.69, 155.43, 154.58, 152.97, 152.49, 136.55, 136.45, 135.69, 135.56, 132.87, 123.95, 123.02, 118.21, 116.19, 115.93, 115.81, 109.70, 109.47, 80.70, 60.54, 29.80, 29.34, 28.53, 21.16, 17.65, 14.25. HRMS (m/z): calcd. for 622.1930 ([M+H]+), obsd.622.1930. Calcd. for 644.1750 ([M + Na]+), obsd.644.1793.
Compound 13i: tert-butyl-4-{2-fluoro-4-(1-((4-fluorophenyl)carbamoyl)cyclobutanecarboxamido)phenoxy}-5,6-dihydropyrido(4’,3’:4,5)thieno(2,3-d)pyrimidine-7(8H)-carboxylate. Yellow solid, yield 83%, m.p. 101–103 °C. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.48 (s, 1H), 8.36 (s, 1H), 7.96 (s, 1H), 7.78 (dd, J = 11.9, 2.1 Hz, 1H), 7.56–7.41 (m, 2H), 7.27–7.18 (m, 2H), 7.04 (t, J = 8.6 Hz, 2H), 4.74 (s, 2H), 3.80 (t, J = 5.4 Hz, 2H), 3.18 (s, 2H), 2.85–2.65 (m, 4H), 2.05–1.99 (m, 2H), 1.51 (s, 9H). 13C-NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 170.48, 170.16, 169.07, 162.68, 160.91, 158.51, 155.46, 154.54, 152.99, 152.47, 136.60, 135.79, 135.55, 134.32, 133.24, 131.70, 124.05, 121.99, 121.91, 118.09, 115.91, 115.68, 115.47, 109.04, 108.81, 80.56, 61.84, 55.94, 31.93, 29.75, 29.70, 28.43, 15.68. HRMS (m/z): calcd. for 636.2087 ([M + H]+), obsd.636.2068. Calcd. for 658.1906 ([M + Na]+), obsd.658.1912.
3.2. Cell Proliferative Assay
The anti-proliferative activities of synthesized compounds against HeLa, Hep-G2 and MCF-7 cells were evaluated by MTT assay [10]. HeLa cells were grown to log phase in RPMI 1640 medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum. Hep-G2 and MCF-7 cells were grown to log phase in DMEM medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum. After diluting to 5 × 105 cells∙L−1 with the complete medium, 100 µL of the obtained cell suspension was added to each well of 96-well culture plates. The subsequent incubation was permitted at 37 °C, 5% CO2 atmosphere for 48 h before the anti-proliferative assessments. Tested samples at pre-set concentrations were added to 6 wells. Before the anti-proliferative assessments, 20 µL of PBS containing 2.5 mg∙mL−1 of MTT was added to each well. Four h later, 100 µL extraction solution (DMSO) was added to each well and the optical density was measured at a wavelength of 570 nm on an ELISA microplate reader.
3.3. In Vitro Kinase Assay
In vitro kinase inhibitory ability was determined using HTScan MET Kinase Assay Kit, HTScan VEGF Receptor 2 Kinase Assay Kit, HTScan c-Kit Kinase Assay Kit, HTScan PDGF Receptor β Kinase Assay Kit and HTScan EGFR Kinase Assay Kit(purchased from Cell Signaling Technology, Inc. Danvers, MA, USA) by colorimetric ELISA assay according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Briefly, reaction cocktail containing recombinant human MET kinase or other kinases were incubated with various concentrations of tested compounds or DMSO (0.1%) for 5 min at room temperature, and then ATP/substrate peptide cocktail was added to the pre-incubated reaction cocktail. After incubation at room temperature for 30 min, the reaction was stopped and transferred to a 96-wellstreptavidin-coated plate, and incubated for 1 h at room temperature. Primary antibody (phosphorylated tyrosine monoclonal antibody (pTyr-100), 1:1000 in PBS/T with 1% bovine serum albumin (BSA)) was added into per well until the wells were washed thrice with PBS/T. After incubated at room temperature for 1 h, phosphorylation of the substrate was monitored with HRP-labeled anti-mouse IgG antibody (1:500 in PBS/T with 1% BSA), followed by a chromogenic reaction. Finally, the kinase assay was detected at 450 nm with microplate reader. The reaction processed with only DMSO (0.1%) served as a vehicle control. The results were expressed as percent kinase activity of the vehicle control, and IC50 was defined as the compound concentration that resulted in 50% inhibition of enzyme activity. The kinase assay was performed thrice independently.
3.4. Molecular Dockingand Dynamics Simulation
Molecular docking of compounds into the three dimensional X-ray structure of c-MET (PDB code: 4MXC) and VEGFR-2 (PDB code: 4ASE) was carried out using the Discovery Studio (version3.1) as implemented through the graphical user interface Discovery Studio CDOCKER protocol [32].
The three-dimensional structure of all compounds was constructed using ChemBio 3D Ultra 11.0 software (Chemical Structure Drawing Standard; Cambridge Soft corporation, Waltham, MA, USA), then it was energetically minimized by using MMFF94 with 5000iterations and minimum RMS gradient of 0.10. The crystal structures of VEGFR-2 kinase were retrieved from the RCSB Protein Data Bank (http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/home). All bound waters and ligands were eliminated from the protein and the polar hydrogen was added. The whole protein structure was defined as are acceptor and the site sphere was selected based on ATP binding site of 4ASE or 4MXC. Compounds were placed during the molecular docking procedure. Types of interactions of the docked protein with ligand were analyzed after the end of molecular docking.
To further confirm the binding model of compound 13b with c-MET and VEGFR-2, respectively, MD simulations was performed using the GROMACS package (version 4.5, University of Groningen) [33]. By using the AMBER99 force field and general AMBER force field (gaff), receptor and ligands were charged, respectively [34]. The simulations study were carried out under periodic boundary conditions (PBC) with minimum distance (0.1 nm) between the kinase and the edge of the box. The complex of compound 13b with protein were solvated in a cubic box of TIP3P water molecules and neutralized by adding Na+ and Cl− to mimic physiological NaCl concentration of 0.15 M. Prior to MD simulations, energy minimization were performed to remove bad contacts, 100-ps NVT and 100-ps NPT ensembles with protein and ligand position restraints were carried out to equilibrate each system. Finally, 3-ns MD production simulations were carried out for each system with a 2-fs time step at constant pressure (1 atm) and temperature (300 K).
4. Conclusions
In this study, a series of 3-methoxy-N-phenylbenzamide derivatives, N-(3-(tert-butyl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl) benzamide derivatives and N1-(3-fluoro-4-methoxyphenyl)-N3-(4-fluorophenyl) malonamide derivatives were synthesized, and some of them were identified as potent and selective c-MET inhibitors. Compound 13b showed the most potent inhibitory activity against c-MET with IC50 of 0.02 µM, and it exhibited good anticancer activity against tested cancer cell lines. In addition, compound 11c, 11i, 13h also demonstrated potent c-MET inhibitory activity and excellent anticancer activity in vitro. Importantly, compound 13h showed the highest anti-proliferation activity against Hep-G2 with IC50 of 1.7 µM, which is better than the c-MET inhibitor XL184, suggesting that compound 13h may have great potential for liver cancer therapy. Kinase selectivity assay suggested that compound 13b and 13h also showed a little inhibitory activity against VEGFR-2. Moreover, molecular docking results disclosed binding modes of these potent inhibitors and c-MET. Therefore, compound 11c, 11i, 13b, 13h are potent c-MET inhibitors and could be potential anticancer agents.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to TANG Bioscience (Shanghai, China) for their help in kinase assay. This work is supported by grants from Key Projects of the National Science and Technology Pillar Program (2012BAI30B02), National Natural Science Foundation (Nos. 81260628, 81303270, and U1303124) and Liaoning Science and Technology Project (2013226027-4).
Author Contributions
J.-H.W. and L.-X.C. conceived and designed the experiments; Y.-N.J., K.Z., S.-Y.G. and G.-H.W. performed the experiments; Y.-N.J. and K.Z. analyzed the data; J.H. contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools; J.-H.W. wrote the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Liao, J.J. Molecular recognition of protein kinase binding pockets for design of potent and selective kinase inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 409–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilhelm, S.; Chien, D.S. BAY 43-9006: Preclinical data. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2002, 8, 2255–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jennifer, S.; Lazarus, R.A.; Xiaoyi, Y. Crystal structure of the HGF β-chain in complex with the Sema domain of the MET receptor. Embo J. 2004, 23, 2325–2335. [Google Scholar]
- Bottaro, D.P.; Rubin, J.S.; Faletto, D.L. Identification of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor as the c-MET protooncogene product. Science 1991, 251, 802–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naldini, L.; Weidner, K.M.; Vigna, E. Scatter factor and hepatocyte growth factor are indistinguishable ligands for the MET receptor. Int. J. Miner. Metal. Mater. 1991, 10, 2867–2878. [Google Scholar]
- Huh, C.G.; Factor, V.M.; Sánchez, A. Hepatocyte growth factor/c-MET signaling pathway is required for efficient liver regeneration and repair. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 4477–4482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkmann, V.; Foroutan, H.; Sachs, M. Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor induces a variety of tissue-specific morphogenic programs in epithelial cells. J. Cell Biol. 1995, 131, 1573–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comoglio, P.M.; Giordano, S.; Trusolino, L. Drug development of MET inhibitors: Targeting oncogene addiction and expedience. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 504–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trusolino, L.; Comoglio, P.M. Scatter-factor and semaphorin receptors: Cell signalling for invasive growth. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.Y.; Li, S.N.; Yu, G.J. Discovery of novel 4-anilinoquinazoline derivatives as potent inhibitors of epidermal growth factor receptor with antitumor activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 6084–6091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seiwert, T.Y.; Jagadeeswaran, R.; Faoro, L. The MET receptor tyrosine kinase is a potential novel therapeutic target for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 3021–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuda, K.; Sasaki, H.; Yukiue, H.; Yano, M.; Fujii, Y. MET gene copy number predicts the prognosis for completely resected non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Sci. 2008, 99, 2280–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Newton, R.C.; Scherle, P.A. Development of c-MET pathway inhibitors. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2011, 20, 1225–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, S.; Miyamoto, N.; Hirayama, T. Structure-based design, synthesis, and evaluation of imidazo[1,2-b]pyridazine and imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine derivatives as novel dual c-MET and VEGFR2 kinase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 7686–7698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saavedra, O.; Szhan, C. N3-arylmalonamides: A new series of thieno[3,2-b]pyridine based inhibitors of c-MET and VEGFR2 tyrosine kinases. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 6836–6839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Q.; Zhang, G.; Du, X. Discovery of novel 6,7-disubstituted-4-phenoxyquinoline derivatives bearing 5-(aminomethylene)pyrimidine-2,4,6-trione moiety as c-MET kinase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 1236–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mifune, Y.; Matsumoto, T.; Takayama, K. The effect of platelet-rich plasma on the regenerative therapy of muscle derived stem cells for articular cartilage repair. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2013, 21, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simard, J.R.; Getlik, M.; Grütter, C. Fluorophore labeling of the glycine-rich loop as a method of identifying inhibitors that bind to active and inactive kinase conformations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 4152–4160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamed, M.M. Quinazoline and tetrahydropyridothieno[2,3-d]pyrimidine derivatives as irreversible EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors: Influence of the position 4 substituent. Med. Chem. Commun. 2013, 4, 1202–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Norman, M.H.; Lee, M. Structure-based design of novel class II c-MET inhibitors: 2. SAR and kinase selectivity profiles of the pyrazolone series. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 1868–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dussault, I.; Bellon, S.F. From concept to reality: The long road to c-MET and RON receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors for the treatment of cancer. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2009, 9, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowles, D.W.; Kessler, E.R.; Jimeno, A. Multi-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitors in clinical development: focus on XL-184 (cabozantinib). Drugs of Today 2011, 47, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- She, N.; Zhuo, L.; Jiang, W. Design, synthesis and evaluation of highly selective pyridone-based class II MET inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 3351–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Wu, T.T.; Wang, Z. Discovery of quinazolin-4-amines bearing benzimidazole fragments as dual inhibitors of c-MET and VEGFR-2. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 4735–4744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Kang, Y.; Kim, J.T. The anti-angiogenic and anti-tumor activity of synthetic phenylpropenone derivatives is mediated through the inhibition of receptor tyrosine kinases. Eur. J. Pharmaco. 2012, 677, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadek, M.M.; Serrya, R.A.; Kafafy, A.H. Discovery of new HER2/EGFR dual kinase inhibitors based on the anilinoquinazoline scaffold as potential anti-cancer agents. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2014, 29, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.H.; Coumar, M.S.; Chu, C.Y. Design and synthesis of tetrahydropyridothieno[2,3-d]pyrimidine scaffold based epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) kinase inhibitors: The role of side chain chirality and michael acceptor group for maximal potency. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 7316–7326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nourry, A.; Zambon, A.; Davies, L. BRAF inhibitors based on an imidazo[4,5]pyridin-2-one scaffold and a meta substituted middle ring. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 1964–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chackalamannil, S.; Chung, S.; Stamford, A.W. Highly potent and selective inhibitors of endothelin converting enzyme. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1996, 6, 1257–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ai, J.; Peng, X. Novel 2,4-diarylaminopyrimidine analogues (DAAPalogues) showing potent c-MET/ALK multikinase inhibitory activities. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 304–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.M.; Tsai, C.H.; Hung, W.C. Foretinib inhibits angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis and tumor growh of pancreatic cancer in vivo by decreasing VEGFR-2/3 and TIE-2 signaling. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 14940–14952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Discovery Studio Modeling Environment; Version 3.5; Accelrys Software Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 2011.
- Pronk, S.; Páll, S.; Schulz, R.; Larsson, P.; Bjelkmar, P.; Apostolov, R.; Shirts, M.R.; Smith, J.C.; Kasson, P.M.; van der Spoel, D.; et al. GROMACS 4.5: A high-throughput and highly parallel open source simulation toolkit. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wolf, R.M.; Caldwell, J.W.; Kollman, P.A.; Case, D.A. Development and testing of a general amber force field. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1157–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors.
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).