Abstract
A novel twin drug consisting of nicotinic acid (VB3) and quercetin tetramethyl ether (QTME) has been synthesized as an antihypertensive in a total yield of 79.2% through methylation, hydrolysis, acylation and esterification starting from rutin. The structures of synthesized compounds were elucidated by 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR and elemental analysis. The anti-hypertensive effects of an oral daily dose (15 mg/kg) of the synthesized compounds in spontaneously hypertensive (SHR) rats and normotensive Wistar Kyoto (WKY) rats were analysed. The data demonstrate that the twin drug VB3-QTME both reduces the elevated blood pressure and prolongs the action time in SHR rats without effect on WKY rats. However, definitive evidence of a precise mechanism of action by which VB3-QTME might decrease blood pressure remains elusive. Based on the results, the therapeutic potential of this twin drug is discussed.
Keywords:
rutin; nicotinic acid; synthesis; twin drug; VB3-QTME; SHR rats; anti-hypertensive effects 1. Introduction
Hypertension is a chronic medical condition that can cause diverse complications which may not only markedly impair the quality of life but also cause a heavy financial burden on families and society. Currently, the incidence of hypertension is the highest in the world among all diseases, affecting one-third of the global adult population []. As an important public-health challenge worldwide, the prevention, detection, treatment, and control of hypertension should receive high priority []. A majority of hypertensive patients receive two or more antihypertensive drugs, and it shows that although many patients reach blood pressure goal, combination antihypertensive therapy is often needed [,,,]. A drug with a single target cannot meet the demands of complex diseases and thus lack efficacy, although considerable progress has been made in the field of antihypertensive drugs. In fact, adverse events with monotherapy and combination therapy were as anticipated for the specific classes of antihypertensive therapy []. Thus, the enthusiasm still remains about the development and development of safer antihypertensive.
Western medicines show rapid and remarkable effects against hypertension, but these drugs show toxic effects clinically. Although Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has gained much attention clinically because of its advantages of lower toxicity and fewer side effects, protection of target organs, multiple targets, and multiple pathways, its disadvantage is that these drugs require a long time to exert their effects [,,]. There are potential advantages in giving such agents with complementary pharmacological activities in the form of a single chemical entity [,].
Epidemiological studies have shown an inverse association of flavonoid-rich diet consumption with the risk of hypertension and cardiovascular disease []. Quercetin is the most common flavone in the human diet, it has a wide range of reported biological effects, including antioxidant, antihypertensive, antimicrobial, and antiprotozoal activities [,,,,]. Nicotinic acid (niacin, VB3), one of the older drugs used to treat hyperlipidemia, was shown to reduce low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (LDL-C) and triglycerides and to markedly increase high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (HDL-C) levels [,,,]. However, because of nicotinic acid’s acute vasodilatory effects, it also reduces blood pressure (BP), which is an cardiovascular disease risk factor [,,,,].
In the present study, quercetin was selected for conjugation with nicotinic acid to obtain a quercetin-antihypertensive double prodrug. Although, linking of quercetin with VB3 in 1:1 ratio is difficult due to the presence of a number of hydroxyl groups, we have been able to conjugate this agent in the form of its derivative, quercetin tetramethyl ether (QTME) with VB3. In this paper, synthesis and anti-hypertensive activity of the twin drug of nicotinic acid and quercetin tetramethyl ether (VB3-QTME) are reported.
2. Results and Discussion
To conjugate the polyphenolic flavonoid quercetin with carboxyl group containing anti-antihypertensive drugs in 1:1 ratio, an alternative strategy was developed. For this purpose, rutin (2), the glycoside of quercetin was treated with methyl iodide (CH3I) in dry dimethyl formamide (DMF) in the presence of potassium carbonate (K2CO3). The methylated glycoside 3 was obtained as semisolid, which was subjected to hydrolysis by refluxing in acidic aqueous solution to obtain the quercetin derivative, quercetin tetramethyl ether (QTME, 4). The free hydroxyl group generated at 3-position in this derivative was used as a synthetic handle for conjugation with the VB3 (5). Compound 5 was treated with thionyl chloride (SOCl2) by stirring at reflux and after removing excess of SOCl2, nicotinoyl chloride hydrochloride 6 was obtained as a white solid. QTME was treated with compound 6, dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC) and 4-dimethylaminopyridine (DMAP) using dichloromethane as solvent and the desired derivative, VB3-QTME (1) was obtained as light yellow solid, with a total yield of 79.2%. The sequence of various steps involved in the reactions is shown in Scheme 1.
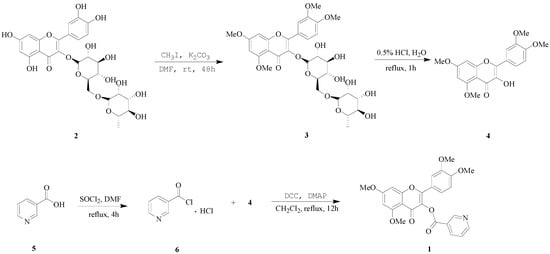
Scheme 1.
Synthetic route to VB3-QTME.
We tested the antihypertensive effects of this VB3-QTME twin drug in sixteen-week-old SHR where the hypertension is well established. Our results showed that, while having no effect on blood pressure in control WKY rats, the VB3-QTME caused significantly more pronounced reduction in systolic blood pressure in SHR compared to combined use of VB3 and QTME. The antihypertensive effects of VB3-QTME appeared to last slightly longer than the combined use of two agents. And it is not surprising that a number of laboratories have reported that quercetin lowers blood pressure in spontaneously hypertensive [] and Dahl salt-sensitive rats [] as well as rats that consume a high-sucrose diet [], are deficient in NO [], are infused with angiotensin [], or have experimentally induced pressure overload using aortic constriction []. The aforementioned animal studies have provided important proof-of-principle that quercetin may be efficacious in decreasing blood pressure. What is more, mechanism of hypotensive action of nicotinic acid remains elusive. As to VB3-QTME, potential mechanisms maybe more complex, as it could include both mechanisms of VB3 and QTME/quercetin, definitive evidence of a precise mechanism remains elusive.
3. Experimental
3.1. General Information
All commercial reagents and solvents were used as received without further purification unless specified and reactions were monitored by thin-layer chromatography (TLC) on normal-phase silica gel GF254 plates. Spots on the TLC plates were visualized using ultraviolet light (254 nm or 365 nm). Silica gel (200–300 mesh) was used as stationary phase to isolate the compounds. 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR spectra were run on Bruker Advance DPX 500- and 125-MHz spectrometers in CDCl3-d or DMSO-d6, and tetramethylsilane (TMS) was used as the internal standard. High resolution (HR)-electrospray ionization (ESI)-mass spectroscopy (MS) was measured on a Bruker APEX IV FT-MS (7.0 T) mass spectrometer in positive-ion mode. ESI-MS was obtained on an Agilent XCT 6320 IT mass spectrometer.
3.2. Chemistry Synthesis
3.2.1. Preparation of 5,7,3',4'-O-tetramethylrutin (3)
To a fine suspension of rutin (2, 1.8 g, 3.0 mmol) in dry N,N-dimethylformamide (30 mL), anhydrous potassium carbonate (4.2 g, 30.0 mmol) and methyl iodide (1.9 mL, 30.0 mmol) were added and the reaction mixture was refluxed for 48 h. The solution was filtered and insoluble potassium salts were washed with acetone. The washings were combined with the filtrate and solvent was removed under reduced pressure to obtain methylated glycoside 3 as a semisolid residue.
3.2.2. Preparation of Quercetin 5,7,3',4'-tetramethyl Ether (QTME, 4)
The above product was refluxed with aqueous hydrochloric acid (0.5%, 300 mL) for 1 h. The solvent was removed after cooling and the residue obtained was washed with distilled water to neutral to give QTME (4, 0.99 g, 92.2%), yellow solid, mp 195–197 °C (lit []: mp 194 °C). 1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 6.33 (1H, d, J = 2.01 Hz, C-6-H), 6.53 (1H, d, J = 2.01 Hz, C-8-H), 7.53 (1H, d, J = 8.50 Hz, C-5'-H), 7.72 (1H, dd, J = 8.50 Hz, J = 2.50 Hz, C-6'-H), 7.79 (1H, d, J = 2.50 Hz, C-2'-H), 9.47 (s, 1H, 3-OH), 3.87–3.97 (s, 12H, 4 × -OCH3). 13C-NMR (DMSO-d6) δ: 172.658 (C-4), 164.147 (C-9), 160.528 (C-7), 156.572 (C-2), 150.338 (C-5), 146.608 (C-4'), 142.148 (C-3'), 138.030 (C-3), 123.705 (C-1'), 120.666 (C-6'), 110.995 (C-2'), 110.341 (C-5'), 106.302 (C-1'), 96.198 (C-6), 95.555 (C-8), 56.581, 56.086, 55.831, 55.627 (4-OCH3). Anal. calcd. for C19H18O7: C, 63.68; H, 5.06; O, 31.25. Found: C, 63.81; H, 5.11. HRMS (ESI) m/z: 359.11804 [M+H]+, calcd. for C19H19O7 359.11253. Spectroscopic data of the compound was consistent with those in the literatures [,,].
3.2.3. Preparation of Nicotinoyl Chloride Hydrochloride (6)
Under the anhydrous condition, nicotinic acid (8.12 mmol) and 2 drops of dry DMF were added into the vigorously stirred SOCl2 (10 mL) at 0 °C. The reaction mixture was heated to 78 °C to reflux for 3 h to yield the yellow solid after the excess SOCl2 was evaporated under reduced pressure. Then 10 mL diethyl ether was added to reflux for 1 h, and then filtered to obtain the white solid nicotinoyl chloride hydrochloride 1.388 g (yield: 96.0%).
3.2.4. Synthesis of VB3-QTME (1)
QTME (0.050 g, 0.14 mmol) and nicotinoyl chloride hydrochloride (0.027 g, 0.15 mmol) were dissolved in dichloromethane (30 mL) containing DCC (0.173 g, 0.84 mmol) and DMAP (0.149 g, 0.84 mmol). The reaction mixture was stirred at reflux for 12 h. After reaction, the solvent was removed under reduced pressure. After washing with saturated Na2CO3 and NH4Cl, successively, the solid product obtained was chromatographed on silica gel column using petroleum ether/ethyl acetate/acetone/methyl alcohol (200:100:30:40) as eluent and the solvent was removed under reduced pressure to obtain light yellow needle-like crystals of VB3-QTME (1); yield (0.058 g, 89.5%), mp 168–170 °C. 1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 6.40 (1H, d, J = 2.02 Hz, C-6-H), 6.59 (1H, d, J = 2.02 Hz, C-8-H), 6.94 (1H, d, J = 2.50 Hz, C-2'-H), 7.53 (2H, ABq, J = 8.50 Hz, C-5'-H, C-6'-H), 9.47 (1H, s, PyC-2-H), 8.90 (1H, d, PyC-6-H), 8.47 (1H, d, PyC-4-H), 7.41 (1H, t, PyC-5-H), 3.84–3.94 (s, 12H, 4 × -OCH3). 13C-NMR (DMSO-d6) δ: 172.519 (C-4), 164.505 (C-7), 163.295 (ester C=O), 160.528 (C-5), 159.294 (C-9), 155.294 (C-2), 152.526 (PyC-3'), 151.293 ((PyC-2'), 142.148 (C-3'), 141.171 (C-4'), 138.005 (C-3), 135.028 (PyC-5'), 125.521 (PyC-1'),124.677 (PyC-4'), 121.511 (C-1'), 120.666 (C-6'), 110.995 (C-2'), 110.341 (C-5'), 108.087 (C-1'), 96.198 (C-6), 93.908 (C-8), 56.577, 56.093, 55.826, 55.622 (4 -OCH3). Anal. calcd. for C25H21NO8: C, 64.79; H, 4.57; N, 3.02; O, 27.62. Found: C, 64.83; H, 4.59; N, 2.97. HRMS (ESI) m/z: 464.13925 [M+H]+, calcd. for C25H22NO8 464.13400.
3.3. Animal Experiments
Sixteen-week-old, male SHR and WKY rats were obtained from Weitong-Lihua Experimental Animal Technical Co., LTD (Beijing, China). All the experiments were performed in accordance with Institutional Guidelines for the ethical care of animals. All rats were maintained three per cage at a constant temperature (24 + 1 °C), with a 12 h dark/light cycle and on standard rat chow. An adaptation period of 2 weeks for vehicle administration and blood pressure measurements was allowed before the initiation of the experimental protocols.
Twenty-four SHR (six rats/group) were randomly assigned to a VB3-QTME group (15.0 mg/kg/day, 32.4 mmol/kg/day, mixed in 1 mL of 0.5% carboxymethylcellulose sodium), a quercetin group (9.8 mg/kg/day, 32.4 mmol/kg/day, mixed in 1 mL of 0.5% carboxymethylcellulose sodium), a nicotinic acid+QTME group (15.6 mg/kg/day, nicotinic acid and QTME each 32.4 mmol/kg/day, mixed in 1 mL of 0.5% carboxymethylcellulose sodium), a SHR vehicle group(1 mL of 0.5% carboxymethylcellulose sodium). Six WKY were assigned to a vehicle group (1 mL of 0.5% carboxymethylcellulose sodium), another six WKY were assigned to a VB3-QTME group (15.0 mg/kg/day, 32.4 mmol/kg/day, mixed in 1 mL of 0.5% carboxymethylcellulose sodium). During the experimental periods all the rats had free access to tap water and chow.
Before treatment, rats were trained to the procedure and measurements were recorded. Then rats were dosed once daily by oral gavage with 32.4 mmol/kg of test compounds on each of the 7 days. Systolic blood pressures were measured 4 hours after the oral gavage on each of the 7 days in awake rats by the tail-cuff method (Softron BP-98A, Softron, Beijing, China). At least six determinations were made in every session and the mean of the middle four values was taken as the systolic blood pressure level. At the end of the last day’s treatment, tail systolic blood pressures were then continuously measured in conscious rats in the following 4 h, 8 h, 12 h, 24 h, 48 h, 72 h.
The data were given as means ± SEM. Comparison between experimental groups were made by using one-way ANOVA, followed by student Newman Keuls test. p values < 0.05 were considered significant (SPSS (PASW)17.0). Systolic blood pressures of SHR and Wistar rats before and after treatment are presented on Figure 1. Systolic blood pressures of SHR after the 7 days’ treatment VB3-QTME or nicotinic acid+QTME are presented on Figure 2.
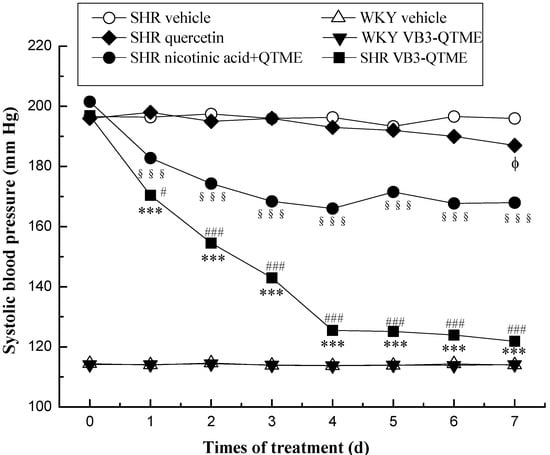
Figure 1.
SBP in SHR and WKY rats before and after treatment. Antihypertensive effect of test compounds (SHR VB3-QTME, 15.0 mg/kg/day; SHR nicotinic acid+QTME, 15.6 mg/kg/day; SHR vehicle; WKY VB3-QTME, 15.0 mg/kg/day; WKY vehicle) during continuous feeding in rats. Each point represents the mean SBP in six rats. The data were given as means ± SEM. Comparison between experimental groups were made by using one-way ANOVA, followed by student Newman Keuls test. p values < 0.05 were considered significant (SPSS (PASW) 17.0). *** p < 0.001, between before and after VB3-QTME treatment; §§§ p < 0.001, between before and after nicotinic acid+QTME treatment; ϕ p < 0.05, between before and after quercetin treatment; # p < 0.05, ### p < 0.001, SHR VB3-QTME compared to SHR nicotinic acid+QTME.
Figure 1, ● represents the changes in tail systolic blood pressures of SHR orally administered nicotinic acid+QTME (each 32.4mmol/kg), and it was observed that the blood pressure remarkably declined after administration (§§§ p < 0.001). ◆ represents the changes in tail systolic blood pressures of SHR with quercetin(32.4mmol/kg), and it was observed that the blood pressure declined after 7 days’ administration (ϕ p < 0.05). ■ represents the changes in tail systolic blood pressures of SHR orally administered VB3-QTME (32.4mmol/kg), and it was observed that the blood pressure remarkably declined after administration (*** p < 0.001). However, the VB3-QTME group exhibited more significant (# p < 0.05 on the first day, ### p < 0.001 on the next other days) reduction effects on blood pressure.
Figure 2, ◆ represents the changes in tail systolic blood pressures of SHR with VB3-QTME, it was observed that the maximal reduction of blood pressure at the eighth hour after the 7 days’ administration, and the anti-hypertensive activity of VB3-QTME can last 48 h (*** p < 0.001). ● represents the changes in tail systolic blood pressures of SHR with nicotinic acid+QTME, it was observed that the maximal reduction of blood pressure at the fourh hour after the 7 days’ administration, and the anti-hypertensive activity of VB3-QTME can last 24 h (*** p < 0.001). However, the VB3-QTME group exhibited longer duration effects on blood pressure.
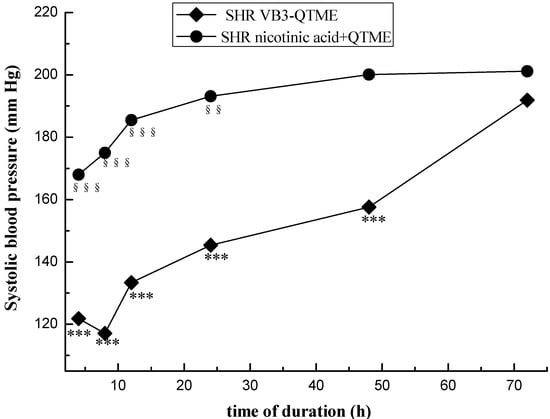
Figure 2.
Duration time after the 7 days’ VB3-QTME and nicotinic acid+QTME treatment in SHR. Each point represents the mean SBP in six rats. The data were given as means ± SEM. *** p < 0.001, between before treatment and after the 7 days’ treatment VB3-QTME; §§ p < 0.01, §§§ p < 0.001, between before treatment and after the 7 days’ treatment nicotinic acid+QTME.
Herein we demonstrated that treatment with nicotinic acid+QTME for 7 days (15.6 mg/kg/day, each 32.4 mmol/kg/day) produced an around 15%-reduction in systolic blood pressure, and the treatment with VB3-QTME for 7 days (15.0 mg/kg/day) almost normalized systolic blood pressure. Similar to our data, other study in SHR documented that treatment with quercetin for 7 days (10.0 mg/kg/day) produced a 10%-reduction in mean blood pressure []. Another study in SHR documented that treatment with quercetin for five weeks (10 mg/kg/day) reduced blood pressure around 21%, but had no effect in normotensive animals []. In addition, data from the literature indicates that there is no difference between the oral administration of quercetin as a single or divided into two daily doses [].
Evidence exists to support several potential mechanisms whereby quercetin might decrease blood pressure and decrease the severity of hypertension in animals and humans. These mechanisms are a decrease in oxidative stress, interference with the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), and/or improving vascular function in an endothelium-dependent or -independent manner [,,,,]. As to VB3-QTME, potential mechanisms maybe more complex, as it could include both mechanisms of VB3 and QTME/quercetin, definitive evidence of a precise mechanism remains elusive. Furthermore, it needs to be determined whether VB3-QTME is an effective treatment for all forms of hypertension regardless of pathological origin. However, despite the uncertainty of the mechanism of action of VB3-QTME, it has promise for the treatment of hypertension.
4. Conclusions
Herein, an efficient and convenient synthesis of VB3-QTME consisting of VB3 and QTME has been achieved by a four-step reaction starting from the readily available nicotinic acid and rutin through methylation, hydrolysis, acylation and esterification in 79.2% yields is presented. The anti-hypertensive activity of VB3-QTME was recorded, and the data demonstrate that this twin drug both reduces the elevated blood pressure and prolongs the action time in SHR rats without effect on WKY rats. Based on the results, the exact mechanism of VB3-QTME and its applications are yet to be explored further.
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the Analytical and Testing Center of Beijing Normal University and the Experimental Animal Center of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine for their constant encouragement and support.
Author Contributions
Zhonglei Wang, Liyan Yang, and Xiaohua Zhang participated in designing the study. Zhonglei Wang, Shuai Cui and Yingxi Liang conducted the study. Data was collected and analyzed by Zhonglei Wang. Manuscript was written by Zhonglei Wang. Xiaohua Zhang approved for manuscript final version.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gammon, K. Drugs: Blood battles. Nature 2013, 493, S14–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearney, P.M.; Whelton, M.; Reynolds, K.; Muntner, P.; Whelton, P.K.; He, J. Global burden of hypertension: Analysis of worldwide data. Lancet 2005, 365, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.J.; Palmer, C.R.; Castaigne, A.; de Leeuw, P.W.; Mancia, G.; Rosenthal, T.; Ruilope, L.M. Morbidity and mortality in patients randomised to double-blind treatment with a long-acting calcium-channel blocker or diuretic in the International Nifedipine GITS study: Intervention as a Goal in Hypertension Treatment (INSIGHT). Lancet 2000, 356, 366–372. [Google Scholar]
- Wing, L.M.; Reid, C.M.; Ryan, P.; Beilin, L.; Brown, M.; Jennings, G.; Johnston, C.; McNeil, J.; Macdonald, G.; Marley, J.; et al. A comparison of outcomes with angiotensin-converting–enzyme inhibitors and diuretics for hypertension in the elderly. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staessen, J.A.; Fagard, R.; Thijs, L.; Celis, H.; Arabidze, G.G.; Birkenhäger, W.H.; Bulpitt, C.J.; de Leeuw, P.W.; Dollery, C.T.; Fletcher, A.E.; et al. Randomised double-blind comparison of placebo and active treatment for older patients with isolated systolic hypertension. The Systolic Hypertension in Europe (Syst-Eur) Trial Investigators. Lancet 1997, 350, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamerson, K.; Weber, M.A.; Bakris, G.L.; Dahlöf, B.; Pitt, B.; Shi, V.; Hester, A.; Gupte, J.; Gatlin, M.; Velazquez, E.J. Benazepril plus amlodipine or hydrochlorothiazide for hypertension in high-risk patients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 2417–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakris, G.; Sarafidis, P.; Agarwal, R.; Ruilope, L. Review of blood pressure control rates and outcomes. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. 2014, 8, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabassum, N.; Ahmad, F. Role of natural herbs in the treatment of hypertension. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2011, 5, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.J.; Yang, X.C.; Liu, Y.M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, P.Q.; Wang, J. Chinese herbal formulas for treating hypertension in traditional Chinese medicine: Perspective of modern science. Hypertens. Res. 2013, 36, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Yang, L.Y.; Yang, X.W.; Zhang, X.H. Advances in the first total synthesis of natural flavonoids. Synthetic. Commun. 2013, 23, 3093–3114. [Google Scholar]
- Bhosle, D.; Bharambe, S.; Gairola, N.; Dhaneshwar, S.S. Mutual prodrug concept: Fundamentals and applications. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 1994, 56, 69–79. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.H.; Xu, X.J.; Zhang, M.Z.; Wang, L. A New Practice: Study on the Molecular Mechanism of Traditional Chinese Medicine by Computational Pharmacology Methods: Part 2: Pharmacodynamic Modeling and Distribution on Ligand-Target Space of Effective Components. Lett. Drug Des. Discov. 2011, 8, 1009–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cienfuegos-Jovellanos, E.; Quiñones, M.M.; Muguerza, B.; Moulay, L.; Miguel, M.; Aleixandre, A. Antihypertensive effect of a polyphenol-rich cocoa powder industrially processed to preserve the original flavonoids of the cocoa beans. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 6156–6162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca-Silva, F.; Inacio, J.D.F.; Canto-Cavalheiro, M.M.; Almeida-Amaral, E.E. Reactive oxygen species production by quercetin causes the death of leishmania amazonensis intracellular amastigotes. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 1505–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.Y.; Kim, M.K.; Mok, H.; Choo, H.; Chong, Y. Separation of quercetin’s biological activity from its oxidative property through bioisosteric replacement of the catecholic hydroxyl groups with fluorine atoms. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 6499–6506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, F.A.; Takaishi, Y.; Shirotori, M.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Tsuchiya, K.; Shibata, H.; Higuti, T.; Tadokoro, T.; Takeuchi, M. Antibacterial and antioxidant activities of quercetin oxidation products from yellow onion (allium cepa) skin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 3551–3557. [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Vizcaino, F.; Duarte, J.; Jimenez, R.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Osuna, A. Antihypertensive effects of the flavonoid quercetin. Pharmacol. Rep. 2009, 61, 67–75. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Oue, E. Antihypertensive effect of quercetin in rats fed with a high-fat high-sucrose diet. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2006, 70, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschini, G.; Favari, E.; Calabresi, L.; Simonelli, S.; Bondioli, A.; Adorni, M.P.; Zimetti, F.; Gomaraschi, M.; Coutant, K.; Rossomanno, S.; et al. Differential effects of fenofibrate and extended-release niacin on high-density lipoprotein particle size distribution and cholesterol efflux capacity in dyslipidemic patients. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2013, 7, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boden, W.E.; Sidhu, M.S.; Toth, P.P. The therapeutic role of niacin in dyslipidemia management. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 19, 141–158. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, J.; Chan, D.C.; Hamilton, S.J.; Tenneti, V.S.; Watts, G.F.; Barrett, P.H. Effect of niacin on high-density lipoprotein apolipoprotein A-I kinetics in statin-treated patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scoffone, H.M.; Krajewski, M.; Zorca, S.; Bereal-Williams, C.; Little, P.; Seamon, C.; Mendelsohn, L.; Footman, E.; Abi-Jaoudeh, N.; Sachdev, V.; et al. Effect of extended-release niacin on serum lipids and on endothelial function in adults with sickle cell anemia and low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels. Am. J. Cardiol. 2013, 112, 1499–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulaeva-Panova, M.V. Effect of nicotinic acid on blood pressure and on electrolyte content of the blood; in hypertension; mechanism of hypotensive action of nicotinic acid. Ter. Arkh. 1952, 24, 30–35. [Google Scholar]
- Ruggieri, R. Various nicotinic acid derivatives & their hypotensive & vasodilatation effects. G. Med. Mil. 1957, 107, 460–462. [Google Scholar]
- Bays, H.E.; Maccubbin, D.; Meehan, A.G.; Kuznetsova, O.; Mitchel, Y.B.; Paolini, J.F. Blood pressure-lowering effects of extended-release niacin alone and extended-release niacin/laropiprant combination: A post hoc analysis of a 24-week, placebo-controlled trial in dyslipidemic patients. Clin. Ther. 2009, 31, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bays, H.E.; Rader, D.J. Does nicotinic acid (niacin) lower blood pressure? Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2009, 63, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadegbeku, C.A.; Dhandayuthapani, A.; Shrayyef, M.Z.; Eqan, B.M. Hemodynamic effects of nicotinic acid infusion in normotensive and hypertensive subjects. Am. J. Hypertens. 2003, 16, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, J.; Galisteo, M.; Ocete, M.A.; Perez-Vizcaino, F.; Zarzuelo, A.; Tamargo, J. Effects of chronic quercetin treatment on hepatic oxidative status of spontaneously hypertensive rats. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2001, 221, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackraj, I.; Govender, T.; Ramesar, S. The antihypertensive effects of quercetin in a salt-sensitive model of hypertension. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2008, 51, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchal, S.K.; Poudyal, H.; Brown, L. Quercetin Ameliorates Cardiovascular, Hepatic, and Metabolic Changes in Diet-Induced Metabolic Syndrome in Rats. J. Nutr. 2012, 142, 1026–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, A.; Witman, M.A.; Guo, Y.; Ives, S.; Richardson, R.S.; Bruno, R.S.; Jalili, T.; Symons, J.D. Acute, quercetin-induced reductions in blood pressure in hypertensive individuals are not secondary to lower plasma angiotensin-converting enzyme activity or endothelin-1: Nitric oxide. Nutr. Res. 2012, 32, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Zhang, J.D.; Wang, B.; Lv, Y.J.; Jiang, H.; Liu, G.L.; Qiao, Y.; Ren, M.; Guo, X.F. Quercetin inhibits left ventricular hypertrophy in spontaneously hypertensive rats and inhibits angiotensin II-induced H9C2 cells hypertrophy by enhancing PPAR-γ expression and suppressing AP-1 activity. PLoS One 2013, 8, e72548. [Google Scholar]
- Jalili, T.; Carlstrom, J.; Kim, S.; Freeman, D.; Jin, H.; Wu, T.C.; Litwin, S.E.; Symons, J.D. Quercetin-supplemented diets lower blood pressure and attenuate cardiac hypertrophy in rats with aortic constriction. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2006, 47, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangaswamy, S.; Sambamurthy, K. Chemical examination of the leaves of Rhododendron nilagiricum Zenk. Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. 1959, 50, 366–373. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, W.J.; Han, X.W.; Yu, B. Synthesis of C-aryl-flavonoid derivatives via Suzuki-Miyaura coupling reaction. Chin. J. Chem. 2006, 24, 1154–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heijnen, C.G.; Haenen, G.R.; Vekemans, J.A.; Bast, A. Peroxynitrite scavengingof flavonoids: Structure activity relationship. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2001, 10, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.W.; Wu, H.T.; Lee, Y.J. Regioselective hydroxylationof 2-hydroxychalcones by dimethyldioxirane towards polymethoxylated flavonoids. Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 2647–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, M.M.O.; França-Silva, M.S.; Alves, N.F.B.; Porpino, S.K.P.; Braga, V.A. Quercetin improves baroreflex sensitivity in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Molecules 2012, 17, 12997–13008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, J.; Pérez-Palencia, R.; Vargas, F.; Ocete, M.A.; Pérez-Vizcaino, F.; Zarzuelo, A.; Tamargo, J. Antihypertensive effects of the flavonoid quercetin in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 133, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo, P.; González-Manzano, S.; Zarzuelo, M.J.; Gómez-Guzmán, M.; Quintela, A.M.; González-Paramás, A.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Pérez-Vizcaíno, F.; Duarte, J.; Jiménez, R. Different cardiovascular protective effects of quercetin administered orally or intraperitoneally in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Food Funct. 2012, 3, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häckl, L.P.; Cuttle, G.; Dovichi, S.S.; Lima-Landman, M.T.; Nicolau, M. Inhibition of angiotensin-converting enzyme by quercetin alters the vascular response to bradykinin and angiotensin I. Pharmacology 2002, 65, 182–186. [Google Scholar]
- Duarte, J.; Jimenez, R.; O’Valle, F.; Galisteo, M.; Perez-Palencia, R.; Vargas, F.; Perez-Vizcaino, F.; Zarzuelo, A.; Tamargo, J. Protective effects of the flavonoid quercetin in chronic nitric oxide deficient rats. J. Hypertens. 2002, 20, 1843–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Vizcaino, F.; Ibarra, M.; Cogolludo, A.L.; Duarte, J.; Zaragoza-Arnaez, F.; Moreno, L.; Lopez-Lopez, G.; Tamargo, J. Endothelium-independent vasodilator effects of the flavonoid quercetin and its methylated metabolites in rat conductance and resistance arteries. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2002, 302, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, A.J.; Symons, J.D.; Jalili, T. Therapeutic potential of quercetin to decrease blood pressure: Review of efficacy and mechanisms. Adv. Nutr. 2012, 3, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, M.; Jiménez, R.; Sánchez, M.; López-Sepúlveda, R.; Zarzuelo, M.J.; O’Valle, F.; Zarzuelo, A.; Pérez-Vizcaíno, F.; Duarte, J. Quercetin inhibits vascular superoxide production induced by endothelin-1: Role of NADPH oxidase, uncoupled eNOS and PKC. Atherosclerosis 2009, 202, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 1–6 are available from the authors.
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).