Abstract
Two novel series of RGD-MEKI conjugates derived from a MEK1/2 kinase inhibitor—PD0325901—have been developed for integrin receptor mediated anticancer therapy. The first series, alkoxylamine analog RGD-MEKI conjugates 9a–g showed anti-proliferation activity in melanoma A375 cells by the same mechanism as that of PD0325901. PEGylation increased the IC50 value of 9f three-fold in the A375 assay, and the multi-cRGD peptide cargo significantly improved the receptor specific anti-proliferation activity of 9g in integrin-overexpressing U87 cells. In the second series, RGD-PD0325901 13 exhibited significantly increased antitumor properties compared to the alkoxylamine analogs by both inhibition of the ERK pathway activity and DNA replication of the cancer cells. Furthermore, 13 displayed more potent anti-proliferation activity in the U87 assay than PD0325901 in a dose-dependent manner. All these data demonstrate that RGD-MEKI conjugates with an ester bond linkage enhanced anticancer efficacy with improved targeting capability toward integrin-overexpressing tumor cells.
1. Introduction
The RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK signaling cascade plays an important role in normal cell biological process, and is activated in many human tumors to mediate tumor progression and metastasis [1,2]. MEK1/2 kinases are downstream effectors of the ERK pathway. These dual-specificity protein kinases are considered as the important targets for new cancer drug development and have attracted much attention of medicinal chemists over the years [3,4,5,6]. PD0325901 is an oral active and selective second generation non-ATP-competitive MEK inhibitor. In the past decade, PD0325901 has shown great promise to treat advanced malignancies, such as melanoma, breast, lung (NSCLC), colon cancer, and papillary thyroid cancer [7,8,9]. However, many clinical studies revealed unacceptable ocular and neurologic toxicities, and its use as second-line therapy was stopped. We hypothesized that tumor-targeted modification of PD0325901, aiming at improving the tumor uptake and accumulation of this inhibitor, would reduce the undesired systemic toxicity and improve its therapeutic effect.
Peptide-drug conjugation is one of the most promising strategies to overcome the undesired side effects of anti-cancer drugs by the selective delivery of drug conjugates to tumor cells [10]. These peptides recognize and bind to specific receptors with high-affinity, on the tumor-cell surfaces. With subsequent internalization (via receptor-mediated endocytosis) of the ligand-receptor complex, drugs covalently linked to the peptide ligands travel into the targeted tumor cells to exhibit inhibition activity. Among various types of targeting peptides, the ligands containing RGD (Arg-Gly-Asp) amino acid sequences usually have a high affinity for integrin αvβ3 and αvβ5 receptors, membrane proteins abundant on several classes of cancer cells, widely used as carrying vehicles to deliver anti-cancer drugs [11]. In addition, these ligands also worked for integrin targeted delivery of gene therapeutics to tumors with overexpressing integrin receptors [12]. We herein report the conjugation of PD0325901 and its modified analogs with integrin αvβ3 receptor specific peptides c(RGDyk) for the MEK1/2 inhibition in integrin-overexpressing tumor.
Based on the reported X-ray co-crystal structure of a close analogue of PD0325901 with its kinase target, the halo-substituted diphenylamine core and hydroxamate oxygens show important H-bonding interactions with the residues in an allosteric pocket of the target kinase [13], while the dihydroxy propylhydroxamate side chain which showed the improved microsomal stability and solubility of PD0325901, is not directly involved in PD0325901’s binding activity [14,15], and therefore, could be modified by peptide conjugation. In the first series of peptide-drug conjugates, an amine was introduced into PD0325901derivatives (MEKIs, MEK inhibitors) to allow conjugation to the targeting moiety—cRGD peptide via an amide bonds. In order to evaluate the kinase inhibiting and receptor recognizing property of the RGD-MEKI conjugate, a group of MEKIs and RGD-MEKI conjugates with variable chain length were initially evaluated by the introduction of 2–5 carbon linker between the hydroxamate group and the amide group (Figure 1).
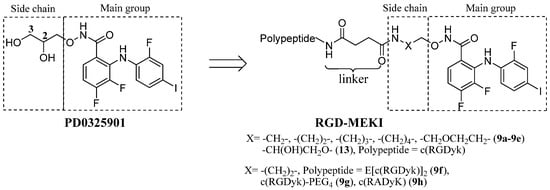
Figure 1.
The structures of two series of RGD-PD0325901 conjugates.
We also developed another type of RGD-PD0325901 conjugate with unmodified drug structure and an ester linkage. The hydroxyl group of dihydroxypropyl hydroxamate side chain was carboxylated with succinic anhydride for the tumor targeting peptide cRGD’s conjugation. All the conjugates 9a–h and 13 were investigated for their biological properties, including inhibition to phosphorylated and unphosphorylated MEK1 kinase, ERK pathway inhibition, and anti-proliferation effects.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Development of the RGD-MEKI Conjugates with Alkoxylamine Analog MEKIs
2.1.1. Synthesis of the Alkoxylamine Analog Conjugates 9a–g
The synthesis of alkoxylamine analog MEKIs started with preparation of the side chains. As shown in Scheme 1, five side chains 5a–e were synthesized in three steps. After amine protection with (Boc)2O in 2a [16], the hydroxyl group in 2-aminoethanol 3a was transformed into an 2-alkoxylamine through Mitsunobu reaction and the subsequent hydrazine reduction [17]. Using the same method, the five alkoxylamine analogues 5a–e were prepared (Scheme 1).
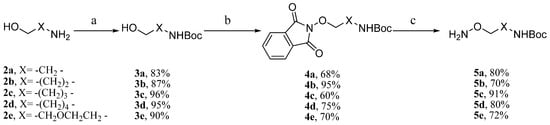
Scheme 1.
Synthesis of compounds 5a–e.
According to the previous procedure, coupling of the side chain 5a with 3,4-difluoro-2-((2-fluoro-4-iodophenyl)amino)benzoic acid (1) was then performed. Compound 1 and side chain 5a were treated with PyBOP in the presence of DIPEA in a mixture of THF and DCM, followed by the removal of the Boc group. PD0325901 analogue 7a was obtained in 68% yield (two steps) [15,18]. Derivation of the terminal amine group of 7a with succinic anhydride provided the hemisuccinate ester 8a in 85% yield [19]. The peptide conjugation reaction was initiated from the activation of 8a with PyBOP in the presence of DIPEA, followed by the addition of c(RGDyk) peptide, which afforded RGD-MEKI conjugate 9a in 45% yield. Other peptide conjugates 9b–e were similarly synthesized using the same synthetic route (Scheme 2).
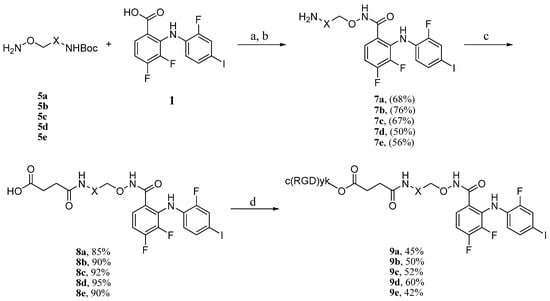
Scheme 2.
Synthesis of conjugates 9a–e.
Based on a receptor-mediated endocytosis mechanism, peptide carriers with higher receptor-binding affinities should greatly promote the inhibitory activity and specificity of RGD-MEKI conjugates for tissue selective targeted cancer treatment. Multimeric cRGD peptides, such as E[c(RGDyK)2] (dimer-cRGD) and E{E[c(RGDyK)2]2} (tetra-cRGD) showed much better tumor targeting capability with higher tumor uptake and longer tumor retention times by compared with their monomeric RGD peptide conjugates [20,21]. Moreover, the PEG linkers are often used in peptide conjugation to increase both the distance and the hydrophilicity of the conjugates. After brief screening of several synthetic methods, a two-step route was finally used for the synthesis of dimer-cRGD and cRGD-PEG4 conjugated RGD-MEKI analogs. As shown in Scheme 3, compound 8b was transformed into the MEKI-succinimydyl ester (MEKI-OSu) 10 in the condition of NHS (N-hydroxy succinimide) and DCC in DMF, which then reacted with dimer-cRGD and cRGD-PEG4 in base condition to give the corresponding conjugates 9f and 9g. In the previous direct activation synthetic method, the dimer-cRGD unit with two free carboxylic acids could be activated by the coupling reagents, leading to a complex reaction mixture. The bio-conjugating method using the activated ester of MEKI 10b avoided the side reactions and gave dimer-cRGD conjugate 9f in moderate yield.
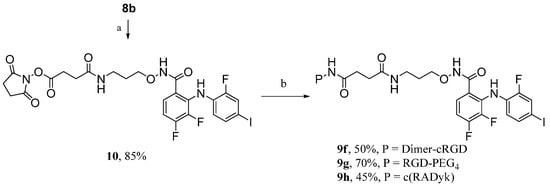
Scheme 3.
Synthesis of compounds 9f (dimer-RGD conjugate), 9g (PEGylated RGD conjugate), and 9h (scrambled peptide—RAD conjugate).
2.1.2. Kinase-Inhibiting Activity Study of Conjugates 9a–g
The kinase-inhibiting activity of RGD-MEKI conjugates 9a–g with alkoxylamine side chains were initially evaluated by Homogenous Time Resolved Fluorescence (HTRF) kinase assays as presented in Table 1. In HTRF phosphor-MEK1 assay, conjugates 9a–d showed higher activity in inhibiting the phosphorylation and activation of inactive MEK1 than in inhibiting the activity of activated MEK1 in the HTRF phosphor-ERK2 assay. The order of inhibition values of 9a–d were 9d > 9c > 9b > 9a in both assays, indicating that the kinase inhibitory property of the conjugates was only slightly affected by the spacer length between the cRGD vehicle and kinase inhibitor units. Although the activity of these conjugates was not as good as PD0325901 (PD0325901: IC50 = 2.6 nM, 9b: IC50 = 47.9 nM, in BRAF-MEK1 assay), they worked as the same non-ATP-competitive inhibition fashion and also similar to the unconjugated compounds. Compared to the mono-cRGD conjugates 9b, which has the same MEKIs part, the PEGylated conjugate 9g exhibited increasing activity, and the dimer-cRGD conjugate 9f showed similar activity as 9b (Table 1).

Table 1.
HTRF phosphor-MEK1 assay and HTRF phosphor-ERK2 assay results for PD0325901 and RGD-MEKI conjugates 9a–d, 9f, 9g and 13.
| Compound | BRAF-MEK1 assay (%) a | MEK1-ERK2 assay (%) b | A375 cell c | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 μM | 0.1 μM | 0.01μM | 10 μM | 1 μM | IC50(μM) | |
| PD0325901 | 97.3 ± 1.9 | 95.0 ± 1.4 | 94.0 ± 1.4 | 100.6 ± 0.4 | 100.0 ± 1.5 | 0.00045 |
| 9a | 74.2 ± 7.2 | 30.0 ± 4.7 | 0.3 ± 0.0 | 88.4 ± 1.4 | 66.5 ± 7.7 | 4.4 |
| 9b | 77.6 ± 7.5 | 58.5 ± 8.5 | 6.7 ± 8.5 | 93.5 ± 2.2 | 69.9 ± 3.2 | 2.1 |
| 9c | 91.5 ± 0.7 | 48.5 ± 9.5 | 38.9 ± 10 | 99.5 ± 0.7 | 63.8 ± 2.9 | 4.0 |
| 9d | 97.9 ± 2.4 | 46.0 ± 12.5 | 26.1 ± 15 | 99.9 ± 1.4 | 80.5 ± 2.0 | 5.6 |
| 8b | 57.5 ± 1.7 | 39.6 ± 9.3 | 12.5 ± 3.2 | 83.4 ± 1.2 | 29.1 ± 12.0 | 14.2 |
| 9g | 78.8 ± 4.4 | 39.0 ± 7.2 | 25.9 ± 11 | 91.8 ± 2.5 | 40.6 ± 5.5 | 0.65 |
| 9f | 80.5 ± 2.9 | 42.6 ± 5.6 | 39.0 ± 7.4 | 95.0 ± 1.0 | 49.1 ± 7.8 | 3.1 |
| 13 | 95.7 ± 1.9 | 95.1 ± 0.9 | 48.4 ± 3.2 | - | - | 0.0176 |
a BRAF-MEK1 assay (HTRF phosphor-MEK1 assay) was used to determine the activity of RGD-MEKI conjugates to inhibit the phosphorylation of the inactive MEK1 kinase. Values are means of three experiments, standard deviation is given after them; b MEK1-ERK2 assay (HTRF phosphor-ERK2 assay) was used to determine the activity of RGD-MEKI conjugates to inhibit the active MEK1 kinase to phosphorylate the inactive ERK2 protein. Values are means of three experiments; standard deviation is given after them; c In vitro anti-proliferation assay on melanoma A375 cells by the SRB method.
2.1.3. In Vitro Anti-Proliferation Assay of Conjugates 9a–g
In vitro properties of RGD-MEKI conjugates 9a–d were evaluated against melanoma A375 cells by the SRB method. A375 cells which harbor activating BRAFV600E mutation (the valine 600 to glutamate mutation of BRAF kinase) with higher ERK pathway activity are exquisitely sensitive to PD0325901 treatment. All the conjugates exhibited moderate cytotoxicity in A375 cell-proliferation assay in which 9b exhibited a better inhibition activity (Table 1).Although increasing the space length between the modified PD0325901 and peptide cargo is beneficial to the kinase activity of alkoxylamine analog conjugates, we considered that a longer carbon chain would decrease the aqueous solubility of conjugates, and thus influence the conjugate’s cell-based activity. In an effort to combine long chain length with better hydrophilicity, the RGD-MEKI conjugate 9e was designed by using an ethoxyethyl amine unit instead of the alkoxylamine structure. However, 9e showed much lower activity than its carbon chain homologues 9d in cytotoxicity assay.
The cytotoxic potency and selectivity of conjugates 9b, 9f and 9g were measured against three different tumor cell lines, including A375, U87 (glioblastoma) and A549 (NSCLC). Different from melanoma A375, U87 cells were found to be moderately sensitive to PD0325901, while A549 was the lowest. As shown in Figure 2, 9f and 9g exhibited selective cytotoxicity against the tested carcinoma cell lines (A375 > U87 > A549) as the same order observed in PD0325901. As shown in Table 1 and Figure 2B, the hydrophilic PEG4 linker improved the cytotoxic potency of 9g with a sub-µM IC50 value (0.65 ± 0.03 µM) in A375 proliferation assay, which is 3-fold more potent than its homolog 9b (2.1 ± 0.8 µM). This indicated that longer and hydrophilic spacer between MEKI and peptide cargo was beneficial for the ligand-to-receptor-binding and inhibitor-kinase-interaction. However, in the less sensitive A549 proliferation assay 9b and 9g were found to exhibit similar lower growth-inhibitory activity as PD0325901.
Although the dimer-cRGD conjugate 9f (IC50 = 3.0 ± 1.3 µM) was found to be less potent than the monomer conjugate analog 9b (IC50 = 2.1 ± 0.8 µM) in A375 proliferation assay, it showed the best U87 cell growth-inhibiting activity in all alkoxylamine analogs RGD-MEKIs, much better than mono- RGD conjugate (* p < 0.05). Especially, its activity was as good as that of PD0325901 at a high concentration (10 µM). U-87 cells, human neuronal glioblastoma cells, expressed a high level of integrin αvβ3 receptors on cell surface with a ratio of receptors/cell (cell receptor density) up to (1.28 ± 0.46) × 105 [22]. We considered that the better receptor-binding affinity exhibited by the dimer-cRGD conjugate 9f could enhance its antitumor activity against the receptor overexpressed U87 cells. This specific receptor-mediated tumor inhibition activity could be blocked by the scramble peptide—c(RADyK) conjugated MEKI—9h (Scheme 3). As shown in Figure 2, the A375 cell-growth inhibition was decreased from 81.4% (9b) to 25.1% (9h) (** p < 0.01), and the U87 cell-growth inhibition was decreased from 21.3% (9b) to 5.4% (9h), respectively.
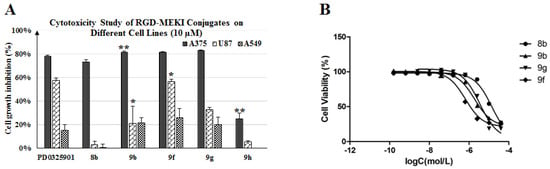
Figure 2.
(A) Cytotoxicity study of RGD-MEKI conjugates 9b, 9f–h, compared with the parent drug (PD0325901) and MEKI—8b on different tumor cell lines (melanoma-A375, glioblastoma-U87, NSCLC-A549) at 10 µM concentration by the SRB method. (B) IC50 value of 8b, 9b, 9f and 9g in A375 cells. The effect of cRGD peptide cargo on conjugates was analyzed by student’s t-test, and (*) indicates p value < 0.05, (**) indicates p value < 0.01.
2.1.4. Inhibition of ERK Pathway
Inhibition of the ERK phosphorylation has been proposed as a primary biomarker of MEK inhibition activity [23,24]. As exhibited in Figure 3A, western blotting analyses showed that up to 90% inhibition of the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 protein (44/42 kDa) was observed in conjugate 9b and 9g—treated A375 cells, which is the same as the parent drug, while the cRGD peptides themselves exhibited no inhibitory activity (Figure 3).
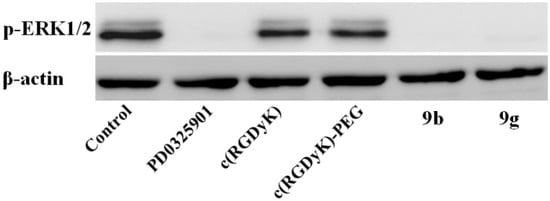
Figure 3.
Western blotting analyses of melanoma A375 cells lysates were performed for p-ERK1/2 after 2h. Β-actin served as loading control. Cells were treated with 10 μM of PD0325901, c(RGDyK) peptides, and RGD-MEKI conjugates 9b and 9g.
2.1.5. The Cell Cycle Analysis of Conjugates
Although these newly developed alkoxylamine analogs MEKIs conjugates did not show attractive tumor-inhibition properties, multivalent RGD ligands enhanced receptor-mediated drug endocytosis in receptor over-expressed tumor cells, as evidenced by 9f, and PEGylation improved the cell-based anti-proliferation properties of conjugate 9g. Cell-cycle analysis revealed that A375 cell-growth reduction was associated with loss of cells in S and G2 phase (Figure 4). Cell proliferation is regulated during the first pause in the cell cycle at the G1 checkpoint.
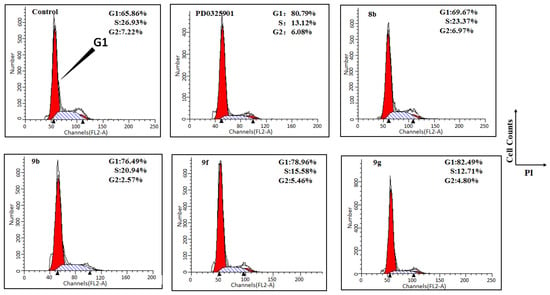
Figure 4.
RGD-MEKI induced cell cycle arrest in melanoma A375 cells.
We tried to improve the conjugate’s hydrophilicity in 9e and 9f, but 9e showed a decreased activity compared to its chain analog 9d. We suggest that 9e’s poor performance might be attributed to the unfavored side-chain modification. As compared with the side-chain structure of the lead compound PD0325901, the hydroxyl methylene group in PD0325901 was replaced by an oxygen atom in conjugate 9e (IC50 = 9.5 ± 0.16 µM), in which, the former unit can act as the hydrogen-bond donor, while the latter one can only act as the hydrogen-bond acceptor. The relative lower biological activity of conjugate 9e might be due to the modified electron density, or more specific to the inverted hydrogen bonding potential. Thus, we suggest that C2-hydroxy group of dihydroxypropyl side chain might be essential to PD0325901’s biological activity, not only by increasing its aqueous solubility. Further exploration of structural requirements led to the synthesis of the RGD-PD0325901 direct conjugate 13, in which, the terminal hydroxyl group of PD0325901 was carboxylated with succinic anhydride for the tumor-targeting peptide cRGD’s conjugation.
2.2. Development of the RGD-PD0325901 Direct Conjugates 13
2.2.1. Synthesis of Conjugate 13
Following the previous procedure, PD0325901 1 was transformed into the hemisuccinate ester 11 by reacting with succinic anhydride and pyridine. Subsequent activation of the free carboxylic acid with NHS (N-hydroxy succinimide) and DCC in DMF, followed by the reaction with c(RGDyk) gave the corresponding conjugates 13 in a moderate yield (Scheme 4).
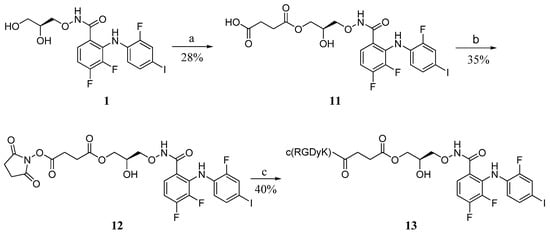
Scheme 4.
Synthesis of the RGD-PD0325901 direct conjugate 13.
2.2.2. In Vitro Biological Evaluation of Conjugate 13
To our delight, this new RGD-MEKI conjugate 13 showed potent enzymatic activity in phosphor-MEK1 assay (Table 1), and also displayed comparable cellular activity (IC50 = 17.6 nM) to its parent drug—PD0325901 (IC50 = 0.47 nM) in the A375 proliferation assay (Figure 5A). Without the cRGD cargo, its analogue 11 lost almost 10-fold antitumor efficacy (IC50 value of 230 nM) compared to 13, Furthermore, conjugate 13 exhibited higher anti-proliferative activity than PD0325901 in U87 glioblastoma cells with an IC50 value of 2.38 µM, while PD0325901 showed around 50% inhibitory activity at high concentrations (>1 µM) in a concentration-independent manner (Figure 5B). All these results demonstrated that the RGD-PD0325901 conjugate 13 enters tumor cells through a receptor-mediated mechanism in integrin αvβ3-overexpressing cells.
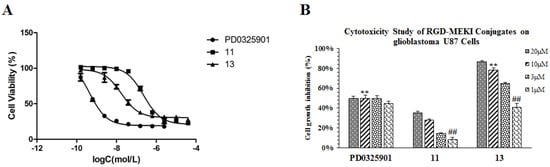
Figure 5.
Cytotoxicity study of conjugate 13, compared with parent drug (PD0325901) and MEKI (11) on both melanoma A375 (A, IC50 value) and glioblastoma-U87 (B) cells after 72h treatment by the SRB method.
Consistent with its anti-proliferation effects, the conjugate 13 showed a dose-dependent pERK1/2 suppression in A375 cells (Figure 6A), with up to 90% inhibition of pERK1/2 protein at 0.01 µM concentration. This result was in agreement with the inhibition manner of DNA replication. As shown in Figure 6B, conjugate 13 and 9g inhibited DNA replication of A375 cells with the same efficiency as the parent drug PD0325901.
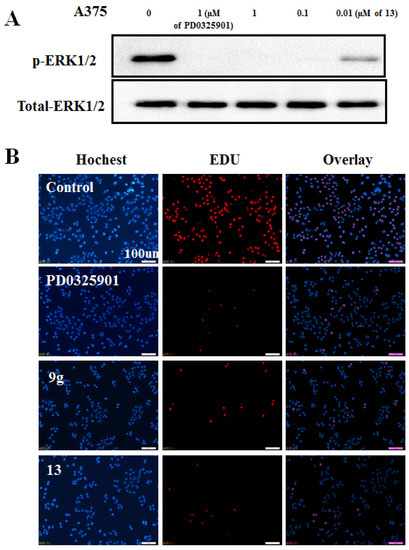
Figure 6.
(A) Western blots analyses of melanoma A375 cells lysates were performed for p-ERK1/2 after 2 h*. (B) DNA replication study of 9f and 13 on A375 cells by EdU method *.
In order to increase the therapeutic efficacy of PD0325901 while decreasing it systemic toxicity, the cleavable carboxylic acid ester bond was introduced into the RGD-MEKI conjugates. In our study, this conjugate 13 exhibited specific and potent activity in MEK enzyme inhibition, anti-cell-proliferation, p-ERK-1/2 inhibition, and DNA replication inhibition. All these data demonstrate that conjugate 13 was potential MEK1/2 kinase inhibitor with improved tumor targeting capability. The ester bond of molecules can be hydrolyzed by either blood or cellular esterases. How stable the conjugate is in blood circulation system and if it can be cleaved to release drug in target cancer cells are two important properties of prodrugs. In the further research, we will focus on the study to answer these two questions as well as the pharmacological activity study of RGD-MEKI conjugate.
3. Experimental
3.1. General Experimental Conditions
All reactions were run under an inert atmosphere (N2) with flame-dried glassware using standard techniques for manipulating air-sensitive compounds. Commercial reagents were used as supplied or purified by standard techniques where necessary. THF and CH2Cl2 were used fresh distilled over sodium/benzophenone or calcium hydride respectively. The cyclic RGD peptides, such as c(RGDyk), c(RGDyk)-PEG4 (cRGD-PEG4), c(RADyk), and E[c(RGDyK)2] (dimer-cRGD) were purchased from GL Biochem (Shanghai) Ltd., with the purity higher than 95%. Column chromatography was performed using 200-300 mesh silica with the proper solvent system according to TLC analysis using KMnO4 stain and UV light to visualize the reaction components. Unless otherwise noted, 1H-NMR (400 MHz), 19F-NMR spectra (376 MHz) were recorded at ambient temperature using a BrukerAvance III400 MHz spectrometer (Bruker, Karlsruhecity, Germany). NMR data were reported as follows: chemical shift, multiplicity (s = singlet, d = doublet, t = triplet, m = multiplet and bs = broad singlet), coupling constant in Hz and integration. Chemical shifts are expressed in ppm relative to tetramethylsilane. IR spectra were recorded on a FTIR spectrometer (IR Prestige-21, Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) in KBr pellets and reported in reciprocal centimeters (cm−1). Low-resolution MS and HRMS data were obtained using ESI ionization (Bruker DALTONICS APEX IV 70e, Germeringcity, Germany). All melting points were taken with an X-6melting point apparatus (Beijing Focus Instrument Co., Ltd., Beijing, China) and are reported without correction. Analytical as well as semi-preparative reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) were performed on a LC3000 Binary chromatography system with a UV3000 UV-VIS Detector (CXTH, Beijing Chuangxintongheng Science & Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China).The semi-preparative HPLC was performed with a Daisogel C18 10 μm 100A column (10 micron, 250 × 30 mm). The flow was 20 mL/min, with the mobile phase starting from 95% solvent A (0.1% TFA in water) and 5% solvent B (0.1% TFA in acetonitrile) (0–5 min) to 5% solvent A and 95% solvent B at 45 min. Analytical HPLC was performed using the same gradient system, but with a Gemini 5 μm C18 110A column (250 × 10 mm) and flow of 2 mL/min. Ultraviolet (UV) absorbance was monitored at 254 nm.
3.2. Chemistry
3.2.1. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Tert-butyl-(2-hydroxyethyl)carbamate 3a and Its Derivatives (3b–e) [25,26,27,28,29]
To a solution of 2a (or 2b–e, 20 mmol) in a mixture of dioxane (15 mL) and H2O (7 mL), was added 5N NaOH (4.8 mL) and a solution of Boc2O (5.0 g, 23 mmol) in dioxane at 0 °C. After stirred at rt overnight, the reaction mixture was concentrated in vacuo. The residue was extracted from 10% citric acid with AcOEt, and dried over anhydrous Na2SO4. Evaporation of the solvents gave the pure product 3a–e. 3a was obtained as a colorless oil (2.67 g, 83%).
3.2.2. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Tert-butyl-(2-((1,3-dioxoisoindolin-2-yl)oxy)ethyl) carbamate 4a and Its Derivatives (4b–e) [30,31,32,33]
To a solution of 3a (or 3b–e, 10 mmol), N-hydroxy-phthalimide (1.79 g, 11 mmol), and triphenylphosphine (2.88 g, 11 mmol) in CH2Cl2 (25 mL), was added diethyl azodicarboxylate (DEAD, 1.92 g, 11 mmol) at 0 °C. The reaction mixture was stirred at rt overnight. The reaction was concentrated and purified by column chromatography to give the product 4a–e. 4a was obtained as a white solid (2.08 g, 68%).
3.2.3. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Tert-butyl-(2-(aminooxy)ethyl) carbamate 5a and Its Derivatives (5b–e) [32,33,34]
To a solution of 4a (or 4b–e, 5.8 mmol ) in EtOH (10 mL), was added hydrazine (187 uL, 5.97 mmol) in drop. The reaction mixture was stirred at rt. until the reaction was completed as judged by TLC. The mixture was filtered and the filtrate was concentrated and purified by column chromatography to give the product 5a–e. 5a was obtained as a white solid (817 mg, 80%).
3.2.4. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Tert-butyl-(2-((3,4-difluoro-2-(2-fluoro-4-iodobenzyl) benzamido)oxy)ethyl)carbamate 6a and Its Derivatives (6b–e)
To a stirring mixture comprised of 3,4-difluoro-2-((2-fluoro-4-iodophenyl)amino)benzoic acid (755 mg, 1.92 mmol), 5a (or 5b–e, 2 mmol) and diisopropylethylamine (0.7 mL, 4.23 mmol) in 40 mL of 1:1 (v/v) THF-DCM, was added directly the benzotriazole-1-yl-oxy-tris-pyrrolidino-phosphonium hexafluorophosphate (PyBOP) (1.04 g, 2 mmol). The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature under argon atmosphere overnight. The mixture was concentrated to an oil under reduced pressure. The oil was partitioned between diethyl ether (60 mL) and 10% aqueous hydrochloric acid (45 mL). The organic phase was washed with saturated aqueous sodium bicarbonate (40 mL) and brine (45 mL), and then dried with MgSO4, concentrated in vacuo. The residue was purified through column chromatography to give the product 6a–e.
Tert-butyl-(2-((3,4-difluoro-2-(2-fluoro-4-iodobenzyl)benzamido)oxy)ethyl)carbamate (6a). 6a was obtained as a brown solid (592 mg, 83%). Mp. 61.2–63.2 °C; IR (neat) 1666, 1602, 1494, 1288, 1166; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 10.44 (br, 1H), 8.58 (br, 1H), 7.37(dd, J = 10.2, 1.4 Hz, 1H), 7.34 (t, J = 7.3 Hz, 1H), 7.30 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 6.87–6.81 (m, 1H), 6.59–6.54 (m, 1H), 5.18 (br, 1H), 3.98–3.85 (m, 2H), 3.40–3.36 (m, 2H), 1.43 (s, 9H); 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −127.78, −129.53, −142.35; HRMS (ESI) calcd. for C20H22F3IN3O4 [M+H]+ 552. 0607; found, 552.0601.
Tert-butyl(3-((3,4-difluoro-2-((2-fluoro-4-iodophenyl)amino)benzamido)oxy)propyl)carbamate (6b). 6b was obtained as a white solid (82% yield); mp. 138.5–139.5 °C; IR (neat) 1681, 1602, 1496, 1276, 1168; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 9.97 (br, 1H), 8.60 (br, 1H), 7.40–7.37 (m, 2H), 7.31 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 6.83–6.77 (m, 1H), 6.60–6.55 (m, 1H), 5.10 (br, 1H), 4.02 (t, J = 5.6 Hz, 2H), 3.33–3.30 (m, 2H), 1.84–1.78 (m, 2H), 1.42 (s, 9H); 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −127.99, −129.13, −142.75(d, J = 19.0Hz); HRMS (ESI) calcd for C21H24F3IN3O4 [M+H]+ 566.0764; found, 566.0745.
Tert-butyl(4-((3,4-difluoro-2-((2-fluoro-4-iodophenyl)amino)benzamido)oxy)butyl)carbamate (6c). 6c was obtained as a brown solid; yield 70%; mp. 125.1–127.1 °C; IR (neat) 1683, 1602, 1498, 1276, 1170; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 10.74 (br, 1H), 8.57 (br, 1H), 7.35 (t, J = 7.3 Hz, 1H), 7.34 (dd, J = 10.2, 1.4 Hz, 1H), 7.26 (d, J = 7.4 Hz, 1H), 6.77–6.71 (m, 1H), 6.55–6.50 (m, 1H), 4.84 (br, 1H), 3.94–3.92 (m, 2H), 3.15–3.13 (m, 2H), 1.61–1.54 (m, 4H), 1.37 (s, 9H); 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −127.59, −130.39, −142.35; HRMS (ESI) calcd. for C22H26F3IN3O4 [M+H]+ 580.0920; found, 580.0892.
Tert-butyl(5-((3,4-difluoro-2-((2-fluoro-4- iodophenyl)amino)benzamido)oxy)pentyl)carbamate (6d). 6d was obtained as a white solid (70% yield); mp. 133.1–135.1 °C; IR (neat) 1681, 1602, 1496, 1276, 1168; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 10.17 (br, 1H), 8.06 (br, 1H), 7.44 (t, J = 6.9 Hz, 1H), 7.39 (dd, J = 10.3, 1.8 Hz, 1H), 7.30 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 6.90–6.84 (m, 1H), 6.58–6.52 (m, 1H), 3.92 (t, J = 5.8 Hz, 2H), 3.14 (t, J = 5.8 Hz, 2H), 1.69–1.63 (m, 2H), 1.53–1.46 (m, 4H), 1.41 (s, 9H); 19F NMR (376 MHz, DMSO) δ −127.82, −130.17, −142.63; HRMS (ESI) calcd. for C23H28F3IN3O4 [M+H]+ 594.1077; found, 594.1037.
Tert-butyl(2-(2-((3,4-difluoro-2-((2-fluoro-4-iodophenyl)amino)benzamido)oxy)ethoxy)ethyl) carbamate (6e). 6e was obtained as a brown solid (74% yield); mp. 78.5–79.5 °C; IR (neat) 1681, 1602, 1496, 1278, 1068; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 10.16 (br, 1H), 8.52 (br, 1H), 7.45 (t, J = 5.6 Hz, 1H), 7.38 (dd, J = 10.3, 1.8 Hz, 1H), 7.29 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 6.87–6.81 (m, 1H), 6.58–6.52 (m, 1H), 4.11 (t, J = 3.9 Hz, 2H), 3.71 (t, J = 4.2 Hz, 2H), 3.54 (t, J = 4.8 Hz, 2H), 3.33 (t, J = 4.8 Hz, 2H), 1.38 (s, 9H); 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −127.57, −130.74, −142.26; HRMS (ESI) calcd. For C22H26F3IN3O5 [M+H]+ 596.0869; found, 596.0827.
3.2.5. General Procedure for the Synthesis of N-(2-aminoethoxy)-3,4-difluoro-2-((2-fluoro-4-iodophenyl)amino)benzamide 7a and Its Derivatives (7b−e)
To a solution of 6a (or 6b−e, 2.36 mmol) in CH2Cl2 (5 mL) was added trifluoroacetic acid (5 mL, 50 v/v %), and the mixture was stirred at 0 °C for 1 h. The mixture was diluted with AcOEt and was then basified to pH > 7.0 by the addition of aqueous NaOH. The organic phase was then sequencely washed with saturated aqueous sodium bicarbonate and brine, was dried (MgSO4), and was concentrated and purified by column chromatography to give the product 7a−e.
N-(2-aminoethoxy)-3,4-difluoro-2-((2-fluoro-4-iodophenyl)amino)benzamide (7a). 7a was obtained as a white solid (1.0 g, 95%); mp. 186.5−187.5 °C; IR (neat) 1683, 1496, 1288, 1136, 1047; 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO) δ 7.67 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 7.57 (dd, J = 10.8, 1.7 Hz, 1H), 7.37 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 7.08–7.01 (m, 1H), 6.63−6.57 (m, 1H), 3.98−3.85 (m, 2H), 2.94−2.90(m, 2H); 19F NMR (376 MHz, DMSO) δ −130.81, −136.27, −146.62 (d, J = 20.1Hz); HRMS (ESI) calcd. for C15H14F3IN3O2 [M+H]+ 452.0083; found, 452.0065.
N-(3-aminopropoxy)-3,4-difluoro-2-((2-fluoro-4-iodophenyl)amino)benzamide (7b). 7b was gave as a white solid (90% yield); mp. 197.5−198.5 °C; IR (neat) 1602, 1496, 1327, 1122, 1045; 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO) δ 7.69 (t, J = 7.0 Hz, 1H), 7.56 (dd, J = 10.7, 1.8 Hz, 1H), 7.36 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 7.04−6.97 (m, 1H), 6.62−6.56 (m, 1H), 3.83−3.81 (m, 2H), 2.92–2.89 (m, 2H), 1.79−1.76 (m, 2H); 19F NMR (376 MHz, MeOD) δ −128.52, −132.20 (d, J = 17.8Hz), −144.53 (d, J = 18.5Hz); HRMS (ESI) calcd. for C16H16F3IN3O2 [M+H]+ 466.0239; found, 466.0225.
N-(4-aminobutoxy)-3,4-difluoro-2-((2-fluoro-4-iodophenyl)amino)benzamide (7c). 7c was obtained as a brown solid (95% yield); mp. 146.7–147.7 °C; IR (neat) 1602, 1496, 1290, 1138, 1045; 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO) δ 7.57 (dd, J = 10.7, 1.5 Hz, 1H), 7.45 (t, J = 7.0 Hz, 1H), 7.37 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 7.21−7.15 (m, 1H), 6.69−6.63 (m, 1H), 3.83−3.80 (m, 2H), 2.85−2.82 (m, 2H), 1.70−1.62 (m, 4H); 19F NMR (376 MHz, DMSO) δ −131.47, −140.30, −146.52 (d, J = 12.1Hz); HRMS (ESI) calcd. For C17H18F3IN3O2 [M+H]+ 480.0396; found, 480.0372.
N-((5-aminopentyl)oxy)-3,4-difluoro-2-((2-fluoro-4-iodophenyl)amino)benzamide (7d). 7d was obtained as a white solid (72% yield); mp. 88.5−89.5 °C; IR (neat) 1678, 1496, 1276, 1203, 1060; 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO) δ 11.81 (br, 1H), 8.71 (br, 1H), 7.73 (br, 1H), 7.59 (dd, J = 10.8, 1.7 Hz, 1H), 7.41−7.36 (m, 2H), 7.25−7.19 (m, 1H), 6.70−6.64 (m, 1H), 3.78 (t, J = 5.9 Hz, 2H), 2.80–2.75 (m, 2H), 1.56−1.53 (m, 4H), 1.42−1.37 (m, 2H); 19F NMR (376 MHz, DMSO) δ −129.61, −134.57(d, J = 19.7 Hz), −145.69(d, J = 19.2Hz); HRMS (ESI) calcd. for C18H20F3IN3O2 [M+H]+ 494.0552; found, 494.0540.
N-(2-(2-aminoethoxy)ethoxy)-3,4- difluoro-2-((2-fluoro-4-iodophenyl)amino)benzamide (7e). 7e was obtained as a white solid (75% yield); mp. 197.5–198.5 °C; IR (neat) 1598, 1494, 1354, 1288, 1124; 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO) δ 7.58 (dd, J = 10.8, 1.3 Hz, 1H), 7.48 (t, J = 6.1 Hz, 1H), 7.37(d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 7.21−7.15 (m, 1H), 6.68−6.62 (m, 1H), 3.95 (t, J = 4.6 Hz, 2H), 3.64−3.61 (m, 4H), 2.97 (t, J = 4.8 Hz, 2H); 19F NMR (376 MHz, DMSO) δ −130.92, −136.75, −146.75 (d, J = 20.5Hz); HRMS (ESI) calcd. for C17H18F3IN3O3 [M+H]+ 496.0345; found, 496.0318.
3.2.6. General Procedure for the Synthesis of 4-((2-((3,4-Difluoro-2-((2-fluoro-4-iodophenyl)amino) benzamido)oxy)ethyl)amino)-4-oxobutanoic Acid 8a and Its Derivatives (8b−e)
A solution of 7a (or 7b−e, 0.36 mmol) and succinic anhydride (470 mg, 4.6 mmol) in pyridine (7 mL) was stirred for 30 min. The mixture was diluted with AcOEt and then washed with 1M HCl. The organic phase was dried (MgSO4), and was concentrated and purified by column chromatography to give the product 8a−e.
4-((2-((3,4-Difluoro-2-((2-fluoro-4-iodophenyl)amino)benzamido)oxy)ethyl)amino)-4-oxobutanoic acid (8a). 8a was obtained as a white solid (168 mg, 85%); mp. 96.5−98.5 °C; IR (neat) 1714, 1631, 1604, 1496, 1278; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 10.51 (br, 1H), 8.40 (br, 1H), 7.38 (t, J = 7.3 Hz, 1H), 7.35(dd, J = 10.2, 1.4 Hz, 1H), 7.29(d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 6.86−6.80(m, 1H), 6.56−6.51 (m, 1H), 3.92−3.88 (m, 2H), 3.47−3.43 (m, 2H), 2.66−2.62 (m, 2H), 2.56−2.52 (m, 2H); 19F NMR (376 MHz, DMSO) δ −129.02, −133.97, −145.13(d, J = 18.3 Hz); HRMS (ESI) calcd. for C19H18F3IN3O5 [M+H]+ 552.0243; found, 552.0203.
4-((3-((3,4-Difluoro-2-((2-fluoro-4-iodophenyl)amino)benzamido)oxy)propyl)amino)-4-oxobutanoic acid (8b). 8b was obtained as a white solid (90% yield); mp. 161.5−162.5 °C; IR (neat) 1726, 1645, 1604, 1494, 1280; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 10.55 (br, 1H), 8.37 (br, 1H), 7.90 (br, 1H), 7.40 (t, J = 6.7 Hz, 1H), 7.36 (dd, J = 10.3, 1.8 Hz, 1H), 7.28 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 6.88–6.81 (m, 1H), 6.55−6.49 (m, 1H), 3.97−3.95 (m, 2H), 3.40−3.36 (m, 2H), 2.61–2.53 (m, 4H), 1.76−1.73 (m, 2H); 19F NMR (376 MHz, DMSO) δ −129.05, −134.06 (d, J = 18.1 Hz), −145.20 (d, J = 19.1Hz); HRMS (ESI) calcd. for C20H20F3IN3O5 [M+H]+ 566.0399; found, 566.0377.
4-((4-((3,4-Difluoro-2-((2-fluoro-4-iodophenyl)amino)benzamido)oxy)butyl)amino)-4-oxobutanoic acid (8c). 8c was obtained as a white solid (92% yield); mp. 120.9−121.9 °C; IR (neat) 1716, 1647, 1606, 1496, 1278; 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO) δ 11.67 (br, 1H), 8.71 (br, 1H), 7.83 (br, 1H), 7.57 (dd, J = 10.8, 1.4 Hz, 1H), 7.38 (t, J = 5.6 Hz, 1H),7.36 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H), 7.23−7.16 (m, 1H), 6.70−6.65 (m, 1H), 3.80−3.77 (m, 2H), 3.07−3.03 (m, 2H), 2.41−2.40 (m, 2H), 2.31-2.28(m, 2H), 1.55−1.47 (m, 4H); 19F NMR (376 MHz, DMSO) δ −129.04, −134.14 (d, J = 18.6 Hz), −145.25 (d, J = 19.2Hz); HRMS (ESI) calcd. for C21H22F3IN3O5 [M+H]+ 580.0556; found, 580.0530.
4-((5-((3,4-Difluoro-2-((2-fluoro-4-iodophenyl)amino)benzamido)oxy)pentyl)amino)-4-oxobutanoic acid (8d). 8d was obtainedas a white solid (95% yield); mp. 186.5−187.5 °C; IR (neat) 1714, 1651, 1608, 1496, 1278; 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO) δ 11.76(br, 1H), 8.70(br, 1H), 7.82(t, J = 5.4 Hz, 1H), 7.58 (dd, J = 10.8, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.40−7.35(m, 2H), 7.24−7.18(m, 1H), 6.69-6.64 (m, 1H), 3.76 (t, J = 6.1 Hz, 2H), 3.01 (q, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H), 2.41 (t, J = 6.6 Hz, 2H), 2.29 (t, J = 6.6 Hz, 2H), 1.57−1.50 (m, 2H), 1.40−1.31 (m, 4H); 19F NMR (376 MHz, DMSO) δ −129.07, −134.21 (d, J = 19.3Hz), −145.349 (d, J = 19.3Hz); HRMS (ESI) calcd. for C22H24F3IN3O5 [M+H]+ 594.0712; found, 594.0695.
1-(3,4-Difluoro-2-((2-fluoro-4-iodophenyl)amino)phenyl)-1,10-dioxo-3,6-dioxa-2,9-diazatridecan-13-oic acid (8e). 8e was obtainedas a white solid (90% yield); mp. 135.1–136.1 °C; IR (neat) 1714, 1651, 1608, 1496, 1280; 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO) δ 11.87 (br, 1H), 8.70 (br, 1H), 7.91 (t, J = 5.4 Hz, 1H), 7.58 (dd, J = 10.7, 1.4 Hz, 1H), 7.40 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 7.36 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 1H), 7.24−7.17 (m, 1H), 6.69−6.64 (m, 1H), 3.93 (s, 2H), 3.58 (s, 2H), 3.41 (t, J = 5.8 Hz, 2H), 3.21–3.16 (m, 2H), 2.40 (t, J = 6.5 Hz, 2H), 2.31 (t, J = 6.4 Hz, 2H); 19F NMR (376 MHz, DMSO) δ −129.10, −134.05 (d, J = 18.2 Hz), −145.19 (d, J = 19.1 Hz); HRMS (ESI) calcd. for C21H22F3IN3O6 [M+H]+ 596.0505; found, 596.0482.
3.2.7. General Procedure for the Synthesis of 2,5-Dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl4-((3-(3,4- difluoro-2-((2-fluoro-4-iodophenylamino)benzamido)propyl)amino)-4-oxobutanoate 10
To a solution of 4-((3-((3,4-difluoro-2-((2-fluoro-4-iodophenyl)amino)benzamido)oxy)propyl) amino)-4-oxobutanoic acid 8b (282 mg, 0.5 mmol) in 5 mL of (DMF) were added NHS (0.126 g, 1.1 mmol) and DCC (0.226 g, 1.1 mmol). The resulting mixture was stirred at room temperature for 10 h. The dicyclohexylurea (DCU) by-product was filtered off. The filtrate was evaporated to dryness under vacuum to give a crude product, which was then taken up in 1 mL of CH2Cl2. The insoluble solid was filtered off. The filtrate was concentrated and purified by column chromatography to give the product 10 as a white solid (281 mg, yield 85%); mp. 103.5−104.5 °C; IR (neat) 1737, 1653, 1590, 1497, 1496; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 10.24 (br, 1H), 7.84 (br, 1H), 7.44−7.38 (m, 2H), 7.31 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 6.96−6.90 (m, 1H), 6.56−6.51 (m, 1H), 3.96 (t, J = 5.4 Hz, 2H), 3.49 (q, J = 5.6 Hz, 2H), 3.01 (t, J = 6.7 Hz, 2H), 2.82 (s, 4H), 2.76 (t, J = 6.7 Hz, 2H), 1.85-1.79(m, 2H); 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −128.49, −129.02 (d, J = 19.2Hz), −142.57 (d, J = 19.5Hz); HRMS (ESI) calcd. for C24H22F3IKN4O6 [M+K]+ 685.0173; found, 685.0355.
3.2.8. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Conjugate 9a and 9b−e
A solution of 8a (2.2 mg, 4 μmol), PyBOP (2.1 mg, 4 μmol), diisopropylethylamine (0.52 mg, 4 μmol) was stirred for 30 min at 0 °C. Then the cyclo(RGDyK) (1.2 mg, 2 μmol) was added to the solution and stirred until the peptide was completely disappeared. The desired product was isolated by semi-preparative HPLC. The collected fractions were combined and lyophilized to give a fluffy white powder 9a. The yield was 1.0 mg (45%); HRMS (ESI) calcd for C46H55F3IN12O12 [M-H]+ 1151.3059; found, 1151.3623. The conjugate 9a was purified on a LC3000 HPLC system with a UV3000 UV-VIS Detector (CXTH) using a Daisogel C-18, 30 × 250 mm, 10 µm, 100 Å column. Elution was performed by a linear gradient with an increase of 2.25% acetonitrile per minute in the presence of 0.1% TFA (20 mL/min, 254 nm). The purity of the conjugate 9a was confirmed by the same gradient system using a Gemini C-18, 10 × 250 mm, 5µm, 110 Å column with a flow of 2 mL/min; Rt = 34.0 min; purity = 98.3%.
9b was obtained in 50% yield by using the same method of 9a. HRMS (ESI) calcd for C47H59F3IN12O12 [M+H]+ 1167.3372; found, 1167.04; The purity of the conjugate 9b was confirmed by using the same HPLC procedure; Rt = 34.2 min; purity = 97.9%.
9c was obtained in 52% yield by using the same method of 9a. HRMS (ESI) calcd for C48H62F3IN12O12 [M+2H]+ 1182.36; found, 1182.15; The purity of the conjugate 9c was confirmed by using the same HPLC procedure; Rt =34.5 min; purity = 95.7%.
9d was obtained in 60% yield by using the same method of 9a. HRMS (ESI) calcd for C49H63F3IN12O12 [M+2H]+ 1196.38; found, 1196.11; The purity of the conjugate 9d was confirmed by using the same HPLC procedure; Rt = 34.4 min; purity = 95.4%.
9e was obtained in 42% yield by using the same method of 9a. HRMS (ESI) calcd for C48H60F3IN12O13 [M]+ 1196.3400; found, 1196.7208; The purity of the conjugate 9e was confirmed by using the same HPLC procedure; Rt = 34.2 min; purity = 97.5%.
3.2.9. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Conjugates 9f–h
To a solution of the 2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl4-((3-(3,4-difluoro-2-((2-fluoro-4-iodophenyl)amino) benzamido)propyl)amino)-4-oxobutanoateactivated ester10 (4.05 mg, 3 μmol) in anhydrous DMF (1.5 mL) was added the cyclic RGD peptide dimer E[c(RGDyK)]2 (4.0 mg, 6 μmol). The pH of the resulting mixture was adjusted to 8.5–9.0 with diisopropylethyl amine (DIPEA). The reaction was stirred at room temperature overnight and the desired product was isolated by semi-preparative HPLC. The collected fractions were combined and lyophilized to give a fluffy white powder 9f (2.89 mg, yield 50%); HRMS (ESI) calcd. for C79H105F3IN22O22 [M+H]+ 1897.6771; found, 1897.8009; The purity of the conjugate 9f was confirmed by using the same HPLC procedure of 9a; Rt = 31.7 min; purity = 96.8%.
9g was obtained in 70% yield by using the same method of 9f. HRMS (ESI) calcd. for C59H82N12F3IO17 [M+H]+ 1414.49; found, 1414.38; The purity of the conjugate 9g was confirmed by using the same HPLC procedure; Rt = 34.2 min; purity = 98.5%.
9h was obtained in 45% yield by using the same method of 9f. HRMS (ESI) calcd. for C48H61F3IN12O12 [M+H]+ 1181.35, found, 1181.51; The purity of the conjugate 9h was confirmed by using the same HPLC procedure; Rt = 34.1 min; purity = 98.3%.
3.2.10. General Procedure for the Synthesis of (S)-4-(3-((3,4-difluoro-2-((2-fluoro-4-iodophenyl) amino)benzamido)oxy)-2-hydroxypropoxy)-4-oxobutanoic Acid 11
11 was obtained through the method similar to compound 8a as a white solid(91% yield); mp. 64.1−66.7 °C; IR (neat) 2926, 1732, 1602, 1496, 1280, 1166, 831; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 16.13 (s, 1H), 8.12 (br, 1 H), 7.37 (d, J = 10.0 Hz, 2H), 7.29 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 6.89−6.82 (m, 1H), 6.56−6.51 (m, 1H), 4.30−3.76 (m, 5H), 2.65 (s, 4H); 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −127.91, −129.10, −142.65; HRMS (ESI) calcd. for C20H19F3IN2O7 [M+H]+ 583.0189; found, 583.0187.
3.2.11. General Procedure for the Synthesis of (S)-3-((3,4-difluoro-2-((2-fluoro-4-iodophenyl)amino) benzamido)oxy)-2-hydroxypropyl (2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl) succinate 12
12 was obtained through the method similar to compound 10 as a white solid (35% yield); mp. 76.1−78.2 °C; IR (neat) 2926, 1737, 1516, 1496, 1274, 1205, 1070, 763, 750; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 9.83 (s, 1H), 8.26 (br,1H), 7.40−7.37 (m, 2H), 7.30 (d, J = 8.5Hz), 6.88−6.82 (m, 1H), 6.58−6.53(m, 1H), 4.23−3.72(m, 5H), 2.96−2.92(m, 2H), 2.82 (s, 4H), 2.78−2.75(m, 2H); 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −128.14 (d, J = 4.4Hz), −128.98 (d, J = 3.2Hz), −143.15 (d, J = 20.9Hz); HRMS (ESI) calcd. for C24H22F3IN3O9 [M+H]+ 680.0353; found, 680.0338.
3.2.12. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Conjugate 13
13 was obtained through the method similar to compound 9f as a white soild (40% yield); HRMS (ESI) calcd for C47H59F3IN12O13 [M+H]+ 1184.3162; found, 1184.1226. The purity of the conjugate 13 was confirmed by the same HPLC procedure; Rt = 34.2 min; purity = 95.7%.
3.3. General Procedure for the HTRF Phosphor-MEK1 and HTRF Phosphor-ERK2 Assays
The HTRF phosphor-MEK1 assay was used to test for capability of compounds to inhibit the phosphorylation reaction of inactive MEK1. The assay was performed under the following reaction conditions: a constitutively active BRAF was obtained from Carna Biosciences (Kobe, Japan) and it was tested at a concentration of 7 nM.The test compounds dissolved in DMSO at 10 mM were diluted in assay buffer (50 mM HEPES buffer, pH 7.0, 10 mM MgCl2, 1 mM DTT, 0.5 mM or thovanadate, and 0.01% BSA) and added to 40 nMGST-labeled inactive MEK1, and the reaction was initiated with 100 μM ATP. Phosphorylated MEK1 was determined quantitatively by formation of a complex with specific Eu-labeled anti-phospho p44/42 MAPK (Thr202/Tyr204) antibody and anti-GST-XL665.After 3 h, time-resolved fluorescence was read using a FlexStation 3 plate reader (Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, CA, USA). Excitation of europium (the donor) using a 314 nm excitation filter results in energy transfer to the fluorophore of anti-GST-XL665 which is detected by an increase in the fluorescence emission of anti-GST-XL665 at 668 nm and a decrease in the fluorescence emission of europium at 620 nm. The curve-fitting software GraphPad Prism 4.0 was used to generate the curves and determine the IC50 values. The HTRF phosphor-ERK2assay was used to test for inhibition of compounds relative to active MEK1. The assay was performed under the following reaction conditions: A constitutively active MEK1 was obtained from Carna Biosciences and it was tested at a concentration of 5.72 nM with 40 nM inactive ERK2, 30 μM ATPand test compounds at a variety of concentrationsin assay buffer. After 2 h reaction at RT, the phosphop-ERK2 was terminated by the addition of 5 μL Anti-Phospho p44/42 MAPK (Thr202/Tyr204)-Cryptate(CisBiol) and 26 nM Anti-GST-XL665. The calculation method of HTRF ratio was the same with that in HTRF phosphor-MEK1 assay.
3.4. Cell-Based Assays
3.4.1. Cell Culture
A375, U87, A549 cell line, which were obtained from the National Platform of Experimental Cell Resources for Sci-Tech (Beijing, China), were cultured in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM; Hyclone, Logan, UT, USA), supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated FBS (Hyclone), 100 U/mL penicillin, and 100 μg/mL streptomycin (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd., Osaka, Japan). The cells were cultured in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2 in air at 37 °C.
3.4.2. Anti-Proliferation Assay
The cytotoxicity of the RGD-MKE1 conjugates on A375 melanoma cells, ERK signal pathway hyper-activated cell line, was studied in vitro by using an SRB assay. A375 cells (4.5 × 103) or U87 cells (5.0 × 103) were plated in each well of a 96-well tissue culture plate. Medium supplemented with 10% FBS was added, and cells were allowed to adhere for 24h. Cells were then incubated with serial dilutions of PD0325901 and RGD-MKE1 conjugates for 72 h in triplicate. Then the medium was removed from the 96-well plate, and 10% ice-cold trichloroacetic acid (TCA, 200 μL) was added. The plate was kept at 4 for one hour after which was washed five times with deionized water, then stained with Sulforhodamine B (SRB, 100 μL, Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) before air drying. After washing with 1% acetic acid, the bound dye was solubilized with Tris base A (Sigma) and 100 μL of each sample were transferred into a 96-well plate, and then absorbance was read in a 96-well plate reader at 540 nm.Inhibitory ratio (%) = [(ODcontrol − ODtreated)/(ODcontrol)] × 100%. Cytotoxicity was also expressed as the concentration of compounds inhibiting cell growth by 50% (IC50 value) which was calculated by the GraphPad Prism 5 software.
3.4.3. Western Blotting Assay
To evaluate the expression levels of ERK singal pathway after treated with conjugates, A375 cells were treated with compounds for 2 h respectively. Confluent cells were washed with ice-cold phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), and treated with lysis buffer (Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology, Suzhou, China) on ice for 1 h. Then the lysates were collected by scraping from the plates and then centrifuged at 13,000 rpm at 4 °C for 15 min. The protein concentration was quantitated using a Pierce BCA Protein Assay Kit (Thermo Scientific, Rockford, IL, USA) ona FlexStation 3 Benchtop Multi-Mode Microplate Reader at 562 nm (Molecular Devices). An equal amount of proteins (10 μg per lane) for each sample were analyzed by SDS-PAGE on a 10% gel. After electro-blotting to PVDF membrane (Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA) at 400 mA for 1 h, membranes were blocked with 5% nonfat dry milk for 1 h at room temperature. Membrane were washed with 0.1% PBST three times and then incubated with primary antibodies overnight at 4 °C. Antibodies against pERK and ERK (Cell Signaling Technology, Inc., Danvers, MA, USA) were utilized as the primary antibodies. After removal of the primary antibody, the membranes were washed with PBST and incubated for 3 h at room temperature with a secondary horseradish peroxidase-coupled IgG antibody (Cell Signaling Technology, Inc.). Finally, protein products were analyzedby Image LabTM software(ChemiDocTM XRS System, BIO-RAD, Hercules, CA, USA) with. Expression levels of pERK and ERK protein were normalized against β-actin protein expression levels.
3.4.4. Flow Cytometric Cell Cycle Analysis
The proportion of A375 cells in different phases were measured by flow cytometry analysis. A375 cells were seeded in 6-well plates (3 × 106 cells/well) at 37 °C under an atmosphere of 5% CO2 for 24 h. After 24 h incubation with compounds, the cells were collected and washed twice with PBS. Each group was fixed overnight in ice-cold 70% ethanol at 4 °C and re-suspended in PBS containing 0.1 mg/mL RNase A and 5 ug/mL propidiumidodide (PI). After incubated for 30min at room temperature in the dark, the cells were analyzed by flow cytometry using a FACS Calibur instrument (Becton-Dickinson, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA). Here the untreated cells were used as the control. The analysis of cell cycle distribution was subsequently performed using the Modfit software.
3.4.5. DNA Replication Study
Proliferating A375 cells were determined by the EdU In Vitro Imaging Kit (Ribobio, Guangzhou, China).EdU (5-ethynyl-2'-deoxyuridine) is a nucleoside analog of thymidine that is incorporated into DNA during active DNA synthesis only by proliferating cells. After incorporation, a fluorescent molecule was added that reacted specifically with EdU, making possible fluorescent visualization of proliferating cells. According to the manufacturer’s protocol, A375 cells were cultured in 96-well plates at 4.5 × 103cells per well and left to grow at 37 °C under an atmosphere of 5% CO2 24 h. Cells were treated with the compounds of 1 μM for 24 h. After that, cells were incubated with 50 μMEdU for 2 h at 37 °C, and then were fixated with 4% paraformaldehyde for 15 min. The cells were stained by 1× Apollo staining fluid (included in the kit) before permeabilization with 0.5% TritonX-100. Cell nucleuses were stained with 1× Hoechst 33342 for 30 min.The cells were tested by the OLYMPUS IX81 inverted fluorescence microscope (Olympus America Inc., Center Valley, PA, USA). The EdU+ cells were detected at the excitation of 550 nm. The EdU− cells were detected at the excitation of 350 nm.
4. Conclusions
We have designed, synthesized and biologically evaluated two novel series of RGD-MEKI conjugates based on the MEK1/2 inhibitor PD0325901 for specific integrin receptor-targeting anti-cancer therapy. The biological analysis showed that all the conjugates efficiently inhibited ERK pathway and arrested melanoma A375 cells at G1 phase with the same drug mechanism as the parent drugPD0325901. The anti-proliferation activity of conjugates was inhibited by the scrambled peptide conjugate 9h, which indicated that the RGD-MEKI conjugates underwent an integrin receptor mediated route. Compared to the alkoxylamine analog conjugates 9a–g, direct conjugate RGD-PD0325901 (13) exhibited excellent anti-tumor properties. Future reports will describe modifications of this conjugating drug candidate for optimization of in vivo properties. We believe that these preliminary studies lay a foundation that may be built upon for a new tumor targeting therapy based on small molecule targeted drugs.
Abbreviations
| MEK | mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal regulated kinase |
| ERK | mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| pERK | phosphor-ERK; HTRF, homogeneous time-resolved fluorescence |
| NSCLC | non-small cell lung cancer; SRB, sulforhodamine B |
| PyBOP | benzotriazole-1-yl-oxy-tris-pyrrolidino-phosphonium hexafluoro phosphate |
| NHS | N-hydroxy succinimide |
| DCC | N, N'-dicyclohexyl-carbodiimide |
| CH2Cl2 | methylene chloride |
| FBS | fetal bovine serum |
| BCA | bicinchoninic acid |
| SDS-PAGE | sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| PVDF membrane | polyvinylidenedifluoride membrane |
| PBST | phosphate buffered saline Tween-20 |
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary materials can be accessed at: http://www.mdpi.com/1420-3049/18/11/13957/s1.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education (No.20120001120023) and grant from the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2009ZX09301-010) and the grant from National Sciences Foundation of China (Nos. 21072224 and Nos. 21272268), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, and the Research Funds of Renmin University of China (11XNI003).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- McCubrey, J.A.; Steelman, L.S.; Chappell, W.H.; Abrams, S.L.; Wong, E.W.; Chang, F.; Lehmann, B.; Terrian, D.M.; Milella, M.; Tafuri, A.; et al. Roles of the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in cell growth, malignant transformation and drug resistance. Biochimi. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1773, 1263–1284. [Google Scholar]
- Sebolt-Leopold, J.S.; Herrera, R.; Ohren, J.F. The mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway for molecular-targeted cancer treatment. Recent Results Canc. Res. 2007, 172, 155–167. [Google Scholar]
- Cobb, M.H. MAP kinase pathways. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 1999, 71, 479–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolch, W. Meaningful relationships: The regulation of the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway by protein interactions. Biochem. J. 2000, 351, 289–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagut, C.; Settleman, J. Targeting the RAF-MEK-ERK pathway in cancer therapy. Cancer Lett. 2009, 283, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanasekaran, N.; Premkumar Reddy, E. Signaling by dual specificity kinases. Oncogene 1998, 17, 1447–1455. [Google Scholar]
- Henderson, Y.C.; Chen, Y.; Frederick, M.J.; Lai, S.Y.; Clayman, G.L. MEK inhibitor PD0325901 significantly reduces the growth of papillary thyroid carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2010, 9, 1968–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haura, E.B.; Ricart, A.D.; Larson, T.G.; Stella, P.J.; Bazhenova, L.; Miller, V.A.; Cohen, R.B.; Eisenberg, P.D.; Selaru, P.; Wilner, K.D.; et al. A phase II study of PD-0325901, an oral MEK inhibitor, in previously treated patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 2450–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LoRusso, P.A.; Krishnamurthi, S.S.; Rinehart, J.J.; Nabell, L.M.; Croghan, G.A.; Chapman, P.B.; Selaru, P.; Kim, S.; Ricart, A.D.; Wilner, K.D. Clinical aspects of a phase I study of PD-0325901, a selective oral MEK inhibitor, in patients with advanced cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2007, 6, 3469S–3470S. [Google Scholar]
- Majumdar, S.; Siahaan, T.J. Peptide-mediated targeted drug delivery. Med. Res. Rev. 2012, 32, 637–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danhier, F.; Le Breton, A.; Preat, V. RGD-based strategies to target alpha (v) beta (3) integrin in cancer therapy and diagnosis. Mol. Pharm. 2012, 9, 2961–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juliano, R.L.; Ming, X.; Nakagawa, O.; Xu, R.; Yoo, H. Integrin targeted delivery of gene therapeutics. Theranostics 2011, 1, 211–219. [Google Scholar]
- Ohren, J.F.; Chen, H.; Pavlovsky, A.; Whitehead, C.; Zhang, E.; Kuffa, P.; Yan, C.; McConnell, P.; Spessard, C.; Banotai, C.; et al. Structures of human MAP kinase kinase 1 (MEK1) and MEK2 describe novel noncompetitive kinase inhibition. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2004, 11, 1192–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, M.B.; Adams, M.E.; Kanouni, T.; Mol, C.D.; Dougan, D.R.; Feher, V.A.; O’Connell, S.M.; Shi, L.; Halkowycz, P.; Dong, Q. Structure-based design and synthesis of pyrrole derivatives as MEK inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 4156–4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, S.D.; Bridges, A.J.; Dudley, D.T.; Saltiel, A.R.; Fergus, J.H.; Flamme, C.M.; Delaney, A.M.; Kaufman, M.; LePage, S.; Leopold, W.R.; et al. The discovery of the benzhydroxamate MEK inhibitors CI-1040 and PD 0325901. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 6501–6504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neustadt, B.R. Facile Preparation of N-(Sulfonyl)Carbamates. Tetrahedron Lett. 1994, 35, 379–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.F.; Atkinson, R.N.; King, S.B. Preparation and evaluation of new L-canavanine derivatives as nitric oxide synthase inhibitors. Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 6557–6565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassis, S.; Karigiannis, G.; Balayiannis, G.; Militsopoulou, M.; Mamos, P.; Francis, G.W.; Papaioannou, D. Simple syntheses of N-alkylated spermidine fragments and analogues of the spermine alkaloid kukoamine A. Tetrahedron Lett. 2001, 42, 1579–1582. [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch, H.M.; Glinski, J.A.; Hernandez, M.; Haugwitz, R.D.; Narayanan, V.L.; Suffness, M.; Zalkow, L.H. Synthesis of congeners and prodrugs .3. Water-soluble prodrugs of taxol with potent antitumor-activity. J. Med. Chem. 1989, 32, 788–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, X.Z.; Xiong, Z.M.; Cheng, Z.; Fisher, D.R.; Liu, S.; Gambhir, S.S.; Chen, X.Y. microPET imaging of glioma integrin alpha(V)beta(3) expression using Cu-64-labeled tetrameric RGD peptide. J. Nucl. Med. 2005, 46, 1707–1718. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Cai, W.B.; Chen, X.Y. Near-infrared fluorescence imaging of tumor integrin alpha(v)beta(3) expression with Cy7-labeled RGD multimers. Mol. Imaging. Biol. 2006, 8, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Z.; Xiong, Z.M.; Wu, Y.; Cai, W.B.; Tseng, J.R.; Gambhir, S.S.; Chen, X.Y. Quantitative PET imaging of tumor integrin alpha(v)beta(3) expression with F-18-FRGD2. J. Nucl. Med. 2006, 47, 113–121. [Google Scholar]
- Lorusso, P.M.; Adjei, A.A.; Varterasian, M.; Gadgeel, S.; Reid, J.; Mitchell, D.Y.; Hanson, L.; DeLuca, P.; Bruzek, L.; Piens, J.; et al. Phase I and pharmacodynamic study of the oral MEK inhibitor CI-1040 in patients with advanced malignancies. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 5281–5293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjei, A.A.; Cohen, R.B.; Franklin, W.; Morris, C.; Wilson, D.; Molina, J.R.; Hanson, L.J.; Gore, L.; Chow, L.; Leong, S.; et al. Phase I pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of the oral, small-molecule mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1/2 inhibitor AZD6244 (ARRY-142886) in patients with advanced cancers. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 2139–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elduque, X.; Sánchez, A.; Sharma, K.; Pedroso, E.; Grandas, A. Protected maleimide building blocks for the decoration of peptides, peptoids, and peptide nucleic acids. Bioconjugate Chem. 2013, 24, 832–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aufort, M.; Gonera, M.; Lelait, M.A.; Czarny, B.; Clainche, L.L.; Thaï, R.; Landra, A.; Brimont, M.R.; Dugave, C. Synthesis, in vitro screening and in vivo evaluation of cyclic RGD analogs cyclizedthrough oxorhenium and oxotechnetium coordination. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 1779–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Wickenden, J.G.; Campbell, N.E.; Leung, J.C.T.; Johnson, K.M.; Sammis, G.M. Construction of carbo- and heterocycles using radical relay cyclizations initiated by alkoxy radicals. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 2019–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballini, R.; Petrini, M. A new procedure for dethioacetalization via equilibrium exchange with aqueous acetone, paraformaldehyde and amberlyst 15 as acidic catalyst. Synthesis 1990, 4, 336–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.Y.; Bae, S.J.; Lee, M.Y.; Baek, S.H.; Chang, S.; Kim, S.H. Chemical affinity matrix-based identification of prohibitin as a binding protein to anti-resorptive sulfonyl amidine compounds. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 727–729. [Google Scholar]
- Ramalingam, K.; Raju, N. Heteroatom-Bearing Ligands and Metal Complexes Thereof. U.S. Patent 5608110, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, Z.W.; Liu, J.J.; Thea, N.; Russell, D. Compositions Containing, Methods Involving, and Uses of Non-Natural Amino Acids and Polypeptides. WO 2006/069246, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Barrett, S.D.; Biwersi, C.M.; Chen, M.H.G.; Kaufman, M.D.; Tecle, H.; Warmus, J.S. Oxygenated Esters of 4-Lodo Phenylamino Benzhydroxamic Acids. U.S. Patent 2004/0054172A1, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, Z.W.; Atkinson, K.C.; Biroc, S.; Buss, T.; Cook, M.; Krayonv, V.; Marsden, R.; Pinkstaff, J.; Skidmore, L.; Sun, Y.; Szydlik, A.; Valenta, I. Compositions Containing, Methods Involving, and Uses of Non-Natural Amino Acid Linked Dolastatin Derivatives. WO 2012/166560A1, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, E.; Hurley, B.; Yang, H.W.; Lyssikatos, J.; Blake, J.; Marlow, A.L. Heterocyclic Inhibitors of MEK and Methods of Use Thereof. U.S. Patent 2005/0054701A1, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors.
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).