Abstract
Three homoisoflavanones were isolated from the “piña” and leaves of Agave tequilana Weber. The compounds were identified as: 5,7-dihydroxy-3-(4-methoxybenzyl)-chroman-4-one (1), 7-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-chroman-4-one (2) and 4’-demethyl-3,9-dihydro-punctatin (3). This is the first phytochemical study carried out to Agave tequilana Weber.
1. Introduction
The Agavaceae is a family plant with nine genera and about 293 species. The most important genus is Agave, with about 166 species. Agaves are rosette, monocotyledoneous and monocarpic plants [1,2]. The agave plant has two main parts: the long spiked leaves from which sisal type fibres can be obtained and the “head” or “piña” from which juices are extracted for alcohol production. After the leaves are removed, the head looks like a pine cone, hence, the Spanish name piña (Figure 1). After removal of the leaves the piña weighs roughly 30–50 kg [3]. The most important diversity centre of agave is the Mexican territory, with species spread from southwestern United States through Central America, the Caribbean and into northern South America. Blue agave (Agave tequilana Weber), a member of the lily family, is grown extensively in the east and west regions of Guadalajara in Central Mexico. It is the raw material for production of the alcoholic beverage tequila. The origin-domination tequila name is applicable only to distillate from Weber blue agave grown within the limits of the State of Jalisco [4].

Figure 1.
“Head” or “piña” (pine cone) from Agave tequilana Weber.
In an ample research work, Lopez et al. have described the carbohydrate composition [5,6,7] and volatile constituents [8] of Agave tequilana Weber. In this context and with the goal to contribute to enrich this knowledge we decided to perform a phytochemical study of Agave tequilana Weber. It is important to emphasize that to date no similar study has been reported in literature. Thus, this paper describes the isolation and structural elucidation of homoisoflavanones from ethyl acetate extracts of the “head” or “piña” and leaves.
2. Results and Discussion
The “piña” of Agave tequilana Weber (35 kg) was ground and extracted with water. The shredded agave fiber obtained from this first step was dried on air and at room temperature. Then, the solid was extracted with hexane and ethyl acetate at room temperature in a closed container several times. The extracts were concentrated under reduced pressure at 40 °C yielding 5 g and 13.5 g of dry extract, respectively. After removal of solvent, the hexane extract was fractionated on a silica gel column, eluted with a gradient hexane:ethyl acetate (9:1→1:9) yielding 9 fractions (IA-IXA). A sample of the first refined fraction (2 g) was analyzed by CG/MS to identify the compounds shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
CG/MS analysis of a fraction of hexane extract from “piña” of Agave tequilana Weber.
| Entry | Compound | Time | Area % |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | (E,E)-2,4-decadienal | 10.38 | 0.98 |
| 3 | Methyl 8-methyl-decanoate | 18.45 | 0.89 |
| 4 | Phenylmethyl benzoate | 19.46 | 18.83 |
| 5 | Palmitic acid | 19.73 | 41.86 |
| 6 | Z-9-Decanoic acid | 21.97 | 18.36 |
| 7 | 5-Octadecine | 22.24 | 11.60 |
In the same way, the extract obtained with ethyl acetate was fractionated on a silica gel column, eluted with a gradient hexane:ethyl acetate (9:1→1:9) yielding 9 fractions (IB-IXB). From the first refined fraction we were able to isolate 120 mg of the homoisoflavanone 1 (Figure 2), which was identified by means of NMR and comparison with the data previously reported in the literature.
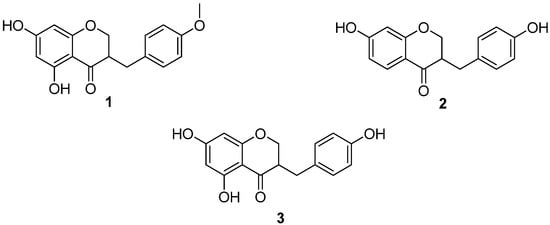
Figure 2.
Homoisoflavanones from Agave tequilana Weber.
The 1H-NMR spectrum of 1 was characterized by the presence of two sets of peaks from an ABX system attributable to the presence of non-equivalent protons at C-2 and C-9. These signals were observed at δ 4.0–4.3 and 2.6–2.8 ppm, respectively. The methine proton at C-3 gave resonance signals at about δ 2.81 (Table 2). The 13C-NMR spectrum also exhibited signals for C-2, C-3 and C-9 carbons at δ 68.9, 46.8 and 32.0 ppm, respectively (Table 3). The 1H-NMR spectrum of 1 showed an AA’BB’ system at δ 7.14 and 6.87 ppm (Table 2), due to the protons of ring B. The assignment was further confirmed by the 13C-NMR spectrum (δ 130 for C-2’/C-6’ and δ 114.1 for C-3’/C-5’, Table 3). Additionally, the 1H-NMR spectrum of 1 showed the presence of meta coupled signals at δ 5.99 and 6.92 ppm and these were assigned to H-6 and H-8 of ring A respectively (Table 2). These observations suggest that the C-5 and C-7 positions were oxygenated. Homoisoflavanone 1 is known to occur in Eucomis bicolour [9], Ladebouria graminifolia [10], Ladebouria floribundia [11] and Agave barbadensis [12]. The spectroscopic data given for that compound in these reports were identical to those measured by us in this study.
Additionally, the leaves of Agave tequilana Weber were dried on air and at room temperature and 650 g of them extracted several times with hexane, acetone and methanol at room temperature in a closed container. The extracts were concentrated under reduced pressure at 40 °C yielding 4.3 g, 3.9 and 44.2 g of dry extract, respectively. After purification on a chromatographic column sitosterol and stigmasterol were identified as the major components of the hexane extract, while glucose, sucrose and fructose were obtained from the methanolic extract. To our delight, the acetone extract resulted more interesting because was possible to isolate other homoisoflavanones. Thus, the acetone extract was fractionated on a silica gel column, eluting with a hexane-ethyl acetate (9:1→1:9) gradient yielding 9 fractions (IC-IXC). The homoisoflavanone 1 (5 mg) was isolated from the first refined fraction, while the homoisoflavanones 2 (3 mg) and 3 (2.5 mg) were isolated from the third fraction (Figure 2). The 1H- NMR spectra of 2 show the presence of two ABX systems attributable to the presence of non-equivalent protons at C-2 and C-9. These signals were observed at δ 4.11–4.36 and 2.6–2.8 ppm, respectively. The methine proton at C-3 gave resonance signals at about δ 2.81 (Table 2). The 13C- NMR spectrum also exhibited signals for the C-2, C-3 and C-9 carbons at δ 68.9, 46.8 and 32.0 ppm, respectively (Table 3). The 1H-NMR spectrum of 2 showed an AA’BB’ system at δ 7.09 and 6.78 ppm (Table 2), due to the protons of ring B. The assignment was further confirmed by the 13C-NMR spectrum (δ 130 for C-2’/C-6’ and δ 114 for C-3’/C-5’, Table 3). For ring A, the 1H-NMR spectrum of 2 showed the presence of an ortho coupled signal at δ 7.83 that was assigned to H-5. In the same spectrum it is possible to see an ABX system at δ 6.52 which corresponds to H-6. Finally, the signal at δ 6.38 was assigned to H-8 (Table 2). The structure of this compound was confirmed by comparison with the data described in literature for the same homoisoflavanone isolated of the Dracaena draco [13,14] and Dracaena cochinchinesis [15].

Table 2.
1H-NMR spectral data, δ (J Hz) for compounds 1, 2 and 3 in CDCl3 (300 MHz).
| Proton | Homoisoflavanone | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| H-2b | 4.11, dd, (11.7, 6.6) | 4.15, dd, (11.4, 7.5) | 4.14, dd, (11.4, 7.5) |
| H-3 | 2.81, m | 2.8, m | 2.8, m |
| H-5 | - | 7.83, d, (8.7) | - |
| H-6 | 5.99, d, (2.1) | 6.52, dd, (8.7, 2.4) | 6.0, d, (2.4) |
| H-8 | 5.92, d, (2.1) | 6.38, d, (2.4) | 5.98, d, (2.4) |
| H-9a | 3.17, dd, (13.2, 3.6) | 3.17, dd, (13.5, 4.2) | 3.1, dd, (17.1, 4.2) |
| H-9b | 2.73, dd, (13.2, 3.6) | 2.65, dd, (13.5, 10.8) | 2.65, dd, (17.1, 10.5) |
| H-2’ | 7.14, d, (8.4) | 7.09, d, (8.4) | 7.33, d, (8.7) |
| H-3’ | 6.87, d, (8.4) | 6.78, d, (8.4) | 6.88, d, (8.7) |
| H-5’ | 6.87, d, (8.4) | 6.78, d, (8.4) | 6.88, d, (8.7) |
| H-6’ | 7.14, d, (8.4) | 7.09, d, (8.4) | 7.33, d, (8.7) |
| 4’-OMe | 3.8, s | - | - |

Table 3.
13C-NMR spectral data, δ (J Hz) for compounds 1, 2 and 3 in CDCl3 (300 MHz).
| Carbon | Homoisoflavanone | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| 3 | 46.8 | 47.6 | 45.5 |
| 4 | 197.8 | 193 | 197.7 |
| 4a | 102.5 | 103 | 101 |
| 5 | 164.5 | 128.8 | 163.6 |
| 6 | 96.6 | 114.5 | 95 |
| 7 | 164.5 | 167.9 | 166.7 |
| 8 | 95 | 103 | 94.7 |
| 8a | 163.1 | 163.6 | 162.6 |
| 9 | 32 | 31.8 | 31.2 |
| 1’ | 129.7 | 130.2 | 128 |
| 2’ | 130 | 130.1 | 129.8 |
| 3’ | 114.1 | 114.1 | 115.1 |
| 4’ | 158.3 | 158.3 | 155.5 |
| 5’ | 114.1 | 114.1 | 115.1 |
| 6’ | 130 | 130.1 | 129.8 |
| 4’-OMe | 55.3 | - | - |
In the case of homoisoflavanone 3, the 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR spectra are similar to the spectra of 1. The difference is the absence of the methoxyl substituent at C-4’, which shows signals at δH 3.8 and δC 55.3 ppm in the case of the 1. The 1H-NMR (Table 2) and 13C-NMR (Table 3) dates are identical to the described in the literature for the homoisoflavanone isolated from Dracaena draco [13], Dracaena loureiri [16,17], Muscari comosum [18], Muscari neglectum [19], Chinodoxa luciliae [20], Ledeboria graminifolia [10] and Ledeboria floribunda [11].
3. Experimental
3.1. General
The solvents used in this work were purchased from Aldrich. Flash column chromatography (FCC) was performed using flash silica gel (32–63 μm) and a solvent polarity correlated with TLC mobility was employed. The chromatographic columns were monitored by TLC carried out on 0.25 mm E. Merck silica gel plates. Developed TLC plates were visualized under a short-wave UV lamp and by heating plates that were dipped in ethanol/H2SO4 (15:1). Melting points, determined with Reichert apparatus, are uncorrected. Optical rotations were measured at 598 nm on a Jasco DIP-370 digital polarimeter using a 100 mm cell. NMR experiments were conducted on a Varian 300 MHz instrument using CDCl3 (99.9% D) as the solvent. Chemical shifts are reported in ppm with respect to TMS (tetramethylsilane).
3.2. Plant material
Agave tequilana Weber was obtained from the Jose Cuervo Tequila plant in Tequila Jalisco in Central Mexico in 2003. The leaves were cut off, keeping the stems and bases leaves, a part usually called “piña” due to it similarity to a pine cone fruit.
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
The fresh “piña” of Agave tequilana Weber (35 kg) were ground and extracted with water. The shredded agave fibrous obtained from this first step was dried on air and at room temperature for a week. Then, dry solid (3 kg) was extracted three times, at room temperature for 48 h with hexane (12 L) in a closed container. The combined extracts were concentrated under reduced pressure at 40 °C to give a viscous concentrate (5 g). In a second stage, the solid residue was extracted with EtOAc (12 L) three times for 48 h, at room temperature in a closed container. After solvent elimination 13.5 g of a viscous concentrate was obtained.
The hexane extract was fractionated on a silica gel column, eluted with a hexane-ethyl acetate gradient (9:1→1:9) yielding 9 fractions (IA-IXA). The quantitative determination of the volatile compounds hexanal, (E,E)-2,4-decadienal, methyl 8-methyldecanoate, phenylmethyl benzoate, palmitic acid, Z-9-decanoic acid and 5-octadecene from fraction IIA, was carried out using gas chromatography with flame ionization detection, as reported in the literature [21].
The residue obtained with AcOEt (13.5 g) was dissolved in CH2Cl2, Celite was added, and after the solvent had been removed in vacuo, the extract was subjected to silica gel chromatography eluting with a hexane-ethyl acetate gradient (9:1→1:9) to give 9 fractions (IB-IXB). The homoisoflavanone 1 (120 mg) was obtained from fraction IIB by flash chromatography using hexane-ethyl acetate as eluent (8:2).
The air dried powdered leaves of Agave tequilana Weber (650 g) were extracted three times with hexane, acetone and methanol (3 L), at room temperature for 48 h, to give 4.3 g, 3.9 and 44.2 g of dry extract, respectively. Sitosterol and stigmasterol were obtained from the hexane extract, and glucose, sucrose and fructose were identified from methanolic extract, using gas chromatography with flame ionization detection.
The acetone extract was dissolved in CH2Cl2, Celite was added, and after the solvent had been removed in vacuo, the extract was subjected to silica gel chromatography eluting with a hexane-ethyl acetate gradient (9:1→1:9) to give 9 fractions (IC-IXC). The homoisoflavanone 1 (5 mg) was obtained from fraction IC. From fraction IIIC were isolated the homoisoflavanones 2 (3 mg) and 3 (2.5 mg).
5,7-Dihydroxy-3-(4-methoxybenzyl)-chroman-4-one (1). IR-KBr Pellet (ν, cm-1): 3384, 2922, 2851, 1639, 1454, 1379, 1270, 1161, 833; 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR, see Table 1 and Table 2; HRMS: [M]+m/z: 300.0992. Calc. for C17H16O5 300.0998.
4. Conclusions
In summary, we were able to isolate three known compounds from the EtOAc and acetone extracts of Agave tequilana Weber. These compounds belong to a small homogeneous group of naturally occurring oxygen heterocycles called homoisoflavanones, whose basic structure consists of a 16 carbon skeleton, including a chromanone system with a benzyl group at position 3. It is the first time that the compounds 2 and 3 have been isolated from the genus Agave. Finally, is important to remark that, the value of present study lies in the importance of the plant to the tequila industry.
Acknowledgements
The present work was supported for Allied DOMECQ Company. We wish to thank Gabriela Salcedo for her technical assistance.
References and Notes
- Good-Avila, S.V.; Souza, V.; Gaut, B.S.; Eguiarte, L.E. Timing and rate of speciation in Agave (Agavaceae). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 9124–9129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cházaro-Basañez, M.; Valencia-Pelayo, O.; Lomelí-Sención, J.A.; Vargas-Rodríguez, Y.L. Agave vazquezgarciae (Agavaceae), a new species from Jalisco, México. Novon 2006, 16, 458–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idarraga, G.; Ramos, J.; Zuñiga, V; Sahin, T.; Young, R.A. Pulp and paper from blue Agave waste from tequila production. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 4450–4455. [Google Scholar]
- Santacruz-Ruvalcaba, F.; Portillo, L. Thin cell suspension layer as a new methodology for somatic embryogenesis in Agave tequilana Weber cultivar azul. Ind. Crops Prod. 2009, 29, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancilla-Margalli, N.A.; López, M.G. Generation of Maillard compounds from inulin during the thermal processing of Agave tequilana Weber var. azul. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 806–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, M.G.; Mancilla-Margalli, N.A.; Mendoza-Diaz, G. Molecular structures of fructans from Agave tequilana Weber var. azul. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 7835–7840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancilla-Margalli, N.A.; López, M.G. Water-soluble carbohydrates and fructan structure patterns from Agave and Dasylirion species. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 7832–7839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachenmeier, D.W.; Sohnius, E.-M.; Attig, R.; López, M.G. Quantification of selected volatile constituents and anions in Mexican Agave spirits (Tequila, mezcal, sotol, bacanora). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 3911–3915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, W.; Andermatt, P.; Schaad, W.A.; Tamm, C. Homoisoflavanone, IV. Neue inhaltstoffe der Eucomin-Reihe von Eucomis bicolour. Helv. Chim. Acta 1976, 59, 2048–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutanyatta, J.; Matapaa, B.G.; Shushu, D.D.; Abegaz, B.M. Homoisoflavonoids and xanthones from the tubers of wild and in vitro regenerated Ledebouria graminifolia and cytotoxic activities of some of the homoisoflavonoids. Phytochemistry 2003, 62, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, M.S. Homoisoflavanones from Ledebouria floribunda. Fitoterapia 2009, 80, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinto, W.F.; Simmons-Boyce, J.L.; McLean, S.; Reynolds, W.F. Constituents of Agave Americana and Agave barbadensis. Fitoterapia 2005, 76, 594–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camarda, L.; Merlini, L.; Nasini, G. Dragon’s blood from Dracaena draco, structure of novel homoisoflavonoids. Heterocycles 1983, 20, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, A.G.; León, F.; Sánchez-Pinto, L.; Padrón, J.I.; Bermejo, J. Phenolic Compounds of Dragon’s Blood from Dracaena draco. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 1297–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.A.; Li, H.Z.; Zhang, Y.J.; Yang, C.R. Flavonoids from the Resin of Dracaena cochinchinensis. Helv. Chim. Acta 2004, 87, 1167–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichikawa, K.; Kitaoka, M.; Taki, M.; Takaishi, S.; Lijima, Y.; Boriboon, M.; Akiyama, T. Retrodihydrochalcones and homoisoflavones isolated from Thai medicinal plant Dracaena loureiri and their estrogen agonist activity. Planta Med. 1997, 63, 540–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likhitwitayawuid, K.; Sawasdee, K.; Kirtikara, K. Flavonoids and stilbenoids with COX-1 and COX-2 inhibitory activity from Dracaena loureiri. Planta Med. 2002, 68, 841–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adinolfi, M.; Barone, G.; Lanzetta, R.; Laonigro, G.; Mangoni, L.; Parrilli, M. Three 3-benzyl-4-chromanones from Muscari comosum. Phytochemistry 1985, 24, 624–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, G.; Corsaro, M.M.; Lanzeta, R.; Parrilli, M. Homoisoflavanones from Muscari neglectum. Phytochemistry 1988, 27, 921–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsaro, M.M.; Lanzeta, R.; Mancino, A.; Parrilli, M. Homoisoflavanones from Chinodoxa luciliae. Phytochemistry 1992, 31, 1395–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors.
© 2010 by the authors;