Quaternion Entropy for Analysis of Gait Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Background
2.2. Quaternion Approximate Entropy
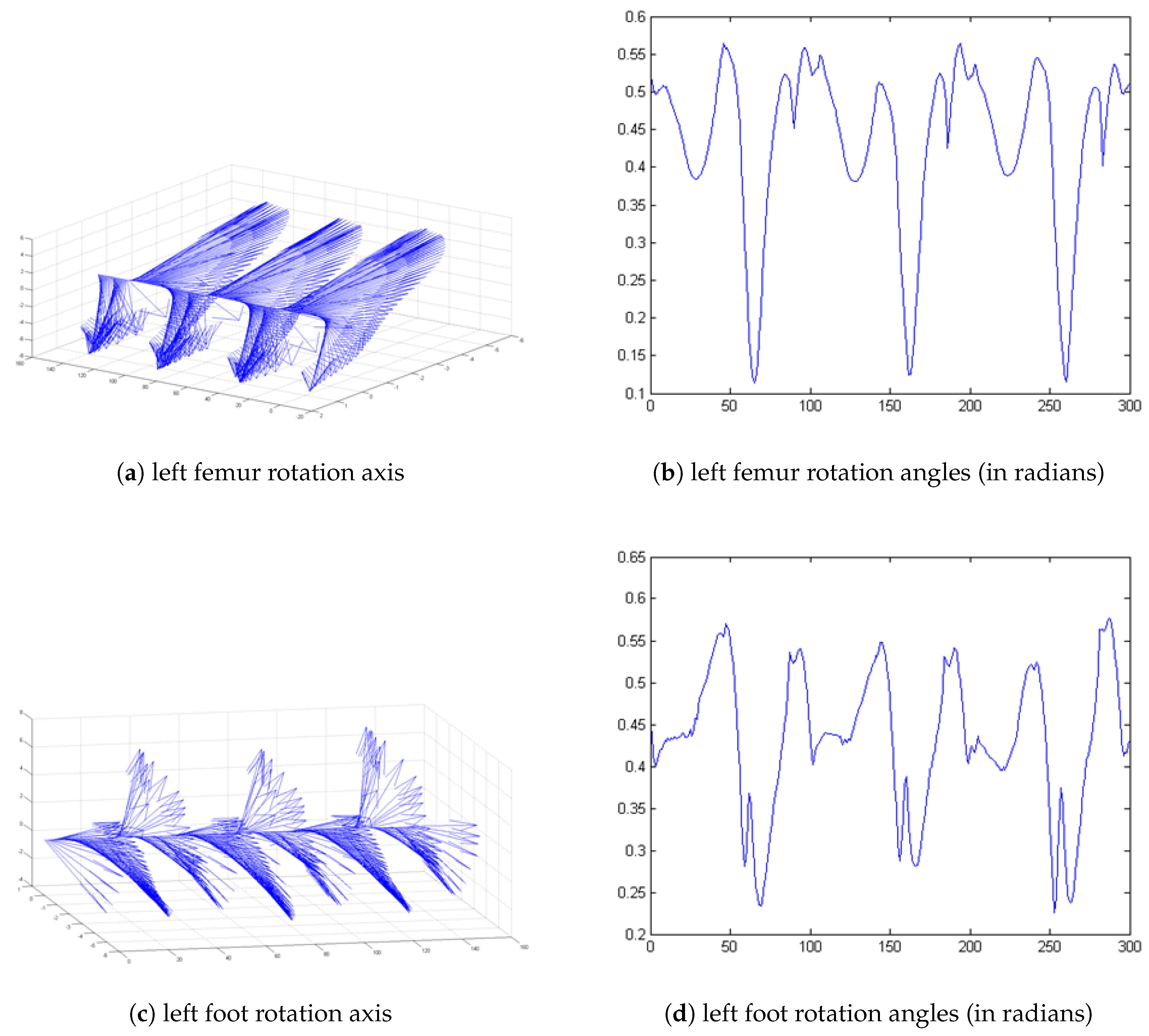
2.3. Treadmill Experiments
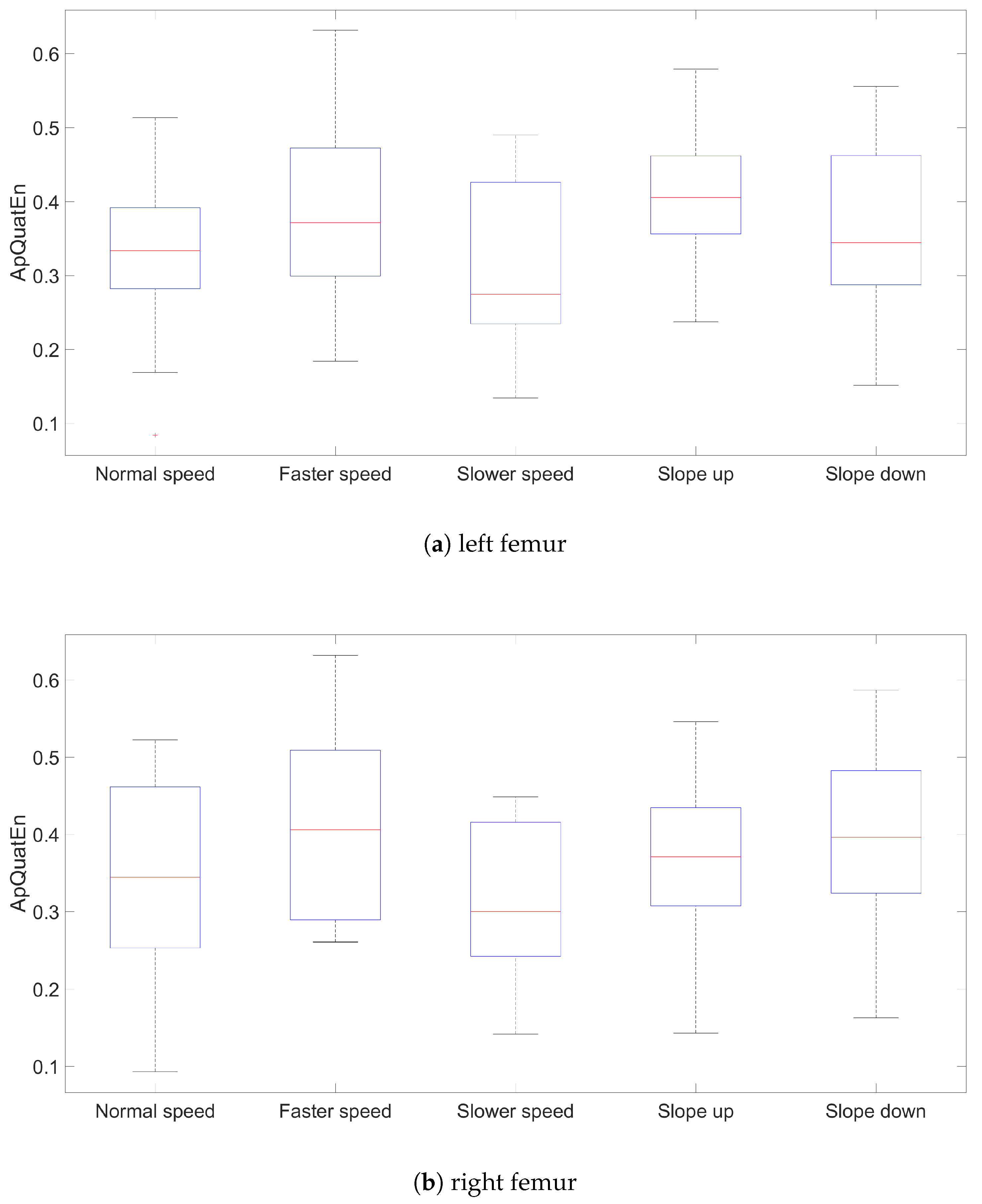
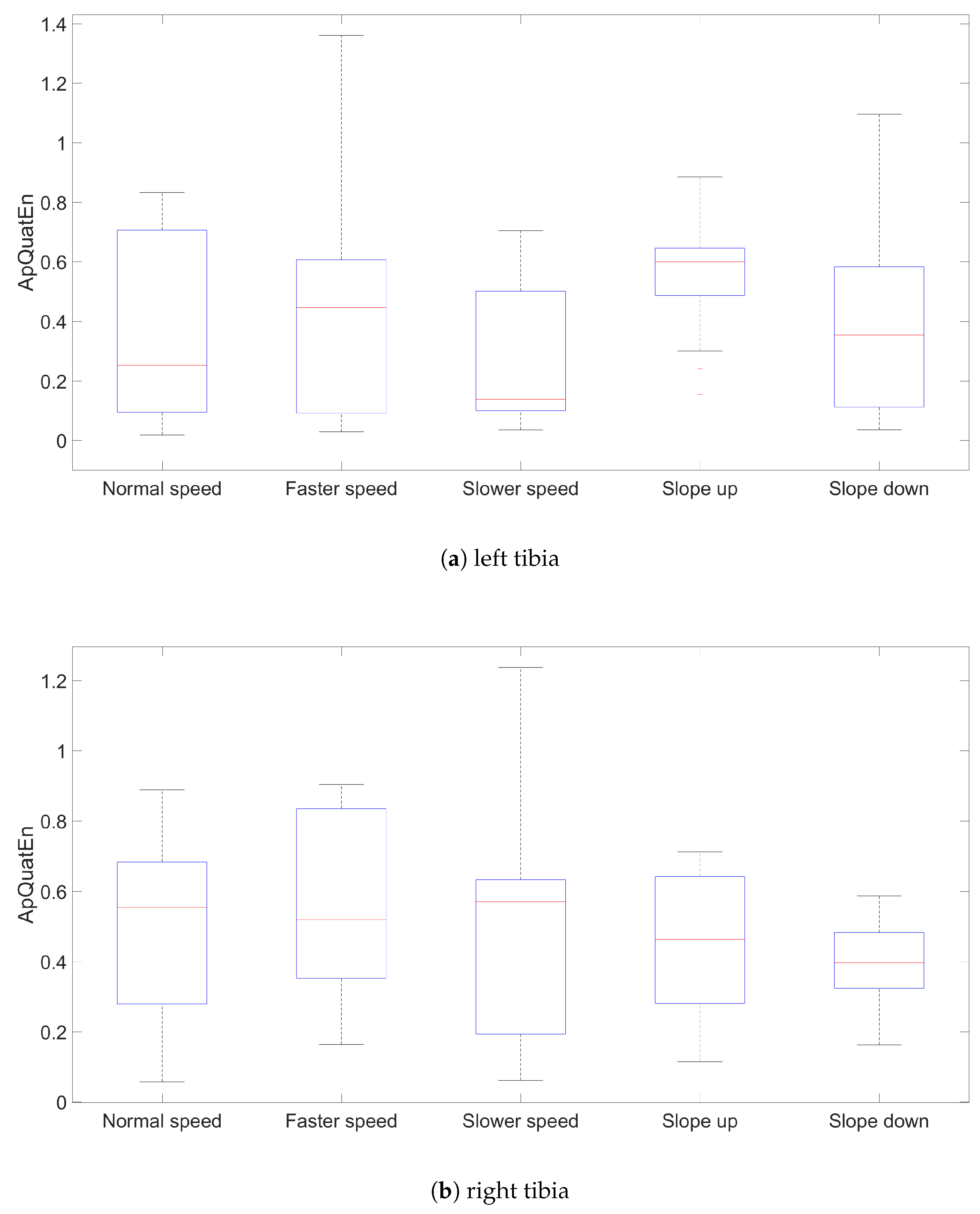
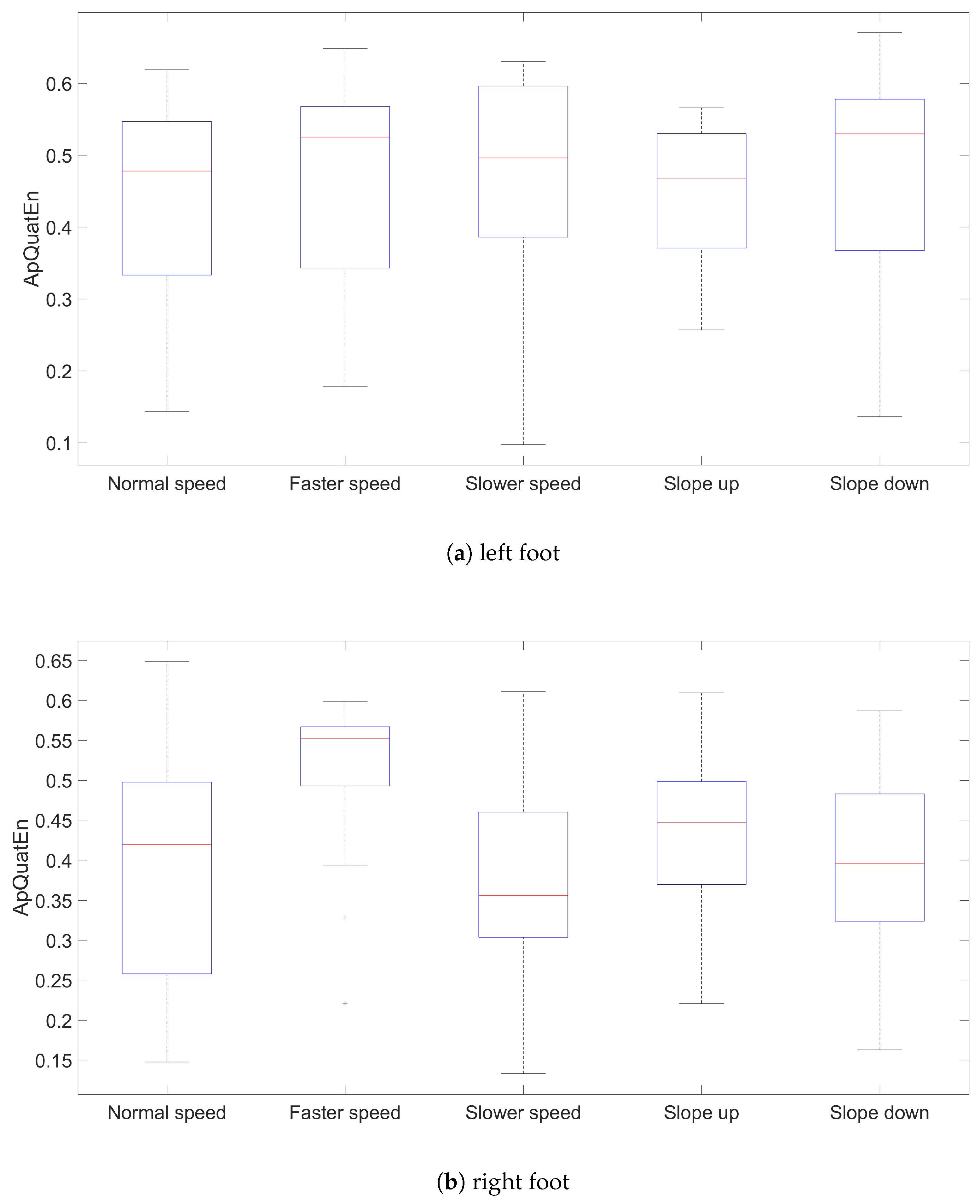
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schuster, H.G.; Just, W. Deterministic Chaos: An Introduction; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, A.; Swift, J.B.; Swinney, H.L.; Vastano, J.A. Determining Lyapunov exponents from a time series. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 1985, 16, 285–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pincus, S. Approximate entropy (ApEn) as a complexity measure. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 1995, 5, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pincus, S.M. Approximate entropy as a measure of system complexity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 2297–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckmann, J.P.; Ruelle, D. Ergodic theory of chaos and strange attractors. In The Theory of Chaotic Attractors; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1985; pp. 273–312. [Google Scholar]
- Richman, J.S.; Moorman, J.R. Physiological time-series analysis using approximate entropy and sample entropy. Am. J. Physiol.-Heart Circ. Physiol. 2000, 278, H2039–H2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pincus, S.M.; Viscarello, R.R. Approximate entropy: A regularity measure for fetal heart rate analysis. Obstet Gynecol 1992, 79, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, D.; Furman, M.; Pincus, S.; Ryan, S.; Lipsitz, L.; Goldberger, A. Aging and the complexity of cardiovascular dynamics. Biophys. J. 1991, 59, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Liu, C.; Shao, P.; Li, L.; Sun, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, F. Comparison of different threshold values r for approximate entropy: Application to investigate the heart rate variability between heart failure and healthy control groups. Physiol. Meas. 2010, 32, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abásolo, D.; Hornero, R.; Espino, P.; Poza, J.; Sánchez, C.I.; de la Rosa, R. Analysis of regularity in the EEG background activity of Alzheimer’s disease patients with Approximate Entropy. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2005, 116, 1826–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.S.; Roy, R.J.; Jensen, E.W. EEG complexity as a measure of depth of anesthesia for patients. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2001, 48, 1424–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannathal, N.; Choo, M.L.; Acharya, U.R.; Sadasivan, P. Entropies for detection of epilepsy in EEG. Comput. Methods Progr. Biomed. 2005, 80, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharya, U.R.; Molinari, F.; Sree, S.V.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Ng, K.H.; Suri, J.S. Automated diagnosis of epileptic EEG using entropies. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2012, 7, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yentes, J.M.; Hunt, N.; Schmid, K.K.; Kaipust, J.P.; McGrath, D.; Stergiou, N. The appropriate use of approximate entropy and sample entropy with short data sets. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 41, 349–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, M.; Peng, C.K.; Goldberger, A.L.; Hausdorff, J.M. Multiscale entropy analysis of human gait dynamics. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2003, 330, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, S.; Sepehri, N.; Wu, C.; Szturm, T. Sample Entropy of Human Gait Center of Pressure Displacement: A Systematic Methodological Analysis. Entropy 2018, 20, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramdani, S.; Seigle, B.; Lagarde, J.; Bouchara, F.; Bernard, P.L. On the use of sample entropy to analyze human postural sway data. Med. Eng. Phys. 2009, 31, 1023–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisi, M.; Stagni, R. Complexity of human gait pattern at different ages assessed using multiscale entropy: From development to decline. Gait Posture 2016, 47, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, M.; Goldberger, A.L.; Peng, C.K. Multiscale entropy analysis of biological signals. Phys. Rev. E 2005, 71, 021906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGregor, S.J.; Busa, M.A.; Skufca, J.; Yaggie, J.A.; Bollt, E.M. Control entropy identifies differential changes in complexity of walking and running gait patterns with increasing speed in highly trained runners. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 2009, 19, 026109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczęsna, A.; Świtoński, A.; Słupik, J.; Josiński, H.; Wojciechowski, K. Wavelet features in motion data classification. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Numerical Analysis and Applied Mathematics 2015 (ICNAAM-2015), Rhodes, Greece, 23–29 September 2015; AIP Publishing: Melville, NY, USA, 2016; Volume 1738. [Google Scholar]
- Piórek, M.; Josiński, H.; Michalczuk, A.; Świtoński, A.; Szczęsna, A. Quaternions and joint angles in an analysis of local stability of gait for different variants of walking speed and treadmill slope. Inf. Sci. 2017, 384, 263–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczęsna, A. Verification of the blobby quaternion model of human joint limits. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2018, 39, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczęsna, A. Quaternion wavelet-based energy and entropy to analysis human gait data. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Numerical Analysis and Applied Mathematics 2017 (ICNAAM-2017), Thessaloniki, Greece, 25–30 September 2017; AIP Publishing: Melville, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Szczęsna, A.; Świtoński, A.; Słupik, J.; Zghidi, H.; Josiński, H.; Wojciechowski, K. Quaternion Lifting Scheme Applied to the Classification of Motion Data. Inf. Sci. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Switonski, A.; Josinski, H.; Wojciechowski, K. Dynamic time warping in classification and selection of motion capture data. Multidimens. Syst. Signal Process. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, A.J. Visualizing Quaternions; Morgan Kaufmann: Burlington, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Goldman, R. Understanding quaternions. Gr. Models 2011, 73, 21–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, D.Q. Metrics for 3D rotations: Comparison and analysis. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 2009, 35, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramkow, C. On averaging rotations. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 2001, 15, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josiński, H.; Michalczuk, A.; Świtoński, A.; Mucha, R.; Wojciechowski, K. Quantifying chaotic behavior in treadmill walking. In Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Intelligent Information and Database Systems, Bali, Indonesia, 23–25 March 2015; pp. 317–326. [Google Scholar]
- Arellano-Valle, R.B.; Contreras-Reyes, J.E.; Stehlík, M. Generalized skew-normal negentropy and its application to fish condition factor time series. Entropy 2017, 19, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
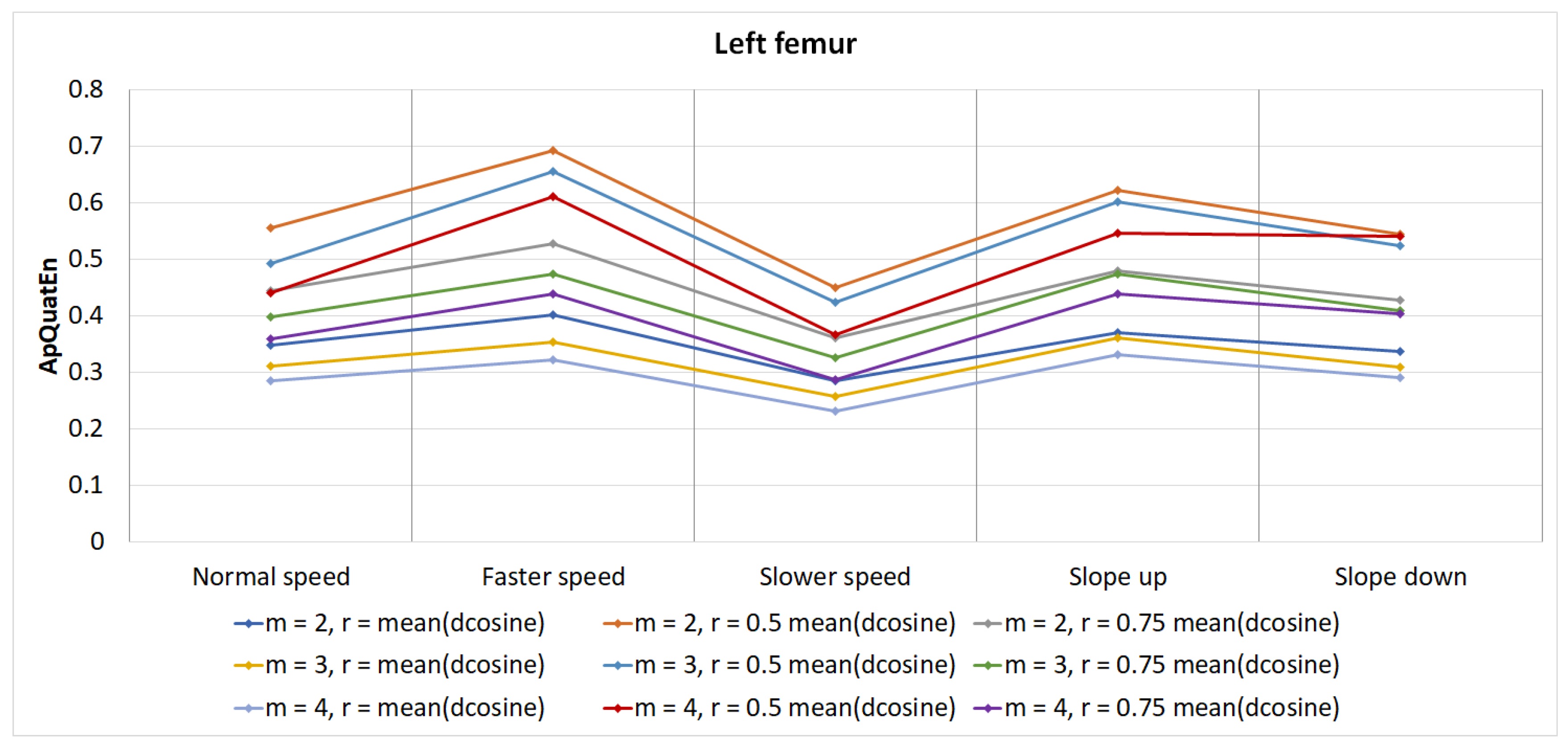
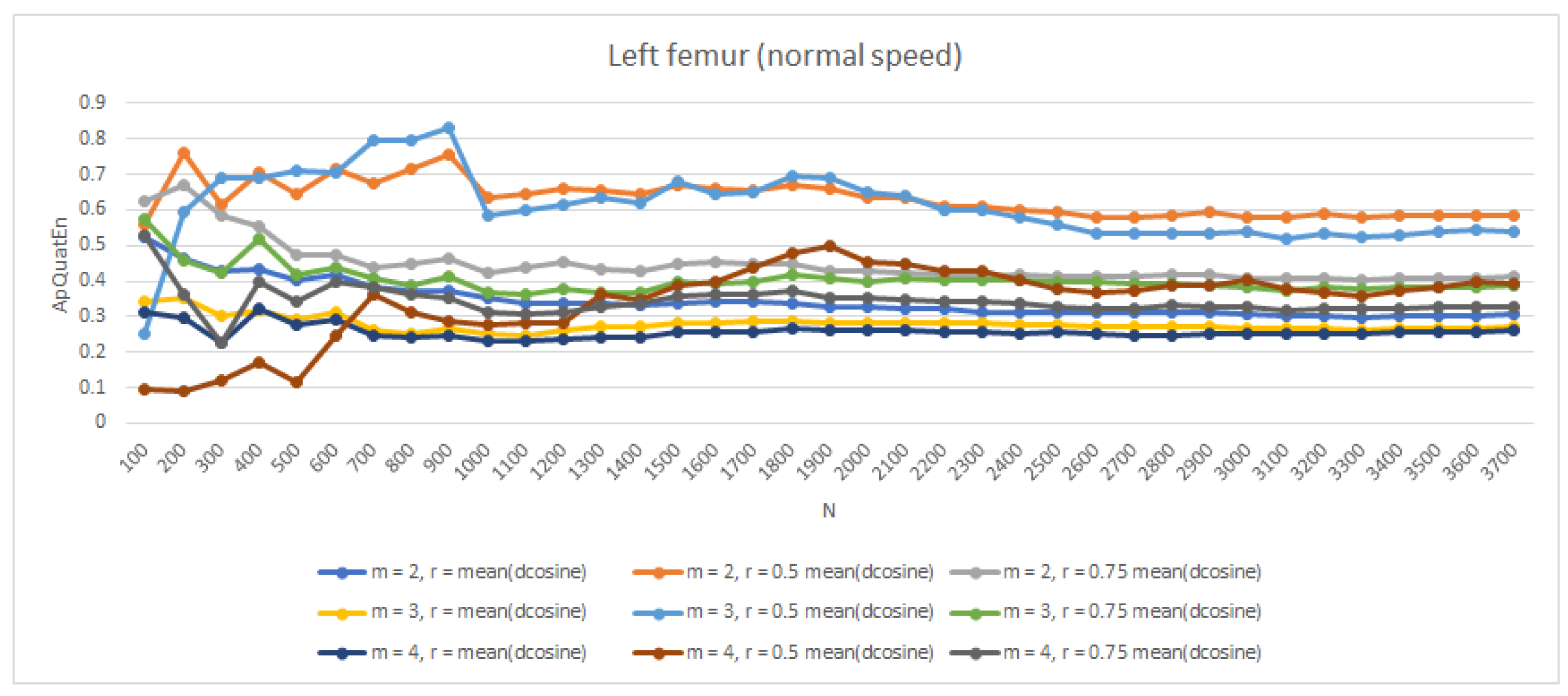
| Normal | Faster | Slower | Up | Down | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lfemur | 0.334 | 0.371 | 0.274 | 0.405 | 0.344 |
| rfemur | 0.345 | 0.406 | 0.300 | 0.371 | 0.396 |
| femur | 0.337 | 0.388 | 0.286 | 0.387 | 0.371 |
| ltibia | 0.252 | 0.446 | 0.138 | 0.599 | 0.353 |
| rtibia | 0.554 | 0.519 | 0.570 | 0.463 | 0.396 |
| tibia | 0.338 | 0.519 | 0.233 | 0.537 | 0.385 |
| lfoot | 0.478 | 0.525 | 0.496 | 0.467 | 0.529 |
| rfoot | 0.420 | 0.552 | 0.356 | 0.447 | 0.396 |
| foot | 0.443 | 0.544 | 0.410 | 0.447 | 0.447 |
| Left Femur | Right Femur | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | Faster | Slower | Up | Down | Normal | Faster | Slower | Up | Down | ||
| Normal | 1.000 | 0.699 | 0.378 | 0.157 | 0.334 | Normal | 1.000 | 0.862 | 0.412 | 0.347 | 0.343 |
| Faster | 0.699 | 1.000 | 0.462 | 0.303 | 0.476 | Faster | 0.862 | 1.000 | 0.699 | 0.537 | 0.604 |
| Slower | 0.378 | 0.462 | 1.000 | 0.921 | 0.941 | Slower | 0.412 | 0.699 | 1.000 | 0.899 | 0.951 |
| Up | 0.157 | 0.303 | 0.921 | 1.000 | 0.944 | Up | 0.347 | 0.537 | 0.899 | 1.000 | 0.834 |
| Down | 0.334 | 0.476 | 0.940 | 0.944 | 1.000 | Down | 0.343 | 0.604 | 0.951 | 0.834 | 1.000 |
| Left Tibia | Right Tibia | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | Faster | Slower | Up | Down | Normal | Faster | Slower | Up | Down | ||
| Normal | 1.000 | 0.695 | 0.733 | 0.143 | 0.564 | Normal | 1.000 | 0.611 | 0.718 | 0.874 | 0.458 |
| Faster | 0.695 | 1.000 | 0.632 | 0.328 | 0.549 | Faster | 0.611 | 1.000 | 0.505 | 0.496 | 0.439 |
| Slower | 0.733 | 0.632 | 1.000 | 0.409 | 0.744 | Slower | 0.718 | 0.505 | 1.000 | 0.797 | 0.685 |
| Up | 0.143 | 0.328 | 0.409 | 1.000 | 0.542 | Up | 0.874 | 0.496 | 0.797 | 1.000 | 0.646 |
| Down | 0.564 | 0.549 | 0.744 | 0.542 | 1.000 | Down | 0.458 | 0.439 | 0.685 | 0.646 | 1.000 |
| Left Foot | Right Foot | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | Faster | Slower | Up | Down | Normal | Faster | Slower | Up | Down | ||
| Normal | 1.000 | 0.728 | 0.510 | 0.439 | 0.491 | Normal | 1.000 | 0.721 | 0.491 | 0.135 | 0.390 |
| Faster | 0.728 | 1.000 | 0.778 | 0.573 | 0.773 | Faster | 0.721 | 1.000 | 0.449 | 0.241 | 0.237 |
| Slower | 0.510 | 0.778 | 1.000 | 0.837 | 0.923 | Slower | 0.491 | 0.449 | 1.000 | 0.901 | 0.909 |
| Up | 0.439 | 0.573 | 0.837 | 1.000 | 0.751 | Up | 0.135 | 0.241 | 0.901 | 1.000 | 0.841 |
| Down | 0.491 | 0.773 | 0.923 | 0.751 | 1.000 | Down | 0.390 | 0.237 | 0.909 | 0.841 | 1.000 |
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szczęsna, A. Quaternion Entropy for Analysis of Gait Data. Entropy 2019, 21, 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/e21010079
Szczęsna A. Quaternion Entropy for Analysis of Gait Data. Entropy. 2019; 21(1):79. https://doi.org/10.3390/e21010079
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzczęsna, Agnieszka. 2019. "Quaternion Entropy for Analysis of Gait Data" Entropy 21, no. 1: 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/e21010079
APA StyleSzczęsna, A. (2019). Quaternion Entropy for Analysis of Gait Data. Entropy, 21(1), 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/e21010079





