Abstract
For ecological economic evaluation based on the unified biophysical matrix this research illustrates an updated emergy synthesis in terms of embodied cosmic exergy instead of embodied solar energy, which successes the foundation of systems ecological theory but changes the starting point for the estimation from simply the sun to the cosmos. According to the modified definition implicating explicit scarcity and strict additivity based on the fundamental thermodynamics laws, the updated emergy approach overcomes the confusable and intractable deficiencies of traditional one and shows firmer theoretical basis as well as better applicability. As a case study for the regional socio-economic ecosystem, a cosmic emergy based ecological economic evaluation of the Beijing urban ecosystem during the period 1978-2004 is presented. The local and external resources supporting the concerned ecosystem are accounted and analyzed in a common unit, i.e., cosmic Joule, according to which a series of indicators are applied to reveal its evolutional characteristics through five aspects as emergy structure, emergy intensity, emergy welfare, environmental impacts, and degree of exploitation and economic efficiency. During the analyzed period, the major emergy source sustaining the operation of the ecosystem had changed from the renewable resources exploited locally to the nonrenewable resources purchased from outside. Emergy intensity for the Beijing urban ecosystem kept rising owing to the continuous investment of resources, which not only improved the living standard but also intensified the environmental pressure. Moreover, the increase of exploitation degree was accompanied with the decline of economic efficiency, while the rising emergy investment ratio implicates that Beijing was at the risks of resources shortage and high dependence on external resources.
Keywords:
emergy synthesis; embodied cosmic exergy; ecological economic evaluation; urban ecosystem; Beijing PACS Codes:
88.05.Jk
1. Introduction
Emergy synthesis is one of the unified biophysical matrices for ecological economic evaluation, whose origin can be traced back to Odum’s theory of systems ecology based on the maximum empower principle, the feedback on cybernetics, and the energy transformation hierarchy of the universe [1,2]. In view of the defects of conventional market-oriented approaches and classical energetics, emergy synthesis takes not only the free natural resources, but also the hierarchy of mass, energy, and information into account [3,4]. The traditional emergy synthesis in terms of embodied solar energy, which considers solar energy as the primary driving force for the ecosphere, is a prevalent approach to evaluate the ecological economic wealth embodied in resources, products, and services by accounting the total work previously involved to generate them and has been applied to a variety of natural and social ecosystems [5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44].
In spite of the extensive applications, the synthesis of solar emergy has undergone some critics (e.g., [45,46,47])), the main concerns of which are the intractable issue of double counting and confusable nature of energy embodiment [48,49,50]. Consequently, Odum and his successors came to realize what matters is available energy, i.e., exergy, and emergy should be explained and defined as exergy embodiment instead of energy embodiment, since there is no possibility for anything to embody energy which is always in conservative cycling and never consumed [4,49]. As a modification, emergy has been reformulated as a function of exergy to associate the physical and mathematical validities of exergy consumption or entropy increase [51]. Meanwhile, discussions also emerged on the relations between emergy evaluation and exergy analysis (e.g., [49,51,52,53]).
The scarcity and usefulness of exergy as the fundamental resource for the ecosphere have been well illustrated by the global thermodynamics with the earth as a cosmic heat engine operating between the solar radiation as a heat source and the cosmic background microwave (CBM) field as a cold sink [54,55], which reveals that cosmic exergy originated in the thermal difference between solar and CBM radiations is the ultimate driving force of the ecosphere instead of solar energy as conventionally supposed. Subsequently, Chen [56] updated the concept of emergy as embodied cosmic exergy (or cosmic emergy) using to the unit of cosmic Joule (Jc) in contrast to the solar Joule (sej) in solar emergy. The cosmic emergy synthesis modifies the solar one through the starting point and clarifies the confusing issues of energy conservation and exergy embodiment according to the first and second laws of thermodynamics. Moreover, the updated emergy synthesis with strict additivity as a result of the renovated emergy power base (EPB) (see below) overcomes the double counting problem and thus is technically more applicable.
A city, or an urban ecosystem, is a super-organism generated for the benefit of human beings and is observed as a significant heterotrophic and self-regulating ecosystem in the biosphere [31]. However, the urban ecosystems are not sustainable without maintaining stable links with their hinterlands, from which energy, food, and materials are obtained and into which wastes are released. In the light of the systems perspective, it is possible to incorporate “emergy” into the conceptualization of a city to thread together both urban and natural systems, despite most of the existing work (see e.g., [17,21,22,23,42,43,57]) constructed on the traditional emergy concept in terms of embodied solar energy. In this paper, as an application of the cosmic emergy approach to the study of urban ecosystem, the Beijing city witnessing significant changes related to its structure, function, and organization is chosen and evaluated in order to reveal its ecological economic vicissitudes during the period 1978-2004.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows. In Section 2, we describe the methodological perspectives of the cosmic emergy synthesis with emphasis on introductions for systems diagram, transformity, and indicators. Section 3 presents the detailed cosmic emergy account of the Beijing urban ecosystem. In Section 4, the accounting results are systematically integrated into five sets of indicators, and corresponding ecological economic characteristics of the concerned system are analyzed. And finally, concluding remarks are drawn in the ending section.
2. Methodology
2.1. General Introduction for Cosmic Emergy
In conventional emergy studies, the solar emergy as embodied solar energy is usually used as a common numeraire for the analyses of industrial and ecological systems since most territorial processes are considered to be driven directly or indirectly by sunlight. Although the definition of emergy as the embodiment of available energy is theoretically sound in the very beginning, the later induced notion of embodied energy is misleading (because energy is conserved according to the first law of thermodynamics and is neither consumable nor can be embodied) and thus would be more appropriately replaced by that of embodied exergy. Differing from energy, exergy (or available energy) is defined as the maximal amount of work that can be extracted from a given system in the process of reaching equilibrium with its local environment [58,59], implying the consumable and irreversible characteristics according to the second law of thermodynamics, which makes it the essential resource for the functioning of all systems and applicable to measure the degradation of quality for energy, mass, and information [56,60].
Considering the earth as a heat engine driven by exergy flows associated with the thermodynamic contrast between the sun and the outer space, the scarcity of cosmic exergy is notable [55,57]. Accordingly, the ultimate and fundamental resource sustaining the ecosphere can be conceptualized as the cosmic exergy obtained by the material earth, instead of the conventionally assumed ones such as solar energy, fossil fuels, or mineral ores. Everything and every system in the earth have to be produced and maintained by work process embodying cosmic exergy consumption, either it is helped by people or not. Therefore, for a general commodity as a product, a service, or an emission the ecological economic cost can be well measured by the cosmic exergy directly or indirectly consumed in making or sustaining it associated with the concerned time and spatial scales. Thus cosmic emergy is brought forward as an update of solar emergy, which is also recognized as the generalization of Szargut's cumulative exergy theory by extending the evaluation baseline of natural resources in traditional narrow sense of fossil fuels and mineral ores to the cosmic exergy availability in the material earth [61,62,63].
In the updated emergy synthesis, the real cost of the generation, as an ecological chain in general, of a product or a service is measured by the cosmic emergy, then each form of resource is translated into cosmic exergy equivalent in unit of Jc based on its conversion factor termed transformity. On the basis of the genuine scarcity and usefulness of cosmic exergy as the fundamental resource for the ecosphere, the cosmic emergy synthesis is rooted in a firm ground with superior adaptability, thus has been applied fruitfully in a variety of studies with different scales [54,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71]. The cosmic emergy budget of the earth was presented by Chen [54] while the resources consumption for the Chinese society from 1981 to 2001 was analyzed by applying the ecological footprint account modified by cosmic emergy [64]. To integrate the social activities with their supporting environment for urban ecosystems, a concrete cosmic emergy accounting scheme was established by Jiang [55] and further developed by Ji [65] with respect to the health issues. In other cases [66,67,68,69], the input-output structures of economies in different scales were analyzed based on cosmic emergy. And most recently, Chen et al. [70] processed an ecological economic modeling for the municipality of Beijing with special focus on the forecasting towards 2100. These studies have greatly expanded the scope of cosmic emergy research and presented solid background for further investigation.
2.2. From Energy Diagram to Exergy Diagram
For the visualization of resource flows and transformation processes, energy diagram is constructed with a series of energy systems symbols according to the graphic directives given by the Odum brothers [4,71,72]. This diagram is still effective in the updated emergy synthesis, but need to be modified according to the properties of exergy, as shown in Figure 1.
In energy diagram, the free renewable resources input including sunlight, precipitation, wind, and earth cycle are shown only partly flowing into the border of system considering most of these resources are not available by the concerned system. However, since all exergy correlated with these free renewable resources has been exhausted in the irreversible input process, the arrow representing corresponding flow points directly into the system without any branches in exergy diagram. In energy diagram, the symbol “hint sink” is applied to represent the dispersal of available energy into a degraded, used state, which is not capable of further work [4]. In exergy diagram, the meaning of the same symbol is updated to “environmental impacts”, indicating all possible influences upon environment during the operation of system. Meanwhile, an additional dotted line with opposite direction is presented as “virtual environmental input” to indicate the work done by environment to dilute emissions.
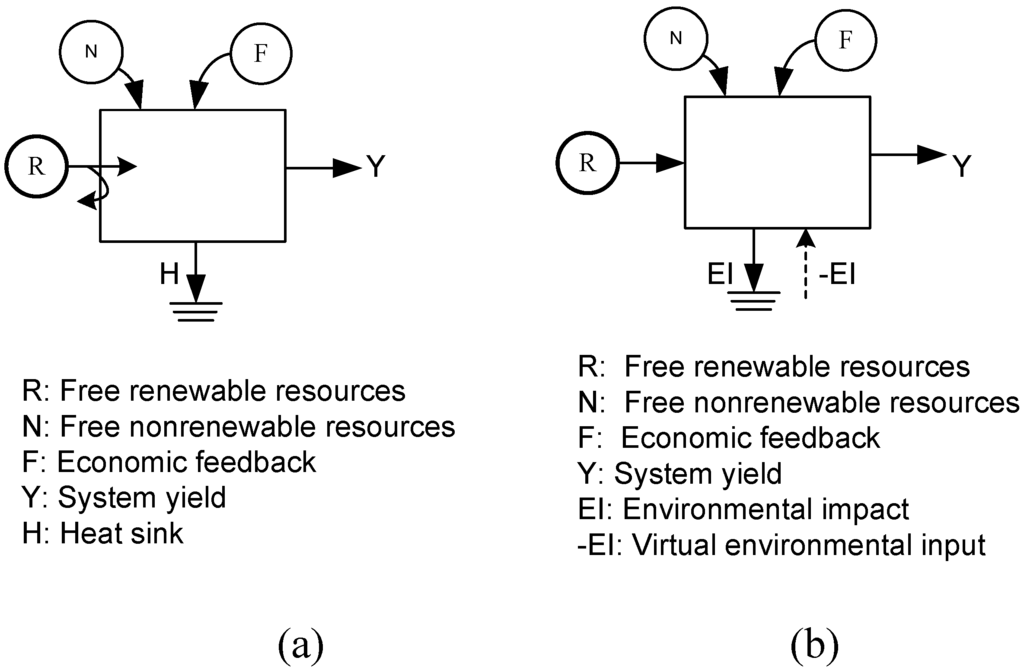
Figure 1.
Comparison between energy diagram and exergy diagram: (a) typical energy diagram; (b) typical exergy diagram.
2.3. Transformity of Cosmic Emergy
In emergy synthesis, transformity is defined as the magnitude of emergy input required for making per unit of output [4]. The larger the transformity is, the higher that item locates in the ecological hierarchy chain. The cosmic emergy synthesis integrates environmental, economic, and social values on a common counting base through transforming multiple forms of energy, mass, and information into the same form, i.e., cosmic exergy, using their respective transformities. In the global cosmic exergy budget indicating a total terrestrial consumption of 1.38 × 1021 Jc/yr [54], seven basic terrestrial exergy flows (i.e., exergy of surface wind, physical exergy of rainfall, chemical exergy of rainfall, physical exergy of runoff, chemical exergy of runoff, exergy of wave, and exergy of earth cycle) are considered, which are coupled with each other and reasonable to be assigned equal importance. Consequently, each of the basic flow is allocated with one seventh of the total terrestrial exergy, i.e., 1.97 × 1020 Jc/yr, and this quantity is termed as the EPB, based on which the transformities of the principal flows are calculated and presented in Table 1. Though progress in earth systems science might give more accurate understanding on the coupled basic flows, the present manipulation ensures all transformities are calculated according to the same baseline and guarantees consistent and comparable cosmic emergy values are obtained as the measures of ecological economic wealth. Using the renovated EPB distributing global cosmic exergy flows without overlapping, the emergy content consumed in any ecological process can be estimated while double counting is avoided.
Despite cosmic transformities in different socio-economic scales have been calculated in [66,67,68,69] using the input-output model, the dataset is not applicable in the present study due to its regional and temporal coverage. Consequently, relevant transformities of goods, products, and materials are inferred taking use of data previously calculated by Odum and his successors [4,2].
For example, the transformity associated with mineral deposits is around 2.10 × 104 Jc/g, as the quotient of the cosmic exergy supporting the earth cycle (1.97 × 1020 Jc/yr) to the annual average sediment yields (9.36 × 1015 g/yr) [4]. Considering the formation of one gram of new soil needs two gram of weathering rock [4], the soil transformity is 4.21 × 104 Jc/g. Referring to the solar transformities of rock and soil as 1.0 × 109 sej/g and 2.0 × 109 sej/g, separately, the cosmic transformities of minerals can be inferred by multiplying a conversion factor of 2.10 × 10-5 Jc/sej to the solar transformities. Based on similar process, the cosmic transformities associated with the organic products on the earth can be inferred by multiplying a conversion factor of 9.00 × 10-4 Jc/sej to the solar ones for convenience.

Table 1.
EPBs, exergy flows, and transformities of basic terrestrial flows (based on [4,55,56].) .
| Note | Item | EPB (Jc/yr) | Exergy flow (J/yr) | Transformity (Jc/J) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Global flows | 1.38 × 1021 | |||
| 1 | Surface wind | 1.97 × 1020 | 6.31 × 1021 | 0.03 |
| 2 | Rain on land, physical | 1.97 × 1020 | 5.61 × 1020 | 0.35 |
| 3 | Rain on land, chemical | 1.97 × 1020 | 3.24 × 1020 | 0.61 |
| 4 | Overland runoff, physical | 1.97 × 1020 | 3.40 × 1020 | 0.58 |
| 5 | Overland runoff, chemical | 1.97 × 1020 | 1.95 × 1020 | 1.01 |
| 6 | Wave | 1.97 × 1020 | 3.09 × 1020 | 0.64 |
| 7 | Earth cycle | 1.97 × 1020 | 2.75 × 1020 | 0.72 |
Although the calculated cosmic transformities in the present edition are far from satisfaction, they are still meaningful and can be treated as a reference before more comprehensive transformity database for the updated methodology is presented systematically. For more detailed illustration on cosmic transformity readers can refer to [55,56].
2.4. Cosimic Emergy Based Indicators
As a systematic reversion, rephrasing, and update of traditional solar emergy synthesis, the cosmic one has obeyed the theoretical basis of systems ecology strictly and thus indicators illustrating various characteristics of ecosystem in terms of efficiency and sustainability are still effective, in spite of the fact that the unit and equivalent is changed from sej to Jc. Consequently, a series of indicators based on the fundamental resource flows are introduced to evaluate the systems performance for the urban ecosystem through five aspects involving emergy structure, emergy intensity, emergy welfare, environmental impacts, and degree of exploitation and economic efficiency.
2.4.1. Emergy Structure
Change in resource type in terms of emergy structure is closely connected with the economic development and ecological organization of a socio-ecological ecosystem [20,25]. Therefore, the estimation of the composition of emergy source is crucial to reveal the ecological economic characteristics of an urban ecosystem. The concrete indicators applied in the present study include local renewable emergy fraction, free emergy fraction, emergy self-sufficiency fraction, purchased emergy fraction, and imported service emergy fraction.
2.4.2. Emergy Intensity
Emergy intensity is generally evaluated by two indicators as empower density and concentrated to rural use ratio. The former represents the emergy flow allocated in one unit of area as a measure of spatial concentration, while the latter reflects the inner structure of available resources and the basic character of a city in terms of emergy use. A developed city with large emergy use and relatively small area usually has high empower density, suggesting that a great deal of emergy resources have to be consumed to maintain its structure and function. Besides, the higher the concentrated to rural use ratio is, the more industrialized a city is.
2.4.3. Emergy Welfare
Emergy as a measure of the real wealth provides a better approximation of actual welfare integrating both economic input and environmental costs than the marker-oriented measures, and five concrete indicators illustrating the average occupation, the comparison between import and export, as well as the diversity of emergy are adopted in the present study.
The emergy use per capita indicators, including the per capita total emergy use and per capita fuel emergy use, evaluate the living standard of local residents effectively. The higher these ratios are, the more emergy can be enjoyed by local residents and thus indicating a higher living standard.
For an urban ecosystem, the emergy welfare for its residents also can be revealed through comparing the resources embodied in imports and exports, which are accounted as the export-import difference and export-import ratio.
Emergy use diversity can be applied to evaluate the resource types which are available by an urban ecosystem. There are many definitions for diversities and the present study adopts that from Huang et [22], which will be explained in detail in the below context. Generally speaking, the higher this indicator is, the more abundant resource types a city uses.
2.4.4. Environmental Impacts
The rapid industrialization not only enhances the quality of living standard, but also brings great environmental impacts, which can be revealed by the emergy indicators of waste to renewable emergy use ratio and waste to total emergy use ratio. Besides the implications to reflect the utilization efficiencies of resources, the two ratios are also indications of the environmental pressure since the higher they are, the larger the stress on the environment is.
2.4.5. Degree of Exploitation and Economic Efficiency
Four indicators, i.e., electricity emergy fraction, emergy investment ratio, emergy to dollar ratio, and economic efficiency, are selected to indicate the degree of exploitation and economic efficiency for an urban ecosystem in this study. Although the amount of total resource use is closely correlated with the degree of urban exploitation, the structure of how the resource is used, i.e. the resources use efficiency, is also important to raise the vitality and competitive power of a city, which can be revealed to some extent by the advanced indicators.
Electricity as a form of secondary energy, which implies high quality along with high transformity, is widely used in urban ecosystems. The ratio of electricity emergy to total emergy use can be used as measure for both resource structure and local living standard.
The degree of urban development can also be revealed through the emergy investment ratio, which is taken as the total purchased nonrenewable emergy input divided by the emergy of the renewable resources. The higher this ratio is, the more purchased resources the urban ecosystem needs to sustain its development. Only proper collocation of the free local resources and purchased external resources can ensure the sustainable development of a city.
Emergy to dollar ratio of a city, reflecting the emergy use efficiency and the purchasing power (for real wealth) of money, is calculated by the total emergy use of a city divided by the urban GNP. Increase of this ratio indicates decrease of emergy use efficiency, and vice versa.
The economic efficiency indicator presented by Huang [22] as a ratio of the total emergy use to the purchased emergy is analyzed in the updated emergy synthesis to investigate the general efficiency of an urban ecosystem.
3. Cosmic Emergy Account for the Beijing Urban Ecosystem
As a case study for the regional socio-economic ecosystem using the modified emergy concept as embodied cosmic exergy, a historical analysis of the Beijing urban ecosystem is conducted. In what follows, the terms emergy is applied to indicate cosmic emergy specifically, if no extra denotation is provided.
3.1. General Review of the Case
As the capital of China, Beijing witnesses the great change of this country, especially since the start of the Reform and Opening-up policy in 1978, which therefore is chosen as the case of this research, with geographic and economic boundary as its administrative area of 16807.8 km2 involving 16 districts and 2 counties and concerned time span from 1978 to 2004.
Beijing enjoys a large variety of mineral resources including iron pyrite, fluorite, steatite, and limestone but is limited in fuels, most of which are input from other domestic areas such as Shanxi, Gansu, and Inner Mongolia. As the second largest energy consuming city of China, Beijing is undergoing a whopping energy consumption-production gap of 94%, as consumption soars while production and reserves decline continually.
The evolution of the Beijing urban ecosystem, as many other metropolises, can be treated as a history of resource consumption and accumulation, which in turn bring changes in living standard, economic structure, and urban organization. During the past centuries, Beijing has transformed from a traditional agricultural society relied mostly on local dispersed natural resources to a modern industrial society supported mainly by imported concentrated resources such as coal, oil, natural gas, and electricity. Meanwhile, most of the flows of resources are accompanied with human services and money flows and detailed exergy diagram of the Beijing urban ecosystem is portrayed in Figure 2. It should be noticed that the cross boundary input/output might comes from/goes to either other domestic regions or foreign countries, which is not indicated in the figure for succinctness but will be taken into account substantially in later calculation.
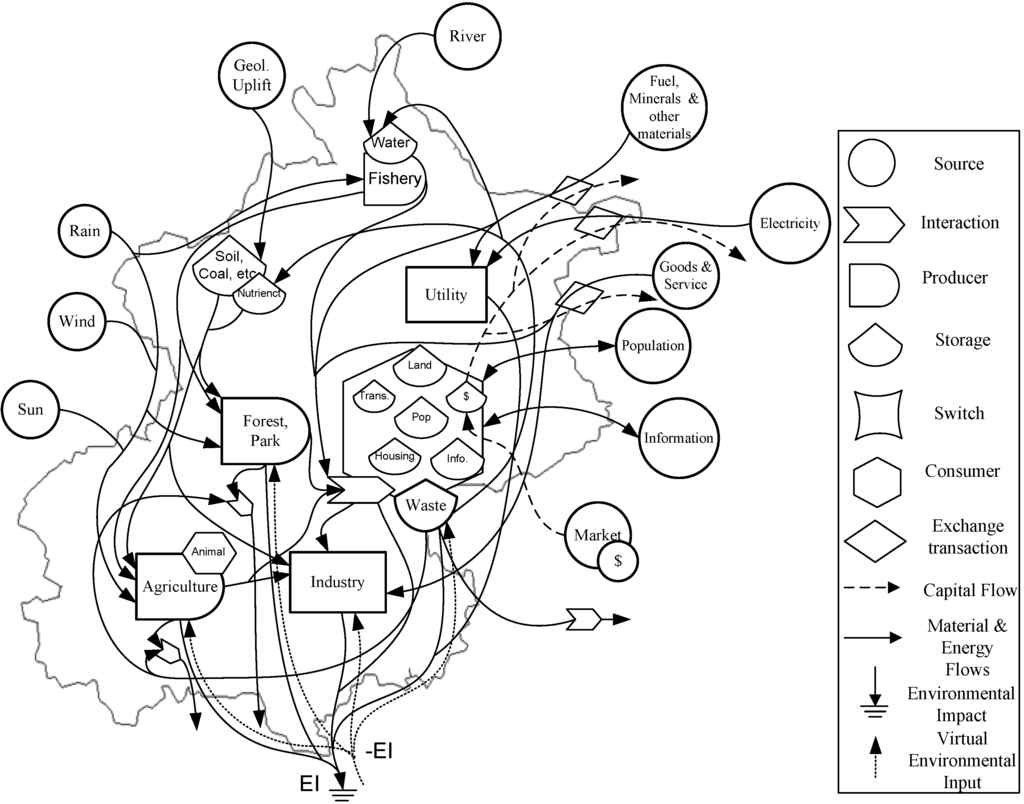
Figure 2.
Exergy diagram for Beijing.
Primary data used in this research are adopted from the official sources on the internet and public issued yearbooks such as China Statistical Yearbook, China Agriculture Yearbook, Beijing Statistical Yearbook, and Annual of Beijing EPA, while one year is taken as the time cycle for analysis.
3.2. Cosmic Emergy Account
According to the detailed ecological economic flows illustrated in Figure 2, a compressed systems diagram for the Beijing urban ecosystem is portrayed in Figure 3, described in which are only the major components and flows propelling the development of this system. The inputs are aggregated into five categories, i.e., free renewable environmental resources (R), exploited local nonrenewable resources (N) that is divided into dispersed rural sources (N0) and concentrated use sources (N1), imported fuels and minerals (F), imported goods (G), and purchased services (P2I). Correspondingly, the outputs from the system involve exported goods (B) and services (P1E). All the processes mentioned above will inevitably produce environmental impacts (EI), for which environment will work as a buffer (-EI), as shown in the bottom of Figure 3.
Table 2 and Table 3 list the evaluated emergy values of the detailed flows and the aggregated flows associated with the Beijing urban ecosystem, respectively.
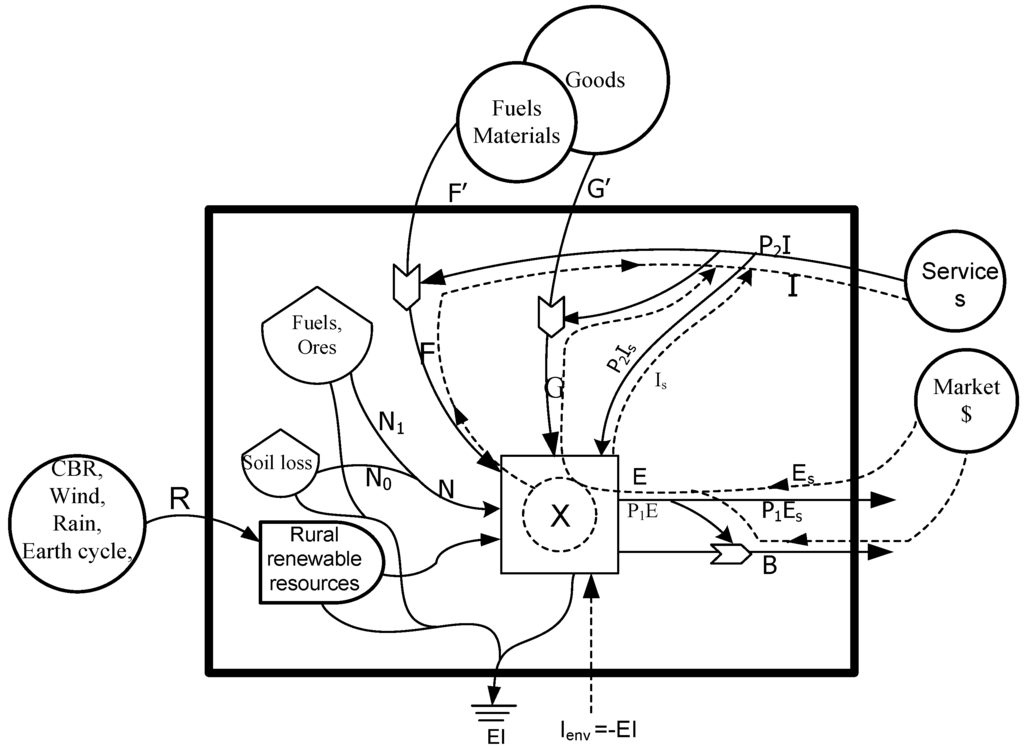
Figure 3.
Exergy diagram for Beijing with major emergy flows.
Since 1978, Beijing has adhered to the policy of Reform and Opening-up with the focus on economic development, and has gradually transformed into a market economy system maintaining rapid economic growth. As a result, the consumptions of energy, materials, and labors increased correspondingly. The account shows that the total emergy use displayed a fluctuating increase from 1.10 × 1019 Jc to 9.46 × 1019 Jc with the development of Beijing during 1978-2004. According to the different sources and categories, the total emergy consumed by the urban ecosystem can be divided into five parts, free renewable sources, local nonrenewable resources, imported fuels and electricity, imported goods, and imported services as shown in Figure 4.
As a result of the rapid increment of the imported goods and services, especially since 1999, the annual consumption reached the maximum value in 2004, which equals 8.57 times of that in 1978. The environmental free renewable resources, involving earth cycle, rain, wind, waves, and tide, maintained in a stable level (between 1.84 × 1016 Jc and 2.17 × 1016 Jc) and held a relatively small share compared with those of nonrenewable resources, which are found to be the fundamental impetus for Beijing as a developed urban ecosystem with long history. It is worthy to mention that in the account process based on the modified emergy as embodied cosmic exergy, the emergy of different renewable resources can be added up directly without the problem of double counting because of the renovated definition of EPB. Figure 5 reveals the composition of free environmental renewable resources from 1978 to 2004. As the predominant free renewable input, (physical and chemical) fraction of emergy of rainfall fluctuated between the minimum value of 81.3% in 1999 to the maximum value of 94.2% in 1991 due to the change in precipitation. Although Beijing is rich in free renewable resources, the exploitation was comparatively insufficient. If this urban ecosystem can take better use of the natural environmental resources, the controversy between the explosive population growth, the economic development, and the shortage of resources might be alleviated.

Table 2.
Emergy account table for Beijing of selected years.
| No. | Item | Units | 1978 | 1980 | 1985 | 1990 | 1995 | 2000 | 2004 |
| Renewable resources | |||||||||
| 1 | Photosynthesis | Jc | 6.94E + 14 | 6.94E + 14 | 6.94E + 14 | 6.94E + 14 | 6.94E + 14 | 6.94E + 14 | 6.94E + 14 |
| 2 | Wind, kinetic | Jc | 1.52E + 15 | 1.52E + 15 | 1.52E + 15 | 1.52E + 15 | 1.52E + 15 | 1.52E + 15 | 1.52E + 15 |
| 3 | Precipitation, geopotential | Jc | 2.01E + 14 | 1.94E + 14 | 3.61E + 14 | 3.49E + 14 | 2.87E + 14 | 1.86E + 14 | 2.42E + 14 |
| 4 | Precipitation, chemical | Jc | 1.58E + 16 | 1.53E + 16 | 2.84E + 16 | 2.75E + 16 | 2.26E + 16 | 1.46E + 16 | 1.90E + 16 |
| 5 | Earth cycle | Jc | 2.44E + 14 | 2.44E + 14 | 2.44E + 14 | 2.44E + 14 | 2.44E + 14 | 2.44E + 14 | 2.44E + 14 |
| Total | Jc | 1.84E + 16 | 1.79E + 16 | 3.12E + 16 | 3.03E + 16 | 2.53E + 16 | 1.73E + 16 | 2.17E + 16 | |
| Local renewable resources | |||||||||
| 6 | Hydroelectricity | Jc | 2.57E + 15 | 1.72E + 15 | 1.72E + 15 | 1.79E + 15 | 2.87E + 15 | 7.80E + 15 | 2.59E + 15 |
| 7 | Agriculture Production | Jc | 9.25E + 18 | 9.20E + 18 | 1.08E + 19 | 1.39E + 19 | 1.41E + 19 | 9.93E + 18 | 6.92E + 18 |
| 8 | Livestock Production | Jc | 1.06E + 19 | 1.48E + 19 | 2.95E + 19 | 4.95E + 19 | 5.26E + 19 | 6.57E + 19 | 1.24E + 20 |
| 9 | Fisheries Production | Jc | 2.84E + 16 | 5.74E + 16 | 2.27E + 17 | 7.33E + 17 | 1.14E + 18 | 1.07E + 18 | 9.52E + 17 |
| Total | Jc | 1.99E + 19 | 2.41E + 19 | 4.06E + 19 | 6.41E + 19 | 6.78E + 19 | 7.67E + 19 | 1.32E + 20 | |
| Local nonrenewable resources | |||||||||
| 10 | Coal | Jc | 3.66E + 18 | 3.18E + 18 | 4.36E + 18 | 4.49E + 18 | 4.44E + 18 | 2.47E + 18 | 4.06E + 18 |
| 11 | Soil losses | Jc | 7.37E + 17 | 7.23E + 17 | 6.79E + 17 | 6.52E + 17 | 6.16E + 17 | 5.80E + 17 | 6.79E + 17 |
| 12 | Top soil losses | Jc | 1.32E + 16 | 1.29E + 16 | 1.22E + 16 | 1.17E + 16 | 1.10E + 16 | 1.04E + 16 | 1.22E + 16 |
| Total | Jc | 4.41E + 18 | 3.91E + 18 | 5.05E + 18 | 5.15E + 18 | 5.07E + 18 | 3.06E + 18 | 4.75E + 18 | |
| Imports and outside sources | |||||||||
| 13 | Goods from China | Jc | 5.93E + 18 | 5.81E + 18 | 7.08E + 18 | 8.06E + 18 | 1.76E + 19 | 2.30E + 19 | 4.09E + 19 |
| 14 | Goods from abroad | Jc | 4.77E + 17 | 6.80E + 17 | 4.98E + 17 | 2.40E + 17 | 1.40E + 18 | 5.10E + 18 | 8.19E + 18 |
| 15 | Service from China | Jc | 1.89E + 17 | 5.74E + 17 | 1.09E + 19 | 2.81E + 19 | 1.81E + 19 | 1.78E + 19 | 3.36E + 19 |
| 16 | Service from abroad | Jc | 1.52E + 16 | 6.72E + 16 | 7.12E + 17 | 7.27E + 17 | 1.72E + 18 | 3.95E + 18 | 7.14E + 18 |
| 17 | Natural gas | Jc | 2.65E + 13 | 2.65E + 13 | 3.77E + 14 | 4.45E + 16 | 6.16E + 16 | 5.82E + 17 | 1.33E + 18 |
| 18 | Coal | Jc | 8.10E + 17 | 2.63E + 18 | 3.02E + 18 | 8.87E + 18 | 9.30E + 18 | 1.05E + 19 | 1.21E + 19 |
| 19 | Oil | Jc | 1.61E + 18 | 2.81E + 18 | 4.98E + 18 | 5.48E + 18 | 5.26E + 18 | 9.18E + 18 | 1.13E + 19 |
| 20 | Electricity | Jc | 4.70E + 17 | 5.47E + 17 | 7.07E + 17 | 1.04E + 18 | 1.67E + 18 | 2.37E + 18 | 3.62E + 18 |
| Total | Jc | 6.61E + 18 | 7.13E + 18 | 1.92E + 19 | 3.71E + 19 | 3.88E + 19 | 4.98E + 19 | 8.98E + 19 | |
| Exports | |||||||||
| 21 | Goods | Jc | 3.45E + 18 | 3.52E + 18 | 8.01E + 18 | 9.86E + 18 | 2.05E + 19 | 2.86E + 19 | 5.67E + 19 |
| 22 | Services | Jc | 3.52E + 18 | 3.28E + 18 | 4.96E + 18 | 1.29E + 19 | 1.14E + 19 | 2.02E + 19 | 6.25E + 19 |
| Total | Jc | 6.96E + 18 | 6.80E + 18 | 1.30E + 19 | 2.27E + 19 | 3.19E + 19 | 4.87E + 19 | 1.19E + 20 | |
| Resource consumption by urban system | |||||||||
| 23 | Natural gas | Jc | 2.65E + 13 | 2.65E + 13 | 3.77E + 14 | 4.45E + 16 | 6.16E + 16 | 5.82E + 17 | 1.33E + 18 |
| 24 | Coal | Jc | 4.47E + 18 | 5.80E + 18 | 7.39E + 18 | 1.07E + 19 | 1.19E + 19 | 1.21E + 19 | 1.25E + 19 |
| 25 | Oil | Jc | 1.61E + 18 | 2.81E + 18 | 4.98E + 18 | 5.48E + 18 | 5.26E + 18 | 5.86E + 18 | 7.40E + 18 |
| 26 | Electricity | Jc | 8.83E + 17 | 1.03E + 18 | 1.33E + 18 | 1.95E + 18 | 2.68E + 18 | 2.46E + 18 | 5.43E + 18 |
| Total | Jc | 6.96E + 18 | 9.65E + 18 | 1.37E + 19 | 1.82E + 19 | 1.99E + 19 | 2.10E + 19 | 2.67E + 19 | |
| Waste | |||||||||
| 27 | Solid waste | Jc | 1.72E + 18 | 1.86E + 18 | 3.14E + 18 | 7.81E + 18 | 1.35E + 19 | 1.44E + 19 | 1.65E + 19 |
| 28 | Water discharged | Jc | 8.30E + 17 | 9.87E + 17 | 1.23E + 18 | 1.30E + 18 | 1.17E + 18 | 1.25E + 18 | 1.43E + 18 |
| Total | Jc | 2.55E + 18 | 2.85E + 18 | 4.37E + 18 | 9.11E + 18 | 1.47E + 19 | 1.57E + 19 | 1.79E + 19 | |
| Currency | |||||||||
| 29 | GNP | US$ | 7.00E + 09 | 9.28E + 09 | 8.75E + 09 | 1.05E + 10 | 1.67E + 10 | 3E + 10 | 5.17E + 10 |
| Population | |||||||||
| 30 | Population | capita | 8.72E + 06 | 9.04E + 06 | 9.81E + 06 | 1.09E + 07 | 1.25E + 07 | 1.36E + 07 | 1.49E + 07 |

Table 3.
Summary flows of Beijing for selected years.
| No. | Item | Variable | 1978 | 1980 | 1985 | 1990 | 1995 | 2000 | 2004 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Renewable sources (Jc) | R | 1.84E + 16 | 1.79E + 16 | 3.12E + 16 | 3.03E + 16 | 2.53E + 16 | 1.73E + 16 | 2.17E + 16 |
| 2 | Local nonrenewable resources (Jc) | N | 4.41E + 18 | 3.91E + 18 | 5.05E + 18 | 5.15E + 18 | 5.07E + 18 | 3.06E + 18 | 4.75E + 18 |
| 3 | Dispersed rural resource (Jc) | N0 | 7.50E + 17 | 7.35E + 17 | 6.91E + 17 | 6.63E + 17 | 6.27E + 17 | 5.91E + 17 | 6.91E + 17 |
| 4 | Concentrated resource (Jc) | N1 | 3.66E + 18 | 3.18E + 18 | 4.36E + 18 | 4.49E + 18 | 4.44E + 18 | 2.47E + 18 | 4.06E + 18 |
| 5 | Imported goods (Jc) | G | 6.40E + 18 | 6.49E + 18 | 7.58E + 18 | 8.30E + 18 | 1.90E + 19 | 2.81E + 19 | 4.91E + 19 |
| 6 | Imported fuels (Jc) | F | 2.89E + 18 | 5.99E + 18 | 8.71E + 18 | 1.54E + 19 | 1.63E + 19 | 2.26E + 19 | 2.83E + 19 |
| 7 | Dollars paid for imports ($) | I | 6.96E + 07 | 3.03E + 08 | 4.46E + 09 | 1.12E + 10 | 1.10E + 10 | 1.58E + 10 | 3.36E + 10 |
| 8 | Emergy of imported goods and fuels (Jc) | P2I | 2.04E + 17 | 6.41E + 17 | 1.16E + 19 | 2.88E + 19 | 1.98E + 19 | 2.17E + 19 | 4.07E + 19 |
| 9 | Dollars received from exports ($) | E | 2.23E + 09 | 2.75E + 09 | 1.79E + 09 | 3.18E + 09 | 4.35E + 09 | 1.14E + 10 | 3.42E + 10 |
| 10 | Exported goods (Jc) | B | 3.45E + 18 | 3.52E + 18 | 8.01E + 18 | 9.86E + 18 | 2.05E + 19 | 2.86E + 19 | 5.67E + 19 |
| 11 | Exported services (Jc) | P1E | 3.52E + 18 | 3.28E + 18 | 4.96E + 18 | 1.29E + 19 | 1.14E + 19 | 2.02E + 19 | 6.25E + 19 |
| 12 | Environmental impacts (Jc) | EI | 2.55E + 18 | 2.85E + 18 | 4.37E + 18 | 9.11E + 18 | 1.47E + 19 | 1.57E + 19 | 1.79E + 19 |
| 13 | GNP of Beijing ($) | X | 7.00E + 09 | 9.28E + 09 | 8.75E + 09 | 1.05E + 10 | 1.67E + 10 | 3.00E + 10 | 5.17E + 10 |
| 14 | Total emergy use (Jc) | U | 1.10E + 19 | 1.11E + 19 | 2.42E + 19 | 4.23E + 19 | 4.39E + 19 | 5.29E + 19 | 9.46E + 19 |
As an important support to the economic development, the local nonrenewable inputs, mainly coal and soil loss for Beijing, are the guarantees for the energy supply security. Similar to the renewable one, the local nonrenewable input contributed stably during the concerned years with emergy between 4.41 × 1018 Jc and 4.75 × 1018 Jc.
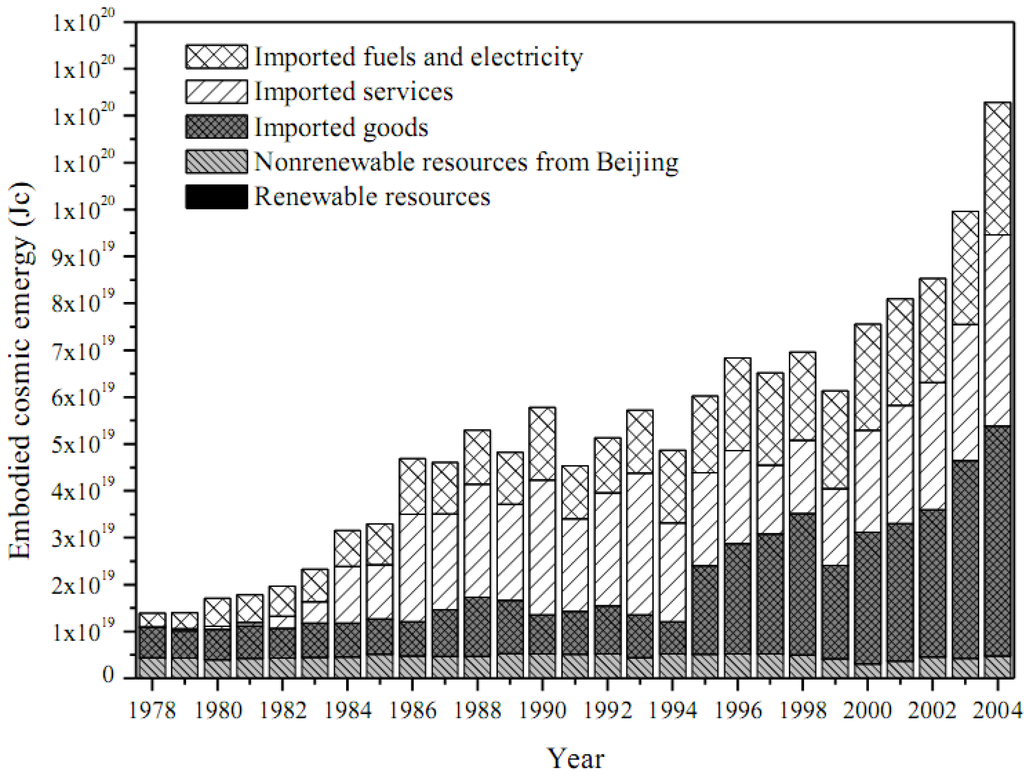
Figure 4.
Annual emergy consumption of Beijing.
4. Cosmic Emergy Based Indicator Analysis
In this sector, eighteen indicators based on the analyzed resource flows are applied to reveal the changes in resource structure and evolutionary mechanism for the Beijing urban ecosystem through five aspects involving emergy structure, emergy intensity, emergy welfare, environmental impacts, and degree of exploitation and economic efficiency (see Table 4).
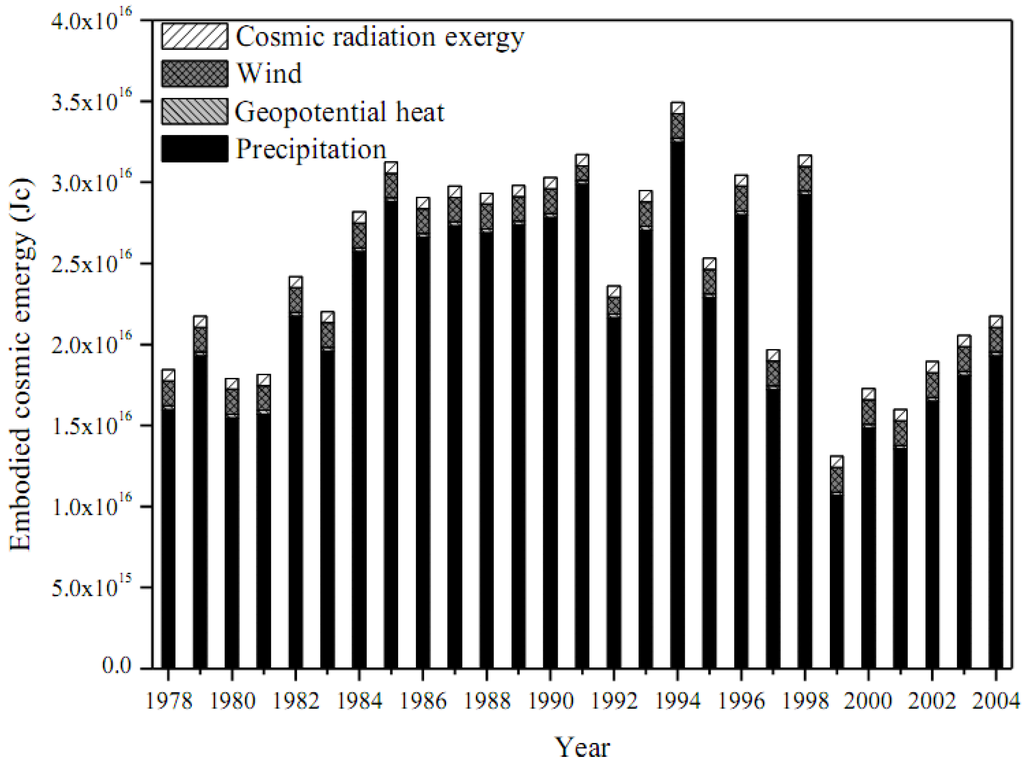
Figure 5.
Annual free renewable resource consumption of Beijing.

Table 4.
Emergy based indicators for Beijing of selected years.
| No. | Item | Symbol | 1978 | 1980 | 1985 | 1990 | 1995 | 2000 | 2004 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Emergy source | |||||||||
| 1 | Local renewable emergy fraction | R/U | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| 2 | Free emergy fraction | (R + N0)/U | 0.070 | 0.068 | 0.030 | 0.016 | 0.015 | 0.011 | 0.008 |
| 3 | Emergy self-sufficiency fraction | (R + N0 + N1)/U | 0.401 | 0.355 | 0.210 | 0.122 | 0.116 | 0.058 | 0.050 |
| 4 | Purchased emergy fraction | (G + P2I)/U | 0.599 | 0.645 | 0.790 | 0.878 | 0.884 | 0.942 | 0.950 |
| 5 | Imported service emergy fraction | P2I/U | 0.018 | 0.058 | 0.478 | 0.681 | 0.451 | 0.410 | 0.430 |
| Emergy intensity | |||||||||
| 6 | Empower density(108 Jc/m2) | U/area | 6.6 | 6.6 | 14.4 | 25.2 | 26.1 | 31.5 | 57.6 |
| 7 | Concentrated to rural use ratio | (G + P2I + N1)/(R + N0) | 13.4 | 13.7 | 32.6 | 60.0 | 66.3 | 86.0 | 131.7 |
| Emergy welfare | |||||||||
| 8 | Per capita emergy use (1012 Jc/cap.) | U/P | 1.26 | 1.22 | 2.47 | 3.90 | 3.51 | 3.88 | 6.33 |
| 9 | Per capita fuel emergy use (1011 Jc/cap.) | F/P | 3.3 | 6.6 | 8.9 | 14.2 | 13.0 | 16.6 | 19.0 |
| 10 | Export-import difference | (P1E + B) -(P2I + G) | 3.50E + 17 | -3.30E + 17 | -6.20E + 1-8 | 1.44E + 1-9 | 6.90E + 1-8 | 1.10E + 18 | 2.92E + 19 |
| 11 | Export-import ratio | (P1E + B)/(P2I + G) | 1.05 | 0.95 | 0.68 | 0.61 | 0.82 | 0.98 | 1.33 |
| 12 | Emergy use diversity | * | 0.93 | 1.07 | 1.24 | 0.95 | 1.22 | 1.32 | 1.29 |
| Environmental impacts | |||||||||
| 13 | Waste to renewable emergy use ratio | W/R | 138.5 | 159.0 | 139.9 | 300.9 | 580.3 | 907.3 | 824.2 |
| 14 | Waste to total emergy use ratio | W/U | 0.231 | 0.257 | 0.180 | 0.215 | 0.335 | 0.296 | 0.190 |
| Degree of exploitation and economic efficiency | |||||||||
| 15 | Electricity emergy fraction (%) | (el)/U | 8.01 | 9.29 | 5.48 | 4.60 | 6.10 | 4.66 | 5.74 |
| 16 | Emergy investment ratio | (G + P2I + N0 + N1)/R | 597.5 | 616.5 | 774.9 | 1396.4 | 1732.2 | 3061.6 | 4348.4 |
| 17 | Emdollar ratio(109 Jc/US$) | U/GNP | 1.58E + 09 | 1.19E + 09 | 2.77E + 09 | 4.04E + 09 | 2.63E + 09 | 1.77E + 09 | 1.83E + 09 |
| 18 | Economic efficiency | U/(G + P2I) | 1.67 | 1.55 | 1.27 | 1.14 | 1.13 | 1.06 | 1.05 |
* In this equation, ni indicates the emergy value of the i-th kind of resource used by the concerned system.
4.1. Emergy Source
Although the local input kept stable in quantity, its share of the total emergy use, i.e., the emergy self-sufficiency fraction, declined rapidly from 40.1% in 1978 to 5.04% in 2004, which means that the imported emergy had increased its importance and turned into the predominant force for the expansion of Beijing. This indicator reflects simultaneously the acceleration of urbanization and the improvement of local living standard, but also reveals the reduction in resource independence, which will raise the frangibility of the urban ecosystem.
The imported resources were from either other domestic regions or foreign countries, with the former contributing mainly goods and fuels while the latter mainly services. In 1978, the proportion from domestic service input was only 1.72% of the total emergy use but it rose dramatically to 45.0% in 1985, indicating that the immigrations with their services turned into a major force for the development of Beijing.
The change in resource type and structure is closely connected with the development of an urban ecosystem, and results in the modification of urban organization [19,22]. Therefore, according to the emergy structure account for Beijing, the development of this urban ecosystem can be divided into three distinctive periods as follows.
4.1.1. Period I—Pre-Industrializing and Transforming Period
The first period is from 1978 to 1986, when Beijing had established an independent and relatively complete heavy industrial system covering steel, automobile, and building materials. Nevertheless, the urban ecosystem was on its transition phase of industrialization with relatively undeveloped economic structure and high immigration rate. In this period, the total emergy use increased from 1.10 × 1019 Jc to 3.50 × 1019 Jc with considerable supports from local ecosystem, despite its proportion declined from 40.1% in 1978 to 13.8% in 1986. Less than 5% of the total emergy use came from foreign countries while the contribution from other domestic regions rose from 55.4% to 82.3%. Meanwhile, the contribution of local and imported services increased significantly from 1.71% in 1978 to 62.5% in 1986.
4.1.2. Period II—Industrializing and Fluctuating Period
During the second period from 1986 to 1999, Beijing experienced a great change from a planned economy system to a market economy system and the total emergy use fluctuated between the minimum value of 3.31 × 1019 Jc in 1994 and the maximum value of 5.08 × 1019 Jc in 1998. During this period, the contribution of local resources was around 12% when agriculture was an important department providing various products to local residents. With significant variation appears in structure, resources from abroad increased rapidly from 3.91% in 1986 to 15.9% in 1999. But domestically imported resources were still the major support for development, contributing more than 80% of emergy in most years. During this period, the economic growth was constructed on the extensive use of resources accompanied with a rising pressure on environment, which was revealed by the increasing waste output from 4.71 × 1018 Jc in 1986 to 1.69 × 1019 Jc in 1999.
4.1.3. Period III—Post-Industrializing and Fast Developing Period
Recovered from the short-term decrease from 1998 to 1999, Beijing stepped into a stage of rapid growth in all aspects thanks to the holding of the 29th Olympic Games. For the construction of the infrastructure facilities, a great deal of resources were input to the urban ecosystem and total emergy use rose from 4.05 × 1019 Jc to 9.46 × 1019 Jc within 5 years (from 1999 to 2004). In this period, the economic structure of Beijing experienced significant change, as its production value experienced great declines in the first and second industries, in contrast to the increase in the service industry, which contributed to over 60% of GDP in 2004. The proportion from local resources declined further while more than 90% of the total emergy use was imported. As a result of the improving economic structure and the increasing resource use efficiency, the environmental pressure was alleviated.
4.2. Emergy Intensity
As shown in Figure 6, the empower density of Beijing increased from 6.56 × 108 Jc/m2 in 1978 to 5.76 × 109 Jc/m2 in 2004. This growth is mainly caused by the input of imported goods and services embedding relatively high emergy content.
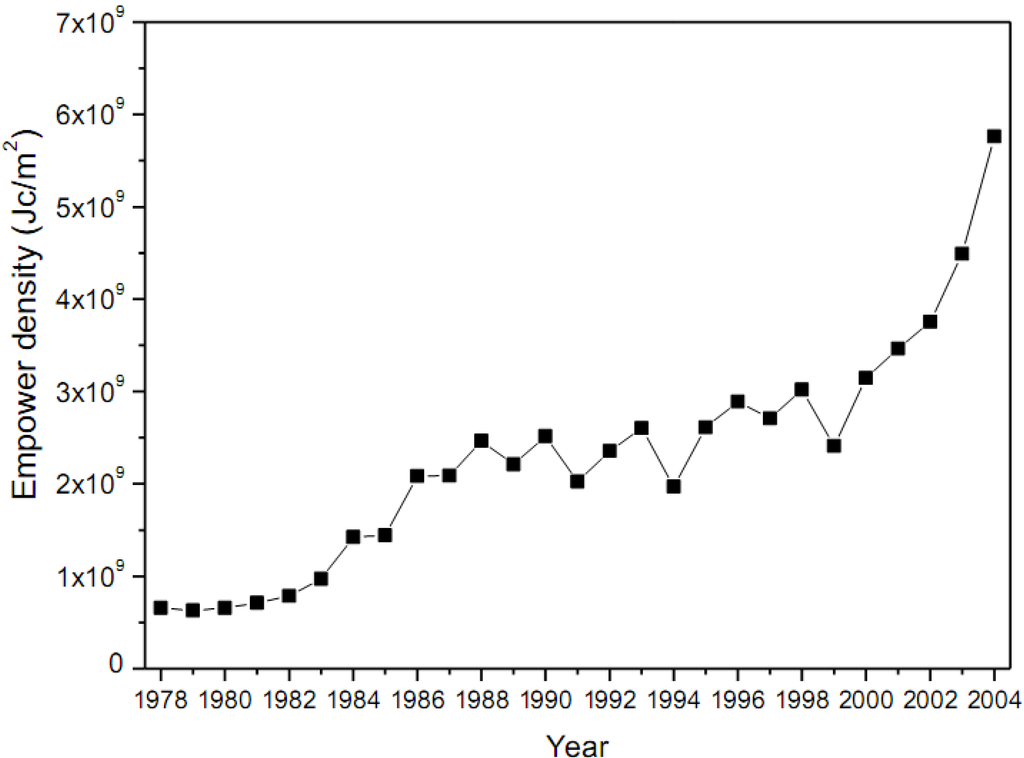
Figure 6.
Annual empower density for Beijing.
For Beijing, the concentrated to rural use ratio increased from 13.4 in 1978 to 131.7 in 2004 as shown in Figure 7. This result shows that Beijing as the capital of China enjoyed an emergy use structure relied heavily on concentrated energy such as coal, oil, and electricity since the start of Reform and Opening-up.
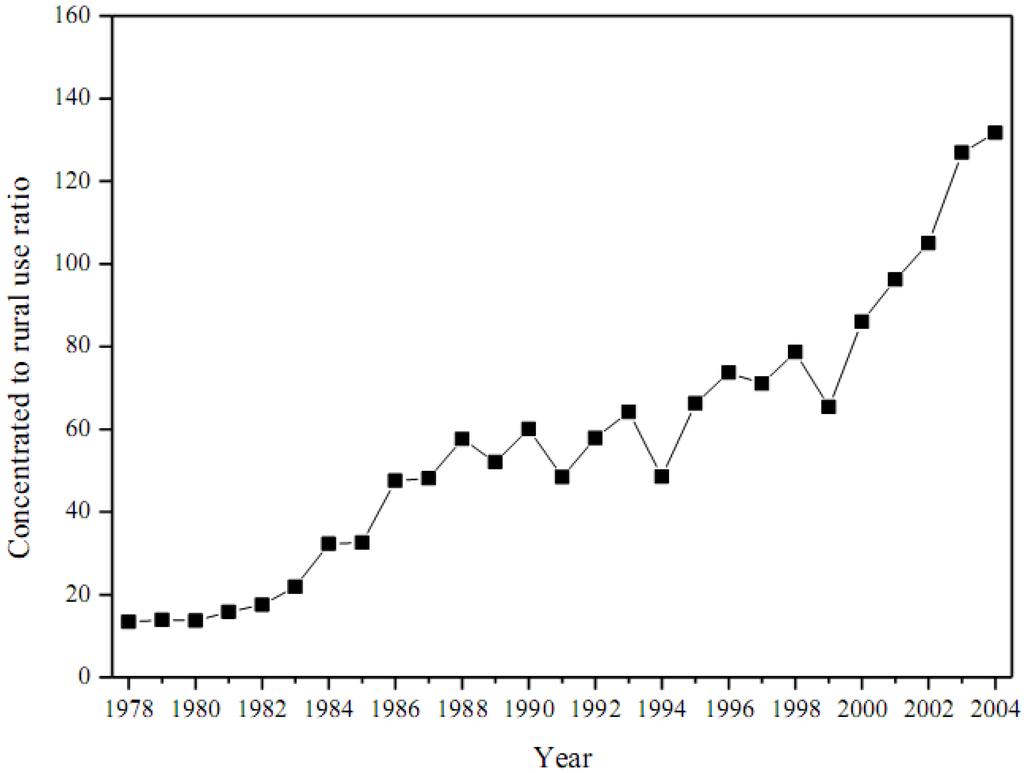
Figure 7.
Annual concentrated to rural use ratio for Beijing.
4.3. Emergy Use Welfare
The evaluation of emergy welfare of a city incorporates five indicators: per capita total emergy use, per capita fuel emergy use, export-import difference, export-import ratio, and emergy use diversity.
Taking into account the different qualities and sources of input, the emergy based per capita welfare indicators are more appropriate evaluations of the real living standard than energy-based indicators which often neglect the input of environment. Figure 8 shows that the per capita total emergy use for Beijing increased by 5.01 times from 1.26 × 1012 Jc in 1978 to 6.33 × 1012 Jc in 2004. The variation of this ratio is great taking into account that the population of Beijing almost doubled in the same period. After the year 1999, the construction of infrastructural facilities in Beijing was strengthened along with the launching of Subway Line No.5 and Ba-Tong Subway Line, and the extending of the Fourth Ring Road, which stimulated the demand for material and energy and expedited the increments of per capita welfare.
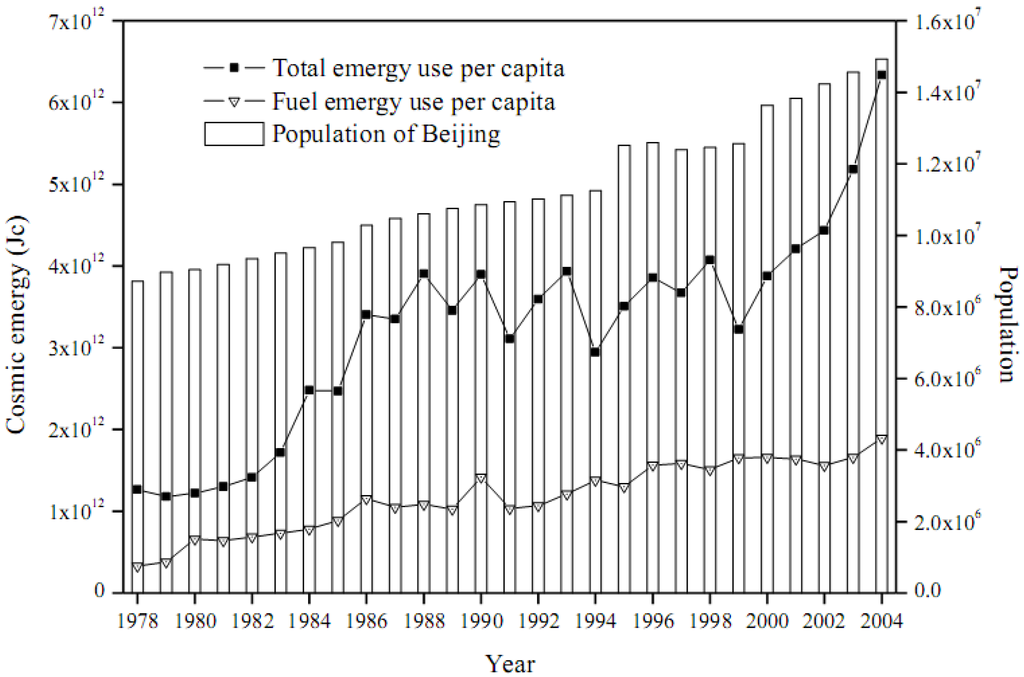
Figure 8.
Annual emergy welfare per capita for Beijing.
The trade evaluated in terms of emergy reveals the exchange of “real wealth”, thus is quite different from the traditional evaluation in terms of monetary value. The emergy based comparisons of imports and exports for the Beijing urban ecosystem are portrayed in Figure 9, according to which both the exports-imports ratio and difference assume U-shape distributions during the analyzed period. Before the year 1982, the export-import difference is positive with corresponding ratio larger than 1, indicating that the Beijing urban ecosystem exported more resources than it imported during this period. Statistics show that industrial products such as coal, steal, and cement occupied large proportion of the exports, most of which were sold to other domestic regions while only a little part was exported abroad. During the period from 1983 to 2002, the rapid development of Beijing industry brought a considerable demand for energy and the imported emergy exceeded the exported one with the largest gap appears in 1993. However, as a result of the fast increase of export, emergy trade surplus was obtained again in 2003 and 2004 and the export-import ratio also reached the maximum value of 1.33 in 2004, which is beneficial for the sustainable development of Beijing.
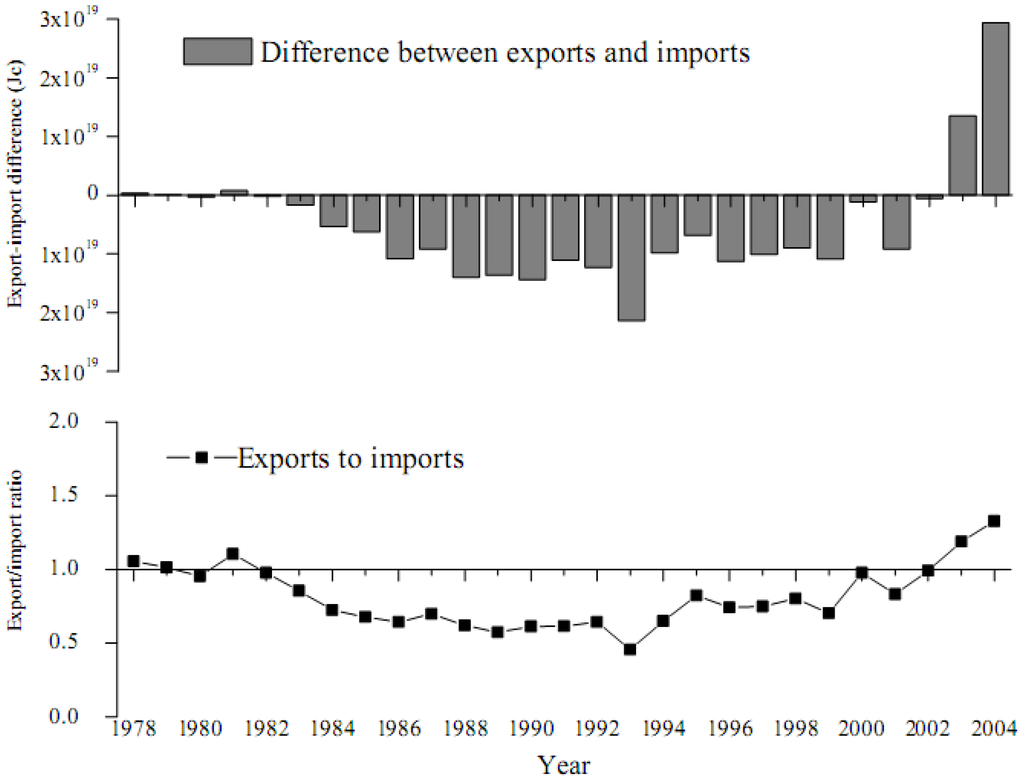
Figure 9.
Annual emergy based comparison between import and export for Beijing.
Adopted from Huang et al. (2005), the emergy use diversity is calculated as
in which H is the emergy use diversity indicator, U is the total emergy use, and is the emergy value of the i-th kind of resource used by the concerned system. As shown in Figure 10, the emergy use diversity of Beijing was stable during the past decades, with the highest value of 1.37 in 1999 and lowest one of 0.95 in 1990. The relatively low emergy use diversity in Beijing indicated that this urban ecosystem was taking a risk of limited resources supply with high dependency on imported resources.
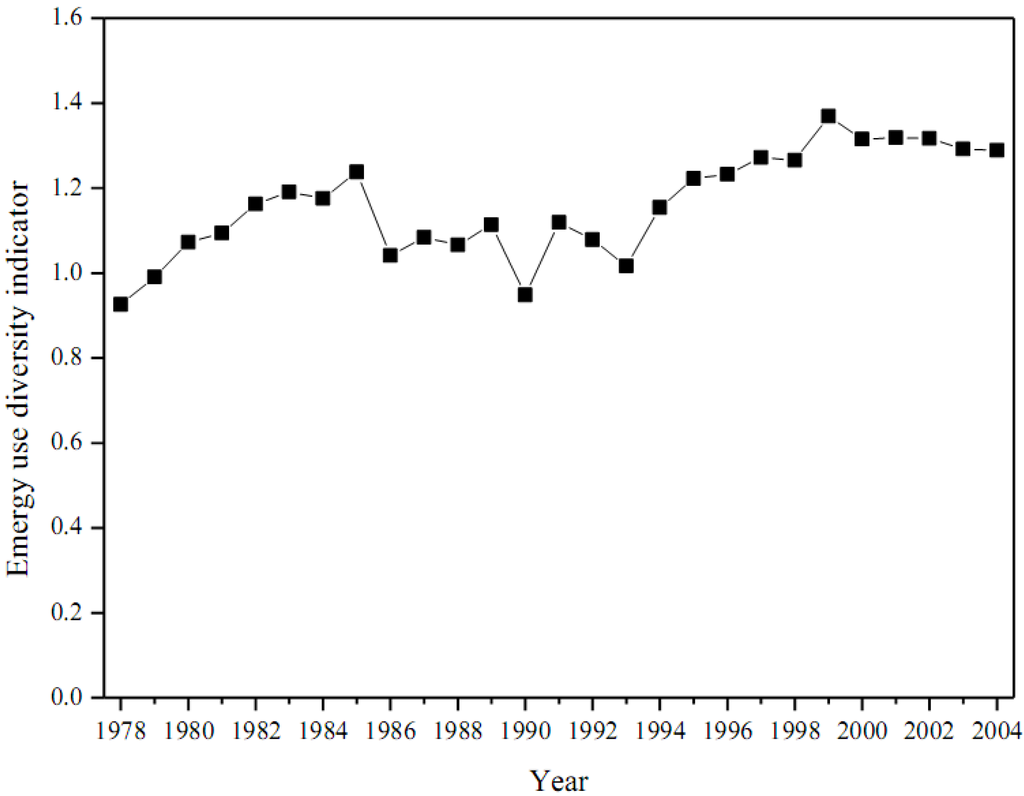
Figure 10.
Annual emergy use diversity for Beijing.
4.4. Environment Impact
The ratios of waste to renewable emergy use and total emergy use reveal the pressure sustained by the environment, both of which increased rapidly from 1978 to 1999 as the result of the Reform and Opening-up policy, but decline obviously since 2001 owing to the approaching of the Olympic Games.
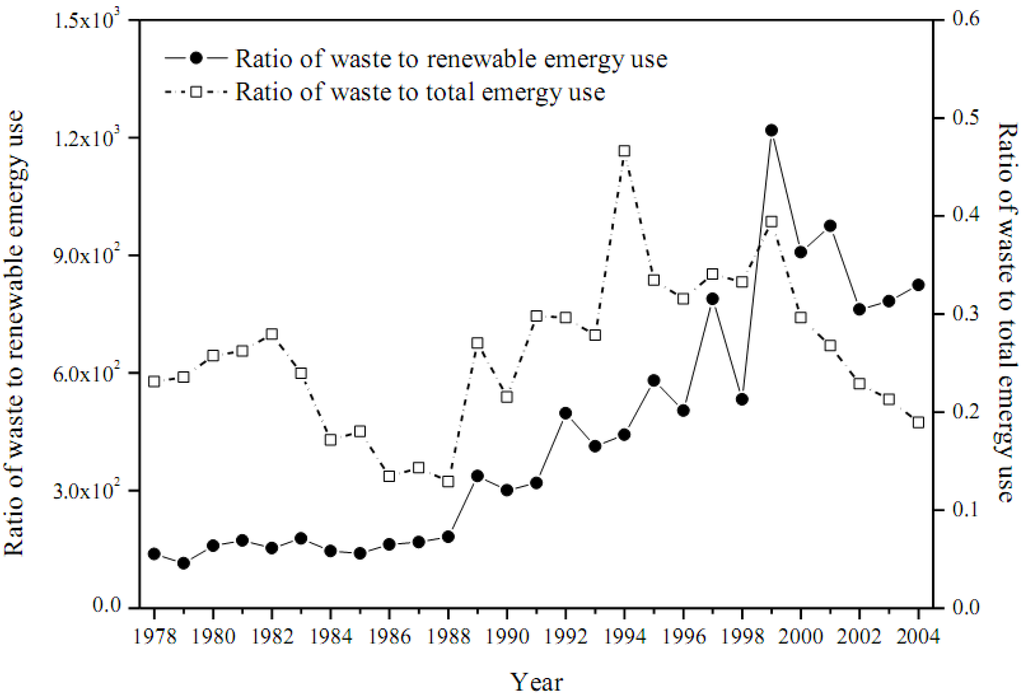
Figure 11.
Annual environmental impact for Beijing.
4.5. Degree of Exploitation and Economic Efficiency
In Beijing, the consumption of electricity kept rising during 1978 to 2004 with emergy increased from 8.83 × 1017 Jc to 5.43 × 1018 Jc, of which more than 60% was transferred from the Jing-Jin-Tang power network and the North China power network. As shown in Figure 12, the fraction of power use to total emergy use for Beijing decreased slowly due to the rapid increase of input of other resources. Meanwhile, the emergy investment ratio in Beijing increased by 6.28 times from 1978 to 2004, which implicates that the dependency on external resources was enhanced accompanied with the development of the Beijing urban ecosystem.
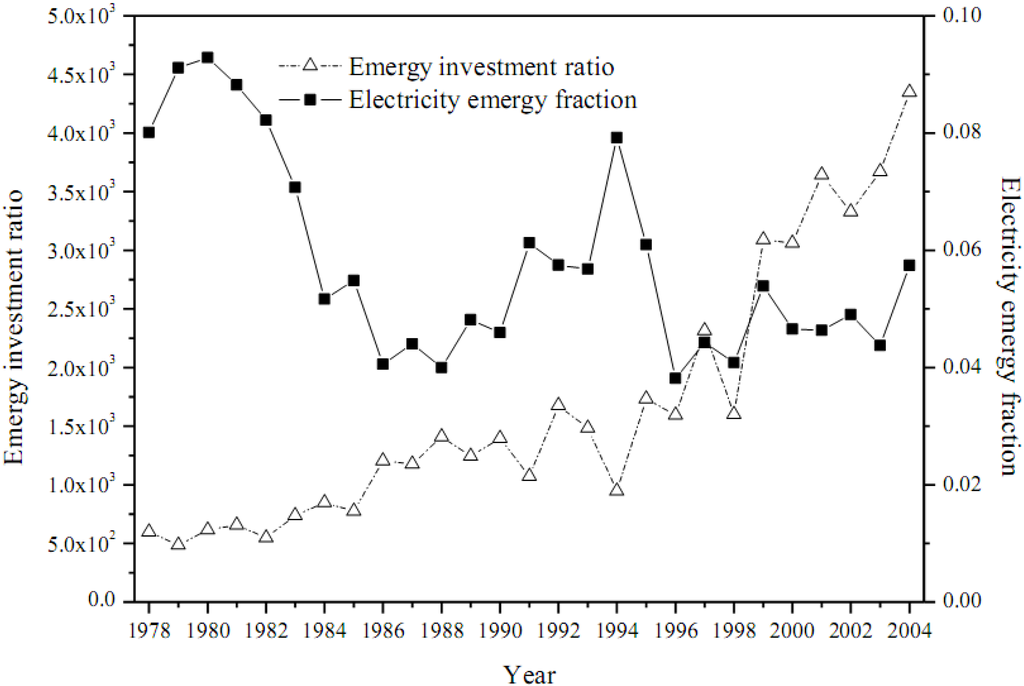
Figure 12.
Annual electricity emergy fraction and investment ratio for Beijing.
From 1978 to 1986, the emergy to dollar ratio of Beijing rose from 1.58 × 109 Jc/$ to 4.24 × 109 Jc/$ (see Figure 13), when the low cost or free local resources were the major support for the development. Afterwards, as a result of the declining share of local resources, the emergy to dollar ratio decreased from 4.04 × 109 Jc/$ in 1990 to 1.83 × 109 Jc/$ in 2004. The emergy to dollar ratio of China experienced similar trend as that of Beijing and the two values were close in recent years. However, the emergy to dollar ratio of Beijing was always higher than that of the world, which indicates that more real wealth had to be consumed to create the same unit of GDP by the Beijing urban ecosystem.
As shown in Figure 14, this economic efficiency indicator of Beijing declined slowly towards 1, from 1.67 in 1978 to 1.05 in 2004, revealing that more and more resources were purchased from outside, despite the degree of exploration increased.
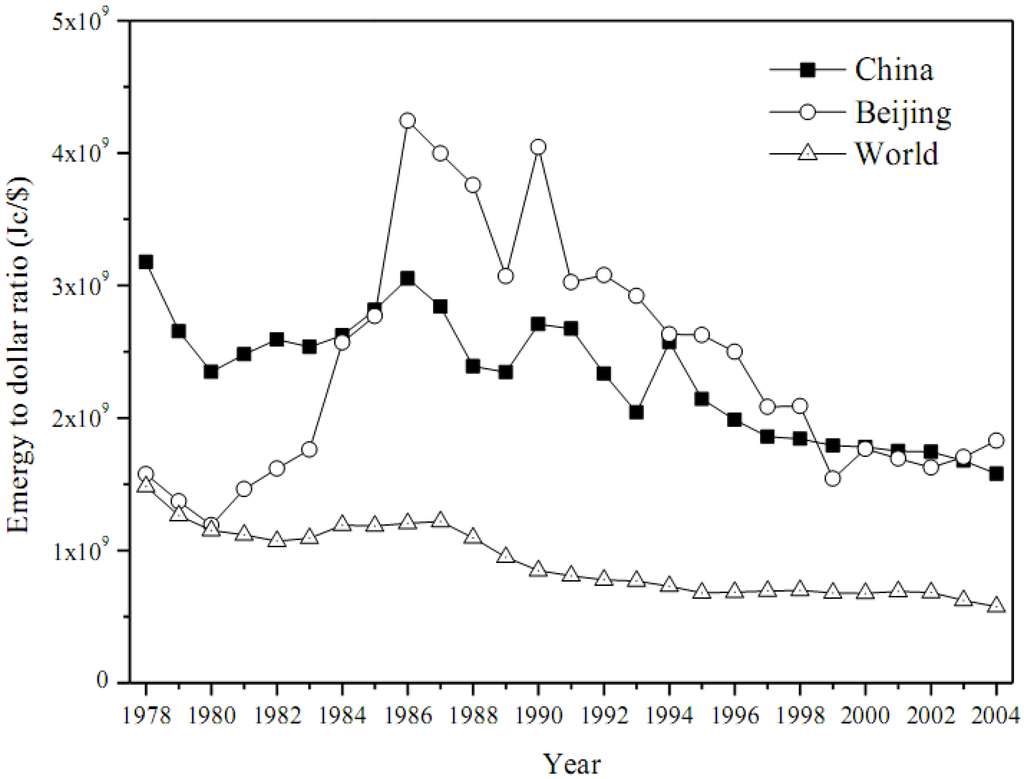
Figure 13.
Annual emergy to dollar ratio for Beijing, China, and the world.
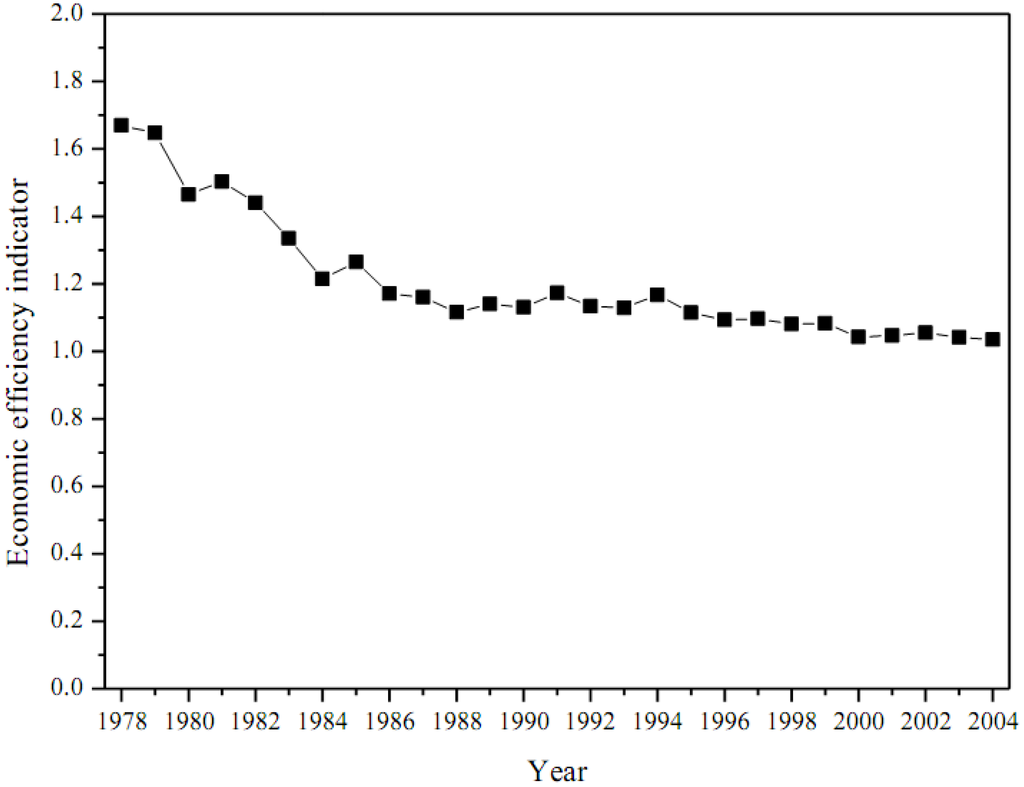
Figure 14.
Annual economic efficiency for Beijing.
5. Concluding Remarks
This research investigates the Beijing urban ecosystem based on an updated emergy synthesis in terms of embodied cosmic exergy instead of embodied solar energy, which successes foundations from Odum’s systems ecological theory but changes the starting point for the estimation from simply the sun to the cosmos represented by the thermodynamic contrast between the solar and CBM radiations. Based on the second law of thermodynamics implicating irreversible exergy consumption and entropy increase as well as the renovated EPB definition, the updated approach avoids the confusable and intractable defects of traditional one and shows firmer theoretical basis and better applicability.
Upgraded systems diagram with particular arms of free renewable resources, free nonrenewable resources, economic feedback, economic yield, environmental impact, and virtual environmental input along with the revised transformity dataset is illustrated, on the basis of which an ecological economic evaluation of the Beijing urban ecosystem is carried out. Detailed characteristics of the concerned urban ecosystem over a quarter century, i.e., from 1978 to 2004, are examined and results suggest its development can be divided into three distinctive periods: pre-industrializing and transforming period from 1978 to 1986, industrializing and fluctuating period from 1986 to 1999, and post-industrializing and fast developing period from 1999 to 2004. In the first period, local resources played an important role to support the economic development and less than 5% of total emergy was imported. During the second period, the contribution from local resources declined dramatically to around 10% while that from import increased rapidly from 3.91% to 15.9%. Considerable change of the domestic service input is observed during the first two periods, as the share of which rose by almost twenty times from 1.71% in 1978 to 33.2% in 1999. In the last period characterized by the accelerating economy development, the total emergy use increased by 1.33 times in 5 years with more than 90% of these resources came from outside, especially from other domestic regions.
The evolution of the Beijing urban ecosystem is also analyzed in detail through a series of indicators in respect to emergy intensity, emergy welfare, environmental impacts, and degree of exploitation and economic efficiency. During the focused period, the emergy intensity for Beijing increased continuously as a result of the sustained investment of resources, which not only improved living standard in many aspects, but also aggravated pressure on environment. Meanwhile, the rising emergy investment ratio implicates that Beijing was at the risks of resources shortage and high dependency on external resources, which is a hidden peril for its sustainable development. Furthermore, the examined indicators of electricity emergy fraction, emergy to dollar ratio, and economic efficiency reveal that although the degree of exploitation for the Beijing urban ecosystem increased, its economic efficiency declined during the past decades.
Acknowledgement
The authors thank the editor and three anonymous referees for their helpful suggestions. Financial support for this research was provided by the National Key Program for Basic Research (973 Program, Grant no. 2005CB724204), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 40801233, 40871056, and 40971052), and in part by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant Nos. 20080430317, 200902057).
References
- Odum, H.T. Self organization, transformity and information. Science 1988, 242, 1132–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, M.T.; Odum, H.T.; Jørgensen, S.E. Energy hierarchy and transformity in the universe. Ecol. Model. 2004, 178, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odum, H.T. Energy ecology and economics. Ambio. 1973, 2, 220–227. [Google Scholar]
- Odum, H.T. Environmental Accounting—Emergy and Environmental Decision Making; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, M.T.; Brandt-Williams, S.; Tilley, D.R.; Ulgiati, S. Emergy synthesis: An introduction. In Emergy Synthesis: Theory and Applications of the Emergy Methodology; Brown, M.T., Brandt-Williams, S., Tilley, D.R., Ulgiati, S., Eds.; University of Florida: Gainesville, FL, USA, 2000; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, M.T.; Ulgiati, S. Emergy and environmental accounting. In Encyclopedia of Energy; Cleveland, C., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, NL, 2004; Volume 1, pp. 329–353. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, M.T.; Herendeen, R. Embodied energy analysis and emergy analysis: A comparative view. Ecol. Econ. 1996, 20, 2210–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, D.E. Emergy analysis of human carrying capacity and regional sustainability: An example using the state of Maine. Environ. Monit. Assess. 1998, 51, 531–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, D.E.; Brandt-Williams, S.L.; Meisch, M.E.A. Environmental Accounting Using Emergy: Evaluation of the State of West Virginia; USEPA: Narragansett, RI, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Chen, G.Q. Ecological footprint accounting based on emergy—A case study of the Chinese society. Ecol. Model. 2006, 198, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Chen, G.Q. Emergy–based energy and material metabolism of the Yellow River basin. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simulat. 2009, 14, 923–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Chen, Z.M; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, J.B.; Chen, G.Q. Emergy as embodied energy based assessment for local sustainability of a constructed wetland in Beijing. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simulat. 2009, 14, 622–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.Q.; Jiang, M.M.; Chen, B.; Yang, Z.F.; Lin, C. Emergy analysis of Chinese agriculture. Ag. Ecosyst. Environ. 2006, 115, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.Y.; Zhang, B.; Cai, Z.F. Emergy analysis of a farm biogas project in China: A biophysical perspective of agricultural ecological engineering. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simulat. 2010, 15, 1408–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herendeen, R.A. Energy analysis and EMERGY analysis—A comparison. Ecol. Model. 2004, 178, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.B. Emergy analysis of the Oak Openings region. Ecol. Eng. 2003, 21, 75–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.L.; Hsu, W.L. Energy hierarchy and urban landscape system. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2001, 53, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.L.; Odum, H.T. Ecology and economy: Emergy synthesis and public policy in Taiwan. J. Environ. Manage. 1991, 32, 313–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.L.; Wong, J.H.; Chen, T.C. A Framework of Indicator system for Measuring Taipei’s Urban Sustainability. Landsc. Urban Plan. 1998, 42, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.L. Energy Basis for Urban Ecological Economic System; Chan’s Arch Books Co., LTD: Taipei, China, 2004. (in Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.L. Urban ecosystems, energetic hierarchies and ecological economics of Taipei metropolis. J. Environ. Manage. 1998, 52, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.L.; Chen, C.W. Theory of urban energetics and mechanisms of urban development. Ecol. Model. 2005, 189, 49–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.L.; Hsu, W.L. Materials flow analysis and emergy evaluation of Taipei’s urban construction. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2003, 63, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.L.; Li, S.; Budd, W.W.; Chan, S.L.; Lin, Y.C. Stream order, hierarchy, and energy convergence of land use. Ecol. Model. 2007, 205, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.L; Lee, C.L.; Chen, C.W. Socioeconomic metabolism in Taiwan: Emergy synthesis versus material flow analysis. Resour. Conserv. Recy. 2006, 48, 166–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.M.; Chen, B.; Zhou, J.B; Tao, F.R.; Li, Z.; Yang, Z.F.; Chen, G.Q. Emergy account for biomass resource exploitation by agriculture in China. Energy Policy 2007, 35, 4704–4719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.M.; Zhou, J.B.; Chen, B.; Chen, G.Q. Emergy-based ecological account for the Chinese economy in 2004. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simulat. 2008, 13, 2337–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.M.; Zhou, J.B.; Chen, B.; Yang, Z.F; Ji, X.; Zhang, L.X.; Chen, G.Q. Ecological evaluation of Beijing economy based on emergy indices. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simulat. 2009, 14, 2482–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Park, S.S. Emergy evaluation perspectives of a multipurpose dam proposal in Korea. J. Environ. Manage. 2002, 66, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, S.F.; Odum, H.T. Emergy evaluation of environment and economy of Hong Kong. J. Environ. Sci. 1994, 4, 56–74. [Google Scholar]
- Odum, H.T. Emergy and evolution. In Annual Meeting of International Society for the Systems Sciences, 33rd ed.; Holberg, S.C., Samuelson, K., Eds.; International Society for the Systems Sciences: Ostersund, Sweden, 1989; Volume 1, pp. 211–218. [Google Scholar]
- Odum, H.T. Energy systems concepts and self-organization: A rebuttal. Oecologia 1995, 104, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Introduction to Ecological Engineering with Brazilian Case Studies; Ortega, E.; Safonov, P.; Comar, V. (Eds.) UNICAMP: Campinas, Brazil, 1999.
- Patten, B.C. Toward a more holistic ecology, and science: The contribution of H.T. Odum. Oecologia 1993, 93, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulselli, F.M.; Pulselli, R.M.; Picchi, M.P. Emergy evaluation of the ‘emternalities’ in non industrialized regions: The case of two mountain communities in Italy. In Proceedings of the Second Emergy Research Conference—Emergy Synthesis 2; Brown, M.T., Odum, H.T., Tilley, D., Ulgiati, S., Eds.; Center for Wetlands, University of Florida: Gainsville, FL, USA, 2001; pp. 397–408. [Google Scholar]
- Pulselli, R.M.; Pulselli, F.M.; Rustici, M. Emergy accounting of the Province of Siena: Towards a thermodynamic geography for regional studies. J. Environ. Manage. 2008, 86, 342–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilley, D.R.; Swank, W.T. Emergy-based environmental systems assessment of a multi-purpose temperate mixed-forest watershed of the southern Appalachian Mountains, USA. J. Environ. Manage. 2003, 69, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulgiati, S.; Odum, H.T.; Bastianoni, S. Emergy use, environmental loading and sustainability. An emergy analysis of Italy. Ecol. Model. 1994, 73, 215–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield, D.F. Emergy Basis for Urban Land Use Patterns in Jacksonville; Department of Landscape Architecture, University of Florida: Gainesville, FL, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.F.; Jiang, M.M.; Chen, B.; Zhou, J.B.; Chen, G.Q. Solar emergy evaluation for Chinese economy. Energy Policy 2010, 38, 875–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.X.; Yang, Z.F.; Chen, G.Q. Emergy analysis of cropping-grazing system in Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China. Energy Policy 2007, 35, 3845–3855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.X.; Chen, B.; Yang, Z.F.; Chen, G.Q.; Jiang, M.M.; Liu, G.Y. Comparison of typical mega cities in China using emergy synthesis. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simulat. 2009, 14, 2827–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z.F.; Yu, X.Y. Evaluation of urban metabolism based on emergy synthesis: A case study for Beijing (China). Ecol. Model. 2009, 14, 1690–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.B.; Jiang, M.M.; Chen, B.; Chen, G.Q. Emergy evaluations for constructed wetland and conventional wastewater treatments. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simulat. 2009, 14, 1781–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansson, B.A.; McGlade, J.M. Ecology, thermodynamics and H.T. Odum's conjectures. Oecologia 1993, 93, 582–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, C.J.; Kaufmann, R.K.; Stern, D.I. Aggregation and the role of energy in the economy. Ecol. Econ. 2000, 32, 301–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hau, J.L.; Bakshi, B.R. Promise and problems of emergy analysis. Ecol. Model. 2004, 178, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastianoni, S.; Marchettini, N. The problem of co-production in environmental accounting by emergy analysis. Ecol. Model. 2000, 129, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastianoni, S.; Nielsen, S.N.; Marchettini, N.; Jørgensen, S.E. Use of thermodynamic functions for expressing some relevant aspects of sustainability. Int. J. Energy Res. 2004, 29, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastianoni, S.; Facchini, A.; Susani, L.; Tiezzi, E. Emergy as a function of exergy. Energy 2007, 32, 1158–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillet, G. Exergy, emergy, and entropy. In Environmental Economics; Pillet, G., Murota, T., Eds.; Roland Leimgruber: Geneva, Switzerland, 1987; pp. 277–302. [Google Scholar]
- Reini, M; Valero, A. Towards a unified formulation of exergy cost theory and emergy algebra for ecological and technological energy system evaluation. In Advances in Energy Studies: Reconsidering the Importance of Energy; Ulgiati, S., Brown, M.T., Giampietro, M., Herendeen, R.A., Mayumi, K., Eds.; S. G. E: Padova, Italy, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Sciubba, E; Ulgiati, S. Emergy and exergy analyses: Complementary methods or irreducible ideological options? Energy 2005, 30, 1953–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.Q. Exergy consumption of the earth. Ecol. Model. 2005, 184, 363–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.M. Study of thermodynamic mechanisms of the urban development and its application: Beijing as a case. Ph.D. Dissertation, Peking University, Beijing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.Q. Scarcity of exergy and ecological evaluation based on embodied exergy. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simulat. 2006, 11, 531–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.R.; Chen, B.; Yang, Z.F.; Ulgiati, S. Urban ecosystem health assessment based on emergy and set pair analysis—A comparative study of typical Chinese cities. Ecol. Model. 2009, 220, 2341–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall, G. Exergy—A useful concept within resource accounting. Institute of Theoretical Physics; ISBN 99-1767571-X and 99-. 0342612-7. Göteborg, Report No. 77(42): 1-77(42); 1977; Available online: http://www.exergy.se/ftp/paper1.pdf (Accessed on 14 December 2009).
- Jørgensen, S.E. Exergy and buffering capacity in ecological system. In Energetics and Systems; Mitsh, W.J., Ragade, R.K., Bosserman, R.W., Dillon, J.A., Eds.; Ann Arbor Science, Ann Arbour: Michigan, MI, USA, 1982; pp. 61–72. [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen, S.E. The thermodynamic concept: Exergy. In Thermodynamics and Ecological Modelling; Jørgensen, S.E., Ed.; Lewis Publishers: Baton Rouge, Louisiana, LA, USA, 2001; pp. 153–164. [Google Scholar]
- Szargut, J.T. Application of exergy for the determination of ecological costs. Bull Polish Acad. Sci. Ser. Technol. 1986, 34, 475–480. [Google Scholar]
- Szargut, J.T. Anthropogenic and natural exergy losses. Energy 2003, 28, 1047–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szargut, J.T.; Ziebik, A.; Stanek, W. Depletion of the non-renewable natural exergy resources as a measure of the ecological cost. Energ. Convers. Manage. 2002, 43, 1149–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Chen, G.Q. Modified ecological footprint accounting and analysis based on embodied exergy—A case study of the Chinese society 1981–2001. Ecol. Econ. 2007, 61, 355–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X. Urban ecosystem accounting, modeling and regulation in Beijing based on embodied cosmic exergy. Ph.D. Dissertation, Peking University, Beijing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.B. Embodied ecological elements accounting of national economy. Ph.D. Dissertation, Peking University, Beijing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.M.; Chen, G.Q.; Zhou, J.B.; Jiang, M.M.; Chen, B. Ecological input–output modeling for embodied resources and emissions in Chinese economy 2005. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simulat. 2010, 15, 1942–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.Q.; Chen, Z.M. Carbon emissions and resources use by Chinese economy 2007: A 135–sector inventory and input–output embodiment. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simulat. 2010, 15, 3647–3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.Y.; Chen, H.; Li, S.C. Resources use and greenhouse gas emissions in urban economy: Ecological input–output modeling for Beijing 2002. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simulat. 2010, 15, 3201–3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chen, G.Q.; Ji, X. Cosmic emergy based ecological systems modelling. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simulat. 2010, 15, 2672–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odum, H.T. System Ecology: An Introduction; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Odum, H.T.; Odum, E.C. Computers Minimodels and Simulations. Exercises for Science and Social Science, Center for Environmental Policy; University of Florida: FL, USA, 1994; Available online: http://emsim.sourceforge.net (Accessed on 14 May 2010).
© 2010 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an Open Access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).