Abstract
Background/Objectives: Nutrigenetics investigates the role of genetic variants that contribute to the inter-individual variation in response to food intake. Risk factors for cardiovascular disease (CVD) are influenced by the complex interplay of genetic and environmental factors, including the diet. The aim of this scoping review is to analyze the literature on the effect of genotypes on the response to dietary interventions for the treatment of CVD risk factors. Methods: A literature search was conducted in MEDLINE to identify published articles fulfilling the inclusion criteria. Studies published in English between 2014 and 2024 were selected. Data were extracted according to the population, intervention, comparison, and outcome (PICO) format. Results: Forty-eight studies met the inclusion criteria. The studies differed in design, intervention characteristics, tested genotypes, and ancestry. The most frequently analyzed variants were single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in genes associated with lipid metabolism, inflammation, and energy balance, among others. The interventions tested the effects of different dietary patterns, diets modified in macronutrient content and types of fat, natural and processed foods, nutraceuticals, and nutrient supplements. Common APOE variants were the most analyzed genotypes showing significant interactions with different dietary interventions affecting blood lipids. Other genotypes found in pathways involving folic acid, lipid metabolism and transport have shown interactions with diverse dietary components across studies. Conclusions: Gene–diet interactions are observed in multiple dietary interventions. Replication of findings of nutrigenetic studies is required across different populations. The response to dietary treatments modifies CVD-related risk factors and shows variation associated with genotypes.
1. Introduction
Chronic, non-communicable diseases are the main causes of disease and mortality in adults []. Data from the World Health Organization showed that cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the leading cause of death globally, taking an estimated 17.9 million lives each year []. Obesity is a multifactorial disease and a risk factor for other diseases such as CVD []. CVD is a group of disorders of the heart and blood vessels and includes coronary heart disease, cerebrovascular disease, rheumatic heart disease and other conditions, and it is the leading cause of morbidity and mortality in adults worldwide []. Dietary habits influence diverse cardiometabolic risk factors including blood lipids, obesity, hypertension, glucose–insulin homeostasis, lipoprotein concentrations and function, oxidative stress, inflammation, and endothelial health, among others []. These phenotypes are well-established risk factors for CVD and other diseases that exhibit high inter-individual variability in response to diet. This variation is explained, to some extent, by variants across multiple genes [,].
In this sense, nutrigenetics refers to the study of the interaction between genetics and nutrition, investigating the effect of genetic variation on the response to diet, or its components [,,]. There is wide evidence that genetic variation, particularly single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), has a significant influence on the absorption, synthesis, utilization, and transport of substances present in food or their metabolites, with an impact on health. Some of these effects were identified in cross-sectional studies showing differences in phenotypes (i.e., body mass index (BMI), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C)) as an outcome of the interaction between nutrients and gene variants. A classic example of gene–diet interaction is the effect of the T allele of the -1131 T > C in APOA5 variant (rs662799) and dietary fat intake on BMI [] and the capacity to clear chylomicron triglycerides (TGs) or hydrolyze TGs []. Some of these effects have been replicated across populations [,,]. Other factors that contribute to diversity are epigenetic mechanisms and the activity of the gut microbiome, that interact with other environmental, social and demographic individual characteristics []. Later studies are clinical trials that identified numerous significant gene–diet interactions [,], and more recently, researchers developed genetic risk scores (GRSs) that integrate the weighted effect of a group of variants in order to predict the response to an intervention [].
The characterization of gene–diet interactions influencing CVD provide information for developing more efficient tools for promoting health and wellness and is required for personalized nutrition and precision healthcare.
The aim of the present review is to map and describe the scientific literature on the effect of genotypes or groups of them (i.e., GRS) on the response to dietary interventions for the treatment of risk factors for CVD.
2. Materials and Methods
This review was based on the international guide Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic review and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR) []. The research question was as follows: What is the effect of genetic variation (SNPs) on changes in phenotypes associated with CVD, in response to dietary interventions? A search was conducted in MEDLINE using the following algorithm: (diet OR gene-diet OR dietary OR nutrient OR nutraceutic OR functional food OR bioactive compound) AND (cholesterol OR blood lipids OR hypertension OR cardiovascular OR coronary) AND (SNP OR polymorphism OR genetic variant) NOT (children) NOT (review), using the filter Adults. The search considered publications between 2014 and 2024. The date for the last search was 27 August 2024. The criteria for study eligibility were as follows: published studies, in English language, testing a dietary intervention conducted in adults (>18 y), using a nutrigenomic approach (studies testing the effect of a genotype, or group of them, on the response to an intervention with a dietary pattern, modified diet or compound from food origin); the search was limited to effects of SNPs and included studies on individual or collective SNPs’ effects. The dietary intervention included modified diets, dietary patterns, consumption of specific foods according to an indication, nutraceuticals or nutrient supplements, regardless of duration, with the exception of acute or single-dose effects. Cardiovascular disease-related risk factors included total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), HDL-C, TG, lipoproteins a (Lp-a), blood pressure (BP), and homocysteine blood concentrations.
Exclusion criteria were as follows: studies evaluating the effect of a single dose of any meal, nutrient, food, or bioactive compound, reviews, and interventions that included other components different from diet or diet-derived compounds, such as exercise or other lifestyle changes, medication, etc. Records retrieved were screened and pre-selected based on the titles and abstracts. Examination of the full document was conducted according to eligibility criteria. The data extraction followed a population, intervention, comparison, and outcome (PICO) format. The included information was as follows: characteristics of the studied population (sample size, age, BMI, diagnosis, and ancestry), intervention (description of treatment, dose, time) comparison (genotypes of GRS, and in some cases, different diets), and outcome (effects of genotypes on the main phenotype/s).
Additionally, this study adhered to the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews; PRISMA-ScR) guidelines (Supplementary Materials). This protocol was registered in Open Science Frame work (OSF; https://osf.io/ub2rd, accessed on 12 November 2024) doi: 10.17605/OSF.IO/UB2RD.
3. Results
The search on nutrigenetic studies on CVD and related phenotypes retrieved 190 articles (Figure 1). The search identified original studies published between January 2014 and July 2024. This review selected intervention studies in order to investigate cause and effect relationships. A group of 48 studies that fulfilled the inclusion criteria were considered for data extraction and classified into groups according to the intervention characteristics (Table 1, Table 2, Table 3, Table 4, Table 5 and Table 6). The studies were conducted in participants with diseases such as obesity, different forms of dyslipidemia and other CVD risk factors, and other conditions, and healthy adults. The most investigated group is Caucasians in Europe and North America. As observed, a small number of studies have been conducted in other populations across the world.
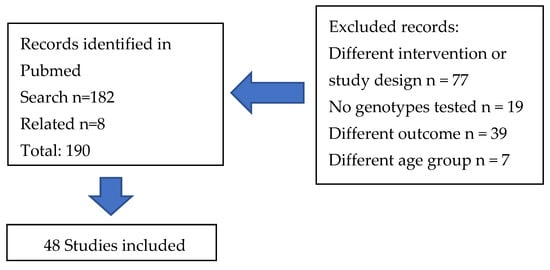
Figure 1.
Flow diagram of the study selection.

Table 1.
Fatty acid interventions: Gene by diet interaction in the treatment of cardiovascular disease risk factors.

Table 2.
Dietary pattern interventions: Gene by diet interaction in the treatment of cardiovascular disease risk factors.

Table 3.
Vitamin interventions: Gene by diet interaction in the treatment of cardiovascular disease risk factors.

Table 4.
Macronutrient interventions. Gene by diet interaction in the treatment of cardiovascular disease risk factors.

Table 5.
Hypocaloric diet interventions: Gene by diet interaction in the treatment of cardiovascular disease risk factors.

Table 6.
Other nutrient interventions: Gene by diet interaction in the treatment of cardiovascular disease risk factors.
The sample size ranged between 36 and 7170 participants, and there was a wide variation in duration, characteristics of the interventions, and study designs, which makes it difficult to compare or integrate results. The selected investigations analyzed the effect of a single variant, the separated or combined effects of two or more variants, and polygenic scores. The most frequently analyzed SNPs are located at genes involved in lipid metabolism (apoproteins, enzymes, and other proteins involved in cholesterol and fatty acid metabolism, and receptors, among other functional proteins), inflammation (TNFα, ADIPOQ), appetite regulation (NPY, BDNF), circadian rhythm (CLOCK) energy balance (PPARs, ADBR2), folic acid metabolism (MTHFR, MTR, MTRR) and other less investigated pathways. Interventions were classified as dietary patterns (n = 11), supplementation with vitamins with mixed or isolated nutrients (n = 3), and diets modified in fat content (n = 15) (this category included studies using fatty acid supplements). Diets modified in macronutrient content (n = 3) were assigned to a different category that investigated the effect of macronutrient composition, fat types and glycemic index, hypocaloric diets (n = 2), and the last category contains studies with interventions different from the previously described, classified as “others” (n = 14). This category included studies using unprocessed foods, such as kiwi, oatmeal, rice, drinks (red wine), salt, processed food (a snack containing cholesterol-lowering compounds), food groups (dairy products), a nutraceutic (artichoke leaf extract), and isolated food compounds (low- and high-molecular-weight β-glucans).
The phenotypes significantly affected by gene–diet interactions were LDL-C, HDL-C and TG, together with other circulating lipid fractions, blood homocysteine, and markers for glucose metabolism and inflammation. Three studies tested interaction effects on BP.
4. Discussion
As shown in Table 1, Table 2, Table 3, Table 4, Table 5 and Table 6, the gene–diet interaction affecting CVD risk factors has been extensively investigated using a wide variety of experimental approaches.
4.1. Effects of Genotypes
In the case of apolipoprotein E (APOE) variants, the present review identified seven studies showing significant interactions with dietary interventions using different types of fatty acids, phytostanols, and β-glucans [,,,,,,]. APOE participates in the lipoprotein-mediated lipid transport between organs via the plasma and interstitial fluids. The APOE2, 3 and 4 phenotypes had a significant effect on CVD risk factors and dietary response [,]. The study by Rajediran et al., 2021 [] analyzed the interaction between a group of variants in genes involved in cholesterol metabolism, and only variants in the APOE and ABCA1 genes showed consistent effects across interventions using different types of fat modifying HDL-C, LDL-C, and other CVD-associated risk factors. In the mentioned study, the APOE2 genotype exhibited significantly lower serum LDL-C concentrations than E4 carriers following a diet containing butter as a source for saturated fat, and they had lower serum LDL-C concentrations than E3 carriers following a diet containing PUFAs (p = 0.011). A previous study [] reported a differential response to the substitution of saturated fats (SFAs) by monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs) and low glycemic index (GI) carbohydrate in lipids by APOE. Another study [] showed genotype-dependent effects in the response to diets containing different types of fat. Findings of this investigation showed that APOE rs1064725 and a high-MUFA diet had a significant interaction, and TT homozygotes had significantly lower total cholesterol with this diet compared with a high saturated fatty acid (SFA) diet and ω-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) diet (p = 0.003 and p = 0.004) (Table 1). A possible mechanism explaining these findings is that a high-MUFA diet could shorten the residence time of very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) particles in the circulation, increasing the triglyceride-rich lipoprotein clearance rate among TT homozygotes of APOE rs1064725. These studies indicate that APOE4 carriers are responsive to dietary MUFAs. In line with these findings, similar genotype-dependent effects were observed after the exposure to diets with different content and type of fat, and less beneficial effects were found in APOE4 carriers []. According to Fallaize et al., 2017, APOE4 carriers generally have higher TC and LDL-C levels []. The study found that APOE variants modify the decrease in LDL-C after treatment with phytostanols. According to this study, APOE4 had a greater decrease in this cholesterol fraction as compared to APOE3 carriers []. In addition, APOE isoforms are associated with different responses to soluble fiber in lowering circulating LDL-C concentrations []. There is a controversy on the effect of the APOE isoform on the response to diet and association with risk factors for CVD. It is believed that the isoforms of APOE alter the physical structure of the lipoprotein itself, and E2 isoform reduces the affinity of the particle to bind to LDL receptors (LDL-R), explaining why E2 transport is associated with low levels of LDL-C; however, Minihane et al. (2007) considered that E3 and E4 protein isoforms do not bind differently to the LDL-R []. It has been proposed that the E4 isoform has a preferential association with triglyceride-rich lipoproteins (TRLs), resulting in more APOE bound to these particles, causing competition at the LDL-R, and an increase in circulating cholesterol; in addition, the conversion of VLDL into LDL occurs at a faster rate in APOE4 carriers [].
The G allele of the rs3808607 variant in the gene cytochrome P450, family 7, subfamily A, polypeptide 1 (CYP7A1) showed differential effects on LDL-C levels after treatment with phytostanols, with G carriers having a larger decrease (p < 0.001) []. This gene encodes an enzyme that regulates bile acid biosynthesis and cholesterol homeostasis. The mentioned variant is within the gene promoter region and enhances gene expression, increasing bile acid synthesis []. A few studies testing the cholesterol lowering effects of the consumption of oatmeal and its β-glucans and the interaction with the rs3808607 variant have been conducted. The study by Ye M. et al. [] found a significant interaction between this genotype and oatmeal intake reducing LDL-C. In this study, the TT carriers had a larger reduction in LDL-C as compared with the G allele. A previous study found that CYP7A1 rs3808607-G carriers are more responsive to the cholesterol-lowering effect of high-molecular-weight β-glucan than TT carriers. The main proposed underlying mechanism is the interruption of bile acid metabolism. No effect of the APOE variants was observed in this study, although the sample size is small []. The combined effect of this SNP with variants in genes associated with cholesterol metabolism (rs6720173 and rs760241) affected cholesterol levels in response to dairy product consumption []. Interestingly, these findings suggest that the rs3808607 variant may modulate the effect of dietary interventions with compounds (soluble fiber and dairy fat) that are expected to affect cholesterol metabolism through different mechanisms.
The FADS1 and FADS2 genes (encoding for fatty acid desaturases 1 and 2, respectively) have multiple SNPs. The variant rs174550 in FADS1 is an intronic variant in the gene encoding the enzyme that converts linoleic acid (LA) into arachidonic acid (AA), and the effect of the SNP on the protein expression or function is unknown. A study showed that this SNP had no effect in the blood lipid response to the dietary intake of LA and linolenic acid (ALA) []. The PUFA-induced Lp(a)-lowering effects are not modified by the FADS1 rs174550 genotype. In the study of Lankinen et al. [], the rs174550 variant showed genotype by diet interactions modifying proportions of circulating PUFAs in response to an 8-week high-LA diet. It is well known that this genotype modifies proportions of PUFAs in plasma lipids. According to the study conducted by Lankinen et al., 2021, this genotype exerted differential effects on C reactive protein (CRP) plasma levels after consumption of LA [], although the mechanism is poorly understood [].
The cholesterol ester transport protein (CETP) is a transporter of cholesteryl esters from HDL to lower-density apoB-containing lipoproteins. At the same time, triglyceride is transferred in the opposite direction to HDL. This gene contains polymorphisms with significant interactions with dietary fat. The SNP rs3764261 in the CEPT gene has been associated with CVD risk factors and has shown significant interactions with the dietary pattern (Mediterranean diet) modifying HDL-C (p = 0.006) and triglyceride concentrations (p = 0.040) []. The effect of the variant rs5882 in CETP was tested as a modifier of the response to the consumption of high-oleic canola oil (HOCO) and HOCO-DHA oil. This combined treatment decreased TG levels by 24% compared to HOCO. There were not significant interactions affecting lipid levels due to the DHA supplementation [].
The gene LIPC encodes for the enzyme hepatic lipase, which is produced in the liver and released to the bloodstream. Its function is to hydrolyze TG and phospholipids from lipoproteins (Table 4). SNPs in this gene have shown interactions with dietary compounds in cross-sectional studies. In the study by Smith et al. [], the major allele carriers (CC/CT) of rs1800588 variant had higher HDL-C following the Western diet, rich in saturated fat, compared with the Hispanic diet, containing MUFAs. In contrast, HDL-C levels in individuals carrying the TT genotype did not differ by diet. Dietary fat intake modifies the effect of the variant rs2070895 in LIPC on changes in serum lipids during a long-term weight-loss intervention in adults with obesity []. This SNP is in high linkage disequilibrium with rs1800588. These findings suggest that variants in this gene increase circulating HDL-C in response to the amount of total dietary fat.
The interactions of SNP within other genes relevant for CVD, such as the ATP binding cassete A member 1 (ABCA1), ATP-binding cassette transporter G5 and G8 (ABCG5, ABCG8) [,], apolipoprotein A1, APOA1 [], apolipoprotein A5, APOA5 [], have been analyzed in a smaller number of studies that fulfilled the inclusion criteria and have shown less consistent effects on CVD risk factors. These genotypes influence changes in blood lipids in response to modifications of dietary fat. In the case of variants within the peroxisome proliferated activated receptors (PPARs) alfa and gamma genes, four studies were found showing significant interactions with the diet [,,,]. The role of common SNPs in these genes on the response to the intake of different fatty acids has been tested showing that the intake of omega-3 PUFAs exerts different effects on triglycerides and insulin metabolism, according to PPARs genotype []. In contrast, a study testing the interaction between the intake of milk with different fat content and rs135549 in PPARα showed no effect on CVD risk factors, probably due to the limited effect of saturated fat on this transcription factor [].
Variants in enzymes in the folic acid metabolism affect homocysteine levels. The enzyme methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) is an enzyme in the folate metabolism necessary for one-carbon metabolism and production of nucleic acids. Studies on the variants in enzymes of the mentioned pathway analyzed the effect of supplementation with B vitamins on the levels of blood homocysteine and LDL-C, showing a significant reduction in the treatment group as compared to placebo []. A similar genotype effect was observed in patients with hemodialysis supplemented with folic acid and vitamin B12 []. The variant rs1076991 C > T in the gene methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase (MTHFD1) is associated with increased risk of acute myocardial infraction (AMI), although the risk seems to be dependent on specific vitamin B supplementation []. This variant exerts a significant effect on the promoter activity of this gene.
4.2. Effects of Interventions
The modification of the amount and type of fat is a well-known factor to induce changes in circulating lipids and other metabolic parameters. The interventions testing the effects of dietary lipids analyzed the effects of decreasing total dietary fat and the substitution of saturated fat by MUFAs and PUFAs.
The effects of the dietary MUFAs and PUFAs on biomarkers for CVD have been demonstrated [,,,]. The intake of fatty acids change the composition of cell membranes, influencing fluidity, intracellular signaling, gene expression and availability of substrates for lipid-derived inflammatory regulators []. Diets containing MUFAs produce larger and less atherogenic chylomicrons compared with diets with saturated fat; this difference may explain the association of consumption of MUFAs with a decrease in the risk for CVD []. Differences in the metabolic effects between omega-3 and omega-6 PUFAs have been thoroughly analyzed. In the study by Nuotio et al., 2024, the omega-3 alfa-linolenic acid (ALA) appears to decrease LDL-C, non-HDL-C, remnant-C and ApoB more effectively than omega-6 linoleic acid (LA) []. Omega-3 fatty acids reduce TG and inflammation and may modify insulin sensitivity. In addition, differential effects of omega-3 and omega-6 PUFAs on lipoprotein characteristics have been reported []. Some of the effects of omega-3 PUFAs are mediated by the activation of the PPAR transcription factors that increase oxidation of fatty acids, decrease VLDL, and may improve insulin sensitivity [,].
The Mediterranean dietary pattern (Table 2) is characterized by a high content of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats and has been consistently associated with better cardiovascular health. Thus, it combines the effects of a group of bioactive compounds such as fatty acids, fibers, and phytochemicals []. According to the present review, this dietary pattern may reduce TG, total cholesterol, and inflammation-related phenotypes, and these effects may vary according to genotypes in lipid metabolism. Interestingly, a study found an effect of the C677T (rs1801133) variant in MTHFR on the response to the Italian Mediterranean diet (IMD) and the Italian Mediterranean organic diet (IMOD). A significant interaction between this genotype and the diet on homocysteine levels was found when compared to a low protein diet (p < 0.001) in patients with chronic kidney disease and stable renal function [].
The studies using vitamins (B12, B6, folate) as intervention showed genotype-depending effects on homocysteine concentrations, particularly in participants with variants in the MTHFR gene. The rs1801133 SNP in this enzyme is known to decrease the activity. These studies suggest that patients with genetic susceptibility may benefit from a personalized treatment [,,] (Table 3).
The hypocaloric diets (Table 5) with different macronutrient compositions (high protein, low fat) had effects on weight loss and lipid metabolism, modifying the risk for CVD. The observed effects on cardiometabolic markers are very likely influenced by changes in body composition primarily and, to a lesser extent yet in some cases significant, to the effects of specific genotypes.
As observed in Table 6, studies using interventions that included the intake of foods, drinks, or isolated compounds achieved some changes in CVD risk factors. Studies using fiber in the form of oatmeal, glucans, kiwi fruit and avocado reduced TG, total cholesterol, and LDL-C and increased HDL-C. These effects were mediated by genotypes in lipid-related genotypes such as rs708272 in CETP and rs3808607 in CYP7A1 and APOE. The study by Hannon et al. (Table 1) used an intervention with one avocado per day, which combines the effects of fiber and MUFAs in improving dyslipidemia. This study suggests that the intake of a specific food in isoenergetic diets may exert significant genotype-related effects on CVD risk factors, as observed in the study using Hass avocado [].
The use of isolated nutrients or bioactive compounds allows for testing their effects in a specific manner, using a controlled dose, removing the effect of other components or the overall caloric intake [,,,,,].
In summary, this review identified studies testing gene–diet interactions discovered or confirmed in human experimental studies, providing valuable scientific evidence on the contribution of genetic variation to individual responses to diet. As mentioned before, there is a large methodological diversity among the selected studies as well as a lack of replication studies, particularly across populations other than Caucasian, that may have different variant frequencies and genetic backgrounds. Other considerations are that most of the studies have been conducted in relatively small samples and the fact that the functional effect of most of the identified variants are unknown. Therefore, new studies with proper statistical power are required, testing the effects of known or novel dietary interventions in order to improve the alternatives for prevention and treatment of CVD in populations around the world.
5. Conclusions
Numerous gene–diet interactions influencing the response to dietary interventions for CVD-related factors have been identified in intervention studies conducted in humans. Diverse dietary interventions have shown interactions with genotypes which may contribute to understanding inter-individual variation. In CVD, genetic variants in lipid transport and metabolism have shown significant effects, although variation in genes belonging to different pathways have interesting interactions. Replication and validation of the clinical significance of these effects across different populations are required in order to develop tools for precision nutrition.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/healthcare12222292/s1, Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analysis extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR) Checklist. Reference [] is cited in the supplementary materials.
Author Contributions
Search, data extraction, writing and editing, G.K.G.-Q., G.L.-R. and E.L.R. Conceptualization, writing and editing, M.E.T. Critical review and editing, O.R.-L., J.A.M. and D.A.d.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Hartmann, M.; Servotte, N.; Aris, E.; Doherty, T.M.; Salem, A.; Beck, E. Burden of Vaccine-Preventable Diseases in Adults (50+) in the United States: A Retrospective Claims Analysis. BMC Public Health 2024, 24, 2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardiovascular Diseases. Available online: https://www.who.int/europe/news-room/fact-sheets/item/cardiovascular-diseases (accessed on 26 September 2024).
- World Obesity Atlas 2024 World Obesity Federation. Available online: https://www.worldobesity.org/news/world-obesity-atlas-2024 (accessed on 26 September 2024).
- Mozaffarian, D. Dietary and Policy Priorities for Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes, and Obesity: A Comprehensive Review. Circulation 2016, 133, 187–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masson, L.F.; McNeill, G. The Effect of Genetic Variation on the Lipid Response to Dietary Change: Recent Findings. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2005, 16, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah, M.M.H.; Jones, P.J.H.; Eck, P.K. Nutrigenetics of Cholesterol Metabolism: Observational and Dietary Intervention Studies in the Postgenomic Era. Nutr. Rev. 2015, 73, 523–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah, M.M.H.; Vazquez-Vidal, I.; Baer, D.J.; House, J.D.; Jones, P.J.H.; Desmarchelier, C. Common Genetic Variations Involved in the Inter-Individual Variability of Circulating Cholesterol Concentrations in Response to Diets: A Narrative Review of Recent Evidence. Nutrients 2021, 13, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcum, J.A. Nutrigenetics/Nutrigenomics, Personalized Nutrition, and Precision Healthcare. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2020, 9, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeo, G.; Donato, K.; Micheletti, C.; Cristoni, S.; Miertus, S.; Miertus, J.; Veselenyiova, D.; Iaconelli, A.; Aquilanti, B.; Matera, G.; et al. Nutrigenomics: SNPs Correlated to Lipid and Carbohydrate Metabolism. Clin. Ter. 2023, 174, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corella, D.; Lai, C.Q.; Demissie, S.; Cupples, L.A.; Manning, A.K.; Tucker, K.L.; Ordovas, J.M. APOA5 Gene Variation Modulates the Effects of Dietary Fat Intake on Body Mass Index and Obesity Risk in the Framingham Heart Study. J. Mol. Med. 2007, 85, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Kim, O.Y.; Koh, S.J.; Jang, Y.; Lee, J.H.; Jang, Y.; Yun, S.S.; Ordovas, J.M. Comparison of Low-Fat Meal and High-Fat Meal on Postprandial Lipemic Response in Non-Obese Men According to the -1131T>C Polymorphism of the Apolipoprotein A5 (APOA5) Gene (Randomized Cross-over Design). J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2006, 25, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Reyes, T.; Astudillo-López, C.C.; Salgado-Goytia, L.; Muñoz-Valle, J.F.; Salgado-Bernabé, A.B.; Guzmán-Guzmán, I.P.; Castro-Alarcón, N.; Moreno-Godínez, M.E.; Parra-Rojas, I. Interaction of Dietary Fat Intake with APOA2, APOA5 and LEPR Polymorphisms and Its Relationship with Obesity and Dyslipidemia in Young Subjects. Lipids Health Dis. 2015, 14, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemánková, K.; Dembovská, R.; Piťha, J.; Kovář, J. Glucose Added to a Fat Load Suppresses the Postprandial Triglyceridemia Response in Carriers of the -1131C and 56G Variants of the APOA5 Gene. Physiol. Res. 2017, 66, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guevara-Cruz, M.; Medina-Vera, I.; Flores-López, A.; Aguilar-López, M.; Smith, C.E.; Parnell, L.D.; Lee, Y.C.; Lai, C.Q.; Tovar, A.R.; Ordovás, J.M.; et al. Development of a Genetic Score to Predict an Increase in HDL Cholesterol Concentration After a Dietary Intervention in Adults with Metabolic Syndrome. J. Nutr. 2019, 149, 1116–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morand, C.; De Roos, B.; Garcia-Conesa, M.T.; Gibney, E.R.; Landberg, R.; Manach, C.; Milenkovic, D.; Rodriguez-Mateos, A.; Van De Wiele, T.; Tomas-Barberan, F. Why Interindividual Variation in Response to Consumption of Plant Food Bioactives Matters for Future Personalised Nutrition. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2020, 79, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcotte, B.V.; Guénard, F.; Marquis, J.; Charpagne, A.; Vadillo-Ortega, F.; Tejero, M.E.; Binia, A.; Vohl, M.C. Genetic Risk Score Predictive of the Plasma Triglyceride Response to an Omega-3 Fatty Acid Supplementation in a Mexican Population. Nutrients 2019, 11, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, M.D.J.; Marnie, C.; Tricco, A.C.; Pollock, D.; Munn, Z.; Alexander, L.; McInerney, P.; Godfrey, C.M.; Khalil, H. Updated Methodological Guidance for the Conduct of Scoping Reviews. JBI Evid. Synth. 2020, 18, 2119–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuotio, P.; Lankinen, M.A.; Meuronen, T.; de Mello, V.D.; Sallinen, T.; Virtanen, K.A.; Pihlajamäki, J.; Laakso, M.; Schwab, U. Dietary N-3 Alpha-Linolenic and n-6 Linoleic Acids Modestly Lower Serum Lipoprotein(a) Concentration but Differentially Influence Other Atherogenic Lipoprotein Traits: A Randomized Trial. Atherosclerosis 2024, 395, 117597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendiran, E.; Lamarche, B.; She, Y.; Ramprasath, V.; Eck, P.; Brassard, D.; Gigleux, I.; Levy, E.; Tremblay, A.; Couture, P.; et al. A Combination of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms Is Associated with the Interindividual Variability in the Blood Lipid Response to Dietary Fatty Acid Consumption in a Randomized Clinical Trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 114, 564–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lankinen, M.A.; de Mello, V.D.; Meuronen, T.; Sallinen, T.; Ågren, J.; Virtanen, K.A.; Laakso, M.; Pihlajamäki, J.; Schwab, U. The FADS1 Genotype Modifies Metabolic Responses to the Linoleic Acid and Alpha-Linolenic Acid Containing Plant Oils-Genotype Based Randomized Trial FADSDIET2. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2021, 65, 2001004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannon, B.A.; Edwards, C.G.; Thompson, S.V.; Reeser, G.E.; Burd, N.A.; Holscher, H.D.; Teran-Garcia, M.; Khan, N.A. Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms Related to Lipoprotein Metabolism Are Associated with Blood Lipid Changes Following Regular Avocado Intake in a Randomized Control Trial among Adults with Overweight and Obesity. J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 1379–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lankinen, M.A.; Fauland, A.; Shimizu, B.I.; Ågren, J.; Wheelock, C.E.; Laakso, M.; Schwab, U.; Pihlajamäki, J. Inflammatory Response to Dietary Linoleic Acid Depends on FADS1 Genotype. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 109, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbuMweis, S.S.; Panchal, S.K.; Jones, P.J.H. Triacylglycerol-Lowering Effect of Docosahexaenoic Acid Is Not Influenced by Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms Involved in Lipid Metabolism in Humans. Lipids 2018, 53, 897–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, H.; Futatsuya, C.; Miki, A.; Tabuchi, E.; Sugano, M. Supplementation with Trans Fatty Acid at 1% Energy Did Not Increase Serum Cholesterol Irrespective of the Obesity-Related Genotypes in Healthy Adult Japanese. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 27, 797–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binia, A.; Vargas-Martínez, C.; Ancira-Moreno, M.; Gosoniu, L.M.; Montoliu, I.; Gámez-Valdez, E.; Soria-Contreras, D.C.; Angeles-Quezada, A.; Gonzalez-Alberto, R.; Fernández, S.; et al. Improvement of Cardiometabolic Markers after Fish Oil Intervention in Young Mexican Adults and the Role of PPARα L162V and PPARγ2 P12A. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2017, 43, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallaize, R.; Carvalho-Wells, A.L.; Tierney, A.C.; Marin, C.; Kieć-Wilk, B.; Dembińska-Kieć, A.; Drevon, C.A.; Defoort, C.; Lopez-Miranda, J.; Risérus, U.; et al. APOE Genotype Influences Insulin Resistance, Apolipoprotein CII and CIII According to Plasma Fatty Acid Profile in the Metabolic Syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shatwan, I.M.; Weech, M.; Jackson, K.G.; Lovegrove, J.A.; Vimaleswaran, K.S. Apolipoprotein E Gene Polymorphism Modifies Fasting Total Cholesterol Concentrations in Response to Replacement of Dietary Saturated with Monounsaturated Fatty Acids in Adults at Moderate Cardiovascular Disease Risk. Lipids Health Dis. 2017, 16, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minihane, A.M.; Armah, C.K.; Miles, E.A.; Madden, J.M.; Clark, A.B.; Caslake, M.J.; Packard, C.J.; Kofler, B.M.; Lietz, G.; Curtis, P.J.; et al. Consumption of Fish Oil Providing Amounts of Eicosapentaenoic Acid and Docosahexaenoic Acid That Can Be Obtained from the Diet Reduces Blood Pressure in Adults with Systolic Hypertension: A Retrospective Analysis. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, B.L.; Cormier, H.; Rudkowska, I.; Lemieux, S.; Couture, P.; Vohl, M.C. Association between Polymorphisms in Phospholipase A2 Genes and the Plasma Triglyceride Response to an N-3 PUFA Supplementation: A Clinical Trial. Lipids Health Dis. 2015, 14, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, B.L.; Rudkowska, I.; Couture, P.; Lemieux, S.; Julien, P.; Vohl, M.C. Modulation of C-Reactive Protein and Plasma Omega-6 Fatty Acid Levels by Phospholipase A2 Gene Polymorphisms Following a 6-Week Supplementation with Fish Oil. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids 2015, 102–103, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchard-Mercier, A.; Rudkowska, I.; Lemieux, S.; Couture, P.; Pérusse, L.; Vohl, M.C. SREBF1 Gene Variations Modulate Insulin Sensitivity in Response to a Fish Oil Supplementation. Lipids Health Dis. 2014, 13, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.Y.; Mayneris-Perxachs, J.; Lovegrove, J.A.; Todd, S.; Yaqoob, P. Fish-Oil Supplementation Alters Numbers of Circulating Endothelial Progenitor Cells and Microparticles Independently of ENOS Genotype. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 100, 1232–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J.I.; Lind, M.V.; Moller, G.; Hansen, T.; Pedersen, H.; Christensen, M.M.B.; Laursen, J.C.; Nielsen, S.; Ottendahl, C.B.; Larsen, C.V.L.; et al. The Effect of Traditional Diet on Glucose Homoeostasis in Carriers and Non-Carriers of a Common TBC1D4 Variant in Greenlandic Inuit: A Randomised Crossover Study. Br. J. Nutr. 2023, 130, 1871–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corella, D.; Ramírez-Sabio, J.B.; Coltell, O.; Ortega-Azorín, C.; Estruch, R.; Martínez-González, M.A.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Sorlí, J.V.; Castañer, O.; Arós, F.; et al. Effects of the Ser326Cys Polymorphism in the DNA Repair OGG1 Gene on Cancer, Cardiovascular, and All-Cause Mortality in the PREDIMED Study: Modulation by Diet. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2018, 118, 589–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Rios, A.; Alcala-Diaz, J.F.; Gomez-Delgado, F.; Delgado-Lista, J.; Marin, C.; Leon-Acuña, A.; Camargo, A.; Rodriguez-Cantalejo, F.; Blanco-Rojo, R.; Quintana-Navarro, G.; et al. Beneficial Effect of CETP Gene Polymorphism in Combination with a Mediterranean Diet Influencing Lipid Metabolism in Metabolic Syndrome Patients: CORDIOPREV Study. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roncero-Ramos, I.; Rangel-Zuñiga, O.A.; Lopez-Moreno, J.; Alcala-Diaz, J.F.; Perez-Martinez, P.; Jimenez-Lucena, R.; Castaño, J.P.; Roche, H.M.; Delgado-Lista, J.; Ordovas, J.M.; et al. Mediterranean Diet, Glucose Homeostasis, and Inflammasome Genetic Variants: The CORDIOPREV Study. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, 1700960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corella, D.; Asensio, E.M.; Coltell, O.; Sorlí, J.V.; Estruch, R.; Martínez-González, M.Á.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Castañer, O.; Arós, F.; Lapetra, J.; et al. CLOCK Gene Variation Is Associated with Incidence of Type-2 Diabetes and Cardiovascular Diseases in Type-2 Diabetic Subjects: Dietary Modulation in the PREDIMED Randomized Trial. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2016, 15, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Delgado, F.; Garcia-Rios, A.; Alcala-Diaz, J.F.; Rangel-Zuñiga, O.; Delgado-Lista, J.; Yubero-Serrano, E.M.; Lopez-Moreno, J.; Tinahones, F.J.; Ordovas, J.M.; Garaulet, M.; et al. Chronic Consumption of a Low-Fat Diet Improves Cardiometabolic Risk Factors According to the CLOCK Gene in Patients with Coronary Heart Disease. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2015, 59, 2556–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Tsai, L.T.; Zhou, Y.; Evertts, A.; Xu, S.; Griffin, M.J.; Issner, R.; Whitton, H.J.; Garcia, B.A.; Epstein, C.B.; et al. Identification of Nuclear Hormone Receptor Pathways Causing Insulin Resistance by Transcriptional and Epigenomic Analysis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 17, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corella, D.; Sorlí, J.V.; Estruch, R.; Coltell, O.; Ortega-Azorín, C.; Portolés, O.; Martínez-González, M.Á.; Bulló, M.; Fitó, M.; Arós, F.; et al. MicroRNA-410 Regulated Lipoprotein Lipase Variant Rs13702 Is Associated with Stroke Incidence and Modulated by Diet in the Randomized Controlled PREDIMED Trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 100, 719–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Daniele, N.; Di Renzo, L.; Noce, A.; Iacopino, L.; Ferraro, P.M.; Rizzo, M.; Sarlo, F.; Domino, E.; De Lorenzo, A. Effects of Italian Mediterranean Organic Diet vs. Low-Protein Diet in Nephropathic Patients According to MTHFR Genotypes. J. Nephrol. 2014, 27, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Delgado, F.; Alcala-Diaz, J.F.; Garcia-Rios, A.; Delgado-Lista, J.; Ortiz-Morales, A.; Rangel-Zuñiga, O.; Tinahones, F.J.; Gonzalez-Guardia, L.; Malagon, M.M.; Bellido-Muñoz, E.; et al. Polymorphism at the TNF-Alpha Gene Interacts with Mediterranean Diet to Influence Triglyceride Metabolism and Inflammation Status in Metabolic Syndrome Patients: From the CORDIOPREV Clinical Trial. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 1519–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Azorín, C.; Sorlí, J.V.; Estruch, R.; Asensio, E.M.; Coltell, O.; González, J.I.; Martínez-González, M.Á.; Ros, E.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Fitó, M.; et al. Amino Acid Change in the Carbohydrate Response Element Binding Protein Is Associated with Lower Triglycerides and Myocardial Infarction Incidence Depending on Level of Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet in the PREDIMED Trial. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2014, 7, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pokushalov, E.; Ponomarenko, A.; Bayramova, S.; Garcia, C.; Pak, I.; Shrainer, E.; Ermolaeva, M.; Kudlay, D.; Johnson, M.; Miller, R. Effect of Methylfolate, Pyridoxal-5′-Phosphate, and Methylcobalamin (SolowaysTM) Supplementation on Homocysteine and Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Levels in Patients with Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase, Methionine Synthase, and Methionine Synthase Reductase Polymorphisms: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achour, O.; Elmtaoua, S.; Zellama, D.; Omezzine, A.; Moussa, A.; Rejeb, J.; Boumaiza, I.; Bouacida, L.; Rejeb, N.B.; Achour, A.; et al. The C677T MTHFR Genotypes Influence the Efficacy of B9 and B12 Vitamins Supplementation to Lowering Plasma Total Homocysteine in Hemodialysis. J. Nephrol. 2016, 29, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.P.; Pedersen, E.K.R.; Johansson, S.; Gregory, J.F.; Ueland, P.M.; Svingen, G.F.T.; Helgeland; Meyer, K.; Fredriksen; Nygård, O.K. B Vitamin Treatments Modify the Risk of Myocardial Infarction Associated with a MTHFD1 Polymorphism in Patients with Stable Angina Pectoris. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2016, 26, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.; Zhou, T.; Li, X.; Heianza, Y.; Liang, Z.; Bray, G.A.; Sacks, F.M.; Qi, L. Genetic Susceptibility, Dietary Protein Intake, and Changes of Blood Pressure: The POUNDS Lost Trial. Hypertension 2019, 74, 1460–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, B.A.; Walker, C.G.; Jebb, S.A.; Moore, C.; Frost, G.S.; Goff, L.; Sanders, T.A.B.; Lewis, F.; Griffin, M.; Gitau, R.; et al. APOE4 Genotype Exerts Greater Benefit in Lowering Plasma Cholesterol and Apolipoprotein B than Wild Type (E3/E3), after Replacement of Dietary Saturated Fats with Low Glycaemic Index Carbohydrates. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.E.; Van Rompay, M.I.; Mattei, J.; Garcia, J.F.; Garcia-Bailo, B.; Lichtenstein, A.H.; Tucker, K.L.; Ordovás, J.M. Dietary Fat Modulation of Hepatic Lipase Variant -514 C/T for Lipids: A Crossover Randomized Dietary Intervention Trial in Caribbean Hispanics. Physiol. Genom. 2017, 49, 592–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luis, D.A.; Aller, R.; Izaola, O.; Romero, E. Effect of -55CT Polymorphism of UCP3 on Insulin Resistance and Cardiovascular Risk Factors after a High Protein/Low Carbohydrate versus a Standard Hypocaloric Diet. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 68, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Ng, S.S.; Bray, G.A.; Ryan, D.H.; Sacks, F.M.; Ning, G.; Qi, L. Dietary Fat Intake Modifies the Effect of a Common Variant in the LIPC Gene on Changes in Serum Lipid Concentrations during a Long-Term Weight-Loss Intervention Trial. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 1289–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopecky, S.L.; Alias, S.; Klodas, E.; Jones, P.J.H. Reduction in Serum LDL Cholesterol Using a Nutrient Compendium in Hyperlipidemic Adults Unable or Unwilling to Use Statin Therapy: A Double-Blind Randomized Crossover Clinical Trial. J. Nutr. 2022, 152, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Sun, J.; Chen, Y.; Ren, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Pan, Y.; Xue, H. Response of Serum LDL Cholesterol to Oatmeal Consumption Depends on CYP7A1_rs3808607 Genotype in Chinese. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 29, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah, M.M.H.; Eck, P.K.; Couture, P.; Lamarche, B.; Jones, P.J.H. The Combination of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms Rs6720173 (ABCG5), Rs3808607 (CYP7A1), and Rs760241 (DHCR7) Is Associated with Differing Serum Cholesterol Responses to Dairy Consumption. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2018, 43, 1090–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimi-Mameghani, M.; Asghari-Jafarabadi, M.; Rezazadeh, K. TCF7L2-Rs7903146 Polymorphism Modulates the Effect of Artichoke Leaf Extract Supplementation on Insulin Resistance in Metabolic Syndrome: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. J. Integr. Med. 2018, 16, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, X.; Gu, D.; He, J.; Rao, D.C.; Hixson, J.E.; Chen, J.; Li, J.; Huang, J.; Wu, X.; Rice, T.K.; et al. Resequencing Epithelial Sodium Channel Genes Identifies Rare Variants Associated With Blood Pressure Salt-Sensitivity: The GenSalt Study. Am. J. Hypertens. 2018, 31, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Harding, S.V.; Thandapilly, S.J.; Tosh, S.M.; Jones, P.J.H.; Ames, N.P. Barley β-Glucan Reduces Blood Cholesterol Levels via Interrupting Bile Acid Metabolism. Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 118, 822–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.; Wang, Y.; Ren, K.Y.; Yan, D.Y.; Guo, T.S.; Zheng, W.L.; Yuan, Z.Y.; Mu, J.J. Genetic Variants in Adiponectin and Blood Pressure Responses to Dietary Sodium or Potassium Interventions: A Family-Based Association Study. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2016, 30, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gepner, Y.; Henkin, Y.; Schwarzfuchs, D.; Golan, R.; Durst, R.; Shelef, I.; Harman-Boehm, I.; Spitzen, S.; Witkow, S.; Novack, L.; et al. Differential Effect of Initiating Moderate Red Wine Consumption on 24-h Blood Pressure by Alcohol Dehydrogenase Genotypes: Randomized Trial in Type 2 Diabetes. Am. J. Hypertens. 2016, 29, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Liu, F.; Chen, S.; Yang, X.; Huang, J.; He, J.; Jaquish, C.E.; Zhao, Q.; Gu, C.C.; Hixson, J.E.; et al. Common Variants in the Na(+)-Coupled Bicarbonate Transporter Genes and Salt Sensitivity of Blood Pressure: The GenSalt Study. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2016, 30, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Harding, S.V.; Eck, P.; Thandapilly, S.J.; Gamel, T.H.; Abdel-Aal, E.S.M.; Crow, G.H.; Tosh, S.M.; Jones, P.J.H.; Ames, N.P. High-Molecular-Weight β-Glucan Decreases Serum Cholesterol Differentially Based on the CYP7A1 Rs3808607 Polymorphism in Mildly Hypercholesterolemic Adults. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKay, D.S.; Eck, P.K.; Gebauer, S.K.; Baer, D.J.; Jones, P.J.H. CYP7A1-Rs3808607 and APOE Isoform Associate with LDL Cholesterol Lowering after Plant Sterol Consumption in a Randomized Clinical Trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 102, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, D.S.; Eck, P.K.; Rideout, T.C.; Baer, D.J.; Jones, P.J.H. Cholesterol Ester Transfer Protein Polymorphism Rs5882 Is Associated with Triglyceride-Lowering in Response to Plant Sterol Consumption. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2015, 40, 846–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gammon, C.S.; Minihane, A.M.; Kruger, R.; Conlon, C.A.; Von Hurst, P.R.; Jones, B.; Stonehouse, W. TaqIB Polymorphism in the Cholesteryl Ester Transfer Protein (CETP) Gene Influences Lipid Responses to the Consumption of Kiwifruit in Hypercholesterolaemic Men. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 111, 1077–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loria-Kohen, V.; Espinosa-Salinas, I.; Ramirez de Molina, A.; Casas-Agustench, P.; Herranz, J.; Molina, S.; Fonollá, J.; Olivares, M.; Lara-Villoslada, F.; Reglero, G.; et al. A Genetic Variant of PPARA Modulates Cardiovascular Risk Biomarkers after Milk Consumption. Nutrition 2014, 30, 1144–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallaize, R.; Celis-Morales, C.; MacReady, A.L.; Marsaux, C.F.M.; Forster, H.; O’Donovan, C.; Woolhead, C.; San-Cristobal, R.; Kolossa, S.; Hallmann, J.; et al. The Effect of the Apolipoprotein E Genotype on Response to Personalized Dietary Advice Intervention: Findings from the Food4Me Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 104, 827–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, D.J.A.; Hegele, R.A.; Jenkins, A.L.; Connelly, P.W.; Hallak, K.; Bracci, P.; Kashtan, H.; Corey, P.; Pintilia, M.; Stern, H.; et al. The Apolipoprotein E Gene and the Serum Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Response to Dietary Fiber. Metabolism 1993, 42, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minihane, A.M.; Jofre-Monseny, L.; Olano-Martin, E.; Rimbach, G. ApoE Genotype, Cardiovascular Risk and Responsiveness to Dietary Fat Manipulation. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2007, 66, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Castro-Orós, I.; Pampín, S.; Cofán, M.; Mozas, P.; Pintó, X.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Rodríguez-Rey, J.C.; Ros, E.; Civeira, F.; Pocoví Miguel, M. Promoter Variant -204A > C of the Cholesterol 7α-Hydroxylase Gene: Association with Response to Plant Sterols in Humans and Increased Transcriptional Activity in Transfected HepG2 Cells. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 30, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meuronen, T.; Lankinen, M.A.; Kärkkäinen, O.; Laakso, M.; Pihlajamäki, J.; Hanhineva, K.; Schwab, U. FADS1 Rs174550 Genotype and High Linoleic Acid Diet Modify Plasma PUFA Phospholipids in a Dietary Intervention Study. Eur. J. Nutr. 2022, 61, 1109–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Luis, D.A.; Izaola, O.; Primo, D.; Aller, R. Role of Rs670 Variant of APOA1 Gene on Lipid Profile, Insulin Resistance and Adipokine Levels in Obese Subjects after Weight Loss with a Dietary Intervention. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 142, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, R.; Kim, M.; Chae, J.S.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, J.H. Consumption of Whole Grains and Legumes Modulates the Genetic Effect of the APOA5 -1131C Variant on Changes in Triglyceride and Apolipoprotein A-V Concentrations in Patients with Impaired Fasting Glucose or Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes. Trials 2014, 15, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Calzón, S.; Martínez-González, M.A.; Razquin, C.; Corella, D.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Alfredo Martínez, J.; Zalba, G.; Marti Del Moral, A. Pro12Ala Polymorphism of the PPARγ2 Gene Interacts with a Mediterranean Diet to Prevent Telomere Shortening in the PREDIMED-NAVARRA Randomized Trial. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2015, 8, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kar, A.; Ghosh, P.; Patra, P.; Chini, D.S.; Nath, A.K.; Saha, J.K.; Chandra Patra, B. Omega-3 Fatty Acids Mediated Cellular Signaling and Its Regulation in Human Health. Clin. Nutr. Open Sci. 2023, 52, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiNicolantonio, J.J.; O’Keefe, J.H. Effects of Dietary Fats on Blood Lipids: A Review of Direct Comparison Trials. Open Heart 2018, 5, e000871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakrim, S.; Aboulaghras, S.; Aanniz, T.; Benali, T.; El Omari, N.; El-Shazly, M.; Lee, L.H.; Mustafa, S.K.; Sahib, N.; Rebezov, M.; et al. Effects of Mediterranean Diets and Nutrigenomics on Cardiovascular Health. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 64, 7589–7608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzi, F.; Conti, C.; Dogliotti, E.; Terranegra, A.; Salvi, E.; Braga, D.; Ricca, F.; Lupoli, S.; Mingione, A.; Pivari, F.; et al. Interaction between Polyphenols Intake and PON1 Gene Variants on Markers of Cardiovascular Disease: A Nutrigenetic Observational Study. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K.K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L.; et al. PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMAScR): Checklist and Explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).