Advances in Fatigue Crack Growth of Metals and Their Alloys
A special issue of Materials (ISSN 1996-1944). This special issue belongs to the section "Metals and Alloys".
Deadline for manuscript submissions: closed (20 October 2023) | Viewed by 517
Special Issue Editor
Interests: fatigue; creep; thermomechanical fatigue; constitutive modeling; life prediction
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Special Issue Information
Dear Colleagues,
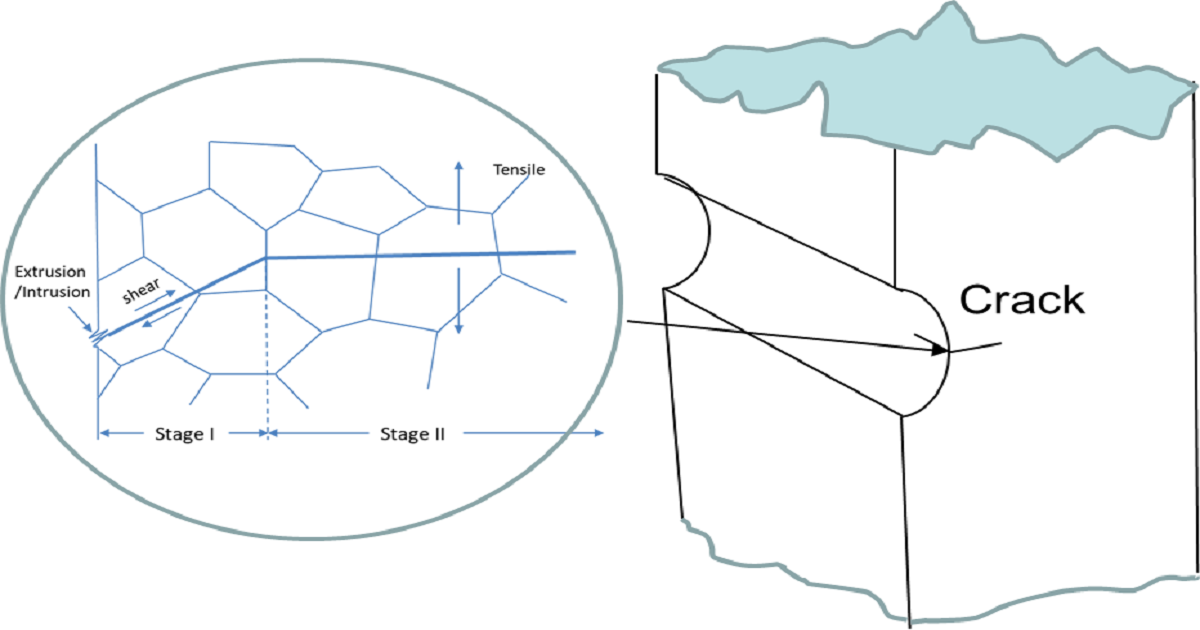
Fatigue crack growth is an important area of research, the results of which have been applied in damage tolerance design to ensure the structural integrity of operating engineering platforms. Since Paris observed and proposed a fatigue crack growth rate law based on the linear elastic fracture mechanics concept in 1960, significant advances have been achieved in this field. Notably, non-destructive inspection and high-resolution imaging techniques have been advanced to allow for the early and reliable detection of cracks, enabling researchers to study crack growth and behavior in more detail. Computational modeling has gone into great detail to perform more complex simulations of fatigue crack growth using finite element analysis (FEA) and other computational methods. Materials development under the concept of damage tolerance design has led to new materials that are more resistant to fatigue cracking. In recent years, machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) have also been utilized to analyze large amounts of experimental and service data, with the hope of identifying patterns and relationships of fatigue crack growth under real (complex) service conditions.
Despite these recent advances, there are still some important issues that need to be addressed:
- A multiscale modeling framework to bridge the gap between crack initiation, and short and long crack growth;
- Environmental effects on the initiation and propagation of fatigue cracks and modelling;
- Fatigue crack closure under real service conditions;
- More robust and reliable ML and AI methods for the study of fatigue crack growth;
- The standardization of testing methods to address the above issues.
This Special Issue welcomes researchers to disseminate their research results on the above issues in an open access environment. This will facilitate information exchange and hopefully deepen our understanding of real fatigue crack growth processes for holistic damage-tolerant structural integrity.
Dr. Xijia Wu
Guest Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the special issue website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 250 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for assessment.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Materials is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- fatigue crack growth rate
- damage tolerance
- holistic structural integrity
- non-destructive evaluation
- microstructural effects
- environmental effects
- residual strength
Benefits of Publishing in a Special Issue
- Ease of navigation: Grouping papers by topic helps scholars navigate broad scope journals more efficiently.
- Greater discoverability: Special Issues support the reach and impact of scientific research. Articles in Special Issues are more discoverable and cited more frequently.
- Expansion of research network: Special Issues facilitate connections among authors, fostering scientific collaborations.
- External promotion: Articles in Special Issues are often promoted through the journal's social media, increasing their visibility.
- Reprint: MDPI Books provides the opportunity to republish successful Special Issues in book format, both online and in print.
Further information on MDPI's Special Issue policies can be found here.






