-
 Examining Strategies to Manage Climate Risks of PPP Infrastructure Projects
Examining Strategies to Manage Climate Risks of PPP Infrastructure Projects -
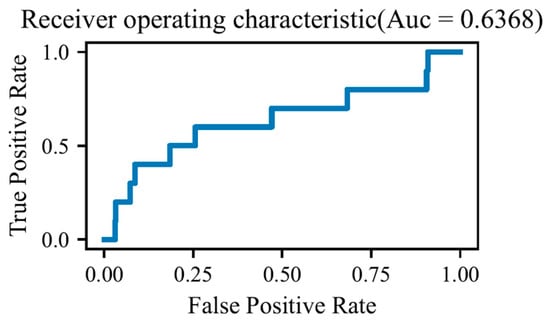
 The Association of Financial Knowledge, Attitude, and Behavior with Investment Loss Tolerance: Evidence from Japan
The Association of Financial Knowledge, Attitude, and Behavior with Investment Loss Tolerance: Evidence from Japan -
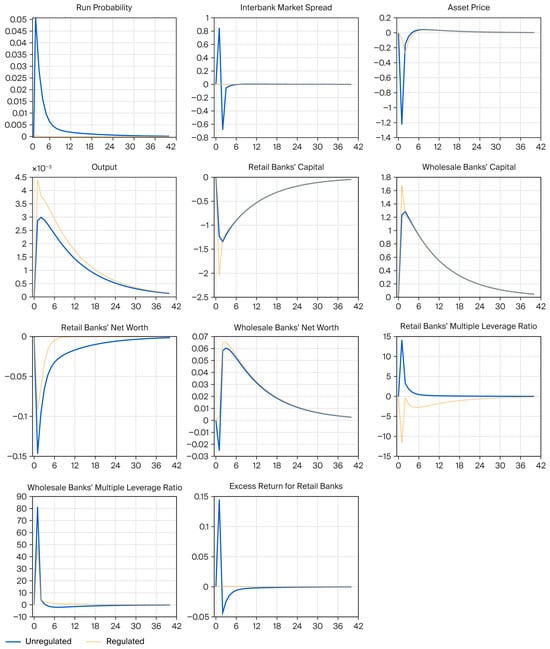
 Beyond the Rating: How Disagreement Among ESG Agencies Affects Bond Credit Spreads
Beyond the Rating: How Disagreement Among ESG Agencies Affects Bond Credit Spreads -
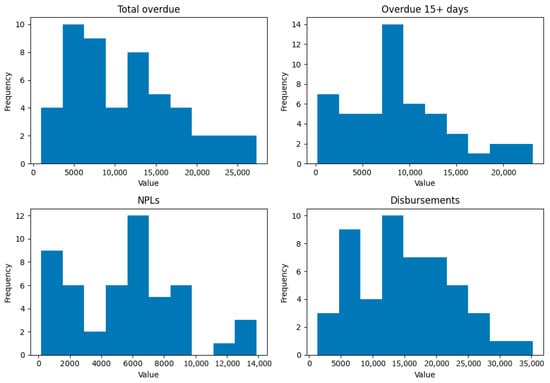
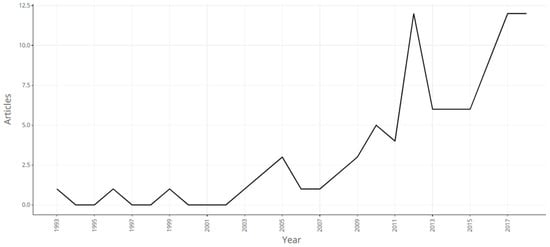
 Cryptocurrencies as a Tool for Money Laundering: Risk Assessment and Perception of Threats Based on Empirical Research
Cryptocurrencies as a Tool for Money Laundering: Risk Assessment and Perception of Threats Based on Empirical Research
Journal Description
Risks
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High visibility: indexed within Scopus, ESCI (Web of Science), EconLit, EconBiz, RePEc, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: CiteScore - Q1 (Economics, Econometrics and Finance (miscellaneous))
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 20 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 6.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers for a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done
Latest Articles
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Deadline: 30 May 2026
Deadline: 31 July 2026
Deadline: 31 October 2026
Deadline: 31 December 2026
Conferences
Special Issues
Deadline: 31 January 2026
Deadline: 31 January 2026
Deadline: 28 February 2026
Deadline: 28 February 2026