Journal Description
Metrics
Metrics
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on informetrics published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- Rapid Publication: first decisions in 19 days; acceptance to publication in 8 days (median values for MDPI journals in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
Latest Articles
Literature Review on Decarbonization Through Sustainability-Oriented Contractor Selection in IPD Projects: Bibliometric Analysis
Metrics 2025, 2(4), 25; https://doi.org/10.3390/metrics2040025 - 10 Dec 2025
Abstract
►
Show Figures
This paper presents a bibliometric and literature review on decarbonization strategies in sustainability-oriented contractor selection within Integrated Project Delivery (IPD) frameworks. The study analyzes 972 journal articles published between 2002 and 2024 from Scopus, complemented by Google Scholar for thematic insights. Bibliometric techniques
[...] Read more.
This paper presents a bibliometric and literature review on decarbonization strategies in sustainability-oriented contractor selection within Integrated Project Delivery (IPD) frameworks. The study analyzes 972 journal articles published between 2002 and 2024 from Scopus, complemented by Google Scholar for thematic insights. Bibliometric techniques in R were applied to identify influential publications, research trends, and thematic clusters. The review highlights documented benefits of integrating decarbonization into contractor evaluation, including lifecycle carbon reduction, ESG alignment, and early-stage material optimization. Challenges remain in terms of limited lifecycle data, absence of standard benchmarks, and organizational resistance. Critical success factors identified include policy alignment, availability of assessment data, and collaborative stakeholder engagement. The findings demonstrate that incorporating carbon-related performance indicators into early procurement decisions can reshape prequalification standards and strengthen sustainable project delivery. Citation and co-word analysis reveal emerging research trends, including digital innovations such as artificial intelligence for contractor evaluation and emissions tracking. This study provides both a research foundation and a strategic guide for construction professionals, policymakers, and sustainability advocates aiming to align IPD with global decarbonization targets.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
One Size Fits None: Rethinking Bibliometric Indicators for Fairer Assessment and Strategic Research Planning
by
Dimitrios Kouis, Evangelia Triperina, Ioannis Drivas, Foteini Efthymiou, Alexandros Koulouris and Ruben Comas-Forgas
Metrics 2025, 2(4), 24; https://doi.org/10.3390/metrics2040024 - 3 Nov 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Bibliometric indicators play a key role in assessing research performance at individual, departmental, and institutional levels, influencing both funding allocation, and university rankings. However, despite their widespread use, bibliometrics are often applied indiscriminately and without discrimination, overlooking contextual factors that affect research productivity.
[...] Read more.
Bibliometric indicators play a key role in assessing research performance at individual, departmental, and institutional levels, influencing both funding allocation, and university rankings. However, despite their widespread use, bibliometrics are often applied indiscriminately and without discrimination, overlooking contextual factors that affect research productivity. This research investigates how gender, academic discipline, institutional location, and academic rank influence bibliometric outcomes within the Greek Higher Education system. A dataset of 2015 faculty profiles from 18 universities and 92 departments was collected and analyzed using data from Google Scholar and Scopus. The findings reveal significant disparities in publication and citation metrics: female researchers, faculty in peripheral institutions, and those in specific disciplines (such as humanities) tend to score lower values across several indicators. These inequalities underscore the risks of applying one-size-fits-all evaluation models in performance-based research funding systems. The paper moves beyond a one-size-fits-all perspective and proposes that bibliometric evaluations should be context-sensitive and grounded in discipline and rank-specific benchmarks. By establishing more refined and realistic expectations for researcher productivity, institutions and policymakers can use bibliometrics as a constructive tool for strategic research planning and fair resource allocation, rather than as a mechanism that reinforces the existing biases. The study also contributes to ongoing international discussions on the responsible use of research metrics in higher education policy.
Full article
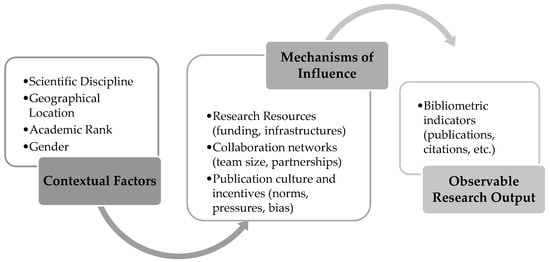
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Mapping Contemporary AI-Education Intersections and Developing an Integrated Convergence Framework: A Bibliometric-Driven and Inductive Content Analysis
by
Muhammad Ali, Ming Ma, Mian Muneeb and Gary K. W. Wong
Metrics 2025, 2(4), 23; https://doi.org/10.3390/metrics2040023 - 3 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Artificial intelligence (AI) has rapidly permeated education since 2014, propelled by technological innovation and global investment, yet scholarly discourse on contemporary AI-Education intersections remains largely fragmented. The present study addresses this notable gap through a bibliometric-driven and inductive content analysis to inform future
[...] Read more.
Artificial intelligence (AI) has rapidly permeated education since 2014, propelled by technological innovation and global investment, yet scholarly discourse on contemporary AI-Education intersections remains largely fragmented. The present study addresses this notable gap through a bibliometric-driven and inductive content analysis to inform future research and practice. A total of 317 articles published between 2014 and October 2024 were retrieved from WOSCC and Scopus following the PRISMA protocol. Keyword co-occurrence and co-citation analyses with VOSviewer (version 1.6.20) were employed to visualize the intellectual structures shaping the field, while qualitative inductive content analysis was conducted to address the limitations of bibliometric methods in revealing deeper thematic insights. This dual-method approach identified four thematic clusters and eleven prevailing research trends. Subsequently, through interpretive synthesis, five interrelated research issues were identified: limited congruence between technological and pedagogical affordances, insufficient bottom-up perspectives in AI literacy frameworks, an ambiguous relationship between computational thinking and AI, a lack of explicit interpretation of AI ethics, and limitations of existing professional development frameworks. To address these gaps pragmatically, thirty issue-specific recommendations were consolidated into five overarching themes, culminating in the Integrated AI-Education Convergence Framework. This framework advocates for pedagogy-centric, ethically grounded, and contextually responsive AI integration within interdisciplinary educational research and practice.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Predicting Star Scientists in the Field of Artificial Intelligence: A Machine Learning Approach
by
Koosha Shirouyeh, Andrea Schiffauerova and Ashkan Ebadi
Metrics 2025, 2(4), 22; https://doi.org/10.3390/metrics2040022 - 11 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Star scientists are highly influential researchers who have made significant contributions to their field, gained widespread recognition, and often attracted substantial research funding. They are critical for the advancement of science and innovation and significantly influence the transfer of knowledge and technology to
[...] Read more.
Star scientists are highly influential researchers who have made significant contributions to their field, gained widespread recognition, and often attracted substantial research funding. They are critical for the advancement of science and innovation and significantly influence the transfer of knowledge and technology to industry. Identifying potential star scientists before their performance becomes outstanding is important for recruitment, collaboration, networking, and research funding decisions. This study utilizes machine learning techniques and builds four different classifiers, i.e., random forest, support vector machines, naïve bayes, and logistic regression, to predict star scientists in the field of artificial intelligence while highlighting features related to their success. The analysis is based on publication data collected from Scopus from 2000 to 2019, incorporating a diverse set of features such as gender, ethnic diversity, and collaboration network structural properties. The random forest model achieved the best performance with an AUC of 0.75. Our results confirm that star scientists follow different patterns compared to their non-star counterparts in almost all the early-career features. We found that certain features, such as gender and ethnic diversity, play important roles in scientific collaboration and can significantly impact an author’s career development and success. The most important features in predicting star scientists in the field of artificial intelligence were the number of articles, betweenness centrality, research impact indicators, and weighted degree centrality. Our approach offers valuable insights for researchers, practitioners, and funding agencies interested in identifying and supporting talented researchers.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Mapping the Research Landscape of Sustainable Fashion: A Bibliometric Analysis
by
Sai-Leung Ng and Shou-Hung Chen
Metrics 2025, 2(4), 21; https://doi.org/10.3390/metrics2040021 - 4 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The fashion industry, despite its global economic importance, is a major contributor to environmental degradation and social inequality. In response, sustainable fashion has emerged as a growing movement advocating ethical, ecological, and socially responsible practices. This study presents a comprehensive bibliometric analysis of
[...] Read more.
The fashion industry, despite its global economic importance, is a major contributor to environmental degradation and social inequality. In response, sustainable fashion has emerged as a growing movement advocating ethical, ecological, and socially responsible practices. This study presents a comprehensive bibliometric analysis of 1134 peer-reviewed journal articles on sustainable fashion indexed in Scopus from 1986 to 2025. Results show an exponential rise in research output after 2015, with interdisciplinary contributions from social sciences, business, environmental science, and engineering. By applying performance analysis and science mapping techniques, the study identifies five major research themes: “Consumer Behavior,” “Design Ethics,” “Circular Economy,” “Innovation,” and “Digital Media.” The geographic distribution reveals strong outputs from both developed and emerging economies. This study provides an integrative overview of the intellectual landscape of sustainable fashion and serves as a roadmap for researchers, policymakers, and practitioners who are interested in the development of sustainable fashion.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Synthetic Indicator of the Use of Mobile Technologies in Spanish Universities by Teachers of Social Sciences
by
Rosaura Fernández-Pascual, María Pinto and David Caballero Mariscal
Metrics 2025, 2(4), 20; https://doi.org/10.3390/metrics2040020 - 4 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Digital transformation in higher education necessitates a central role for university faculty, yet there is a lack of comprehensive tools to measure their actual pedagogical use of technology. This study aims to refine the definition of a composite indicator to evaluate mobile technology
[...] Read more.
Digital transformation in higher education necessitates a central role for university faculty, yet there is a lack of comprehensive tools to measure their actual pedagogical use of technology. This study aims to refine the definition of a composite indicator to evaluate mobile technology adoption among social science university teachers. Using the results of the validated MOBILE-APP questionnaire, administered to a sample of N = 295 teachers from various social science degree programs, we employed multilevel structural equation modeling (SEM) to develop and implement a synthetic indicator for assessing mobile technology adoption levels among educators. The analysis of the considered factors (motivation, training, tools, and use) revealed differences in mobile technology adoption based on degree program, age, and previous experience. High motivation, training, use of institutional tools, and propensity for use promote the adoption of mobile technologies. Three levels of mobile technology adoption are identified and characterized. This synthetic indicator can be used both technically and socially to track the evolution of mobile technology adoption, enabling comparative analyses and longitudinal assessments that inform strategic decisions in training, infrastructure, and curriculum development. This research represents a step forward in the development of quantitative indicators and the assessment of research practices.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Can Social Innovation and Agriculture Serve as a Turning Point in Rural Areas? Insights from a Bibliometric Literature Review
by
Mattia Mogetta, Deborah Bentivoglio, Giulia Chiaraluce, Giacomo Staffolani and Adele Finco
Metrics 2025, 2(3), 19; https://doi.org/10.3390/metrics2030019 - 10 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Rural areas are facing major challenges and profound changes that directly affect the quality of life of rural populations. In this context, new ideas and opportunities are emerging, where social innovation initiatives are leading to solutions that attempt to revitalize the social fabric
[...] Read more.
Rural areas are facing major challenges and profound changes that directly affect the quality of life of rural populations. In this context, new ideas and opportunities are emerging, where social innovation initiatives are leading to solutions that attempt to revitalize the social fabric of rural areas. Considering this, the aim is to conduct a productivity measurement and a bibliometric analysis that examines the research landscapes of social innovations in rural areas. With a comprehensive analysis of 178 publications, this study examines main authors, countries, journals, research areas, and key themes in the field. The results show the relevance of principal areas such as agriculture, digitalization, and forestry. Alongside these, new organizational models are being developed, such as rural hubs, living labs, and community cooperatives. Future research could explore the role of these organizations in rural areas in greater depth.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
CTAARCHS: Cloud-Based Technologies for Archival Astronomical Research Contents and Handling Systems
by
Stefano Gallozzi, Georgios Zacharis, Federico Fiordoliva and Fabrizio Lucarelli
Metrics 2025, 2(3), 18; https://doi.org/10.3390/metrics2030018 - 8 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This paper presents a flexible approach to a multipurpose, heterogeneous archive and data management system model that merges the robustness of legacy grid-based technologies with modern cloud and edge computing paradigms. It leverages innovations driven by big data, IoT, AI, and machine learning
[...] Read more.
This paper presents a flexible approach to a multipurpose, heterogeneous archive and data management system model that merges the robustness of legacy grid-based technologies with modern cloud and edge computing paradigms. It leverages innovations driven by big data, IoT, AI, and machine learning to create an adaptive data storage and processing framework. In today’s digital age, where data are the new intangible gold, the “gold rush” lies in managing and storing massive datasets effectively—especially when these data serve governmental or commercial purposes, raising concerns about privacy and data misuse by third-party aggregators. Astronomical data, in particular, require this same thoughtful approach. Scientific discovery increasingly depends on efficient extraction and processing of large datasets. Distributed archival models, unlike centralized warehouses, offer scalability by allowing data to be accessed and processed across locations via cloud services. Incorporating edge computing further enables real-time access with reduced latency. Major astronomical projects must also avoid common single points of failure (SPOFs), often resulting from suboptimal technological choices driven by collaboration politics or In-Kind Contributions (IKCs). These missteps can hinder innovation and long-term project success. The principal goal of this work is to outline best practices in archival and data management projects—from policy development and task planning to use-case definition and implementation. Only after these steps can a coherent selection of hardware, software, or virtual environments be made. The proposed model—CTAARCHS (Cloud-based Technologies for Astronomical Archiving Research Contents and Handling Systems)—is an open-source, multidisciplinary platform supporting big data needs in astronomy. It promotes broad institutional collaboration, offering code repositories and sample data for immediate use.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
A Scoping Review of Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) and Pedagogy Nexus: Implications for the Higher Education Sector
by
Subas P. Dhakal
Metrics 2025, 2(3), 17; https://doi.org/10.3390/metrics2030017 - 1 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The higher education sector is increasingly being reshaped and reimagined in the era of Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI). For instance, the promise of GenAI to innovate pedagogical approaches in the way teaching and learning (T&L) occur across universities has been increasingly recognised. It
[...] Read more.
The higher education sector is increasingly being reshaped and reimagined in the era of Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI). For instance, the promise of GenAI to innovate pedagogical approaches in the way teaching and learning (T&L) occur across universities has been increasingly recognised. It is in this context that the question of how literature on the GenAI and Pedagogy (GenAIP) nexus has evolved in recent years has the potential to generate insights that inform and shape T&L policies and practices. However, the systematic analysis of scholarly literature on the GenAIP nexus has remained under the radar. This study responds to this gap and draws on PRISMA for the Scoping Review (PRISMA-ScR) method to carry out a Bibliometric Scoping Review of the GenAIP nexus. It examines scholarly research outputs (n = 310) published between 2023 and 2025 that are available on the Scopus database with two research objectives: (i) to ascertain research trends, thematic emphasis, prominent authors, countries and outlets, and (ii) to map various pedagogical approaches. Beyond revealing that authors from developing economies have produced significantly fewer research outputs than those from developed economies, the analysis highlights an urgent need for appropriate GenAI policies and curriculum redesign. It also documents 40 distinct pedagogical approaches reported in the literature. In light of the growing academic integrity challenges posed by GenAI, this article discusses three key implications for the higher education sector and future research: (i) redesigning courses and assessments to foster AI literacy, (ii) developing fit-for-purpose academic integrity policies, and (iii) delivering AI-focused professional development for academic staff.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
On the Dearth of Retractions in Social Work: A Cross-Sectional Study of Ten Leading Journals
by
Daniel J. Dunleavy
Metrics 2025, 2(3), 16; https://doi.org/10.3390/metrics2030016 - 1 Sep 2025
Abstract
In recent decades, there has been an increase in the number of retractions across the biomedical and social sciences. A high rate of retractions undermines the integrity of scholarly journals and threatens the credibility of scientific disciplines. It is unknown how common retractions
[...] Read more.
In recent decades, there has been an increase in the number of retractions across the biomedical and social sciences. A high rate of retractions undermines the integrity of scholarly journals and threatens the credibility of scientific disciplines. It is unknown how common retractions are within the field of social work. The aim of this study was to determine the prevalence of retractions among ten leading social work journals. This cross-sectional study employed three search strategies. First, each journal’s website was searched using the keywords “retracted” and “retraction”. The same procedure was employed, for each journal, using Google Scholar’s advanced search function. Finally, the Retraction Watch Database was queried using the name of each journal. None of the 196 results produced from these search strategies resulted in the identification of a single retracted article. Reasons for this absence are explored and recommendations to enhance the integrity of social work research and journals are discussed.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Emergence and Evolution of ‘Big Data’ Research: A 30-Year Scientometric Analysis of the Knowledge Field
by
Ignacio Perez Karich and Simon Joss
Metrics 2025, 2(3), 15; https://doi.org/10.3390/metrics2030015 - 13 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In the ongoing ‘data revolution’, the ubiquity of digital data in society underlines a transformative era. This is mirrored in the sciences, where ‘big data’ has emerged as a major research field. This article significantly extends previous scientometric analyses by tracing the field’s
[...] Read more.
In the ongoing ‘data revolution’, the ubiquity of digital data in society underlines a transformative era. This is mirrored in the sciences, where ‘big data’ has emerged as a major research field. This article significantly extends previous scientometric analyses by tracing the field’s conceptual emergence and evolution across a 30-year period (1993–2022). Bibliometric analysis is based on 17 data categories that co-constitute the conceptual network of ‘big data’ research. Using Scopus, the search query resulted in 70,163 articles and 315,235 author keywords. These are analysed aggregately regarding co-occurrences of the 17 data categories and co-occurrences of data categories with author keywords, and regarding their disciplinary distributions and interdisciplinary reach. Temporal analysis reveals two major development phases: 1993–2012 and 2013–2022. The study demonstrates: (1) the rapid expansion of the research field concentrated on seven main data categories; (2) the consolidation of keyword (co-)occurrences on ‘machine learning’, ‘deep learning’, ‘artificial intelligence’ and ‘cloud computing’; and (3) significant interdisciplinarity across four main subject areas. Scholars can use the findings to combine data categories and author keywords in ways that align scholarly work with specific thematic and disciplinary interests. The findings could also inform research funding, especially concerning opportunities for cross-disciplinary research.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Directed Energy Deposition: A Scientometric Study and Its Practical Implications
by
Mehran Ghasempour-Mouziraji, Daniel Afonso, Behrouz Nemati and Ricardo Alves de Sousa
Metrics 2025, 2(3), 14; https://doi.org/10.3390/metrics2030014 - 5 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Directed Energy Deposition is an additive manufacturing subgroup that uses a laser beam to melt the wire or powder to create a melt pool. In the current study, a scientometric analysis has been carried out to analyze the contribution of countries, publication type
[...] Read more.
Directed Energy Deposition is an additive manufacturing subgroup that uses a laser beam to melt the wire or powder to create a melt pool. In the current study, a scientometric analysis has been carried out to analyze the contribution of countries, publication type analysis, distribution of publications over the years, keywords analysis, author analysis, cited journal, categories, institutes of publication, and report the practical implications. Firstly, the database was extracted from the Web of Science and then post-processed with CiteSpace 6.2.R4 and VOSviewer 1.6.20 software. Afterward, the associated results had been extracted and reported. It was found that China is the leader according to publication, followed by the USA and Germany, which mostly published their achievements in article and proceeding paper formats, which are increasing annually. According to the keywords, additive manufacturing, Laser Metal Deposition, and fabrication are the most commonly used. Based on the CiteSapce and VOSviewer results, Lin, Xin and Huang, Weidong are the authors with the highest publication rates. In addition, Additive Manufacturing, Materials & Design, and Materials Science and Engineering: A are the most cited journals, and regarding the categories, materials science, multidisciplinary, applied physics, and manufacturing engineering are the most commonly used DED processes. Northwestern Polytechnical University, Fraunhofer Gesellschaft, and the United States Department of Energy (DOE) have performed the most research in the field of DED.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Simulation in the Built Environment: A Bibliometric Analysis
by
Saman Jamshidi
Metrics 2025, 2(3), 13; https://doi.org/10.3390/metrics2030013 - 4 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Simulation has become a pivotal tool in the design, analysis, and optimization of the built environment, and has been widely adopted by professionals in architecture, engineering, and urban planning. These techniques enable stakeholders to test hypotheses, evaluate design alternatives, and predict performance outcomes
[...] Read more.
Simulation has become a pivotal tool in the design, analysis, and optimization of the built environment, and has been widely adopted by professionals in architecture, engineering, and urban planning. These techniques enable stakeholders to test hypotheses, evaluate design alternatives, and predict performance outcomes prior to construction. Applications span energy consumption, airflow, thermal comfort, lighting, structural behavior, and human interactions within buildings and urban contexts. This study maps the scientific landscape of simulation research in the built environment through a bibliometric analysis of 12,220 publications indexed in Scopus. Using VOSviewer 1.6.20, it conducted citation and keyword co-occurrence analyses to identify key research themes, leading countries and journals, and central publications in the field. The analysis revealed seven primary thematic clusters: (1) human-focused simulation, (2) building-scale energy performance simulation, (3) urban-scale energy performance simulation, (4) sustainable design and simulation, (5) indoor environmental quality simulation, (6) building aerodynamics simulation, and (7) computing in building simulation. By synthesizing these trends and domains, this study provides an overview of the field, facilitating greater accessibility to the simulation literature and informing future interdisciplinary research and practice in the built environment.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Use of Video Games in Language Learning: A Bibliometric Analysis
by
Alain Presentación-Muñoz, Alberto González-Fernández, Miguel Rodal and Jesús Acevedo-Borrega
Metrics 2025, 2(3), 12; https://doi.org/10.3390/metrics2030012 - 21 Jul 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Advances in technology and changes in the way people entertain themselves have made video games a cultural agent on a par with more traditional games, including language learning. In addition, the use of video games in education is becoming increasingly common and numerous
[...] Read more.
Advances in technology and changes in the way people entertain themselves have made video games a cultural agent on a par with more traditional games, including language learning. In addition, the use of video games in education is becoming increasingly common and numerous benefits associated with their use have been discovered. The aim of this article is to analyze the search trends in studies dealing with the use of video games in language learning. To this end, a bibliometric analysis was carried out by applying the traditional laws of bibliometrics (Price’s law, Bradford’s law of concentration, Lotka’s law, Zipf’s law and h-index) to documents published in journals indexed in the Core Collection of the Web of Science (WoS). Annual publications between 2009 and 2022 show an exponential growth R2 = 86%. The journals with the most publications are Computer assisted language learning (Taylor & Francis) and Computers and Education (Elsevier). Jie Chi-Yang and Gwo Jen-Hwan were the most cited authors. The United States and Taiwan were the countries with the highest scientific output. The use of video games in language learning has been of particular interest in recent years, with benefits found for students who use them in their classes, although more research is needed to establish criteria and requirements for each video game for its intended purpose.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Cognitive Systems and Artificial Consciousness: What It Is Like to Be a Bat Is Not the Point
by
Javier Arévalo-Royo, Juan-Ignacio Latorre-Biel and Francisco-Javier Flor-Montalvo
Metrics 2025, 2(3), 11; https://doi.org/10.3390/metrics2030011 - 17 Jul 2025
Abstract
A longstanding ambiguity surrounds the operationalization of consciousness in artificial systems, complicated by the philosophical and cultural weight of subjective experience. This work examines whether cognitive architectures may be designed to support a functionally explicit form of artificial consciousness, focusing not on the
[...] Read more.
A longstanding ambiguity surrounds the operationalization of consciousness in artificial systems, complicated by the philosophical and cultural weight of subjective experience. This work examines whether cognitive architectures may be designed to support a functionally explicit form of artificial consciousness, focusing not on the replication of phenomenology, but rather on measurable, technically realizable introspective mechanisms. Drawing on a critical review of foundational and contemporary literature, this study articulates a conceptual and methodological shift: from investigating the experiential perspective of agents (“what it is like to be a bat”) to analyzing the informational, self-regulatory, and adaptive structures that enable purposive behavior. The approach combines theoretical analysis with a comparative review of major cognitive architectures, evaluating their capacity to implement access consciousness and internal monitoring. Findings indicate that several state-of-the-art systems already display core features associated with functional consciousness—such as self-explanation, context-sensitive adaptation, and performance evaluation—without invoking subjective states. These results support the thesis that cognitive engineering may progress more effectively by focusing on operational definitions of consciousness that are amenable to implementation and empirical validation. In conclusion, this perspective enables the development of artificial agents capable of autonomous reasoning and self-assessment, grounded in technical clarity rather than speculative constructs.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue AI and the Digital Cultural Ecosystem: Enhancing or Eroding Socio-Cultural Dynamics)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Research Assessment and the Hollowing out of the Economics Discipline in UK Universities
by
James Johnston and Alan Reeves
Metrics 2025, 2(3), 10; https://doi.org/10.3390/metrics2030010 - 23 Jun 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This paper explores the link between the results of the UK’s Research Evaluation Exercises (REEs) and university decisions on which Units of Assessment (UOA) to submit to in future REEs. How the raw data from REEs can be converted into two novel measurements
[...] Read more.
This paper explores the link between the results of the UK’s Research Evaluation Exercises (REEs) and university decisions on which Units of Assessment (UOA) to submit to in future REEs. How the raw data from REEs can be converted into two novel measurements of research performance—an internal and an external measurement—is explained. Data on two UOAs, Business and Management Studies (BMS) and Economics and Econometrics (E&E), from five consecutive REEs undertaken in the United Kingdom (UK) between 1992 and 2014, was then used to assess whether and how the results of one REE were related to UOA submissions in the next. The findings reveal that both the internal and external assessments of performance were associated with changes in the probability of resubmission to the same UOA in the next REE, with the external comparisons being particularly important. It also appears that while one instance of poor performance might be tolerated by a university, repeated poor performance was associated with a heightened risk of withdrawal from both the BMS and E&E UOAs in the next REE. In addition, holding research performance constant, universities were significantly more likely to withdraw from the E&E UOA than the BMS UOA. New (post-1992) universities were also more likely to continue to submit to a UOA in the next REE than pre-1992 institutions. There is also some evidence that the quality of submissions to the BMS UOA is catching up with that of submissions to the E&E UOA. The somewhat worrying implications of these findings for the health of the Economics discipline in UK universities are assessed.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Comprehensive Review of Metrics and Measurements of Quantum Systems
by
Hassan Soubra, Hatem Elsayed, Yousef Elbrolosy, Youssef Adel and Zeyad Attia
Metrics 2025, 2(2), 9; https://doi.org/10.3390/metrics2020009 - 19 Jun 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Quantum computing promises to offer significant computational advantages over classical computing, leveraging principles such as superposition and entanglement. This necessitates effective metrics and measurement techniques for evaluating quantum systems, aiding in their development and performance optimization. However, due to fundamental differences in computing
[...] Read more.
Quantum computing promises to offer significant computational advantages over classical computing, leveraging principles such as superposition and entanglement. This necessitates effective metrics and measurement techniques for evaluating quantum systems, aiding in their development and performance optimization. However, due to fundamental differences in computing paradigms and current immaturity of quantum software abstractions, classical software and hardware metrics may not directly apply to quantum computing, where the distinction between software and hardware can still be somewhat indiscernible compared to classical computing. This paper provides a comprehensive review of existing quantum software and hardware metrics in the scientific literature, highlighting key challenges in the field. Additionally, it investigates the application of Functional Size Measurement (FSM), based on the COSMIC ISO 19761 FSM Method, to measure quantum software. Three FSM approaches are analyzed by applying them to Shor’s and Grover’s algorithms, with measurement results compared to assess their effectiveness. A comparative analysis highlights the strengths and limitations of each approach, emphasizing the need for further refinement. The insights from this study contribute to the advancement of quantum metrics, especially software metrics and measurement, paving the way for the development of a unified and standardized approach to quantum software measurement and assessment.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
HOTGAME: A Corpus of Early House and Techno Music from Germany and America
by
Tim Ziemer
Metrics 2025, 2(2), 8; https://doi.org/10.3390/metrics2020008 - 29 May 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Many publications on early house and techno music have the character of documentation and include (auto-)biographical statements from contemporaries of the scene. This literature has led to many statements, hypotheses, and conclusions. The weaknesses of such sources are their selective and subjective nature,
[...] Read more.
Many publications on early house and techno music have the character of documentation and include (auto-)biographical statements from contemporaries of the scene. This literature has led to many statements, hypotheses, and conclusions. The weaknesses of such sources are their selective and subjective nature, and the danger of unclear memories, romanticization, and constructive memory. Consequently, a validation through content-based, quantitative music analyses is desirable. For this purpose, the HOuse and Techno music from Germany and AMErica (HOTGAME) corpus was built. Metrics from the field of data quality control show that the corpus is representative and explanatory for house and techno music from Germany and the United States of America between 1984 and 1994. HOTGAME can serve as a reliable source for the analysis of early house and techno music using big data methods, like inferential statistics and machine learning.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Pre-Service Secondary Science Teachers and the Contemporary Epistemological and Philosophical Conceptions of the Nature of Science: Scientific Knowledge Construction Through History
by
Abdeljalil Métioui
Metrics 2025, 2(2), 7; https://doi.org/10.3390/metrics2020007 - 22 May 2025
Abstract
In this research, we aim to synthesize the complex issue of students’ and science teachers’ conceptions of the nature of science (NOS). We identified the conceptions of ninety-five pre-service science teachers (PSTcs) enrolled in the Qualifying Master’s Program in Teaching Science at the
[...] Read more.
In this research, we aim to synthesize the complex issue of students’ and science teachers’ conceptions of the nature of science (NOS). We identified the conceptions of ninety-five pre-service science teachers (PSTcs) enrolled in the Qualifying Master’s Program in Teaching Science at the secondary level in Quebec (Canada) about the NOS, particularly relative to the development of science through history and approaches to constructing scientific knowledge, especially regarding the relationship between observation, hypothesis, experiment, measure and theory. To this end, we constructed a multiple-choice questionnaire (MCQ) comprising 11 statements to characterize their conceptions. The qualitative data analysis underscores the intricate nature of scientific knowledge construction. The PSTcs identified are as follows: 1. Scientific theories today correspond to improving ancient theories; 2. Science progresses by accumulation; 3. Science advancement results from improving current theories thanks to experimentation; 4. The observation is a pure observation that is preconceived; 5. We must experiment with scientific equipment in a laboratory to disprove a theory; and 6. Experiments precede scientific theory. These conceptions are crucial not only for developing training programs that help pre-service science teachers (PSTs) to study the concepts of science prescribed in the curriculum within the history and epistemology of science, but also to underscore the urgency and importance of addressing these conceptions.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Region Partitioning Framework (RCF) for Scatterplot Analysis: A Structured Approach to Absolute and Normalized Data Interpretation
by
Eungi Kim
Metrics 2025, 2(2), 6; https://doi.org/10.3390/metrics2020006 - 8 Apr 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Scatterplots can reveal important data relationships, but their visual complexity can make pattern identification challenging. Systematic analytical approaches help structure interpretation by dividing scatterplots into meaningful regions. This paper introduces the region partitioning framework (RCF), a systematic method for dividing scatterplots into interpretable
[...] Read more.
Scatterplots can reveal important data relationships, but their visual complexity can make pattern identification challenging. Systematic analytical approaches help structure interpretation by dividing scatterplots into meaningful regions. This paper introduces the region partitioning framework (RCF), a systematic method for dividing scatterplots into interpretable regions using k × k grids, in order to enhance visual data analysis and quantify structural changes through transformation metrics. RCF partitions the x and y dimensions into k × k grids (e.g., 4 × 4 or 16 regions), balancing granularity and readability. Each partition is labeled using an R(p, q) notation, where p and q indicate the position along each axis. Two perspectives are supported: the absolute mode, based on raw values (e.g., “very short, narrow”), and the relative mode, based on min–max normalization (e.g., “short relative to population”). I propose a set of transformation metrics—density, net flow, relative change ratio, and redistribution index—to quantify how data structures change between modes. The framework is demonstrated using both the Iris dataset and a subset of the airquality dataset, showing how RCF captures clustering behavior, reveals outlier effects, and exposes normalization-induced redistributions.
Full article

Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Metrics
Open Large Language Models for Scientometrics
Guest Editor: Robin HaunschildDeadline: 15 April 2026







