-
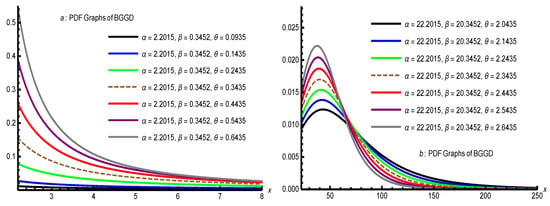
 Assessing Standard Error Estimation Approaches for Robust Mean-Geometric Mean Linking
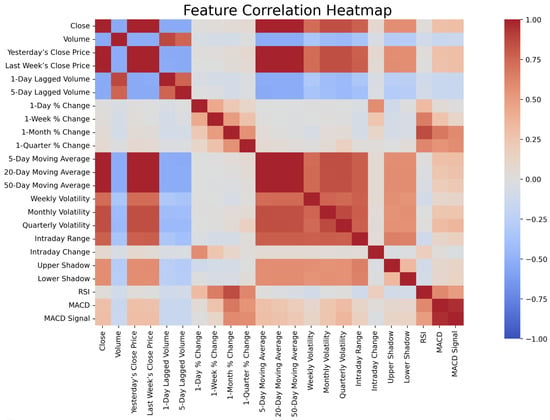
Assessing Standard Error Estimation Approaches for Robust Mean-Geometric Mean Linking -
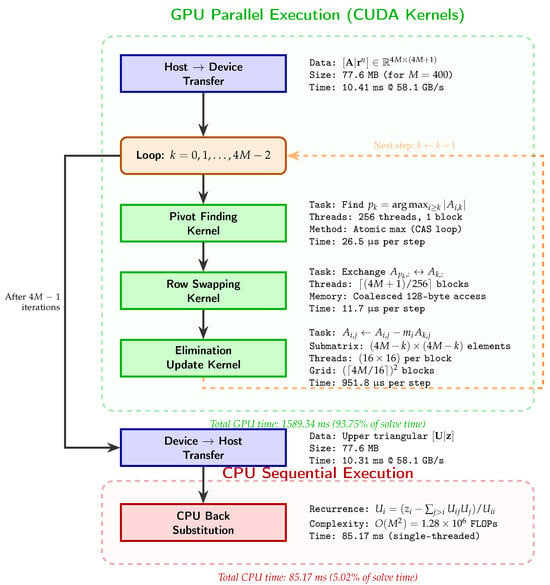
 On the Differential Topology of Expressivity of Parameterized Quantum Circuits
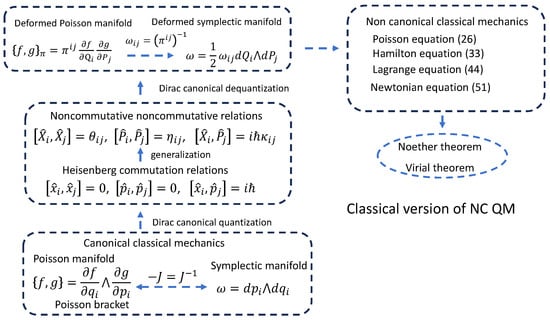
On the Differential Topology of Expressivity of Parameterized Quantum Circuits -
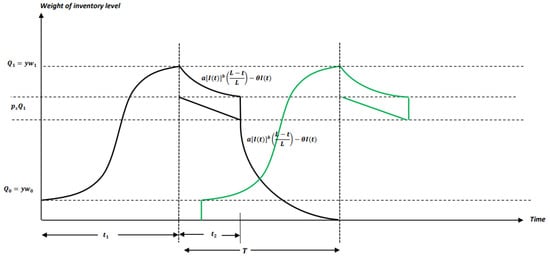
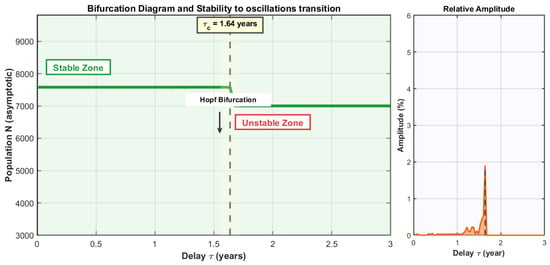
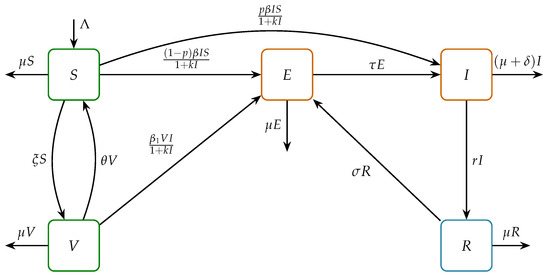
 Mathematical Model for Economic Growth, Corruption and Unemployment: Analysis of the Effects of a Time Delay in the Economic Growth
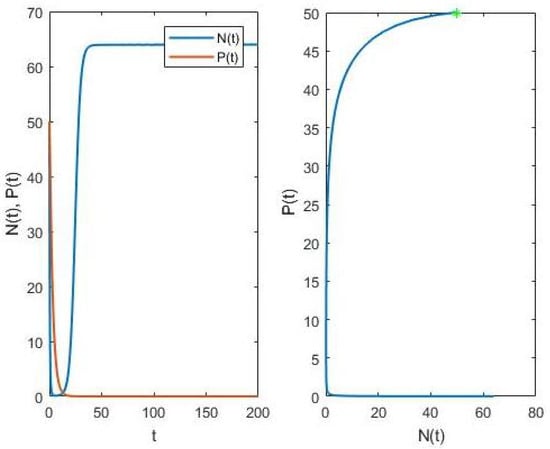
Mathematical Model for Economic Growth, Corruption and Unemployment: Analysis of the Effects of a Time Delay in the Economic Growth -
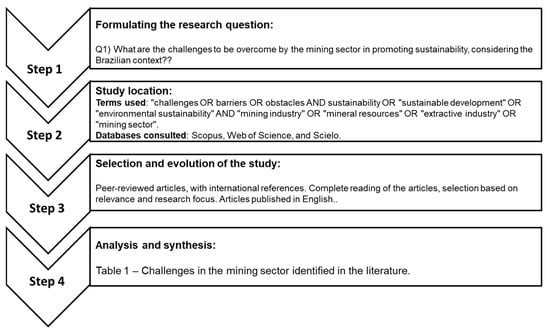
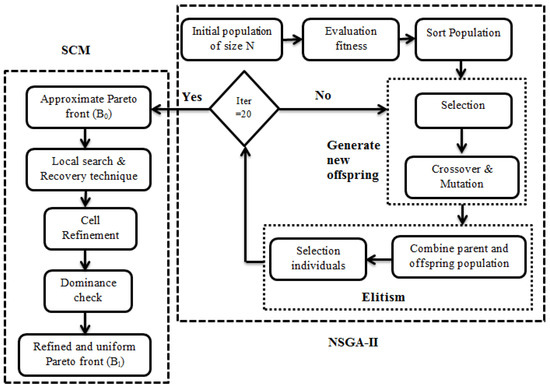
 A Novel Approach for Modeling Strain Hardening in Plasticity and Its Material Parameter Identification by Bayesian Optimization for Automotive Structural Steels Application
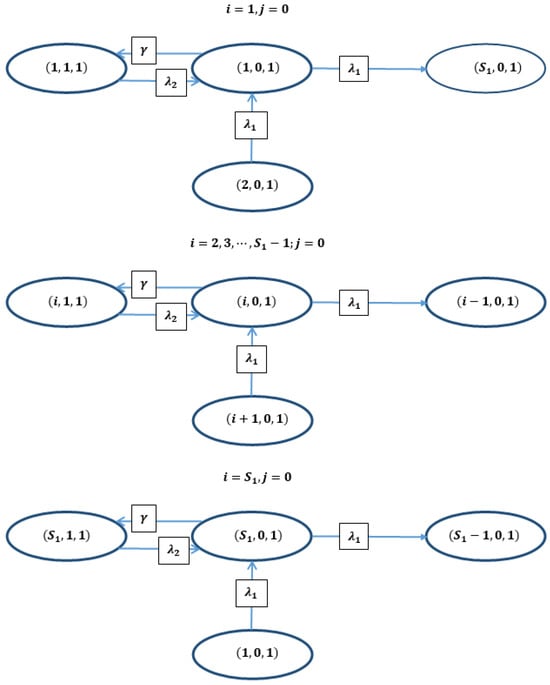
A Novel Approach for Modeling Strain Hardening in Plasticity and Its Material Parameter Identification by Bayesian Optimization for Automotive Structural Steels Application
Journal Description
AppliedMath
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within ESCI (Web of Science), Scopus, EBSCO, and other databases.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 23.5 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 6.9 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
- Journal Cluster of Mathematics and Its Applications: AppliedMath, Axioms, Computation, Fractal and Fractional, Geometry, International Journal of Topology, Logics, Mathematics and Symmetry.
Latest Articles
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Deadline: 31 December 2025
Deadline: 28 February 2026
Deadline: 31 March 2026
Deadline: 30 June 2026
Conferences
Special Issues
Deadline: 31 December 2025
Deadline: 31 January 2026
Deadline: 28 February 2026
Deadline: 31 March 2026