Abstract
Picture fuzzy nano topological spaces is an extension of intuitionistic fuzzy nano topological spaces. Every decision in life ends with an answer such as yes or no, or true or false, but we have an another component called abstain, which we have not yet considered. This work is a gateway to study such a problem. This paper motivates an enquiry of the third component—abstain—in practical problems. The aim of this paper is to investigate the contemporary notion of picture fuzzy nano topological spaces and explore some of its properties. The stated properties are quantified with numerical data. Furthermore, an algorithm for Multiple Attribute Decision-Making (MADM) with an application regarding the file selection of building material under uncertainty by using picture fuzzy nano topological spaces is developed. As a practical problem, a comparison table is presented to show the difference between the novel concept and the existing methods.
Keywords:
picture fuzzy topology; picture fuzzy nano topological spaces; picture fuzzy nano-closed sets; picture fuzzy interior and closure MSC:
54A05; 54A40; 03D45
1. Introduction
Multiple Attribute Decision-Making (MADM) is a method that specifically considers the best possible alternatives. In medieval times, decisions were made without coping with data uncertainties, which could lead to a potential outcome. Inadequate outcomes had real-life organizational conditions. The results would be ambivalent, undefined, or wrong if we deduced the result of obtained data without hesitation. MADM played an important role in real life problem such as management, diagnosing diseases, economics and industries. Each time, hundreds of decisions are taken by each decision maker to execute the major part of his/her work but it should be a logical judgment. MADM is used to solve complex and complex problems with various parameters for this. In MADM, the issue must be identified by defining potential alternatives, evaluating each alternative on the basis of the criteria set by the decision-maker or community of decision-makers and, ultimately, choosing the best alternative. A variety of valuable mathematical methods, such as fuzzy sets, neutrosophic sets, and soft sets, were developed to tackle the complexities and complexity of MADM problems.
Fuzzy set theory was introduced by Zadeh [1]. MADM algorithm via rough fuzzy information was introduced and developed by Zafer et al. [2]. Among different generalized FSs, in sight of IFSs introduced by Atanassov [3], lacking a logical scheme to effectively process inconsistent and indeterminate knowledge embedded in practical situations, Smarandache [4] introduced the structure of neutrosophic logic, and NSs, which could be viewed as a generalized form of fuzzy logic and intuitionistic fuzzy logic, FSs, and IFSs. Compared with IFSs, through incorporating an indeterminacy membership function which is focused on separately, NSs are able to effectively express the informations of inconsistency, incompleteness, and indeterminacy. NS has been applied in scientific and engineering fields. Salama [5] introduced neutrosophic topological space and its operation. Later, Salama [6] introduced and investigated neutrosophic closed sets and its continuous functions. Properties of closed and continuous functions of the same are presented in his work. Parimala et al. [7] studied neutrosophic homeomorphism in neutrosophic topological spaces. Parimala et al. [8] established a pre-open set and continuous functions in neutrosophic topology. Parimala et al. [9] implemented the concept of ideal in neutrosophic nano topological space. Parimala et al. [6] and Alharbi [10] proposed an algorithm for decision making. Parimala et al. [11] introduced new type of closed set called neutrosophic closed set in neutrosophic topological space.
One of extensions of IFS is picture fuzzy set (PFS) and it was developed by Cuong [3]. In PFS theory, there are three components, namely positive, neutral, and negative terms and sum of three components is less than or equal to one. simultaneously, PFS was applied in scientific and engineering fields. The development of PFS can be found in many fields [6,12,13,14]. In real life, there is more than one option for every decision. For instance, a person wants to purchase a motor bike or a car or both or neither. Membership function related to purchase a motor bike, negative membership function related to purchase a car because the person did not choose a motor bike. Neutrality is related to purchase both car and motor bike. Refusal related to purchase neither a car nor a motorbike. PFS deals with these kind of cases. Lellis Thivagar et al. [6] developed the concept of neutrosophic topology (NT) in the literature. It gained the attention of researchers to develop the theory of nano topology and via picture fuzzy sets [15,16].
FS theory talks about the membership of an object, IFS consider both membership and non-membership of an object. PFS theory added a component to the IFS theory, called abstinence. There is a choice called abstinence, different from yes or no choices, in decision making. Problems related to these cases are interesting and develop a theory for the same motived many researched to pay attention on it. Wei [17] solved multiple attribute decision-making (MADM) problems using picture fuzzy cross-entropy method. Thong and Son [13] proposed a hybrid method called Automatic Picture Fuzzy Clustering (AFC-PFS) between Particle Swarm Optimization and fuzzy clustering algorithms on Picture Fuzzy set. Wei [14] presented new similarity measures between PFSs based on the cosine function between PFSs. Wei [18] presented a similarity measure between PFS and applied the same on building material and minerals field recognition. Wang et al. [19] proposed a tool for risk ranking problems under picture fuzzy environment. Garg [20] presented some aggregation operators for PFSs and investigated application of decision making approach based on proposed picture fuzzy aggregation operator. Peng and Dai [21] proposed an algorithm for PFS and applied in decision making based on new distance measure. In this era, several mathematicians have been focusing on correlation coefficients, similarity measures, aggregation operators, topological spaces, and applications for decision-making. These structures provide different formula for different sets and have better solution to decision-making problems. It has various applications in different fields, such as medical diagnosis, pattern recognition, social sciences, artificial intelligence, business, and decision making problems with multi-attributes.
Motivation and Objective
The notion of PFS [12], nano topological spaces [6], and neutrosophic complex topological space [6] motivates us to propose this novel notion of picture fuzzy nano topological space and apply this notion in the MADM problem. The expanded and hybrid motivation and goal work is given in the entire manuscript, step by step. We make sure other hybrid systems of FS are special PFS cases, under some necessary circumstances. The robustness, durability, superiority and simplicity of our proposed model and algorithms are discussed. This model is the most common type and is used to collect large-scale data in Artificial Intelligence, Engineering and medical applications. Similar research can be easily replicated in the future with other methods and different forms of hybrid structure.
The scheme of this manuscript is organized as follows. Section 2, gives the preliminary definitions of the literature in NS are discussed. In Section 3, we introduced a novel idea of PFNTSs and established some of its operations such as interior and closure with the help of illustrations, and defined a score function. In Section 4, We proposed an algorithm and flowchart for MADM problem. In Section 5, As a numerical example, we established a method for the solution of MADM problem related to civil engineering (material selection) using PFNTS. We also presented the efficiency, advantage, consistency and validity of the algorithms proposed. With some current methodologies we provided a brief overview and comparative review of our proposed approach. The conclusion of this work is essentially summed up and future scope of research are presented in Section 6.
2. Preliminaries
The definitions from [12,20] are used in sequel.
Definition 1
([12]). A PFS on is defined as:
where are called membership, abstinence and non-membership functions. The condition for a PFS is that the sum of all three functions must lie within the unit interval and the degree of refusal is defined as . A triplet is called a picture fuzzy number (PFN)
Definition 2
([20]). Two objects and are two picture fuzzy sets defined on , the universe of discourse, and their union and intersection are defined and denoted as follows
- 1.
- The union of and is
- 2.
- The intersection of and is
- 3.
- The symmetric difference of and is
- 4.
- if and only if
Definition 3
([12]). Let be a family of PFS on . Then is called a picture fuzzy topological space if it satisfies the following:
- and are member of .
- Arbitrary union of picture fuzzy set S in if each S in
- Finite intersection of picture fuzzy set S in if each S in
Definition 4
([12]). Let and be the equivalence relation and picture fuzzy set, respectively defined on universe of discourse . The membership , the abstinence and nonmembership are the components of . The approximation space has three components, namely lower , upper , and boundary approximation where
- (i)
- The upper approximation of S with respect to R is denoted by , i.e.,
- (ii)
- The lower approximation of S with respect to R is the set is denoted by , i.e.,
- (iii)
- The boundary region of S with respect to R is the set of all objects which can be classified neither as S nor as not S with respect to R and is denoted by . , where
3. Picture Fuzzy Nano Topological Spaces
Definition 5.
Let the Universe be , equivalence relation on the non-void set be and if , where and satisfies the following axioms:
- 1.
- 2.
- If , for , then
- 3.
- If , for , thenthen is termed as PFNTS on with respect to . where the picture fuzzy sets and are defined by and respectively. Whereas, we call as PFNTS. The components of are called PFNOS.The complement of a PFNOS in a PFNTS. is called a PFNCS in .
Example 1.
Suppose we have a IC-chip company. The company has three workers in the fabrication section. Each employee in this plant gets 10 (in hundreds) IC-chip components, that to be fabricated every day. The number of chips fabricated, incomplete, and damaged by the employee is denoted by the membership value, the abstinence value, and the negative membership value of the PFS respectively and their major, minor and border approximations are given below:
Let be the universe of discourse. Let be an equivalence relation on and be a picture fuzzy set on , then
,
and
.
, , ,
, , ,
, , ,
, , ,
Therefore, forms a topology.
Remark 1.
In PFNTS, the picture fuzzy nano border will be a non-void set. Since the symmetric difference between picture fuzzy nano major and picture fuzzy nano minor approximations is defined here as the maximum and minimum of the values in the picture fuzzy sets.
Proposition 1.
Let be a non-void universe and be a picture fuzzy set on . Then the following statements hold:
- 1.
- The collection , is the in-discrete picture fuzzy nano topology on .
- 2.
- If , then the picture fuzzy nano topology is.
- 3.
- If , then is a picture fuzzy nano topology.
- 4.
- If , then the picture fuzzy nano topology is
Definition 6.
Let be any PFNTS with respect to picture fuzzy subset of and let be a picture fuzzy nano set in . Then the picture fuzzy nano interior and picture fuzzy nano closure of are defined as follows:
- 1.
- = is a PFNOS in and ,
- 2.
- = is a PFNCS in and .
Remark 2.
For any picture fuzzy nano set in , we have
- 1.
- = .
- 2.
- = .
- 3.
- is a PFNCS if and only if .
- 4.
- is a PFNOS if and only if .
- 5.
- is a PFNCS in .
- 6.
- is a PFNOS in .
Theorem 1.
Let be a picture fuzzy nano topological space with respect to where is a picture fuzzy subset of . Let and be picture fuzzy subsets of . Then the following statements hold:
- 1.
- .
- 2.
- is picture fuzzy nano closed if and only if .
- 3.
- = and = .
- 4.
- .
- 5.
- = .
- 6.
- = .
- 7.
- =.
Proof.
- 1.
- By definition of picture fuzzy nano closure,
- 2.
- If is a picture fuzzy nano closed set, then is the smallest picture fuzzy nano closed set containing itself and hence . Conversely, if = , then is the smallest picture fuzzy nano closed set containing itself and hence is a picture fuzzy nano closed set.
- 3.
- Since and are picture fuzzy nano closed sets in , and .
- 4.
- If PFN set is a subset of PFN set , since PFN set is a subset of , then PFN set is a subset of , i.e., is a PFNCS containing . However, is the smallest PFNCS containing . Therefore,
- 5.
- Since PFN set is a subset of union of two PFN sets and and PFN set is a subset of union of two PFN sets and , . Then closure of PFN set is a subset of closure of union of two PFN sets and and closure of PFN set is a subset of closure of union of two PFN sets and . Therefore, union of closure of PFN sets , is a subset of closure of union of , . By the fact that , and since is the smallest picture fuzzy nano closed set containing , so . Thus, .
- 6.
- Since and , .
- 7.
- Since is a picture fuzzy nano closed set, then .
□
Theorem 2.
be a picture fuzzy nano topological space with respect to where is a picture fuzzy subset of . Let be a picture fuzzy subset of . Then
- 1.
- = .
- 2.
- = .
Theorem 3.
Let be a picture fuzzy nano topological space with respect to where is a picture fuzzy subset of . Let and be picture fuzzy subsets of . Then the following statements hold:
- 1.
- is picture fuzzy nano open if and only if .
- 2.
- and .
- 3.
- .
- 4.
- .
- 5.
- .
- 6.
- .
Proof.
- 1.
- is a picture fuzzy nano open set if and only if is a picture fuzzy nano closed set, if and only if , if and only if if and only if .
- 2.
- Since and are picture fuzzy nano open sets in , and .
- 3.
- If , since , then , i.e., is a picture fuzzy nano open set containing . However, is the largest picture fuzzy nano open set contained in . Therefore,
- 4.
- Since and , and . Therefore, . By the fact that , and since is the largest picture fuzzy nano open set containing , so . Thus, .
- 5.
- Since and , .
- 6.
- Since is a picture fuzzy nano open set, then = .
□
Definition 7.
Let be PFSs, then the score function and the accuracy function of are defined as , and .
Let and be two PFSs, the following comparison rules are used
- 1.
- if , then
- 2.
- if , then if
- 3.
- , then
- (i)
- if , then
- (ii)
- if , then
4. Picture Fuzzy Nano Topology in Multiple Attribute Decision-Making
MADM is a procedure for seeking a best solution that has the highest degree of satisfaction from a set of possible alternative solutions. These types of MADM problems arise in a many real-time situations, and they are characterized by multiple attributes.
The proposed algorithm deals with abstinence of an object other than a yes or no choice, while the other algorithm in fuzzy set theory and intuitionistic fuzzy set theory failed to handle these cases. This algorithm shows how picture fuzzy nano topology is influenced in decision making. The procedure we carried out in the algorithm is simple and is an elementary one to handle.
A novel picture fuzzy nano topological approach is presented in this section for decision-making problems with picture fuzzy information. A methodological procedure for selecting the right alternatives and attributes in the decision-making environment is proposed as the following necessary steps.
Proposed Algorithm and Flowchart
The flow chart of proposed Algorithm 1 for MADM is given in Figure 1.
| Algorithm 1: Ideal decision making with PFTSs |
|
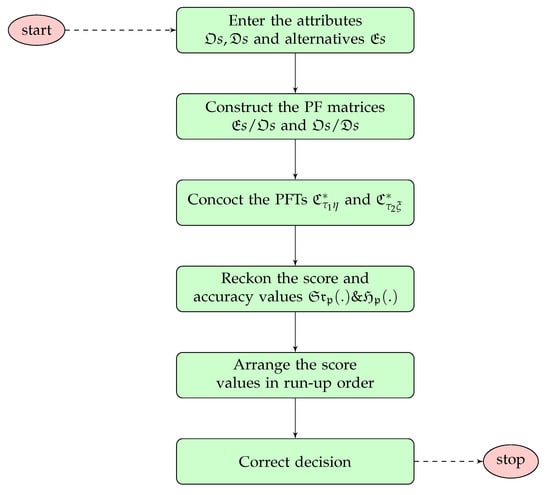
Figure 1.
Flow chart representation of Algorithm 1.
The flow chart of proposed Algorithm for MADM is given in Figure 2.
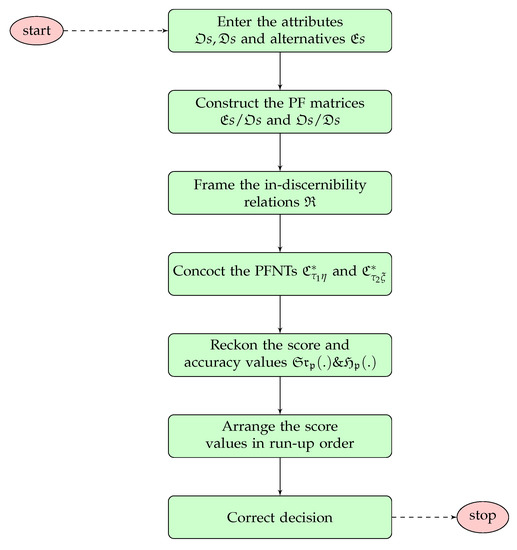
Figure 2.
Flow chart representation of Algorithm 2.
| Algorithm 2: Ideal decision making with PFNTSs |
|
5. Numerical Example
The proposed algorithms helps the builder to find the suitable building material. The method of classifying various sets of features of the material for flooring under a single form is very critical and complicated. In certain realistic circumstances, each dimension has the possibility within a form of the picture fuzzy sets. Therefore, further abstinence is involved in the medical diagnosis. Complicated situations are addressed by picture fuzzy nano topologies. This strategy is generally more versatile when it comes to less places of abstinence, and easier to use. With a score function between builder versus feature requirement and features versus material type, the proposed algorithms of picture fuzzy topological spaces and picture fuzzy nano topological spaces has the right choice of selection of material in picture fuzzy milieu.
First, we solve the material problem by using first PFTS-MADM method as given in Algorithm 1.
The key feature of this suggested method is that it appraises the factual participation, specific indeterminate and misrepresentation of each dimension in the form of a picture fuzzy set.
Step-1: Let be the set of builders, be the set of flooring material and be the set of feature space. The following are the different types of flooring materials: line concrete, flag stones, Marble, Ceramic.
Our work is to analyze the builder’s choice and decide on the flooring type of material suitable for them in a picture fuzzy environment.
Step-2: Frame the matrix of picture fuzzy system of relationship between builders and features and the matrix of picture fuzzy system of relationship between features and flooring material are given in Table 1 and Table 2 respectively.

Table 1.
The picture fuzzy system of relationship between builders and features.

Table 2.
The picture fuzzy system of relationship between features and flooring material.
Step-3: Construct the picture fuzzy topological spaces for each builder and each flooring material with respect to the features as follows:
Picture fuzzy topologies for builders are
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
Picture fuzzy topologies for flooring material are
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
Step-5: Computation of picture fuzzy score functions for the builders and flooring materials are done as in step-5 of the algorithm are as follows:
Score values for the builders are
Score values for the flooring materials are
As the score functions are not equal, the accuracy function does not need to be calculated.
Step-6: Arrange the picture fuzzy score values for the alternatives and the attributes in run-up order. We consider the sequences below and . Thus, the builder can choose the flooring material = ceramic flooring, the builder can choose the flooring material = marble, the builder can choose the flooring material = flag stones and the builder can choose the flooring material = line concrete.
Now we solve the same problem by using second PFNTS-MADM method as given in Algorithm 2.
Step 1 and Step 2 are same as in Algorithm 1.
Step-3: Construct the in-discernibility relation for the correlation between the symptoms is given as .
Step-4: Construct the picture fuzzy nano topological spaces for each builder and each flooring material with respect to the features as follows:
Picture fuzzy nano topologies for builders are
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
Picture fuzzy nano topologies for flooring material are
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
Step-5: Computation of picture fuzzy score functions for the builders and flooring materials are done as in step-5 of the algorithm are as follows:
Score values for the builders are
Score values for the flooring materials are
As the score functions are not equal, the accuracy function does not need to be calculated.
Step-6: Arrange the picture fuzzy score values for the alternatives and the attributes in run-up order. We consider the sequences below and . Thus, the builder can choose the flooring material = ceramic flooring, the builder can choose the flooring material = flag stones, the builder can choose the flooring material = marble and the builder can choose the flooring material = line concrete.
We propose two algorithms for MADM of the real world problems. The first two steps and last two steps of Algorithm 1 and Algorithm 2 are the same. In Step 3 of Algorithm 1 we find PFTS while in step 3 and step 4 of Algorithm 2 we find in-discernibility relations and PFNTSs. Both algorithms give approximately same ranks; this difference does not mean incomplete information. This is only because both algorithms have different formulae. The constructed algorithms are valid and practical. Finally both algorithms gives the same final decision.
The comparison Table 3 shows the difference between novel picture fuzzy nano topological space with existing work.

Table 3.
The difference between novel picture fuzzy nano topological space with existing work
6. Conclusions and Future Work
The application of the rough picture fuzzy set gained attention among researchers. However, the boundary of the region was not studied further by Nguyen [12]. In this paper, we introduced boundary of a region on picture fuzzy set along with upper and lower approximation. It is our opinion that picture fuzzy information can be best dealt with by unclear, vague, indeterminate, contradictory, and incomplete periodic / redundant information work. This paper aimed at bringing out the picture fuzzy nano topology which is more versatile and adaptable to real-time issues than rest of the types of general fluffy sets. Definitions of nano topology in picture fuzzy sets were identified, followed by the closure and interior operations. A new form of MADM technique in the picture fuzzy set has been introduced and applied to a building material selection process. To show the advantages and applicability, a comparison was made between the proposed method and the existing methods. The results are critical for enriching the picture fuzzy set awareness provided for decision making applications. Future research plans are to use the MADM technique for more practical applications and advance the practical interval valued complex picture fuzzy nano topological logic method for prediction of forecasting problems.
Author Contributions
All authors have contributed equally to this paper. The individual responsibilities and contributions of all authors can be described as follows: the idea of this whole paper was put forward by P.M. and C.O., I.A. and H.G. completed the preparatory work of the paper. C.O. and H.G. analyzed the existing work. The revision and submission of this paper was completed by P.M. and I.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research, University of Hafr Al Batin for funding this work through the research group project No: G-104-2020.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| MADM | multiple attribute decision making |
| RFS | Rough Fuzzy Set |
| NS | neutrosophic set |
| IFS | intuitionistic fuzzy sets |
| NT | nano topology |
| PFS | picture fuzzy set |
| PFNT | picture fuzzy nano Topological spaces |
| PFNCS | picture fuzzy nano closed set |
| PFN | picture fuzzy nano |
| PFNOS | picture fuzzy nano open set |
| PFNTS | picture fuzzy nano topological space |
References
- Zadeh, L.A. Fuzzy Sets. Inf. Control 1965, 18, 338–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafer, F.; Akram, M. A novel decision-making method based on rough fuzzy information. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coker, D. An introduction to fuzzy topological spaces. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1997, 88, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smarandache, F. Neutrosophy and Neutrosophic Logic, First International Conference on Neutrosophy, Neutrosophic Logic Set, Probability and Statistics; University of New Mexico: Gallup, NM, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Salama, A.A.; Alblowi, S.A. Neutrosophic Set and Neutrosophic Topological Spaces. IOSR J. Math. 2012, 3, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smarandache, F. Extension of HyperGraph to n-SuperHyperGraph and to Plithogenic n-SuperHyperGraph, and Extension of HyperAlgebra to n-ary (Classical-/Neutro-/Anti-) HyperAlgebra. Neutrosophic Sets Syst. 2020, 33, 290–296. [Google Scholar]
- Parimala, M.; Jafari, S.; Murali, S. Nano Ideal Generalized Closed Sets in Nano Ideal Topological Spaces. Ann. Univ. Sci. Budapest. 2017, 60, 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Parimala, M.; Jeevitha, R.; Selvakumar, A. A New Type of Weakly Closed Set in Ideal Topological Spaces. Int. J. Math. Its Appl. 2017, 5, 301–312. [Google Scholar]
- Parimala, M.; Karthika, M.; Dhavaseelan, R.; Jafari, S. On neutrosophic supra pre-continuous functions in neutrosophic topological spaces. New Trends Neutrosophic Theory Appl. 2018, 2, 371–383. [Google Scholar]
- Alharbi, N.; Aydi, H.; Ozel, C.; Topal, S. Rough topologies on classical and based covering rough sets with applications in making decisions on chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Int. J. Intell. Eng. Informatics 2020, 8, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parimala, M.; Perumal, R. Weaker form of open sets in nano ideal topological spaces. Glob. J. Pure Appl. Math. 2016, 12, 302–305. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, X.T.; Nguyen, V.D. Rough Picture Fuzzy Set and Picture Fuzzy Topologies. J. Comput. Sci. Cybern. 2015, 31, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thong, P.H.; Son, L.H. A novel automatic picture fuzzy clustering method based on particle swarm optimization and picture composite cardinality. Knowl. Based Syst. 2016, 109, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.W. Some Cosine Similarity Measures for Picture Fuzzy Sets and Their Applications to Strategic Decision Making. Informatica 2017, 28, 547–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.D.; Nguyen, X.T. Some measures of picture fuzzy sets and their application in multi-attribute decision making. Int. J. Math. Sci. Comput. 2018, 3, 23–41. [Google Scholar]
- Parimala, M.; Karthika, M.; Jafari, S.; Smarandache, F.; Udhayakumar, R. Decision-Making via Neutrosophic Support Soft Topological Spaces. Symmetry 2018, 10, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.W. Picture fuzzy cross-entropy for multiple attribute decision making problems. J. Bus. Econ. Manag. 2016, 17, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.W. Some similarity measures for picture fuzzy sets and their application. Iran. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2018, 15, 77–89. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Peng, J.J.; Wang, J.Q. A multi-criteria decision-making framework for risk ranking of energy performance contracting project under picture fuzzy environment. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 191, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, H. Some Picture Fuzzy Aggregation Operators and Their Applications to Multicriteria Decision-Making. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2017, 42, 5275–5290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parimala, M.; Smarandache, F.; Jafari, S.; Udhayakumar, R. On Neutrosophic αψ -Closed Sets. Information 2018, 9, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).