Outcomes Following Peripheral Vascular Interventions in Patients with End-Stage Renal Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design
2.2. Variables and Outcomes
2.3. Definitions
2.4. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Patient-Related Factors
3.2. Description of Surgical Interventions
3.3. Patient-Related Outcomes
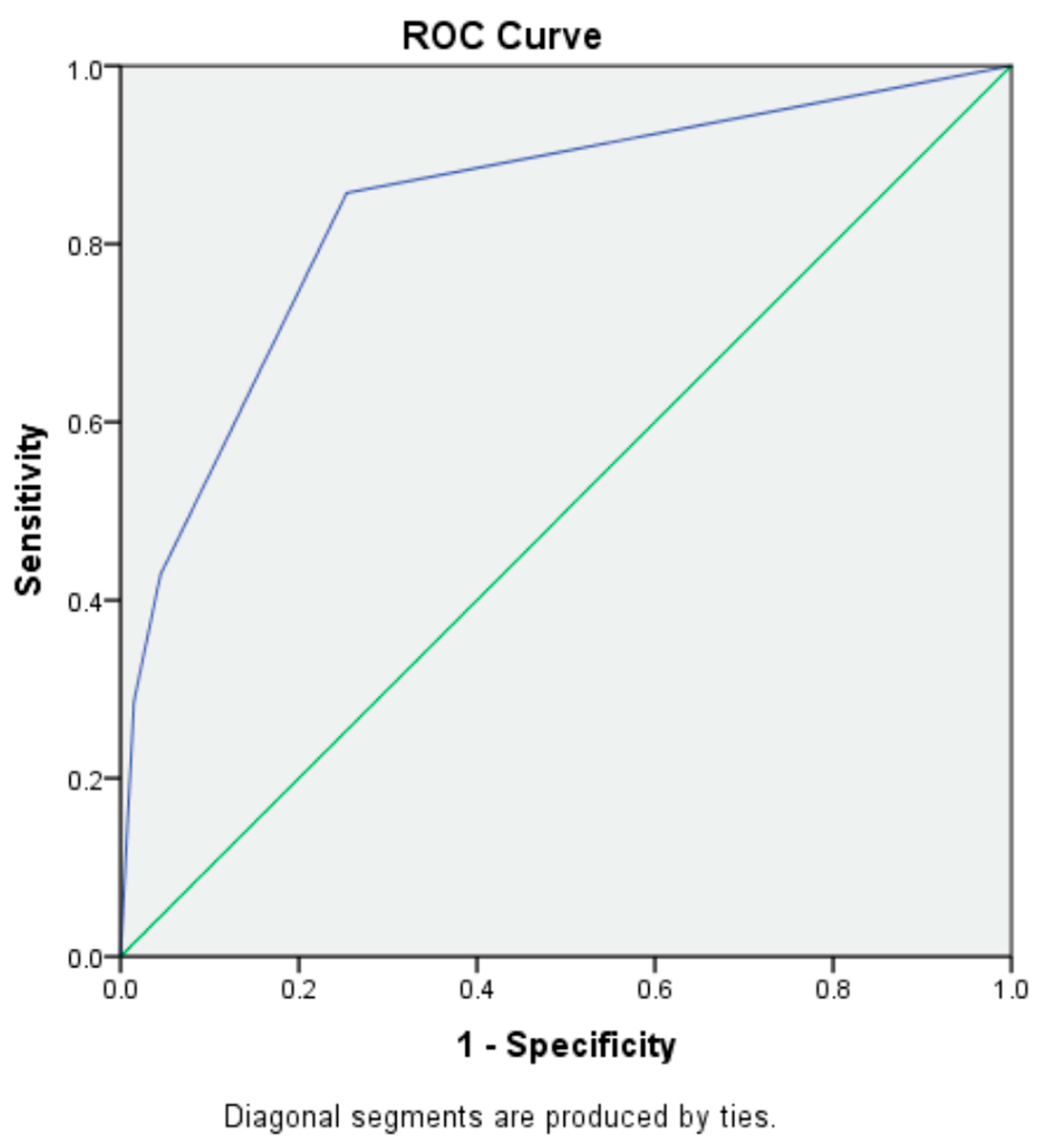
3.4. Predictive Modeling for Readmissions and Mortality
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ESRD | End-Stage Renal Disease |
| PAD | Peripheral Arterial Disease |
| AKA | Above-Knee Amputation |
| CHF | Congestive Heart Failure |
| CLTI | Chronic Limb-Threatening Ischemia |
References
- Sarnak, M.J.; Levey, A.S.; Schoolwerth, A.C.; Coresh, J.; Culleton, B.; Hamm, L.L.; McCullough, P.A.; Kasiske, B.L.; Kelepouris, E.; Klag, M.J.; et al. Kidney Disease as a Risk Factor for Development of Cardiovascular Disease: A Statement from the American Heart Association Councils on Kidney in Cardiovascular Disease, High Blood Pressure Research, Clinical Cardiology, and Epidemiology and Prevention. Hypertension 2003, 42, 1050–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United States Renal Data System. 2013 USRDS Annual Data Report: Atlas of End-Stage Renal Disease in the United States; National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- United States Renal Data System. 2015 USRDS Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of Kidney Disease in the United States; National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Garimella, P.S.; Balakrishnan, P.; Correa, A.; Poojary, P.; Annapureddy, N.; Chauhan, K.; Patel, A.; Patel, S.; Konstantinidis, I.; Chan, L.; et al. Nationwide Trends in Hospital Outcomes and Utilization After Lower Limb Revascularization in Patients on Hemodialysis. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2017, 10, 2101–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumada, Y.; Nogaki, H.; Ishii, H.; Aoyama, T.; Kamoi, D.; Takahashi, H.; Murohara, T. Clinical Outcome after Infrapopliteal Bypass Surgery in Chronic Hemodialysis Patients with Critical Limb Ischemia. J. Vasc. Surg. 2015, 61, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trocciola, S.M.; Chaer, R.; Dayal, R.; Lin, S.C.; Kumar, N.; Rhee, J.; Pierce, M.; Ryer, E.J.; McKinsey, J.; Morrissey, N.J.; et al. Comparison of Results in Endovascular Interventions for Infrainguinal Lesions: Claudication versus Critical Limb Ischemia. Am. Surg. 2005, 71, 474–479, discussion 479–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, A.T.; Criqui, M.H.; Treat-Jacobson, D.; Regensteiner, J.G.; Creager, M.A.; Olin, J.W.; Krook, S.H.; Hunninghake, D.B.; Comerota, A.J.; Walsh, M.E.; et al. Peripheral Arterial Disease Detection, Awareness, and Treatment in Primary Care. JAMA 2001, 286, 1317–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvin, E.; Erlinger, T.P. Prevalence of and Risk Factors for Peripheral Arterial Disease in the United States: Results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1999–2000. Circulation 2004, 110, 738–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, A.; Lang, W.; Borowski, M.; Torsello, G.; Bisdas, T. CRITISCH collaborators In-Hospital Outcomes in Patients with Critical Limb Ischemia and End-Stage Renal Disease after Revascularization. J. Vasc. Surg. 2016, 63, 966–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Ohta, T.; Ishibashi, H.; Sugimoto, I.; Iwata, H.; Takahashi, M.; Kawanishi, J. Clinical Reliability and Utility of Skin Perfusion Pressure Measurement in Ischemic Limbs--Comparison with Other Noninvasive Diagnostic Methods. J. Vasc. Surg. 2008, 47, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biancari, F.; Arvela, E.; Korhonen, M.; Söderström, M.; Halmesmäki, K.; Albäck, A.; Lepäntalo, M.; Venermo, M. End-Stage Renal Disease and Critical Limb Ischemia: A Deadly Combination? Scand. J. Surg. 2012, 101, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, A.; Sugimoto, M.; Kuma, S.; Okazaki, J.; Mii, S.; Komori, K. Clinical Outcomes after Infrainguinal Bypass Grafting for Critical Limb Ischaemia in Patients with Dialysis-Dependent End-Stage Renal Failure. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2014, 48, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hare, A.; Johansen, K. Lower-Extremity Peripheral Arterial Disease among Patients with End-Stage Renal Disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2001, 12, 2838–2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Hare, A.M.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Bacchetti, P.; Johansen, K.L. Peripheral Vascular Disease Risk Factors among Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2002, 13, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feinglass, J.; Pearce, W.H.; Martin, G.J.; Gibbs, J.; Cowper, D.; Sorensen, M.; Khuri, S.; Daley, J.; Henderson, W.G. Postoperative and Amputation-Free Survival Outcomes after Femorodistal Bypass Grafting Surgery: Findings from the Department of Veterans Affairs National Surgical Quality Improvement Program. J. Vasc. Surg. 2001, 34, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawarada, O.; Fujihara, M.; Higashimori, A.; Yokoi, Y.; Honda, Y.; Fitzgerald, P.J. Predictors of Adverse Clinical Outcomes after Successful Infrapopliteal Intervention. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2012, 80, 861–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawarada, O.; Yokoi, Y.; Higashimori, A.; Fujihara, M.; Sakamoto, S.; Ishihara, M.; Yasuda, S.; Ogawa, H. Impact of End-Stage Renal Disease in Patients with Critical Limb Ischaemia Undergoing Infrapopliteal Intervention. EuroIntervention 2014, 10, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Hare, A.M.; Sidawy, A.N.; Feinglass, J.; Merine, K.M.; Daley, J.; Khuri, S.; Henderson, W.G.; Johansen, K.L. Influence of Renal Insufficiency on Limb Loss and Mortality after Initial Lower Extremity Surgical Revascularization. J. Vasc. Surg. 2004, 39, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farber, A.; Menard, M.T.; Conte, M.S.; Kaufman, J.A.; Powell, R.J.; Choudhry, N.K.; Hamza, T.H.; Assmann, S.F.; Creager, M.A.; Cziraky, M.J.; et al. Surgery or Endovascular Therapy for Chronic Limb-Threatening Ischemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 2305–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Kidney Foundation. Kidney Disease Quality Outcomes Initiative (K/DOQI). Available online: https://www.kidney.org/professionals/kdoqi (accessed on 2 May 2020).
- Dormandy, J.A.; Rutherford, R.B. Management of Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD). TASC Working Group. TransAtlantic Inter-Society Consensus (TASC). J. Vasc. Surg. 2000, 31, S1–S296. [Google Scholar]
- von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. STROBE Initiative The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) Statement: Guidelines for Reporting Observational Studies. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2008, 61, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.-T.; Tsai, M.-L.; Wang, C.-Y.; Wen, M.-S.; Hsieh, I.-C.; Hung, M.-J.; Wang, C.-H.; Chen, C.-C.; Chen, T.-H. Outcomes and Characteristics of Patients Undergoing Percutaneous Angioplasty Followed by Below-Knee or Above-Knee Amputation for Peripheral Artery Disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, A.T.; Allison, M.A.; Gomes, A.S.; Corriere, M.A.; Duval, S.; Ershow, A.G.; Hiatt, W.R.; Karas, R.H.; Lovell, M.B.; McDermott, M.M.; et al. A Call to Action: Women and Peripheral Artery Disease: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2012, 125, 1449–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wisman, P.P.; Tangelder, M.J.; van Hattum, E.S.; de Borst, G.J.; Moll, F.L. Young Women with PAD Are at High Risk of Cardiovascular Complications. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2012, 43, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaller, M.S.; Ramirez, J.L.; Gasper, W.J.; Zahner, G.J.; Hills, N.K.; Grenon, S.M. Frailty Is Associated with an Increased Risk of Major Adverse Cardiac Events in Patients with Stable Claudication. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2018, 50, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schweitzer, C.D.; Anagnostakos, J.P.; Nagarsheth, K.H. Frailty as a Predictor of Adverse Outcomes After Peripheral Vascular Surgery in Patients with End-Stage Renal Disease. Am. Surg. 2022, 88, 686–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variables | N (%) |
|---|---|
| Age (mean ± SD years) | 66 ± 12.3 (31–90) |
| Elderly (aged ≥ 65 years) | 41 (55%) |
| Gender [n (%)] | |
| Males | 54 (73%) |
| Comorbidities | |
| Prior stroke | 12 (16.2%) |
| Prior lower extremity bypass graft surgery | 15 (21%) |
| Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) | 18 (24.3%) |
| Coronary artery bypass (CABG) | 16 (21.6%) |
| Myocardial infarction (MI) | 18 (24%) |
| Congestive heart failure (CHF) | 27 (37%) |
| Angina | 4 (3.1%) |
| Transient ischemic attacks | 4 (5%) |
| Hypertension | 63 (85%) |
| Diabetes Miletus | 44 (63.5%) |
| Hyperlipidemia | 42 (57%) |
| Medications | |
| Insulin/oral hypoglycemic | 47 (63.5%) |
| Antiplatelet | 46 (62%) |
| Statins | 42 (57%) |
| Anticoagulant | 37 (50%) |
| Antibiotics for prior infection | 16 (22%) |
| Variables | N (%) |
|---|---|
| Open surgical intervention | |
| Endarterectomy | 17 (23%) |
| Lower extremity bypass | 17 (23%) |
| Debridement | 40 (54%) |
| Amputation type | |
| Toe amputation | 35 (47%) |
| Trans-metatarsal amputation (TMA) | 23 (31%) |
| Below-knee amputation (BKA) | 14(19%) |
| Above-knee amputation (AKA) | 9 (8%) |
| Endovascular surgical intervention | |
| Angioplasty | 68 (91%) |
| - Iliac angioplasty | 15 (21%) |
| - Femoral angioplasty | 17 (23%) |
| - Popliteal angioplasty | 6 (8%) |
| - Tibial angioplasty - Peroneal angioplasty | 22 (30%) 8 (11%) |
| Drug-eluting stents | 15 (20%) |
| Bare-metal stents | 14 (19%) |
| Type of Bypass | |
| Aorto-femoral | 2 (3%) |
| Femoro-popliteal | 8 (11%) |
| Popliteo-tibial | 8 (11%) |
| Femoral-tibial | 6 (8%) |
| Fem-fem bypass | 3 (4%) |
| Tibio-peroneal | 1 (1.3%) |
| Type of Conduit used | |
| Cadaveric vein | 7 (10%) |
| Autologous vein | 5 (7%) |
| PTFE graft | 9 (12%) |
| Variables | Mean ± SD |
|---|---|
| Hospital length of stay (HLOS) (mean ± SD) (days) | 38 ± 47 (1–285) |
| Toes amputated | 1.2 ± 1.8 (0–10) |
| Variables | N (%) |
| Angioplasty failure leading to bypass/amputation | 24 (32%) |
| Bypass failure | 9 (12.1%) |
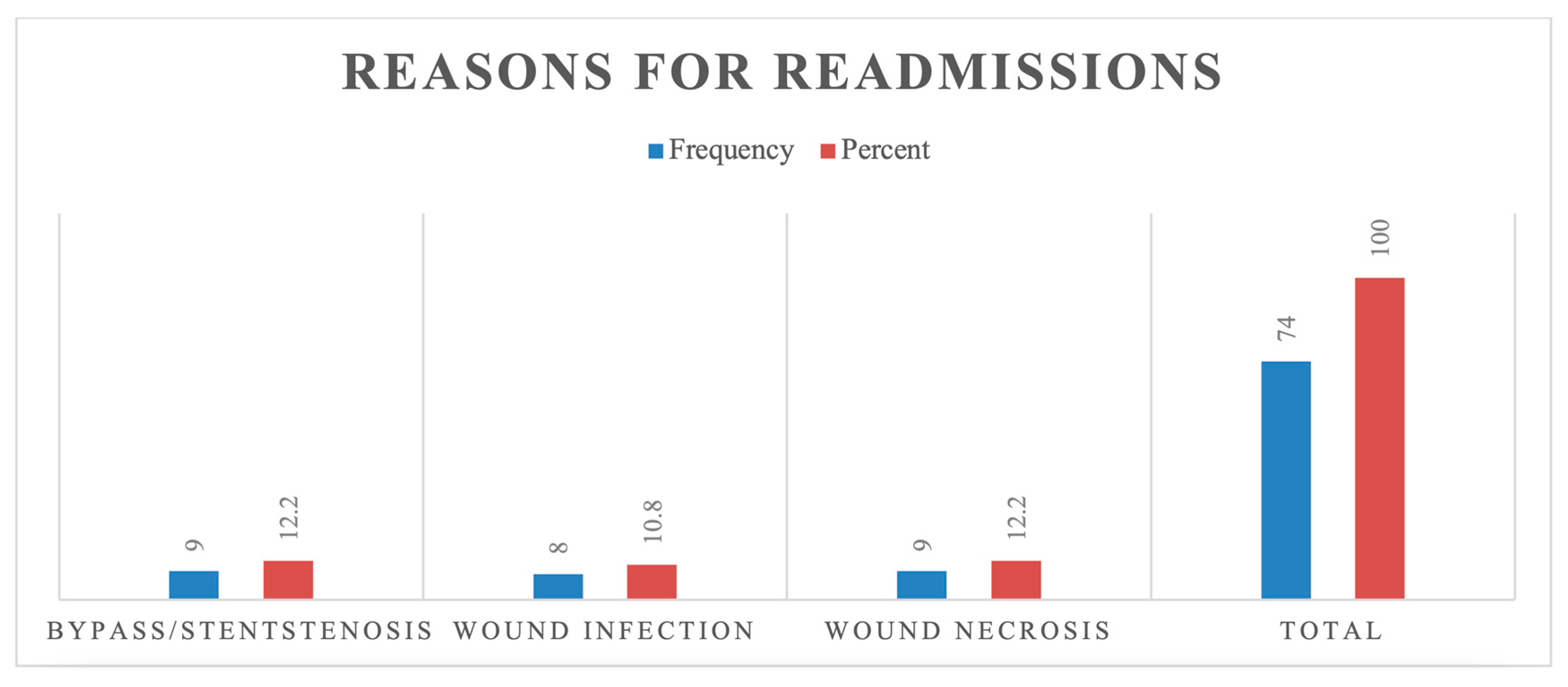
| Readmissions | |
| 30-day readmission | 11 (15%) |
| 90-day readmission | 15 (20%) |
| 120-day readmission | 20 (27%) |
| Days to readmission (mean ± SD) | 12 ± 34 (0–159) |
| Mortality | 7 (10%) |
| Variables | Univariable Predictors | Multivariable Predictors | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | p-Value | OR | 95% CI | p-Value | |
| Stroke | 5.27 | 1.43–19.3 | 0.01 | 6.37 | 1.62–35 | <0.01 |
| Age | 0.96 | 0.92–0.99 | 0.10 | 0.94 | 0.91–0.99 | 0.05 |
| Females | 0.59 | 0.17–2.00 | 0.41 | Eliminated by backward regression | ||
| Variables | Univariable Predictors | Multivariable Predictors | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | p-Value | OR | 95% CI | p-Value | |
| Female | 6.00 | 1.44–24.00 | 0.01 | 8.01 | 1.21–53.3 | 0.03 |
| Above-knee amputation | 16.00 | 2.41–106.0 | <0.01 | 14.45 | 1.73–120.75 | 0.01 |
| Lower extremity bypass failure | 7.62 | 1.37–42.4 | 0.02 | Eliminated by backward regression | ||
| Trans-metatarsal amputation | 3.30 | 0.68–16.4 | 0.13 | |||
| Age | 1.05 | 0.97–1.13 | 0.16 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gopal, A.P.; Patel, A.; Elias, M.; Agrawal, S.; Goyal, P.; Samson, D.; Laskowski, I.; Mateo, R.; Goyal, A.; Babu, S. Outcomes Following Peripheral Vascular Interventions in Patients with End-Stage Renal Disease. J. Vasc. Dis. 2025, 4, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/jvd4020023
Gopal AP, Patel A, Elias M, Agrawal S, Goyal P, Samson D, Laskowski I, Mateo R, Goyal A, Babu S. Outcomes Following Peripheral Vascular Interventions in Patients with End-Stage Renal Disease. Journal of Vascular Diseases. 2025; 4(2):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/jvd4020023
Chicago/Turabian StyleGopal, Amar Premdatt, Ankoor Patel, Murad Elias, Shreeya Agrawal, Priya Goyal, David Samson, Igor Laskowski, Romeo Mateo, Arun Goyal, and Sateesh Babu. 2025. "Outcomes Following Peripheral Vascular Interventions in Patients with End-Stage Renal Disease" Journal of Vascular Diseases 4, no. 2: 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/jvd4020023
APA StyleGopal, A. P., Patel, A., Elias, M., Agrawal, S., Goyal, P., Samson, D., Laskowski, I., Mateo, R., Goyal, A., & Babu, S. (2025). Outcomes Following Peripheral Vascular Interventions in Patients with End-Stage Renal Disease. Journal of Vascular Diseases, 4(2), 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/jvd4020023






