Abstract
Introduction: Patients with hematologic malignancies are more likely to develop severe and prolonged SARS-CoV-2 infection, often showing viral persistence despite the use of authorized antivirals. Herein, we report the cases of four patients who received rituximab for different conditions and developed persistent COVID-19 treated with an extended course of dual antivirals, Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir and Remdesivir. Moreover, we describe the pharmacokinetics and pharmacogenetics (PK/PG) characteristics of Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir and Remdesivir treatment in two of these patients. Methods: Plasma specimens for evaluation of trough concentrations (Ctrough) were collected 10 min before the daily dose administration, in addition to 3 h (Cmax), 4 h (C4h), 6 h (C6h) and 1 h (Cmax) after the administration of Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir and Remdesivir, respectively. The following gene single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) were investigated: ABCB1 3435 (rs1045642) C > T, ABCB1 1236 (rs1128503) C > T, PXR 63396 (rs2472667) T > C, CYP2D6 (rs1135840) G > C, and CYP3A4*1B (rs2740574) G > A. Results: Double antiviral treatment was successful in terms of symptoms resolution, whereas three out of four patients achieved microbiological eradication. Based on our results, concentrations of Nirmatrelvir ranging from 50 to 5000 ng/mL were effective, whereas a higher concentration (range 1068–3377 ng/mL), compared to that previously reported in patients with similar weight and BMI, was evidenced for Ritonavir. Considering the genetic variant analysis, ABCB1 3435 CT and 1236 CT genotypes were found in patient 1; and ABCB1 3435 CC and 1236 CC in patient 2. In conclusion, this real-life study supports the usefulness of TDM and genetics in immunocompromised patients with persistent SARS-CoV-2 infection, a challenging setting for clinicians in which personalized medicine may improve outcome.
1. Introduction
Patients with hematologic malignancies are more likely to develop severe and prolonged SARS-CoV-2 infection, often showing viral persistence despite the use of authorized antivirals [1,2]. The effectiveness of Remdesivir and Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir has been demonstrated in vitro and in randomized controlled trials for the treatment of early symptomatic COVID-19 in order to avoid the risk of progression to severe disease [3,4]; however, unfortunately, these therapies are not approved for patients with prolonged and late COVID-19, and the off-label use of direct antivirals and their combination has been reported in few cases as a possible and effective approach in immunocompromised populations [5,6,7,8].
COVID-19 can persist for up to 100 days in immunocompromised patients, with a prolonged viral shedding that is likely to be attributable to both humoral and cellular immune deficiency [9]. Innate and adaptive immune responses synergistically cooperate to limit SARS-CoV-2 infection. In particular, CD8+ T cells take part in acute reactions, while B and CD4+ T cells play a pivotal role in viral clearance and prevention of SARS-CoV-2 recurrence. In fact, patients receiving B-cell targeting treatments, such as rituximab, are exposed to a decrease in humoral immunity that limits the clearance of SARS-CoV-2, even after a full vaccination cycle [2,10].
Remdesivir acts against viral RNA polymerase, whereas Nirmatrelvir is a direct antiviral agent that targets the SARS-CoV-2 3-chymotrypsin-like cysteine protease enzyme, thus determining a strong inhibition of Mpro activity and virus replication across a broad spectrum of coronaviruses. Furthermore, Nirmatrelvir is a substrate of the efflux pump P-glycoprotein (P-gp, encoded by ABCB1 gene) and Cyp3A4, whereas Ritonavir, besides being an inhibitor of CYP3A4 and CYP2D6, also represents their substrate [11,12,13]. Moreover, pregnane-X-receptor (PXR) transcription factor can regulate the expression of ABCB1, CYP2D6 and CYP3A4 genes [14].
Herein, we report the cases of four patients who received Rituximab for different clinical conditions and presented persistent COVID-19 infection treated with an extended course of dual antivirals, Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir and Remdesivir; we also report the pharmacokinetics and genetic analysis (PK/PG) of Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir and Remdesivir treatment in two of these patients. Moreover, a literature revision regarding therapeutic approaches to prolonged COVID-19 infection in immune-compromised patients is presented.
2. Materials and Methods
Patients were admitted to the City of Health and Sciences, Molinette Teaching Hospital in Turin, Italy, from November 2022 to February 2023. Patients were treated for ten days with Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir 300/100 mg q12h if estimated glomerular filtration rate (EGFR) > 60 mL/min or Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir 150/100 mg q12h if EGFR > 30–60 mL/min and Remdesivir 200 mg loading dose, followed by 100 mg as recommended by Italian Regulatory Agency (https://www.aifa.gov.it/documents/20142/1123276/Remdesivir_update03_06.06.2022.pdf; https://www.aifa.gov.it/documents/20142/1616529/PAXLOVID_PT_04.04.2023.pdf, accessed on 20 December 2023). The off-label 10-day combination of Remdesivir and Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir was authorized from the Internal Ethical Committee as of 24 January 2020, protocol number 0008195; a signed informed consent form was collected for each patient.
2.1. Molecular Assays
Nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs) are the methods of choice for SARS-CoV-2 diagnostic testing. In particular, real-time RT-PCR is the most widely used test for viral RNA detection of SARS-CoV-2. Prior to nucleic acid amplification, specimens are purified by using defined extraction protocols. Generally, SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acids from whole blood or plasma samples are obtained by extraction performed with many automated instruments. More complex matrices, such as biopsies and feces, require specific pre-treatments, including incubation with lysis buffer and proteinase K at 56 °C in order to obtain the total disintegration of samples. Viral RNA amplification is performed by using commercial qualitative kits that contain fluorescent probes designed to detect the specific SARS-CoV-2 E, N, ORF8 and RdRp genes.
In addition to conventional molecular assays, RT-PCR rapid tests are widely used for identification of RNA SARS-CoV-2, as they provide rapid results in about 45 min with minimal operator intervention. Among these, the Xpert Xpress SARS-CoV-2 assay, developed for the Cepheid GeneXpert platform, contains specific primers and probes for qualitative detection of unique sequences in the nucleocapsid (N), envelope (E), and RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRP) genes of the SARS-CoV-2 genome in upper respiratory specimens, including nasopharyngeal, anterior nasal, mid-turbinate nasal, and oropharyngeal swab, as well as nasal wash/aspirate specimens. The Xpert Xpress CoV-2 plus test was used in the present study.
2.2. Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) of SARS-CoV-2 Genome
With the development of high-throughput next-generation sequencing (NGS) approaches allowing for the analysis of SARS-CoV-2 whole genome, identification of COVID-19 pandemic origins and variants, delineation of transmission events and the monitoring of viral populations’ evolution over time can be demonstrated. Viral RNA extraction and metagenomic analysis are performed with a whole-genome shotgun sequencing approach using different platforms (Illumina, Ion Torrent) that provide automated library and template preparation.
Drug quantification by LC/MS-MS: Plasma samples for therapeutic drug monitoring of Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir and Remdesivir (detected as GS-441524, the predominant metabolite of remdesivir circulating in the serum) were collected on day 6 of treatment after steady-state achievement. Plasma samples to determine trough concentrations (Ctrough) were collected 10 min before the daily dose administration. The other considered timings for Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir were 3 h (Cmax), 4 h (C4h), and 6 h (C6h) after administration of Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir, whereas for GS-441524, 1 h (Cmax) after one-hour infusion. Plasma samples were isolated after whole blood centrifugation at 1400× g for 10 min at 4 °C and then stored at −80 °C until the analysis. Plasma samples were shipped on dry ice in a time span of 30 min to the Laboratory of Clinical Pharmacology and Pharmacogenetics, Amedeo di Savoia Hospital in Turin, Italy.
The quantification was performed on total Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir (free and bounded drug fraction to plasma proteins) through a validated ultra high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UHPLC-MS/MS) assay, using a method developed in the Laboratory of Clinical Pharmacology and Pharmacogenetics, Amedeo di Savoia Hospital in Turin, under validation. The analytical process consisted in a fast protein precipitation of a mixture of 50 µL of plasma and 50 µL of internal standard solution with 4000 µL of freezing precipitating solution; samples were then kept 10 min at room temperature in a sonicator bath before being ultra-centrifuged at 10,000× g 10 min. All of the supernatant was transferred into a vacuum concentrator. All of the dried samples were then resuspended with 250 µL of diluting solution and, finally, 1.50 µL was injected into the column and analyzed with the Perkin Elmer LX-50® UHPLC system coupled with a Triple Quadrupole QSight 220® (Perkin Elmer, Milan, Italy).
Genotyping of SNPs: Patients’ DNA was extracted from whole blood samples with a semi-automated instrument (MagnaPure Compact, Roche, Monza, Italy). This kit contains materials allowing for DNA purification starting from 200 µL of blood or plasma. Genotypes were assessed with allelic discrimination (Taqman, Thermofisher: Waltham, MA, USA) through a real-time polymerase chain reaction allelic discrimination system (LightCycler 96, Roche, Monza, Italy). The following gene single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) were investigated: ABCB1 3435 (rs1045642) C > T, ABCB1 1236 (rs1128503) C > T, PXR 63396 (rs2472667) T > C, CYP2D6 (rs1135840) G > C, and CYP3A4*1B (rs2740574) G > A.
3. Results
Case Descriptions
The main clinical and demographic characteristics of patients are summarized in Table 1. In two out of four patients, pharmacokinetic (Figure 1) and genetic analysis was performed.

Table 1.
Clinical characteristics of patients treated for prolonged COVID-19.
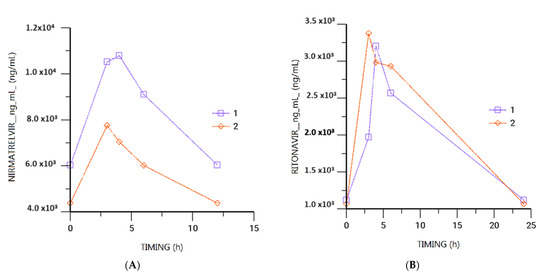
Figure 1.
Nirmatrelvir (A) and Ritonavir (B) plasma area under the curve (AUC) levels available for patients 1 and 2 (2 out of 4 patients underwent PK/PG analysis). Patient 1 concentrations are described by purple line, patients 2 concentrations are described by orange line.
Patient 1. A 3-dose SARS-CoV2 mRNA-vaccinated 65-year-old man (weight 70 kg, BMI 23.2, EGFR 60 mL/min) with glomerulonephritis was hospitalized in November 2022 for exacerbation of nephrotic syndrome and was treated with Rituximab, Cyclosporine and Prednisone until December 2022. By the beginning of December, he was hospitalized for progressively worsening dyspnea and tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection. High-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) chest scans revealed bilateral posterior basal areas of consolidation, and he required O2 supplementation up to HFNC. Intravenous steroid therapy was incremented with daily Dexamethasone 12 mg with partial beneficial effect, but after tapering of steroid, worsening dyspnea and recurrent fever reappeared. A new course of Dexamethasone 6 mg was started; however, following the appearance of multifocal areas of ground opacities, a bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) was collected and tested positive for P. jirovecii DNA. A 21-day course of Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole was administered. Due to the lack of clinical improvement and the persistence of fever, asthenia and oxygen demand, an extensive microbiological investigation was performed and evidenced only SARS-CoV-2 positivity with a low cycle threshold at the early-February 2023 timepoint (Table 2). The patient was treated with combination therapy with Remdesivir and Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir for 10 days. Nevertheless, positive molecular assay results persisted with a low cycle threshold at the mid-February 2023 timepoint (Table 2). The patient was treated with off-label combination therapy with Remdesivir and Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir for 10 days. The Cthrough of Nirmatrelvir was 4386 ng/mL, C3h 7759 ng/mL, C4h 7045 ng/mL, and C6h 6022 ng/mL. The Cthrough of Ritonavir was 1068 ng/mL, C3h 3377 ng/mL, C4h 2983 ng/mL, and C6h 2933 ng/mL. The Cthrough of Remdesivir was not detectable, whereas Cmax was 356 ng/mL. The Cthrough of GS-441524 was 41 ng/mL, whereas Cmax was 61 ng/mL. Concomitantly administered drugs were levotiroxine 0.125 microg, alprazolam 0.25 mg, entecavir 0.5 mg, furosemide 50 mg, allopurinol 150 mg, canrenone 50 mg, and ganciclovir 200 mg. For suspected organizing pneumonia, the patient also received Methylprednisolone 250 mg, followed by slow steroid tapering. Concerning genetic analysis, the following genotypes were described: ABCB1 3435 CC, ABCB1 1236 CC, PXR63396 CC and CYP2D6 CG and CYP3A4*1B AA.

Table 2.
Cycle threshold according to envelope (E), nucleocapsid (N) and RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) in Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir and Remdesivir treated patients.
By the end of antiviral therapy, he obtained respiratory weaning from oxygen supplementation and clinical resolution of fever and asthenia. SARS-CoV-2 nasopharyngeal swab tested negative in late February 2023. Nonetheless, despite virological negativization, the patient’s condition worsened again, determining the need for restarting non-invasive ventilation due to a recurrence of P. jirovecii and concomitant bacterial septic shock that eventually led to death.
Patient 2. A 5-dose SARS-CoV-2 mRNA-vaccinated 81-year-old woman (weight 48 kg, BMI 19.3, EGFR 50 mL/min), with renal B-cell lymphoma treated with Rituximab at 4 doses/week since July 2022 and stabilization therapy with Chlorambucil, was hospitalized for fever and cough in late December 2022 and tested positive for SARS-CoV-2. Chest HRCT revealed blurred bibasal ground-glass infiltrates, requiring treatment with steroid therapy and prednisone 50 mg. Due to the patient’s worsening clinical condition and the enlargement of HRCT chest infiltrates, intravenous (iv) steroid therapy with Dexamethasone 6 mg was started. Since clinical resolution of symptoms was achieved and steroid therapy tapered, she was discharged with a persistent positive SARS-CoV-2 swab. However, she came back to the Emergency Department in mid-February 2023 for remittent and worsening dyspnea, cough and chest pain. At this point, chest CT scan excluded pulmonary thromboembolic events and revealed further increase in ground-glass opacities and areas of parenchymal consolidation with pleural effusion; SARS-CoV-2 nasopharyngeal swab repeatedly tested positive. Antibiotic therapy with empiric Ceftriaxone 2 gr q24h iv, dexamethasone 12 mg iv and O2 supplementation with nasal cannula were started. Double antiviral therapy was started with Remdesivir and Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir 150/100 mg q12h for 10 days. The Cthrough of Nirmatrelvir was 6042 ng/mL, C3h 10,527 ng/mL, C4h 10,794 ng/mL, and C6h 9104 ng/mL. The Cthrough of Ritonavir was 1123 ng/mL, C3h 1973 ng/mL, C4h 3205 ng/mL, and C6h 2569 ng/mL. The Cthrough of Remdesivir was not detectable, whereas the Cmax was 1377 ng/mL. The Cthrough of GS-441524 was 299 ng/mL, whereas the Cmax was 393 ng/mL. Concomitant drugs were enoxaparin 4000 UI, amlodipine 2.5 mg, and alizapride 50 mg. Rapid resolution of clinical symptoms and normalization of lab tests were observed on the third day of treatment, and a complete weaning from supplementary O2 was obtained as well as tapering of Prednisone. SARS-CoV-2 nasopharyngeal swab was still positive by the time of discharge (Table 2). Concerning genetic analysis, the following genotypes were described: ABCB1 3435 CT, ABCB1 1236 CT, PXR63396 CT, CYP2D6 CG and CYP3A4*1B AA.
Patient 3. A 3-dose SARS-CoV-2 mRNA-vaccinated 63-year-old male patient with chronic lymphatic leukemia (CLL), previously treated with fludarabine, cyclophosphamide and rituximab, underwent a chest HRCT scan in September 2022 because of episodes of remittent fever, revealing a ground-glass pneumonia. A nasal antigenic test was negative for SARS-CoV-2, whereas the bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid tested positive. A five-day course of Remdesivir was started with rapid clinical response, but the patient experienced a relapse of fever. HRCT scan showed no improvement. The patient started oral Prednisone, but as soon as the dose was tapered, fever reappeared, alongside dyspnea with minimum effort and desaturation. The patient was readmitted at the end of December 2022, requiring low flows of oxygen, and tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 on molecular swab. Treatment with 1 mg/kg/day of Prednisone was started, resulting in the resolution of fever. Nevertheless, following 24 days of hospitalization, the results of an IgG titer against SARS-CoV-2 was negative, and viral persistence of SARS-CoV-2 was noted. Furthermore, a widening of the ground-glass areas with consolidative opacities was detected by a CT scan of chest alongside increasing oxygen requirement up to the combination of continuous positive-airway pressure (CPAP) sessions and high-flow nasal cannula (HFNC). Hence, an off-label 10-day combination of Remdesivir and Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir 150/100 mg q12h was started, and intravenous Methylprednisolone 80 mg was added. A rapid resolution of fever and progressive lowering of inflammation markers were observed. Supplementary oxygen was subsequently reduced, until complete weaning. Results of molecular SARS-CoV-2 tests showed a much-increased cycle threshold (Table 2), and an HRCT showed a clear improvement of bilateral lung opacities.
Patient 4. A 66-year-old man (weight 73 kg, BMI 24.4, EGFR 82 mL/min) who received a 3-dose SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination was admitted to the emergency department at the beginning of February 2023 due to fever, asthenia, and dry cough. A month before admission, the patient was hospitalized at our center for severe COVID-19 related pneumonia and pulmonary embolism treated with a 5-day regimen of Remdesivir, supplementary O2, anticoagulant, and dexamethasone. After a rapid worsening of respiratory failure, the patient’s condition significantly improved during the following days. He was finally discharged at the end of January with molecular assay still testing positive for SARS-CoV-2. Patient history evidenced follicular lymphoma with mediastinal, abdominal, and hepatic involvement, diagnosed in late 2021 and treated with 6-month Rituximab-based chemotherapy with cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone administered monthly in complete remission. Given the recent clinical history, a nasopharyngeal swab for SARS-CoV-2 was repeated and turned out positive. A general physical examination showed mild respiratory failure and breathlessness; oxygen supplementation was started via nasal cannula. A chest CT revealed a new onset of parenchymal thickening in the right upper lobe. Chronic treatment with prednisone 10 mg/day was continued, and broad-spectrum antibiotic treatment with ceftobiprole and azithromycin was started. Serological anti-SARS-CoV-2 levels were sustained (IgG antibodies 1360 BAU/mL; reference < 33.8 BAU/mL). On day 7, due to worsening symptoms, including high fever, sweating, and persistent dry cough with negative cultures and serum galactomannan antigen, he was administered combination therapy with Remdesivir and Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir 300/100 mg q12h for 10 days. Treatment also included pantoprazole 20 mg, metoprolol 100 mg, and lorazepam 1 mg. No adverse effect was observed during treatment. From day 9, the patient remained afebrile, with clinical improvement and subsequent reduction and finally complete weaning of oxygen demand. On day 21, nasopharyngeal swab for SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR was negative.
4. Discussion
Herein, we presented the cases of four patients previously treated with anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), who developed prolonged COVID-19 infection and were treated with off-label antiviral combination therapy with Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir and Remdesivir. In our case series, prolonged treatment with Remdesivir and Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir allowed the patients to achieve a clinical and virological improvement with no reported adverse effect. An increase in the cycle threshold of SARS-CoV-2 (likely suggesting a reduction in viral load) was achieved on molecular nasal swab in three patients out of four by the end of the 10-day treatment. We reviewed the available literature on prolonged COVID-19 management in immunocompromised patients in Table 3. The association of two different antiviral pharmacodynamic mechanisms has been considered useful in order to eradicate SARS-CoV-2 infections in immunocompromised patients [5,11]. In the cases reported by Trottier and Snell [6,11], a 20-day and 10-day course of Remdesivir and Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir, respectively, resulted in the clinical improvement and negativization of nasopharyngeal swab in patients with prolonged SARS-CoV-2 positivity. Even a prolonged course or retreatment with Remdesivir alone up to 30 days has been shown effective in clinical improvement of symptoms in the works by Rüfenacht et al. [5] and Martinez et al. [15], despite no proof of virological negativization in the former. In addition to the work of Ford and colleagues [7], the largest published case series by Mikulska et al. [16], including 22 patients, showed a higher rate of virological and clinical response in immunocompromised patients with prolonged/relapsed COVID-19 after combination therapy with two antivirals (mainly Remdesivir and Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir), including mAbs.
The second aim of the study was to determinate the pharmacokinetics of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir and investigate whether polymorphisms in the genes involved in their metabolism could affect the interindividual pharmacokinetic variability of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir and ritonavir concentrations in patients with COVID-19. Results showed that concentrations of Nirmatrelvir appeared comparable to those reported by Liu et al. [17], ranging from 50 to 5000 ng/mL, whereas Ritonavir measurements showed higher concentrations (range 1068–3377 ng/mL) compared to the 10–1000 ng/mL range previously reported in patients with similar weight and BMI. Considering the genetic variant analyses, in patient 1, genotypes ABCB1 3435 CT and 1236 CT were found. P-glycoprotein (P-gp) is one of 49 members in the superfamily of human adenosine triphosphate ATP-binding cassette transporters (ABC), responsible for cellular homeostasis and drug efflux (https://www.pharmgkb.org/vip/PA166170352; accessed on 20 December 2023). In the literature, several data points described the sequence variations for ABCB1; however, there is no clear consensus regarding the contribution of ABCB1 variation to disease risk. Instead, the literature reported the role of ABCB1 genetic polymorphisms in different phenotypes, such as P-gp expression, function, drug response, and disease susceptibility, with little consensus (https://www.pharmgkb.org/vip/PA166170352; accessed on 20 December 2023). Some of the most common SNPs in the protein coding region are 3435 and 1236 (https://www.pharmgkb.org/vip/PA166170352; accessed on 20 December 2023): they have been studied in the context of pharmacokinetics and disease, obtaining controversial results (https://www.pharmgkb.org/vip/PA166170352; accessed on 20 December 2023). In our study, patient 1 presented ABCB1 3435 CT and 1236 CT genotypes: these are associated with an intermediate activity of drug extrusion. In addition, the PXR 63396 CT genotype is associated with an intermediate modulation of ABCB1 gene expression: overall, this can contribute to the slightly increased values of nirmatrelvir. In particular, PXR is encoded by the NR1I2 gene and is a member of the nuclear receptor superfamily of transcription factors modulating the induction of many genes.
CYP2D6 is one of the key pharmacogenes involved in the implementation of pharmacogenomics all around the world. It is one of the most polymorphic genes and has an impact on the metabolism of up to 25% of the drugs commonly used in routine therapeutic management. Concerning the CYP2D6 840 SNP, the CC genotype is related to a faster elimination rate. Patient 1 presented the CG genotype: consequently, he could have had a possible slowdown in metabolism, potentially affecting drugs concentrations (particularly for ritonavir) and viral clearance. In addition, it should be noted that CYP2D6 is highly polymorphic; thus, other genetic variants could have an impact on metabolism (further studies with an increased number of patients have to be performed). Furthermore, basically, conflicting data on CYP2B6 genetic variants are present in the literature [18,19] (differences could be highlighted in other populations, for example in the African population).
Finally, the CYP3A4 AA genotype is associated with a normal function activity in metabolism, but its impact in our population seems to be weak, since most patients belong to the AA genotype.
Concerning patient 2, the ABCB1 3435 CC and 1236 CC genotypes were reported: they seem to be associated with an increased efflux function, and PXR63396 influences ABCB1 gene expression. CYP2D6 CG is related to an intermediate speed of metabolism, and CYP3A4*1B AA with a normal function allele. Consequently, on this subject, genetics seems to have no impact on drug exposure. It is important to highlight that these data refer to a single patient; therefore, more defined conclusions could be obtained in a larger cohort of patients.
In conclusion, despite the low number of the reported case series, this real-life study supports the usefulness of TDM and genetics in immunocompromised patients with persistent SARS-CoV-2 infection, a challenging setting for clinicians in which personalized medicine may improve outcomes. To the best of our knowledge, no other study reporting this kind of analysis has been published; therefore, further studies are warranted because other genetic and non-genetic factors could contribute to these AUC levels.

Table 3.
Literature review of the studies describing off-label treatment for prolonged COVID-19 in immunocompromised patients.
Table 3.
Literature review of the studies describing off-label treatment for prolonged COVID-19 in immunocompromised patients.
| References | Sex and Median Age of Patient | COVID-19 Vaccine | Immunocompromising Condition/Chemotherapy | Median Length of Hospital Stay (days) | Time from Last Anti-CD20 to COVID-19 | Treatment of the First and Prolonged COVID-19 | Duration of COVID-19 after Admission | Symptoms | Radiology | Serum Title | Cycle Threshold | Treatment of the Prolonged COVID-19 | Clinical and Virological Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Snell et al. [6] | M/60 | 4 doses | Follicular Lymphoma/ R-CHOP | 117 | 5 years | Prednisone 60 mg, Remdesivir 10 days Remdesivir 5 days + Methylprednisone 500 mg + Sotrovimab 500 mg Sotrovimab 1000 mg + Paxlovid + Baricitinib + Methylprednisolone 1000 mg | 4 months | Dyspnea, fever, cough | COVID-19 related pneumonia with ground-glass opacities + pulmonary embolism | negative | NA | Remdesivir 10 days + Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir 10 days | Shortness of breath—afebrile, no cough, improvement of exercise tolerance Negative SARS-CoV-2 swab |
| Rüfenacht et al. [5] | 4 M/ 7 F/ 66 | NA | 6 Lymphoma 1 Optic neuritis 1 Multiple sclerosis 1 CLL 1 Limbic encephalitis | 42 | NA | NA | NA | Fever, dyspnea, respiratory failure | NA | negative | 24.6 at the beginning 29.7 after Remdesivir course | 8 Patients: Remdesivir 5 days 2 Patients: Remdesivir 10 days 1 Patient: Remdesivir 17 days | Clinical improvement in 8 of 11 patients Not available SARS-CoV-2 swab |
| Ford et al. [7] | M/40 | NA | B-cell ALL/Rituximab + hyperCVAD | 150 | 1 month | Sotrovimab Remdesivir 10 days + Dexamethasone Remdesivir iv + Prednisone 0.5/kg | 5 months | Dyspnea, cough | COVID-19 related pneumonia with ground-glass opacities ground and interstitial disease | negative | NA | Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir 20 days + Remdesivir 10 days | Afebrile Improvement of dyspnea and asthenia Negative SARS-CoV-2 swab |
| Ueda et al. [9] | F/63 | NA | Follicular Lymphoma/GB | 30 | NA | Prednisolone 60 mg | 122 days | Fever, cough, dyspnea, rhinorrhea | COVID-19 related pneumonia and development of organizing pneumonia | negative | 23 at the beginning 33.9 and 34.3 after one month of disease | Remdesivir 5 days + Dexamethasone tapering | Asymptomatic at discharge Not available SARS-CoV-2 swab |
| Trottier et al. [12] | M/64 | 3 doses | CCL/ Venetoclax + Obinutuzumab | 75 | 1 month | Nirmatrelvir/ritonavir 5 days Dexamethasone 6 mg + Remdesivir 10 days Prednisone 60 mg + Bebtelovimab 80 mg | 5 months | Dyspnea, cough, recurrent fever, body aches | COVID-19 related pneumonia with ground-glass opacities and development of organizing pneumonia | negative | 22 serum 25 BAL | Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir 20 days + Remdesivir 20 days | Afebrile Resolving of dyspnea and asthenia Negative SARS-CoV-2 swab |
| Martinez et al. [15] | M/44 | NA | Granulomatosis with polyangiitis | 142 days | 4 years | Remdesivir 5 days + Dexamethasone 6 mg Plasma IVIG | 108 days | Fever, chills, exertional dyspnea, and diarrhea | COVID-19 related pneumonia | negative | >50 | Remdesivir 30 days | Clinical recovery Negative SARS-CoV-2 swab |
| Thorton et al. [20] | M/49 | No | Follicular lymphoma | 107 days | 1 month | Dexamethasone 6 mg Remdesivir 5 days + Dexamethasone 6 mg | 189 days | Fever, cough, asthenia, dyspnea | Remittent ground-glass opacities with bilateral interstitial pneumonia evolving in organizing pneumonia | negative to the nucleocapsid antibody/positive to the spike antibody | >50 | Bamlanivimab 700 mg + IVIG 75 mg + Remdesivir 10 days | Afebrile, clinical recovery, improvement in exercise tolerance Negative SARS-CoV-2 swab |
| Mikulska et al. [16] | 13 M/ 9 F/70 | 3 doses | Hematological malignancies and renal transplant/Anti CD20 in previous 12 months | NA | <12 months | 1 Bamlanivimab/Casirivimab, 3 Sotrovimab 5 Molnupiravir, 3 nirmatrelvir/ritonavir 5 days, 1 Remdesivir 5 days | 42 days | Oxygen requirement in 8 patients | NA | 8 patients positive | NA | Remdesivir and nirmatrelvir/ritonavir or molnupiravir (of which 18 with mAbs) | Alive, asymptomatic and negative SARS-CoV-2 swab at last follow-up 82% |
| Colombo et al. [21] | F/67 | No | Follicular Lymphoma/R-CHOP | 70 | 1 month | Remdesivir + Corticosteroids Methylprednisolone 1.5 mg/Kg | 90 days | Fever, cough, dyspnea | COVID-19 related pneumonia | negative | NA | Corticosteroids + IVIG + Hyperimmune plasma | Afebrile, no respiratory distress Not available SARS-CoV-2 swab |
| Wada et al. [22] | M/51 M/74 | Yes | 2 Follicular lymphoma | 14 and 19 days | NA | Remdesivir | NA | NA | NA | negative | 18.6 and 19.8 at the beginning | Pt 1: Remdesivir 10 days Pt 2: Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir for the other | Clinical improvement Not available SARS-CoV-2 swab |
| Rabscall et al. [23] | M/35 | NA | Myasthenia gravis in Thymoma with pleural metastasis | NA | 4 months | Remdesivir 5 days + Dexamethasone 6 mg | 35 days | Remittent fever, cough, dyspnea | Ground-glass opacities and consolidation consistent with COVID-19 | negative to the nucleocapsid antibody/positive to the spike antibody | NA | Casirivimab– Imdevimab | Afebrile, clinical recovery Negative SARS-CoV-2 swab |
| Breeden et al. [24] | F/79 M/72 M/72 F/60 | 3 doses 2 doses 2 doses 4 doses | Follicular lymphoma/Lenalidomide, rituximab, zandelisib, and epcoritamab Large B-cell lymphoma/chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy Mantle cell lymphoma/venetoclax, lenalidomide, and rituximab Multiple myeloma and HSCT, then B-cell ALL | 180 NA NA NA | 2 years 1 year 2 years | Prior tixagevimab/cilgavimab, then molnupinavir and remdesivir Prior tixagevimab/cilgavimab, then nirmatrelvir/ritonavir 5 days Prior tixagevimab/cilgavimab Prior tixagevimab/cilgavimab, then nirmatrelvir/ritonavir 5 days | 42 days 30 days 60 days 60 days | cough, shortness of breath, and fatigue fever and cough, then hypoxia shortness of breath and night sweats recurrent fatigue and fevers | Ground-glass opacities and multilobar consolidation Multifocal ground-glass opacities NA Bilateral airspace opacities | NA NA NA NA | 20–25 27.5 28.2 NA | Nirmatrelvir/ritonavir 21 days Remdesivir 10 days followed by nirmatrelvir/ritonavir 20 days Remdesivir 10 days, then nirmatrelvir/ritonavir 15 days Remdesivir 7 days and bebtelovimab once, then nirmatrelvir/ritonavir 20 days | Symptoms resolved Negative SARS-CoV-2 swab |
Abbreviations: CLL: chronic lymphocytic leukemia; NA: not applicable; R-CHOP: rituximab-cyclophosphamide-hydroxydaunorubicin-Oncovin-prednisone; ALL: acute lymphocytic leukemia; IVIG: immunoglobulin IV.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.C., F.G.D.R. and A.D.; methodology, S.S., F.S., J.C. and C.C.; formal analysis, I.D.B., E.Z., F.S., A.P., L.S., M.B., C.C. and J.C.; investigation, I.D.B., C.G. (Cecilia Costa), C.G. (Carlotta Giambra), S.M.P., A.P. and T.L.; data curation, C.G. (Cecilia Grosso), M.F., T.L. and C.G. (Cecilia Costa); Data analysis, A.P., J.C., M.B., E.Z. and C.C.; writing, I.D.B., S.C., T.L. and E.Z.; original draft preparation, I.D.B., C.G. (Carlotta Giambra), M.F. and T.L.; writing—review and editing, S.C., A.D., F.G.D.R. and L.S.; supervision, A.D., F.G.D.R., L.S. and C.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by EU funding within the MUR PNRR Extended Partnership initiative on Emerging Infectious Diseases (Project no. PE00000007, INF-ACT).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board of AOU Città della Salute e della Scienza, Turin, Italy (Protocol number: 0008195, date of approval: 24 January 2020).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Data can be available upon reasonable requested to the corresponding author for scientific purpose, according to the Declaration of Helsinki and according to Review Board Regulation.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Sun, J.; Zheng, Q.; Madhira, V.; Olex, A.L.; Anzalone, A.J.; Vinson, A.; Singh, J.A.; French, E.; Abraham, A.G.; Mathew, J.; et al. Association between immune dysfunction and COVID-19 breakthrough infection after SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in the US. JAMA Intern. Med. 2022, 182, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeWolf, S.; Laracy, J.C.; Perales, M.A.; Kamboj, M.; van den Brink, M.R.; Vardhana, S.L.; Perales, M.-A.; Kamboj, M.; van den Brink, M.R.M.; Vardhana, S. SARS-CoV-2 in immunocompromised individuals. Immunity 2022, 5, 1779–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottlieb, R.L.; Vaca, C.E.; Paredes, R.; Mera, J.; Webb, B.J.; Perez, G.; Oguchi, G.; Ryan, P.; Nielsen, B.U.; Brown, M.; et al. GS-US-540-9012 (PINETREE) Investigators. Early Remdesivir to Prevent Progression to Severe Covid-19 in Outpatients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammond, J.; Leister-Tebbe, H.; Gardner, A.; Abreu, P.; Bao, W.; Wisemandle, W.; Baniecki, M.; Hendrick, V.M.; Damle, B.; Simón-Campos, A.; et al. EPIC-HR Investigators. Oral Nirmatrelvir for High-Risk, Nonhospitalized Adults with COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 1397–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rüfenacht, S.; Gantenbein, P.; Boggian, K.; Flury, D.; Kern, L.; Dollenmaier, G.; Kohler, P.; Albrich, W.C. Remdesivir in Coronavirus Disease 2019 patients treated with anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies: A case series. Infection 2022, 50, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snell, L.B.; Bakrania, P.; Williams, T.G.S.; Tam, J.C.; Fontoura, D.D.S.; Shaw, E.; Daunt, A.; Edgeworth, J.D.; Hemsley, C.J.; Fields, P.; et al. Severe COVID-19 caused by persistent SARS-CoV-2 infection successfully treated with dual direct acting antivirals. Res. Sq. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, E.S.; Simmons, W.; Karmarkar, E.N.; Yoke, L.H.; Braimah, A.B.; Orozco, J.J.; Ghiuzeli, C.M.; Barnhill, S.; Sack, C.L.; Benditt, J.O.; et al. Successful treatment of prolonged, severe COVID-19 lower respiratory tract disease in a B-cell ALL patient with an extended course of remdesivir and nirmatrelvir/ritonavir. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2023, 76, 926–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Wang, Y.; Lavrijsen, M.; Lamers, M.M.; De Vries, A.C.; Rottier, R.J.; Bruno, M.J.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; Haagmans, B.L.; Pan, Q. SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant is highly sensitive to molnupiravir, nirmatrelvir, and the combination. Cell Res. 2022, 32, 322–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, Y.; Asakura, S.; Wada, S.; Saito, T.; Yano, T. Prolonged COVID-19 in an Immunocompromised Patient Treated with Obinutuzumab and Bendamustine for Follicular Lymphoma. Intern. Med. 2022, 61, 2523–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boross, P.; Leusen, J.H. Mechanisms of action of CD20 antibodies. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2012, 2, 676. [Google Scholar]
- Camprubí, D.; Gaya, A.; Marcos, M.A.; Martí-Soler, H.; Soriano, A.; Mosquera, M.D.M.; Oliver, A.; Santos, M.; Muñoz, J.; García-Vidal, C. Persistent replication of SARS-CoV-2 in a severely immunocompromised patient treated with several courses of Remdesivir. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 104, 379–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trottier, C.A.; Wong, B.; Kohli, R.; Boomsma, C.; Magro, F.; Kher, S.; Anderlind, C.; Golan, Y. Dual antiviral therapy for persistent COVID-19 and associated organizing pneumonia in an immunocompromised host. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2023, 76, 923–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://go.drugbank.com/ (accessed on 20 December 2023).
- Schipani, A.; Siccardi, M.; D’Avolio, A.; Baietto, L.; Simiele, M.; Bonora, S.; Rodríguez Novoa, S.; Cuenca, L.; Soriano, V.; Chierakul, N.; et al. Population pharmacokinetic modeling of the association between 63396C->T pregnane X receptor polymorphism and unboosted atazanavir clearance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 5242–5250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, M.A.; Chen, T.Y.; Choi, H.; Hwang, M.; Navarathna, D.; Hao, L.; Gale, M., Jr.; Camus, G.; Ramirez, H.E.; Jinadatha, C. Extended Remdesivir Infusion for Persistent Coronavirus Disease 2019 Infection. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2022, 9, ofac382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikulska, M.; Sepulcri, C.; Dentone, C.; Magne, F.; Balletto, E.; Baldi, F.; Labate, L.; Russo, C.; Mirabella, M.; Magnasco, L.; et al. Triple combination therapy with two antivirals and monoclonal antibodies for persistent or relapsed SARS-CoV-2 infection in immunocompromised patients. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2023, 77, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhu, M.; Cao, L.; Boucetta, H.; Song, M.; Hang, T.; Lu, Y. Simultaneous determination of nirmatrelvir and ritonavir in human plasma using LC-MS/MS and its pharmacokinetic application in healthy Chinese volunteers. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2022, 36, e5456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, C.; Crosby, I.; Yip, V.; Maguire, P.; Pirmohamed, M.; Turner, R.M. A Review of the Important Role of CYP2D6 in Pharmacogenomics. Genes 2020, 11, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaco, I.; Reis, R.; Gil, P.J.; Ribero, V. CYP3A4*1B and NAT2*14 alleles in a native African population. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2003, 41, 606–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, C.S.; Huntley, K.; Berenger, B.M.; Bristow, M.; Evans, D.H.; Fonseca, K.; Franko, A.; Gillrie, M.R.; Lin, Y.C.; Povitz, M.; et al. Prolonged SARS-CoV-2 infection following rituximab treatment: Clinical course and response to therapeutic interventions correlated with quantitative viral cultures and cycle threshold values. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2022, 11, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, D.; Gatti, A.; Alabardi, P.; Bompane, D.; Bonardi, G.; Mumoli, N.; Faggioli, P.; Clerici, P.; Brando, B.; Mazzone, A. COVID-19-Associated Pneumonia in a B-Cell-Depleted Patient with Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma: Recovery With Hyperimmune Plasma. J. Hematol. 2022, 11, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, D.; Nakamori, Y.; Maruyama, S.; Shimazu, H.; Saito, F.; Yoshiya, K.; Kuwagata, Y. Novel treatment combining antiviral and neutralizing antibody-based therapies with monitoring of spike-specific antibody and viral load for immunocompromised patients with persistent COVID-19 infection. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 11, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabascall, C.X.; Lou, B.X.; Navetta-Modrov, B.; Hahn, S.S. Effective use of monoclonal antibodies for treatment of persistent COVID-19 infection in a patient on rituximab. BMJ Case Rep. 2021, 14, e243469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breeden, M.; Aitken, S.L.; Baang, J.H.; Gravelin, M.; Kaul, D.R.; Lauring, A.S.; Petty, L.A.; Gregg, K.S. Successful Treatment of Prolonged Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Infection in Patients with Immunodeficiency with Extended Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir: Case Series. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2023, 10, ofad189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).