Abstract
Good hand hygiene has proven to be essential in reducing the uncontrolled spread of human pathogens. Cold atmospheric plasma (CAP) may provide an alternative to disinfecting hands with ethanol-based handrubs when handwashing facilities are unavailable. CAP can be safely applied to the skin if the energy is well controlled. In this study, radio frequency (RF) and direct current (DC) plasma sources were built with a pin-to-mesh electrodes configuration inside a fused silica tube with a 5 mm inner diameter. Microbiological assays based on EN 13697:2015+A1:2019 using Escherichia coli DSM 682 or Staphylococcus epidermidis DSM 20044 were used to examine the antimicrobial effect of various plasma conditions. Metal and silicone disks that model skin were used as inoculation matrices. The prototype air RF CAP achieved significant disinfection in the MHz range on stainless steel and silicone substrates. This is equivalent to half the performance of direct current CAP, which is only effective on conductive substrates. Using only electricity and air CAP could, with further optimization to increase its efficacy, replace or complement current hand disinfection methods, and mitigate the economic burden of public health crises in the future.
1. Introduction
1.1. Hand Hygiene
Carrying more than 10,000 organisms per cm2 of normal skin, hands are an important transmission site for communicable diseases [1]. Promoting hand hygiene in public and private environments has proven to be essential in reducing the uncontrolled spread of human pathogens [2]. The practice of handwashing at regular intervals, and in particular after coughing or sneezing, caring for the sick, after using the toilet, before eating, while preparing food and after handling animals or animal waste, has a significant effect on the reduction of transmission rates of pathogenic bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Similarly, handwashing after touching fomites such as doorknobs or handles, or after one comes back home from visiting a public place, provides effective protection. As such, hand hygiene, a very simple action, has been well documented to be one of the primary modes of measures for enhancing public safety [3,4]. With hydro-alcoholic gels becoming widespread once industrial production was able to meet the quantities needed for public use, there are conflicting guidelines for their use [5]. While the alcoholic gel disinfects, it leaves the dead microorganisms on the skin. Handwashing with soap and water, on the other hand, will allow a significant quantity of microorganisms to slide off and be eliminated [6]. While a systematic review of the hand disinfection potential of various products on the market found no difference in their disinfection efficiency, handwashing followed by air-drying was still the most preferred way to clean hands, as shown in a study involving random adults [5,6]. This may be due to alcohol-based disinfectants causing increased skin susceptibility to hand eczema [7]. Unfortunately, since most facilities for handwashing are located inside restrooms, which tend to be highly contaminated areas, the risk of recontamination is evident. For example, studies have found that on average, only about 20 percent of people in airports have clean hands—defined as hands that have been washed with soap and water, for at least 15 s, within the last hour. The other 80 percent are potentially contaminating everything they touch with whatever microorganisms and potential pathogens they may be carrying [4]. Alternative technologies for handwashing are thus needed to increase the capacity of hand disinfection facilities outside washrooms and without alcohol to allow more effective and frequent handwashing [8].
1.2. Cold Atmospheric Plasma for Hand Disinfection
A recent pilot study of virus transmission to the hospital environment found that the use of paper towels resulted in lower rates of contamination than a standard jet air dryer [9]. It is obvious that the integration of a disinfection module would be a radical change. Interesting disinfection capabilities have been obtained with a cold atmospheric plasma (CAP): Beginning with the patent of Menashi [10], research has intensified in the application of plasma for antimicrobial treatments, primarily in low-pressure applications. In 2022, Laroussi et al. concluded that the use of CAP could overcome exceptional health, safety, and medical challenges in the future [11]. Research has shown that CAP can be safely applied to the skin if the energy is well controlled [12]. However, long-term studies still need to be performed to conclusively exclude the risk of carcinogenesis and mutagenesis of CAP [12]. Two types of plasma sources are suitable: APPJ (low-temperature Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Jet) and DBD (Dielectric Barrier Discharge plasma) [13]. DBD has been successfully implemented in the development of a hand hygiene device for hospitals [14]. However, DBD has the disadvantage of generating ozone as a toxic by-product at particularly high concentrations, from the oxygen present in the air. In order not to exceed 5 ppm, the limit of danger specified by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the device works with a misting module that humidifies the air before the plasma treatment. The steam traps the ozone and converts it into free radicals, thus reinforcing the disinfection. However, this requires water, which necessitates the connection of the device to the sanitary water distribution network. In order to replace the use of hydro-alcoholic gels, the device must be installed in places people pass through, such as entrance halls and corridors, in places that are well chosen from a practical point of view, for example, near doors to avoid contamination of fomites such as door handles. These are areas where there is usually no access to the sanitary water system, but where an electrical connection can be added at little cost [14].
In this study, we aim to contribute to the global public health effort by developing a new type of air hand dryer with a disinfection function using CAP that operates without the need for water and soap facilities. While applications of CAP have been found in many food processes, applications using only ambient air as a gas source are still rare and at present, no CAP system can be integrated into an air jet dryer to disinfect hands.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plasma Source and Design
The project was carried out in several phases, with the goal of developing a radio frequency (RF) CAP plasma jet for hand disinfection. Initially, we realized a direct current (DC) atmospheric plasma assembly based on the device developed by Deng et al. [15]. Simpler than an RF device, this prototype gave a good disinfection performance, but it was limited to electrically conductive surfaces [16]. Then, in a second step, a CAP jet of Argon operating at 10 kHz was realized based on the development of Qian et al. [17], as an intermediate step of AC electronic development for non-conducting surfaces, but not stable using air as the plasma gas. The final goal, i.e., using air as plasma gas, was achieved by operating at 15.6 MHz through the development of a specific RF impedance matching device (Figure 1). Two power levels were tested: 50 W and 90 W. To measure the plasma jet temperature, a fiber optic thermometer (FISO FTI-10, FISO, Quebec, QC, Canada)) was placed 5 mm from the tube outlet. In addition, the temperature of the exposed surfaces was controlled using a FLIR A8580 IR camera (Tele-dyne FLIR, Wilsonville, OR, USA). The optical emission spectra analysis of the plasma jet suggested the presence of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species, which are much sought after for disinfection [18,19]. A mounting with drives completed the experimental device, allowing the exposure of the plates to the CAP jet in a controlled manner. An ozone detector (Trotec OZ-ONE, Heinsberg, Germany) was utilized to measure ozone levels during the tests.
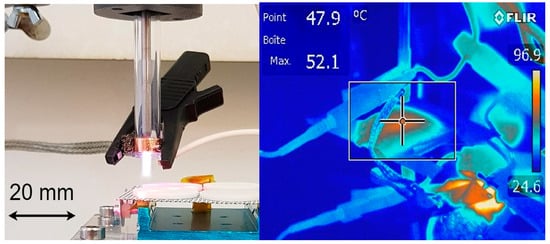
Figure 1.
Overview of RF plasma jet and nozzle outlet temperature.
2.2. Microbiological Testing
Microbiological assays were based on the standard EN 13697:2015+A1:2019 “Chemical disinfectants and antiseptics, Quantitative non-porous surface test for the evaluation of bactericidal and/or fungicidal activity of chemical disinfectants used in food, industrial, domestic and institutional areas (phase 2/step 2)” [20].
2.3. Microbial Cultures
Cultures of Escherichia coli DSM 682 or Staphylococcus epidermidis DSM 20044 were grown at 30 °C for 24 h in Tryptic Soya broth (Casein soya bean digest medium; Oxoid, Basel, Switzerland). Culture cell densities were determined using a Neubauer improved counting chamber with a chamber depth of 0.02 mm (Assistent, Glaswarenfabrik Karl Hecht GmbH & Co KG, Sondheim vor der Rhön, Germany). Suspensions containing approximately 1 × 106 cells/mL E. coli DSM 682 or S. epidermidis DSM 20044 were prepared using physiologic saline solution (pH 7.0; Sigma-Aldrich Chemie GmbH, Buchs, Switzerland).
2.4. Pre-Assays Using Petri Dishes
Initial experiments surveyed the effect of CAP applied directly on Petri dishes inoculated with a 1 mL suspension containing approximately 1 × 106 cells/mL E. coli DSM 682 or S. epidermidis DSM 20044. After treatment, agar plates were incubated 24–48 h at 30 °C. In further preliminary experiments, sterilized stainless steel disks were inoculated with 1 mL of suspensions containing approximately 1 × 106 cells/mL E. coli DSM 682 or S. epidermidis DSM 20044. Afterwards, disks were exposed to CAP treatment for 30 s, 60 s, 90 s, and 120 s before the disks were turned onto Tryptic Soya Agar and left for 1 min. A set of disks were left untreated as a negative control. Replicates of four plates were tested for each type of bacteria with scanning times ranging from 30 to 120 s with an increment of 30 s. These scanning times correspond to the duration necessary to scan the 25 cm2 area of the plate with a 1 cm·s−1 decreasing scanning rate, starting at 4 cm·s−1 for a 30 s scanning time and ending at 1 cm·s−1 for 120 s. Afterwards, the disks were removed and agar plates with the transferred microorganisms were incubated 24–48 h at 30 °C. The distance between the plasma jet and Petri dish was adjusted to 13 mm for both assays.
2.5. Disinfection Assays Using Steel and Silicone Disks
Sterilized stainless steel and silicone disks with a surface area of 25 cm2 were used. Silicone disks were stamped out from Tattoo Practice Skin with an original size of 15 × 15 × 0.3 cm3 and purchased from Amazon Germany (www.amazon.de (accessed on 26 July 2022)). Silicone elastomers were previously shown to simulate dry human skin sufficiently well but were incapable of simulating the behavior of moist human skin [21]. However, silicone is a highly porous water-absorbing hydrophilic material and decreases in friction with increasing water content [22]. Contaminated disks were air-dried in a Class II Type A2 Biological Safety Cabinet (Vitaris AG, Baar, Switzerland) before being used in the CAP disinfection assays. For assays using either the stainless steel or the stamped-out silicone, the disks were initially exposed to DC plasma for 0 s (non-treated control), 30 s, 60 s, and 120 s. Afterwards, the reaction time on the entire surface of the disks was reduced to 75 s for RF plasma assays to allow the surface temperatures of the disks to remain within a 50 °C limit. In all assays, the distance between the nozzle and the surface to be disinfected (d) was adjusted to a height of 14 mm. After CAP application, the disks were transferred into 10 mL of physiologic saline solution (pH 7.0) and placed in a stomacher for 1 min to wash off remaining viable microorganisms. Of the obtained bacterial suspensions, 1:10 dilutions were prepared in physiologic saline solution (pH 7.0) of which 1 mL were plated onto 9 cm Petri dishes before mixing the suspensions with Tryptic Soya Agar (Oxoid, Basel, Switzerland) with a maximum temperature of 48 °C. Plates were thoroughly dried before incubating 24–48 h at 30 °C. Plates with 10–300 colonies were counted to estimate the amount of cfu/mL in the samples. One-way Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) in the Microsoft Office Excel Analysis ToolPak (Microsoft, Redmond, WA, USA) was used to examine the differences between the untreated controls and CAP-treated, inoculated disks. The performance parameters from EN 13697:2015+A1:2019 corresponding to a 4 Log10 reduction of bacteria after treatment were utilized to better mirror the performance of CAP to hydro-alcoholic gels [20].
3. Results
3.1. Plasma Source and Design
The different spectra obtained with the three types of prototypes we have developed (DC, DBD or RF) are compared in Figure 2. The DBD spectrum is quite different from the other two since this torch requires the use of argon. The spectra of plasma jets using only ambient air, DC and RF at 15.6 MHz have similar structures, but the radiation proposition between the 200 to 450 nm range and the 450 to 900 nm range is not the same. In the more energetic photon range (200 to 450 nm), the RF plasma displays a higher concentration of free radicals. This suggested that ultimately more reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) are formed that may be used for inactivating bacterial cells and viruses on the exposed surfaces [22,23].
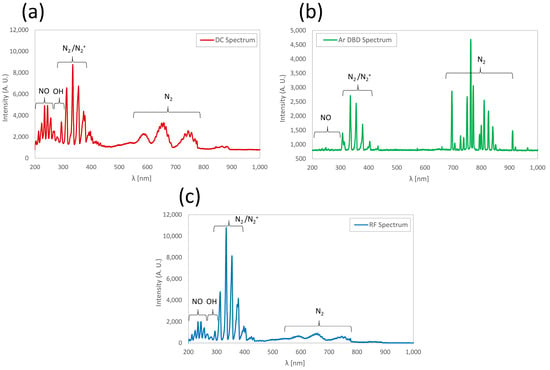
Figure 2.
Optical emission spectra obtained with (a) DC, (b) DBD and (c) RF plasmas.
Hence, further assays were performed only with RF design using an air-based CAP (RF AIR CAP). Assessment of surface temperatures of exposed metal and silicone discs showed that they remained below the limit that microorganisms can withstand, confirming that RF AIR CAP can be used for hand disinfection via the non-thermal action of reactive chemical species (Figure 1).
3.2. Pre-Assays
3.2.1. The Influence of Dying on Culture Viability
The use of air-drying the tested microorganisms in a Class II Type A2 Biological Safety Cabinet before testing was shown not to have any significant effect. When comparing the recovered microorganisms on either the dried surfaces of either the Petri dishes or the stainless steel and silicone disks (non-treated controls) to the calculated cell density of the inoculum, no significant reduction was observed. Hence, this technique was considered a valid method for testing, and was therefore used in all the proceeding steps.
3.2.2. DC Plasma Assays
To test the disinfection power of the DC plasma source, samples of E. coli DSM 682 or S. epidermidis DSM 20044 dried onto Petri dishes and exposed to 15 s, 30 s, and 45 s showed no effect while surface temperature levels remained around 45 °C. A series of qualitative trials was conducted on samples of E. coli DSM 682 or S. epidermidis DSM 20044 dried onto stainless steel and silicone disks. Decontamination experiments were carried out for 30 s, 60 s, 90 s, and 120 s. The results showed that CAP was able to reduce bacterial loads on stainless steel surfaces even after exposure with a duration as short as 30 s. Using a cutoff (α) for statistical significance of 0.05, it was observed that a statistically significant reduction was achieved on stainless steel disks, reaching a log10 1.99 (p = 0.006) reduction after 120 s for E. coli. For S. epiderminis, the reduction after 120 s was log10 1.81 (p = 0.019, Figure 3). However, ozone levels reached 0.5–0.6 ppm, which represents three times the tolerable limit value according to Swiss safety standards [24]. Additional ventilation of the surface treatment area diminished ozone levels to acceptable levels in further trials. Furthermore, temperature levels on the disks were in the vicinity of 60 °C, higher than the biological tolerance temperature of approximately 44 °C [25]. While the reduction in microorganisms was considered statistically significant, levels also did not approach the minimum 4 log10 reduction required by EN 13697:2015+A1:2019 [20].
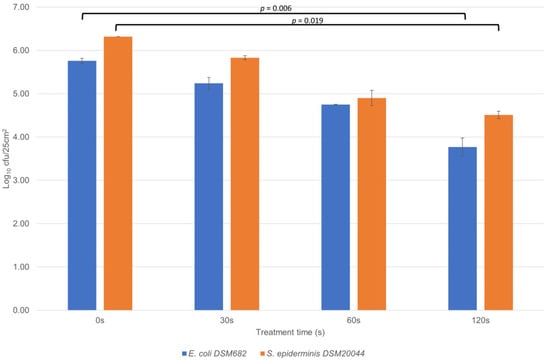
Figure 3.
Direct DC-type CAP treatment on stainless steel for 0 s (control), 30 s, 60 s and 120 s. The vertical scale is logarithmic (unit: log10 cfu/25 cm2). Uncertainty bars indicate standard deviations.
3.3. Disinfection Assays Using RF AIR CAP
After a DC plasma source was rejected due to its incompatibility for human use due to exteme temperature development and ozone development, a CAP plasma jet using a 15.6 MHz radio refquency (RF) was developed. In all the tests we carried out with this plasma, the exposure times did not achieve the level of decontamination specified by EN 13697:2015+A1:2019. However, after 75 s, at a sweep speed of 20 mm/s, the disinfection effect was clear, with the reduction in colony numbers clearly visible (Table 1 and Figure 4). As expected, disinfection of the two types of material (stainless steel and silicone) was comparable: at 50 W, the colony-reduction rate averages 54% (0.34 log10 cfu/mL) on silicone and 64% (0.45 log10 cfu/mL) on stainless steel. At 90 W, these values rise to 87% (0.88 log10 cfu/mL) and 92% (1.12 log10 cfu/mL), respectively. In all RF AIR CAP assays, the temperature remained below the thermal inactivation limit of the bacteria used in the assay (approx. 50 °C). It is important to specify that these exposure times are not equivalent to a plasma projection on the same surface, but to a scan of the entire surface in a given time. Thus, the plasma activity on any spot on the disks is significantly less than the 75 s indicated and is equivalent to approximately 10–15 s of exposure to the RF CAP in a hand dryer. This exposure time is well suited to the equipment market for public places because it corresponds to the drying time with current hand dryers and falls within the 30 s application time for alcoholic gels.

Table 1.
Microbial load reduction with a 15.6 MHz RF-type CAP using dry air at a sweep speed of 20 mm/s, at two RF power levels: 50 and 90 W.
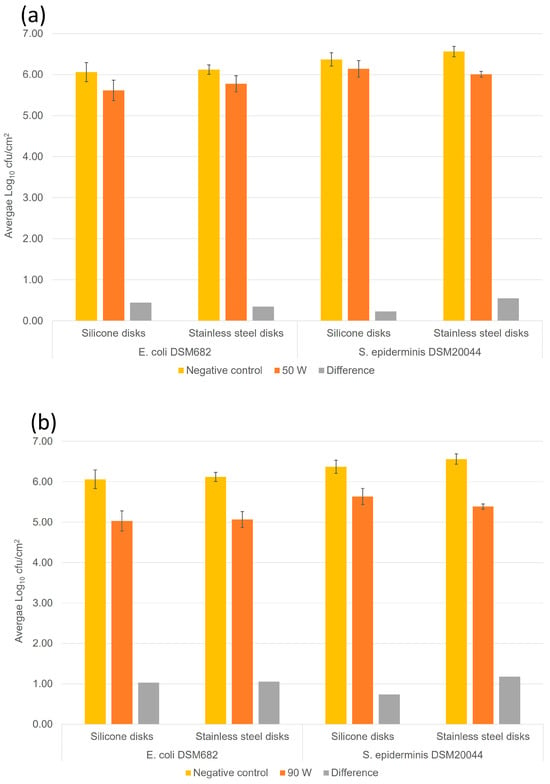
Figure 4.
RF CAP disinfection (15.6 MHz) on stainless steel and artificial skin (silicone) for 75 s. The vertical scale is logarithmic (unit: log10 cfu/mL). Uncertainty bars indicate standard deviations. (a) RF power at 50 W and (b) RF power at 90 W (right).
4. Discussion
4.1. RF Plasma Mechanism of Inactivation
Based on the optical emission spectra obtained from the different plasma generated here, it may be speculated that the action of the plasma is indeed chemical, as it creates reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS), and not thermal. Reactive oxygen species (ROS), including hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), hydroxyl radical (OH−), singlet oxygen (1O2), and superoxide anion (O2−), endogenously produced by the organisms to be inactivated have previously been considered attractive weapons for pathogen clearance [26]. Similarly, reactive nitrogen species (NO2• and ONOO-/HOONO) have been shown to destroy DNA, and may completely suppress viable but nonculturable states of microorganisms and inhibit the reactivation of bacteria [27]. The exact process of inactivation using plasma has, however, not been fully understood, but is is believed that hydrophobic ROS oxidize the lipid bilayer of cells and decreased cell membrane thickness [28,29]. The same effects may be observed in people directly in contact with the plasma. Studies have shown that the ROS and PNS produced by plasma may penetrate and dissolve in some tissues up to 1.25 mm thick [30]. Thus, if not carefully controlled, these species cause tissue damage in skin treatments. However, plasma radiation and temperatures up to 45 °C did not cause any long-term changes [30].
4.2. Plasma Integration into a Hand Dryer
While the tests carried out well represent any use of the plasma on surface that may be found in high traffic public areas or food production sites, they did not correspond exactly to what might happen in a hand dryer. Only one nozzle was in operation and, above all, the aerodynamics of the plasma flow on the hands were not reproduced at all. Nevertheless, assuming there were two facing rows of at least twenty nozzles each, extending over a length of just over 30 cm, so as to expose both hands on each side in a single pass, it can be estimated that a sweep at a speed of approx. 2 cm/s would cover the hands up to the wrists in around 10 to 15 s, equivalent to the drying time required with a standard appliance; the disinfection performance of a hand dryer could therefore reach the levels shown in here.
In comparison, the recommended application time for alcohol gels is half a minute to achieve a level of disinfection that complies with the standard. It should also be noted that, since water vapor promotes the disinfection effect of plasma [14] and our tests were carried out with dry air, for reasons of reproducibility, disinfection should be more efficient using ambient air as the plasmagenic gas.
Air-blade hand dryer models are ideal for integrating plasma nozzles in the mouthpiece aeraulic channels, with a CAP source at each air jet. It should be noted that, as this is a cold plasma, additive 3D printing in plastic can be used to speed up nozzle design [16]. In fact, the design of the aeraulic circuit should be reworked to optimize device ergonomics, hand exposure and air recycling, in order to deactivate ozone with a filter. Of course, the power electronics generating the RF induction will also have to be integrated. They will take the place of the now-useless heating system, whose energy consumption will be reallocated to plasma production. On the basis of a commercial hand dryer with an electrical power rating of 1.5 kW, it is estimated that total power could remain below 3 kW.
5. Conclusions
The disinfection tests presented here were carried out with a CAP using air as the plamagenic gas, which was stabilized by increasing the induction frequency in the megahertz range. This technology, which is compatible with delicate surfaces, is much more environmentally friendly than traditional wet chemical processes, while reducing the risk of contamination of adjacent surfaces through aerosol formation [31]. However, while CAP showed a reduction in cell counts, the activity was less than that observed with currently available methods for surface or hand disinfection. Consequently, the technology presented here needs further optimization to achieve a higher reduction of contaminants. Once optimized, however, it could replace or complement current hand disinfection methods and mitigate the economic burden of public health crises in the future [23]. Furthermore, by increasing disinfection power, it is possible to consider more demanding sanitary applications, such as hand hygiene in hospitals. The exposure time and number of CAP nozzles can be increased to achieve the decontamination rate required for these applications. Furthermore, since CAP has proved to be an effective tool for inactivating pathogens (bacteria, fungi, viruses, etc.), the plasma generators developed here could be of interest to other sectors, such as the food industry, particularly in situations in which heat treatment is not applicable. However, the impacts of this technology will need to be further studied prior to regulatory approval and consumer acceptance [31].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.C. and W.M.B.; methodology, W.M.B. and G.C.; validation, A.S., M.B. and M.E.M.; formal analysis, G.C. and W.M.B.; investigation, A.S., M.B. and M.E.M.; data curation, G.C.; writing—original draft preparation, W.M.B.; writing—review and editing, W.M.B. and G.C.; project administration, G.C.; funding acquisition, G.C. and W.M.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the HES-SO Engineering and Architecture domain under the P2 Interdisciplinary program scheme (IA-INTERDISC20-07). Funding was given to the University of Applied Sciences Western Switzerland Valais-Wallis and the School of Engineering and Management Vaud [grant number 106914].
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated in this document have been stored under https://zenodo.org/record/8096012 (accessed on 26 June 2023).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Villa, C.; Russo, E. Hydrogels in Hand Sanitizers. Materials 2021, 14, 1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephenson, R.E.; Gutierrez, D.; Peters, C.; Nichols, M.; Boles, B.R. Elucidation of bacteria found in car interiors and strategies to reduce the presence of potential pathogens. Biofouling 2014, 30, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathur, P. Hand hygiene: Back to the basics of infection control. Indian. J. Med. Res. 2011, 134, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolaides, C.; Avraam, D.; Cueto-Felgueroso, L.; González, M.C.; Juanes, R. Hand-Hygiene Mitigation Strategies Against Global Disease Spreading through the Air Transportation Network. Risk Anal. 2020, 40, 723–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, L.; Gozdzielewska, L.; Alejandre, J.C.; Stewart, E.; Pittet, D.; Reilly, J. Systematic review on factors influencing the effectiveness of alcohol-based hand rubbing in healthcare. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2022, 11, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breidablik, H.J.; Johannessen, L.; Andersen, J.R.; Søreide, H.; Kleiven, O.T. Effect of Optimal Alcohol-Based Hand Rub among Nurse Students Compared with Everyday Practice among Random Adults; Can Water-Based Hand Rub Combined with a Hand Dryer Machine Be an Alternative to Remove E. coli Contamination from Hands? Microorganisms 2023, 11, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plum, F.; Yüksel, Y.T.; Agner, T.; Nørreslet, L.B. Skin barrier function after repeated short-term application of alcohol-based hand rub following intervention with water immersion or occlusion. Contact Dermat. 2020, 83, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivuti-Bitok, L.W.; Chepchirchir, A.; Waithaka, P.; Ngune, I. Dry Taps? A Synthesis of Alternative “Wash” Methods in the Absence of Water and Sanitizers in the Prevention of Coronavirus in Low-Resource Settings. J. Prim. Care Community Health 2020, 11, 2150132720936858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, I.B.; Ewin, D.; Wilcox, M.H. From the hospital toilet to the ward: A pilot study on microbe dispersal to multiple hospital surfaces following hand drying using a jet air dryer versus paper towels. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2022, 43, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menashi, W.P. Treatment of Surfaces. U.S. Patent US3383163 A, 14 May 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Laroussi, M.; Bekeschus, S.; Keidar, M.; Bogaerts, A.; Fridman, A.; Lu, X.P.; Ostrikov, K.; Hori, M.; Stapelmann, K.; Miller, V.; et al. Low-temperature plasma for biology, hygiene, and medicine: Perspective and roadmap. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2108.03158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridman, A. Plasma Biology and Plasma Medicine. In Plasma Chemistry Cambridge; Fridman, A., Ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009; pp. 848–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busco, G.; Robert, E.; Chettouh-Hammas, N.; Pouvesle, J.M.; Grillon, C. The emerging potential of cold atmospheric plasma in skin biology. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 161, 290–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osman, I.; Ponukumati, A.; Vargas, M.; Bahkta, D.; Ozoglu, B.; Bailey, C. Plasma-activated vapor for sanitization of hands. Plasma Med. 2016, 6, 3–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.L.; Nikiforov, A.Y.; Vanraes, P.; Leys, C. Direct current plasma jet at atmospheric pressure operating in nitrogen and air. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 113, 023305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassir, A.M.; Sonnard, J.; Roulin, L.; Baudin, M.; Courret, G.; Brück, W.M. Fast Prototyping for Atmospheric Plasma Sources Integration into Air Hand Dryers. Int. J. Chem. Mol. Eng. 2022, 16, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, M.Y.; Ren, C.S.; Wang, D.Z.; Fan, Q.-Q.; Nie, Q.-Y.; Wen, X.-Q.; Zhang, J.-L. Investigations on an atmospheric dielectric barrier discharge plasma jet with a concentric wire-mesh cylinder electrode configuration. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2011, 40, 1134–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laroussi, M. Plasma medicine: A brief introduction. Plasma 2018, 1, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Garcia, G., Jr.; Arumugaswami, V.; Wirz, R.E. Cold atmospheric plasma for SARS-CoV-2 inactivation. Phys. Fluids 2020, 32, 111702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 13697:2015+A1:2019; Chemical Disinfectants and Antiseptics, Quantitative Non-Porous Surface Test for the Evaluation of Bactericidal and/or Fungicidal Activity of Chemical Disinfectants Used in Food, Industrial, Domestic and Institutional Areas (Phase 2/Step 2). 2019. Available online: https://connect.snv.ch/en/ (accessed on 4 August 2021).
- Nachman, M.; Franklin, S.E. Artificial Skin Model simulating dry and moist in vivo human skin friction and deformation behaviour. Tribol. Int. 2016, 97, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, S.E.; Baranowska, J.; Furgala, J. Friction of natural human, procine and synthetic skin. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Mechanics of Biomaterials and Tissues, Sitges, Spain, 8–12 December 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Wirz, R. Cold Atmospheric Plasma for COVID-19. Preprints 2020, 2020040126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Suva. Valeurs Limites d’Exposition aux Postes de Travail. Available online: www.suva.ch/1903.f (accessed on 4 February 2021).
- Defrin, R.; Shachal-Shiffer, M.; Hadgadg, M.; Peretz, C. Quantitative Somatosensory Testing of Warm and Heat-Pain Thresholds: The Effect of Body Region and Testing Method. Clin. J. Pain. 2006, 22, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhou, X.; Huang, Y.; Cheng, L.; Ren, B. Reactive Oxygen Species in Pathogen Clearance: The Killing Mechanisms, the Adaption Response, and the Side Effects. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 622534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yin, R.; Tang, Z.; Liu, W.; He, C.; Xia, D. Reactive Nitrogen Species Mediated Inactivation of Pathogenic Microorganisms during UVA Photolysis of Nitrite at Surface Water Levels. Env. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 12542–12552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waskow, A.; Betschart, J.; Butscher, D.; Oberbossel, G.; Klöti, D.; Büttner-Mainik, A.; Adamcik, J.; von Rohr, P.R.; Schuppler, M. Characterization of Efficiency and Mechanisms of Cold Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Decontamination of Seeds for Sprout Production. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhao, T.; Zou, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y. Molecular dynamics simulations of membrane properties affected by plasma ROS based on the GROMOS force field. Biophys. Chem. 2019, 253, 106214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahaya, A.G.; Kristof, J.; Blajan, M.; Mustafa, F.; Shimizu, K. Effect of Plasma Discharge on Epidermal Layer Structure in Pig Skin. Plasma Med. 2021, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domonkos, M.; Tichá, P.; Trejbal, J.; Demo, P. Applications of Cold Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Technology in Medicine, Agriculture and Food Industry. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).