Abstract
Fermented foods containing probiotic Leuconostoc mesenteroides 201607 (LM) were used to extract exopolysaccharides. An incomplete understanding exists regarding the immunomodulatory characteristics of exopolysaccharides (EPSs), which are important constituents of bacterial biofilms. In this instance, we examined the immunomodulatory capacity of EPSs from fermented food extracted from L. mesenteroides 201607. Partially purified exopolysaccharide from L. mesenteroides 201607 (PP-LMEPS) consists of glucose (57.1%), rhamnose (29.53%), and galactose (13.36%). The maximum EPS yield was attained after 30 h of incubation at 37 °C and an initial pH of 7.0. When lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7 was exposed to PP-LMEPS, the inflammatory cytokines were considerably decreased or elevated dose-dependently. Upon the exposure of lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7 cells to PP-LMEPS, a dose-dependent modulation of inflammatory cytokines was observed. This suggests that the extracted EPS possesses immunomodulatory characteristics, as evidenced by a significant decrease or increase in inflammatory cytokine levels. However, further research is warranted to fully elucidate the precise mechanisms and potential therapeutic implications of the immunomodulatory properties of PP-LMEPS.
1. Introduction
Complex sugar polymers known as exopolysaccharides (EPSs) are synthesized by microorganisms, such as bacteria, and are necessary for a number of biological and industrial processes. Leuconostoc mesenteroides (L. mesenteroides) is a widely distributed lactic acid bacteria (LAB) found in various fermented products, particularly in pickled cabbage, fermented soybean and juice. This bacterium is known for its ability to produce exopolysaccharides (EPSs) that are closely associated with human health. It is noteworthy that different bacteria can generate diverse polysaccharides, and even within the same bacterial type, the produced polysaccharides may vary. Exopolysaccharide production is influenced by factors such as the strain of L. mesenteroides, growth conditions (e.g., temperature, pH, and carbon source), and the presence of specific substrates [1].
The production of exopolysaccharides involves the enzymatic synthesis of sugar polymers, which are then released into the extracellular environment. Polysaccharide structure can vary in terms of sugar composition, linkage type, molecular weight, and overall architecture [2]. Exopolysaccharides produced by L. mesenteroides are heteropolysaccharides, meaning they are composed of multiple types of sugar residues. Common sugar residues found in these polysaccharides include glucan, dextran, and mannose [3]. The specific composition and arrangement of these sugar residues determine their unique properties, influencing their solubility, rheological properties, and interactions with other molecules.
Research by Osman Taylan [4] identified a strain of Leuconostoc mesenteroides, namely S81, which produces β-(2→6)-linked fructan EPS. The EPS produced by this strain demonstrated immunomodulatory potential by inducing the production of interleukin-4 (IL-4), indicating its capacity to modulate the immune system. In another study led by Lei Pan [5], the EPS known as XG5 from Leuconostoc pseudomesenteroides XG5 was identified. This EPS, characterized by a linear dextran structure through α1,6 glycosidic bonds, was found to modify the gut microbiota structure in mice. These findings highlight the diverse immunomodulatory properties of EPS produced by Leuconostoc strains. Considering the significance of EPSs produced by L. mesenteroides for human health, it is crucial to explore strains that can produce these beneficial polysaccharides. Despite this, limited research has been conducted on the polysaccharides produced by Leuconostoc in such fermented foods, especially those with immunomodulatory properties.
Moreover, EPSs have potential applications in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and biotechnology. They can be utilized as encapsulation agents, stabilizers for drug delivery systems, and components in wound healing products [6]. Studies suggest that there are potential health benefits associated with the consumption of probiotic L. mesenteroides exopolysaccharides. These benefits may include prebiotic effects [7], the modulation of gut microbiota [7], immunomodulatory properties [8], and cholesterol-lowering effects. The prebiotic effect involves promoting the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, which can contribute to improved gut health and overall well-being [8].
Exopolysaccharides formed by probiotic L. mesenteroides have gained significant focus as a result of their potential immunomodulatory and anticancer properties. Immunomodulation involves the regulation of the immune system, enhancing its response against pathogens or diseases [9]. In this context, we will ll delve into the immunomodulatory properties of exopolysaccharides from probiotic L. mesenteroides (LMEPS). It has been demonstrated that LMEPS activates immunological cells, such as dendritic and macrophage cells. These immune cells are essential for both developing and controlling the body’s defenses against external stimuli. LMEPS can enhance phagocytic activity, cytokine production, and the antigen-presenting abilities of these cells. LMEPS may influence the production of various cytokines, and it plays a crucial in communication between immune cells and is essential for controlling immunological responses [10]. According to recent studies, L. mesenteroides exopolysaccharides (LMEPSs) have anti-inflammatory attributes that inhibit the synthesis of pro-inflammatory mediators that promote inflammation [11]. This can help manage inflammatory conditions and reduce inflammation-related tissue damage. The immunomodulatory properties of these exopolysaccharides can strengthen the immune system’s capacity [12]. The stimulation of immune responses makes these EPSs attractive candidates for further research and potential therapeutic applications [3]. However, it is crucial to remember that additional in-depth investigation is required to completely comprehend and validate the immunomodulatory potential of this exopolysaccharide, including in vivo investigations and clinical trials.
Some prior studies have investigated the functional properties of the exopolysaccharides (EPSs) produced by L. mesenteroides [3,7,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22]. Nonetheless, little research has been carried out on the structural features and immunostimulatory potential of the extracellular polymer that L. mesenteroides (201607) produces [23]. L. mesenteroides (201607), an EPS-producing strain, is used in this investigation. Moreover, various analytical techniques, including Fourier transform–infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR), were employed for the examination of the structural characteristics of EPSs derived from L. mesenteroides (201607). Following this, the in vitro immunomodulatory potential of (LMEPS) was assessed using RAW264.7 macrophages, and its impact on cell viability and cytokine production was investigated.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation and Partial Purification of EPS (PP-LMEPS)
A modified MRS broth was utilized in the procedure (PP-LMEPS was produced by adding 20 g/L of sucrose instead of glucose). The cells were grown in stationary culture for 30 h at 37 °C after adding 10% inoculum. To inactivate the enzymes that break down EPS, the fermented broth was held for 20 min at 4 °C and subjected to 10,000 rpm centrifugation. It was subsequently heated at 100 °C in a water bath for 20 min. Protein precipitation was achieved by treating the cell-free supernatant from the prior step with 7% trichloroacetic acid. The protein-free supernatant was collected after centrifugation. Following this, twice as much ice-cold ethanol was added. The precipitated EPS was extracted using centrifugation after being refined and freeze-dried to a constant dry weight, and this raw EPS formulation was represented as g/L [24].
2.2. Exopolysaccharide Characterization
2.2.1. Determination of the Monosaccharide Composition
The identification of monosaccharides from 10 mg of (PP-LMEPS) involved a series of steps using a HPLC technique with UV detection (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA, Model No: 1100), as outlined in [25]. Initially, the (PP-LMEPS) sample was subjected to hydrolysis for 6 h at 110 °C in the presence of 2 M trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) using 8 mL of TFA. Afterwards, 240 µL of 0.3 M NaOH was introduced to 200 µL of the hydrolyzed EPS or a standard monosaccharide mixture. Following this, the mixture was incubated at 70 °C for two hours with 240 µL of a 0.5 M solution of 1-phenyl-3-methyl-5-pyrazolone (PMP) in methanol, followed by a brief 10-s vortexing. The solution was then allowed to cool to room temperature and neutralized to achieve a balanced pH with 240 µL of 0.3 M HCl. Subsequently, another 240 µL of 0.3 M NaOH was added to 200 µL of the hydrolyzed EPS or the standard monosaccharide mixture, then 240 µL of a 0.5 M PMP solution in methanol, which was added and vortexed for 10 s. The mixture was once again incubated at 70 °C for two hours. The pH was neutralized by adding 240 µL of 0.3 M HCl after the solution had reached room temperature.
2.2.2. Structural Characterization of (PP-LMEPS)
Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) Analysis
Using German-made Bruker Tensor 27 equipment (Bruker, Borken, Germany), FT-IR spectroscopy was used to examine the functional groups in PP-LMEPS in greater detail. One milligram of dry PP-LMEPS powder was mixed with one hundred milligrams of potassium bromide (KBr), and the mixture was then packed into a metal mold. The generated composite was then subjected to FT-IR spectra recording throughout a frequency range of 400 to 4000 cm−1, with a spectral resolution of 1 cm−1 [26].
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy Analysis
After dissolving dry 60 mg PP-LMEPS in D2O, it underwent three cycles of lyophilization. Following these preparatory steps, the resulting material was diluted in D2O to facilitate its analysis through NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance). The 1H and 13C NMR spectra were then recorded using a 600 MHz spectrometer [24].
2.3. Functional Properties of PP-LMEPS
2.3.1. Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Assay of PP-LMEPS
The inhibitory potential of PP-LMEPS on 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) and 2,2′-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid (ABTS) was investigated using the aforementioned formula [27]. Antimicrobial activity against food-borne pathogens was investigated through the use of a disc diffusion assay [28]. Each pathogenic bacteria was grown for 18 h at 37 °C in TSB (Difco Laboratories Inc., Detroit, MI, USA). An amount of 100 μL of the pathogens was added to Muller–Hinton agar plates. After solidification, a 7 mm diameter disc was filled with 30 μL positive control (Ciprofloxacin (20 μg/mL)), 100 μL negative control, and PP-LMEPS. The inhibition zone was measured after 24 h of incubation. The absorbance of the solution was measured at 517 nm for the DPPH assay and 734 nm for the ABTS assay. Trolox was then used to make the standard curve. The scavenging activity was calculated using the following formula:
% inhibition = [(absorbancecontrol − absorbancesample)/absorbancecontrol] × 100
2.3.2. Immunomodulatory Activity of PP-LMEPS
Cell Culture
Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM) was enriched with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 1% penicillin–streptomycin to support the proliferation of RAW264.7. The RAW 264.7 cell lines (third passage) were purchased from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC® TIB-71™) and from Sigma-Aldrich. The cells were cultured in DMEM high-glucose medium supplemented with 10% FBS (all the experiments were performed using the same FBS batch) and 1% penicillin/streptomycin in an atmosphere of 5% CO2 and 95% humidity at 37 °C. The cells were passaged after reaching 90% confluence, detached with a cell scraper and sub-cultivated at a 1:6 ratio in T-75 flasks. All cell culture equipment (flasks, pipettes, etc.) used in this study were from the same batch. The cells were cultured continuously from the third passage until passage no. 50. The cells were frozen every fifth passage, starting from passage number three. Before phenotype and functional analysis, the cells were thawed and cultured for the next two passages (e.g., cells of passage number three were thawed and cultured until passage no. 5 and then subjected to further analyses).
Cells Viability Assay
Using the EZ-cytox test, the sample extract’s cytotoxicity of RAW264.7 was assessed [27]. Living cells have the functioning WST chemical in their respiratory chain of mitochondria. In this study, 4 × 104 cells were loaded onto a 96-well microplate. The cells were rinsed with PBS following a 24 h incubation period. Then, each well received 100 μL of growth media with different concentrations of sample extract (range from 100 to 400 mg/mL). The control group received only medium instead of any sample extract. Every sample was treated with 10 μL of the WST-1 solution after being kept at 37 °C and 5% CO2 for a full day. Cell viability was measured using the previously described formula [27].
IL-6 Assay
Inhibiting the growth of infections and stopping the spread of cancer cells are two functions of cytokines, indicating the activation of macrophage cells [27]. Six-well plates were used to culture the cells (5 × 105 cells/well). The cells were supplemented with 200 μL of PP-LMEPS at different doses based on the viability assay and 1600 μL fresh medium in place of the prior medium. After adding the extract or chemical, 200 μL of Lipopolysaccharide phenol extracted from Escherichia coli 0111:B4 (1 μg/mL) (L2630, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) was added to each well, approximately 1–2 h later. The cells were centrifuged (2000× g for 10 min) following incubation. The amount of IL-6 was determined using ELISA kits ( Human IL-6 ELISA kit, RABO306, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA).
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Graph Pad Prism (8.0, GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA, USA) was used for the collection and analysis of the investigational data. ANOVA one-way variance and Tukey and Duncan tests were used to assess the significance of the differences between the alphabets (a–d) in the superscript (p ≤ 0.05).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. LMEPS Production and Its Characterization
3.1.1. Partial Purification of EPS (PP-LMEPS)
L. mesenteroides (201607) provided the EPS, which was isolated and purified. With a viable count of 9.1 log10 CFU/mL and an inoculum of 10%, the highest yield of EPS was achieved after 30 h of incubation. After 30 h, the highest concentration of EPS obtained was 0.470 (g/L). (Figure 1). Nevertheless, the amount of EPS fell since the growth persisted for more than 30 h. As a result, the current finding demonstrated a substantial relationship between bacterial growth and EPS generation. An exopolysaccharide (EPS)-producing strain, SN-8, isolated from Dajiang, was identified as Leuconostoc mesenteroides [3]. Thus, we have shown that the LAB strains and the length of the fermentation process affect the EPS yield.
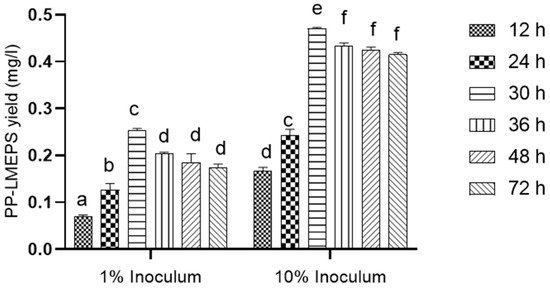
Figure 1.
EPS production using different inoculum sizes and incubation times: 1% and 10% inoculum was used for EPS production with different incubation times, like 12, 24, 30, 36, 48, and 72 h. The Tukey and Duncan tests were 192 used to assess the significance of the differences between the alphabets (a–f) in superscript (p ≤ 0.05).
3.1.2. Monosaccharide Composition Analysis
The monosaccharide content of PP-LMEPS was examined by means of HPLC. Every peak was located individually and assessed using the regular peak. Three peaks were found in the HPLC analysis: glucose, rhamnose, and galactose in PP-LMEPS, making it a heteropolysaccharide (Figure 2). There was less variation in the monosaccharide content of the polysaccharides discovered in PP-LMEPS compared to previous research findings. Monosaccharides from L. mesenteroides, such as glucose and fructose, have been described [8]. On the other hand, further research revealed that the polysaccharides found in L. mesenteroides were made up of mannose, arabinose, galactose, glucose, and fucose [11]. Monosaccharides like mannose, glucose, and galactose are frequently discovered when polysaccharides are separated from bacteria [29]. Since our separated EPS are made up of several types of monosaccharides, they can be thought of as HePSs [30]. The medium’s composition, pH, temperature, and length of incubation are just a few of the variables that can affect the yields and molecular functions of HePSs [31].
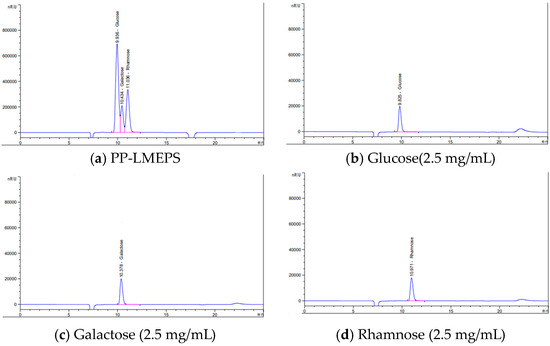
Figure 2.
Monosaccharide composition of PP-LMEPS (a) via HPLC analysis. Monosaccharide derivatives were analyzed using Agilent 1000 series HPLC (Agilent Technologies, Model No. 1100); (b) glucose standard; (c) galactose standard; (d) rhamnose standard.
3.1.3. Structural Characterization
FT-IR Spectrum Analysis
FT-IR analysis was used to look at the functional group in the PP-LMEPS based on specific frequencies (Figure 3). The broad peak of absorption at 3394.56 cm−1 was attributed to the polysaccharide hydroxyl groups (O–H); the spectra that appeared between 1000 and 1200 cm−1 indicate the presence of a pyranose form of sugars. This is the polysaccharide’s typical IR absorption spectrum [32]. The bending vibration peak of the O-H band is thought to be near 1456.25. Peaks at 1204.83 cm−1 and 1039.63 cm−1 are related to C-O-C and C-O-H bond stretching, a polysaccharide property. Comparable outcomes were reported by [33] and [34]. These peaks revealed the presence of the monosaccharides galactose and glucose as well as glycosidic linkage. Studies have shown that glucans exhibit an IR spectrum between 1000 and 1500 cm−1 [35]. The FTIR spectra of the unique absorption peaks of glucose residues found in EPS suggested that the glucose in these EPS contained glycosidic linkages between glycosyl groups as well as OH and C-O groups.
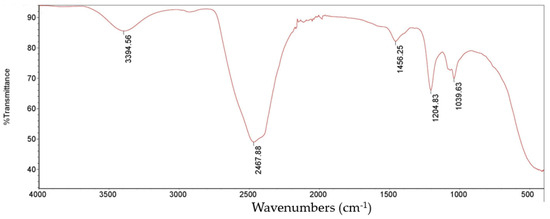
Figure 3.
Fourier-transformed infrared (FT-IR) spectrum of PP-LMEPS (10 mg/mL) produced by L. mesenteroides.
NMR Spectral Analysis
The NMR spectrum analysis of PP-LMEPS is displayed in Figure 4. These were the assignments made to the 1H, 13C, and NMR spectra. In the 600 MHz 1H NMR spectrum, three distinct chemical shift signals from anomeric protons (H-1) were detected at δ5.29, δ5.14, and β 4.68 ppm. (Figure 4a). The residual D2O signal in the EPS was detected at δ4.800 ppm in the anomeric portion of the spectrum. According to this spectrum, the PP-LMEPS was found to have three residues: A-α-D-glucose, B-α-L-rhamnose, and C-β-D-galactose. Reagents A and B were found to have α-configurations based on their δ and J values for the anomeric signals in the 1 H NMR spectrum, while residue C was found to have β-configurations. The molar ratios for residues A, B, and C were estimated using the ratios of the peak area from the integration of the H-1 signals; the results were in agreement with the monosaccharide composition and came out to be around 1.77:1.36:3.37. The 13C NMR spectra (Figure 4b) revealed that the three residues’ C-1 signals could be found at α 96.43 and 92.25, α 93.95, and β 95.87 ppm, in that order. Previous research has discovered a similar structure for the exopolysaccharide from L. casei LC2W [36]. The morphological characteristics of polysaccharides can generally be used to modify their bioactivities. For instance, different polysaccharides identified in earlier research are said to have different immunomodulatory activities. This can be because polysaccharides differ in their shape [3]. We still need to determine the precise relationship between morphology and bioactivity. Food packaging and cosmetics manufacturing can benefit from the usage of porous structures, although particular surface characteristics are anticipated to enhance their capacity in terms of retaining water [37].
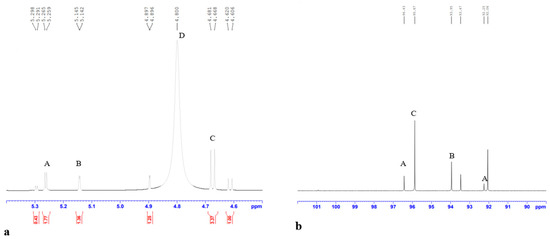
Figure 4.
NMR spectra of PP-LMEPS: (a) region from 1D 1H spectrum; (b) region from 1D 13C spectrum. A-α-D-glucose, B-α-L-rhamnose, C-β-D-galactose and D-D2O. Red color numbers corresponding to ratio of monosaccharides.
3.2. Functional Properties of PP-LMEPS
3.2.1. In vitro Antioxidant Analysis
DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity
To assess the ability of different natural chemicals to neutralize free radicals, find the DPPH free radical scavenging rate [38]. PP-LMEPS had significant radical scavenging action at dosages between 0.0625 and 1 mg/mL, reaching up to 52.43%. (Figure 5a). Nevertheless, at every concentration tested in the study, its scavenging activity was clearly less effective than Trolox’s. According to [38], the scavenging ability of DPPH radicals was measured at 4 mg/mL, while EPS-LR exhibited a 78.7% scavenging ability, which was marginally better than our outcomes. These findings suggested that the functional characteristics varied depending on the strain. Free radical exposure can lead to oxidative stress-related cell damage, which can cause a variety of diseases. As an illustration, the EPS obtained from Weissella cibaria showed a 34% DPPH scavenging activity [34]. Compared to the EPS isolated from the current experiment, L. plantarum YW32’s DPPH scavenging activity was shown to be 30% [39].
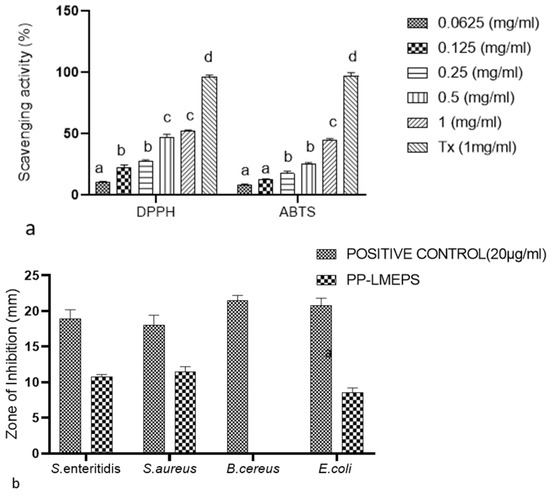
Figure 5.
(a) Scavenging effect of PP-LMEPS on DPPH, ABTS radicals and compared with that of Trolox; (b) antibacterial activities of EPS compared with that of ampicillin. EPS = EPS from L. mesenteroides; Tx = Trolox; Positive control = ampicillin. The Tukey and Duncan tests were used to assess the significance of the differences between the alphabets (a–d) in superscript (p ≤ 0.05).
ABTS Radical Scavenging Activity
The ABTS discoloration method is commonly used to estimate the capacity of lipophilic and hydrophilic antioxidants to scavenge free radicals [40]. The scavenging ability of PP-LMEPS against ABTS radicals in comparison with Trolox was assessed. At all of the tested concentrations (0.0625–1 mg/mL), PP-LMEPS scavenges the ABTS radicals, with the greatest activity of 44.58% (Figure 5a). There has been news of another study. While the EPS obtained from Weissella cibaria exhibited 90% [34] ABTS scavenging activity, the present investigation indicated less than in earlier studies. Chinese cabbage isolate W. cibaria YB-1 exhibits 82.20 ± 1.8% ABTS scavenging activity [41]. When compared to previously published EPS, the difference in carbohydrate and chemical compositions was responsible for SY003 EPS’s increased activity [41].
3.2.2. Antimicrobial Activity of PP-LMEPS
Another crucial function of EPS is its antibacterial action, which keeps disease-causing bacteria out of the intestine or inhibits them. The results of the disc diffusion method (Figure 5b) showed that the PP-LMEPS samples showed suppression of the foodborne pathogens that had been detected. Thus, with the exception of B. cereus ATCC 10987, which is resistant to PP-LMEPS, S. enteritidis ATCC 13076 (11 mm), S. aureus ATCC 13565 (11.5 mm), and E. coli O157:H7 ATCC® 43895 (8.5 mm) all showed growth suppression related to PP-LMEPS. The previous reports showed the antibacterial activity of EPS against food-borne pathogens [42,43,44]. EPS from microbes has been shown to have strong antimicrobial action against a variety of pathogens in vitro. A wide range of putative antibacterial mechanisms have also been put forth, including the ability to stop cell division, rupture the cytoplasmic membrane and cell wall, and degrade DNA [43].
3.2.3. Effect of PP-LMEPS on Cell Viability against RAW 264.7
Various sources of polysaccharides have significant biological effects, including immunostimulatory effects. RAW264.7 cells are frequently utilized in immunological studies of polysaccharides by enhancing cell proliferation, phagocytic capacity, NO generation, and cytokine secretion. RAW264.7 cell viability serves as a marker of the onset of cytotoxicity and immunological activation [45]. The EZ-cytox test in this investigation was used to identify PP-LMEPS-induced activation of RAW264.7 macrophages. The impact of PP-LMEPS on RAW264.7 cell survival was nontoxic to the cells at the measured concentrations (1–3 mg/mL), as Figure 6a illustrates. RAW264.7 cell survival decreased as PP-EPS concentrations rose from 1 to 3 mg/mL, but the numbers continued to be higher than the blank control (p < 0.05). The MTT results demonstrated that the PP-LMEPS treatment significantly increased the proliferation of RAW264.7 cells, indicating that PP-LMEPS stimulated the cells. Similarly, RAW264.7 cells were shown to be unaffected by the R-5-EPS derived from L. helveticus LZ-R-5 at doses ranging from 50 to 400 [33]. Because natural polysaccharides are more biodegradable and less toxic than synthetic polymers, interest in the potential of EPSs for immunostimulatory therapy has quickly increased. Numerous microbial EPSs with new functional characteristics have been discovered recently [46]. The EPSs can interact with micro- and macro-organisms more readily thanks to the surface localization. Furthermore, a range of polysaccharides derived from natural sources are recognized as powerful biological response modifiers with minimal toxicity and are used as safe and efficient adjuvants in immunizations against diseases and cancer [47].
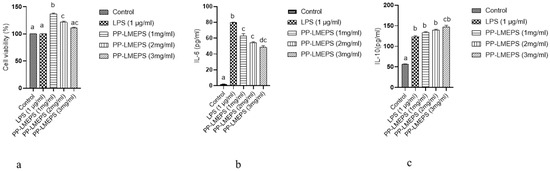
Figure 6.
(a) Effect of PP-LMEPS on the viability of RAW 264.7; (b) effect of PP-LMEPS on the production of IL-6; (c) effect of PP-LMEPS on the production of IL-10. The Tukey and Duncan tests were used to assess the significance of the differences between the alphabets (a–d) in superscript (p ≤ 0.05).
3.2.4. Effect of PP-LMEPS on Immunomodulatory Cytokine Analysis
An important function of macrophages is to mediate the inflammatory response. Bacterial lipopolysaccharides cause macrophages to release a variety of cytokines, nitrogen growth factors, and reactive oxygen (LPS). The cytokines that are released by activated macrophages are employed to kill infections and stop the growth of cancer cells. Immune responses depend on the release of TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1, and IL-10 by stimulated macrophages [48]. To examine the immunomodulatory effects of the material, PP-LMEPS (1 mg/mL, 2 mg/mL and 3 mg/mL) was administered to stimulate murine macrophage RAW264.7 cells. ELISA kits were then used to quantify the amounts of IL-6 and IL-10 in the culture supernatants (Figure 6b,c). The amount of pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-6 in RAW264.7 cells was higher than in cells that were not treated. When cells were grown with LPS (1 µg/mL) alone, their IL-6 levels were significantly lower (79.5 ± 0.7 pg/mL). The IL-6 levels in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages treated with PP-LMEPS were reduced in a dose-dependent manner in comparison to levels produced merely via LPS. When comparing cultures treated with 3 mg/mL PP-LMEPS to LPS-stimulated cells, IL-6 levels were much lower, with cytokine concentrations of 48.5 ± 2.12 pg/mL. When RAW264.7 cells were grown with LPS (1 µg/mL) alone, the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 was measured as being 123 ± 2.82 pg/mL. However, when PP-EPS was added at a dosage of 3 mg/mL, IL-10 levels increased dramatically to 147.5 ± 3.5 pg/mL as compared to LPS treatment alone. The anti-inflammatory qualities of L. mesenteroides strains isolated from kimchi have been studied in the past [11]. In mice fed a high-fat diet, Kang et al. [49] found that L. mesenteroides strain B-512FMCM’s sucrose-derived oligosaccharides, produced via dextransucrase, and had anti-inflammatory characteristics [12,50]. According to recent research, LAB EPSs may exert their anti-inflammatory effects via upregulating TLR negative regulators, specifically by modulating TLR-4 [50].
4. Conclusions
The extraction of Exopolysaccharides (EPS) from probiotic L. mesenteroides (201607) has revealed a multifaceted potential, encompassing antimicrobial and immunomodulatory activities. In conclusion, the study on L. mesenteroides (201607) and its EPS, specifically PP-LMEPS, revealed promising characteristics and potential applications. The efficient isolation and purification of EPS resulted in a high yield after 30 h of incubation. HPLC analysis identified the presence of glucose, rhamnose, and galactose, classifying PP-LMEPS as a heteropolysaccharide. The DPPH and ABTS assays demonstrated significant free radical scavenging activity, though slightly less effective than the standard antioxidant Trolox. Moreover, PP-LMEPS exhibited inhibitory effects against common foodborne pathogens, showcasing its potential as a natural antimicrobial agent. In the evaluation of its impact on macrophages, PP-LMEPS demonstrated non-toxicity at tested concentrations and displayed anti-inflammatory properties by reducing IL-6 levels while enhancing the production of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10. These findings suggest that PP-LMEPS holds promise for various applications, including as an antioxidant and antimicrobial agent, as well as a potential immunomodulator. Further research and exploration of its applications in various industries may unveil additional benefits and contribute to the development of novel bioactive compounds.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.V., J.-R.K. and D.-H.O.; Data curation, S.V. and A.H.H.; Formal analysis, R.C. and K.B.; Funding acquisition, D.-H.O.; Investigation, S.V.; Methodology, S.V. and A.H.H.; Software, S.V.; Supervision, D.-H.O.; Writing—original draft, S.V. and J.-R.K.; Writing—review and editing, S.V., D.-H.O. and A.H.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by a grant from the fourth Brain Korea (BK) 21 Plus Project (Grant No. 4299990913942); Basic Science Research Program (NRF Grant number: 2021R1A6A1A03044242, 2018007551 and 2020R1A6A3A01099837); financed by the Korean Government, Republic of Korea. Researchers Supporting Project number (RSPD2024R677), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia for financial support.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Yang Mi-sook at the Kangwon National University Central Laboratory for instructing and technical support with an HPLC. Ministry of Education, Science and Technology, Republic of Korea.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in study design, data collection, analysis, publishing decisions, or manuscript preparation.
References
- Jurášková, D.; Ribeiro, S.C.; Silva, C.C.G. Exopolysaccharides Produced by Lactic Acid Bacteria: From Biosynthesis to Health-Promoting Properties. Foods 2022, 11, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badel, S.; Bernardi, T.; Michaud, P. New perspectives for Lactobacilli exopolysaccharides. Biotechnol. Adv. 2011, 29, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cao, C.; Zhu, X.; Wang, C.; Wu, R.; Wu, J. Extraction and biological activity of exopolysaccharide produced by Leuconostoc mesenteroides SN-8. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 157, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylan, O.; Yilmaz, M.T.; Dertli, E. Partial characterization of a levan type exopolysaccharide (EPS) produced by Leuconostoc mesenteroides showing immunostimulatory and antioxidant activities. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 136, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, L.; Han, Y.; Zhou, Z. In vitro prebiotic activities of exopolysaccharide from Leuconostoc pseudomesenteroides XG5 and its effect on the gut microbiota of mice. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 67, 103853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, I.; Datta, S. Bacterial exopolysaccharides in drug delivery applications. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 74, 103557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, J.; Shimizu, H.; Hisa, K.; Matsuzaki, C.; Inuki, S.; Ando, Y.; Nishida, A.; Izumi, A.; Yamano, M.; Ushiroda, C.; et al. Host metabolic benefits of prebiotic exopolysaccharides produced by Leuconostoc mesenteroides. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2161271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzaki, C.; Hayakawa, A.; Matsumoto, K.; Katoh, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Hisa, K. Exopolysaccharides produced by Leuconostoc mesenteroides strain NTM048 as an immunostimulant to enhance the mucosal barrier and influence the systemic immune response. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 7009–7015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelin, J.; Kavitha, M. Exopolysaccharides from probiotic bacteria and their health potential. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 853–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.M.; An, J. Cytokines, inflammation and pain. Int. Anesthesiol. Clin. 2007, 45, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kook, S.-Y.; Lee, Y.; Jeong, E.-C.; Kim, S. Immunomodulatory effects of exopolysaccharides produced by Bacillus licheniformis and Leuconostoc mesenteroides isolated from Korean kimchi. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 54, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrutha, T.; Beena, A. Microbial Exopolysaccharides: A Promising Health Booster. J. Phytopharmacol. 2023, 12, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzaki, C.; Nakashima, Y.; Endo, I.; Tomabechi, Y.; Higashimura, Y.; Itonori, S.; Hosomi, K.; Kunisawa, J.; Yamamoto, K.; Hisa, K. Enzymatically synthesized exopolysaccharide of a probiotic strain Leuconostoc mesenteroides NTM048 shows adjuvant activity to promote IgA antibody responses. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1949097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.; Jiao, Z.; Wang, T.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, H. Glucans with Different Degrees of Polymerization from Leuconostoc mesenteroides CICC6055: Analysis of Physicochemical Properties and Intestinal Prebiotic Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 25, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisson, G.; Comuzzi, C.; Giordani, E.; Poletti, D.; Boaro, M.; Marino, M. An exopolysaccharide from Leuconostoc mesenteroides showing interesting bioactivities versus foodborne microbial targets. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 301, 120363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Gu, Y.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, K.; Wu, T.; Cheng, H. Analysis of physicochemical properties of exopolysaccharide from Leuconostoc mesenteroides strain XR1 and its application in fermented milk. LWT 2021, 146, 111449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, I.S.; Ko, S.H.; Lee, M.E.; Kim, H.M.; Yang, J.E.; Jeong, S.G.; Lee, K.H.; Chang, J.Y.; Kim, J.-C.; Park, H.W. Production, characterization, and antioxidant activities of an exopolysaccharide extracted from spent media wastewater after Leuconostoc mesenteroides WiKim32 fermentation. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 8171–8178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, H.; Ha, J.-H.; Lee, J.; Jang, H.; Kwon, D.; Cho, M.; Kang, D.; Kim, I.; Kim, M. The Effect of Fermented Momordica charantia with Leuconostoc mesenteroides MKSR on Metabolic Complications Induced by High-Fat High-Cholesterol Diet in C57BL/6 Mice. Fermentation 2023, 9, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farinazzo, F.S.; Valente, L.J.; Almeida, M.B.; Simionato, A.S.; Fernandes, M.T.C.; Mauro, C.S.I.; Tomal, A.A.B.; Garcia, S. Characterization and antioxidant activity of an exopolysaccharide produced by Leuconostoc pseudomesenteroides JF17 from juçara fruits (Euterpe edulis Martius). Process. Biochem. 2019, 91, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Gu, Y.; Lv, Z. Processing properties of yogurt as affected by the EPS produced by Leuconostoc mesenteroides XR1. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 4076–4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yan, D.; Liu, Y.; Luo, X.; Li, Y.; Cao, C.; Li, M.; Han, Q.; Wang, C.; Wu, R.; et al. Purification, structural characteristics, and biological activities of exopolysaccharide isolated from Leuconostoc mesenteroides SN-8. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 644226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Guo, S.; Ping, W.; Zhao, D.; Ge, J. Optimization production of exopolysaccharide from Leuconostoc lactis L2 and its partial characterization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 159, 630–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuzaki, C.; Takagaki, C.; Tomabechi, Y.; Forsberg, L.S.; Heiss, C.; Azadi, P.; Matsumoto, K.; Katoh, T.; Hosomi, K.; Kunisawa, J.; et al. Structural characterization of the immunostimulatory exopolysaccharide produced by Leuconostoc mesenteroides strain NTM048. Carbohydr. Res. 2017, 448, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyash, M.; Abu-Jdayil, B.; Olaimat, A.; Esposito, G.; Itsaranuwat, P.; Osaili, T.; Obaid, R.; Kizhakkayil, J.; Liu, S.-Q. Physicochemical, bioactive and rheological properties of an exopolysaccharide produced by a probiotic Pediococcus pentosaceus M41. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 229, 115462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Zou, S.; Liang, D.; Luan, L. Structural characterization, antioxidant and hepatoprotective activities of polysaccharides from Sophorae tonkinensis Radix. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 184, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Qian, J.; Zhou, D. Analysis on the Changes of Functional Groups after Coal Dust Explosion at Different Concentrations Based on FTIR and XRD. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2020, 193, 2482–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayalakshmi, S.; Yoo, D.-S.; Kim, D.-G.; Chelliah, R.; Barathikannan, K.; Aloo, S.-O.; Tyagi, A.; Yan, P.; Shan, L.; Gebre, T.S.; et al. Fermented Perilla frutescens leaves and their untargeted metabolomics by UHPLC-QTOF-MS reveal anticancer and immunomodulatory effects. Food Biosci. 2023, 56, 103065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayalakshmi, S.; Adeyemi, D.E.; Choi, I.Y.; Sultan, G.; Madar, I.H.; Park, M.-K. Comprehensive in silico analysis of lactic acid bacteria for the selection of desirable probiotics. LWT 2020, 130, 109617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.; Shah, M.D.; Shah, L.; Lee, P.-C.; Khan, I. Bacterial polysaccharides—A big source for prebiotics and therapeutics. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1031935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhuri, K.V.; Prabhakar, K.V. Microbial Exopolysaccharides: Biosynthesis and Potential Applications. Orient. J. Chem. 2014, 30, 1401–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vuyst, L.; Degeest, B. Heteropolysaccharides from lactic acid bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 1999, 23, 153–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dilna, S.V.; Surya, H.; Aswathy, R.G.; Varsha, K.K.; Sakthikumar, D.N.; Pandey, A.; Nampoothiri, K.M. Characterization of an exopolysaccharide with potential health-benefit properties from a probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum RJF4. LWT 2015, 64, 1179–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, X.; Li, Z.; Ma, K.; Zhang, C.; Chen, X.; Wang, G.; Yang, L.; Dong, M.; Rui, X.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Structural characterization and immunomodulatory activity of an exopolysaccharide produced by Lactobacillus helveticus LZ-R-5. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 235, 115977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Saravanakumar, K.; Sathiyaseelan, A.; Park, S.; Hu, X.; Wang, M.-H. Cellular antioxidant properties of nontoxic exopolysaccharide extracted from Lactobacillales (Weissella cibaria) isolated from Korean kimchi. LWT 2022, 154, 112727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayabaskar, P.; Babinastarlin, S.; Shankar, T.; Sivakumar, T.; Anandapandian, K.T.K. Quantification and characterization of exopolysaccharides from Bacillus subtilis (MTCC 121). Adv. Biol. Res. 2011, 5, 71–76. [Google Scholar]
- Ai, L.; Guo, Q.; Ding, H.; Guo, B.; Chen, W.; Cui, S.W. Structure characterization of exopolysaccharides from Lactobacillus casei LC2W from skim milk. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 56, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, K.Y.; Jaiswal, A.K.; Jaiswal, S. Biopolymer-Based Sustainable Food Packaging Materials: Challenges, Solutions, and Applications. Foods 2023, 12, 2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajoka, M.S.R.; Mehwish, H.M.; Fang, H.; Padhiar, A.A.; Zeng, X.; Khurshid, M.; He, Z.; Zhao, L. Characterization and anti-tumor activity of exopolysaccharide produced by Lactobacillus kefiri isolated from Chinese kefir grains. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 63, 103588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, X.; Tian, Z.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Z. Characterization of an exopolysaccharide produced by Lactobacillus plantarum YW11 isolated from Tibet Kefir. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 125, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyasov, I.R.; Beloborodov, V.L.; Selivanova, I.A.; Terekhov, R.P. ABTS/PP Decolorization Assay of Antioxidant Capacity Reaction Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, G.; Chen, Y.; Wang, C.; Yang, R.; Bin, X. Purification and characterization of exopolysaccharide produced by Weissella cibaria YB-1 from pickle Chinese cabbage. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 1315–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, D.; Kim, D.-H.; Kang, I.-B.; Kim, H.; Song, K.-Y.; Kim, H.-S.; Seo, K.-H. Characterization and antibacterial activity of a novel exopolysaccharide produced by Lactobacillus kefiranofaciens DN1 isolated from kefir. Food Control 2017, 78, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, A.K.; Ayyash, M.M.; Olaimat, A.N.; Osaili, T.M.; Al-Nabulsi, A.A.; Shah, N.P.; Holley, R. Exopolysaccharides as Antimicrobial Agents: Mechanism and Spectrum of Activity. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 664395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, E.; Salimi, F.; Imanparast, S.; Mansour, F. Isolation and characterization of exopolysaccharide derived from Lacticaseibacillus paracasei AS20(1) with probiotic potential and evaluation of its antibacterial activity. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 75, 967–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Nam, J.H.; Rod-In, W.; Monmai, C.; Jang, A.-Y.; You, S.; Park, W.J. Korean Ginseng Berry Polysaccharide Enhances Immunomodulation Activities of Peritoneal Macrophages in Mice with Cyclophosphamide-Induced Immunosuppression. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 33, 840–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, T.W.; Wang, S.L. Recent advances in exopolysaccharides from Paenibacillus spp.: Production, isolation, structure, and bioactivities. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1847–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Wang, F. Polysaccharides: Candidates of promising vaccine adjuvants. Drug Discov. Ther. 2015, 9, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kany, S.; Vollrath, J.T.; Relja, B. Cytokines in inflammatory disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.-G.; Lee, H.J.; Cho, J.-Y.; Kim, K.; Yang, S.J.; Kim, D. Anti-inflammatory effects of sucrose-derived oligosaccharides produced by a constitutive mutant L. mesenteroides B-512FMCM dextransucrase in high fat diet-fed mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 477, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laiño, J.; Villena, J.; Kanmani, P.; Kitazawa, H. Immunoregulatory Effects Triggered by Lactic Acid Bacteria Exopolysaccharides: New Insights into Molecular Interactions with Host Cells. Microorganisms 2016, 4, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).