Machine-Learning-Based Biomechanical Feature Analysis for Orthopedic Patient Classification with Disc Hernia and Spondylolisthesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
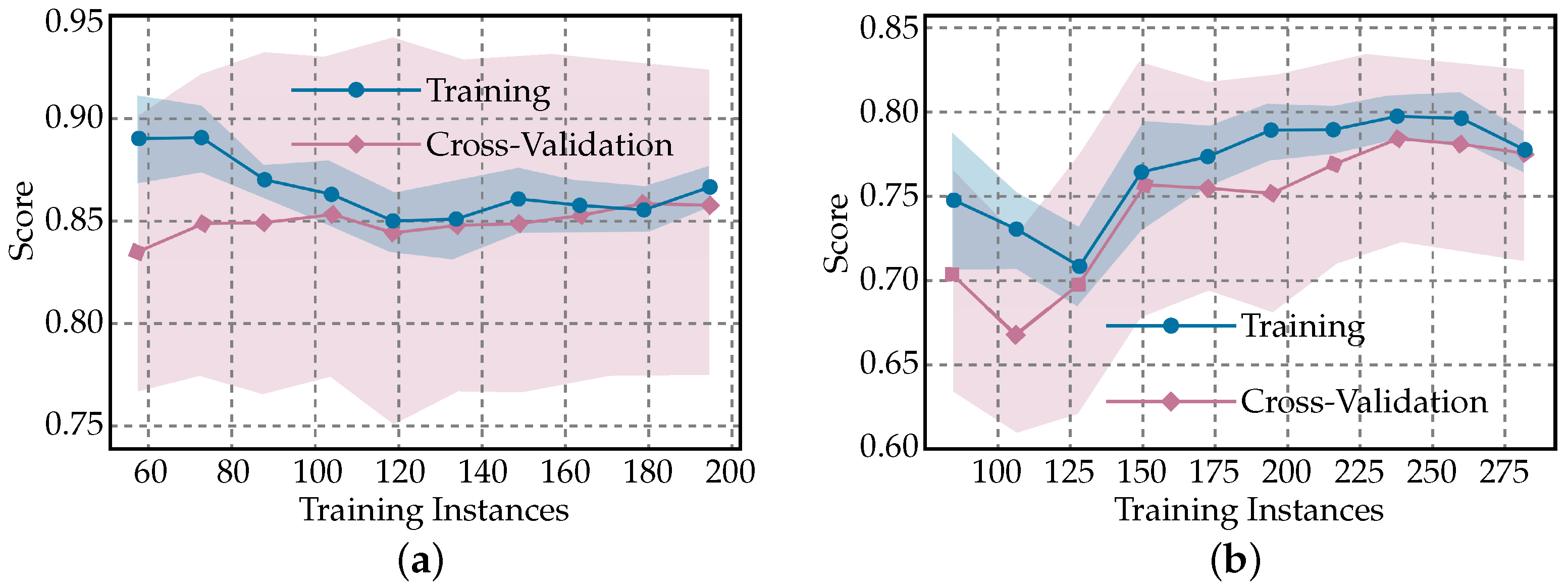
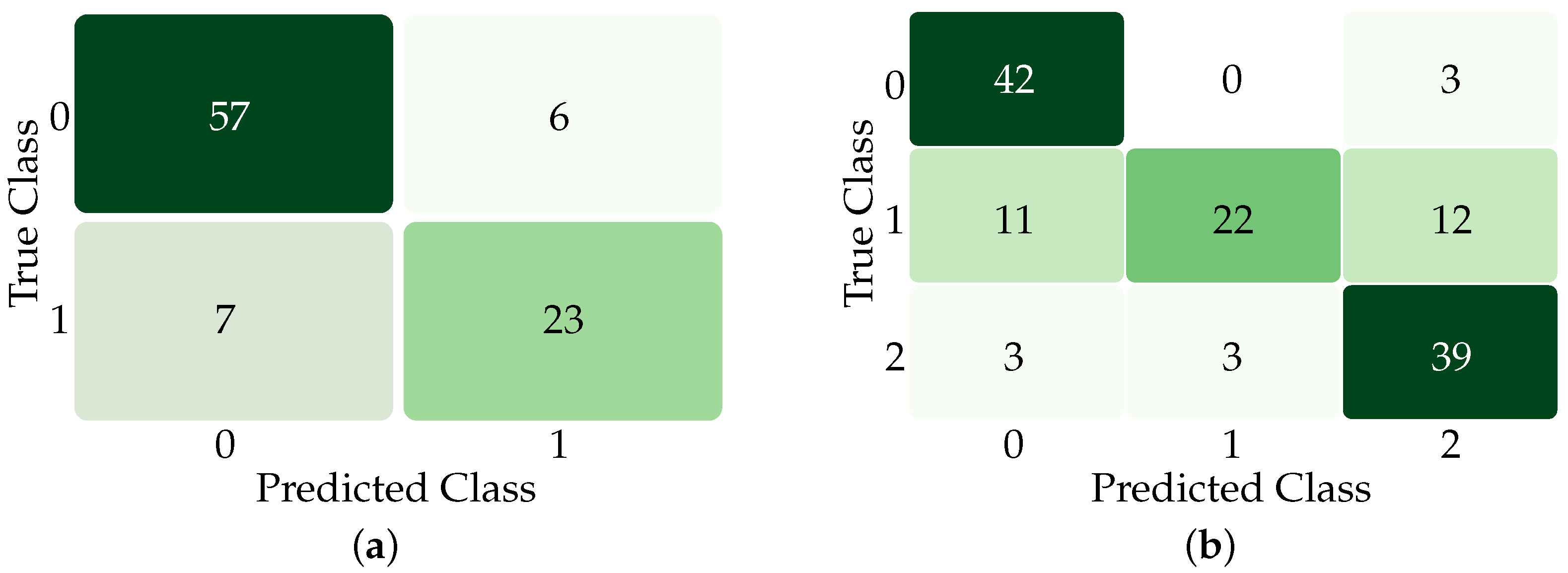
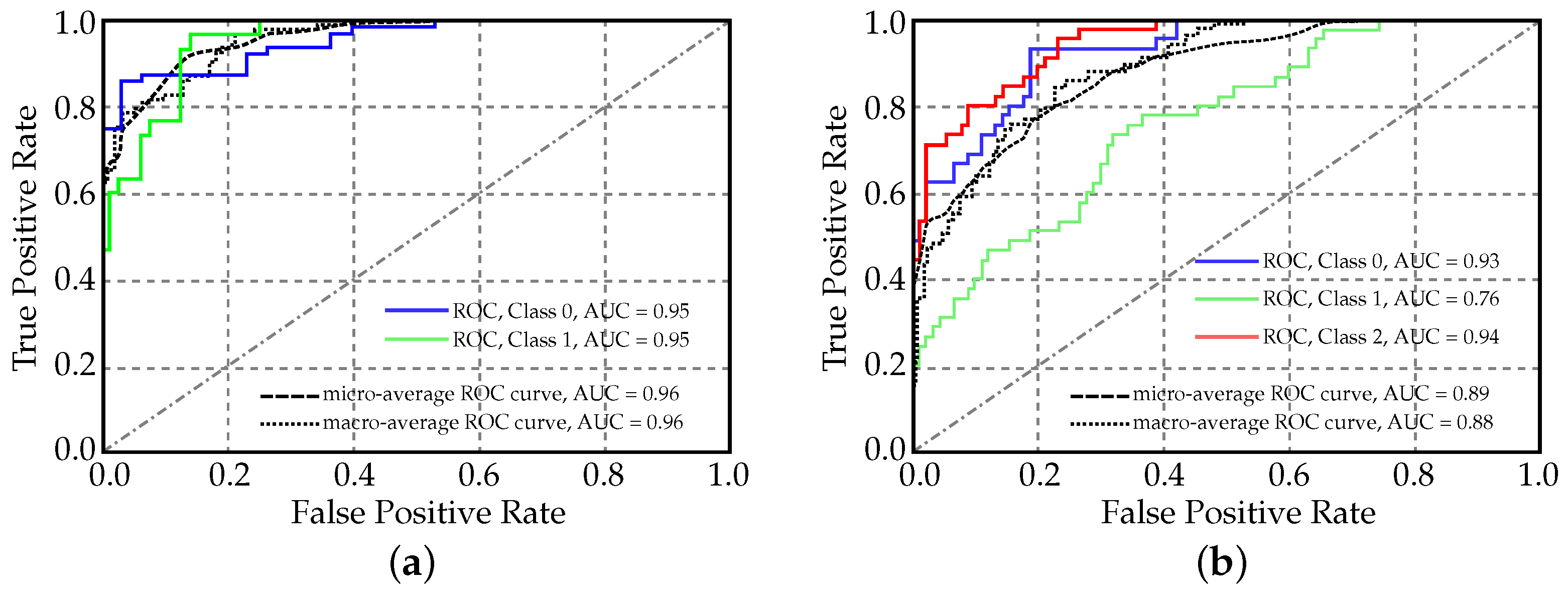
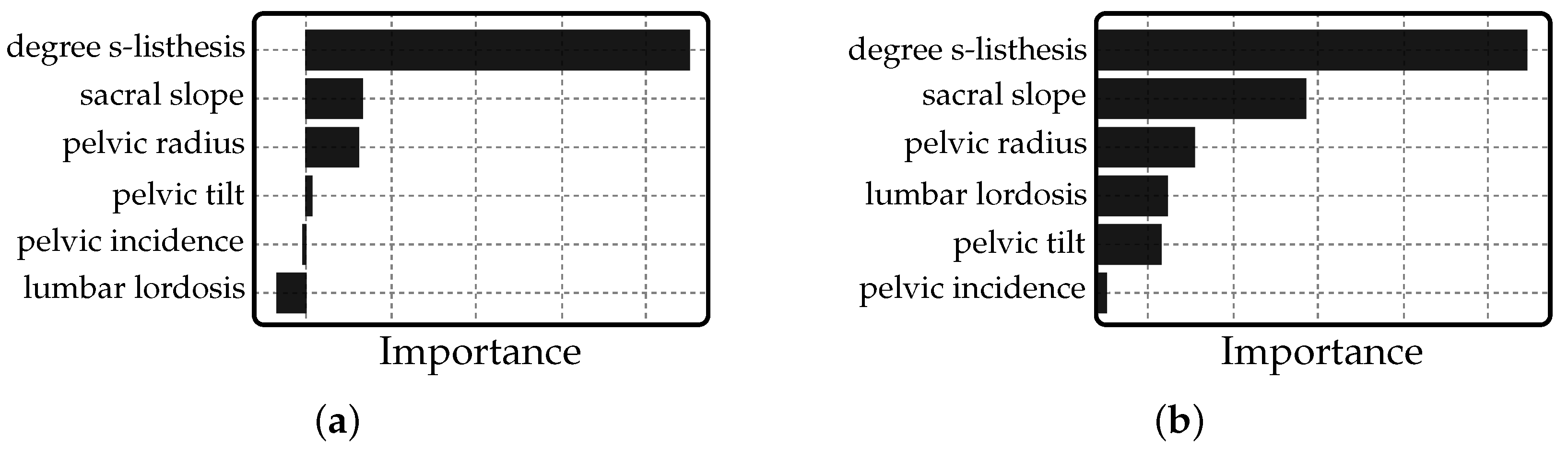
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ML | Machine Learning |
| IVD | Lumbar Intervertebral Disc |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| THP | Total Hip Arthroplasty |
| LBP | Low Back Pain |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
References
- Adams, M.A.; Roughley, P.J. What is Intervertebral Disc Degeneration, and What Causes It? Spine 2006, 31, 2151–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordon, J.; Konstantinou, K.; O’Dowd, J. Herniated lumbar disc. BMJ Clin. Evid. 2009, 2009, 1118. [Google Scholar]
- Qaraghli, M.I.A.; Jesus, O.D. Lumbar Disc Herniation. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Wiltse, L.L. The Etiology of Spondylolisthesis. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 1962, 44, 539–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bydon, M.; Alvi, M.A.; Goyal, A. Degenerative Lumbar Spondylolisthesis. Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 30, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganju, A. Isthmic spondylolisthesis. Neurosurg. Focus 2002, 13, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dydyk, A.M.; Massa, R.N.; Mesfin, F.B. Disc Herniation. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Bednar, D.A. Cauda equina syndrome from lumbar disc herniation. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2015, 188, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KD, W. Spondylolisthesis. In Campbell’s Operative Orthopaedics, 14th ed.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2021; Chapter 40. [Google Scholar]
- Tenny, S.; Hanna, A.; Gillis, C.C. Spondylolisthesis. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Padash, S.; Mickley, J.P.; Vera Garcia, D.V.; Nugen, F.; Khosravi, B.; Erickson, B.J.; Wyles, C.C.; Taunton, M.J. An Overview of Machine Learning in Orthopedic Surgery: An Educational Paper. J. Arthroplast. 2023, 38, 1938–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toma, M.; Wei, O.C. Predictive Modeling in Medicine. Encyclopedia 2023, 3, 590–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouzrokh, P.; Wyles, C.C.; Philbrick, K.A.; Ramazanian, T.; Weston, A.D.; Cai, J.C.; Taunton, M.J.; Lewallen, D.G.; Berry, D.J.; Erickson, B.J.; et al. A Deep Learning Tool for Automated Radiographic Measurement of Acetabular Component Inclination and Version After Total Hip Arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2021, 36, 2510–2517.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouzrokh, P.; Ramazanian, T.; Wyles, C.C.; Philbrick, K.A.; Cai, J.C.; Taunton, M.J.; Maradit Kremers, H.; Lewallen, D.G.; Erickson, B.J. Deep Learning Artificial Intelligence Model for Assessment of Hip Dislocation Risk Following Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty From Postoperative Radiographs. J. Arthroplast. 2021, 36, 2197–2203.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Antoni, F.; Russo, F.; Ambrosio, L.; Bacco, L.; Vollero, L.; Vadalà, G.; Merone, M.; Papalia, R.; Denaro, V. Artificial Intelligence and Computer Aided Diagnosis in Chronic Low Back Pain: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, Z.; Liu, L.; Ren, G.; Guo, Z.; Xu, L.; Yin, X.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Natural Language Processing-Driven Artificial Intelligence Models for the Diagnosis of Lumbar Disc Herniation with L5 and S1 Radiculopathy: A Preliminary Evaluation. World Neurosurg. 2024, 189, e300–e309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirries, A.; Geiger, F.; Hammad, A.; Bäumlein, M.; Schmeller, J.N.; Blümcke, I.; Jabari, S. AI Prediction of Neuropathic Pain after Lumbar Disc Herniation-Machine Learning Reveals Influencing Factors. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Qiao, X.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, L.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Q. Artificial Intelligence-Based CT Imaging on Diagnosis of Patients with Lumbar Disc Herniation by Scalpel Treatment. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 3688630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekbolatova, M.; Mayer, J.; Ong, C.W.; Toma, M. Transformative Potential of AI in Healthcare: Definitions, Applications, and Navigating the Ethical Landscape and Public Perspectives. Healthcare 2024, 12, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, C. Biomechanical Features of Orthopedic Patients. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/uciml/biomechanical-features-of-orthopedic-patients (accessed on 9 September 2024).
- Chen, H.; Chen, J.; Ding, J. Data Evaluation and Enhancement for Quality Improvement of Machine Learning. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2021, 70, 831–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebert, J.; Joeckel, L.; Heidrich, J.; Trendowicz, A.; Nakamichi, K.; Ohashi, K.; Namba, I.; Yamamoto, R.; Aoyama, M. Construction of a quality model for machine learning systems. Softw. Qual. J. 2022, 30, 307–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, P.; Knight, S. Misdiagnosis in Sports Medicine. Curr. Sports Med. Rep. 2002, 1, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, B.N.; Pedersen, K.Z.; Andersen, O.; Meier, N. Minimizing the Risk of Diagnostic Errors in Acute Care for Older Adults: An Interdisciplinary Patient Safety Challenge. Healthcare 2024, 12, 1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, Y.; Hong, G.S.; Park, K.J.; Lee, C.W.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.O. Impact of diagnostic errors on adverse outcomes: Learning from emergency department revisits with repeat CT or MRI. Insights Into Imaging 2021, 12, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dora, C.; Wälchli, B.; Elfering, A.; Gal, I.; Weishaupt, D.; Boos, N. The significance of spinal canal dimensions in discriminating symptomatic from asymptomatic disc herniations. Eur. Spine J. 2002, 11, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnally, C.J., III; Hanna, A.; Varacallo, M. Lumbar Degenerative Disk Disease; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Epstein, N.E.; Hood, D.C. Unnecessary spinal surgery: A prospective 1-year study of one surgeon’s experience. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2011, 2, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Model | Accuracy | AUC | Recall | Precision | F1 | Kappa | MCC | TT (Sec) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Logistic Regression | 0.8576 | 0.9294 | 0.8576 | 0.8683 | 0.8590 | 0.6840 | 0.6910 | 0.2380 |
| Ridge Classifier | 0.8437 | 0.8922 | 0.8437 | 0.8524 | 0.8359 | 0.6188 | 0.6385 | 0.0050 |
| Linear Discriminant Analysis | 0.8437 | 0.8922 | 0.8437 | 0.8534 | 0.8377 | 0.6255 | 0.6430 | 0.0050 |
| Gradient Boosting Classifier | 0.8338 | 0.9106 | 0.8338 | 0.8373 | 0.8329 | 0.6180 | 0.6230 | 0.0190 |
| Extra Trees Classifier | 0.8299 | 0.9167 | 0.8299 | 0.8302 | 0.8237 | 0.5914 | 0.6009 | 0.0240 |
| Random Forest Classifier | 0.8251 | 0.9078 | 0.8251 | 0.8261 | 0.8232 | 0.5934 | 0.5976 | 0.0270 |
| Light Gradient Boosting Machine | 0.8208 | 0.8935 | 0.8208 | 0.8233 | 0.8181 | 0.5838 | 0.5894 | 0.0680 |
| K Neighbors Classifier | 0.8121 | 0.8901 | 0.8121 | 0.8221 | 0.8128 | 0.5771 | 0.5842 | 0.0120 |
| Quadratic Discriminant Analysis | 0.7931 | 0.9185 | 0.7931 | 0.8615 | 0.7985 | 0.5947 | 0.6362 | 0.0050 |
| Naive Bayes | 0.7792 | 0.8823 | 0.7792 | 0.8286 | 0.7847 | 0.5494 | 0.5772 | 0.0050 |
| Decision Tree Classifier | 0.7792 | 0.7474 | 0.7792 | 0.7828 | 0.7785 | 0.4962 | 0.4994 | 0.0060 |
| Ada Boost Classifier | 0.7606 | 0.8293 | 0.7606 | 0.7634 | 0.7563 | 0.4421 | 0.4501 | 0.0140 |
| SVM-Linear Kernel | 0.7002 | 0.8865 | 0.7002 | 0.7062 | 0.6489 | 0.2789 | 0.3289 | 0.0060 |
| Dummy Classifier | 0.6773 | 0.5000 | 0.6773 | 0.4587 | 0.5470 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0040 |
| Model | Accuracy | AUC | Recall | Precision | F1 | Kappa | MCC | TT (Sec) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Random Forest Classifier | 0.9083 | 0.9783 | 0.9083 | 0.9186 | 0.9066 | 0.8623 | 0.8689 | 0.0310 |
| Gradient Boosting Classifier | 0.8989 | 0.0000 | 0.8989 | 0.9067 | 0.8979 | 0.8482 | 0.8528 | 0.0520 |
| Extra Trees Classifier | 0.8956 | 0.9833 | 0.8956 | 0.9030 | 0.8942 | 0.8432 | 0.8478 | 0.0310 |
| Light Gradient Boosting Machine | 0.8891 | 0.9681 | 0.8891 | 0.8997 | 0.8875 | 0.8335 | 0.8401 | 0.2950 |
| Decision Tree Classifier | 0.8634 | 0.8978 | 0.8634 | 0.8758 | 0.8608 | 0.7949 | 0.8034 | 0.0080 |
| Logistic Regression | 0.8446 | 0.0000 | 0.8446 | 0.8568 | 0.8451 | 0.7667 | 0.7720 | 0.0330 |
| Ridge Classifier | 0.8225 | 0.0000 | 0.8225 | 0.8354 | 0.8148 | 0.7336 | 0.7439 | 0.0080 |
| Linear Discriminant Analysis | 0.8225 | 0.0000 | 0.8225 | 0.8286 | 0.8201 | 0.7335 | 0.7385 | 0.0090 |
| Naive Bayes | 0.7875 | 0.9115 | 0.7875 | 0.7946 | 0.7806 | 0.6813 | 0.6895 | 0.0100 |
| Quadratic Discriminant Analysis | 0.7872 | 0.0000 | 0.7872 | 0.7967 | 0.7846 | 0.6804 | 0.6871 | 0.0090 |
| K Neighbors Classifier | 0.5943 | 0.7767 | 0.5943 | 0.6310 | 0.5959 | 0.3910 | 0.4013 | 0.0120 |
| Ada Boost Classifier | 0.5106 | 0.0000 | 0.5106 | 0.5668 | 0.4622 | 0.2668 | 0.3048 | 0.0190 |
| SVM-Linear Kernel | 0.4200 | 0.0000 | 0.4200 | 0.3752 | 0.2916 | 0.1230 | 0.1951 | 0.0100 |
| Dummy Classifier | 0.3175 | 0.5000 | 0.3175 | 0.1009 | 0.1531 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0070 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nasef, D.; Nasef, D.; Sawiris, V.; Girgis, P.; Toma, M. Machine-Learning-Based Biomechanical Feature Analysis for Orthopedic Patient Classification with Disc Hernia and Spondylolisthesis. BioMedInformatics 2025, 5, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics5010003
Nasef D, Nasef D, Sawiris V, Girgis P, Toma M. Machine-Learning-Based Biomechanical Feature Analysis for Orthopedic Patient Classification with Disc Hernia and Spondylolisthesis. BioMedInformatics. 2025; 5(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics5010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleNasef, Daniel, Demarcus Nasef, Viola Sawiris, Peter Girgis, and Milan Toma. 2025. "Machine-Learning-Based Biomechanical Feature Analysis for Orthopedic Patient Classification with Disc Hernia and Spondylolisthesis" BioMedInformatics 5, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics5010003
APA StyleNasef, D., Nasef, D., Sawiris, V., Girgis, P., & Toma, M. (2025). Machine-Learning-Based Biomechanical Feature Analysis for Orthopedic Patient Classification with Disc Hernia and Spondylolisthesis. BioMedInformatics, 5(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics5010003







