Abstract
Existing literature on dolphin-fisheries interaction focused on Greece reveals both an undeveloped area for research, but also a lack of relevant data in this field. Although imperative, relevant research has been slow on innovation and cooperation among universities, official bureaus, and NGOs that are obliged to work together as European and national laws dictate. Most of the research in this new field focuses on the interaction between marine mammals and local fisheries, suggesting that this relationship may be problematic for both parties since the former are being treated (at least occasionally) with brutality, while the latter try to deal with economic loss. Dolphins and fishermen operate within the same ecological niches for their survival, the main area of conflict being nutritious fish. Anthropological research on ethnic identity has long dealt with antagonistic relationships over resources between adjacent groups of people. Marine biologists’ research in Greece focuses on the human factor, and some of its shortcomings may well be seen as the result of limited, or an absence of, training in social sciences. This article attempts to draw from anthropological theory to shed light on a particular symbiosis between humans and dolphins. Multidisciplinary approaches gain ground in a wide range of research interests and seem to be fruitful in terms of theoretical and practical results.
1. Introduction
Greek fishermen employ modern technology to catch their pray, which they then provide to the consumers directly or indirectly in a market-oriented economy aiming for financial gain [1]. Based on a classification system that diminishes the importance of preservation over the security of profit, human action at the local level may be seen as falling into the category of negative reciprocity in Sahlins’ [2] scheme of exchange. In his continuum, Sahlins suggests that the unsociable extreme is about taking something for nothing, classic examples of which “exchange” can be theft or war. The Greek financial crisis of recent years, along with the socioeconomic effects of the pandemic, seem to have amplified preexisting issues and justify the prioritization of survival [3]. Within these strained circumstances, local fishers at Pagasitikos Gulf (Greece, eastern Mediterranean Sea) see the maximization of profit as the only viable solution, even at the expense of the natural environment.
The dynamic field of the Cetaceans-Fisheries complex is looking for answers on the way such a problematic interaction is instantiated at the local level due to overlapping ecological niches, while at the same time drawing from the wider context of capitalism that permeates levels of interaction and fashions socially constructed realities [4,5]. Although the issue of agency is important in said studies, a combination of Bailey’s [6] perception of the rational “strategizing man”, along with Tsing’s [7] methods, shift the focus on more-than-human associations to better understand how such interactions are shaped by and reshape cultural and natural landscapes [8,9]. Anthropological approaches in different parts of the world take into account the local cultural aspect in relation to the wider economic system that the locality is part of in order to propose culturally compatible solutions [10,11,12].
Currently, dolphins are regarded in many countries as conservation icons [13,14,15], and any interactions with humans is subject to animal welfare concerns [16]. Certain species and populations are likely to mitigate climate related changes [17], including those with a specific site-fidelity and home range [18]. Such climate changes may shift algal, plankton, fish abundance, and distribution in conjunction with oceanographic alterations including increase in temperature, a rise in sea levels, alterations in salinity, and ocean circulation [19]. Thus, the likely interaction between fisheries and cetaceans may rely on food availability with respect to environmental features. Various research methods employed in the field, such as interviews [20] and food-web modeling [15], reveal that cetacean-human interactions generally intensify in times of overexploitation of resources from the part of the fisheries, as in the case of overfishing [21,22,23]. Such food-resource niche overlap suggests a rather over the top competition, with severe potential ecological and economic losses that can arise from marine mammal population decline [24]. On the other hand, societies are making decisions that influence climate change, e.g., [25] and any conservation plans on the latter should point to increasing the resilience of cetacean species in the face of climate change [26]. Thus, cetaceans’ conservation has a social and economic value that is identified when the issue is treated according to a holistic vision [27].
Friese [28] argues that the documented fisheries’ crisis in the Mediterranean has an augmented impact on the local small-scale fishing effort. Local fishermen consider the absence of state intervention, fish-stock reduction, and economic loss due to the destruction of fishing gear by marine mammals, as well as austerity, to be the main setbacks toward economic security [1]. Despite the fact that the piscatorial products account for 11.4% of the total exported agricultural products according to the Federation of Greek Maricultures, local fisheries have seen a 40% decrease of their income during the time of the pandemic according to estimations articulated by the local Union. To this day, the Greek state seems to favor agricultural production over piscatorial products despite that both sectors are subjected to European laws. Oftentimes, fishers have complained about unequal treatment in the above terms. Although state compensations are prescribed in national and European laws, only a small number of fishers can actually capitalize due to legal setbacks (personal communication). In this case social patterns seem to clash with law, as, for example, a fishing enterprise that is jointly owned by family members cannot be compensated by the state [29].
To contextualize the local reality, we focus on the city of Volos, which is situated in central-eastern Greece (Figure 1) [30] and has therefore been an important city and harbor ever since antiquity. Today, the city counts for around 150,000 inhabitants when Greece’s total population is almost 11 million. Greece’s workforce counts quasi four million people, and out of the almost 20,000 individuals that are occupied directly or indirectly in fishery, only 300 are settled at Volos [31]. Despite the fact that fishing may occupy a peripheral position in economic activity [32], piscatorial products are highly appreciated at Volos due to tradition and eating habits, resulting in a distinct cuisine that has also been commercialized in local restaurants and taverns [33]. Conflict for resources has been intensified at Volos, especially for local fisheries, since the 19th century when the city’s industrialization process began [34]. Adaptation to the new antagonistic socioeconomic conditions became a matter of survival for the local fisheries. Circumstances became even more strained since 2008 with the implementation of neoliberal policies in an attempt to deal with Greece’s debt crisis [3], which came after at least two decades of economic growth within capitalism. This triggered a reaction toward making up economic loss and maintaining previous standards of living through the exploitation of resources [35].
Figure 1.
Study area of the 34 collected questionnaires from small-scale fishermen in the harbor of the city of Volos, Pagasitikos Gulf, central Greece after [30].
This study is based on archival research and interviews with local fishers in the area of Volos, conducted under the auspices of the University of Thessaly between 2018 and 2020. An interdisciplinary approach combining marine biology with sociocultural anthropology is employed to research human/dolphin interaction at the given area. Our interviews with local fishers reveal a growing concern for economic security that does not always promote conservation. On the contrary, issues of ownership that have been raised as a response to the economic crisis hint on a sometimes conscious degradation of the natural environment for the sake of profit. This society’s trajectory informs an anthropocentric view of the natural surrounding that is intertwined with notions of ownership over landscape and seascape. The aim of this article is to shed light on the conflictual relationship between fisheries and dolphins in the specific area, and thus contribute to future research on the subject-matter by providing a case-study that is locally grounded. Taking into account the importance of the local context in the conservation of biodiversity, we attempt to analyze a range of parameters that play an important role in providing culturally relevant solutions toward sustainable development.
2. Materials and Methods
A total of 34 questionnaires were collected from small-scale fishermen in the harbor of the city of Volos (Pagasitikos Gulf, central Greece—Figure 1). A semi-structured interview was based on ten open-ended questions, which are listed below. These questions guided the conversation and allowed the interviewers to ensure flow, but did not limit the interviewees’ answers. The discussion began after a short introduction on the scope of the research and the ethics involved, clarifying that anonymity is ensured. The interviewers kept notes on all pieces of information being communicated, the interviewees responding at their own pace and sharing information on fishing gear voluntarily that was then cross-checked with the official data provided by the Periphery.
- What is your relationship with the sea?
- Is fishing a difficult profession?
- Is there any kind of orientation/updating on the sector?
- Is there any kind of support? If yes, from whom?
- Are there monetary compensations as in the case of agriculture?
- Is overfishing a reality?
- How would you describe the relationship between fishers and marine mammals?
- Are you aware of any technological equipment that discourages predations?
- Do you believe that a healthier ecosystem would have a positive impact on the sector?
- Would you be interested in exchanging ideas and knowledge with experts in the field toward a better understanding of the issues that concern the sector?
The first question is meant to open the discussion, make sure that the interviewees were still active in the sector, and reveal perceptions of the sea reflecting on the local classification system. Fishers see themselves and claim to be seen by others as a distinct group within the local and national socioeconomic system. The vast majority of the interviewees attested to the family tradition of the sector, explaining that their love for, fear of, and respect toward the sea is based on a particular enculturation process within their family unit. Most joined the sector at a young age and along with close family members. The second question focused on the difficulties local fisheries meet, revealing patterns validated by relevant bibliography in terms of depredation and the destruction of fishing gear. However, it also provided insights in the local experience, as depredation was suggested to be becoming the main issue of concern in the last fifteen years, a period which coincides with the recent economic depression. The fourth question opted for more detailed answers on the kind of support fisheries have, or should have. Compensations, or the lack of, revealed a perfect consensus.
There was unanimity among all interviewees that the state should help the sector under these strained circumstances. The fifth question aimed at revealing perceptions of the self in contrast to neighbor agricultural areas that constitute the backbone of the Greek economy. A definition of the self by opposition to the “other” was not based on occupation but rather on the diverse support of the state toward these two economic activities. Given the economic context, question 6 was meant to test if overfishing that was mentioned in earlier discussions is a coping mechanism for income loss or a practice that links to lack of environmental awareness.
Question seven focused on the relationship between fishers and marine mammals, with emphasis put on dolphins by the interviewers. Fishers claimed that depredation is a great issue of concern since damages are most common nowadays and the relevant costs are just unsustainable. Following almost naturally, the eighth question aimed at revealing measures being employed against depredation. The last two questions were set to explore any possible future cooperation toward culturally compatible solutions. Fishers extended invitations to the interviewers.
The vessels operated primarily gill nets with a variety of target species. The answers of the questionnaires were analyzed regarding the negative impact of marine mammals on nets and fish depredation. Negative impacts were focused on the usage of acoustic pingers, fishing ground, time of day, and depth of nets soaking.
A contigency ad-hoc analysis was performed on the frequency values [36] with respect to the collected responses (Fisher exact test). For underlying the value of the responses, a Principal component analysis was assessed using Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) method, and all variables were scaled so that they would be equally important (variance = 1) [37]. All analyses were implemented in R v 3.6.0 software [38].
3. Results
Analysis shows primarily that acoustic pingers did not benefit depredation or net damage, suggesting that the usage of this apparatus was useless. Paired comparisons for depth (Figure 2) were statistically significant (p < 0.05), meaning that both depredation and net damage frequency were higher in shallower waters (<200 m). More on spatial impact, the fishing ground was significantly correlated with depredation possibly due to a complex association between target species and dolphins’ prey-favorites (Figure 2). However, there was a different impact regarding the time of day of net soaking. Net damage was always significant regardless of the time, but afternoon hours of net soaking were highly correlated with the negative impacts of depredation. Overall, Principal Component Analyses (Figure 3) revealed that acoustic pingers were not perceived to play a role in the rate of catch-loss, and that the combination of fishing ground and time of the day may be an important factor.
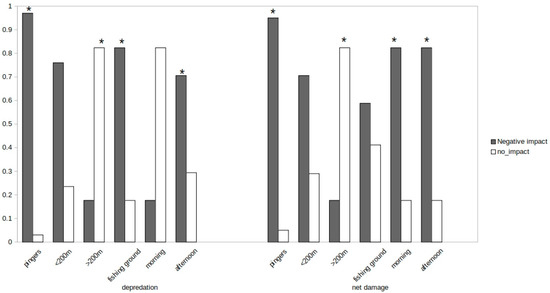
Figure 2.
Frequencies on negative impact on fish depredation and net damage with respect to usage of acoustic pingers, depth, fishing ground, and time of the day of net soaking. Stars (*) denote significance level (p < 0.05).
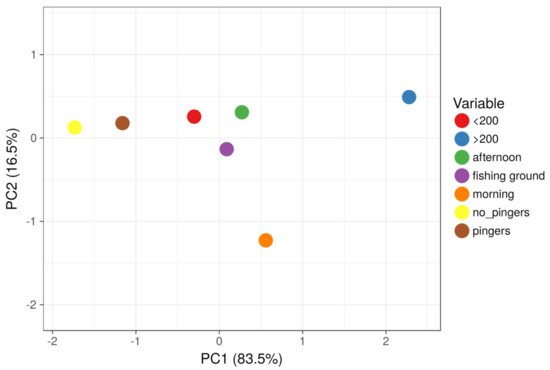
Figure 3.
PCA plot on the negative impact on depredation and net damage. Circles represent the frequencies of fishermen responses with respect to depth, fishing ground, time of day, and acoustic pingers.
Interviews revealed that the type of fishing gear plays a pivotal role in the interactions with cetaceans. Compared to hook and lines gear gillnets were identified as the most affected ones. Another factor frequently indicated was the fishing ground; namely, fishing within the Gulf or in the open sea. 80% of the interviewees believed that chances to conflict with dolphins are higher when fishing nearshore rather than offshore. Moreover, a few fishermen (<5%) mentioned that weather conditions or the moon cycle may have some impact; since such questions were not included in our methodology, relevant data was omitted.
Interestingly, a rather big part of the fishers (>90%) provided suggestions about how to solve the problem of cetacean–fisheries interactions. These varied from measures to benefit fisheries such as financial compensation to the extreme of reducing local cetacean populations. On the other hand, measures that could benefit cetaceans comprised mainly of the need to find alternative cetacean-friendly fishing methods. To this extent, it was also emphasized that environmental education should be offered by the local university.
4. Discussion
Diet and space render human/dolphin interaction antagonistic over the natural resources that each party makes use of for its survival. For fishers, fish is a product sold for economic profit while some of the species fished are the most nutritious for the dolphins. Accordingly, damage to fishing gear may not be affordable to fishermen, but also dolphins may find it easier to feed on trapped fish even if this practice can be sometimes lethal [39,40,41]. Such a symbiosis can be described at least as peculiar, in the sense that there is an unavoidable coexistence of two species with conflicting interests, unlike other cases such as herdsmen and their flock that are inter-depended for their survival [42]. In terms of the employed fishing strategies, Pardalou and Tsikliras [43] make a useful distinction between “inflexible and adaptive” fishers. The authors argue that some of the fishers may try to find solutions to tackle the issue at hand, but one third of them holds a very negative view of the dolphins which they describe as “pests”, “picky choosers”, and “glutton”.
Questionnaires revealed that all fishers lack any kind of orientation and updating on the sector, blaming primarily the state for indifference to their situation. Their case was often compared to Cyprus and other European countries, where fishers retained the state to be playing “a serious and active role”. Many interviewees were well informed on the legal context and aware of relevant quantitative data, which they claimed to be more easily accessible in other countries. In fact, there was empathy toward agriculturalists for being exposed to the natural elements as fishers are, despite the great financial gap between the two sectors. However, fishers hold that the destruction of agricultural products can be more easily assessed by the state in comparison to the destruction of fishing gear. Although overfishing seems to be taboo, a number of interviewees admitted to existence of the issue, claiming that it is the only way for them to survive within an antagonistic environment. Others suggested that the quantity of fish is stable, but the size of fish is reduced. Some stated that bigger boats damage the seabed severely with their fishing gear, concluding that “if we keep going like that our children will not be able to make a living from the sea.”
Fishers seemed to perceive as an oxymoron that the presence of dolphins is indicative of a healthy natural environment and increased fish stock, but at the same time cases of depredation become more often. An abundance of fish-stock should reduce depredation, and thus net damages and economic loss. Overall, ecological consciousness conflicted with economic activity. Fishers understand that financial gain is directly linked to the quality of the natural environment. However, there is a great discrepancy between the ideal and what is actual. Answers reveal a great concern for the here and now; fishers cannot afford to reduce their catch since this could lead to the extinction of the sector within a very short period of time. Conservation seems to be an issue of interest, coming in second to finance.
Our study reveals that pingers did not benefit depredation or net damage. Instead, the usage of these apparatuses seems to help marine mammals spot their prey. Fishermen stated that after a couple of months or so, dolphins were accustomed to this technology despite the fact that different sounds were produced by the pinger. Associations with depth show that both depredation and net damage frequency were higher and almost inevitable in shallower waters (<200 m), especially due to the geo-morphology of the Pagasitikos Gulf (maximum depth of Pagasitikos Gulf ~100 m). Speaking of spatial impact, the fishing ground was significantly correlated with depredation, possibly due to a complex association between fisheries’ target species and dolphins’ prey-favorites. However, there was a different impact regarding the time of day of net soaking; net damage always had a significant negative impact regardless of the time of day, whereas net soaking was highly correlated with negative impact on depredation during afternoon hours. Taking into account the latter and the significant association between fishing ground and depredation, one could argue that dolphins favor a complex foraging pattern that affect depredation with respect to spatial-temporal social behavior.
In our discussions with local fishermen in Volos, dolphins were paralleled to pigeons. Such descriptions perplex the analysis of ownership issues in regards to the natural environment. Dolphins are seen as intruders in an environment of human economic activity, while just an insignificant percentage of interviewees see it from the other end. However, many fishers were aware of the fact that dolphin-fisheries’ interaction has been intensified within the last few years, which some attribute to fish-stock reduce. It is advantageous for dolphins to feed from nets in terms of fatigue and nutrition, as they spend less energy and chose what they will eat [44,45]. Most often, dolphins consume the most commercial products, such as common sole, red mullets and sardinella, proving in yet another way that antagonism between the two species is over diet and space [46]. Antagonism for resources sharpens the distinction between humans and dolphins, offering another dichotomy that informs anthropocentric views of the natural environment in the case of the fishers of Volos [47]. Therefore, fishers may be claiming that the number of dolphins is indicative of the biodiversity and fish-stock in the area, but also stressing that economic loss does not allow a peaceful coexistence between the two species.
Within this context, dolphins become the significant Other that threatens the well-being of Us; namely, local fisher families. The kinds of dolphins most often interacting with fisheries in Greece are the bottlenose and common dolphin [48]. Bottlenose dolphins have a catholic diet and a coastal distribution, and thus their encounters with fisheries are more common. Although common dolphins prefer more open waters to hunt, their depth distribution at around 250 feet may trouble fisheries [49,50,51]. Dolphins live in groups most often of the same kind; the group moves together and its members cooperate for a number of tasks [52,53]. Research documents cooperation and communication among dolphins in order to feed [54]. All our interviewees agreed that dolphins are smart, and because of this, one of the fishers suggested that the only way to protect their property was to kill them (“the only thing they are afraid of is the sound of my shotgun”). Such drastic solutions are often justified by fishers as the only effective strategy to deal with economic loss. After all, fishers claim, analogous policies have been implemented by the state in the past.
Technology has also been employed to deal with this issue, but again with poor results [40,55,56]. In fact, acoustic pingers that were supposed to push dolphins away from fisheries have worked as “dinner bells”. Fishermen at Volos supported that such a result was expected since they have seen dolphins following their boats out the port, suggesting that dolphins are accustomed to mechanical sounds and use them to their advantage. Interestingly enough, although encounters between fishermen and dolphins may be frequent, incidents seem to be the exception. While ruined nets are a constant, only young dolphins are rarely fished, a fact that demonstrates how smart dolphins are and how well they have adapted to the so-called “super-market” effect. Elastic nets are also ineffective since commercial fish can escape from them as easily as dolphins can, the result being economic loss for the fishermen (personal communication with fishers). Compensations to fisheries are also problematic since the processes cannot be easily monitored nor can this measure be implemented horizontally, let alone bureaucratic obstacles in the way [57].
From an ecological point of view, the need to evaluate possible threats posed by climate change to cetaceans is widely accepted and seen as imperative. However, planning should be taking into account the oceanography and geomorphology of each site in relation to the cetaceans’ adaptation and evolutionary dynamics [58]. Foraging strategies, population dynamics, genomic variability, site-fidelity, and home range are likely to affect cetaceans’ ability to survive the impacts of climate change. To this extent, prioritization in high risk fisheries and vulnerable populations due to climate change, along with knowledge transferring to local fishermen for the evaluation of more appropriate fishing techniques, should be pragmatic. Finally, public programs should be developed to assess and reverse the impact of climate change in terms of scale and extent, stressing the potential ecological and economic losses that can arise from marine mammal population decline, by emphasizing the key role of the species in ecosystem functioning and services [59].
5. Conclusions
These data could be essential in improving human-cetacean interactions through the implementation of appropriate management plans. Fishers’ willingness to cooperate and contribute in the development of local-specific management measures useful to mitigate the controversial dolphins-fisheries interactions is extremely promising. However, it is true that some interactions may lead to serious conservation issues for cetaceans and at the same time result in severe economic loss for fishers. Thus, new technological developments and an environmentally friendly political agenda could help minimize socio-economic and environmental costs.
Interdisciplinary approaches help shed light on the complexity of human-cetaceans’ interaction and the way such a relationship is shaped and reshaped by local parameters. Environmental anthropology focuses on local perceptions of the environment and relevant practices [60]. Qualitative data on ethnoecology can complement quantitative approaches provided by marine biologists toward a new balance between people’s needs and environmental conservation. Although the scale of the issue at hand dictates cooperation at the global level, case studies can provide all interested parts with those local details that play a crucial role in rendering any future interventions successful. Sustainability in this case should be the outcome of an uninterrupted cooperation among experts, local people, and the government. Future research on local realities could facilitate said interactions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.V.P. and G.A.G.; Methodology, S.V.P., A.E. and G.A.G.; Software, G.A.G.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, S.V.P., A.K., A.E. and G.A.G.; Writing—Review & Editing, S.V.P. and G.A.G.; Supervision, G.A.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
“Acquisition of Academic teaching experience in new scientists”, Department of Ichthyology and Aquatic Environment, University Thessaly “. MIS Code: 5064860, Ministy of Education Lifelong Learning and Religious Afair, 2014–2020”.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data available on request due to restrictions.
Acknowledgments
Authors would like to thank Niki Mantzafleri from the Dept. of Fisheries (Directorate for Veterinary Service—Magnesia Prefecture, Greece), as she was our contact with the fishers of the study area.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kyvelou, S.S.I.; Ierapetritis, D.G. Fisheries Sustainability through Soft Multi-Use Maritime Spatial Planning and Local Development Co-Management: Potentials and Challenges in Greece. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahlins, M. On the Sociology of Primitive Exchange. In The Relevance of Models in Social Anthropology; Michael, B., Ed.; Tavistock Publications: London, UK, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Streinzer, A. Stretching Money to Pay the Bills: Temporal Modalities and Relational Practices of ‘Getting By’ in the Greek Economic Crisis. Camb. J. Anthropol. 2016, 34, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, S.; Ghosh, U.; Chauhan, H.; Narayanan, N.; Parthasarathy, D. Uncertainties and Vulnerabilities among the Koli Fishers in Mumbai: A Photo Voice Study. Ind. Anthropol. 2018, 48, 65–80. [Google Scholar]
- Carrier, J.G. A Handbook of Economic Anthropology, 2nd ed.; Edward Elgar Publishing Ltd: Cheltenhamm, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, F.G. Politics and Social Change: Orissa in 1959; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Tsing, A.L. More-than-Human Sociality: A Call for Critical Description. In Anthropology and Nature; Kirsten, H., Ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 27–42. [Google Scholar]
- Loring, P.A.; Harrison, H.L.; Gerlach, S.C. Local perceptions of the sustainability of Alaska’s highly contested cook inlet salmon fisheries. Soc. Nat. Resour. 2014, 27, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durrenberger, E.; Pálsson, G. Ownership at Sea: Fishing Territories and Access to Sea Resources. Am. Ethnol. 1987, 14, 508–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabinyi, M. The Politics of Patronage and Live Fish Trade Regulation. In Fishing for Fairness: Poverty, Morality and Marine Resource Regulation in the Philippines; ANU Press: Canberra, ACT, Australia, 2012; pp. 171–190. [Google Scholar]
- Todd, Z. Fish pluralities: Human-animal relations and sites of engagement in Paulatuuq, Arctic Canada. Études Inuit Stud. 2014, 38, 217–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakley, R. ‘Opening Up’ the Village: Canoes, Conservation and Contending with Transformation in Amazonia. Etnofoor 2019, 31, 33–50. [Google Scholar]
- Banaru, D.; Mellon-Duval, C.; Roos, D.; Bigot, J.L.; Souplet, A.; Jadaud, A.; Beaubrun, P.; Fromentin, J.-M. Trophic structure in the Gulf of Lions marine ecosystem (north-western Mediterranean Sea) and fishing impacts. J. Mar. Syst. 2013, 111, 45–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, P.; Libralato, S.; Capezzuto, F.; D’Onghia, G.; Maiorano, P.; Sion, L.; Tursi, A.; Solidoro, C.; Carlucci, R. Ecosystem functioning of two marine food webs in the North-Western Ionian Sea (Central Mediterranean Sea). Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 10198–10212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlucci, R.; Capezzuto, F.; Cipriano, G.; D’Onghia, G.; Fanizza, C.; Libralato, S.; Maglietta, R.; Maiorano, P.; Sion, L.; Tursi, A.; et al. Assessment of cetacean–fishery interactions in the marine food web of the gulf of Taranto (northern Ionian Sea, central Mediterranean Sea). Rev. Fish Biol. Fish 2020, 31, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolman, S.J.; Brakes, P. Sustainable Fisheries Management and the Welfare of Bycaught and Entangled Cetaceans. Front. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, J.; Estes, J.A.; Morissette, L.; Smith, G. Whales as marine ecosystem engineers. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2014, 12, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmonds, M.; Eliott, W. Climate change and cetaceans: Concerns and recent developments. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2009, 89, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Learmonth, J.A.; Macleod, C.D.; Santos, M.B.; Pierce, G.J.; Crick, H.Q.P.; Robinson, R.A. Potential effects of climate change on marine mammals. In Oceanography and Marine Biology: An Annual Review; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; Volume 44, pp. 431–464. [Google Scholar]
- Bearzi, G.; Bonizzoni, S.; Gonzalvo, J. Dolphins and coastal fisheries within a marine protected area: Mismatch between dolphin occurrence and reported depredation. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2011, 21, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trites, A.W.; Christensen, V.; Pauly, D. Competition between fisheries and marine mammals for prey and primary production in the Pacific Ocean. J. Northw. Atl. Fish Sci. 1997, 22, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bearzi, G. Interactions between cetaceans and fisheries in the Mediterranean Sea. In Cetaceans of Mediterranean and Black Seas: State of Knowledge and Conservation Strategies. A Report to the ACCOBAMS Secretariat; Notarbartolo di Sciara, G., Ed.; ACCOBAMS, Section 9; French Principauté de Monaco: Monte Carlo, Monaco, 2002; p. 20. [Google Scholar]
- Jusufovski, D.; Saavedra, C.; Kuparinen, A. Competition between marine mammals and fisheries in contemporary harvested marine ecosystems. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2019, 627, 207–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaschner, K.; Pauly, D. Competition between Marine Mammals and Fisheries: Food for Thought. In The State of the Animals III; Salem, D.J., Rowan, A.N., Eds.; Humane Society Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ragen, T.J.; Huntington, H.P.; Hovelsrud, G.K. Conservation of Arctic marine mammals faced with climate change. Ecol. Appl. 2008, 18, S166–S174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmonds, M.; Isaac, S. The impacts of climate change on marine mammals: Early signs of significant problems. Oryx 2007, 41, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, D.S.; Tizzi, R.; Mussi, B. Cetaceans value and conservation in the Mediterranean Sea. J. Biodivers. Endanger. Species 2015, S1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friese, H. Thalassographies of Departure, Disaster and Rescue: Fishermen and Undocumented Mobility. Etnofoor 2015, 27, 13–36. [Google Scholar]
- Townsend, R.; Shotton, R.; Uchida, H. Case Studies in Fisheries Self-Governance; FAO Fisheries Technical Paper. No. 504; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2008; p. 451. [Google Scholar]
- Dimarchopoulou, D.; Keramidas, I.; Tsagarakis, K.; Tsikliras, A.C. Ecosystem Models and Effort Simulations of an Untrawled Gulf in the Central Aegean Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ELSTAT. Marine Fishery Research with Motor Vessels; Technical Report; Ελληνική Στατιστική Aρχή: Athens, Greece, 2019; Available online: https://www.statistics.gr/el/statistics/-/publication/SPA03/- (accessed on 10 May 2021).
- Fabinyi, M.; Dressier, W.; Pido, M. Fish, Trade and Food Security: Moving beyond ‘Availability’ Discourse in Marine Conservation. Hum. Ecol. 2017, 45, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlontzos, G.; Niavis, S.; Duquenne, M.N. Introduction on the Market of Tsipouro, a Greek Traditional Liquor, Precursor of Ouzo. IJEMS 2014, 7, 175–188. [Google Scholar]
- Mitoula, R.; Theodoropoulou, E.; Karali, B. Sustainable development in the City of Volos through reuse of industrial buildings. Sustain. Dev. Cult. Tradit. J. 2B 2013, 154–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandrakis, O. Neoliberalism and the New Agora: Exploring Survival, Emergence, and Political Subjectivity Among Pluralized Subaltern Communities in Athens, Greece. Anthr. Quart 2013, 86, 77–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zar, J.H. Biostatistical Analysis, 5th ed.; Prentice-Hall/Pearson: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wall, M.E.; Rechtsteiner, A.; Rocha, L.M. Singular Value Decomposition and Principal Component Analysis. In A Practical Approach to Microarray Data Analysis; Berrar, D.P., Dubitzky, W., Granzow, M., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2017; Available online: https://www.R-project.org (accessed on 29 February 2020).
- Tudela, S.; Kai Kai, A.; Maynou, F.; El Andalossi, M.; Guglielmi, P. Driftnet fishing and biodiversity conservation: The case study of the large-scale Moroccan driftnet fleet operating in the Alboràn Sea (SW Mediterranean). Biol. Conserv. 2005, 121, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brotons, J.M.; Grau, A.; Rendell, L. Estimating the impact of interactions between bottlenose dolphins and artisanal fisheries around the Balearic Islands. Mar. Mammal Sci. 2008, 24, 112–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, C.; Vella, A.; Vidoris, P.; Christidis, A.; Koutrakis, E.; Frantzis, A.; Miliou, A.; Kallianiotis, A. Cetacean stranding and diet analyses in the North Aegean Sea (Greece). J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2018, 98, 1011–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.K. Honour, Family and Patronage: A Study of Institutions and Moral Values in a Greek Mountain Community; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Pardalou, A.; Tsikliras, A. Anecdotal information on dolphin-fisheries interactions based on empirical knowledge of fishers in the northeastern Mediterranean Sea. ESEP 2018, 18, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocklin, D.; Santoni, M.C.; Culioli, J.M.; Tomasini, J.; Pelletier, D.; Mouillot, D. Changes in the catch composition of artisanal fisheries attributable to dolphin depredation in a Mediterranean marine reserve. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2009, 66, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, J.; Wells, R. Recreational fishing depredation and associated behaviors involving common bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) in Sarasota Bay, Florida. Mar. Mammal Sci. 2010, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasi, M.; Giuliani, A.; Boitani, L. Influence of Trammel Nets on the Behaviour and Spatial Distribution of Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) in the Aeolian Archipelago, Southern Italy. Aquat. Mamm. 2015, 41, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yodzis, P. Local Trophodynamics and the Interaction of Marine Mammals and Fisheries in the Benguela Ecosystem. J. Anim. Ecol. 1998, 67, 635–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, C.; Vella, A. Interactions between fisheries and cetaceans in the Thracian Sea (Greece) and management proposals. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2019, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetz, S.; Read, F.; Santos, M.; Pita, C.; Pierce, G. Cetacean-fishery interactions in Galicia (NW Spain): Results and management implications of a face-to-face interview survey of local fishers. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2013, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, M.J.; Menezes, G.; Machete, M.; Silva, M.A. Predicting Interactions between Common Dolphins and the Pole-and-Line Tuna Fishery in the Azores. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, S.J.; Pollock, K.H.; Bouchet, P.J.; Kobryn, H.T.; McElligott, D.B.; Nicholson, K.E.; Smith, J.N.; Loneragan, N.R. Preliminary estimates of the abundance and fidelity of dolphins associating with a demersal trawl fishery. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, F.N.; Abraham, E.R.; Berkenbusch, K. Common Dolphin (Delphinus delphis) Bycatch in New Zealand Commercial Trawl Fisheries. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snape, R.T.E.; Broderick, A.C.; Çiçek, B.A.; Fuller, W.J.; Tregenza, N.; Witt, M.J.; Godley, B.J. Conflict between Dolphins and a Data-Scarce Fishery of the European Union. Hum. Ecol. 2018, 46, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaakkola, K.; Guarino, E.; Donegan, K.; King, S.L. Bottlenose Dolphins Can Understand Their Partner’s Role in a Cooperative Task. Proc. R. Soc. B 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeves, R.; McClellan Press, K.; Werner, T. Marine mammal bycatch in gillnet and other entangling net fisheries, 1990 to 2011. Endanger. Species Res. 2013, 20, 71–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazo, M.; Gonzalvo, J.; Aguilar, A. Pingers as deterrents of bottlenose dolphins interacting with trammel nets. Fish. Res. 2008, 92, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownell, R.L., Jr.; Reeves, R.R.; Read, A.J.; Smith, B.D.; Thomas, P.O.; Ralls, K.; Amano, M.; Berggren, P.; Chit, A.M.; Collins, T. Bycatch in gillent fisheries threatens critically endangered small cetaceans and other aquatic megafauna. Endanger. Species Res. 2019, 40, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkafas, G.A.; Exadactylos, A.; Rogan, E.; Raga, J.A.; Reid, R.; Hoelzel, A.R. Biogeography and temporal progression during the evolution of striped dolphin population structure in European waters. J. Biogeogr. 2017, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Fishing Operations. Guidelines to Prevent and Reduce Bycatch of Marine Mammals in Capture Fisheries; FAO Technical Guidelines for Responsible Fisheries; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2021; No.1; Suppl. 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinyeta, K.; Lynn, K. Exploring the Role of Traditional Ecological Knowledge in Climate Change Initiatives; General Technical Report PNW-GTR-879; Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Pacific Northwest Research Station: Portland, OR, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).